Effect of Radiant Catalytic Ionization and Ozonation on Salmonella spp. on Eggshells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
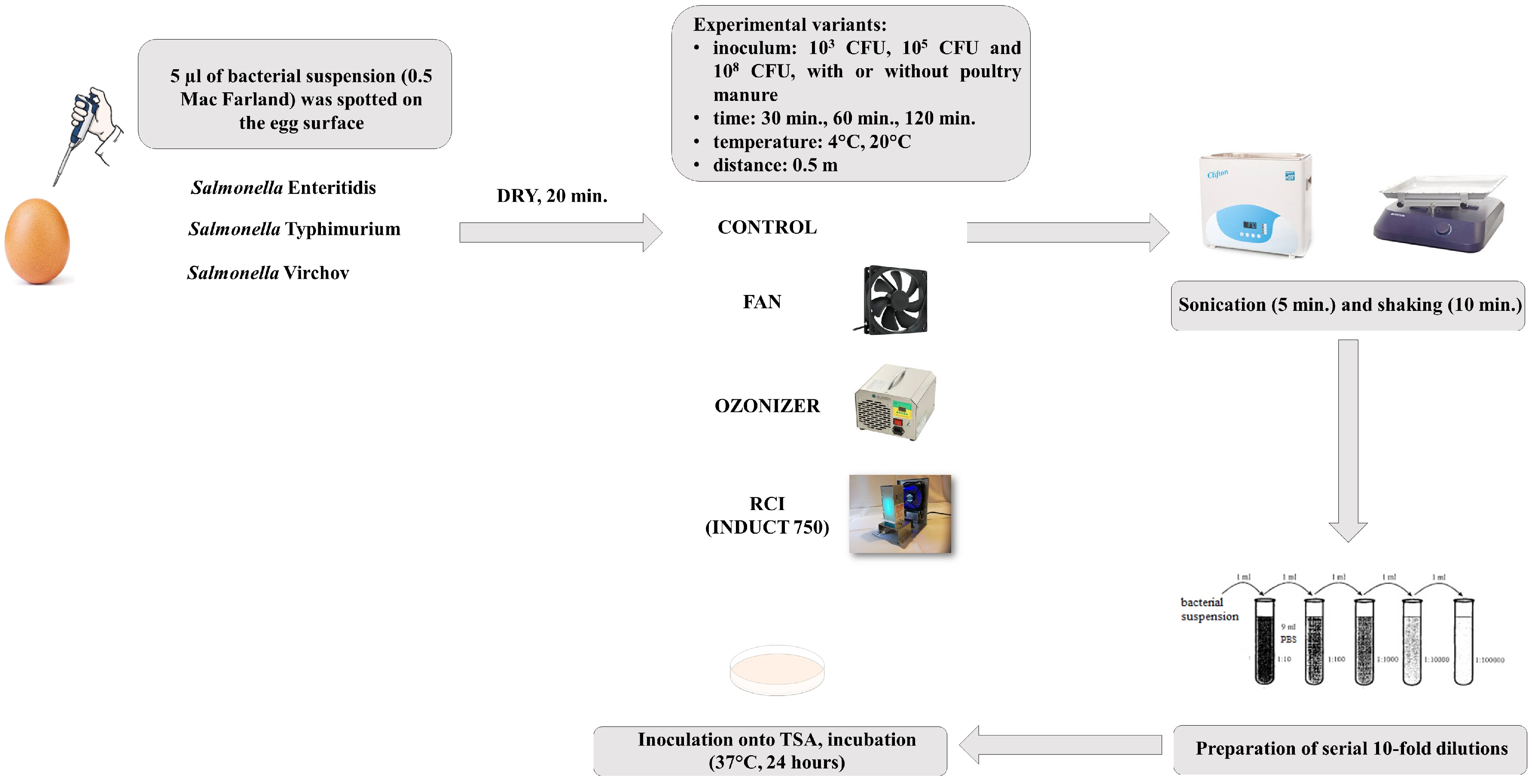
2.2. Eggshells Contamination with Salmonella spp.
2.3. Exposure of Salmonella spp. Contaminated Eggshells to Radiant Catalytic Ionization and Ozonation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effectiveness of Radiant Catalytic Ionization and Ozonation Treatment against Salmonella spp. for Bacterial Suspension of 103 CFU/mL
3.2. Effectiveness of Radiant Catalytic Ionization and Ozonation Treatment against Salmonella spp. for Bacterial Suspension of 105 CFU/mL
3.3. Effectiveness of Radiant Catalytic Ionization and Ozonation Treatment against Salmonella spp. for Bacterial Suspension of 108 CFU/mL
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The European Union One Health 2018 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2019, 15, 5926. [Google Scholar]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Multi-Country Outbreak of Salmonella Enteritidis Infections Linked to Eggs. Third Update (6 February 2020). 2020. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.2903/sp.efsa.2020.EN-1799 (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Okamura, M.; Kamijima, Y.; Miyamoto, T.; Tani, H.; Sasai, K.; Baba, E. Differences among six Salmonella serovars in abilities to colonize reproductive organs and to contaminate eggs in laying hens. Avian Dis. 2001, 45, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Reu, K.; Grijspeerdt, K.; Messens, W.; Heyndrickx, M.; Uyttendaele, M.; Debevere, J.; Herman, L. Eggshell factors influencing eggshell penetration and whole egg contamination by different bacteria, including Salmonella Enteritidis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 112, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trudeau, S.; Thibodeau, A.; Côté, J.-C.; Gaucher, M.-L.; Fravalo, P. Contribution of the Broiler Breeders’ Fecal Microbiota to the Establishment of the Eggshell Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chousalkar, K.K.; Flynn, P.; Sutherland, M.; Roberts, J.R.; Cheetham, B.F. Recovery of Salmonella and Escherichia coli from commercial eggshells and effect of translucency on bacterial penetration in eggs. