Experiences and Lessons from Agri-Food System Transformation for Sustainable Food Security: A Review of China’s Practices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
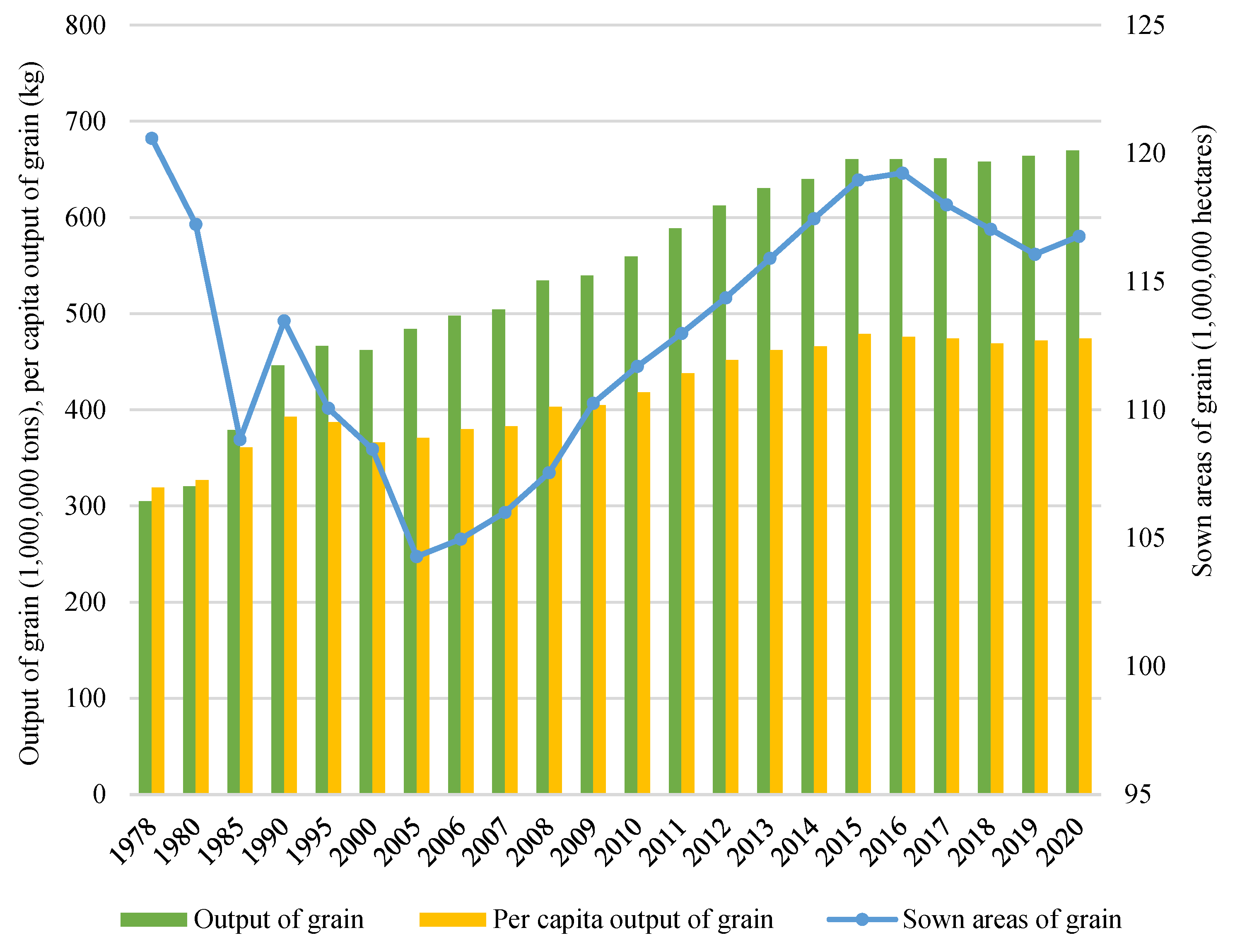
3.1. China’s Food Security Challenges
3.1.1. Increasing Pressure on Resources
3.1.2. Smallholder Vulnerability
3.1.3. Increasing Ecological Impact
3.1.4. Dynamic Global Agricultural and Food Policies
3.2. China’s Food Security Practices
3.2.1. Land Consolidation
3.2.2. Production Technologies
3.2.3. Organization Mode
3.2.4. Food Reserves
3.2.5. Trade Governance
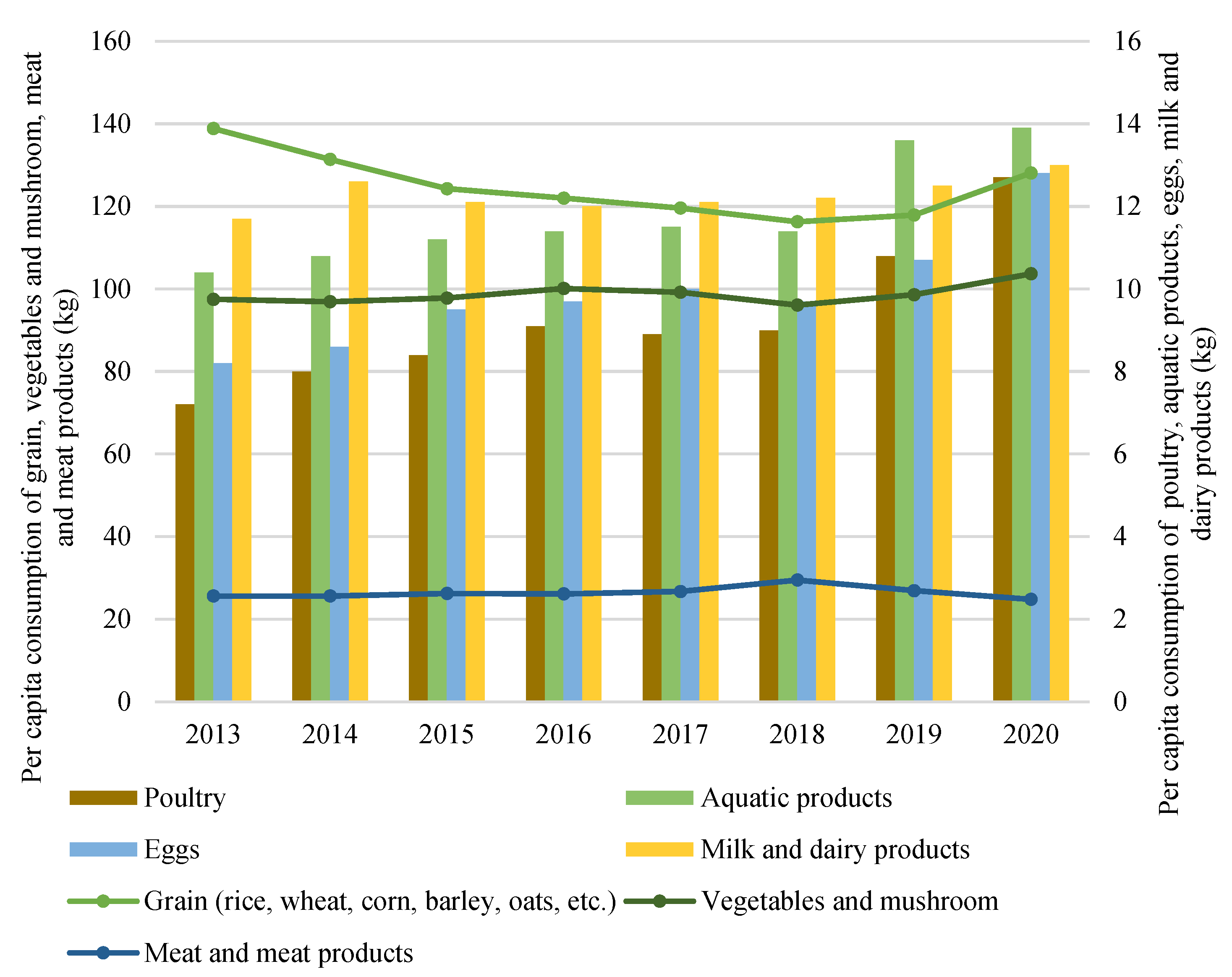
3.2.6. Food Consumption
3.3. China’s Food Security Achievements and Food System Transformation
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, L.M.; Drimie, S.; Maciejewski, K.; Tonissen, P.B.; Biggs, R. Food system transformation integrating a political–economy and social-ecological approach to regime shifts. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- International Panel of Experts on Sustainable Food Systems. A Long Food Movement: Transforming Food Systems by 2045. Available online: https://www.ipes-food.org/_img/upload/files/LongFoodMovementEN.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; International Fund for Agricultural Development; The United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund; The World Food Programme; World Health Organization. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2021: Transforming Food Systems for Food Security, Improved Nutrition and Affordable Healthy Diets for All; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2021; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- 2021 Global Nutrition Report: The State of Global Nutrition. Available online: https://globalnutritionreport.org/reports/2021-global-nutrition-report/ (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Special Report on Climate Change and Land. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/srccl/chapter/summary-for-policymakers/ (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- International Panel of Experts on Sustainable Food Systems. From Uniformity to Diversity: A Paradigm Shift from Industrial Agriculture to Diversified Agroecological Systems. Available online: https://www.ipes-food.org/_img/upload/files/UniformityToDiversity_FULL.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2016).
- Environmental Impacts of Food Production. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/environmental-impacts-of-food (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- International Panel of Experts on Sustainable Food Systems. COVID-19 and the Crisis in Food Systems: Symptoms, Causes, and Potential Solutions. Available online: https://www.ipes-food.org/_img/upload/files/COVID-19_CommuniqueEN(2).pdf (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- International Panel of Experts on Sustainable Food Systems. Breaking away from Industrial Food and Farming Systems: Seven Case Studies of Agroecological Transition. Available online: https://www.ipes-food.org/_img/upload/files/CS2_web.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2018).
