Screening of Bacillus velezensis E2 and the Inhibitory Effect of Its Antifungal Substances on Aspergillus flavus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Pathogen
2.2. Isolation and Identification of Antagonistic Bacterial Strains
2.3. Extraction of Antifungal Substances
2.4. LPs Minimal Inhibitory Concentration
2.5. Effect of LPs on A. flavus Spore Germination
2.6. Effect of LPs on A. flavus Mycelium Growth
2.7. Microscope and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.8. Analysis of LPs by HPLC-MS
2.9. Transcriptomics Study on the Effect of LPs on A. flavus
2.9.1. RNA Extraction and Transcriptome Sequencing
2.9.2. Transcriptome Sequencing
2.9.3. RT-qPCR
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
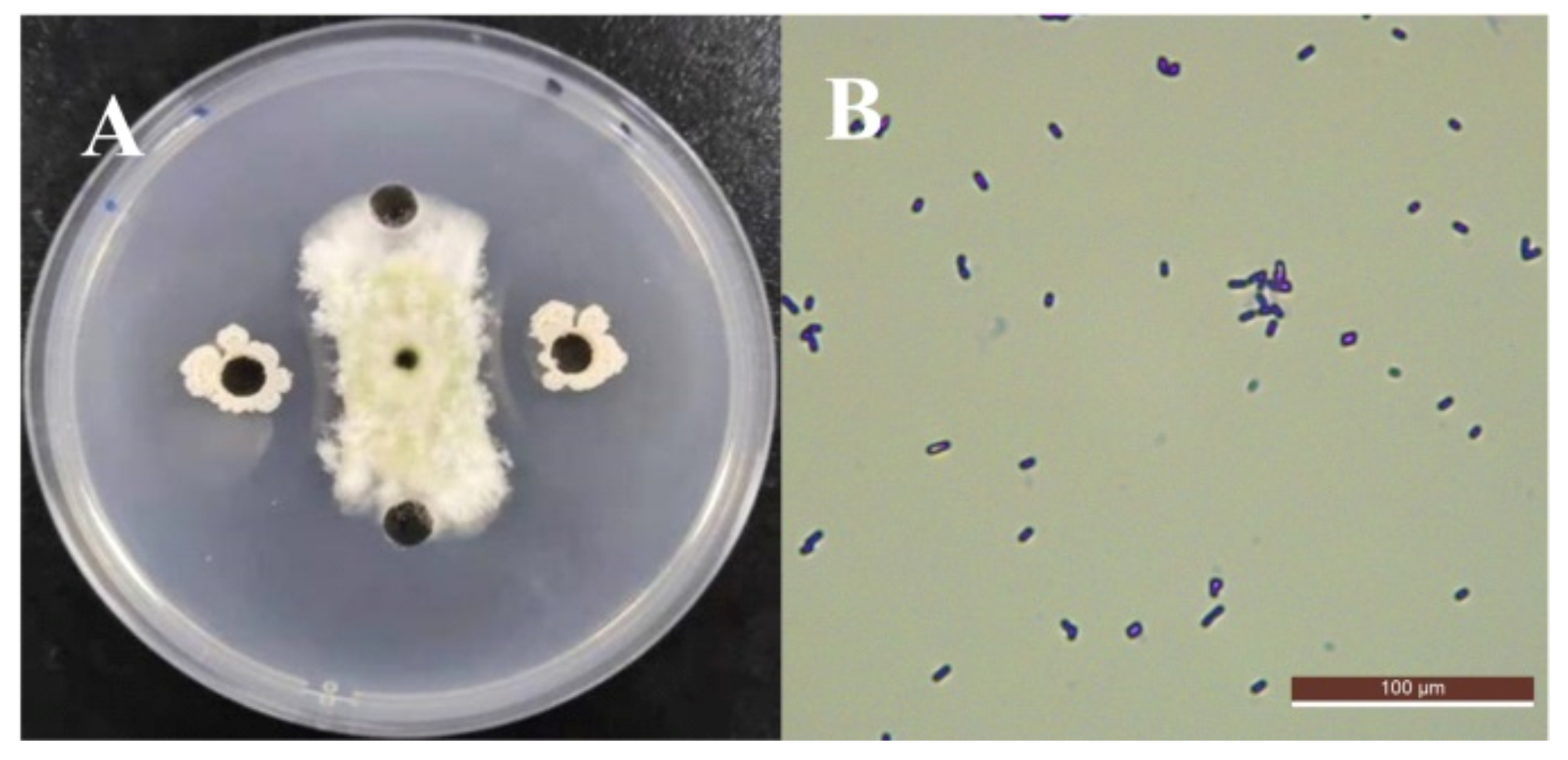
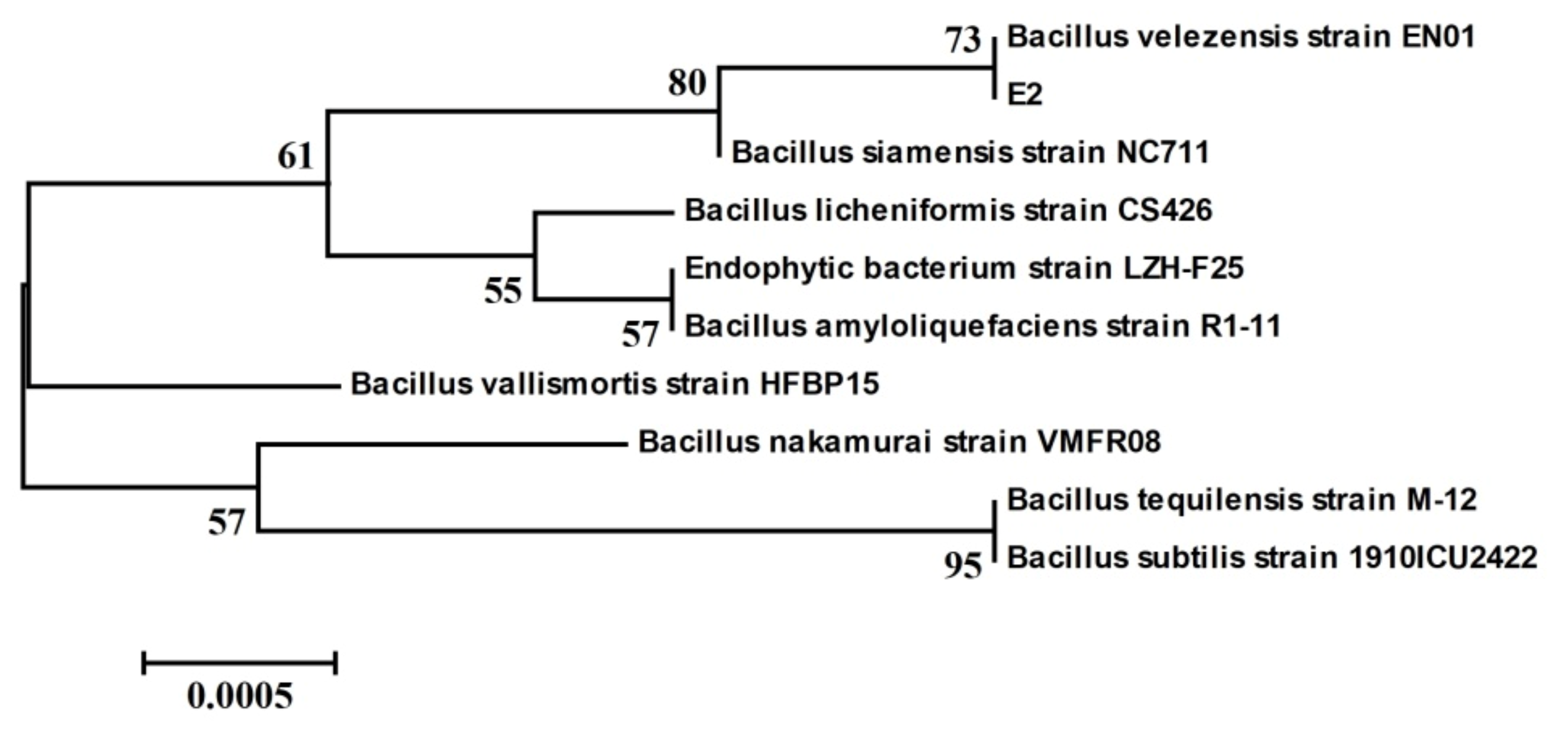
3.1. Screening and Identification of Antagonistic Strains against A. flavus
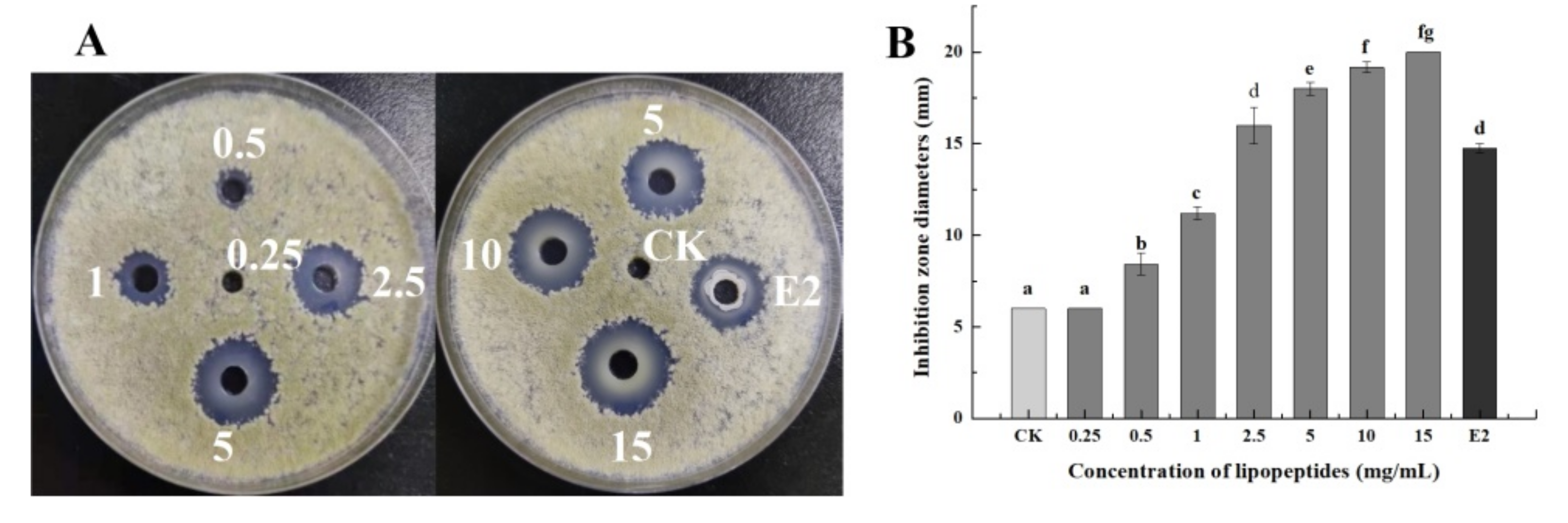
3.2. The Minimal Inhibitory Concentration of LPs
3.3. The Inhibitory Effect of LPs on the Germination of A. flavus Spores
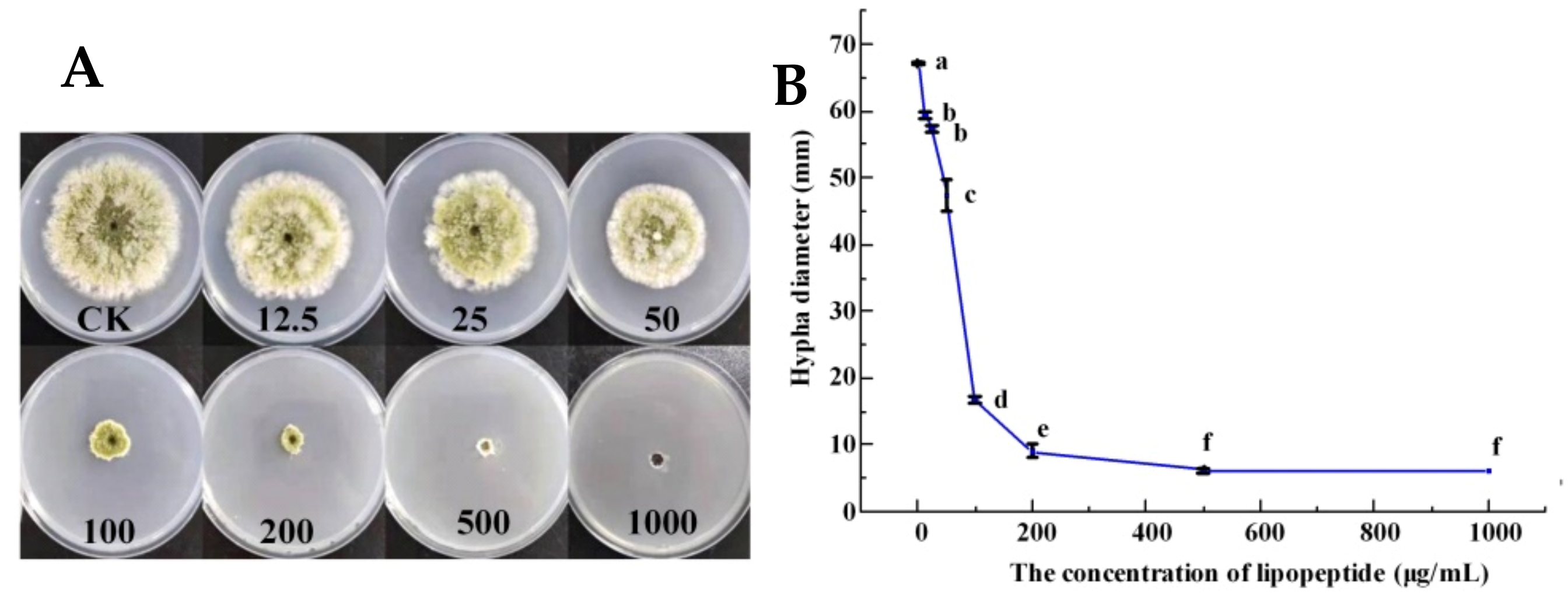
3.4. Inhibitory Effect of LPs on Mycelial Growth
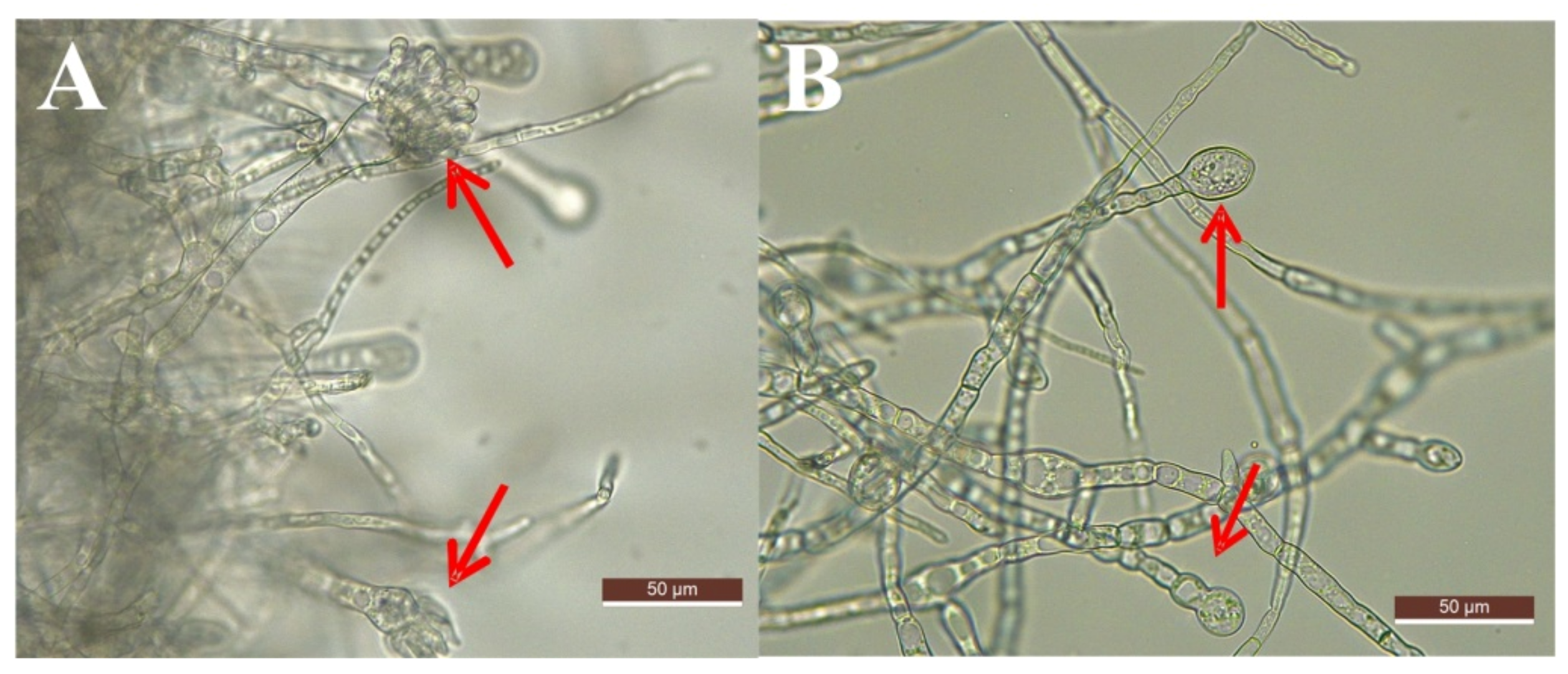
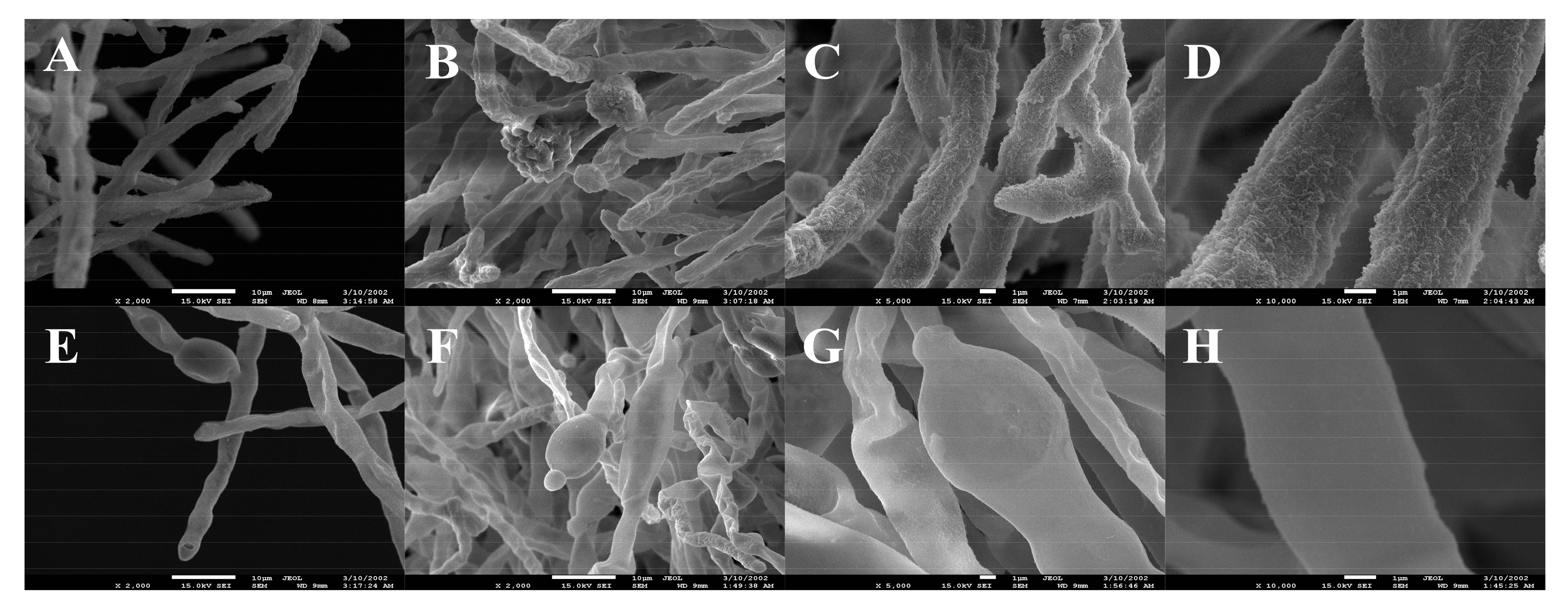
3.5. Microscope and SEM Evaluation
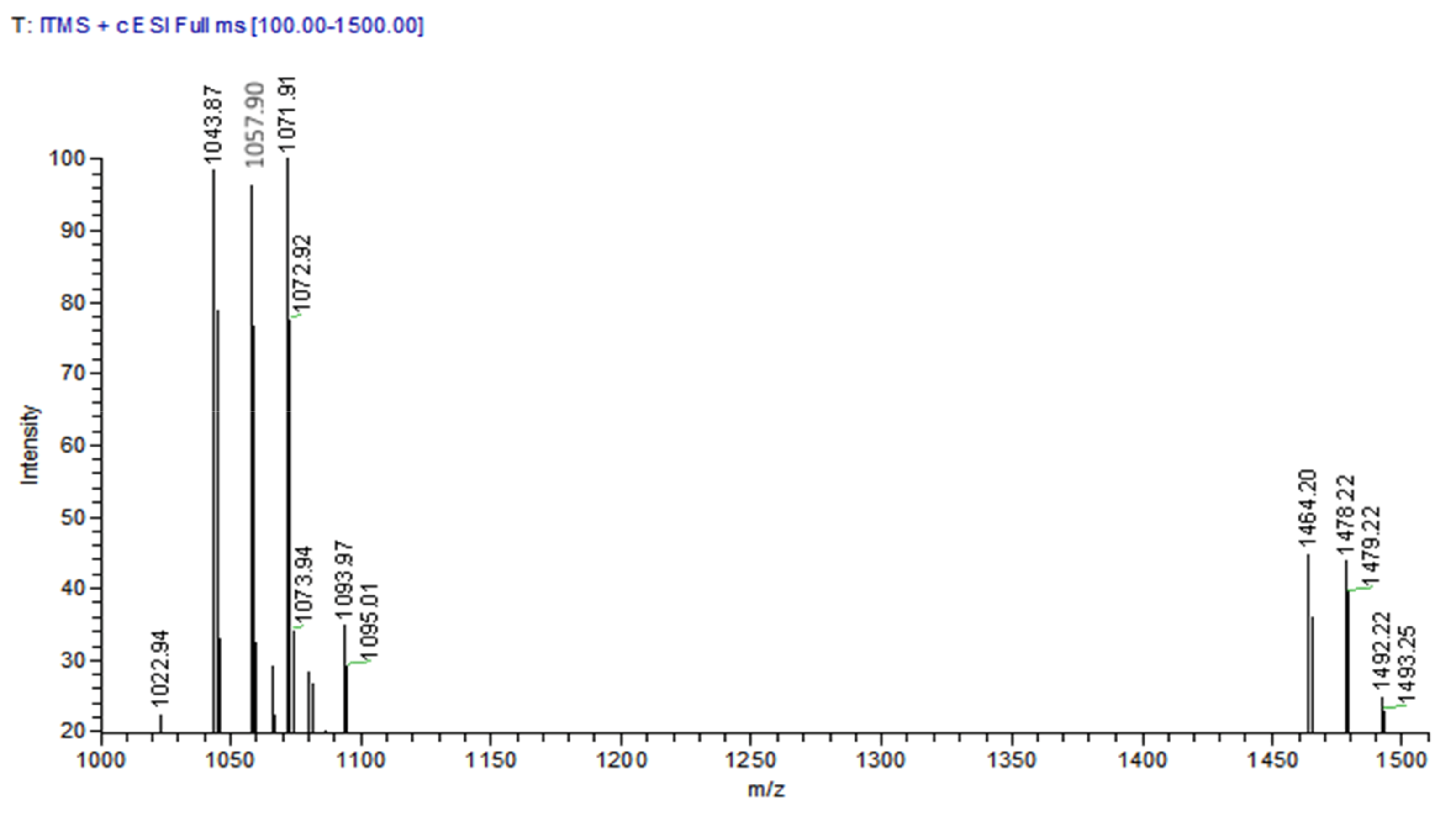
3.6. HPLC-MS Spectrometry Analysis
3.7. LPs Affected the Transcriptome of A. flavus
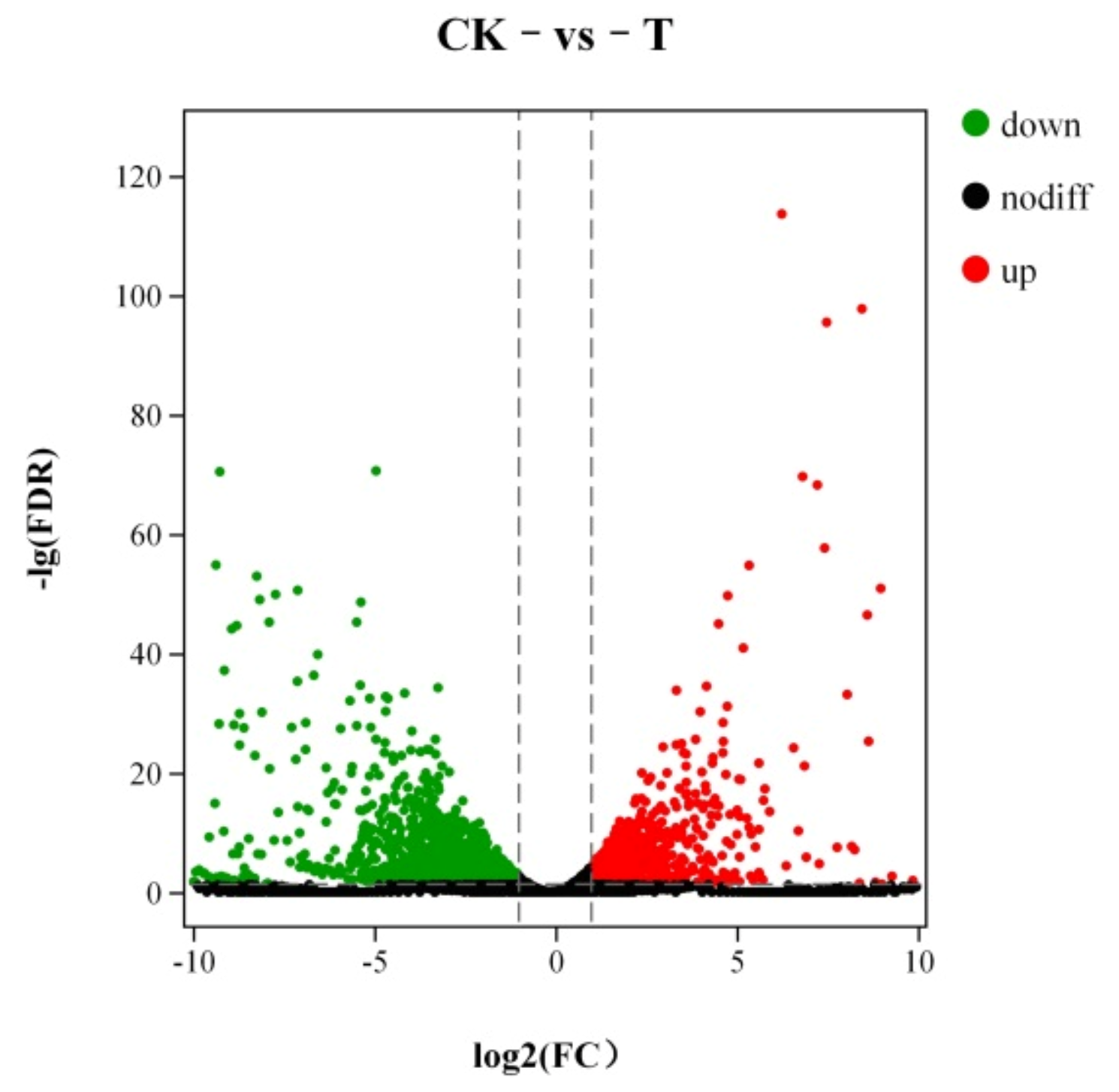
3.7.1. Analysis of Differentially Expression Genes
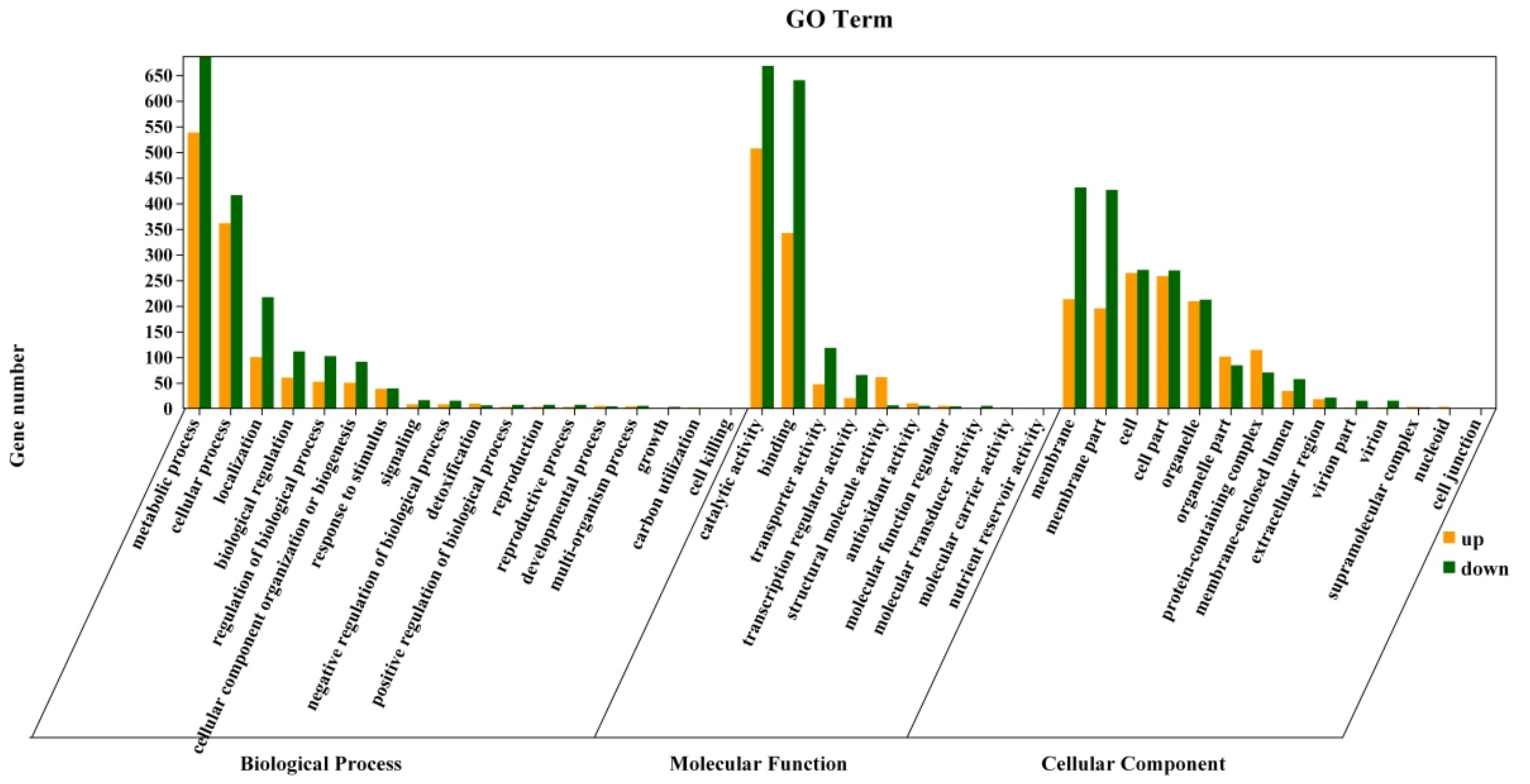
3.7.2. GO Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
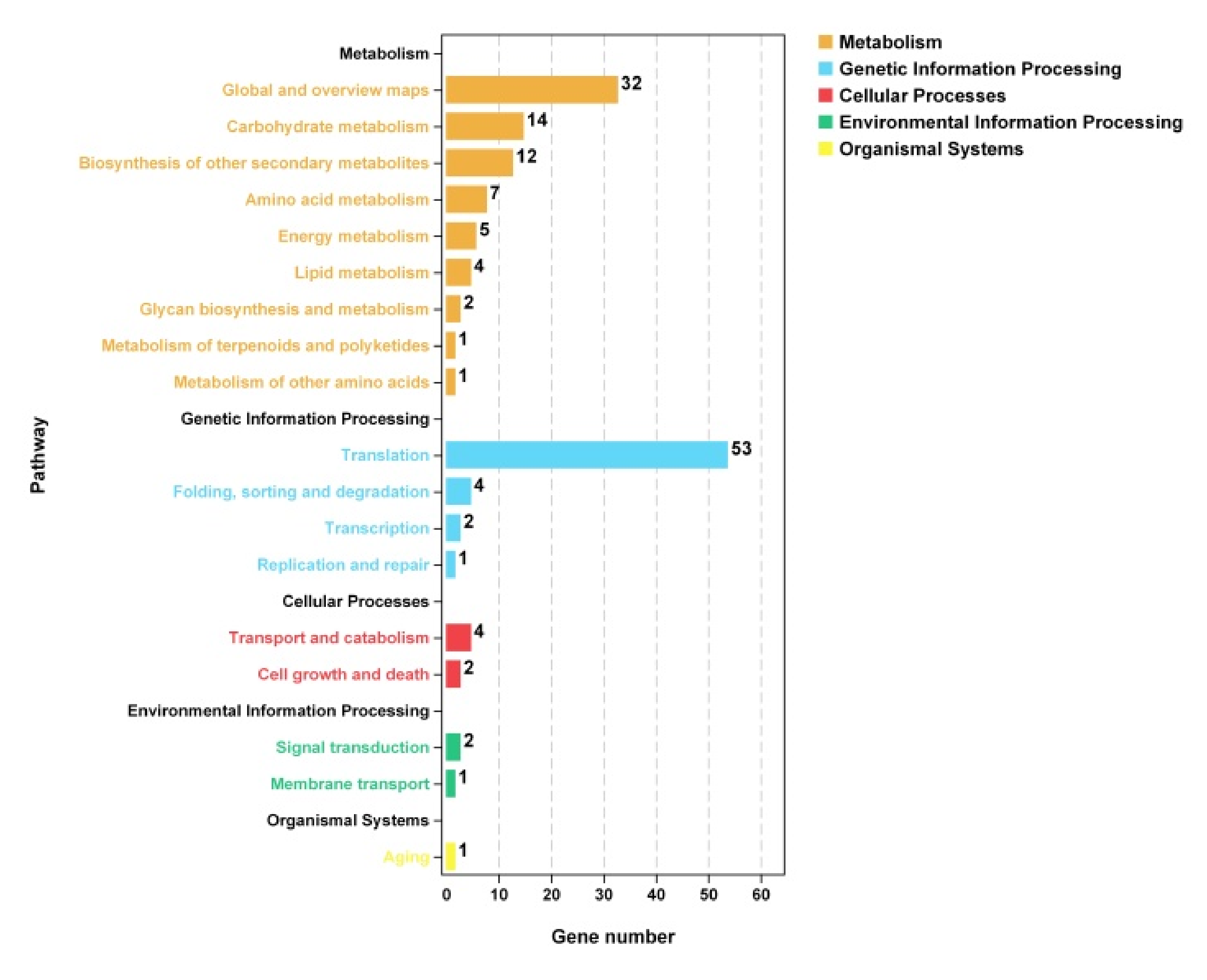
3.7.3. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
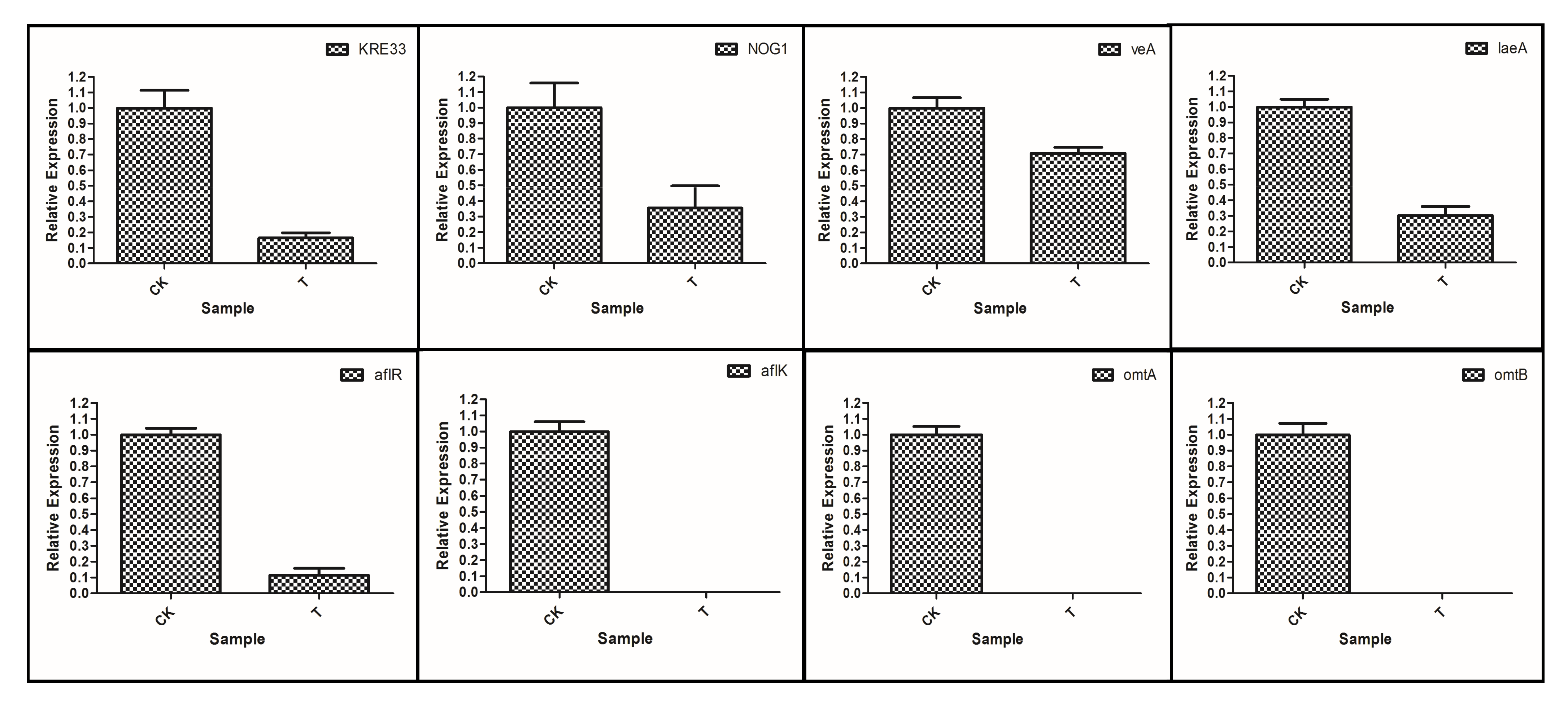
3.7.4. RT-qPCR Verification of Differentially Expressed Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaibangyang, S.; Nasanit, R.; Limtong, S. Effects of temperature and relative humidity on Aflatoxin B1 reduction in corn grains and antagonistic activities against Aflatoxin-producing Aspergillus flavus by a volatile organic compound-producing yeast, Kwoniella heveanensis DMKU-CE82. BioControl 2021, 66, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kang, X.; Wang, S.; Mo, H.; Hu, L. Early detection and monitoring for Aspergillus flavus contamination in maize kernels. Food Control 2021, 121, 107636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wei, M.; Peng, S.; Mo, H.; Huang, L.; Yao, L.; Hu, L. Cuminaldehyde in cumin essential oils prevents the growth and aflatoxin B1 biosynthesis of Aspergillus flavus in peanuts. Food Control 2021, 125, 107985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, Y. O-Vanillin, a promising antifungal