Targeting Virulence Factors of Candida albicans with Natural Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
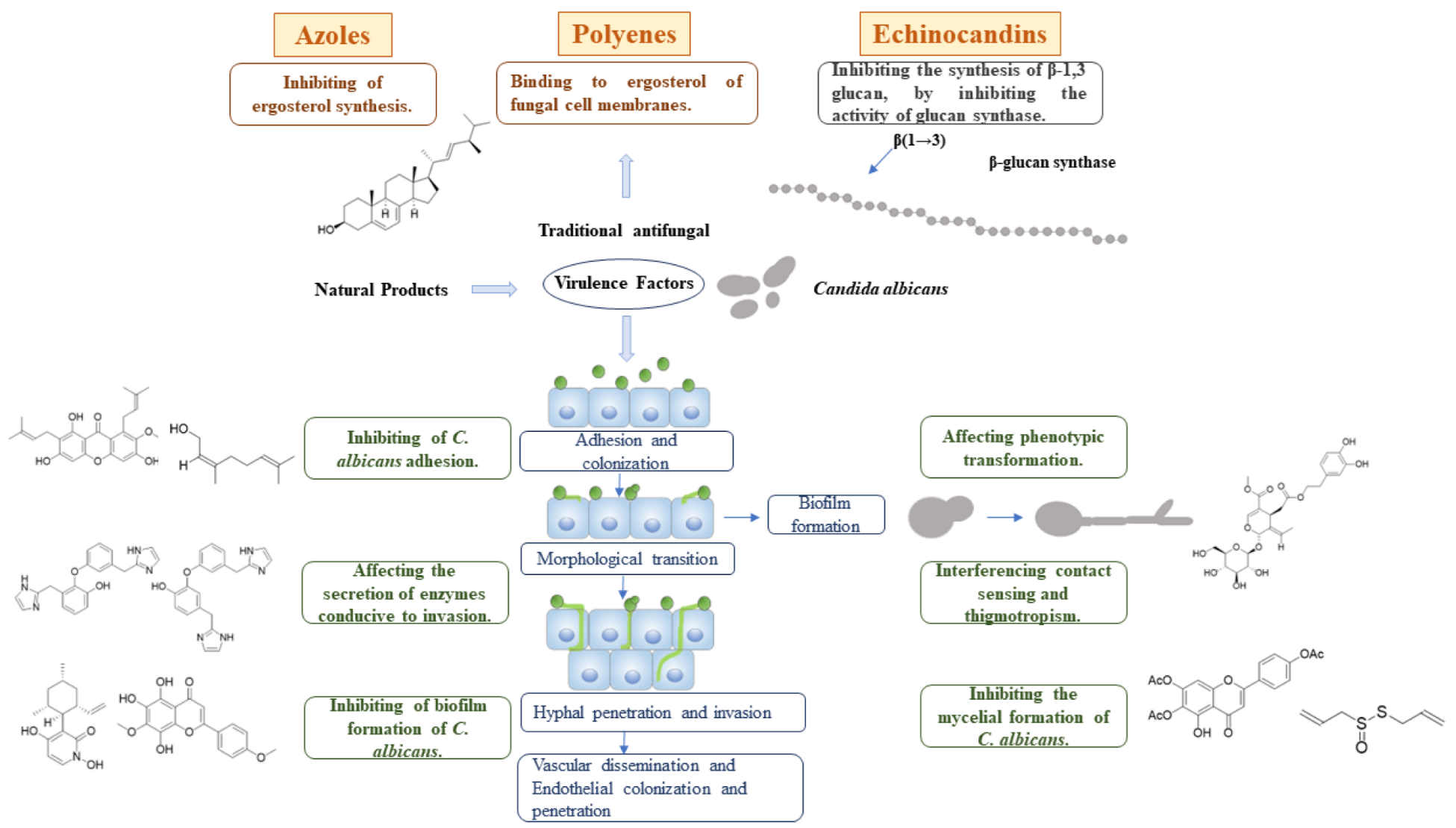
2. Virulence Factors in C. albicans and Natural Products with Regulating Activity
2.1. Adhesion
2.1.1. Adhesin
2.1.2. Invasin
2.2. Invasive Enzymes
2.2.1. Secretory Aspartate Protease (Sap)
2.2.2. Phospholipase (PL)
2.3. Biofilm Formation
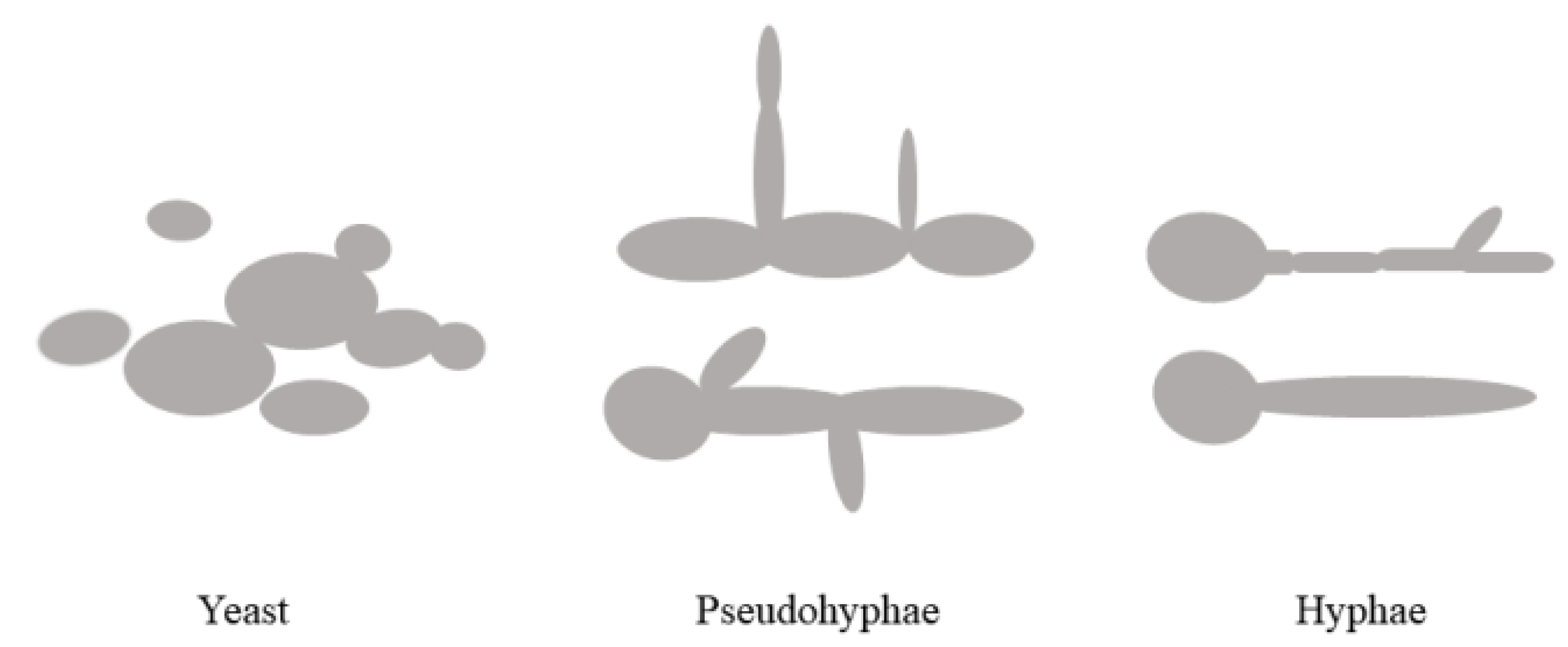
2.4. Phenotypic Transformation
2.5. Contact Sensing and Thigmotropism
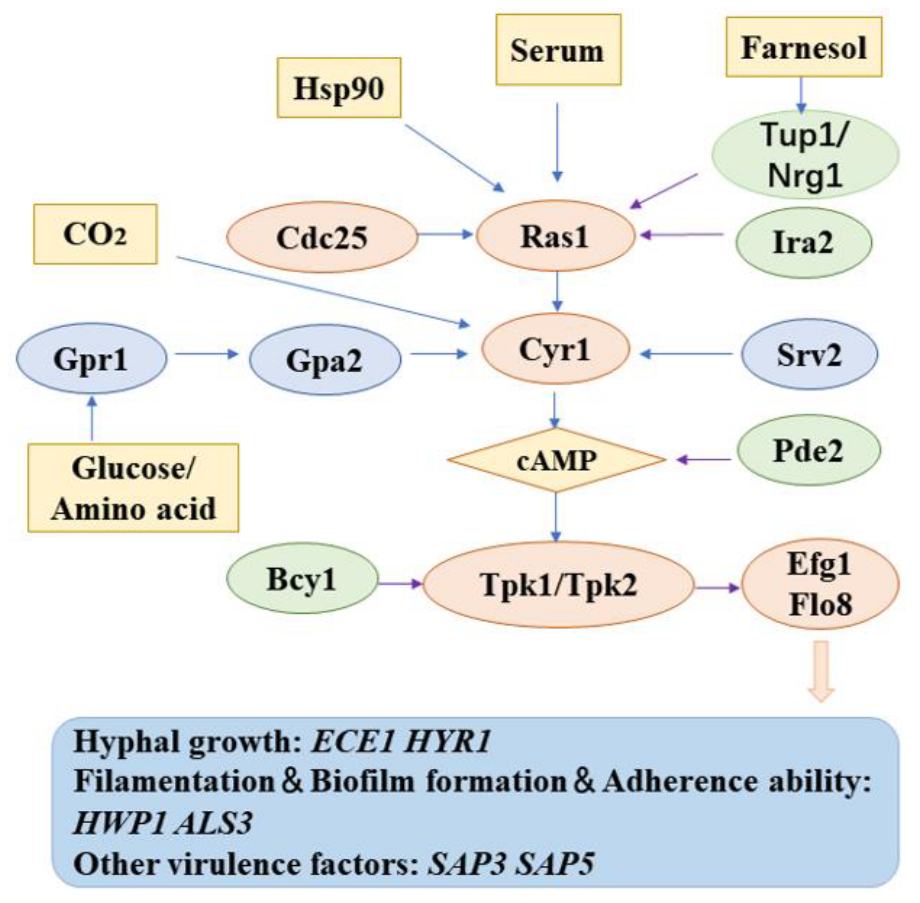
2.6. Signaling Pathways Related to Mycelial Formation
2.6.1. MAPK Signal Pathway
2.6.2. cAMP/PKA Signaling Pathway
3. Other Drugs
4. Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Kuo, S.F.; Chen, F.J.; Lee, C.H. The Impact of Biofilm Formation on the Persistence of Candidemia. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases-Estimate Precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapar, N. Epidemiology and risk factors for invasive candidiasis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2014, 10, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandra, T.; Roberts, J.A.; Antonelli, M.; Bassetti, M.; Vincent, J.L. Diagnosis and management of invasive candidiasis in the ICU: An updated approach to an old enemy. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.; Dos Santos Fontenelle, R.O.; De Brito, E.H.S.; De Morais, S.M. Biofilm of Candida albicans: Formation, regulation and resistance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Looking into Candida albicans infection, host response, and antifungal strategies. Virulence 2015, 6, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, C.J.; Johnson, A.D. Candida albicans Biofilms and Human Disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullberg, B.J.; Arendrup, M.C. Invasive Candidiasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gow, N.A.; Van De Veerdonk, F.L.; Brown, A.J.; Netea, M.G. Candida albicans morphogenesis and host defence: Discriminating invasion from colonization. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 10, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathakumari, B.; Liang, G.; Liu, W. Immune defence to invasive fungal infections: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.R., 3rd; Cadena, J.; Patterson, T.F. Overview of antifungal agents. Clin. Chest Med. 2009, 30, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soysa, N.S.; Samaranayake, L.P.; Ellepola, A.N. Antimicrobials as a contributory factor in oral candidosis--a brief overview. Oral Dis. 2008, 14, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, X.; Zhao, C.; Yan, Z.M.; Hua, H. Efficacy of nystatin for the treatment of oral candidiasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto Reis, C.; Vasques Roque, L.; Baptista, M.; Rijo, P. Innovative formulation of nystatin particulate systems in toothpaste for candidiasis treatment. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2016, 21, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Huang, B.; Ding, Z. Efficacy of antifungal drugs in the treatment of oral candidiasis: A Bayesian network meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, J.D.; Sobel, R. Current treatment options for vulvovaginal candidiasis caused by azole-resistant Candida species. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2018, 19, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revie, N.M.; Iyer, K.R.; Robbins, N.; Cowen, L.E. Antifungal drug resistance: Evolution, mechanisms and impact. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Daele, R.; Spriet, I.; Wauters, J.; Maertens, J.; Mercier, T.; Van Hecke, S.; Brüggemann, R. Antifungal drugs: What brings the future? Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, S328–S343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfect, J.R. The antifungal pipeline: A reality check. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, T.; Romo, J.A.; Pierce, C.G.; McHardy, S.F.; Saville, S.P.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. Targeting Candida albicans filamentation for antifungal drug development. Virulence 2017, 8, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Khadke, S.K.; Yamano, A.; Watanabe, A.; Lee, J. Inhibition of Biofilm Formation by Candida albicans and Polymicrobial Microorganisms by Nepodin via Hyphal-Growth Suppression. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldara, M.; Marmiroli, N. Known Antimicrobials Versus Nortriptyline in Candida albicans: Repositioning an Old Drug for New Targets. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.; Suriyanarayanan, T.; Zeng, G.; Le, T.D.