- World Health Organization. Climate Change and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/climate-change-and-health (accessed on 30 October 2021).
- Tyfield, D. Food systems transition and disruptive low carbon innovation: Implications for a food security research agenda. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3701–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutten, L.F.; Yaroch, A.L.; Story, M. Food systems and food security: A conceptual model for identifying food system deficiencies. J. Hunger Environ. Nutr. 2011, 6, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santeramo, F.G. On the composite indicators for food security: Decisions matter! Food Rev. Int. 2015, 31, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haddad, L.; Kennedy, E.; Sullivan, J. Choice of indicators for food security and nutrition monitoring. Food Policy 1994, 19, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinstrup-Andersen, P. Food security: Definition and measurement. Food Secur. 2009, 1, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Sustainable Food Systems: Concept and Framework. Available online: www.fao.org/3/ca2079en/CA2079EN.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Reflections on China’s food security and land use policy under rapid urbanization. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carducci, B.; Keats, E.C.; Ruel, M.; Haddad, L.; Osendarp, S.J.M.; Bhutta, Z.A. Food systems, diets and nutrition in the wake of COVID-19. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, P.; Ferrero, Y.; De Loma-Osorio, G.; Nabarro, D.; Hainzelin, E.; Guillou, M.; Andersen, I.; Arnold, T.; Astralaga, M.; Beukeboom, M.; et al. Food systems for sustainable development: Proposals for a profound four-part transformation. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, S.; Teng, P.; Chew, P.; Smith, G.; Copeland, L. Food system resilience and COVID-19—Lessons from the Asian experience. Glob. Food Sec.-Agric. Policy 2021, 28, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Si, Z.; Scott, S.; Crush, J.; Yang, K.; Huang, X. Comprehensive food system planning for urban food security in Nanjing, China. Land 2021, 10, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S. Economics in food systems. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Brzeska, J. Feeding more people on an increasingly fragile planet: China’s food and nutrition security in a national and global context. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martindale, L. From land consolidation and food safety to Taobao Villages and alternative food networks: Four components of China’s dynamic agri-rural innovation system. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 82, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; International Fund for Agricultural Development; The United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund; The World Food Programme; World Health Organization. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2020: Transforming Food Systems for Affordable Healthy Diets; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020; pp. 