Glycosylated Zein Composite Nanoparticles for Efficient Delivery of Betulinic Acid: Fabrication, Characterization, and In Vitro Release Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Zein Glycosylated Products
2.3. Characterization of Zein and G-Zein
2.4. Electrophoresis of Zein and G-Zein
2.5. Preparation of BA-Loaded Zein/G-Zein Nanoparticles
2.6. Characterization of BA-Loaded Zein/G-Zein Nanoparticles
2.6.1. Particle Size, Polydispersity Index (PDI), and Zeta-Potential
2.6.2. Encapsulation Efficiency
2.6.3. FTIR
2.6.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6.5. X-ray Diffractometer
2.7. Stability of BA-Loaded Zein/G-Zein Nanoparticles
2.8. In Vitro Sustained Release and Water Dispersibility of BA-Loaded Zein/G-Zein Nanoparticles
2.9. Cytotoxicity of BA-Loaded Zein/G-Zein Nanoparticles to HepG2 Cells
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Sugar Type, Zein Concentration, the Ratio of Sugar to Zein, and Reaction Time on the Grafting Degree of G-Zein
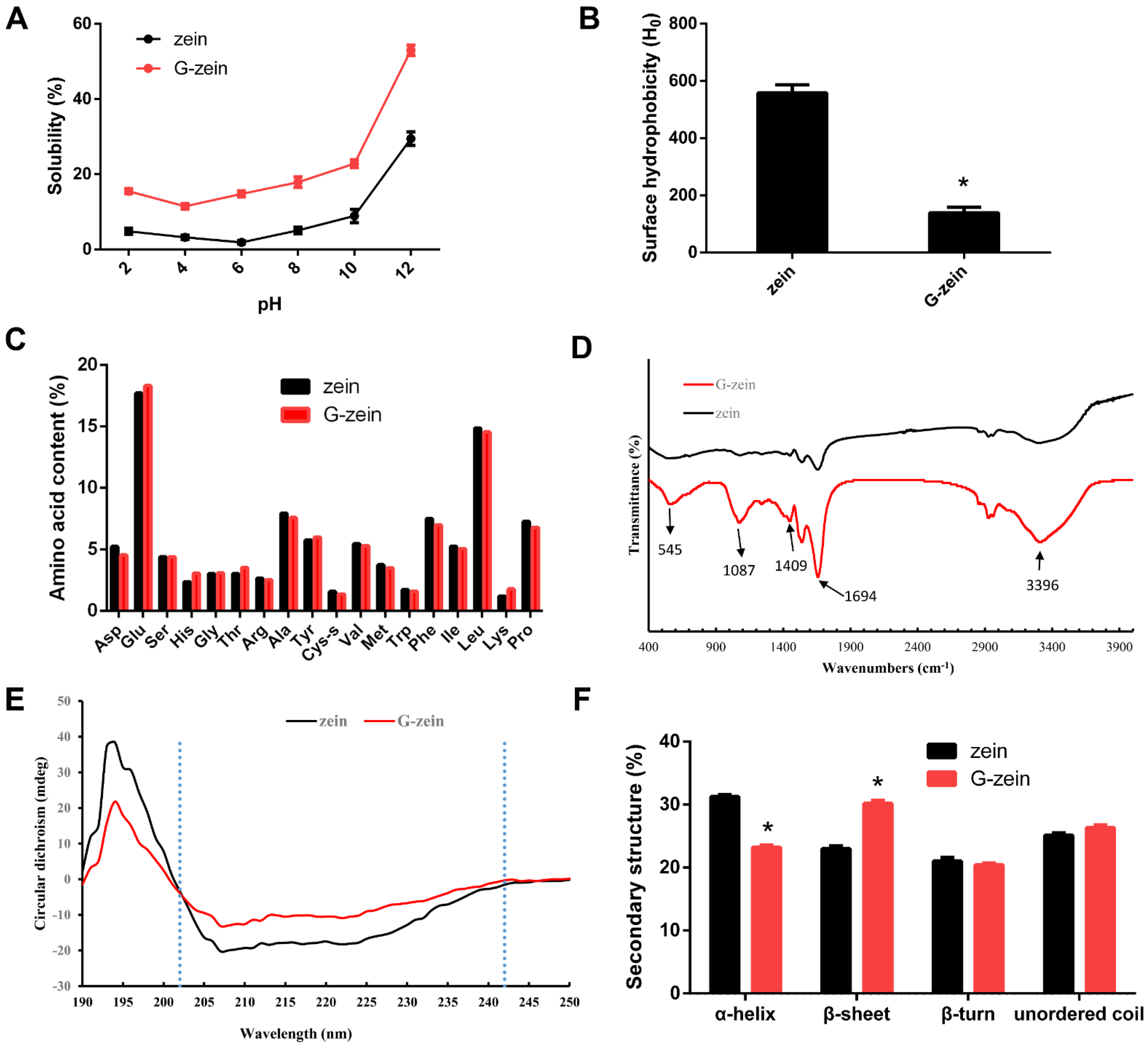
3.2. Interface Characteristics of Zein and G-Zein
3.3. Spectroscopic Analysis of Zein and G-Zein
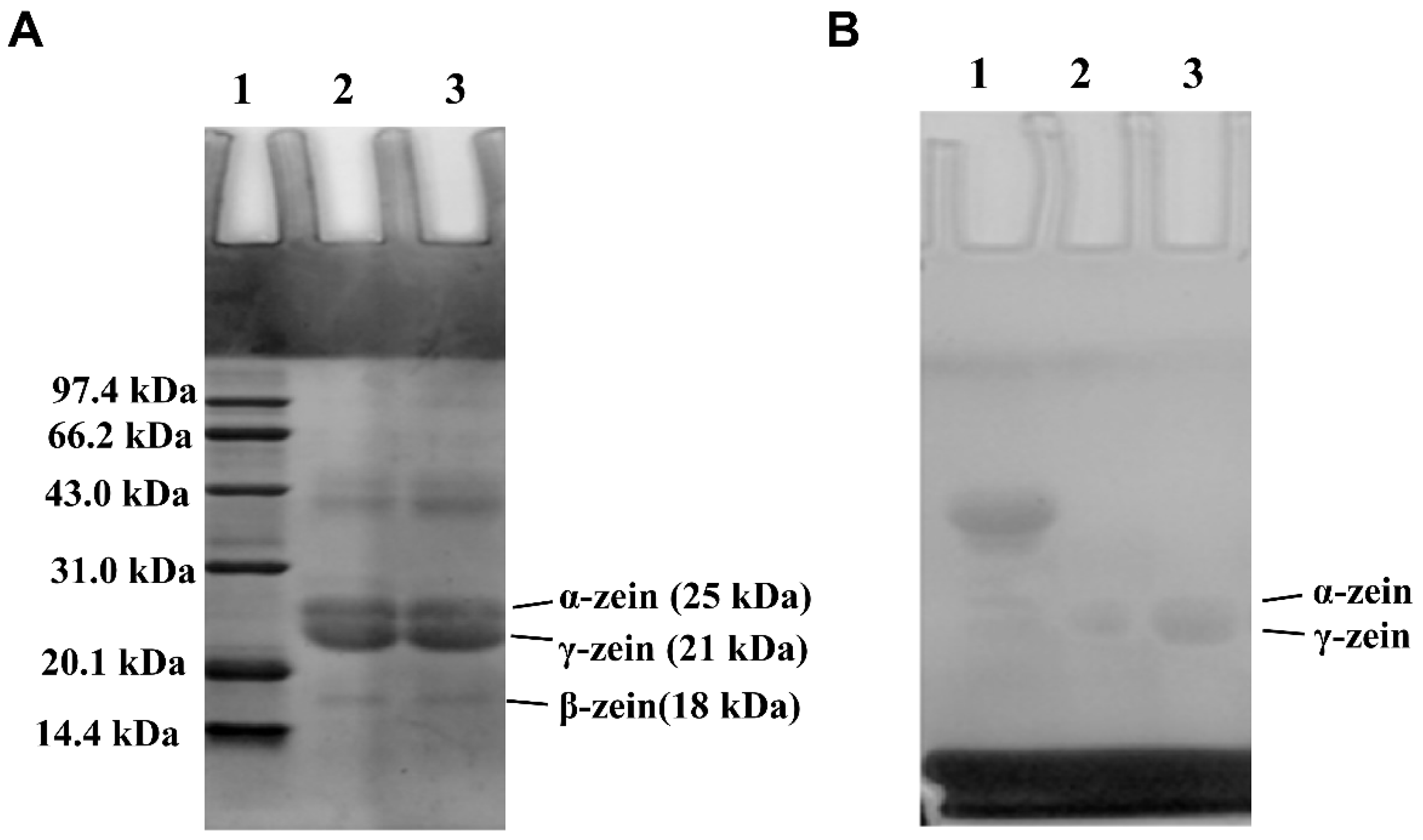
3.4. SDS–PAGE of Zein and G-Zein
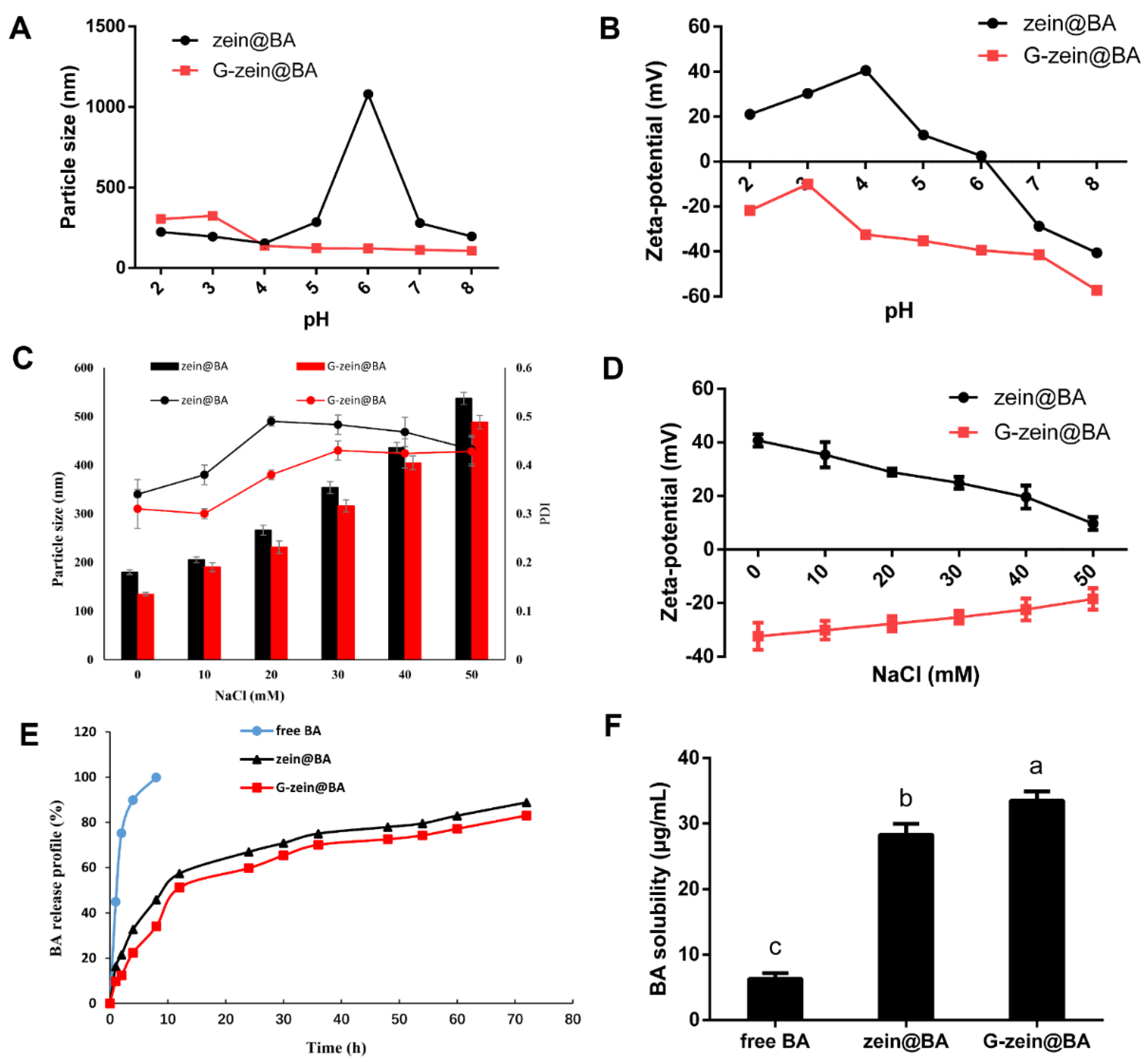
3.5. Particle Size, Zeta-Potential, and Encapsulation Efficiency of BA-Loaded Nanoparticles
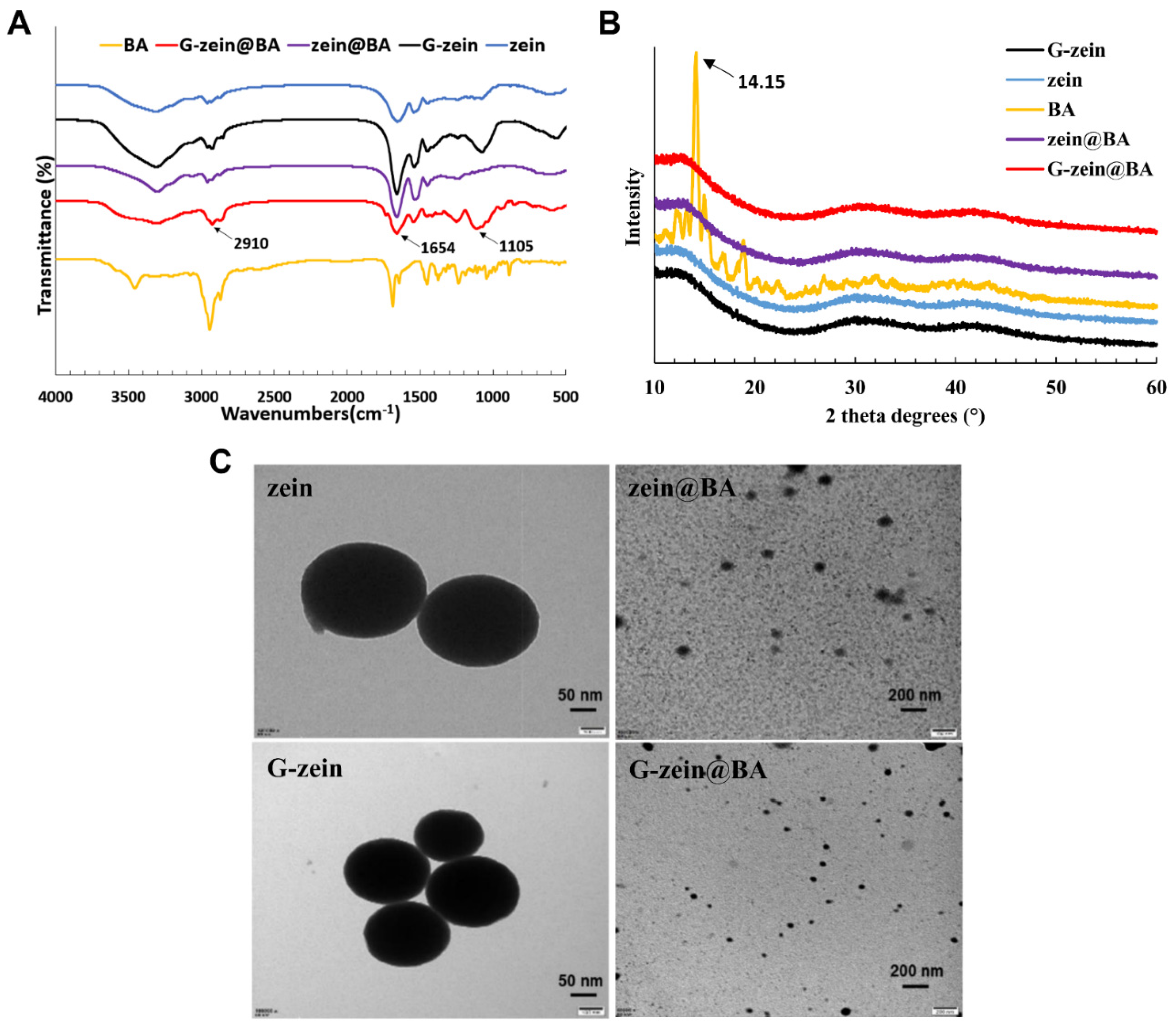
3.6. Morphology and Structural Characterization of BA-Loaded Nanoparticles
3.7. Stability of BA-Loaded Nanoparticles
3.8. In Vitro Sustained Release and Water Dispersibility of BA-Loaded Nanoparticles
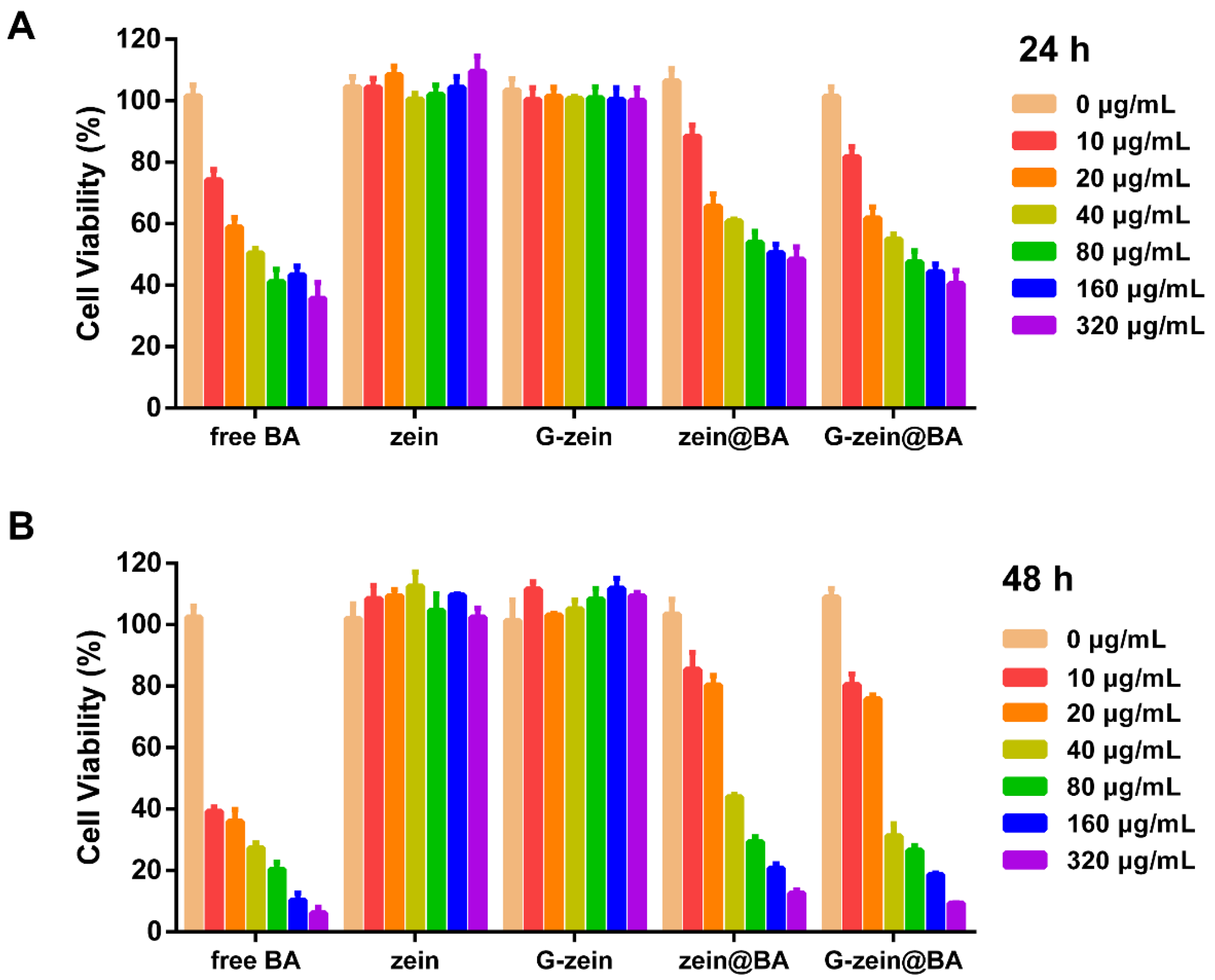
3.9. Cytotoxicity Effect of BA-Loaded Nanoparticles in HepG2 Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lou, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Lu, H.; Chen, Q. A Review on Preparation of Betulinic Acid and Its Biological Activities. Molecules 2021, 26, 5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeleke, G.E.; Adaramoye, O.A. Betulinic acid abates N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced changes in lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammation in the liver and kidney of Wistar rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxic. 2021, 35, 22901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Li, X.; Dong, S.; Zhou, W. Betulinic acid in the treatment of tumour diseases: Application and research progress. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 142, 111990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, R.; Wang, M.; Xu, G.; Liao, S. Prodrugs of triterpenoids and their derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 131, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, S.; Gong, F.; Sui, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, T. Research on the synthesis of nanoparticles of betulinic acid and their targeting antitumor activity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2022, 110, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar]
- Pascoli, M.; de Lima, R.; Fraceto, L.F. Zein Nanoparticles and Strategies to Improve Colloidal Stability: A Mini-Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Heat-induced self-assembly of zein nanoparticles: Fabrication, stabilization and potential application as oral drug delivery. Food Hydrocolloids 2019, 90, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lei, L.; Lei, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Ming, J. Interactions and structural properties of zein/ferulic acid: The effect of calcium chloride. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Han, H. Glycosylated zein as a novel nanodelivery vehicle for lutein. Food Chem. 2022, 376, 131927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saneja, A.; Arora, D.; Kumar, R.; Dubey, R.D.; Panda, A.K.; Gupta, P.N. Therapeutic applications of betulinic acid nanoformulations. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1421, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, A.; Chen, C.; Lu, J.; Sun, J.; Xiao, M.; Yue, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, S.; Zhong, G.; Huang, C.; et al. Preparation of Oral Core-Shell Zein Nanoparticles to Improve the Bioavailability of Glycyrrhizic Acid for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasankhan, S.; Tabibiazar, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ehsani, A.; Ghorbani, M. Fabrication of curcumin-zein-ethyl cellulose composite nanoparticles using antisolvent co-precipitation method. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Ge, X.; Gao, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, M. The distribution of D-chiro-inositol in buckwheat and its antioxidative effect in HepG2. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 89, 102808. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Han, L.; Xiao, Y.; Pan, C.; Li, Y.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, M. D-chiro-Inositol Ameliorates High Fat Di-et-Induced Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance via PKC epsilon-PI3K/AKT Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5957–5967. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, B.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Yao, P. Peptide-polysaccharide conjugates with adjustable hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity as green and pH sensitive emulsifiers. Food Hydrocolloids 2017, 63, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnella, C.; Gargaro, M.T.; Rossano, R.; Monteleone, E. Spectrophotometric assay using o-phtaldialdehyde for the determination of transglutaminase activity on casein. Food Chem. 2002, 78, 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Pirestani, S.; Nasirpour, A.; Keramat, J.; Desobry, S. Preparation of chemically modified canola protein isolate with gum Arabic by means of Maillard reaction under wet-heating conditions. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 155, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zhao, M.; Cui, C.; Zhao, H.; Yang, B. Effect of degree of hydrolysis on the antioxidant activity of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) protein hydrolysates. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2009, 10, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Sun, C.; Li, R.; Mao, L.; Liu, F.; Gao, Y. Structural characterization, formation mechanism and stability of curcumin in zein-lecithin composite nanoparticles fabricated by antisolvent co-precipitation. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, D.P.; Ozturk, O.K.; Selling, G.; Chen, F.; Campanella, O.H.; Hamaker, B.R. Corn zein undergoes conformational changes to higher beta-sheet content during its self-assembly in an increasingly hydrophilic solvent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabra, V.; Arreguin, R.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Farres, A. Effect of alkaline deamidation on the structure, surface hydrophobicity, and emulsifying properties of the Z19 alpha-zein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, S.; Koo, C.K.W.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Continuous production of core-shell protein nanoparticles by antisolvent precipitation using dual-channel microfluidization: Caseinate-coated zein nanoparticles. Food Res. Int. 2017, 92, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, M.R.; Mazaheri, E.; Dormiani, K. Simple Equations Pertaining to the Particle Number and Surface Area of Metallic, Polymeric, Lipidic and Vesicular Nanocarriers. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Liu, X.; Kopparapu, N.; Cong, W.; Deng, Y. Preparation of glycosylated zein and retarding effect on lipid oxidation of ground pork. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.R.; Xu, W.; Mraz, J. Formulation and characterization of zein/chitosan complex particles stabilized Pickering emulsion with the encapsulation and delivery of vitamin D. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5419–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Gao, B.; Yu, L.L. Fabrication and Characterization of Zein Composite Particles Coated by Caseinate-Pectin Electrostatic Complexes with Improved Structural Stability in Acidic Aqueous Environments. Molecules 2019, 24, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, S.; Cai, Q.; Wu, L.; Sun, Y.; Xia, G.; Wang, Y. Establishment and Characterization of Stable Zein/Glycosylated Lactoferrin Nanoparticles to Enhance the Storage Stability and in vitro Bioaccessibility of 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 806623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Yu, D.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L. Effect of ultrasound on the preparation of soy protein isolate-maltodextrin embedded hemp seed oil microcapsules and the establishment of oxidation kinetics models. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 77, 105700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.; Salah, M.; Xu, X. Effect of microencapsulation using soy protein isolate and gum arabic as wall material on red raspberry anthocyanin stability, characterization, and simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Ren, L. The effect of microstructure on mechanical properties of corn cob. Micron 2021, 146, 103070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Wang, X.; Li, M. Structure and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose/soy protein isolate blend edible films crosslinked by Maillard reactions. Carbohyd. Polym. 2010, 79, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kong, B.; Han, J.; Sun, C.; Li, P. Structure and antioxidant activity of whey protein isolate conjugated with glucose via the Maillard reaction under dry-heating conditions. Food Struct. 2014, 1, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, G.; Lu, W.; Wu, Y.; Hu, B.; Xu, L.; Fang, Y.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O. Interfacial and emulsion-stabilizing properties of zein nanoparticles: Differences among zein fractions (alpha-, beta-, and gamma-zein). Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madayi, D.; Surya, P.H.; Elyas, K.K. A Glucose binding lectin from Leucaena leucocephala seeds and its mitogenic activity against human lymphocytes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar Shekoufeh Bahari, L.; Hamishehkar, H. The Impact of Variables on Particle Size of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers; A Comparative Literature Review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Davarani, F.H.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Kalantari, M.; Raji, M.; Samareh Fekri, H.; Saber, R.; Asnani, G.P.; Mortazavi, S.M.; Mozafari, M.R.; Rasti, B.; Taheriazam, A. Probing nanoliposomes using single particle analytical techniques: Effect of excipients, solvents, phase transition and zeta potential. Heliyon 2018, 4, e1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication of biopolymer nanoparticles by antisolvent precipitation and electrostatic deposition: Zein-alginate core/shell nanoparticles. Food Hydrocolloids 2015, 44, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Li, R.; Wei, Y.; Sun, C.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y. Fabrication of zein and rhamnolipid complex nanoparticles to enhance the stability and in vitro release of curcumin. Food Hydrocolloids 2018, 77, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chang, Y.; Li, D.; Sun, X.; Liu, X. Zein-derived peptides as nanocarriers to increase the water solubility and stability of lutein. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saneja, A.; Kumar, R.; Singh, A.; Dubey, R.D.; Mintoo, M.J.; Singh, G.; Mondhe, D.M.; Panda, A.K.; Gupta, P.N. Development and evaluation of long-circulating nanoparticles loaded with betulinic acid for improved anti-tumor efficacy. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, T.; Fernandez, M.L.; Luo, Y. Development of tannic acid cross-linked hollow zein nanoparticles as potential oral delivery vehicles for curcumin. Food Hydrocolloids 2016, 61, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Zheng, X. Preparation and Evaluation of New Glycopeptides Obtained by Proteolysis from Corn Gluten Meal Followed by Transglutaminase-Induced Glycosylation with Glucosamine. Foods 2020, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uskokovic, V.; Castiglione, Z.; Cubas, P.; Zhu, L.; Li, W.; Habelitz, S. Zeta-potential and Particle Size Analysis of Human Amelogenins. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkwood, J.; Hargreaves, D.; O’Keefe, S.; Wilson, J. Using isoelectric point to determine the pH for initial protein crystallization trials. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Ahmed, E.; Hu, T.; Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Hu, H. Effects of different ionic strengths on the physicochemical properties of plant and animal proteins-stabilized emulsions fabricated using ultrasound emulsification. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential—What they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, C.; Yang, M.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, Q.; Tu, K.; Zhang, M. All-in-one theranostic nano-platform based on polymer nanoparticles for BRET/FRET-initiated bioluminescence imaging and synergistically anti-inflammatory therapy for ulcerative colitis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saneja, A.; Kumar, R.; Mintoo, M.J.; Dubey, R.D.; Sangwan, P.L.; Mondhe, D.M.; Panda, A.K.; Gupta, P.N. Gemcitabine and betulinic acid co-encapsulated PLGA - PEG polymer nanoparticles for improved efficacy of cancer chemotherapy. Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2019, 98, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mierina, I.; Vilskersts, R.; Turks, M. Delivery Systems for Birch-bark Triterpenoids and their Derivatives in Anticancer Research. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 1308–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcas, C.G.; Dehelean, C.; Pinzaru, I.A.; Mioc, M.; Socoliuc, V.; Moaca, E.; Avram, S.; Ghiulai, R.; Coricovac, D.; Pavel, I.; et al. Thermosensitive Betulinic Acid-Loaded Magnetoliposomes: A Promising Antitumor Potential for Highly Aggressive Human Breast Adenocarcinoma Cells Under Hyperthermic Conditions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8175–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | BA Concentration (mg/mL) | Particle Size (nm) | Polydispersity Index | Zeta-Potential (mV) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| zein | / | 130 ± 2.8 e | 0.36 ± 0.01 e | 30.3 ± 0.78 b | / |