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 142, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.T.; Rives, D.V.; Carey, J.B. Salmonella contamination in commercial eggs and an egg production facility. Poultr. Sci. 1995, 74, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes, F.J.; Takeballi, M.A. Microbial contamination of the hen’s egg: A review. J. Food Prot. 1983, 46, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.M.; Hung, Y.C.; Lin, C.S.; Brackett, R.E. Efficacy of electrolyzed water in inactivating Salmonella Enteritidis and Listeria monocytogenes on shell eggs. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Slavik, M.F. Bacterial penetration into eggs washed with various chemicals and stored at different temperatures and times. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musgrove, M.T.; Jones, D.; Northcutt, J.K.; Cox, N.A.; Harrison, M.K. Identification of Enterobacteriaceae from washed and unwashed eggs. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 2613–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, I.; Yin, H.-B.; Surendran Nair, M.; Chen, C.-H.; Lang, R.; Darre, M.J.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Inactivation of Salmonella enteritidis on shell eggs by coating with phytochemicals. Poult. Sci. Assoc. 2016, 95, 2106–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, E.F.; Clímaco, W.L.S.; Triginelli, M.V.; Vaz, D.P.; de Souza, M.R.; Baião, N.C.; Pompeu, M.A.; Lara, L.J.C. An evaluation of alternative methods for sanitizing hatching eggs. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2466–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, P.G.; Fernandez, N.; Fuhrmann, H. Investigations on the effect of ozone as a disinfectant of egg surfaces. Ozone Sci. Eng. J. Int. Ozone Assoc. 2011, 33, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, H.; Rupp, N.; Buchner, A.; Braun, P. The effect of gaseous ozone treatment on egg components. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Thompson, A. The inactivation of Salmonella by cold atmospheric plasma treatment. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlazlo, L.; Drabik, K.; Al-Shammari, K.I.A.; Batkowska, J.; Nowakowicz-Debek, B.; Gryzińska, M. Use of reactive oxygen species (ozone, hydrogen peroxide) for disinfection of hatching eggs. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2478–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Space Fundation, Radiant Catalytic Ionization Air & Water Purification. Available online: http://www.spacefoundation.org/programs/space-certification/certified-products/space-technology/radiant-catalytic-ionization-air (accessed on 4 November 2020).