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- 2020 Global Nutrition Report: Action on Equity to End Malnutrition. Available online: https://globalnutritionreport.org/reports/2020-global-nutrition-report/ (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Nosratabadi, S.; Khazami, N.; Abdallah, M.B.; Lackner, Z.S.; Band, S.S.; Mosavi, A.; Mako, C. Social capital contributions to food security: A comprehensive literature review. Foods 2020, 9, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candel, J.J.L. Food security governance: A systematic literature review. Food Secur. 2014, 6, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zhu, J.; Si, W.; Fan, S.; Gu, S.; Hu, B.; et al. New patterns of globalization and food security. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 1362–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Estimating China’s food grains demand from 2020 to 2050 based on reasonable dietary pattern. Syst. Eng.-Theory Pract. 2018, 38, 616–622. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Baiocchi, G.; Hubacek, K.; Feng, K.; Yu, Y. The environmental impacts of rapidly changing diets and their nutritional quality in China. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. International trade and food security: Conceptual discussion, WTO and the case of China. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2016, 8, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China’s Total Grain Demand Will Reach a Peak in 2030. Available online: https://jjsb.cet.com.cn/show_480319.html (accessed on 1 December 2016).
- Dramatic Changes Needed in Global Food Systems to Address Nutrition Disparity, Poverty: IFAD. Available online: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/agriculture/dramatic-changes-needed-in-global-food-systems-to-address-nutrition-disparity-poverty-ifad-79120 (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Du, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Gong, J. The logic innovation of agricultural production trusteeship to promote smallholder’s production modernization. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2021, in press.
- Peng, C.; Liu, H. Agriculture and rural modernization during the 14th Five-Year Plan Period: The situation, problems and countermeasure. Reform 2020, 2, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Chen, Y. Agrarian Capitalization without capitalism? Capitalist dynamics from above and below in China. J. Agrar. Change 2015, 15, 366–391. [Google Scholar]
- National Development and Reform Commission. Compilation of Cost-Benefit Data of National Agricultural Products; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, M.; Ma, Z. Climate change adaptation: Factors influencing Chinese smallholder farmers’ perceived self-efficacy and adaptation intent. Reg. Environ. Change 2017, 17, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Strategic adjustment of land use policy under the economic transformation. