Improvement of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Drying Characteristics and Quality Attributes by a Combination of Salting Pretreatment and Microwave
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Drying Properties
2.3. Water State and Distribution by Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR)
2.4. Determination Salt Content
2.5. Determination of Rehydration Ratio
2.6. Texture Measurement
2.7. Color Measurement
2.8. Determination of Volatile Vomponents by E-Nose
2.9. Determination of Astaxanthin Content
2.10. Determination of Protein Secondary Structure by Raman Spectroscopy
2.11. Determination of Microstructure
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
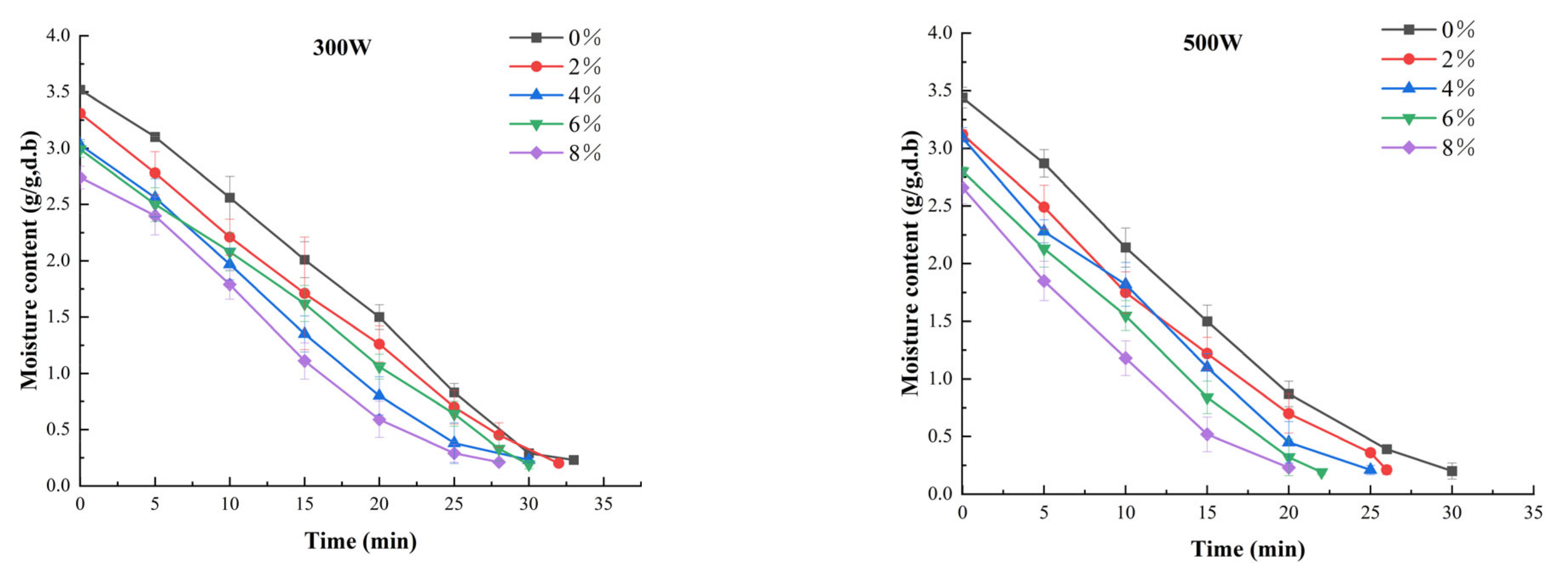
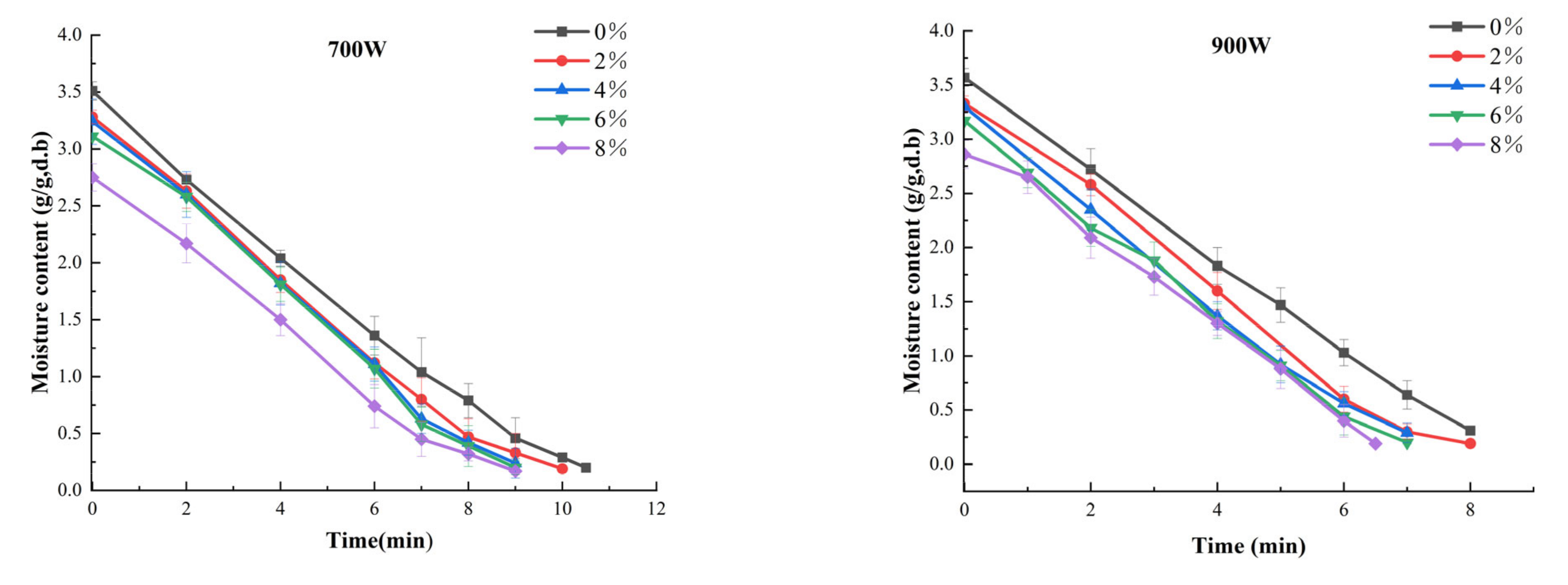
3.1. Drying Kinetics
3.2. Moisture State and Distribution
3.3. Salt Content of Shrimps Pretreated with Different Salt Concentrations
3.4. Rehydration Ratio of Dried Shrimps Treated by Bifferent Salt Concentrations and MW Powers
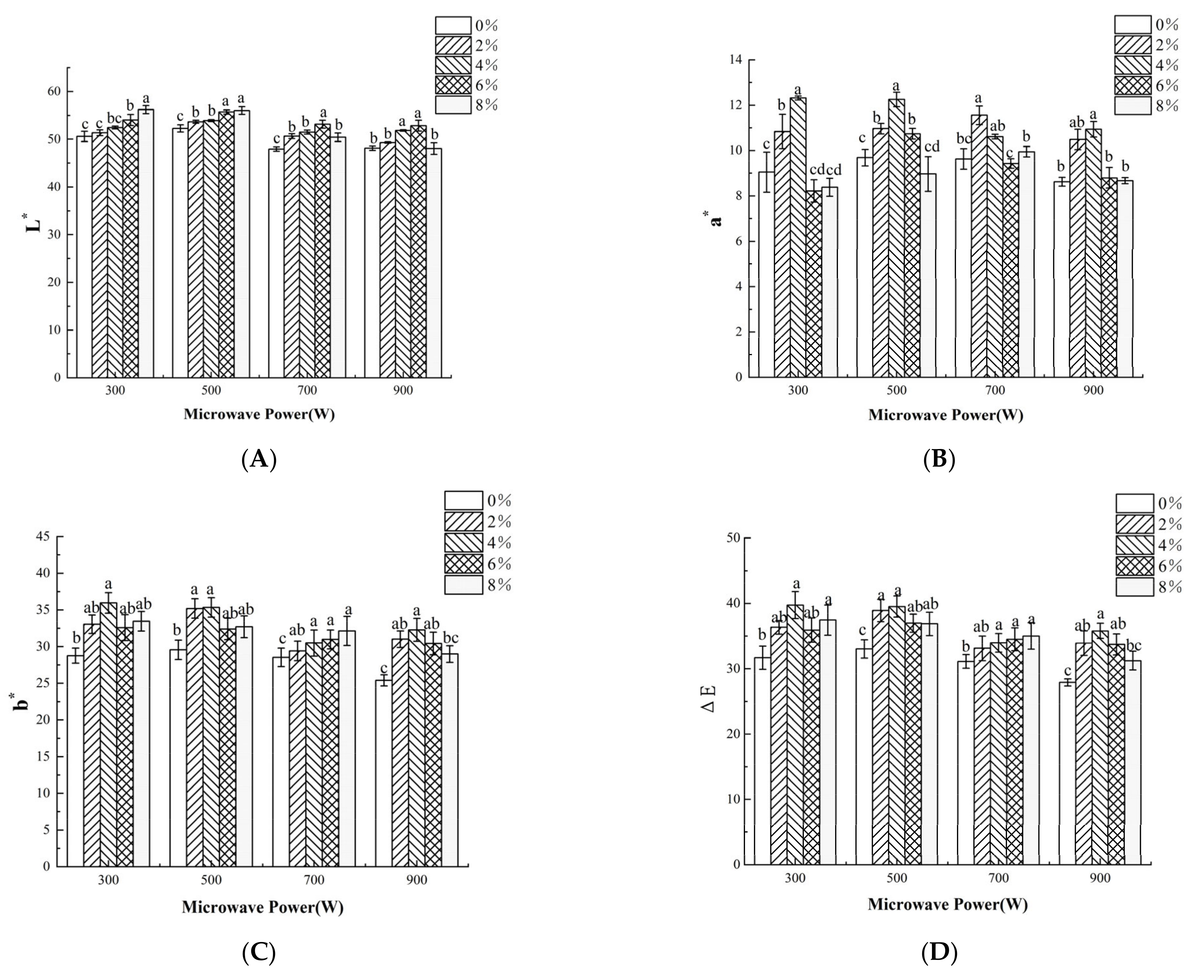
3.5. Color
3.6. Volatile Components
3.7. Protein Secondary Structure Analysis
3.8. Astaxanthin Analysis
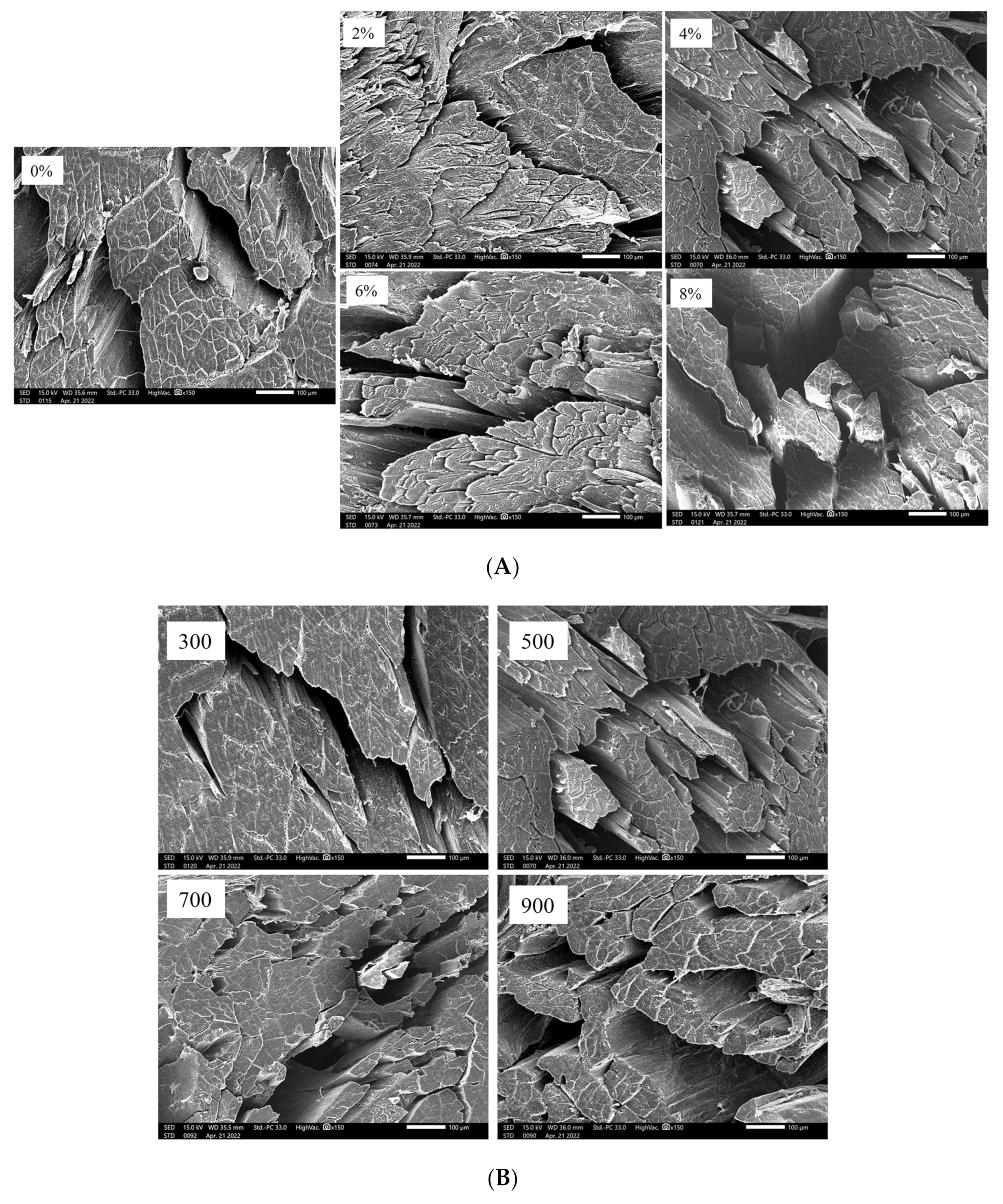
3.9. Microstructure of Dried Shrimps under Different Salt Concentrations and MW Powers
3.10. Texture
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. FaoStat Database. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Mounir, S.; Amami, E.; Allaf, T.; Mujumdar, A.; Allaf, K. Instant controlled pressure drop (DIC) coupled to intermittent microwave/airflow drying to produce shrimp snacks: Process performance and quality attributes. Dry. Technol. 2020, 38, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akonor, P.T.; Ofori, H.; Dziedzoave, N.T.; Kortei, N.K. Drying characteristics and physical and nutritional properties of shrimp meat as affected by different traditional drying techniques. Int. J. Food Sci. 2016, 2016, 7879097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, S.S.; Su, W.T.; Yuan, L.; Tan, M.Q. Recent developments of drying techniques for aquatic products: With emphasis on drying process monitoring with innovative methods. Dry. Technol. 