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Tong, C.; Wang, Y.; Seneviratne, C.J. Use of Haploid Model of Candida albicans to Uncover Mechanism of Action of a Novel Antifungal Agent. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldara, M.; Marmiroli, N. Tricyclic antidepressants inhibit Candida albicans growth and biofilm formation. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, J.; Zu, R.; Huang, X.; Ge, Y.; Li, Y. Synergistic Effect of Berberine Hydrochloride and Fluconazole Against Candida albicans Resistant Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yi, Y.; Yong, J.; Sun, J.; Song, Z.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Inhibitory effect of berberine hydrochloride against Candida albicans and the role of the HOG-MAPK pathway. J. Antibiot. 2021, 74, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpa, R.; França, E.J.G.; Furlaneto-Maia, L.; Andrade, C.; Diniz, A.; Furlaneto, M.C. In vitro antifungal activity of the flavonoid baicalein against Candida species. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Shang, Q.; Lu, H.; Fu, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, Y. Inhibitory effect of Shikonin on Candida albicans growth. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasenapp, Y.; Lucas, C.; Wöltje, T.; Fohrer, J.; Papenbrock, J. Anti-Adhesion Activity of Tannins Isolated from the Mangrove Laguncularia racemosa. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1800632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaomongkolgit, R.; Jamdee, K. Inhibitory Effect of Alpha-Mangostin on Adhesion of Candida albicans to Denture Acrylic. Open Dent. J. 2015, 9, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutreix, L.; Bernard, C.; Juin, C.; Imbert, C.; Girardot, M. Do raspberry extracts and fractions have antifungal or anti-adherent potential against Candida spp? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, K.; Chen, L.; Yan, R.; Qu, S.; Li, Y.X.; Liu, M.; Zeng, H.; Tian, J. Activities of Nerol, a natural plant active ingredient, against Candida albicans in vitro and in vivo. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 5039–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wu, H.; Qiu, W.; Guo, L.; Du, X.; Yu, Q.; Gao, J.; Luo, S. Pulsatilla decoction inhibits Candida albicans proliferation and adhesion in a mouse model of vulvovaginal candidiasis via the Dectin-1 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 223, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.A.E.; Silva, B.L.S.; Takeara, R.; Freitas, R.G.; Brown, A.; De Souza, G.L.C. Probing the antioxidant potential of phloretin and phlorizin through a computational investigation. J. Mol. Model. 2018, 24, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, D.; Kim, J.; Jeon, D.; Shin, H.C.; Kim, Y. Target Proteins of Phloretin for Its Anti-Inflammatory and Antibacterial Activities Against Propionibacterium acnes-Induced Skin Infection. Molecules 2019, 24, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.Y. Biochemical Basis of Anti-Cancer-Effects of Phloretin-A Natural Dihydrochalcone. Molecules 2019, 24, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gacemi, S.; Benarous, K.; Imperial, S.; Yousfi, M. Lepidine B & E as New Target Inhibitors from Lepidium Sativum Seeds Against Four Enzymes of the Pathogen Candida albicans: In Vitro and In Silico Studies. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Pradebon Brondani, L.; Alves Da Silva Neto, T.; Antonio Freitag, R.; Guerra Lund, R. Evaluation of anti-enzyme properties of Origanum vulgare essential oil against oral Candida albicans. J. Mycol. Med. 2018, 28, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, V.; Ahmad, S.I.; Irshad, M.; Wani, W.A.; Siddiqi, W.A.; Shreaz, S. Anticandidal activity of ethanolic root extract of Juglans regia (L.): Effect on growth, cell morphology, and key virulence factors. J. Mycol. Med. 2017, 27, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Rocha, W.P.; De Brito Lemos, V.L.; Ferreira, M.R.; Soares, L.A.; Svidzisnki, T.I.; Milan, E.P.; Chaves, G.M. Effect of the crude extract of Eugenia uniflora in morphogenesis and secretion of hydrolytic enzymes in Candida albicans from the oral cavity of kidney transplant recipients. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Lou, H. Lichen endophyte derived pyridoxatin inactivates Candida growth by interfering with ergosterol biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1762–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Srivastava, V.; Ahmad, A. Dodonaea viscosa var angustifolia derived 5,6,8-trihydroxy-7,4’ dimethoxy flavone inhibits ergosterol synthesis and the production of hyphae and biofilm in Candida albicans. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liao, K.; Wang, D. Effects of magnolol and honokiol on adhesion, yeast-hyphal transition, and formation of biofilm by Candida albicans. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, T.; Qian, W. Antibiofilm Efficacy of Luteolin Against Single and Dual Species of Candida albicans and Enterococcus faecalis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 715156. [Google Scholar]
