Abstract
This study aimed to compare tilapia fish cake drying and sterilization conditions (105, 115, and 121 °C) on the quality of the cakes. The impacts of volatile flavor substances, the chroma value, quality and structure characteristics, microscopic structure, and the types and content of volatile flavor substances were also analyzed. The results showed that after drying and sterilization, the L* value, W value and delta-E value of fish cakes decreased significantly from 77.12 to 64.77, 66.21 to 52.57, 10.46 to 24.50, respectively. However, a* value and b* value increased significantly from 0.30 to 6.97 and 24.85 to 30.89, respectively. The elasticity, hardness, and chewiness increased significantly with the drying process but decreased significantly with the increased sterilization temperature. Scanning electron microscopy results showed that the internal pores of the fish cakes became smaller, and the tissue structure was closer after drying. Gas chromatography—ion mobile spectrometry analysis identified a total of 36 volatile flavor compounds. Among these, ketones comprised the largest content, aldehydes represented the largest variety, and all volatile compounds contributed significantly to the flavor of fish cake. PCA results and nearest-neighbor fingerprint analysis showed that there were obvious differences in volatile flavor compounds between different treatments. In summary, this study conducted a detailed comparative analysis of the quality and flavor of fish cakes subjected to different processing methods. These findings contribute suggestions for sterilization temperatures in industrial production processes.
1. Introduction
Tilapia is the second most economic freshwater fish in the world [1] and is an important aquaculture species in China. Compared to other economic fish, tilapia has a high nutritional value due to the balance of protein and amino acids in its flesh [2]. Currently, tilapia products on the market are predominantly live fish and frozen fillets, which are less refined and processed products [3]. Dried fish fillets, canned fish, waxed products, and surimi products are the primary tilapia products requiring intensive processing. Despite all this, ready-to-eat tilapia products are limited. Therefore, enriching the range of tilapia products is a trending research topic and has great prospects for development.
As an essential part of food processing, sterilization is divided into two categories [4], including thermal sterilization (pasteurization, high temperature sterilization, and ultra-high temperature sterilization) and non-thermal sterilization (ultrasonic, ultraviolet radiation, ozone oxidation, and high hydrostatic pressure sterilization) [5]. Traditional thermal sterilization technology is widely used in industrial production due to its ease of operation, controllability, and low price. Chantakun et al. [6] demonstrated that different heat treatment methods, including pasteurization at a high temperature for a shorter time or at a low temperature for a longer time at 118 °C and 121 °C sterilization, had significant effects on the quality and characteristics of bird’s nest beverages. MA et al. [7] reported that different sterilization methods of Prunus mume juice have significant effects on the microbiological and physicochemical parameters, such as the degree of browning, color measurements, total phenolic content, reducing sugar, ascorbic acid, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, amino acid nitrogen, total soluble solids (TSS), and pH value during storage.
Gas chromatography–ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS) is an emerging technique for the detection of flavor substances, which has the advantages of easy operation, high sensitivity, and fast detection [8,9,10]. It is used heavily in the food industry. Feng et al. [11] used GC-IMS to compare the differences between volatile flavor substances in yak milk powders under ultra-high-pressure sterilization and heat sterilization treatments. GC-IMS was used to analyze the characteristic volatile profiles of quinoas and the contents of volatile flavor substances were counted by normalization method [12]. There have been many studies that analyzed the optimal method of sterilization for surimi products, but there is considerably less research regarding the optimal sterilization temperature for tilapia thermal sterilization methods, which is used in industrial production at this stage. Therefore, the use of GC-IMS can effectively contrast the flavor changes of different treatments fish cakes.
This work investigates the effects of different treatments (untreated, dried, sterilized at 105 °C, sterilized at 115 °C, and sterilized at 121 °C) on the chromaticity values, textural properties, and microstructure of tilapia ready-to-eat fish cakes. Using GC-IMS, the differences of volatile flavor substances in fish cakes under different treatments were compared. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to differentiate the fish cakes under different treatments. This study aims to provide a theoretical basis for the selection of sterilization conditions in the commercial production of tilapia fish.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
Frozen tilapia was purchased from Hainan Xiangtai Fishery Co., Ltd. (Chengmai, China) After cutting into small pieces, the fish were washed with ice water and placed over crushed ice before processing. The fish were then put into a meat grinder and were ground two to three times. The fish cakes were made from a mixture of unrinsed surimi, 25% egg white powder, 30% mashed potatoes, 6% lard, and 100% water. The mixture was further ground for 2 min, placed into molds, and steamed at 90 °C for 25 min.