2021, 39, 1577–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Mowafy, S.; Liu, Y. Comparative analyses of five drying techniques on drying attributes, physicochemical aspects, and flavor components of Amomum villosum fruits. LWT 2022, 154, 112879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Ru, H.; Yan, J.; Li, S.; Li, Z. Effects of cold air dehydration on icefish water dynamics and macromolecular oxidation measured by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.G.; Xuan, X.T.; Yu, N.; Cui, Y.; Shang, H.T.; Liao, X.J.; Lin, X.D.; Yu, J.F.; Liu, D.H. High pressure-assisted vacuum-freeze drying: A novel, efficient way to accelerate moisture migration in shrimp processing. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ye, X.; Yang, W. Effect of different drying processes on the protein degradation and sensory quality of Layú: A Chinese dry-curing grass carp. Dry. Technol. 2013, 31, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Zhou, D.Y.; Zhou, X.; Yin, F.W.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, H.K.; Li, D.Y.; Zhu, B.W.; Wang, T.; Shahidi, F. Effect of Various Hot-Air Drying Processes on Clam Ruditapes philippinarum Lipids: Composition Changes and Oxidation Development. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 2976–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Oh, B.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, Y.S.; Lee, H.I. Effects of Various Drying Methods on Physicochemical Characteristics and Textural Features of Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys Polyactis). Foods 2020, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gang, K.Q.; Wu, Z.X.; Zhou, D.Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Lv, D.D.; Rakariyatham, K.; Liu, X.Y.; Shahidi, F. Effects of hot air drying process on lipid quality of whelks Neptunea arthritica cumingi Crosse and Neverita didyma. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4166–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L. Antibrowning of the Adductor Muscles of Bay Scallop by Glutathione During Hot Air Drying. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Q. Combined Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) and Vacuum Freeze Drying of Sea Cucumber. Dry. Technol. 