- Kolouchová, I.; Maťátková, O.; Paldrychová, M.; Kodeš, Z.; Kvasničková, E.; Sigler, K.; Čejková, A.; Šmidrkal, J.; Demnerová, K.; Masák, J. Resveratrol, pterostilbene, and baicalein: Plant-derived anti-biofilm agents. Folia Microbiol. 2018, 63, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, B.; Chassagne, F.; Vásquez-Ocmín, P.; Tahrioui, A.; Chevalier, S.; Vansteelandt, M.; Triastuti, A.; Amasifuen Guerra, C.A.; Fabre, N.; Haddad, M. Pharmacological validation of Solanum mammosum L. as an anti-infective agent: Role of solamargine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 280, 114473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ha Quang Bao, T.; Shin, Y.K.; Kim, K.Y. Antifungal activity of magnoflorine against Candida strains. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meccatti, V.M.; Oliveira, J.R.; Figueira, L.W.; Lagareiro Netto, A.A.; Zamarioli, L.S.; Marcucci, M.C.; Camargo, S.E.A.; Carvalho, C.A.T.; Oliveira, L.D. Rosmarinus officinalis L. (rosemary) extract has antibiofilm effect similar to the antifungal nystatin on Candida samples. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2021, 93, e20190366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, K.Y. Adenophora triphylla var. japonica Inhibits Candida Biofilm Formation, Increases Susceptibility to Antifungal Agents and Reduces Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, P.L.; Carvalho, L.T.; Paschoal, M.A.; De Sousa, E.M.; Moffa, E.B.; Da Silva, M.A.; Tavarez Rde, J.; Gonçalves, L.M. In vitro Effects of Lemongrass Extract on Candida albicans Biofilms, Human Cells Viability, and Denture Surface. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Byrnes, D.R.; Dinssa, F.F.; Simon, J.E.; Wu, Q. Identification of Polyphenols, Glycoalkaloids, and Saponins in Solanum scabrum Berries Using HPLC-UV/Vis-MS. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorić, N.; Kopjar, N.; Bobnjarić, I.; Horvat, I.; Tomić, S.; Kosalec, I. Antifungal Activity of Oleuropein against Candida albicans-The In Vitro Study. Molecules 2016, 21, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, Y. Development of Candida albicans Biofilms Is Diminished by Paeonia lactiflora via Obstruction of Cell Adhesion and Cell Lysis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.Y.; Ni, G.H.; Liao, Y.C.; Su, L.Q.; Li, J.; Li, J.S.; Rao, G.X.; Wang, R.R. Antifungal Activity and Potential Mechanism of 6,7, 4’-O-Triacetylscutellarein Combined With Fluconazole Against Drug-Resistant C. albicans. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 692693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Lv, Y.; Cui, Z.; Bei, G.; Qin, G.; Zhou, J.; Ge, T. Tetrandrine ameliorates cognitive impairment via inhibiting astrocyte-derived S100B activation in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Neurol. Res. 2013, 35, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralla, E.J.; Coleman, G.L.; Jonas, A.M. Toxicology studies with d-tetrandrine (NSC-77037), a plant alkaloid with vascular and lymphotoxic effects in dogs and monkeys. Cancer Chemother. Rep. 3 1974, 5, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Low, C.F.; Chong, P.P.; Yong, P.V.; Lim, C.S.; Ahmad, Z.; Othman, F. Inhibition of hyphae formation and SIR2 expression in Candida albicans treated with fresh Allium sativum (garlic) extract. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, A.; Pandian, S.K. Piperine Impedes Biofilm Formation and Hyphal Morphogenesis of Candida albicans. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkash, Y.; Feldman, M.; Ginsburg, I.; Steinberg, D.; Shalish, M. Green Tea Polyphenols and Padma Hepaten Inhibit Candida albicans Biofilm Formation. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1690747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Lee, J.H.; Beyenal, H.; Lee, J. Fatty Acids as Antibiofilm and Antivirulence Agents. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Du, F.; Yan, L.; He, G.; He, J.; Wang, C.; Rao, G.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, G. Potent Activities of Roemerine against Candida albicans and the Underlying Mechanisms. Molecules 2015, 20, 17913–17928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanachaikunsopon, P.; Phumkhachorn, P. Bacteriostatic effect of flavonoids isolated from leaves of Psidium guajava on fish pathogens. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chang, W.; Shi, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Lou, H. Biatriosporin D displays anti-virulence activity through decreasing the intracellular cAMP levels. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 322, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chang, W.; Zhang, M.; Ying, Z.; Lou, H. Natural product solasodine-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside inhibits the virulence factors of Candida albicans. FEMS Yeast Res. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witchley, J.N.; Penumetcha, P.; Abon, N.V.; Woolford, C.A.; Mitchell, A.P.; Noble, S.M. Candida albicans Morphogenesis Programs Control the Balance between Gut Commensalism and Invasive Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 432–443e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffin, W.L. Candida albicans cell wall proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2008, 72, 495–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, L.L.; Cota, E. Candida albicans Agglutinin-Like Sequence (Als) Family Vignettes: A Review of Als Protein Structure and Function. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, L.L.; Green, C.B.; Oh, S.H.; Zhao, X. Discovering the secrets of the Candida albicans agglutinin-like sequence (ALS) gene family--a sticky pursuit. Med. Mycol. 2008, 46, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.F.; Kurjan, J.; Lipke, P.N. A pathway for cell wall anchorage of Saccharomyces cerevisiae alpha-agglutinin. Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 14, 4825–4833. [Google Scholar]
- Hager, C.L.; Larkin, E.L.; Long, L.; Zohra Abidi, F.; Shaw, K.J.; Ghannoum, M.A. Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of the Antifungal Activity of APX001A/APX001 against Candida auris. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rast, T.J.; Kullas, A.L.; Southern, P.J.; Davis, D.A. Human Epithelial Cells Discriminate between Commensal and Pathogenic Interactions with Candida albicans. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, C.; Han, J. Hypha essential genes in Candida albicans pathogenesis of oral lichen planus: An in-vitro study. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle, F.; Wächtler, B.; L’Ollivier, C.; Holland, G.; Bannert, N.; Wilson, D.; Labruère, C.; Bonnin, A.; Hube, B. Cellular interactions of Candida albicans with human oral epithelial cells and enterocytes. Cell Microbiol. 2010, 12, 248–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, F.L.; Wilson, D.; Hube, B. Candida albicans pathogenicity mechanisms. Virulence 2013, 4, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassone, A. Development of vaccines for Candida albicans: Fighting a skilled transformer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moragues, M.D.; Rementeria, A.; Sevilla, M.J.; Eraso, E.; Quindos, G. Candida antigens and immune responses: Implications for a vaccine. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2014, 13, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vidal, C.; Viasus, D.; Carratalà, J. Pathogenesis of invasive fungal infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 26, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.N.; Solis, N.V.; Phan, Q.T.; Bajwa, J.S.; Kashleva, H.; Thompson, A.; Liu, Y.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A.; Edgerton, M.; Filler, S.G. Host cell invasion and virulence mediated by Candida albicans Ssa1. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felk, A.; Kretschmar, M.; Albrecht, A.; Schaller, M.; Beinhauer, S.; Nichterlein, T.; Sanglard, D.; Korting, H.C.; Schäfer, W.; Hube, B. Candida albicans hyphal formation and the expression of the Efg1-regulated proteinases Sap4 to Sap6 are required for the invasion of parenchymal organs. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3689–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.P.; Kumar, S.S.; Menon, T. Phospholipase and proteinase activities of clinical isolates of Candida from immunocompromised patients. Mycopathologia 2006, 161, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naglik, J.R.; Rodgers, C.A.; Shirlaw, P.J.; Dobbie, J.L.; Fernandes-Naglik, L.L.; Greenspan, D.; Agabian, N.; Challacombe, S.J. Differential expression of Candida albicans secreted aspartyl proteinase and phospholipase B genes in humans correlates with active oral and vaginal infections. J. Infect Dis. 2003, 188, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, B.E.; Wilhelmus, K.R.; Hube, B. The role of secreted aspartyl proteinases in Candida albicans keratitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 3559–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schild, L.; Heyken, A.; De Groot, P.W.; Hiller, E.; Mock, M.; De Koster, C.; Horn, U.; Rupp, S.; Hube, B. Proteolytic cleavage of covalently linked cell wall proteins by Candida albicans Sap9 and Sap10. Eukaryot Cell 2011, 10, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naglik, J.; Albrecht, A.; Bader, O.; Hube, B. Candida albicans proteinases and host/pathogen interactions. Cell Microbiol. 