Characterization of Rare Himalayan Balsam (Impatiens glandulifera Royle) Honey from Croatia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Honey Samples
2.2. Melissopalynological Analysis
2.3. Physicochemical Analyses
2.3.1. Moisture Content
2.3.2. Electrical Conductivity
2.3.3. Hydroxymethylfurfural
2.3.4. Diastase Activity
2.3.5. Specific Rotation
2.3.6. pH, Free Acidity, Lactones and Total Acidity
2.3.7. Color
2.3.8. Carbohydrates
2.3.9. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.3.10. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP)
2.3.11. Mineral Element Analyses
2.4. Sensory Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
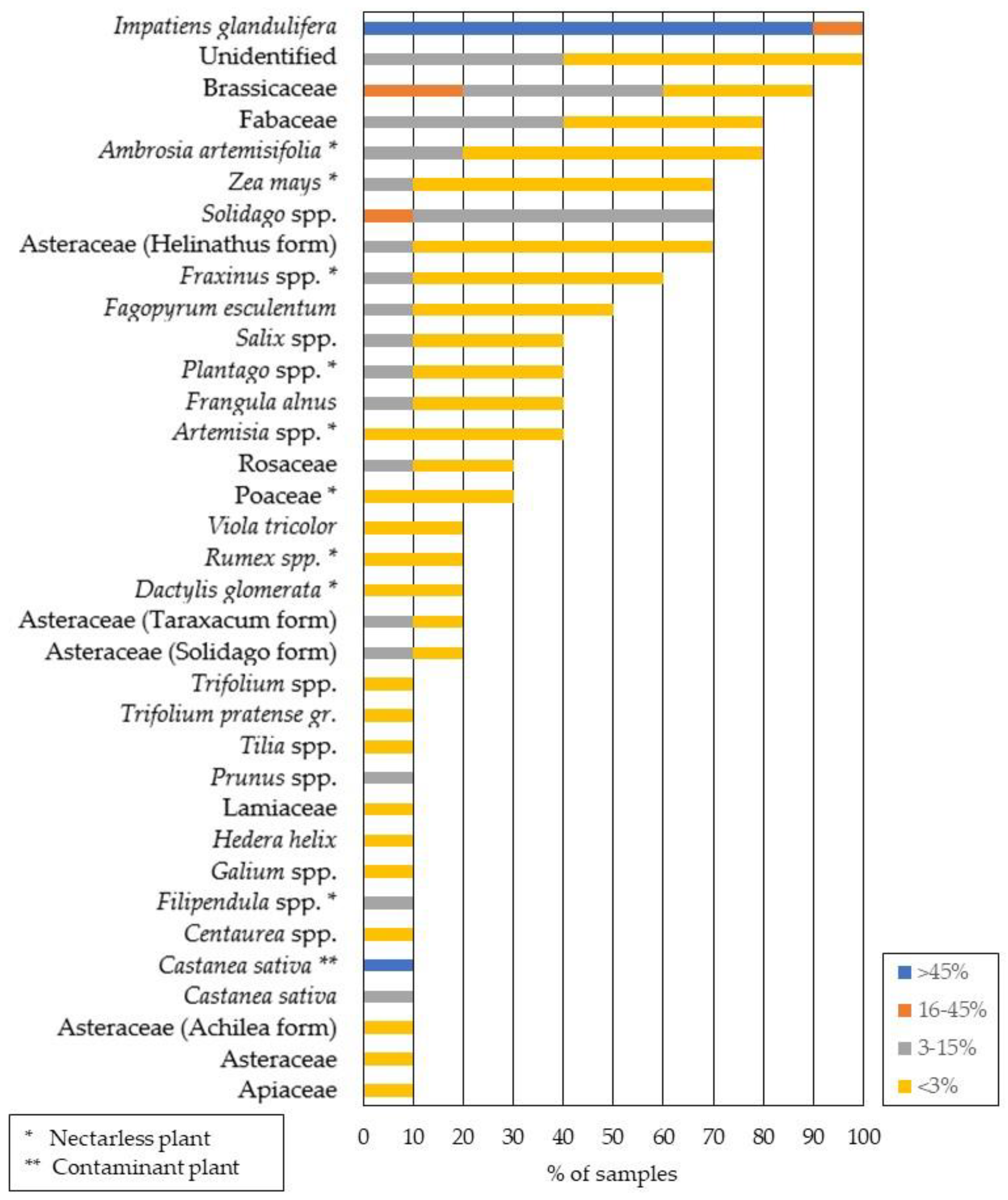
3.1. Melissopalynological Analysis of Himalayan Balsam Honey
3.2. Physicochemical Parameters of Himalayan Balsam Honey
3.3. Mineral Element Analyses
3.4. Sensory Profile of Himalayan Balsam Honey
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Persano Oddo, L.; Piazza, M.G.; Sabatini, A.G.; Accorti, M. Characterization of unifloral honeys. Apidologie 1995, 26, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.; Dias, L.G.; Moreira, L.L.; Rodrigues, P.; Estevinho, L. Physicochemical, microbiological and antimicrobial properties of commercial honeys from Portugal. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Jones, H.; Thrasyvoulou, A. Disseminating research about bee products. Apic. Res. 2011, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano Oddo, L.; Piana, L.; Bogdanov, S.; Bentabol, A.; Gotsiou, P.; Kerkvliet, J.; Martin, P.; Morlot, M.; Ortiz, V.A.; Ruoff, K.; et al. Botanical species giving unifloral honey in Europe. Apidologie 2004, 35, S82–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, V. Die rote Pest aus grüner Sicht: Springkräuter—Von Imkern Geschätzt, von Naturschützern Bekämpft; Leopold Stocker: Graz, Austria, 2015; pp. 50–115. [Google Scholar]
- Beerling, D.J. The impact of temperature on the northern distribution limits of the introduced species Fallopia japonica and Impatiens glandulifera in north-west Europe. J. Biogeogr. 1993, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleš, Ž.; Duka, I.; Bojić, M.; Vilović, T.; Mitić, B.; Hruševar, D. Determination of phenolics and antioxidative activity of two invasive species of the genus Impatiens L. Farmaceutski Glasnik 2020, 76, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Titze, A. The efficiency of insect pollination of the neophyte Impatiens glandulifera (Balsaminaceae). Nord 2000, 20, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittka, L.; Schürkens, S. Successful invasion of a floral market. Nature 2001, 411, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortesniemi, M.; Slupsky, C.M.; Ollikka, T.; Kauko, L.; Spevacek, A.R.; Sjövall, O.; Yang, B.; Kallio, H. NMR profiling clarifies the characterization of Finnish honeys of different botanical origins. Int. Food Res. 2016, 86, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, J.; de Vere, N.; Griffith, A.; Ford, C.R.; Allainguillaume, J.; Hegarty, M.J. Using DNA Metabarcoding to Identify the Floral Composition of Honey: A New Tool for Investigating Honey Bee Foraging Preferences. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, I.; Tananaki, C.; Galán-Soldevilla, H.; Pérez-Cacho, P.R.; Serrano, S. Sensory Profile of Greek Islands Thyme Honey. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von der Ohe, W.; Persano Oddo, L.; Piana, L.; Morlot, M.; Martin, P. Harmonised methods of melissopalynological analysis. Apidologie 2004, 35, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louveaux, J.; Maurizio, A.; Vorwohl, G. Methods of melissopalynology. Bee World 1978, 59, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von der Ohe, K.; Von der Ohe, W. Celle’s Mellisopalynological Collection; Niedersächsisches Landesinstitut für Bienenkunde: Celle, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardelli d’Albore, G. Mediterranean Melissoplaynology; Universita degli Studi di Perugia, Facolta di Agraria, Istituto di Entomologia Agrari: Perugia, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Rural Development. Ordinance on the Quality of Unifloral Honey; Official Gazette 122: Zagreb, Croatia, 2009; pp. 15–16.
- Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Rural Development. Ordinance on the Quality of Honey; Official Gazette 30: Zagreb, Croatia, 2015; pp. 3–5.
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. Revised Codex Standard for honey. Alinorm 2001, 1/25, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- EU Council directive 2001/110EC. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2002, L10, 47–52.
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; Rev. 1, Chapter 44; AOAC Official Methods, Suppl; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Rockville, MD, USA, 2000.
- International Honey Commission. Harmonized Methods of the International Honey Commission. Available online: http://www.ihc-platform.net/ihcmethods2009.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Beretta, G.; Granata, P.; Ferrero, M.; Orioli, M.; Facino, R.M. Standardization of antioxidant properties of honey by a combination of spectrophotometric/fluorimetric assays and chemometrics. Anal. Chim Acta. 2005, 533, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “Antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariba Lovaković, B.; Lazarus, M.; Brčić Karačonji, I.; Jurica, K.; Živković Semren, T.; Lušić, D.; Brajenović, N.; Pelaić, Z.; Pizent, A. Multi-elemental composition and antioxidant properties of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) honey from the coastal region of Croatia: Risk-benefit analysis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 45, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piana, M.; Persano Oddo, L.; Bentabol, A.; Bruneau, E.; Bogdanov, S.; Declerck, C.G. Sensory analysis applied to honey: State of the art. Apidologie 2004, 35 (Suppl. S1), S26–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microsoft Corporation; Microsoft Office Excel: Redmont, WA, USA, 2018.