2012, 30, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, T. Drying and quality characteristics of tilapia fish fillets dried with hot air-microwave heating. Food Bioprod. Process. 2011, 89, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Hwang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-S.; Lin, C.-Y.; Ou, T.-Y.; Chang, T.-H.; Lee, Y.-C. Comparison of microwave-assisted induction heating system (MAIH) and individual heating methods on the quality of pre-packaged white shrimp. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 73, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan-Karabacak, A.; Acoğlu, B.; Yolci Ömeroğlu, P.; Çopur, Ö.U. Microwave pre-treatment for vacuum drying of orange slices: Drying characteristics, rehydration capacity and quality properties. J. Food Process. Eng. 2020, 43, e13511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipcak, A.S.; İsmail, O. Microwave drying of fish, chicken and beef samples. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankyamma, V.; Mokam, S.Y.; Debbarma, J.; Rao, B.M. Effects of microwave vacuum drying and conventional drying methods on the physicochemical and microstructural properties of squid shreds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5778–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Yong-Jun, W. Drying kinetics and quality characteristics of slightly salted grass carp fillets by hot air drying and vacuum microwave drying. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2013, 22, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyprian, O.O.; Nguyen, M.V.; Sveinsdottir, K.; Tomasson, T.; Thorkelsson, G.; Arason, S. Influence of blanching treatment and drying methods on the drying characteristics and quality changes of dried sardine (Sardinella gibbosa) during storage. Dry. Technol. 2016, 35, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Li, M.; Guan, Z.-Q.; Ling, C.-M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Salt alcohol additive pre-treatment to improve the performance of heat pump dried tilapia fillets. Energy Procedia 2017, 123, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, X.; Miao, S.