| G-zein | / | 107.9 ± 2.6 f | 0.39 ± 0.02 de | −35.3 ± 2.31 e | / |
| zein@BA | 1 | 168.1 ± 2.2 e | 0.48 ± 0.02 b | 32.3 ± 0.85 b | 83.12 ± 1.18 b |
| 1.5 | 274.9 ± 5.6 c | 0.45 ± 0.01 bc | 32.05 ± 1.63 b | 69.61 ± 1.85 d | |
| 2 | 484.5 ± 5.3 a | 0.48 ± 0.02 b | 35.1 ± 0.21 a | 40.29 ± 0.86 f | |
| G-zein@BA | 1 | 139.3 ± 0.2 e | 0.42 ± 0.00 cd | −22.65 ± 1.65 c | 89.81 ± 0.79 a |
| 1.5 | 223.8 ± 6.0 d | 0.54 ± 0.00 a | −22.3 ± 0.85 c | 78.24 ± 0.34 c | |
| 2 | 326.9 ± 1.3 b | 0.37 ± 0.00 e | −31.05 ± 0.21 d | 49.89 ± 0.35 e |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, F.; Jin, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, H. Glycosylated Zein Composite Nanoparticles for Efficient Delivery of Betulinic Acid: Fabrication, Characterization, and In Vitro Release Properties. Foods 2022, 11, 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172589
Peng F, Jin Y, Wang K, Wang X, Xiao Y, Xu H. Glycosylated Zein Composite Nanoparticles for Efficient Delivery of Betulinic Acid: Fabrication, Characterization, and In Vitro Release Properties. Foods. 2022; 11(17):2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172589
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Fei, Yu Jin, Kunhua Wang, Xiaojing Wang, Yaqing Xiao, and Huaide Xu. 2022. "Glycosylated Zein Composite Nanoparticles for Efficient Delivery of Betulinic Acid: Fabrication, Characterization, and In Vitro Release Properties" Foods 11, no. 17: 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172589
APA StylePeng, F., Jin, Y., Wang, K., Wang, X., Xiao, Y., & Xu, H. (2022). Glycosylated Zein Composite Nanoparticles for Efficient Delivery of Betulinic Acid: Fabrication, Characterization, and In Vitro Release Properties. Foods, 11(17), 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172589