- Persano Oddo, L.; Bogdanov, S. Determination of honey botanical origin: Problems and issues. Apidologie 2004, 35, S2–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrasyvoulou, A.; Manikis, J. Some physicochemical and microscopic characteristics of Greek unifloral honeys. Apidologie 1995, 26, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassova, J.; Yurukova, L.; Lazarova, M. Pollen and inorganic characteristics of Bulgarian unifloral honeys. Czech J. Food Sci. 2012, 30, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan-Borrás, M.; Soto, J.; Gil-Sánchez, L.; Pascual-Maté, A.; Escriche, I. Antioxidant activity and physico-chemical parameters for the differentiation of honey using a potentiometric electronic tongue. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenjerić, D.; Primorac, L.J.; Mandić, M.L.; Bubalo, D.; Perl Pirički, A.; Flanjak, I. Dalmatian sage (Salvia officinalis L.) honey characterization. Dtsch Lebensmitt Runds 2006, 102, 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Svečnjak, L.; Bubalo, D.; Baranović, G.; Novosel, H. Optimization of FTIR-ATR spectroscopy for botanical authentication of unifloral honey types and melissopalynological data prediction. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primorac, L.; Flanjak, I.; Kenjerić, D.; Bubalo, D.; Novak, I. Physicochemical parameters of Winter savory (Satureja montana L.) honey. Agronomski Glasnik 2013, 5–6, 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Tucak, Z.; Periškić, M.; Škrivanko, M.; Konjarević, A. The influence of the botanic origin of honey plants on the quality of honey. Poljoprivreda 2007, 13, 234–236. [Google Scholar]
- Sabo, M.; Vasić, M.; Banjari, I.; Flanjak, I.; Bačić, T. Melissopalynologycal, physicochemical and sensory characteristic of honey of tree floral species in Croatia. Deut. Lebensm.-Rundsch. 2008, 104, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.; Wu, F.; Cao, W.A. Novel Chinese Honey from Amorpha fruticosa L.: Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Capacity In Vitro. Molecules 2020, 25, 5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesna, T.; Rybak-Chmielewska, H.; Waś, E.; Kachaniuk, K.; Teper, D. Characteristics of Polish unifloral honeys. I. Rape honey (Brassica napus L. Var. oleifera Metzger). J. Apic. Sci. 2011, 55, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Kędzierska-Matysek, M.; Florek, M.; Wolanciuk, A.; Skałecki, P.; Litwińczuk, A. Characterisation of viscosity, colour, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural content and diastase activity in raw rape honey (Brassica napus) at different temperatures. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 3, 2092–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilić Rajs, B.; Flanjak, I.; Mutić, J.; Vukojević, V.; Đurđić, S.; Primorac, L. Characterization of Croatian Rape (Brassica sp.) Honey by Pollen Spectrum, Physicochemical Characteristics and Multielement analysis by ICP-OES. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, N.T.N.; Tuan, N.N.; Thang, T.D.; Kuo, P.C.; Thanh, N.B.; Tam, L.N.; Tuoi, L.H.; Nguyen, T.H.D.; Vu, D.C.; Ho, T.L.; et al. Chemical Composition Analysis and Antioxidant Activity of Coffea robusta Monofloral Honeys from Vietnam. Foods 2022, 11, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrasyvoulou, A.; Tananaki, C.; Goras, G.; Karazafiris, E.; Dimou, M.; Liolios, V.; Kanelis, D.; Gounari, S. Legislation of honey criteria and standards. J. Apic. Res. 2018, 57, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanjak, I.; Kenjerić, D.; Strelec, I.; Bilic Rajs, B.; Primorac, L. Effect of processing and storage on sage (Salvia officinalis L.) Honey quality. J. Microbiol. Biotech. Food. Sci. 2022, 11, e3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano Oddo, L.; Piro, R. Main European unifloral honeys: Descriptive sheets. Apidologie 2004, 35, S38–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S.; Ruoff, K.; Oddo, L. Physico-chemical methods for the characterization of unifloral honeys: A review. Apidologie 2004, 35, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primorac, L.; Flanjak, I.; Kenjerić, D.; Bubalo, D.; Topolnjak, Z. Specific Rotation and Carbohydrate Profile of Croatian Unifloral Honeys. Czech J. Food Sci. 2011, 29, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Arquillué, C.; Conchello, P.; Ariño, A.; Herrera, J.A. Physicochemical attributes and pollen spectrum of some unifloral Spanish honeys. Food Chem. 1995, 54, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontis, J.A.; Costa, L.A.M.A.; Silva, S.J.R.D.; Flach, A. Color, phenolic and flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity of honey from Roraima, Brazil. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 34, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanjak, I.; Kenjerić, D.; Bubalo, D.; Primorac, L. Characterisation of selected Croatian honey types based on the combination of antioxidant capacity, quality parameters, and chemometrics. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mărghitaş, L.A.; Dezmirean, D.; Moisea, A.; Bobis, O.; Laslo, L.; Bogdanov, S. Physico-chemical and bioactive properties of different floral origin honeys from Romania. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuredo, O.; Dobre, I.; Fernández-González, M.; Seijo, C. Contribution of botanical origin and sugar composition of honeys on the crystallization phenomenon. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczyńska, A. Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of different types of Polish honey—A short report. Polish J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2010, 60, 309–313. [Google Scholar]
- Pauliuc, D.; Dranca, F.; Oroian, M. Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolic Content, Individual Phenolics and Physicochemical Parameters Suitability for Romanian Honey Authentication. Foods 2020, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerković, I.; Tuberoso, C.I.G.; Marijanović, Z.; Kranjac, M.; Malenica-Staver, M. Antioxidant Capacity and Chemical Profiles of Satureja montana L. Honey: Hotrienol and Syringyl Derivatives as Biomarkers. Chem. Biodiverse. 2015, 12, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzugan, M.; Tomczyk, M.; Sowa, P.; Grabek-Lejko, F. Antioxidant Activity as Biomarker of Honey Variety. Molecules 2018, 23, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predescu, C.; Papuc, C.; Nicorescu, V. Antioxidant activity of Sunflower and Meadow honey. Vet. Med. 2015, 59, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Solayman, M.; Islam, M.A.; Paul, S.; Ali, Y.; Khalil, M.I.; Alam, N.; Gan, S.H. Physicochemical properties, minerals, trace elements, and heavy metals in honey of different origins: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodó, A.; Radványi, L.; Kőszegi, T.; Csepregi, R.; Nagy, D.U.; Farkas, Á.; Kocsis, M. Quality Evaluation of Light- and Dark-Colored Hungarian Honeys, Focusing on Botanical Origin, Antioxidant Capacity and Mineral Content. Molecules 2021, 26, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S.; Haldimann, M.; Luginbühl, W.; Gallmann, P. Minerals in honey: Environmental, geographical and botanical aspects. J. Apic. Res. 2007, 46, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabagias, I.K.; Badeka, A.; Kontakos, S.; Karabournioti, S.; Kontominas, M.G. Characterisation and classification of Greek pine honeys according to their geographical origin based on volatiles, physicochemical parameters and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.K.; Anjos, V.E.; Felsner, M.L.; Torres, Y.R.; Quináia, S. Direct determination of Cd, Pb, and Cr in honey by slurry sampling electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czipa, N.; Andrási, D.; Kovács, B. Determination of essential and toxic elements in Hungarian honeys. Food Chem. 2014, 175, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratu, I.; Beorgescu, C. Chemical contamination of bee honey–identifying sensor of the environment pollution. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2005, 6, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Bilandžić, N.; Gačić, M.; Đokić, M.; Sedak, M.; Ivanec Šipušić, Đ.; Končurat, A.; Tlak Gajger, I. Major and trace elements levels in multifloral and unifloral honeys in Croatia. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2014, 33, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, A.; Protano, G.; Riccobono, F. Minor and trace elements in different honey types produced in Siena County (Italy). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Unit of Measurement | Average | Minimum | Maximum | SD * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water content | % (w/w) | 17.2 | 15.8 | 20.5 | 1.42 |