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B.J.J.o.F.E. Influence of ultrasound on the rehydration of dried sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus). J. Food Eng. 2016, 178, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobukola, O.; Olatunde, S.J.F.; Processing, B. Effect of salting techniques on salt uptake and drying kinetics of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Food Bioprod. Process. 2011, 89, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guan, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ling, C. Effect of pretreatment on water migration and volatile components of heat pump dried tilapia fillets. Dry. Technol. 2020, 38, 1828–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, J.L.G.; Braga, A.M.P.; Hochheim, M.; Silva, M.A.J.D.T. The influence of ethanol on the convective drying of unripe, ripe, and overripe bananas. Dry. Technol. 2012, 30, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamnuy, C.; Devahastin, S.; Soponronnarit, S. Effects of process parameters on quality changes of shrimp during drying in a jet-spouted bed dryer. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, E553–E563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, J.S.; Raghavan, G.S.V.; Orsat, V.; Yu, X.L.; Liu, Z.L.; Zheng, Z.A.; Wang, S.Y.; Xiao, H.W. Vacuum-steam pulsed blanching (VSPB) enhances drying quality, shortens the drying time of gingers by inactivating enzymes, altering texture, microstructure and ultrastructure. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Karim, M.A.; Vidyarthi, S.K.; Xie, L.; Liu, Z.L.; Gao, L.; Zhang, J.S.; Xiao, H.W. Vacuum-steam pulsed blanching (VSPB) softens texture and enhances drying rate of carrot by altering cellular structure, pectin polysaccharides and water state. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 74, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Qiu, W.; Jin, Y.; Zheng, R.; Row, K.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, Y. Effects of different drying methods on quality changes and energy characteristics of tilapia fillets. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2020, 54, 186–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-L.; Zielinska, M.; Yang, X.-H.; Yu, X.-L.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Xiao, H.-W. Moisturizing strategy for enhanced convective drying of mushroom slices. Renew. Energy 2021, 172, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.