The samples were dried for 10 h at 10–15 °C in an air oven with an air speed of 1.5 m/s at 25% humidity. The dried samples were placed in a sterilizer with a reaction pressure of 0.12 MPa with experimental reaction temperatures of 105 °C, 115 °C, and 121 °C for 20 min, followed by cooling at room temperature. Fish cakes were set aside for further analysis.
2.2. Color Measurement
The color of fish cakes samples was measured according to Cao et al. [13]. The degrees of lightness (L*), redness (a*), and yellowness (b*) of fish cake samples were determined using a colorimeter (Ultra Scan PRO, HunterLab Inc., Reston, VA, USA). Fish cake samples were cut into thin 1 cm slices and placed vertically on a mirror port. Each sample measurement was repeated six times. Whiteness (W) and delta E (ΔE) were calculated according to the following formula:
W = 100 − ((100 − L*)2 + a*2 + b*2)1/2
ΔE = ((L − L0)2 + (a − a0)2 + (b − b0)2)1/2
2.3. Texture Profile Analysis
The texture profile analysis (TPA) of fish cake samples was determined according to methods from Mi et al. [14] The prepared fish cake samples were sliced to 10 mm, and a 22 mm diameter sample was taken with a meat picker and tested on a TA.XT.plus texture analyzer (Stable Micro Systems Co., Ltd., Godalming, Lammas Road, Vienna Court, UK) with a 50 mm cylindrical probe (P/50). The TPA was conducted using two 30% compression cycles with a 5 s interval between compressions. The pre-test, test, and post-test speed were 2, 1, and 1 mm/s, respectively, with a trigger force point of 5 g. Each sample analysis was repeated six times. Results are presented as averages.
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of samples was obtained according to Chen et al. [15]. The filleted surimi samples were placed in a freeze dryer for lyophilization, removed, and placed under a thermal field emission scanning electron microscope for observation and imaging at a magnification of 200.
2.5. Gas Chromatography–Ion Mobility Spectrometry Analysis
The GC-IMS (FlavourSpec®, G.A.S. Instrument, Shandong Haineng Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Rizhao, China) conditions were slightly modified from Chi et al. [16].
Headspace injection conditions were as follows: chopped fish cake (2 g) was placed in a 20 mL headspace injection vial and incubated at 60 °C for 20 min prior to testing. Each sample was repeated three times. The injection needle temperature was 85 °C, and the incubation speed was 500 rpm.
The GC conditions were as follows: MXT-5 column (15 m × 0.53 mm, 1.0 μm) with a column temperature of 60 °C. The flow conditions of the carrier gas were varied as follows: 0–2 min 2 mL/min, 2–10 min 10 mL/min, 10–20 min 100 mL/min, 20–25 min 150 mL/min.
IMS conditions were as follows: IMS temperature was maintained at 45 °C, and both drift and carrier gases were nitrogen (purity ≥ 99.999%).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The experimental values were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using SPSS 26.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). The results are reported as the mean ± standard deviation, and significance was defined at p < 0.05. The volatile flavor compounds in the samples were analyzed using the built-in plug-ins of the GC-IMS instrument (Laboratory Analytical Viewer (LAV), Reporter, and Gallery Plot). LAV was used to view the analysis spectrum, with each point on the graph representing a volatile organic compound, and the GC × IMS Library Search used a two-dimensional cross qualitative method for qualitative analysis. The relative content of each substance was calculated by normalization method based on the ion peak volumes of the volatile flavor substances. The aroma descriptions for the volatile flavor components were compared from the literature.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Properties
3.1.1. Color
Four indicators (L*, a*, b*, W) were used to evaluate the color of food as the color parameters of international standard color and were used to further speculate the quality of food [17]. L* values indicate lightness, a* values represent red/blue, b* values indicate yellow/green, and W values stand for whiteness. The L* value of the dried fish cake was 76.19 ± 1.07, and the W value was 66.46 ± 1.18; both values were significantly lower than that of the untreated group (p < 0.05). However, the b* value (23.54 ± 0.79) was slightly higher than that of the untreated group (p < 0.05). Moreover, there was no significant difference in the a* value before and after drying. This might be due to the Maillard reaction between proteins and starches under dry conditions, resulting in a decrease in the lightness and whiteness values of the sample and an increase in the yellowness value [18].