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z. Disclosing the future food security risk of China based on crop production and water scarcity under diverse socioeconomic and climate scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Yue, T.; Wang, C.; Wilson, J.P. Using models and spatial analysis to analyze spatio-temporal variations of food provision and food potential across China’s agro-ecosystems. Ecol. Model. 2015, 306, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Global Food Losses and Food Waste: Extent, Causes and Prevention; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Liu, X.; Lu, S.; Cheng, G.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Dou, Z.; Cheng, S.; Liu, G. China’s food loss and waste embodies increasing environmental impacts. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H. China’s agricultural supply-side structural reform from an opening-up perspective. Issues Agric. Econ. 2019, 2, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Li, T.; Zang, X. Emerging challenges and coping strategies in China’s food security under the High-level Opening Up. Issues Agric. Econ. 2021, 1, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Long, H.; Tang, Y. Land consolidation and rural vitalization: A perspective of land use multifunctionality. Prog. Geogr. 2021, 40, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Long, H.; Deng, W. Land consolidation: A comparative research between Europe and China. Land Use Policy 2022, in press. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Q.; Dai, J.; Bian, Z. Forecast on China’s cultivated land protection baseline in the new era by multi-scenario simulations. Resour. Sci. 2021, 43, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S. Discussion on China agricultural security: From both sides of supply and demand. Issues Agric. Econ. 2021, 8, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Xia, F.; Bao, H.X.H. Strategic planning framework for land consolidation in China: A top-level design based on SWOT analysis. Habitat Int. 2015, 48, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhang, S. Spatial pattern differentiation of non-grain cultivated land and its driving factors in China. China Land Sci. 2021, 35, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Evaluation on agricultural production space and layout optimization based on resources and environmental carrying capacity: A case study of Fujian Province. Sci. Geol. Sin. 2021, 41, 280–289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Jiang, G.; Xiong, C.; Yan, G.; Su, S. Study on land consolidation function zoning and its consolidation direction. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2021, 42, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Ren, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Reis, S.; Xu, J.; Gu, B. Consolidation of agricultural land can contribute to agricultural sustainability in China. Nat. Food 2021, in press. [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Ma, L. Analysis on the coupling and coordination of land ecological and food security in main grain producing areas. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2021, in press.