-W.; Law, C.-L.; Sun, D.-W.; Gao, Z.-J. Color Change Kinetics of American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolium) Slices During Air Impingement Drying. Dry. Technol. 2014, 32, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolasa, S.; Cakli, S.; Ostermeyer, U. Determination of astaxanthin and canthaxanthin in salmonid. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 221, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix, A.; Pedanou, G.; Berjot, M. Fast determination of the quantitative secondary structure of proteins by using some parameters of the Raman Amide I band. J. Mol. Struct. 1988, 174, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskan, M. Drying, shrinkage and rehydration characteristics of kiwifruits during hot air and microwave drying. J. Food Eng. 2001, 48, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellagha, S.; Sahli, A.; Farhat, A.; Kechaou, N.; Glenza, A. Studies on salting and drying of sardine (Sardinella aurita): Experimental kinetics and modeling. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Tan, M. Approach for monitoring the dynamic states of water in shrimp during drying process with LF-NMR and MRI. Dry. Technol. 2017, 36, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsdottir, K.A.; Arason, S.; Geirsdottir, M.; Bogason, S.G.; Kristbergsson, K. Changes in myofibrillar proteins during processing of salted cod (Gadus morhua) as determined by electrophoresis and differential scanning calorimetry. Food Chem. 2002, 77, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsdottir, K.A.; Arason, S.; Bogason, S.G.; Kristbergsson, K. The effects of various salt concentrations during brine curing of cod (Gadus morhua). Int. J. Food Sci. 2004, 39, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenyang, N.; Ponka, R.; Tiencheu, B.; Djikeng, F.T.; Womeni, H.M. Effect of traditional drying methods on proximate composition, fatty acid profile, and oil oxidation of fish species consumed in the Far-North of Cameroon. Glob. Chall. 