As shown in Figure 1, with the increase of sterilization temperature, the L* and W values gradually decreased, while the a*, b* and delta-E values gradually increased. The color difference of fish cakes gradually increased with the rise of sterilization temperature, indicating that the surface color of fish cakes kept deviating from the initial point, and there were significant differences among the delta-E values of fish cakes treated at different sterilization temperatures, with the delta-E value of 105 °C sterilization being the closest to that of dried fish cakes, and there was no significant difference between them(p > 0.05). This was probably due to the contraction and disintegration of myofibrils during the heat treatment, which led to Maillard reactions between sugars and proteins and Browning reactions between proteins and fats [19]. With the sterilization temperature increased to 121 °C, the L* (64.77 ± 0.97) and W (52.57 ± 2.97) values of the fish cake reached the lowest value, while the a* (6.97 ± 0.72) and b* (30.89 ± 3.87) values reached the highest level. Additionally, there was a significant difference (p < 0.05) with other treatment groups.
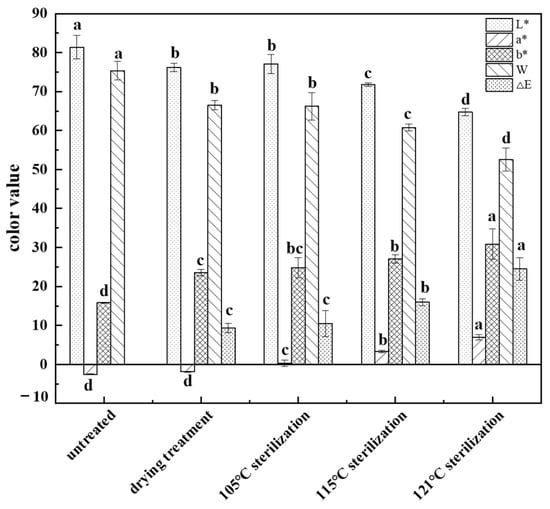
Figure 1.
Influence of different treatments methods on the color of tilapia fish cake. The a, b, c and d represent significant differences among treatment groups, the same letter represents no significant difference between two treatment groups (p > 0.05), and different letters represent significant differences between two treatment groups (p < 0.05).
The deeper color in fish cakes might be caused by a more intense Maillard reaction associated with increasing temperature. Zhu et al. [20] found that the L*, a*, and b* values of pufferfish fillets were dramatically affected by different drying methods, and the color values of fish fillets under high temperature drying conditions were significantly higher than those under low temperature conditions, which mainly resulted from a Maillard reaction. In summary, 105 °C was chosen as the optimum sterilization temperature, which could play a sterilization effect while maintaining the original color of fish cake, being more attractive to consumers.
3.1.2. Texture Analysis
Texture is an important indicator of seafood quality and consumer acceptance. The textures of the fish cake under different treatments are listed in Table 1. The hardness (2124.39 ± 255.03), chewiness (1625.14 ± 203.73), and cohesiveness (0.83) of the dried fish cakes were significantly higher than those of the untreated fish cakes (p < 0.05), but there were no significant differences in the springiness of the dried fish cake (p > 0.05). This might be due to the loss of moisture in the fish cake during the drying process, resulting in a tighter internal structure, which becomes harder and chewier. Becker et al. [21] also found that the hardness and chewiness of fish cakes were higher at a drying temperature of 55 °C, which was related to the degeneration of protein and contraction of myofibrils.

Table 1.
Changes in the texture of tilapia fish cakes under different treatments.
With increasing sterilization temperatures, there were no obvious changes in the springiness, cohesiveness presented a gradual upward trend, but the hardness and chewiness showed an increasing trend followed by a decreasing trend. The hardness and chewiness under sterilization at 105 °C were 4147.75 ± 444.90 and 3284.86 ± 412.35, respectively, which were dramatically different from other groups (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference between hardness and chewiness under 115 °C and 121 °C sterilization conditions (p > 0.05). Zhang et al. [22] also found that the hardness, springiness, cohesiveness, and chewiness of surimi gel decreased when the temperature increased from 100 °C to 121 °C.
3.1.3. SEM Analysis
SEM micrographs of fish cakes of different treatments are displayed in Figure 2. The surface of the untreated fish cake was uneven and rough, and there were many irregular pores inside. After hot air drying and thermal sterilization treatment, the holes in the fish cake were reduced with a more compact structure. Wang et al. [23] found that water molecules were more easily stored in small pores, thus in the gel system, the three-dimensional network structure, which has small and uniform holes, can effectively lock water molecules. The fish cake exhibited good gel properties. This could be attributed to the protein molecules within the fish cakes that are denatured under high temperature conditions, and the interaction force between the molecules is changed to form aggregates [24]. As the sterilization temperature increased from 105 °C to 121 °C, the pores inside the fish cake gradually increased, which might be due to the further destruction of the higher-order structure of the proteins causing the aggregation of the proteins to become more serious [25].

Figure 2.
Comparison of microstructure of tilapia fish cake under different treatments methods.