agent, inhibits Aspergillus flavus by disrupting the integrity of cell walls and cell membranes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 5147–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Kai, K.; Wang, X.; Shi, W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y. Curcumin inhibits gray mold development in kiwifruit by targeting mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades in Botrytis cinerea. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 151, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Aminifard, M.H. In vitro and in vivo antifungal activities of three essential oils against grey mould disease in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Asian J. Plant Sci. 2011, 10, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Massawe, V.C.; Hanif, A.; Farzand, A.; Mburu, D.K.; Ochola, S.O.; Wu, L.; Tahir, H.A.S.; Gu, Q.; Wu, H.; Gao, X. Volatile compounds of endophytic Bacillus spp. have biocontrol activity against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytopathology 2018, 108, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Quan, X.; Xue, B.; Goodwin, P.H.; Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Du, W.; Wu, C. Isolation and identification of Bacillus subtilis strain YB-05 and its antifungal substances showing antagonism against Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici. Biol. Control 2015, 85, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Ge, C.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, M.; Li, W.; Shao, Y. Screening of a broad-spectrum antagonist—Bacillus siamensis, and its possible mechanisms to control postharvest disease in tropical fruits. Biol. Control 2021, 157, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Gao, X.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, W. Control of postharvest grey spot rot of loquat fruit with Metschnikowia pulcherrima E1 and potential mechanisms of action. Biol. Control 2021, 152, 104406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melentiev, A.I.; Galimzianova, N.F.; Gilvanova, E.A.; Shchelchkova, E.A.; Kuzmina, L.Y.; Boyko, T.F.; Usanov, N.G.; Aktuganov, G.E. Characterization of Novel Alkaliphilic Isolate of Bacillus mannanilyticus, Strain IB-OR17, Displaying Chitinolytic and Antifungal Activities. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Balaraju, K.; Jeon, Y. Effects of rhizobacteria Paenibacillus polymyxa APEC136 and Bacillus subtilis APEC170 on biocontrol of postharvest pathogens of apple fruits. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2016, 17, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilming, A.; Begemann, J.; Kuhne, S.; Regestein, L.; Bongaerts, J.; Evers, S.; Maurer, K.H.; Büchs, J. Metabolic studies of γ-polyglutamic acid production in bacillus licheniformis by small-scale continuous cultivations. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 2013. 73, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Zhang, C.; Lu, F.; Zhao, H.; Bie, X.; Lu, Z. Identification of bacillomycin D from Bacillus subtilis fmbJ and its inhibition effects against Aspergillus flavus. Food Control 2014, 36, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Xiang, B.; Yao, Z. Lipopeptide production by Bacillus atrophaeus strain B44 and its biocontrol efficacy against cotton rhizoctoniosis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 43, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Li, C.; Ye, X.; Lian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X. Antifungal activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MG3 against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in loquat fruits. Biol. Control 2020, 146, 104281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touré, Y.; Ongena, M.; Jacques, P.; Guiro, A.; Thonart, P. Role of lipopeptides produced by Bacillus subtilis GA1 in the reduction of grey mould disease caused by Botrytis cinerea on apple. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 96, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyave-Toro, J.J.; Mosquera, S.; Villegas-Escobar, V. Biocontrol activity of Bacillus subtilis EA-CB0015 cells and lipopeptides against postharvest fungal pathogens. Biol. Control 2017, 114, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjundan, J.; Ramasamy, R.; Uthandi, S.; Ponnusamy, M. Antimicrobial activity and spectroscopic characterization of surfactin class of lipopeptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SR1. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathout, Y.; Ho, Y.P.; Ryzhov, V.; Demirev, P.; Fenselau, C. Kurstakins: A new class of lipopeptides isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1492–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajesh, K.; Sudarslal, S.; Arunan, C.; Sreejith, K. Kannurin, a novel lipopeptide from Bacillus cereus strain AK1: Isolation, structural evaluation and antifungal activities. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Y.; Diop, A.; Gancel, F.; Béchet, M.; Jacques, P.; Drider, D. Polynucleotide phosphorylase is involved in the control of lipopeptide fengycin production in Bacillus subtilis. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, S.; An, S.; Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; Wan, L. Preparation, characterization and anti-aflatoxigenic activity of chitosan packaging films incorporated with turmeric essential oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, V.R.R.K.; Nikku, M.Y.; Donthireddy, S.R.R. Screening of antagonistic marine Actinomycetes: Optimization of process parameters for the production of novel antibiotic by Amycolatopsis alba var. nov. DVR D4. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2011, 3, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.H. Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology (5th ed.). Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1939, 29, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Bai, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, L.; Li, M.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y. Isolation and identification of a Bacillus megaterium strain with ochratoxin A removal ability and antifungal activity. Food Control 2019, 106, 106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhir, K.; Glen, S.; Koichiro, T. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Yu, S.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, R. Inhibitory effects of non-volatiles lipopeptides and volatiles ketones metabolites secreted by Bacillus velezensis C16 against Alternaria solani. Biol. Control 2021, 152, 104421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanguy, S.P.-M.; Perrier-Cornet, J.M.; Bensoussan, M.; Dantigny, P. Impact of water activity of diverse media on spore germination of Aspergillus and Penicillium species. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 142, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.-Q.; Sun, Y.-F.; Tang, Y.-J.; Zhou, W.-W. Biocontrol potential of a broad-spectrum antifungal strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B4 for postharvest loquat fruit storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 174, 111439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, H.; Li, B.; Ngea, G.; Zhang, H. The molecular mechanisms of disease-resistance in mandarins induced by Yarrowia lipolytica based on transcriptome technology. Biol. Control 2021, 14, 104607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yang, Q.; Boateng, N.A.S.; Ahima, J.; Dou, Y.; Zhang, H. Ultrastructure observation and transcriptome analysis of Penicillium expansum invasion in postharvest pears. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 165, 111198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.S.; Zhu, H.Y.; Bai, Y.B.; Hui, L.; Cheng, Z.M. RNA sequencing-based transcriptome analysis of mature strawberry fruit infected by necrotrophic fungal pathogen Botrytis cinerea. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 104, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redshaw, N.; Wilkes, T.; Whale, A.; Cowen, S.; Huggett, J.; Foy, C. A comparison of miRNA isolation and RT-qPCR technologies and their effects on quantification accuracy and repeatability. Biotechniques 2013, 54, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergey, D.H.; Krieg, R.N.; Holt, G.J. Bergeys Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Gao, W.; Jiang, J. Bacillus megaterium WL-3 lipopeptides collaborate against Phytophthora infestans to control potato late blight and promote potato plant growth. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, H.; He, J.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, X.; Fan, J. High-cell-density culture enhances the antimicrobial and freshness effects of Bacillus subtilis S1702 on table grapes (Vitis vinifera cv. Kyoho). Food Chem. 2019, 286, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.P.; Lv, Y.Y.; Wei, S.; Zhang, S.B.; Hu, Y.S. Antifungal properties of recombinant Puroindoline B protein against aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 144, 111130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-H.; Liao, M.-J.; Wang, H.-K.; Zheng, M.-Z.; Xu, J.-J.; Guo, J.-H. Bacillus velezensis, a potential and efficient biocontrol agent in control of pepper gray mold caused by Botrytis cinerea. Biol. Control 2018, 126, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, M.; Piccoli, D.; Weselowski, B.; McDowell, T.; Renaud, J.; MacDonald, J.; Yuan, Z.-C. Surfactin-producing Bacillus velezensis 1B-23 and Bacillus sp. 1D-12 protect tomato against bacterial canker caused by Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 102, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Teng, K.; Wang, T.; Dong, E.; Zhong, J. Antimicrobial Bacillus velezensis HC6: Production of three kinds of lipopeptides and biocontrol potential in maize. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 128, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.R.; Park, J.S.; Jung, W.J. Antifungal evaluation of fengycin isoforms isolated from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PPL against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez-Mendizabal, V.; Falconi, C.E. Bacillus subtilis CtpxS2-1 induces systemic resistance against anthracnose in Andean lupin by lipopeptide production. Biotechnol Lett. 2021, 43, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.C.; Wang, Q.; Kifer, C.T.; Parsons, M. The NOG1 GTP-binding protein is required for biogenesis of the 60 S ribosomal subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32204–32211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saveanu, C.; Bienvenu, D.; Namane, A.; Gleizes, P.E.; Gas, N.; Jacquier, A.; Fromont-Racine, M. Nog2p, a putative GTPase associated with pre-60S subunits and required for late 60S maturation steps. EMBO J. 2014, 20, 6475–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Ping, W.; Ma, L.; Zheng, M.; Yang, L.; Xing, F. Large-scale comparative analysis of eugenol-induced/repressed genes expression in Aspergillus flavus using RNA-seq. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1116. [Google Scholar]
- Farzaneh, M.; Shi, Z.Q.; Ahmadzadeh, M.; Hu, L.B.; Ghassempour, A. Inhibition of the Aspergillus flavus growth and Aflatoxin B1 contamination on pistachio nut by Fengycin and Surfactin-producing Bacillus subtilis UTBSP1. Plant Pathol. J. 2016, 32, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, S.; Pacher, S.; Hedtke, M.; Kniemeyer, O.; Fischer, R. A phosphorylation code of the Aspergillus nidulans global regulator VelvetA (VeA) determines specific functions. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, J.; Entwistle, S.; Satterlee, T.; Mack, B.M.; Gilbert, M.K.; Chang, P.K.; Scharfenstein, L.; Yin, Y.; Calvo, A.M. The transcriptional regulator Hbx1 affects the expression of thousands of genes in the Aflatoxin-producing fungus Aspergillus flavus. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2019, 9, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghayum, S.A.; Shamsghahfarokhi, M.; Razzaghiabyaneh, M. Expression of aflR, veA and laeA as regulators of Aflatoxins and cyclopiazonic acid biosynthesis pathway in Aspergillus flavus. Int. J. Mol. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 787–794. [Google Scholar]
- Somashekar, D.; Rati, E.R.; Chandrashekar, A. PCR-restriction fragment length analysis of aflR gene for differentiation and detection of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus in maize. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 93, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Kong, Q.; Yao, Y.; Xu, S.; Xie, X. Fusion expression and anti-Aspergillus flavus activity of a novel inhibitory protein DN-AflR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 290, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, M.S.; Sashidhar, R.B. Antiaflatoxigenic effects of selected antifungal peptides. Peptides 2019, 115, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Fedorova, N.D.; Montalbano, B.G.; Bhatnagar, D.; Cleveland, T.E.; Bennett, J.W.; Nierman, W.C. Tight control of mycotoxin biosynthesis gene expression in Aspergillus flavus by temperature as revealed by RNA-Seq. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 322, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Li, B.; Yin, R.; Weng, Q.; Chen, Q. Development and evaluation of ITS- and aflP-based LAMP assays for rapid detection of Aspergillus flavus in food samples. Can. J. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene ID | Symbol | Primers (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| AFLA_029920 | KRE33 | F: GGGATTTACCAGTCACCGCA R: AGCACGATTCCACCTCCTTC |