2004, 6, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathé, L.; Van Dijck, P. Recent insights into Candida albicans biofilm resistance mechanisms. Curr. Genet. 2013, 59, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Saraswat, D.; Tati, S.; Edgerton, M. Novel Aggregation Properties of Candida albicans Secreted Aspartyl Proteinase Sap6 Mediate Virulence in Oral Candidiasis. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 2614–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Yang, J.; Pan, Y.; Xi, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Ma, Y. The correlation of virulence, pathogenicity, and itraconazole resistance with SAP activity in Candida albicans strains. Can. J. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, H.; Semlali, A.; Chmielewski, W.; Rouabhia, M. E-Cigarettes Increase Candida albicans Growth and Modulate its Interaction with Gingival Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderone, R.A.; Fonzi, W.A. Virulence factors of Candida albicans. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannoum, M.A. Potential role of phospholipases in virulence and fungal pathogenesis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Seshan, K.R.; Leidich, S.D.; Chandra, J.; Cole, G.T.; Ghannoum, M.A. Reintroduction of the PLB1 gene into Candida albicans restores virulence in vivo. Microbiology 2001, 147, 2585–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, S.; Chunyang, L. Correlation between phospholipase of Candida albicans and resistance to fluconazole. Mycoses 2012, 55, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theiss, S.; Ishdorj, G.; Brenot, A.; Kretschmar, M.; Lan, C.Y.; Nichterlein, T.; Hacker, J.; Nigam, S.; Agabian, N.; Köhler, G.A. Inactivation of the phospholipase B gene PLB5 in wild-type Candida albicans reduces cell-associated phospholipase A2 activity and attenuates virulence. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q. Phloretin inhibited the pathogenicity and virulence factors against Candida albicans. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 2420–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, S.H.; Jo, S.J.; Kim, J.C. Control Efficacy of Phloretin Isolated from Apple Fruits Against Several Plant Diseases. Plant Pathol. J. 2010, 26, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Chandra, J. Candida biofilm resistance. Drug Resist. Update 2004, 7, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.W.; Harless, E.L. Effects of practice on SISI scores and the relationship of SISI score to the intensity difference limen. J. Am. Audiol. Soc. 1976, 2, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Cowen, L.E.; Sanglard, D.; Howard, S.J.; Rogers, P.D.; Perlin, D.S. Mechanisms of Antifungal Drug Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 5, a019752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Cao, J.; Yang, W.; Zhao, X. ALS3 Expression as an Indicator for Candida albicans Biofilm Formation and Drug Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 655242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, S.; Wang, P.; Sun, S. Antifungal effects and potential mechanisms of lonidamine in combination with fluconazole against Candida albicans. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brajtburg, J.; Powderly, W.G.; Kobayashi, G.S.; Medoff, G. Amphotericin B: Current understanding of mechanisms of action. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshima, Y.; Shin-ya, K.; Shimazu, A.; Furihata, K.; Chul, H.S.; Furihata, K.; Hayakawa, Y.; Nagai, K.; Seto, H. Isolation and structural elucidation of pyridoxatin, a free radical scavenger of microbial origin. J. Antibiot. 1991, 44, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Park, J.E.; Song, D.J.; Huh, H.J.; Park, S.; Kang, C.I.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, N.Y. First Case of Echinocandin-Resistant Candida albicans in Korea. Ann. Lab. Med. 2017, 37, 556–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Faria, D.R.; Sakita, K.M.; Akimoto-Gunther, L.S.; Kioshima É, S.; Svidzinski, T.I.E.; Bonfim-Mendonça, P.S. Cell damage caused by vaginal Candida albicans isolates from women with different symptomatologies. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.; Shanks, S.; Duncan, V.M.; Yang, M.; Mackenzie, K.; Gow, N.A. Hyphal orientation of Candida albicans is regulated by a calcium-dependent mechanism. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Summers, E.; Guo, B.; Fink, G. Ras signaling is required for serum-induced hyphal differentiation in Candida albicans. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6339–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockmühl, D.P.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Gerads, M.; Sonneborn, A.; Ernst, J.F. Distinct and redundant roles of the two protein kinase A isoforms Tpk1p and Tpk2p in morphogenesis and growth of Candida albicans. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 42, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.R.; Schröppel, K.; Harcus, D.; Marcil, A.; Dignard, D.; Taylor, B.N.; Thomas, D.Y.; Whiteway, M.; Leberer, E. Signaling through Adenylyl Cyclase Is Essential for Hyphal Growth and Virulence in the Pathogenic Fungus Candida albicans. Molec. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.R.; Fink, G.R. Candida albicans strains heterozygous and homozygous for mutations in mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling components have defects in hyphal development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13223–13228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leberer, E.; Harcus, D.; Broadbent, I.D.; Clark, K.L.; Dignard, D.; Ziegelbauer, K.; Schmidt, A.; Gow, N.A.; Brown, A.J.; Thomas, D.Y. Signal transduction through homologs of the Ste20p and Ste7p protein kinases can trigger hyphal formation in the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13217–13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Shao, F. Biochemistry and cell signaling taught by bacterial effectors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matlawska-Wasowska, K.; Finn, R.; Mustel, A.; O’Byrne, C.P.; Baird, A.W.; Coffey, E.T.; Boyd, A. The Vibrio parahaemolyticus Type III Secretion Systems manipulate host cell MAPK for critical steps in pathogenesis. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toenjes, K.A.; Munsee, S.M.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Jeffrey, R.; Edwards, J.E., Jr.; Johnson, D.I. Small-molecule inhibitors of the budded-to-hyphal-form transition in the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toenjes, K.A.; Stark, B.C.; Brooks, K.M.; Johnson, D.I. Inhibitors of cellular signalling are cytotoxic or block the budded-to-hyphal transition in the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, S.M.; Gianetti, B.A.; Witchley, J.N. Candida albicans cell-type switching and functional plasticity in the mammalian host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Su, C.; Liu, H. Candida albicans hyphal initiation and elongation. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, D.A.; Sundstrom, P. The Ras/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway and virulence in Candida albicans. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khoury, M.; Ligot, R.; Mahoney, S.; Stack, C.M.; Perrone, G.G.; Morton, C.O. The in vitro effects of interferon-gamma, alone or in combination with amphotericin B, tested against the pathogenic fungi Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, H.R.; Sanders, D.A.; Mccormick, F. The GTPase superfamily: A conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature 1990, 348, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, J.R.; Figueira, L.W.; Sper, F.L.; Meccatti, V.M.; Camargo, S.E.A.; De Oliveira, L.D. Thymus vulgaris L. and thymol assist murine macrophages (RAW 264.7) in the control of in vitro infections by Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Candida albicans. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpetch, W.; Somboonna, N.; Bulan, D.E.; Issara-Amphorn, J.; Finkelman, M.; Worasilchai, N.; Chindamporn, A.; Palaga, T.; Tumwasorn, S.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Oral administration of live- or heat-killed Candida albicans worsened cecal ligation and puncture sepsis in a murine model possibly due to an increased serum (1→3)-β-D-glucan. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojsen, R.; Regenberg, B.; Gresham, D.; Folkesson, A. A common mechanism involving the TORC1 pathway can lead to amphotericin B-persistence in biofilm and planktonic Saccharomyces cerevisiae populations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, Y.S.; Staab, J.; Sundstrom, P. Increased high-affinity phosphodiesterase PDE2 gene expression in germ tubes counteracts CAP1-dependent synthesis of cyclic AMP, limits hypha production and promotes virulence of Candida albicans. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalon, S.; Frydman, G.; Lauritano, D.; Slutzky, H.; Shlomo, E.; Levartovsky, S.; Carinci, F.; Ormianer, Z. The effect of enriching denture adhesives with chlorhexidine diacetate on the proliferation of Candida albicans: An in vitro analysis. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2017, 31, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.; Tutulan-Cunita, A.; Jung, W.; Hauser, N.C.; Hernandez, R.; Williamson, T.; Piekarska, K.; Rupp, S.; Young, T.; Stateva, L. Deletion of the high-affinity cAMP phosphodiesterase encoded by PDE2 affects stress responses and virulence in Candida albicans. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 65, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacometti, R.; Kronberg, F.; Biondi, R.M.; Hernández, A.I.; Passeron, S. Cross regulation between Candida albicans catalytic and regulatory subunits of protein kinase A. Fung. Genet. Biol. 2012, 49, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Feng, L.; Sun, S. The synergistic antifungal effects of sodium phenylbutyrate combined with azoles against Candida albicans via the regulation of the Ras-cAMP-PKA signalling pathway and virulence. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawara, U.; Small, A.G.; Quach, A.; Gorgani, N.N.; Abbott, C.A.; Ferrante, A. Cytokines regulate complement receptor immunoglobulin expression and phagocytosis of Candida albicans in human macrophages: A control point in anti-microbial immunity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.X.; Li, D.D.; Hu, D.D.; Hu, G.H.; Yan, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.Y. Effect of tetrandrine against Candida albicans biofilms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abirami, G.; Alexpandi, R.; Durgadevi, R.; Kannappan, A.; Veera Ravi, A. Inhibitory Effect of Morin Against Candida albicans Pathogenicity and Virulence Factor Production: An in vitro and in vivo Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 561298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.M.; Dourado, A.; Oliveira, R. Phytotherapy and Nutritional Supplements on Breast Cancer. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7207983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
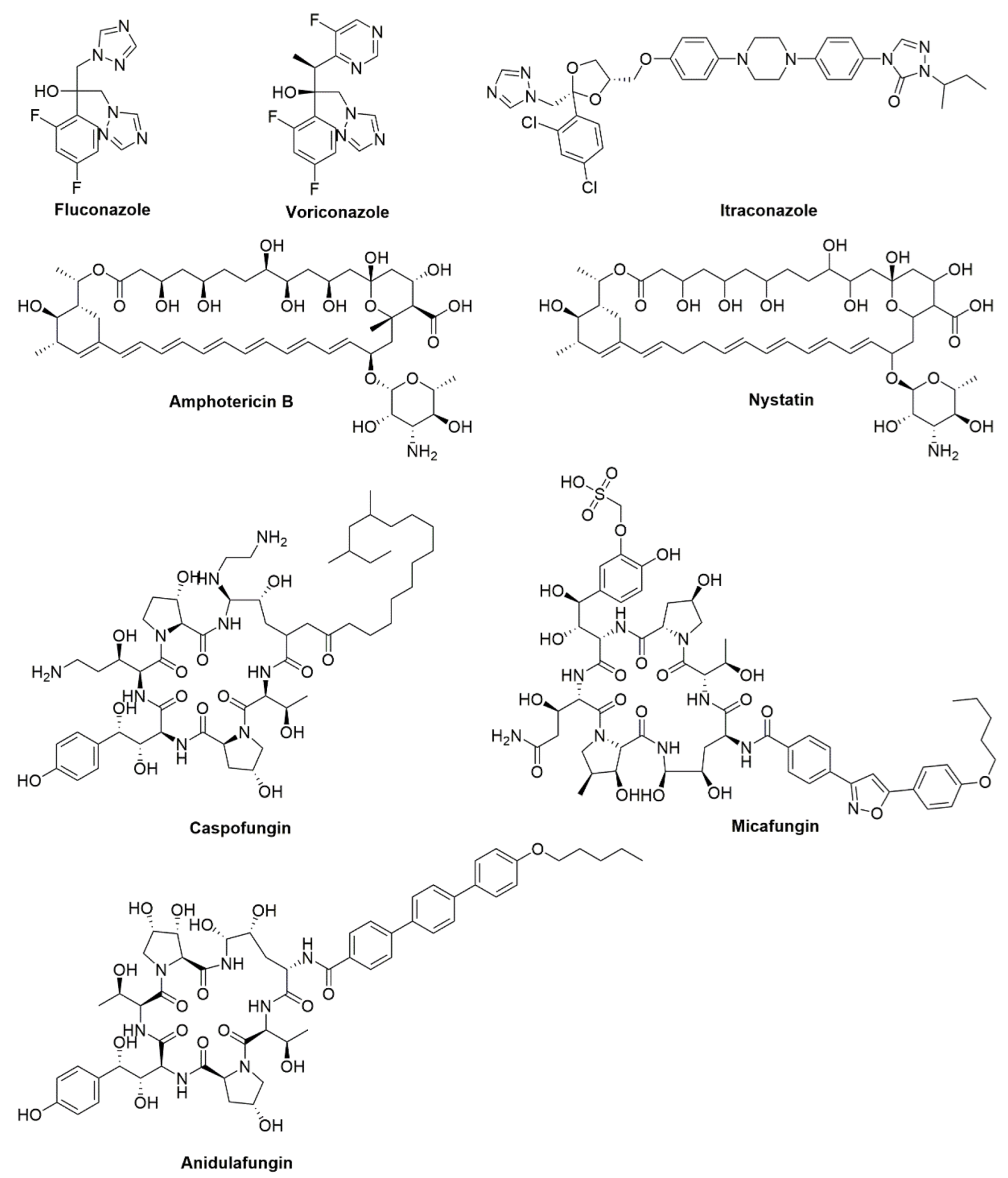
| Traditional Antifungal Agent | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Fluconazole | Azoles | Inhibit cytochrome P450 (CYP)-dependent 14-α-demethylase and prevent the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol. |
| Voriconazole | ||
| Itraconazole | ||
| Amphotericin B | Polyenes | Bind to ergosterol of fungal cell membranes. |
| Nystatin | ||
| Caspofungin | Echinocandins | Inhibit the synthesis of β-1,3 glucan, by inhibiting the activity of glucan synthase. |
| Micafungin | ||
| Anidulafungin |
| No. | Natural Products | Source | Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
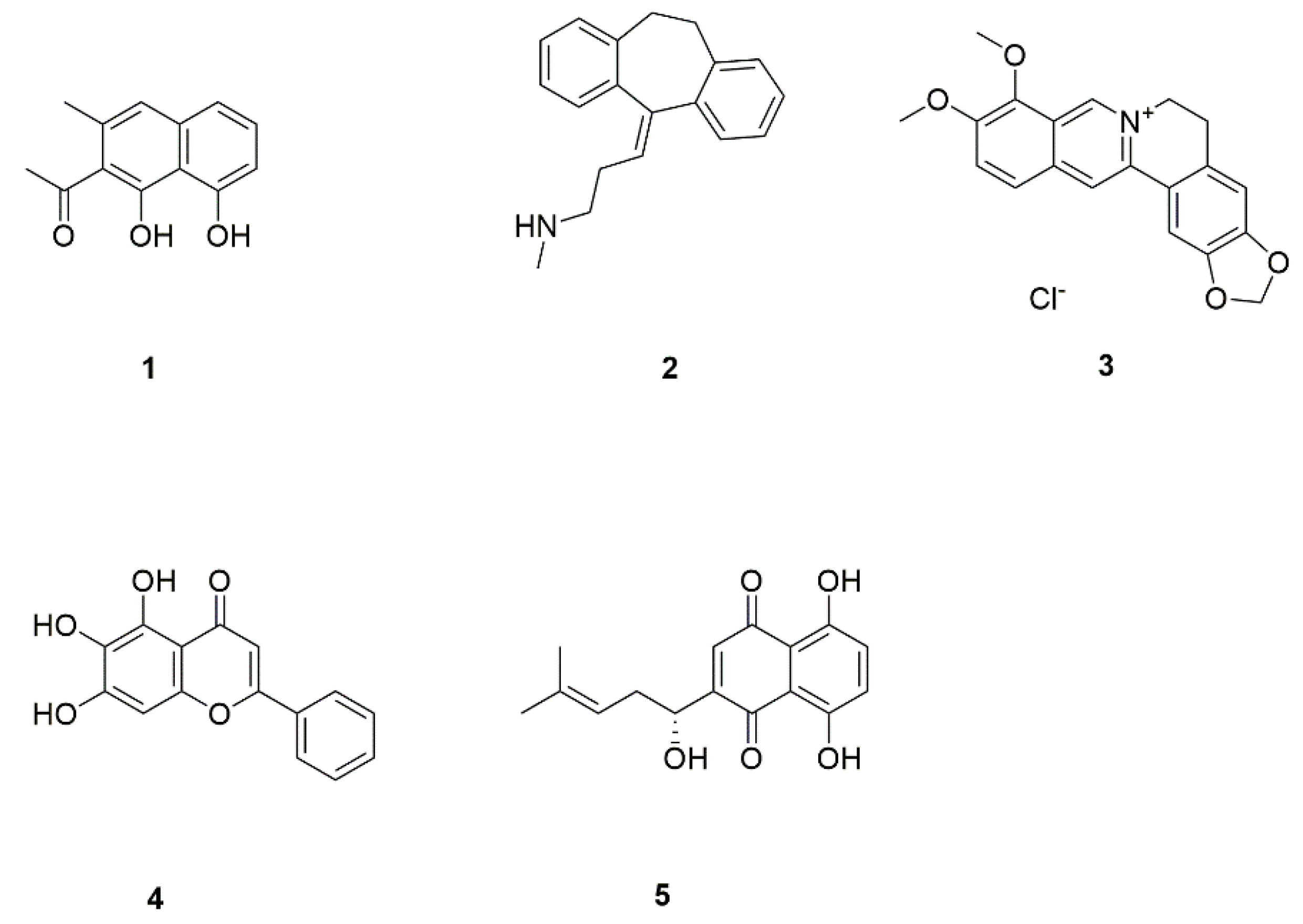
| 1 | Nepodin (1) | Rumex japonicus | Inhibits C. albicans biofilm formation. | [21] |
| 2 | Nortriptyline (2) | Metabolites of amitriptyline | Inhibits the formation of biofilm and hyphae and effectively kills cells in mature biofilm. | [22,23,24] |
| 3 | Berberine (3) | Bayberry, Coptis chinensis | Inhibits the formation of germ tubes and hyphae by regulating the MAPK pathway and increasing exposure of chitin and β-1,3-glucan. | [25,26] |
| 4 | Skullcap (4) | Scutellaria amoena | Reduces drug excretion. | [27] |
| 5 | Shikonin (5) | Echium plantagineum | Inhibits the formation of C. albicans biofilm; inhibits hyphal formation and adhesion, and enhances the production of farnesol. | [28] |
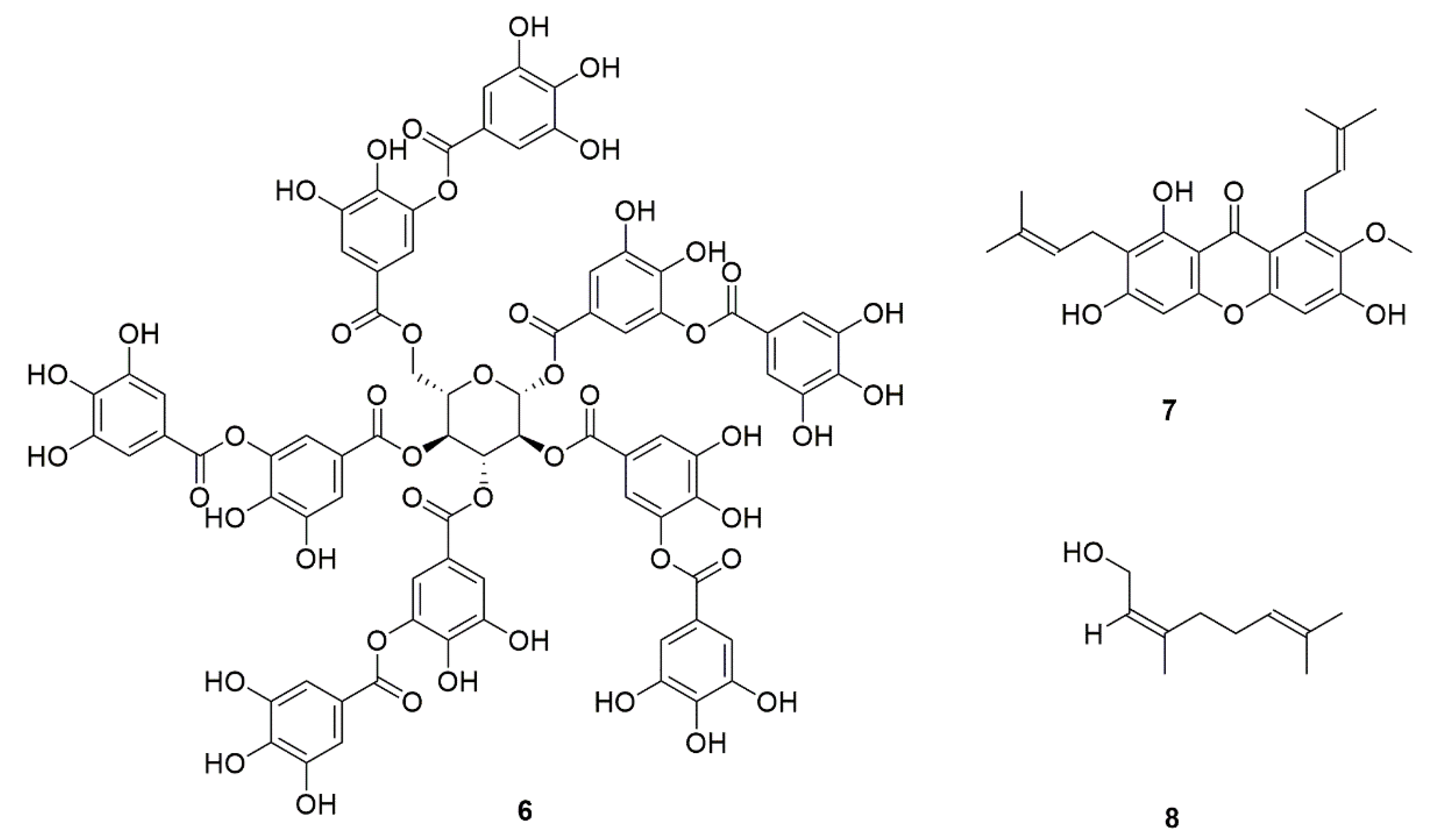
| 6 | Tannins (6) | Blueberry, grape, Mangrove Laguncularia racemosa | Inhibit the adhesion of C. albicans. | [29] |
| 7 | α-Mangostin (7) | Garcinia mangostana | [30] | |
| 8 | Hexane and ethyl acetate extracts of raspberry | Rubus idaeus | [31] | |
| 9 | Nerol (8) | Rutaceous | For the treatment of C. albicans invasion. | [32] |
| 10 | Pulsatilla decoction | Pulsatilla chinensis, Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex, Coptis chinensis, Cortex Fraxini | Inhibits the adhesion of C. albicans. | [33] |
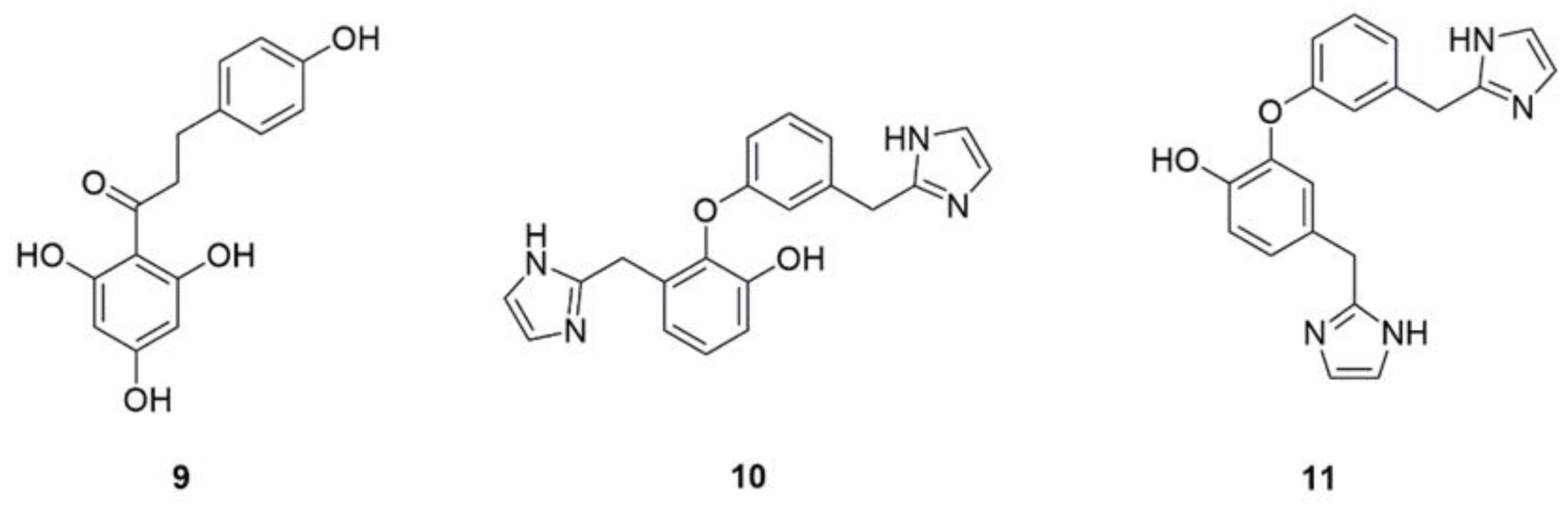
| 11 | Phloretin (9) | Apple peel, pear tree, strawberry | Inhibits the biofilm formation and suppresses the yeast hyphae transition via downregulation genes related to hypha, represses the proteases and phospholipases secretion by reducing the expression of protease-encoding genes Sap1 and Sap2 as well as PLB1. | [34,35,36] |
| 12 | Lepidine B (10) | Lepidium Sativum | Inhibit the production of phospholipase. | [37] |
| 13 | Lepidine E (11) | |||
| 14 | Oil of Origanum vulgare | [38] | ||
| 15 | Methanolic extract of Juglans regia | Affects Candida growth and hydrolytic enzyme secretions. | [39] | |