3.2. GC-IMS Analysis
3.2.1. GC-IMS Spectrum Analysis of Flavor Components of Fish Cakes under Different Conditions
The GC-IMS two-dimensional spectra of volatile flavor compounds in fish cakes under different treatments are shown in Figure 3a. There were significant differences in the flavor compounds of the fish cakes under different treatment conditions, and significant amounts of ammonia gas were detected in all fish cake samples, while a large amount of trimethylamine was detected in sterilized fish cakes. With increasing sterilization temperatures, the content of trimethylamine showed an increasing trend, which could be explained by a large amount of trimethylamine oxide contained in the fresh fish. Under high-temperature conditions, trimethylamine oxide was rapidly decomposed to form trimethylamine [26]. To compare the differences in a clearer fashion, the spectrum of the untreated fish cake sample was selected as the reference, and the same parts of other treatment groups were subtracted from this basis (Figure 3b). If they contain the same volatile organic compounds, the background after deduction is white; red indicates that the content of the substance is higher than the reference, and blue means that the content of the substance is lower than the reference. The content of flavor substances in fish cakes did not change much after the drying treatment. Nevertheless, under different sterilization temperatures, the contents of flavor substances were significantly different, and an increasing or decreasing trend was observed in the contents of different volatile flavor substances. The highest volatile flavor substance content was identified in the samples sterilized at 121 °C. This might be the result of the thermal treatment process promoting the release of some flavor substances, which increases the content of flavor substances in the fish cakes [27]. These findings are similar to Bai et al. [28], which indicated that the content and types of flavor substances in cooked Antarctic krill and white shrimp were significantly increased. Nonanal, benzaldehyde, and limonene were produced, and pyrazines, aldehydes, ketones, and alcohols increased in steamed and cooked shrimp meat. Furthermore, the free glycine level increased from 86.48 to 687.12 mg/100 g in shrimp after steaming.
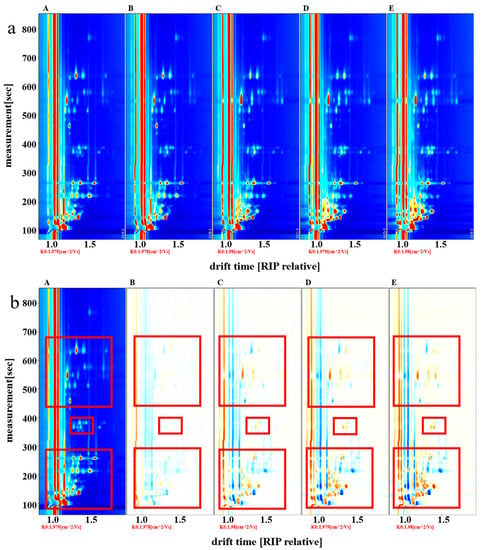
Figure 3.
Two-dimensional GC-IMS spectra of volatile organic compounds in tilapia fish cakes with different processing methods. (a) original spectrum; (b) differential contrast spectrum. (A) untreated fish cake; (B) drying treatment fish cake; (C) 105 °C sterilization fish cake; (D) 115 °C sterilization fish cake; (E) 121 °C sterilization fish cake. Red boxes were the difference of volatile organic compounds among different processing methods.
3.2.2. Qualitative Analysis of Flavor Components by GC-IMS of Fish Cakes Subjected to Different Processing Conditions
Qualitative analysis of flavor substances in fish cakes was conducted by comparisons with the built-in database of the flavor instrument, according to the retention time and migration time of the flavor substances [29]. Forty-four signal peaks were detected, and thirty-six flavor substances, including monomers and dimers, were identified in the samples. These substances comprised ketones, which were divided into seven categories, namely alcohols, esters, aldehydes, olefins, pyrazine, and furfuran. Monomers and dimers had the same chemical formula in the same substance and differed only in form. The figures in Figure 4 correspond to the compounds in Table 2.
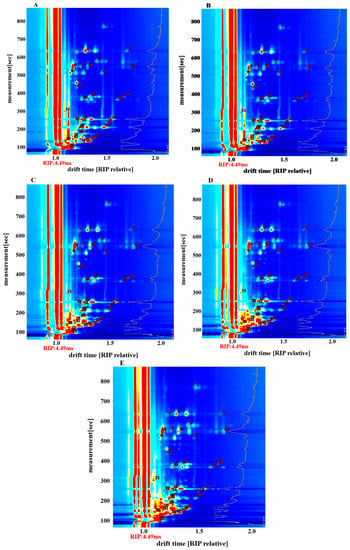
Figure 4.