2020, 4, 2000007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.M.; Durance, T.D.; Scaman, C.H. Characterization of vacuum microwave, air and freeze dried carrot slices. Food Res. Int. 1998, 31, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, D.; Ulucan, O.; Turkan, M. Electronic Nose and Its Applications: A Survey. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2020, 17, 179–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhen, S.; Fang-wei, Y.; Xia, L.; Chun-hui, Z.; Xiao-lei, X. Effects of Freezing and Thawing Treatments on Beef Protein Secondary Structure Analyzed with ATR-FTIR. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi 2016, 36, 3542–3546. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, A.; Cao, M.; Li, J. Effects of ultrasonics combined with far infrared or microwave thawing on protein denaturation and moisture migration of Sciaenops ocellatus (red drum). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 55, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Becerra, J.A.; Ochoa-Flores, A.A.; Soto-Rodriguez, I.; Rodriguez-Estrada, M.T.; García, H.S. Effect of cooking conditions on cholesterol oxidation and astaxanthin in dried salted shrimp. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, L.; Xue, Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Effect of thermal processing on astaxanthin and astaxanthin esters in pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Oleo Sci. 2015, 64, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozuna, C.; Cárcel, J.A.; Walde, P.M.; Garcia-Perez, J.V. Low-temperature drying of salted cod (Gadus morhua) assisted by high power ultrasound: Kinetics and physical properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 23, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ramírez, J.; Arnau, J.; Serra, X.; Gou, P. Relationship between water content, NaCl content, pH and texture parameters in dry-cured muscles. Meat Sci. 2005, 70, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, H.; Pedro, S.; Nunes, M.L.; Costa, R.; Vaz-Pires, P. Processing of Salted Cod (Gadus spp.): A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2012, 11, 546–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
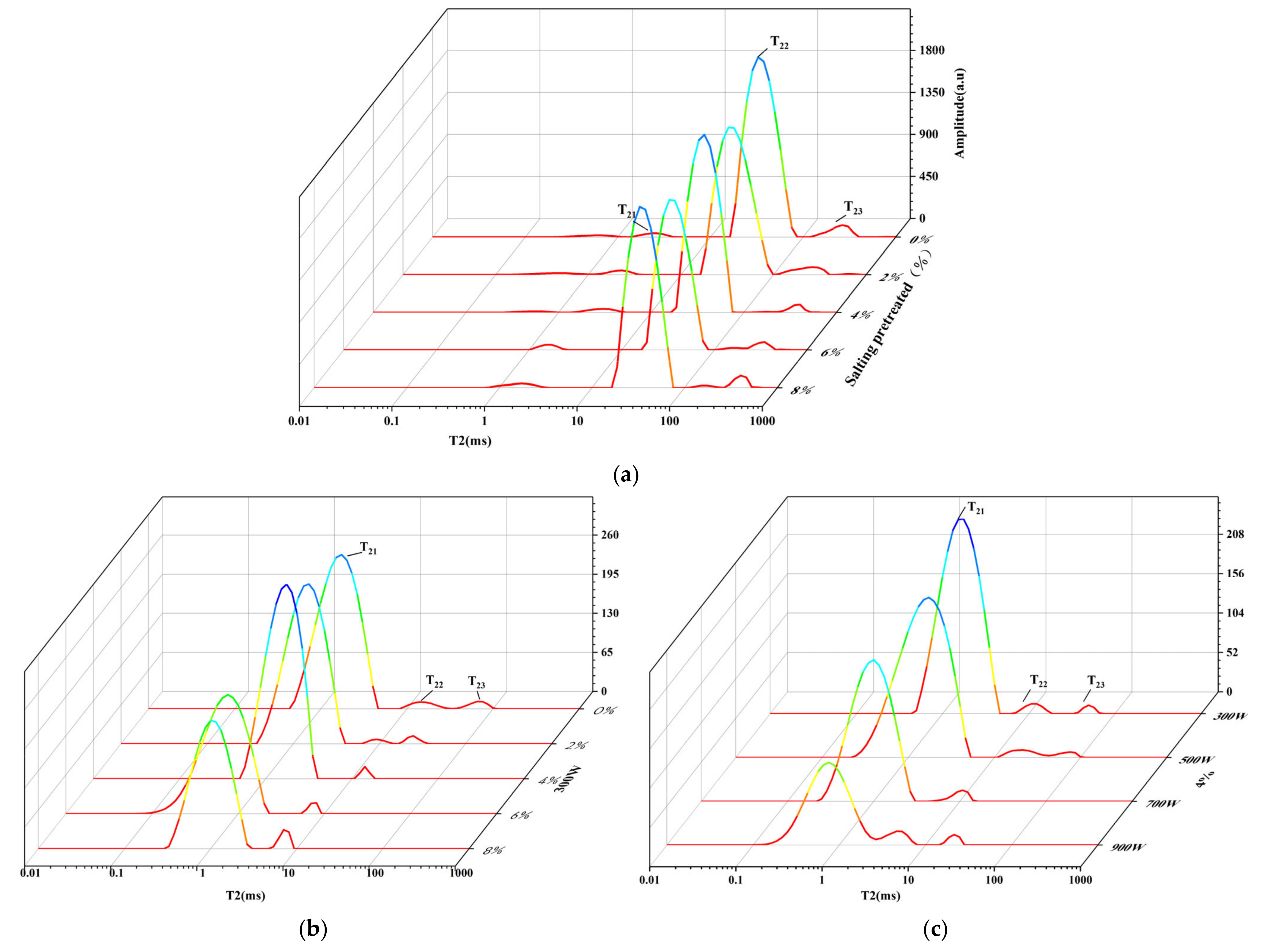
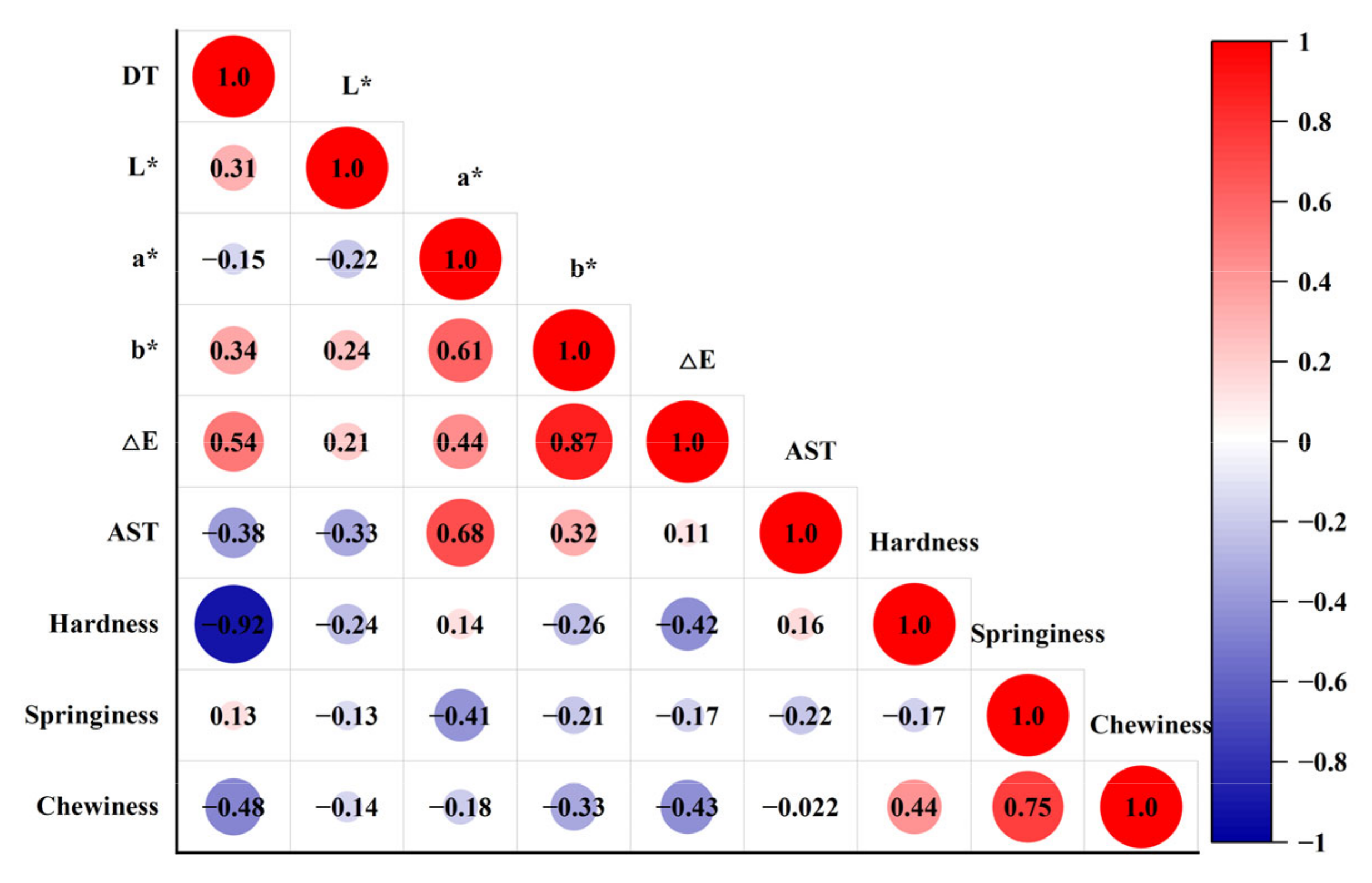
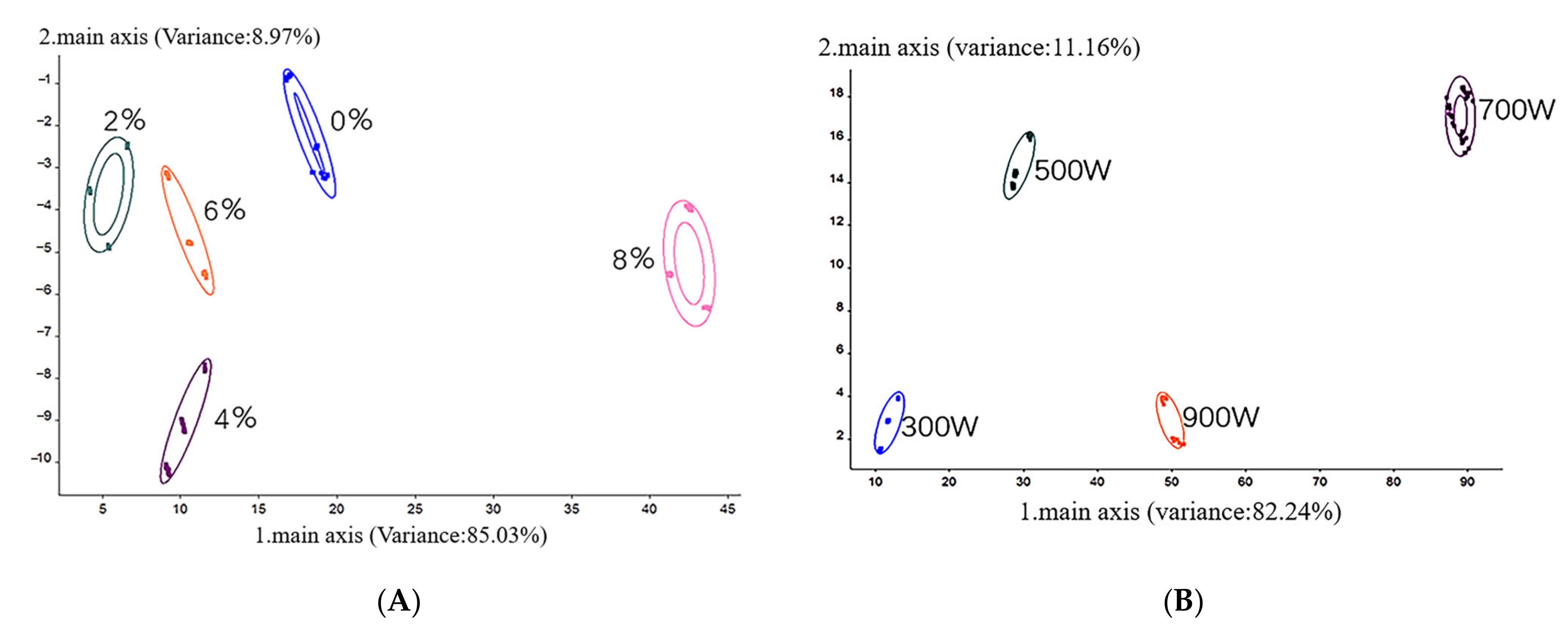
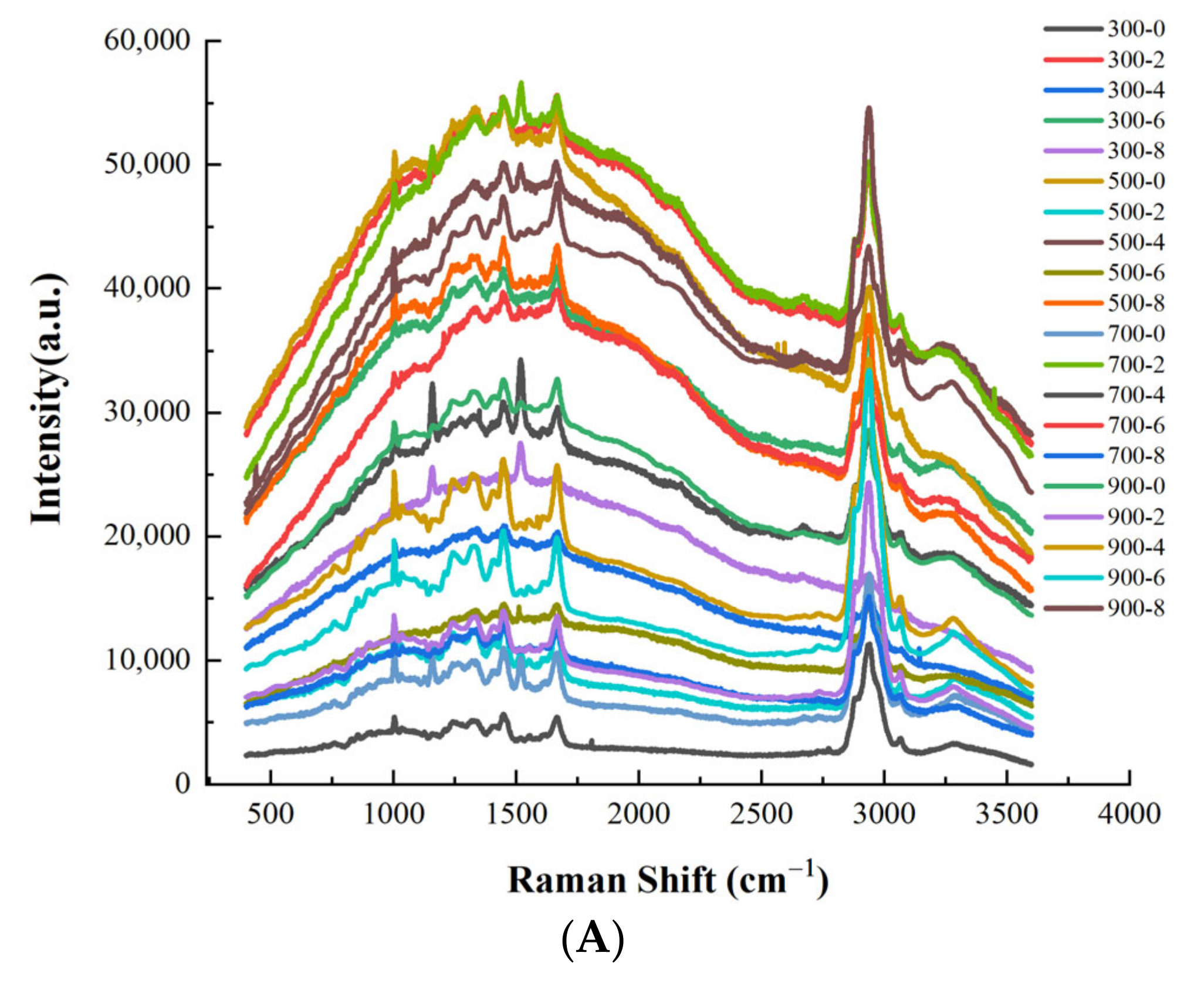
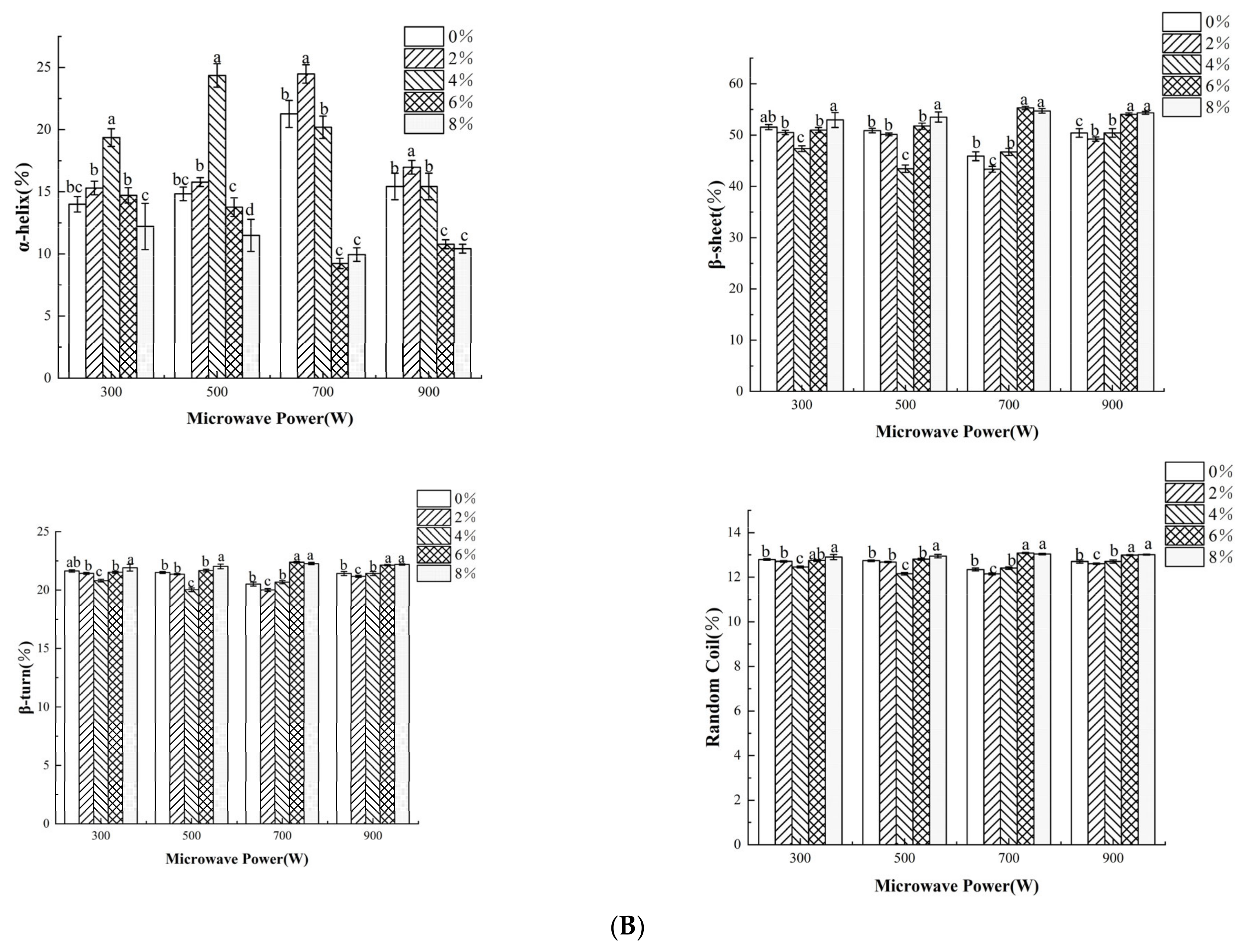