- Grinshpun, S.A.; Adhikari, A.; Honda, T.; Kim, K.Y.; Toivola, M.; Rao, K.S.R.; Reponen, T. Control of aerosol contaminants in indoor air: Combining the particle concentration reduction with microbial inactivation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małecka, I.; Borowski, G. Dezynfekcja powietrza promieniami UV i promieniową jonizacją katalityczną w instalacjach wentylacyjnych. Zesz. Nauk.—Inżyniera Lądowa I Wodna W Kształtowaniu Sr. 2011, 3, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Skowron, K.; Grudlewska, K.; Krawczyk, A.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. The effectiveness of radiant catalytic ionization in inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes planctonic and biofilm cells from food and food contact surfaces as a method of food preservation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannozzi, J.T.; Filbert, V.J.; Mackay, W.J.; Fulford, D.E.; Steele, C.W. Evaluation of radiant catalytic ionization in reducing Escherichia coli, Listeria innocua and Salmonella Typhimuriom on representative food contact surfaces. Tex. J. Sci. 2018, 70, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, M.T.; Franken, L.J.; Hatesohl, P.R.; Marsden, J.L. Efficacy of radiant catalytic ionization cell and ozone at reducing microbial populations on stainless steel surfaces. J. Rapid Methods Autom. Microbiol. 2007, 15, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Pehkonen, S.O.; Yu, L.E.; Ray, M.B. Photocatalytic inactivation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria using fluorescent light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 186, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowron, K.; Grudlewska, K.; Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Gryń, G.; Śrutek, M.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Efficacy of radiant catalytic ionization to reduce bacterial populations in air and on different surfaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowron, K.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Grudlewska, K.; Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Wiktorczyk, N.; Kowalska, M.; Paluszak, Z.; Kosek-Paszkowska, K.; Brożek, K.; Korkus, J.; et al. Effect of Selected Environmental Factors on the Microbicidal Effectiveness of Radiant Catalytic Ionization. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soljour, G.; Assanta, M.A.; Messier, S.; Boulianne, M. Efficacy of egg cleaning compounds on eggshells contaminated with Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bing, S.; Zang, Y.T.; Li, Y.J.; Shu, D.Q. The synergistic effects of slightly acidic electrolyzed water and UV-C light on the inactivation of Salmonella enteritidis on contaminated eggshells. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6914–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Romo, L.A.; Yousef, A.E. Inactivation of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis on shell eggs by ozone and UV radiation. J. Food. Prot. 2005, 68, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, S.; Ortenzi, R.; Scuota, S.; Cartoni Mancinelli, A.; Dal Bosco, A.; Cotozzolo, E.; Castellini, C. Impact of ozone and UV irradiation sanitation treatments on the survival of Salmonella and the physical–chemical characteristics of hen eggs. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüceer, M.; Caner, C. The effects of ozone, ultrasound and coating with shellac and lysozyme–chitosan on fresh egg during storage at ambient temperature. Part II: Microbialquality, eggshell breaking strength and FT-NIR spectral analysis. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 55, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variant | Temperature 4 °C | Temperature 20 °C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM (−) | PM (+) | PM (−) | PM (+) | ||
| Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) * | Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) | Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) | Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) | ||
| Control | 1.59 h (±0.09) | 1.67 h (±0.09) | 1.59 h (±0.09) | 1.67 h (±0.09) | |
| 30 min † | Fan | 0.58 e,f (±0.02) | 0.96 g (±0.02) | 0.57 d,e,f (±0.00) | 0.98 g (±0.02) |
| Ozonizer | 0.34 b,c,d,e (±0.04) | 0.61 e,f (±0.02) | 0.41 c,d,e,f (±0.02) | 0.69 f,g (±0.01) | |
| RCI | 0.09 a,b (±0.07) | 0.28 a,b,c,d (±0.05) | 0.03 a (±0.09) | 0.20 a,b,c (±0.06) | |
| Variant | Temperature 4 °C | Temperature 20 °C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM (−) | PM (+) | PM (−) | PM (+) | |||
| Bacterial suspension 103 CFU | 30 min † | Fan | 1.01 h,i,j,k,l,ł,m,n | 0.71 d,e,f,g,h,i | 1.01 h,i,j,k,l,ł,m,n | 0.69 c,d,e,f,g,h,i |
| Ozonizer | 1.24 k,l,ł,m,n,o,p | 1.05 h,i,j,k,l,ł,m,n | 1.17 i,j,k,l,ł,m,n,o | 0.98 h,i,j,k,l,ł,m | ||
| RCI | 1.50 n,o,p,r,s | 1.39 ł,m,n,o,p,r | 1.56 o,p,r,s,t | 1.47 m,n,o,p,r,s | ||
| 60 min | Fan | BDL * | BDL | BDL | BDL | |
| Ozonizer | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | ||
| RCI | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | ||
| 120 min | Fan | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | |
| Ozonizer | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | ||
| RCI | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | ||
| Bacterial suspension 105 CFU | 30 min † | Fan | 0.38 a,b,c,d,e,f,g | 0.13 a,b | 0.38 a,b,c,d,e,f,g | 0.13 a,b |
| Ozonizer | 1.12 i,j,k,l,ł,m,n,o | 0.28 a,b,c,d,e,f | 0.97 a | 0.26 a,b,c,d,e | ||
| RCI | 1.28 l,ł,m,n,op | 0.30 a,b,c,d,e,f | 1.37 ł,m,n,o,p,r | 0.32 a,b,c,d,e,f | ||
| 60 min | Fan | 0.76 f,g,h,i,j,k | 0.21 a,b,c | 0.74 e,f,g,h,i,,j | 0.21 a,b,c | |
| Ozonizer | 2.00 t,u | 0.39 a,b,c,d,e,f,g | 1.83 r,s,t,u | 1.17 i,j,k,l,ł,m,n,o | ||
| RCI | 1.95 s,t,u | 0.40 a,b,c,d,e,f,g | 2.59 w,x | 1.22 j,k,l,ł,m,n,o,p | ||
| 120 min | Fan | 1.70 p,r,s.t,u | 0.37 a,b,c,d,e,f,g | 1.36 ł,m,n,o,p,r | 0.36 a,b,c,d,e,f,g | |
| Ozonizer | 2.14 u,w | 0.59 b,d,e,f,g,h | 2.64 x,y | 2.73 y | ||
| RCI | 2.15 u,w,x | 0.59 b,d,e,f,g,h | BDL | BDL | ||
| Bacterial suspension 108 CFU | 30 min † | Fan | 0.32 a,b,c,d,e,f | 0.09 a | 0.32 a,b,c,d,e,f | 0.09 a |
| Ozonizer | 0.94 h,i,j,k,l,ł | 0.22 a,b,c,d | 0.85 g,h,i,j,k,l | 0.20 a,b,c | ||
| RCI | 0.98 h,i,j,k,l,ł,m | 0.26 a,b,c,d,e | 1.05 h,i,j,k,l,ł,m,n | 0.26 a,b,c,d,e | ||
| 60 min | Fan | 0.60 b,d,e,f,g,h | 0.19 a,b,c | 0.59 b,d,e,f,g,h | 0.19 a,b,c | |
| Ozonizer | 1.34 l,ł,m,n,o,p,r | 0.34 a,b,c,d,e,f | 1.10 ij,k,l,ł,m,n,o | 0.32 a,b,c,d,e,f | ||
| RCI | 1.65 o,p,r,s,t,u | 0.36 a,b,c,d,e,f,g | 2.12 u,w | 0.38 a,b,c,d,e,f,g | ||
| 120 min | Fan | 0.98 h,i,j,k,l,ł,m | 0.38 a,b,c,d,e,f,g | 0.95 h,i,j,k,l,ł | 0.39 a,b,c,d,e,f,g | |
| Ozonizer | 1.91 s,t,u,w | 0.52 a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h | 1.36 ł,m,n,o,p,r | 0.49 a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h | ||
| RCI | 1.87 s,t,u,w | 0.51 a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h | 3.54 z | 0.55 a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h | ||
| Variant | Temperature 4 °C | Temperature 20 °C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM (−) | PM (+) | PM (−) | PM (+) | ||
| Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) * | Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) * | Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) * | Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) * | ||
| Control | 2.65 a,b (±0.21) | 2.75 a (±0.20) | 2.65 a,b (±0.21) | 2.75 a (±0.20) | |
| 30 min † | Fan | 2.27 a,b,c,d (±0.17) | 2.61 a,b (±0.18) | 2.28 a,b,c,d (±0.17) | 2.62 a,b (±0.18) |