Qualitative analysis by GC-IMS of volatile flavor compounds in tilapia fish cakes with different treatments methods. (A) untreated fish cake; (B) drying treatment fish cake; (C) 105 °C sterilization fish cake; (D) 115 °C sterilization fish cake; (E) 121 °C sterilization fish cake. The lines represented the drift time of volatile components. Each number represented a compound.

Table 2.
Volatile compounds detected from tilapia fish cakes via GC–IMS.
3.2.3. Fingerprint Analysis by GC-IMS of Volatile Components of Fish Cakes under Different Conditions
To further explore the differences between volatile flavor compounds in fish cakes under different processing treatments, the fingerprint analysis of flavor compounds in fish cakes was performed using the Gallery Plot plug-in of the LAV software. As shown in Figure 5, all signals contained in each sample were displayed in the same row, and the signals of one flavor in different samples were shown in the same column. Meanwhile, higher levels of the substance are indicated when more red color is present. Each sample was measured three times in parallel.
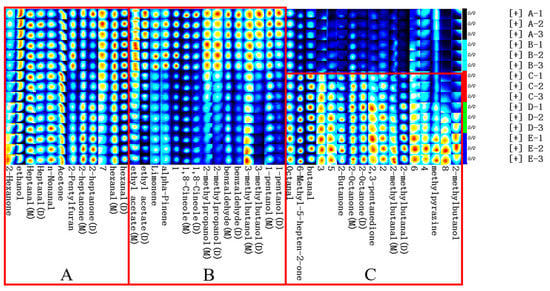
Figure 5.
Fingerprint of volatile organic compounds in tilapia fish cakes with different treatment methods. Numbers represent unidentified components. M and D in the parentheses represent the monomer and dimer of the substance, respectively.
As shown in Figure 5, the common volatile flavor substances in fish cakes under five different conditions are displayed in area A, including 2-hexanone, ethanol, heptanal (monomer, dimer), n-nonanal, acetone, 2-pentylfuran, 2-heptanone (monomer, dimer), and hexanal (monomer, dimer). The flavor substances in untreated and dried treatment fish cakes were mainly concentrated in region B, which was lesser or not detected in sterilized fish cakes, containing ethyl acetate (monomer, dimer), limonene, alpha-pinene, 1,8-cineole (monomer, dimer), 2-methylpropanol (monomer, dimer), benzaldehyde (monomer, dimer), 3-methylbutanol (monomer, dimer), and 1-pentanol (monomer, dimer). The flavor substances in fish cakes after sterilization were mainly focused on region C, including octanal, 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one, butanal, 2-butanone, 2-octanone (monomer, dimer), 2,3-pentanedione, 2-methylbutanal (monomer, dimer), methylpyrazine, and 2-methylbutanol.
The content of various flavor substances in fish cakes was analyzed and compared by the peak volume normalization method. The highest flavor substance content in fish cakes was ketones (36.21–51.30%), which was caused by the degradation of amino acids and the Maillard reaction, in which the contents of acetone and 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one were higher (Figure 6). There was no significant difference in acetone (spicy) content among different treatments, but the content of 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one (fruity and fragrant) in the sterilized fish cake increased significantly, which contributed positively to the overall flavor of the fish cake. However, the ketones had a high threshold and, therefore, contribute less to the overall flavor of the fish cake.
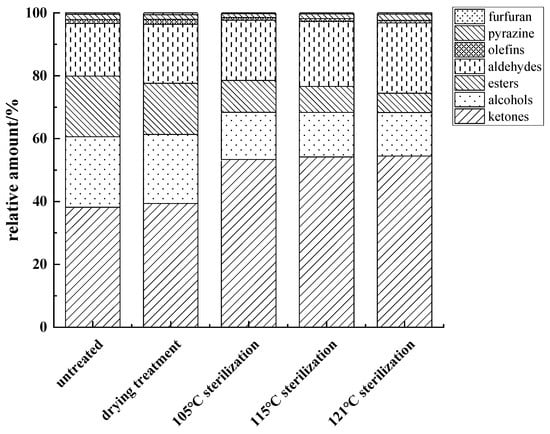
Figure 6.
Relative content changes of volatile components in tilapia fish cakes with different processing methods.
The alcohol content of the untreated fish cakes was the highest and decreased by 8.23% after sterilization treatment, which might be related to the reaction between alcohol and acid. The content of ethanol in fish cakes was relatively high, which is reduced to an extent after sterilization. The content of 1,8-cineole (camphoraceous and herbal) was followed only by ethanol and exemplified a decreasing trend after sterilization.