| 16 | Acetone and water crude extracts of Eugenia uniflora | Affects the transformation from yeast to hyphae and impairs the secretion of phospholipase and proteases. | [40] | |
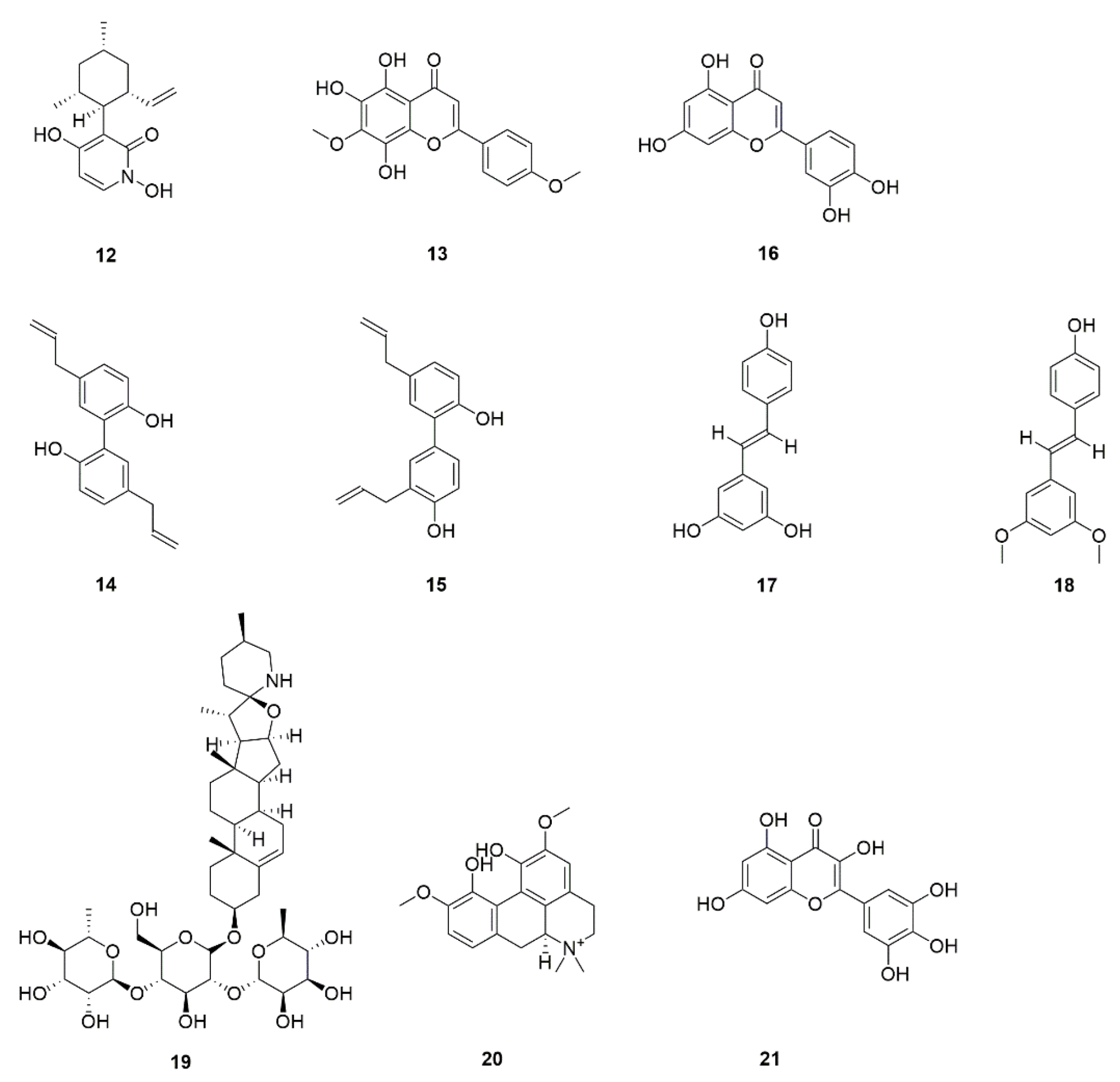
| 17 | Pyridoxatin (VB6) (12) | Fish, animal liver, legumes, Lichen endophyte | Interferes with ergosterol synthesis. | [41] |
| 18 | 5,6,8-Trihydroxy-7,4′dimethoxyflavone (13) | Dodonaea viscosa var. angustifolia | Inhibits ergosterol synthesis and hyphae and biofilm production in C. albicans. | [42] |
| 19 | Magnolol (14) | Magnolia garrettii | Inhibit adhesion and the transition from yeast to hypha and has potential inhibitory effects on C. albicans. biofilm formation. | [43] |
| 20 | Honokiol (15) | |||
| 21 | Luteolin (16) | Perilla, peppermint, Verbascum lychnitis | Inhibits adhesion of C. albicans and biofilm formation. | [44] |
| 22 | Resveratrol (17) | Grape, Berry, peanut | Inhibits biofilm formation and disrupts preformed biofilms. | [45] |
| 23 | Pterostilbene (18) | Vitis rupestris, Pterocarpus marsupium | ||
| 24 | Solamargine (19) | Solanum mammosum | Affects biofilm formation. | [46] |
| 25 | Magnoflorine (20) | Acoruscalamus, Tinospora cordifolia | Reduces C. albicans biofilm formation. | [47] |
| 26 | Propylene glycol extract of Rosmarinus officinalis | Has an antibiofilm effect. | [48] | |
| 27 | Aqueous extract of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica | Inhibits Candida biofilm formation. | [49] | |
| 28 | Ethanol extract of lemongrass | Reduces C. albicans biofilm. | [50] | |
| 29 | Myricetin (21) | Bayberry, Solanum scabrum | Interferes with biofilm formation. | [51] |
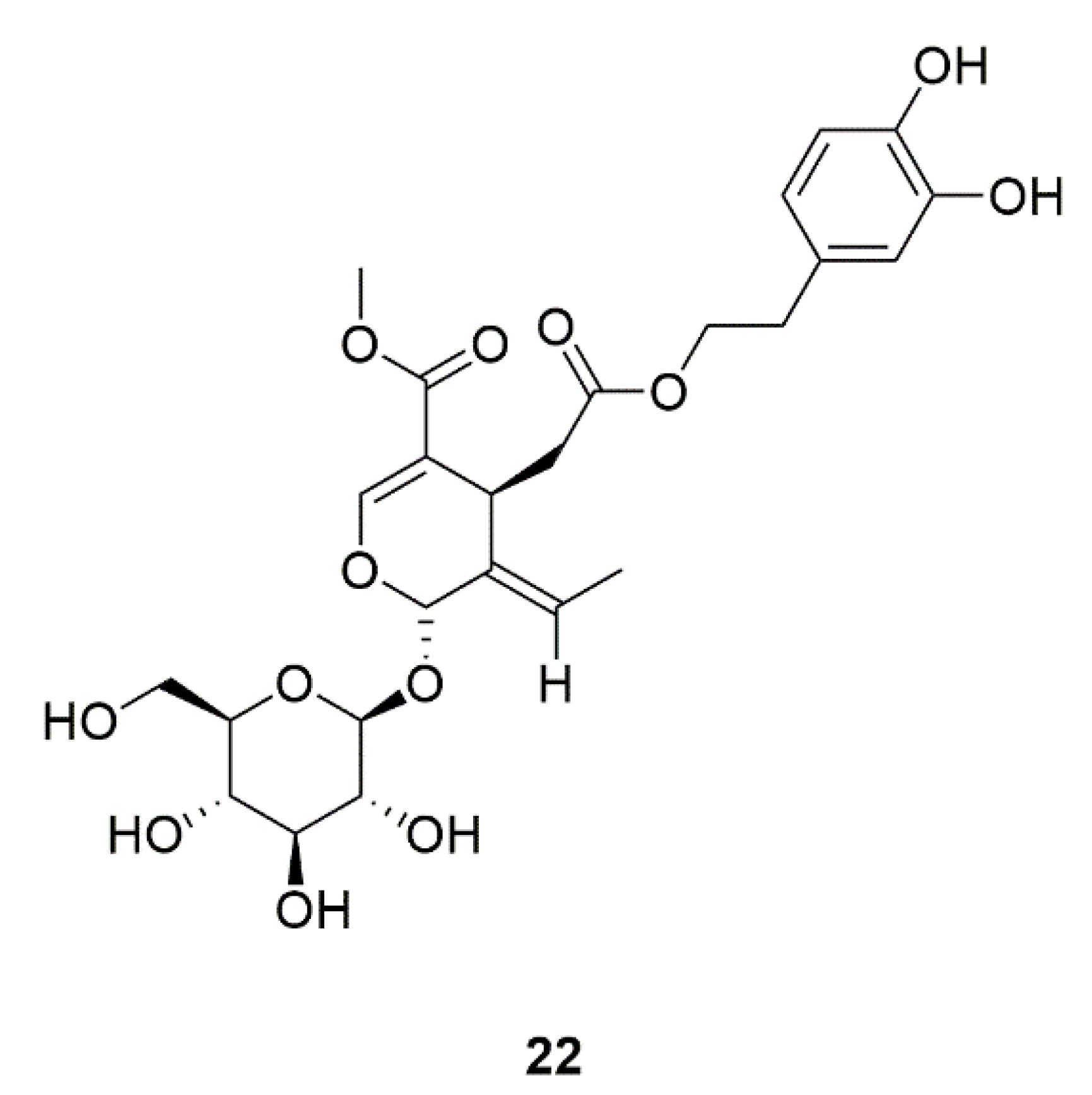
| 30 | Oleuropein (22) | Canarium album, Syringa reticulata | Regulates the morphological transformation of C. albicans. | [52] |
| 31 | Paeonia lactiflora ethanol extract | Inhibits adhesion, morphological transition from pseudohizophae to hyphae, and biofilm formation. | [53] | |
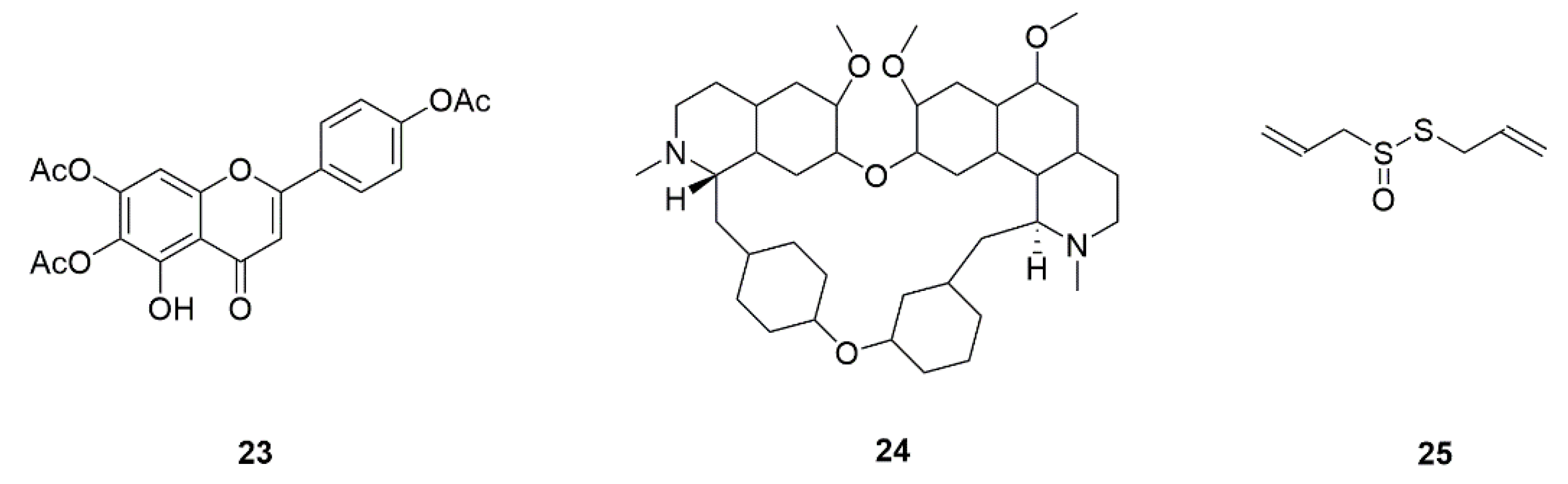
| 32 | 6,7,4′-O-Triacetylxanthin (23) | Scutellaria baicalensis | In combination with FLZ, inhibits the myceliun and biofilm via Ras/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. | [54] |
| 33 | Tetrandrine (24) | Stephania tetrandra | Inhibits biofilm formation by decreasing adhesion and morphological transformation. The mechanism of anti-biofilm may be related to the Ras/cAMP pathway. | [55,56] |
| 34 | Allicin (25) | Allium sativum | Suppresses hyphal formation in C. albicans. | [57] |
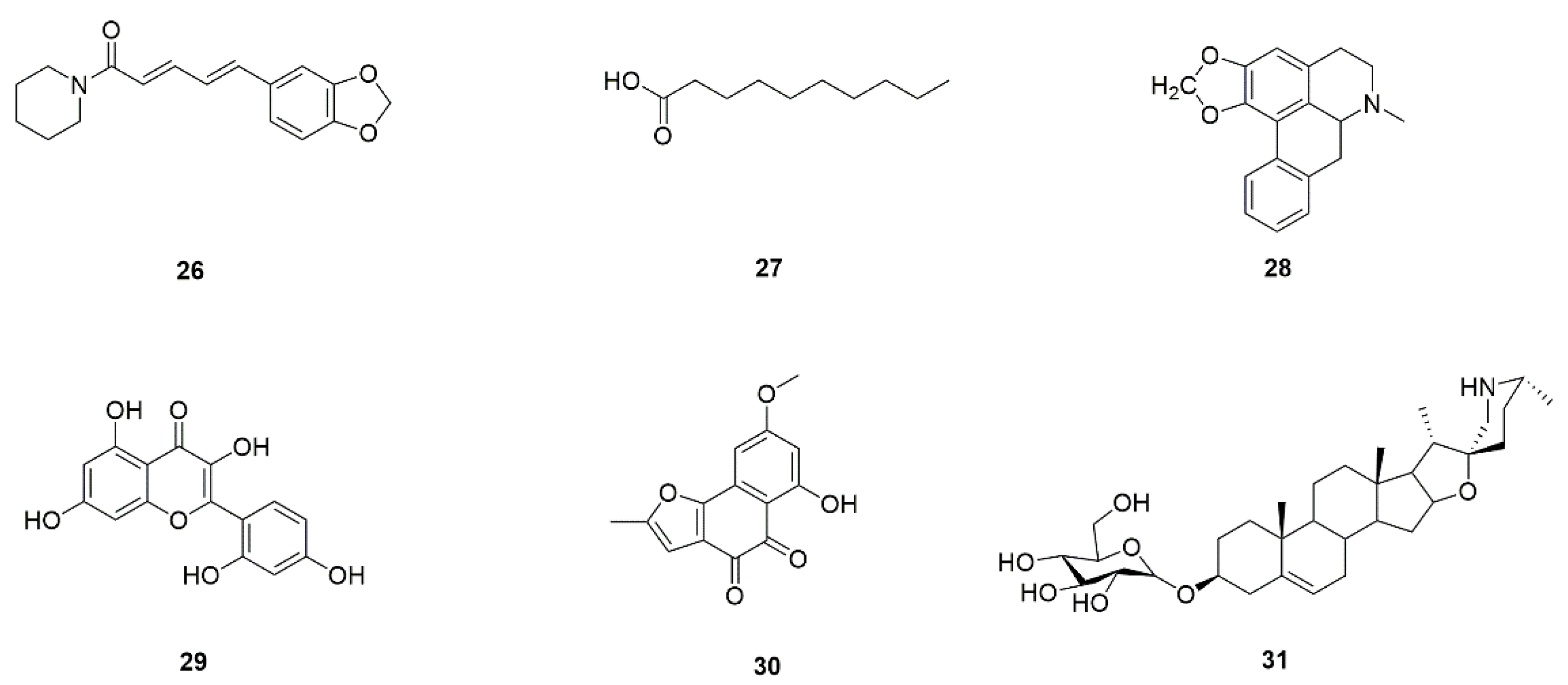
| 35 | Piperine (26) | Pepper | Regulates the morphological transformation between yeast and mycelium via restrain mycelial extension and converting mycelial phase into yeast form. | [58] |
| 36 | Padma Hepaten | Amla fruit, belleric myrobalan | Inhibits C. albicans biofilm growth and the yeast-to-hypha morphogenic change. | [59] |
| 37 | Green tea | Camellia sinensis | ||
| 38 | Decanoic acid (27) | Animal fat | Inhibits transformation from yeast to hyphae, adhesion, and biofilm formation of C. albicans. | [60] |
| 39 | Roemerine (28) | Lotus leaf, Fibraurea recisa | Inhibits yeast-to-hyphae transition of C. albicans and biofilm formation. The antibiofilm mechanism may be in connection with the cAMP pathway. | [61] |
| 40 | Morin (29) | Psidium guajava | Inhibits biofilm formation and production of other virulence factors in C. albicans in a concentration-dependent manner. | [62] |
| 41 | Biatriosporin D (30) | Biatriospora spp. | Inhibits adhesion, hyphal morphogenesis, and biofilm formation of C. albicans. | [63] |
| 42 | Solasodine-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (31) | Solanum nigrum | Inhibits adhesion, morphological transition, and biofilm formation. | [64] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bu, Q.-R.; Bao, M.-Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.-M.; Wang, C.-Z. Targeting Virulence Factors of Candida albicans with Natural Products. Foods 2022, 11, 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11192951
Bu Q-R, Bao M-Y, Yang Y, Wang T-M, Wang C-Z. Targeting Virulence Factors of Candida albicans with Natural Products. Foods. 2022; 11(19):2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11192951
Chicago/Turabian StyleBu, Qing-Ru, Meng-Yuan Bao, Yue Yang, Tian-Ming Wang, and Chang-Zhong Wang. 2022. "Targeting Virulence Factors of Candida albicans with Natural Products" Foods 11, no. 19: 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11192951
APA StyleBu, Q.-R., Bao, M.-Y., Yang, Y., Wang, T.-M., & Wang, C.-Z. (2022). Targeting Virulence Factors of Candida albicans with Natural Products. Foods, 11(19), 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11192951