- Liu, Y.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, C. Review and prospect of the water-food-ecosystem nexus in dryland’s Coupled Human-Earth System. Geogr. Res. 2021, 40, 541–555. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, S.; Si, Z.; Schumilas, T.; Chen, A. Contradictions in state-and civil society-driven developments in China’s ecological agriculture sector. Food Policy 2014, 45, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Yun, W.; Liu, W.; Sang, L. Structural changes changes in the development of China’s farmland consolidation in 1998-2017: Changing ideas and future framework. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Cui, Z.; Miao, Y.; Mi, G. Transforming agriculture in China: From solely high yield to both high yield and high resource use efficiency. Glob. Food Sec.-Agric. Policy 2013, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.; Chen, C.; Feng, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W. Cropping system innovation for coping with climatic warming in China. Crop J. 2017, 5, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, W. Managing nutrient for both food security and environmental sustainability in China: An experiment for the world. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2014, 1, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, X.; He, G.; Cui, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhang, F. Agri-environment policy for grain production in China: Toward sustainable intensification. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2018, 10, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinforcing Ability to Sequestrate Carbon, Reduce Emission, Stabilize Grain Production and Increase Farmers’ Income. Available online: https://szb.farmer.com.cn/2020/20200918/20200918_007/20200918_007_1.htm (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Huang, G.; Tsai, F. Social innovation for food security and tourism poverty alleviation some examples from China. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 712709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M. Dragon head enterprises and the state of agribusiness in China. J. Agrar. Change 2017, 17, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. Achieving rural spatial restructuring in China: A suitable framework to understand how structural transitions in rural residential land differ across peri-urban interface? Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.H.F. E-Commerce and Taobao Villages. A promise for China’s rural development? China Perspect. 2017, 3, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Pan, Y.; Xia, X. Internet can do help in the reduction of pesticide use by farmers: Evidence from rural China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Qi, G. Bottom-up self-protection responses to China’s food safety crisis. Can. J. Dev. Stud. 2019, 40, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Li, Y.; Fang, P.; Zhou, L. “One family, two systems”: Food safety crisis as a catalyst for agrarian changes in rural China. J. Rural Stud. 2019, 69, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Luo, J.Z.; Fang, P. Who will feed China in the 21st Century? Pandemic crisis, glocalization and organized responsibility. Int. Econ. Rev. 2021, 5, 53–80. [Google Scholar]
- Domestic Food Security Provides A Solid Foundation for the Realization of Moderate Prosperity throughout the Country. Available online: http://paper.ce.cn/jjrb/html/2020-08/17/content_425909.htm (accessed on 17 August 2020).
- Zhan, Y.; Chen, K.Z. Building resilient food system amidst COVID-19: Responses and lessons from China. Agric. Syst. 2021, 190, 103102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China. Fighting Covid-19: China in Action. Available online: http://www.scio.gov.cn/ztk/dtzt/42313/43142/index.htm (accessed on 7 June 2020).