Esters, generated by the esterification of carboxylic acid and alcohol, are ethyl acetate monomers and dimers (fruit aroma) [30], and the content in fish cakes was 5.79–18.27%. The threshold value of the ester was lower, but the contribution to flavor substances was greater, which could give a unique ester flavor to fish cakes. With increasing sterilization temperatures, the ester content decreased, indicating that higher sterilization temperature would lead to the loss of flavor substances in food.
Aldehydes were mainly formed by the oxidation and decomposition of fats, and the content in fish cakes ranged from 15.88–21.05%; the threshold of aldehydes was low, which made a great contribution to the overall fish cake flavor. A high content of hexanal (grassy, fatty), benzaldehyde (almondy, fruity), 2-methylbutyraldehyde, and butyraldehyde (spicy) were detected as aldehydes. The progressive increase in the content of 2-methylbutyraldehyde and butyraldehyde adversely affected the flavor of fish cakes, which was accompanied by increased sterilization temperatures.
Olefins (0.77–1.42%) comprised limonene and α-pinene, and pyrazines (1.12–1.87%) was composed of methylpyrazine. The only furan flavor substance (0.28–0.53%) was 2-pentylfuran which provided bean and fruit flavors. Because the relative contents of olefin, pyrazine, and furan in the fish cake were small and the different treatments had little effect on their contents, the overall flavor of the fish cake was generally not affected. As previously mentioned, higher sterilization temperatures not only lead to the loss of positive flavor substances, but they also produce negative flavor substances, affecting the final flavor of fish cakes. Xie et al. [31] studied the effects of different heat treatment temperatures on the flavor compounds of boiled, salted duck and found that low temperature heat treatments better controlled the changes of flavor compounds, similar to the findings of this study.
3.3. PCA and Nearest-Neighbor Distances Analysis
PCA is a dimensionality reduction method for analyzing large amounts of data. Currently, this method in employed in various fields of material identification and classification. For example, it is used in the identification of volatile substances in Chinese dry-cured hams from different regions, assessing peaches with different preservation methods, and analyzing yak milk powder processed by different drying methods [32,33,34]. In this study, PCA analysis was performed on 36 volatile flavor compounds in fish cakes under different processing conditions. The contribution rate of PC1 was 81%; the contribution rate of PC2 was 11%, and the cumulative contribution rate reached 92%, which indicated that the detected flavor substances are highly representative of the information in the fish cake (Figure 7a). The flavor substances in fish cakes with the same treatment conditions were roughly concentrated in one classification area. The flavor substances in the untreated and dried fish cakes were close, indicating little difference in flavor substances between them. Additionally, after the samples were sterilized, the flavor substances were different. Moreover, the flavor substances of fish cakes treated with different sterilization temperatures were significantly different, indicating that the flavor substances of fish cakes treated with sterilization change significantly. Overall, there was no clear overlap between the flavor substances in the fish cakes under different processing treatments, which indicates that the use of PCA could better distinguish the fish cakes under different treatments.
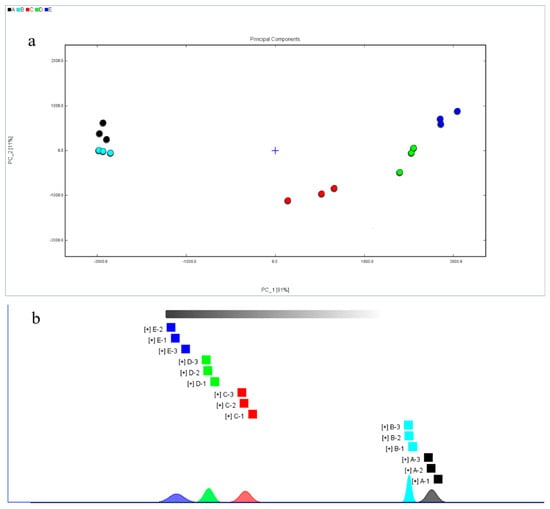
Figure 7.
PCA score (a) and nearest neighbor distances (b) of volatile organic components in tilapia fish cakes with different treatment methods.
The nearest-neighbor analysis showed the same results as did PCA (Figure 7b). The volatile organic compounds of the fish cakes before and after drying did not change significantly, but the volatile organic compounds changed greatly after high temperature sterilization. Concurrently, there were differences in the volatile organic compounds in the fish cakes sterilized at three different temperatures. Thereby, the lower sterilization temperature can maintain the original flavor of the fish cake as much as possible.
4. Conclusions
Sterilization is an essential step in food processing. This study showed that different processing methods have different effects on the quality and flavor of tilapia instant fish cakes.