| Ozonizer | 1.53 a,b,c,d,e,f (±0.10) | 2.46 a,b,c (±0.17) | 1.69 a,b,c,d,e,f (±0.11) | 2.48 a,b,c (±0.17) | |
| RCI | 1.37 b,c,d,e,f (±0.08) | 2.45 a,b,c (±0.17) | 1.29 c,d,e,f,g (±0.07) | 2.43 a,b,c (±0.16) | |
| 60 min | Fan | 1.89 a,b,c,d,e (±0.13) | 2.54 a,b,c (±0.18) | 1.91 a,b,c,d,e (±0.13) | 2.53 a,b,c (±0.18) |
| Ozonizer | 0.66 e,f,g,h (±0.01) | 2.36 a,b,c (±0.16) | 0.82 e,f,g,h (±0.07) | 1.57 a,b,c,d,e,,f (±0.16) | |
| RCI | 0.71 e,f,g,h (±0.01) | 2.35 a,b,c (±0.15) | 0.07 g,h (±0.09) | 1.53 a,b,c,d,e,f (±0.15) | |
| 120 min | Fan | 0.96 d,e,f,g,h (±0.04) | 2.37 a,b,c (±0.16) | 1.30 c,d,e,f,g (±0.07) | 2.38 a,b,c (±0.16) |
| Ozonizer | 0.52 f,g,h (±0.01) | 2.16 a,b,c,d (±0.14) | 0.01 g,h (±0.03) | 0.01 g,h (±0.05) | |
| RCI | 0.50 f,g,h (±0.01) | 2.15 a,b,c,d (±0.17) | 0.00 h (±0.00) | 0.00 h (±0.00) | |
| Variant | Temperature 4 °C | Temperature 20 °C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM (−) | PM (+) | PM (−) | PM (+) | ||
| Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) * | Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) | Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) | Average [log CFU/egg] (±STD) | ||
| Control | 5.81 a,b (±0.51) | 5.89 a (±0.50) | 5.81 a,b (±0.51) | 5.89 a (±0.50) | |
| 30 min † | Fan | 5.48 a,b,c,d (±0.47) | 5.80 a,b (±0.49) | 5.49 a,b,c,d (±0.47) | 5.79 a,b (±0.49) |
| Ozonizer | 4.86 f,g,h (±0.41) | 5.67 a,b,c,d (±0.48) | 4.96 e,f,g (±0.42) | 5.69 a,b,c (±0.48) | |
| RCI | 4.83 f,g,h (±0.41) | 5.63 a,b,c,d (±0.48) | 4.75 f,g,h (±0.40) | 5.63 a,b,c,d (±0.48) | |
| 60 min | Fan | 5.21 d,e,f (±0.45) | 5.70 a,b (±0.48) | 5.22 c,d,e,f (±0.45) | 5.70 a,b (±0.48) |
| Ozonizer | 4.47 h,i (±0.37) | 5.55 a,b,c,d (±0.47) | 4.71 g,h (±0.40) | 5.57 a,b,c,d (±0.47) | |
| RCI | 4.16 i,j (±0.34) | 5.53 a,b,c,d (±0.47) | 3.69 j (±0.29) | 5.51 a,b,c,d (±0.46) | |
| 120 min | Fan | 4.83 f,g,h (±0.41) | 5.51 a,b,c,d (±0.46) | 4.85 f,g,h (±0.41) | 5.50 a,b,c,d (±0.46) |
| Ozonizer | 3.90 j (±0.32) | 5.37 b,c,d,e (±0.45) | 4.45 h,i (±0.37) | 5.40 b,c,d,e (±0.45) | |
| RCI | 3.93 j (±0.32) | 5.38 b,c,d,e (±0.45) | 2.27 k (±0.15) | 5.34 b,c,d,e (±0.45) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grudlewska-Buda, K.; Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, N.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Gryń, G.; Skowron, K.J.; Korkus, J.; Gospodarek-Komkowka, E.; Bystroń, J.; Budzyńska, A.; et al. Effect of Radiant Catalytic Ionization and Ozonation on Salmonella spp. on Eggshells. Foods 2022, 11, 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11162452
Grudlewska-Buda K, Wiktorczyk-Kapischke N, Wałecka-Zacharska E, Kwiecińska-Piróg J, Gryń G, Skowron KJ, Korkus J, Gospodarek-Komkowka E, Bystroń J, Budzyńska A, et al. Effect of Radiant Catalytic Ionization and Ozonation on Salmonella spp. on Eggshells. Foods. 2022; 11(16):2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11162452
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrudlewska-Buda, Katarzyna, Natalia Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, Ewa Wałecka-Zacharska, Joanna Kwiecińska-Piróg, Grzegorz Gryń, Karolina Jadwiga Skowron, Jakub Korkus, Eugenia Gospodarek-Komkowka, Jarosław Bystroń, Anna Budzyńska, and et al. 2022. "Effect of Radiant Catalytic Ionization and Ozonation on Salmonella spp. on Eggshells" Foods 11, no. 16: 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11162452
APA StyleGrudlewska-Buda, K., Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, N., Wałecka-Zacharska, E., Kwiecińska-Piróg, J., Gryń, G., Skowron, K. J., Korkus, J., Gospodarek-Komkowka, E., Bystroń, J., Budzyńska, A., Kruszewski, S., Paluszak, Z., Andrzejewska, M., Wilk, M., & Skowron, K. (2022). Effect of Radiant Catalytic Ionization and Ozonation on Salmonella spp. on Eggshells. Foods, 11(16), 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11162452