- Li, X.; Han, X.; Qi, H. The situation of China’s grain supply and price stability: Status quo, challenges and government’s measures—Based on the perspective of COVID-19 pandemic. Prices Mon. 2021, 1, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Zou, Y. Spatial differences and scale determination of regional grain reserves. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Shi, Q. Household grain storage and food security: An analysis based on data from Shanxi, Zhejiang and Guizhou. Chin. Rural Econ. 2020, 9, 86–104. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, L. Dietary structure upgrade of China’s residents, international trade and food security. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Zhu, D.; Chen, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. How the trade barrier changes environmental costs of agricultural production: An implication derived from China’s demand for soybean caused by the US-China trade war. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 227, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promote Agricultural Cooperation and Share Development Achievements. Available online: http://paper.people.com.cn/rmrb/html/2021-11/25/nw.D110000renmrb_20211125_2-06.htm (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Zhang, J. Beyond the ‘Hidden agricultural revolution’ and ‘China’s overseas land investment’: Main trends in China’s agriculture and food sector. J. Contemp. China 2019, 28, 746–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, D. China’s increased utilization of grain markets and resources in countries along the “One-Belt and One-Road” under the new situation. Res. Agric. Mod. 2021, 42, 827–840. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, N.; Han, W. Awareness of food waste recycling in restaurants: Evidence from China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Bai, J.; Jin, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, G.; Gao, S.; Bao, J.; Li, X.; Li, R.; Jiang, N.; et al. Reducing food loss and food waste: Some personal reflections. J. Nat. Resour. 2017, 32, 529–538. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Qin, W.; Garnett, T.; Zhang, F. Review on drivers, trends and emerging issues of the food wastage in China. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, X. Does dietary knowledge affect household food waste in the developing economy of China? Food Policy 2021, 98, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, A.; Sanchez, M.V.; Torero, M.; Vos, R. Reducing food loss and waste: Five challenges for policy and research. Food Policy 2021, 98, 101974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Qiang, W.; Niu, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, S.; Li, F. Options of Chinese dietary pattern based on multi-objective optimization. Resour. Sci. 2021, 43, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinstrup-Andersen, P.; Pandya-Lorch, R. Food Security: A Global Perspective. In Food Security, Diversification and Resource Management: Refocusing the Role of Agriculture? Peters, G.H., von Braun, J., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 51–76. ISBN 0429854390. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.D.; Ngure, F.M.; Pelto, G.; Young, S.L. What are we assessing when we measure food security? A compendium and review of current metrics. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 481–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qing, P.; Liao, F.; Min, S.; Pei, M.; You, L. Nutrition poverty alleviation: A new mode to help health poverty alleviation and promote targeted poverty alleviation—Literature review based on domestic and foreign research. Issues Agric. Econ. 2020, 5, 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, B. The impact of rural compulsory education nutrition improvement program on students’ health. China Rural Surv. 2021, 2, 97–114. [Google Scholar]
- The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China. Food Security in China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2019-10/14/content_5439410.htm (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China. Poverty Alleviation: China’s Experience and Contribution. Available online: https://english.www.gov.cn/archive/whitepaper/202104/06/content_WS606bc77ec6d0719374afc1b9.html (accessed on 6 April 2019).

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; He, L.; Chen, Y. Experiences and Lessons from Agri-Food System Transformation for Sustainable Food Security: A Review of China’s Practices. Foods 2022, 11, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020137
Lu Y, Zhang Y, Hong Y, He L, Chen Y. Experiences and Lessons from Agri-Food System Transformation for Sustainable Food Security: A Review of China’s Practices. Foods. 2022; 11(2):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020137
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yujia, Yongxun Zhang, Yu Hong, Lulu He, and Yangfen Chen. 2022. "Experiences and Lessons from Agri-Food System Transformation for Sustainable Food Security: A Review of China’s Practices" Foods 11, no. 2: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020137
APA StyleLu, Y., Zhang, Y., Hong, Y., He, L., & Chen, Y. (2022). Experiences and Lessons from Agri-Food System Transformation for Sustainable Food Security: A Review of China’s Practices. Foods, 11(2), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020137