In terms of physical characteristics, color, texture index, and the microstructure of the fish cakes after sterilization changed significantly. With increasing sterilization temperatures, the L* and W values decreased significantly and the a* and b* values increased significantly. The hardness and chewiness of fish cakes showed a decreasing trend with the increase of sterilization temperature. The increase of the sterilization temperature caused the pore size between the tissues to increase gradually. In terms of flavor, the flavor substances in fish cakes after sterilization were mainly octanal, 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one, butanal, 2-butanone, 2-octanone (monomer, dimer), 2,3-pentanedione, 2-methylbutanal (monomer, dimer), methylpyrazine, and 2-methylbutanol. Through the analyses of the color, texture, microstructure, and various flavor substance contents in fish cakes, the results showed that the higher sterilization temperatures changed the original color and the quality of fish cakes, which caused the loss of positive flavor substances. Additionally, more negative flavor substances were produced, and so 105 °C was chosen as the optimal sterilization temperature. In summary, under three different sterilization temperatures, 105 °C sterilization can prepare better quality tilapia instant fish cakes, which provides data references for industrial production of tilapia products.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.J. and P.J.; methodology, C.J.; software, C.J.; validation, Y.C., S.L., B.F. and. and X.D.; formal analysis, Y.C., S.S., B.F. and L.W.; investigation, C.J.; resources, X.D. and P.J.; data curation, S.L. and L.W.; writing—original draft preparation, C.J.; writing—review and ed-iting, S.S., X.D. and P.J.; visualization, Y.C., S.L.; supervision, P.J.; project administration, P.J.; funding acquisition, P.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was funded by National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFD090011) and the Key Science and Technology Program of Liaoning Province (2020JH1/10200001).
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sukri, S.A.M.; Andu, Y.; Harith, Z.T.; Sarijan, S.; Pauzi, M.N.F.; Wei, L.S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Kari, Z.A. Effect of feed-ing pineapple waste on growth performance, texture quality and flesh colour of nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) finger-lings. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 2514–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.T.; Guo, H.; Lu, Z.W.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, R.F.; Tao, N.P.; Wang, X.C.; Zhong, J. Reliability of LipidSearch software identification and its application to assess the effect of dry salting on the long-chain free fatty acid profile of tilapia muscles. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.P.; Guo, H.; Wu, T.T.; Tao, N.P.; Wang, X.C.; Zhong, J. Effect of three types of thermal processing methods on the lipidomics profile of tilapia fillets by UPLC-Q-Extractive Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiozzi, V.; Agriopoulou, S.; Varzakas, T. Advances, Applications, and Comparison of Thermal (Pasteurization, Steriliza-tion, and Aseptic Packaging) against Non-Thermal (Ultrasounds, UV Radiation, Ozonation, High Hydrostatic Pressure) Technologies in Food Processing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Farid, M. A review on recent development in non-conventional food sterilization technologies. J. Food Eng. 2016, 182, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantakun, K.; Benjakul, S. Characteristics and qualities of edible bird’s nest beverage as affected by thermal pasteurization and sterilization. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4056–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, Y.P.; Chen, Y.Y.; Meng, A.L.; Liu, P.; Ye, K.Y.; Yuan, A.Q. Effect of Different Sterilization Methods on the Microbial and Physicochemical Changes in Prunus mume Juice during Storage. Molecules 2022, 27, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Chen, H.T.; Sun, B.G. Recent progress in food flavor analysis using gas chromatography-ion mobility spec-trometry (GC-IMS). Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wang, J.; Ji, X.J.; Min, W.X.; Yan, W.J. Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds by HS-GC-IMS in Powdered Yak Milk Processed under Different Sterilization Conditions. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 5536645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassey, A.P.; Boateng, E.F.; Zhu, Z.S.; Zhou, T.M.; Nasiru, M.M.; Guo, Y.P.; Dou, H.; Ye, K.P.; Li, C.B.; Zhou, G.H. Volatilome evaluation of modified atmosphere packaged chilled and super-chilled pork loins using electronic nose and HS-GC-IMS integration. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Sun, J.Q.; Song, S.Q.; Wang, H.T.; Yao, L.Y.; Min, S.; Wang, K.; Chen, D. Geographical differentiation of Molixiang table grapes grown in China based on volatile compounds analysis by HS-GC-IMS coupled with PCA and sensory evaluation of the grapes. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.X.; Shao, Y.; Yan, Y.M.; Li, X.H.; Peng, J.; Guo, L. Characterization of volatile profiles of three colored quinoas based on GC-IMS and PCA. LWT 2021, 146, 111292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.W.; Fan, D.M.; Jiao, X.D.; Huang, J.L.; Zhao, J.X.; Yan, B.W.; Zhou, W.G.; Zhang, W.H.; Ye, W.J.; Zhang, H. Importance of thickness in electromagnetic properties and gel characteristics of surimi during microwave heating. J. Food Eng. 2019, 248, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.B.