| Electrical conductivity | mS/cm | 0.37 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 0.07 |
| Diastase activity | DN | 39.1 | 26.8 | 52.1 | 7.98 |
| HMF | mg/kg | 21.44 | 2.40 | 45.54 | 12.79 |
| Specific rotation | −21.2 | −26.1 | −10.0 | 6.89 | |
| Color | mm Pfund | 48.5 | 32.0 | 63.5 | 12.69 |
| Net absorbance | mAU | 408.3 | 272.5 | 576.5 | 114.80 |
| pH | - | 4.05 | 3.91 | 4.42 | 0.16 |
| Free acidity | mmol/kg | 33.98 | 23.65 | 44.53 | 6.52 |
| Total acidity | mmol/kg | 35.92 | 23.28 | 51.40 | 8.47 |
| Lactones | mmol/kg | 2.42 | 0.00 | 6.88 | 2.50 |
| Fructose | g/100 g | 39.34 | 38.32 | 40.15 | 0.65 |
| Glucose | g/100 g | 31.91 | 29.56 | 33.86 | 1.42 |
| Sucrose | g/100 g | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.05 |
| Maltose | g/100 g | 3.04 | 1.74 | 4.10 | 0.79 |
| Melezitose | g/100 g | 0.55 | 0.07 | 1.23 | 0.43 |
| Raffinose | g/100 g | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.03 |
| Xylose | g/100 g | ND ** | ND | ND ** | ND ** |
| F + G | g/100 g | 71.25 | 68.13 | 73.39 | 1.63 |
| F/G | - | 1.23 | 1.16 | 1.35 | 0.06 |
| Parameter | Unit of Measurement | Average | Min. | Max. | SD * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total phenolic content | mg gallic acid/kg honey | 130.97 | 117.55 | 150.24 | 11.17 |
| FRAP value | µM Fe(II) | 225.38 | 199.00 | 260.88 | 29.58 |
| Element | Unit of Measurement | Average | Minimum | Maximum | SD * | MDL ** | <MDL *** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | µg/kg | 0.56 | 0.39 | 0.97 | 0.22 | 0.53 | 4/10 |
| Ba | µg/kg | 44.54 | 7.08 | 185.10 | 49.29 | 1.38 | |
| Ca | mg/kg | 43.54 | 18.46 | 63.60 | 17.42 | 1.28 | |
| Cd | µg/kg | 0.79 | 0.42 | 1.62 | 0.35 | 0.06 | |
| Cr | µg/kg | 4.80 | 0.33 | 13.66 | 4.20 | 1.08 | 1/10 |
| Cu | mg/kg | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| Fe | mg/kg | 0.39 | 0.02 | 0.80 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 4/10 |
| K | mg/kg | 533.92 | 337.14 | 819.74 | 139.70 | 6.03 | |
| Mg | mg/kg | 17.36 | 8.57 | 25.73 | 6.54 | 0.46 | |
| Mn | mg/kg | 1.12 | 0.12 | 5.63 | 1.61 | 0.001 | |
| Mo | µg/kg | 1.85 | 1.15 | 2.68 | 0.48 | 0.43 | |
| Pb | µg/kg | 3.52 | 0.34 | 18.12 | 5.02 | 0.23 | |
| Se | µg/kg | 0.84 | 0.30 | 1.73 | 0.42 | 0.89 | 7/10 |
| V | µg/kg | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.58 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 3/10 |
| Zn | mg/kg | 0.80 | 0.34 | 2.67 | 0.66 | 0.01 |
| Sensory Description | |
|---|---|
| Visual assessment | Color intensity: light to medium light |
| Color tone: light amber with orange tone | |
| Olfactory assessment | Intensity of odor: medium Description: warm, sweet, animal |
| Tasting assessment | Sweetness: strong |
| Acidity: weak | |
| Bitterness: absent Intensity of aroma: weak to moderate Description of aroma: warm, candied, malt, molasses Persistence/aftertaste: short to medium | |
| Physical characteristics | Crystallization rate: moderate |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prđun, S.; Flanjak, I.; Svečnjak, L.; Primorac, L.; Lazarus, M.; Orct, T.; Bubalo, D.; Bilić Rajs, B. Characterization of Rare Himalayan Balsam (Impatiens glandulifera Royle) Honey from Croatia. Foods 2022, 11, 3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193025
Prđun S, Flanjak I, Svečnjak L, Primorac L, Lazarus M, Orct T, Bubalo D, Bilić Rajs B. Characterization of Rare Himalayan Balsam (Impatiens glandulifera Royle) Honey from Croatia. Foods. 2022; 11(19):3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193025
Chicago/Turabian StylePrđun, Saša, Ivana Flanjak, Lidija Svečnjak, Ljiljana Primorac, Maja Lazarus, Tatjana Orct, Dragan Bubalo, and Blanka Bilić Rajs. 2022. "Characterization of Rare Himalayan Balsam (Impatiens glandulifera Royle) Honey from Croatia" Foods 11, no. 19: 3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193025
APA StylePrđun, S., Flanjak, I., Svečnjak, L., Primorac, L., Lazarus, M., Orct, T., Bubalo, D., & Bilić Rajs, B. (2022). Characterization of Rare Himalayan Balsam (Impatiens glandulifera Royle) Honey from Croatia. Foods, 11(19), 3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193025