| Treatment Conditions | A21/% | A22/% | A23/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salt pretreatment | 0% | 2.31 ± 0.44 ab | 92.69 ± 0.64 b | 5 ± 0.55 a |
| 2% | 2.73 ± 0.27 a | 92.8 ± 0.19 b | 4.47 ± 0.36 a | |
| 4% | 2.4 ± 0.39 ab | 95.14 ± 0.33 a | 2.46 ± 0.25 b | |
| 6% | 2.03 ± 0.04 b | 94.92 ± 0.45 a | 3.05 ± 0.44 b | |
| 8% | 1.92 ± 0.28 b | 95.3 ± 0.56 a | 2.78 ± 0.31 b | |
| 300 W | 0% | 96.59 ± 0.44 a | 2.31 ± 0.22 b | 1.1 ± 0.22 b |
| 2% | 95.51 ± 0.5 bc | 2.3 ± 0.32 b | 2.2 ± 0.28 a | |
| 4% | 96.4 ± 0.08 ab | 2.22 ± 0.17 b | 1.38 ± 0.15 b | |
| 6% | 94.58 ± 0.65 c | 3.7 ± 0.44 a | 1.72 ± 0.34 ab | |
| 8% | 94.82 ± 0.64 c | 3.83 ± 0.41 a | 1.35 ± 0.32 b | |
| 4% | 300 W | 96.4 ± 0.22 a | 2.2 ± 0.29 b | 1.4 ± 0.16 ab |
| 500 W | 96.65 ± 0.27 a | 2.36 ± 0.19 b | 0.99 ± 0.17 b | |
| 700 W | 95.59 ± 0.35 b | 3.01 ± 0.14 a | 1.4 ± 0.32 a | |
| 900 W | 94.92 ± 0.34 b | 3.28 ± 0.23 a | 1.8 ± 0.11 a | |
| Salt Concentration (%) | NaCl Content (%) | MW Power (W) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 500 | 700 | 900 | ||
| 0 | 0.54 ± 0.08 d | 1.72 ± 0.05 aB | 1.73 ± 0.06 aB | 1.86 ± 0.01 abA | 1.74 ± 0.06 aB |
| 2 | 0.83 ± 0.08 c | 1.73 ± 0.03 aA | 1.7 ± 0.15 aA | 1.72 ± 0.1 bA | 1.72 ± 0.04 aA |
| 4 | 1.24 ± 0.1 b | 1.71 ± 0.05 aAB | 1.65 ± 0.05 aB | 1.81 ± 0.06 abA | 1.74 ± 0.03 aAB |
| 6 | 1.32 ± 0.21 b | 1.78 ± 0.04 aB | 1.75 ± 0.02 aB | 1.9 ± 0.09 aA | 1.78 ± 0.04 aB |
| 8 | 1.83 ± 0.1 a | 1.77 ± 0.03 aB | 1.76 ± 0.01 aB | 1.87 ± 0.01 abA | 1.77 ± 0.04 aB |
| MW Power (W) | Salt Concentration (%) | Hardness/N | Springiness/mm | Chewiness/mj |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 0 | 13,073.57 ± 459.25 cB | 0.74 ± 0.03 bC | 6645.24 ± 742.37 bC |
| 2 | 15,017.03 ± 352.93 bB | 0.77 ± 0.05 bA | 6596.82 ± 3291.31 bA | |
| 4 | 15,315.48 ± 115.71 bC | 0.76 ± 0.01 bA | 6181.45 ± 2484.28 bA | |
| 6 | 15,672.6 ± 495.17 bC | 0.75 ± 0.04 bB | 6226.52 ± 3461.97 abB | |
| 8 | 17,377.07 ± 165.73 aC | 0.9 ± 0.01 aA | 12,898.58 ± 439.85 aAB | |
| 500 | 0 | 13,370.73 ± 382.3 cB | 0.82 ± 0.02 aAB | 7418.47 ± 435.81 abC |
| 2 | 14,110.08 ± 357.07 cB | 0.79 ± 0.07 aA | 7273.6 ± 1565.97 abA | |
| 4 | 15,342.11 ± 737.51 bcC | 0.68 ± 0.1 abA | 5330.66 ± 3011.26 abA | |