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Yi, S.M.; Li, X.P.; Li, J.R. The interaction of starch-gums and their effect on gel properties and protein conformation of silver carp surimi. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Deng, T.Y.; Wang, C.; Mi, H.B.; Yi, S.M.; Li, X.P.; Li, J.R. Effect of hydrocolloids on gel properties and pro-tein secondary structure of silver carp surimi. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.H.; Lin, Y.; Miao, L.H.; Liu, B.; Ge, X.P. Effects of dietary supplementation of a mixture of ferulic acid and probiot-ics on the fillet quality of Megalobrama amblycephala fed with oxidized oil. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhashree, S.N.; Sunoj, S.; Xue, J.; Bora, G.C. Quantification of browning in apples using colour and textural features by image analysis. Food Qual. Saf. 2017, 1, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M. Browning and pigmentation in food through the Maillard reaction. Glycoconj. J. 2021, 38, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Llave, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Sakai, N. Color changes in fish during grilling—Influences of heat transfer and heat-ing medium on browning color. J. Food Eng. 2012, 116, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.T.; Pan, N.; Liu, S.J.; Su, Y.C.; Xiao, M.T.; Shi, W.Z.; Liu, Z.Y. The effects of five different drying methods on the quality of semi-dried takifugu obscurus fillets. LWT 2022, 161, 113340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Boulaaba, A.; Pingen, S.; Krischek, C.; Klein, G. Low temperature cooking of pork meat—Physicochemical and sensory aspects. Meat Sci. 2016, 118, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Chen, S.; Xu, C.H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.C.; Shi, W.Z. Determination of the effects of different high-temperature treatments on texture and aroma characteristics in Alaska pollock surimi. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2079–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xiong, Y.L.; Sato, H. Rheological enhancement of pork myofibrillar protein–lipid emulsion composite gels via glucose oxidase oxidation/transglutaminase cross-linking pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8451–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X. Changes of protein secondary structures of pollock surimi gels under high-temperature (100 °C and 120 °C) treatment. J. Food Eng. 2015, 171, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Xue, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.J.; Xue, C.H. Effects of high-temperature treatment (≥100 °C) on Alaska Pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) surimi gels. J. Food Eng. 2013, 115, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xin, X.Q.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, Y.H.; Xue, C.H. Reduction of formaldehyde residues induced by the thermal decom-position of trimethylamine oxide during the processing and storage of jumbo squid (dosidicus gigas). LWT 2018, 97, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Tao, L.N.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.J.; Wu, T.T.; Luan, D.L.; Ni, L.; Wang, X.C.; Zhong, J. Effect of four types of thermal processing methods on the aroma profiles of acidity regulator-treated tilapia muscles using e-nose, HS-SPME-GC-MS, and HS-GC-IMS. LWT 2021, 147, 111585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, L.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Hou, H. Characteristic flavor of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) and white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) induced by thermal treatment. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, N.Y.; Xu, H.Y.; Jiang, X.; Sun, T.T.; Luo, Y.X.; Shi, W.Z. Evaluation of aroma characteristics in grass carp mince as affected by different washing processes using an E-nose, HS-SPME-GC-MS, HS-GC-IMS, and sensory analysis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Q.; Yang, R.W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.L.; Chen, D.; Lin, S.Y. Development of a flavor fingerprint by HS-GC–IMS with PCA for volatile compounds of Tricholoma matsutake Singer. Food Chem. 2019, 290, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.S.; Xu, B.C.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhu, B.W.; Li, X.F.; Sun, Y. Effects of different thermal treatment temperatures on volatile flavour compounds of water-boiled salted duck after packaging. LWT 2021, 154, 112625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wang, J.; Ji, X.J.; Min, W.X.; Yan, W.J. HS-GC-IMS detection of volatile organic compounds in yak milk powder processed by different drying methods. LWT 2021, 141, 110855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Chen, Y.P.; Blank, I.; Li, F.Y.; Li, C.B.; Liu, Y. GC×GC-ToF-MS and GC-IMS based volatile profile characteriza-tion of the Chinese dry-cured hams from different regions. Food Res. Int. 2021, 142, 110222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, P.; Hu, H.W.; Cui, A.H.; Tang, H.J.; Liu, Y.G. HS-GC-IMS with PCA to analyze volatile flavor compounds of honey peach packaged with different preservation methods during storage. LWT 2021, 149, 111963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).