| AFLA_134410 | NOG1 | F: TGCTCCAGAACCGTCAAACT R: CGGCTGAGAACGACATCCAA |
| AFLA_033290 | laeA | F: CTTGCTCCCATACAGCCCTC R: TCCCATCACACTTCCACACC |
| AFLA_066460 | veA | F: AAGGTTGTCGTGTGCGGATT R: TGGGGTAGAGATTCGGTCAG |
| AFLA_139190 | aflK | F: GTGATTGAGGCGGGAGGAT R: GCCGTGTTGTCGTTGAGAG |
| AFLA_139360 | aflR | F: CCCCACTACCACCGTTTCAG R: CTCATCCACACAATCCTCGC |
| AFLA_139210 | omtA | F: TAGTTCATGGCCCGGTTCC R: AGGTTTGCCTTTCGTCTGCT |
| AFLA_139220 | omtB | F: GAGAGCGACACGCCGATAA R: GAAGAATGCGACCAAGGAGT |
| AFLA_047410 | actin | F: GAAGTTGCTGCTCTCGTCA R: GACCGACAATGGAGGGGAAG |
| Properties | Strain E2 | Properties | Strain E2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gram stain | + | Citrate utilization | + |
| Moveability | + | Glucose ferm entation | + |
| Catalase | + | Mannitol fermentation | + |
| V-P test | + | Carbon utilization–glucose | + |
| Methyl red test | − | Carbon utilization–mannitol | + |
| Starch hydrolusis | + | Carbon utilization–fructose | + |
| Gelaune liquefaction | + | Gelaune liquefaction | + |
| Treatments | Lipopeptide (µg/mL) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12.5 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 200 | 400 | |
| Spore germination rate (%) | 75.34 ±1.07 a | 67.41 ±1.82 b | 54.93 ±1.33 c | 35.49 ±3.14 d | 15.43 ±2.62 e | 5.80 ±1.31 f | 1.33 ±0.52 f |
| Retention Time (min) | MS m/z | Identified Compounds | |
|---|---|---|---|
| [M + H]+ | [M + Na]+ | ||
| 13.25 | 1043.87 | 1065.97 | C14 Iturin A |
| 15.99 | 1057.90 | 1079.96 | C15 Iturin A |
| 16.52 | 1057.90 | 1079.97 | C15 Iturin A |
| 20.95 | 1071.91 | 1093.97 | C16 Iturin A |
| 21.85 | 1071.92 | 1093.97 | C16 Iturin A |
| 24.89 | 1464.20 | - | C16 FengycinA |
| 27.20 | 1478.20 | - | C16 FengycinC |
| 30.61 | 1492.22 | - | C16 FengycinD |
| Gene ID | Gene Description | Log2FC | Style |
|---|---|---|---|
| AFLA_012380 | U3 small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein protein Mpp10 | −2.22 | down |
| AFLA_029920 | nucleolar ATPase Kre33, putative | −2.48 | down |
| AFLA_033570 | SSU processome component Utp10, putative | −2.22 | down |
| AFLA_028940 | small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein complex subunit Utp14 | −2.88 | down |
| AFLA_112310 | small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein complex subunit, putative | −2.03 | down |
| AFLA_113720 | ribosome biogenesis (Nop4), putative | −2.30 | down |