| 6 | 16,608.35 ± 1615.88 abC | 0.54 ± 0.01 bC | 8749.91 ± 1221.77 bC | |
| 8 | 17,856.29 ± 511.98 aC | 0.83 ± 0.1 aA | 10,238.14 ± 3322.58 aB | |
| 700 | 0 | 16,095.26 ± 736.28 dA | 0.87 ± 0.02 aA | 10,242.23 ± 1136.11 aA |
| 2 | 18,042.5 ± 556.24 cA | 0.79 ± 0.06 aA | 9694.33 ± 133.31 aA | |
| 4 | 19,305.52 ± 434.79 cB | 0.79 ± 0.03 aA | 10,032.09 ± 93.04 aA | |
| 6 | 20,841 ± 859.17 bB | 0.74 ± 0.02 aAB | 10,179.21 ± 154.52 aB | |
| 8 | 23,141.2 ± 216.14 aB | 0.78 ± 0.09 aA | 12,255.06 ± 3364.41 aAB | |
| 900 | 0 | 17,109.41 ± 1536.79 cA | 0.74 ± 0.06 bcC | 7951.27 ± 1236.1 bAB |
| 2 | 18,965.85 ± 1298.36 cA | 0.72 ± 0.03 cA | 9196.86 ± 826.01 bA | |
| 4 | 21,919.57 ± 134.57 bA | 0.7 ± 0.08 cA | 9919.01 ± 2931.05 bA | |
| 6 | 24,556.5 ± 1560.21 abA | 0.85 ± 0.02 abA | 16,732.83 ± 2071.49 aA | |
| 8 | 24,932.99 ± 372.49 aA | 0.88 ± 0.01 aA | 18,802.32 ± 864.23 aA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, A.; Wang, L.; Ai, Z.; Xiao, H.; Li, J.; Li, X. Improvement of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Drying Characteristics and Quality Attributes by a Combination of Salting Pretreatment and Microwave. Foods 2022, 11, 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142066
Lin Y, Gao Y, Li A, Wang L, Ai Z, Xiao H, Li J, Li X. Improvement of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Drying Characteristics and Quality Attributes by a Combination of Salting Pretreatment and Microwave. Foods. 2022; 11(14):2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142066
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yawen, Yue Gao, Aiqing Li, Lei Wang, Ziping Ai, Hongwei Xiao, Jianrong Li, and Xuepeng Li. 2022. "Improvement of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Drying Characteristics and Quality Attributes by a Combination of Salting Pretreatment and Microwave" Foods 11, no. 14: 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142066
APA StyleLin, Y., Gao, Y., Li, A., Wang, L., Ai, Z., Xiao, H., Li, J., & Li, X. (2022). Improvement of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Drying Characteristics and Quality Attributes by a Combination of Salting Pretreatment and Microwave. Foods, 11(14), 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142066