| AFLA_134410 | nucleolar GTP-binding protein (Nog1), putative | −2.18 | down |
| AFLA_110550 | nucleolar GTPase, putative | −2.68 | down |
| Gene ID | Gene Description | Log2FC | Style |
|---|---|---|---|
| AFLA_138050 | flavonoid 3-hydroxylase, putative | −5.60 | down |
| AFLA_139140 | aflYa/nadA/NADH oxidase | −4.45 | down |
| AFLA_139190 | aflK/vbs/VERB synthase | −9.25 | down |
| AFLA_139200 | aflQ/ordA/ord-1/oxidoreductase/cytochrome P450 monooxigenase | −9.27 | down |
| AFLA_139210 | aflP/omtA/omt-1/O-methyltransferase A | −8.93 | down |
| AFLA_139220 | aflO/omtB/dmtA/O-methyltransferase B | −8.79 | down |
| AFLA_139260 | aflG/avnA/ord-1/cytochrome P450 monooxygenase | −9.13 | down |
| AFLA_139280 | aflN/verA/monooxygenase | −9.14 | down |
| AFLA_139300 | aflM/ver-1/dehydrogenase/ketoreductase | −7.10 | down |
| AFLA_139310 | aflE/norA/aad/adh-2/NOR reductase/dehydrogenase | −8.23 | down |
| AFLA_139320 | aflJ/estA/esterase | −8.15 | down |
| AFLA_139330 | aflH/adhA/short chain alcohol dehydrogenase | −3.34 | down |
| AFLA_139340 | aflS/pathway regulator | −2.77 | down |
| AFLA_139360 | aflR/apa-2/afl-2/transcription activator | −2.12 | down |
| AFLA_139370 | aflB/fas-1/fatty acid synthase beta subunit | −2.55 | down |
| AFLA_139390 | aflD/nor-1/reductase | −4.68 | down |
| AFLA_139410 | aflC/pksA/pksL1/polyketide synthase | −3.13 | down |
| AFLA_139420 | aflT/aflT/transmembrane protein | −5.48 | down |
| AFLA_066460 | developmental regulator AflYf/VeA | −0.40 | down |
| AFLA_033290 | regulator of secondary metabolism LaeA | −1.63 | down |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Xu, X.; Zhao, T.; Ma, J.; Zhao, L.; Song, Q.; Sun, W. Screening of Bacillus velezensis E2 and the Inhibitory Effect of Its Antifungal Substances on Aspergillus flavus. Foods 2022, 11, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020140
Li S, Xu X, Zhao T, Ma J, Zhao L, Song Q, Sun W. Screening of Bacillus velezensis E2 and the Inhibitory Effect of Its Antifungal Substances on Aspergillus flavus. Foods. 2022; 11(2):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020140
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shengjie, Xingang Xu, Tianyuan Zhao, Jianing Ma, Luning Zhao, Qi Song, and Weihong Sun. 2022. "Screening of Bacillus velezensis E2 and the Inhibitory Effect of Its Antifungal Substances on Aspergillus flavus" Foods 11, no. 2: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020140
APA StyleLi, S., Xu, X., Zhao, T., Ma, J., Zhao, L., Song, Q., & Sun, W. (2022). Screening of Bacillus velezensis E2 and the Inhibitory Effect of Its Antifungal Substances on Aspergillus flavus. Foods, 11(2), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020140





