Temperature and pH Stability of Anthraquinones from Native Aloe vera Gel, Spray-Dried and Freeze-Dried Aloe vera Powders during Storage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Whole-Leaf Aloe vera Gel
2.3. Preparation of Whole-Leaf Aloe vera Spray-Dried and Freeze-Dried Powders
2.4. Evaluation for Temperature and pH Stability
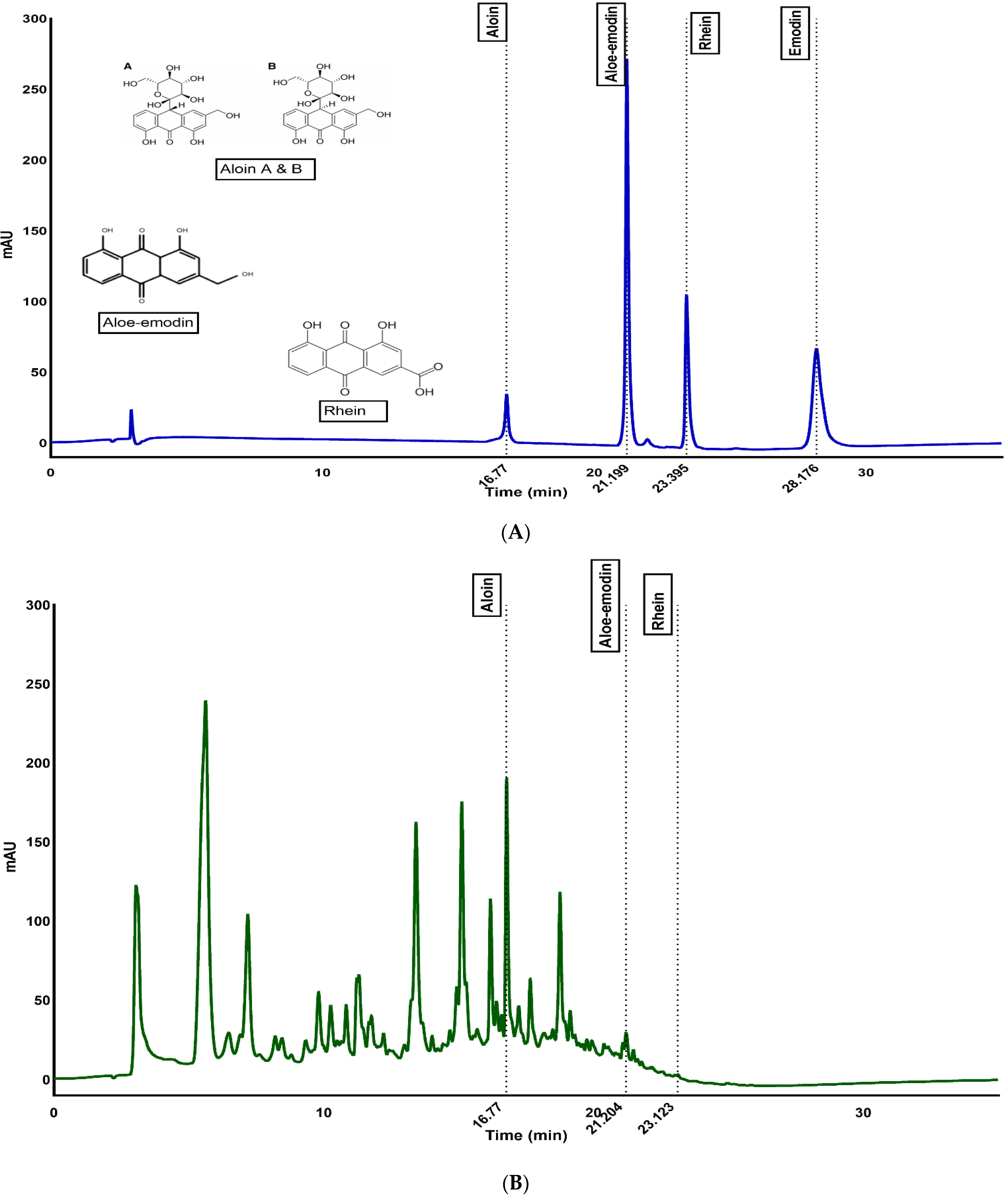
2.5. Quantification of Anthraquinones by HPLC
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Quantification of Anthraquinones through HPLC
3.2. FTIR Analysis
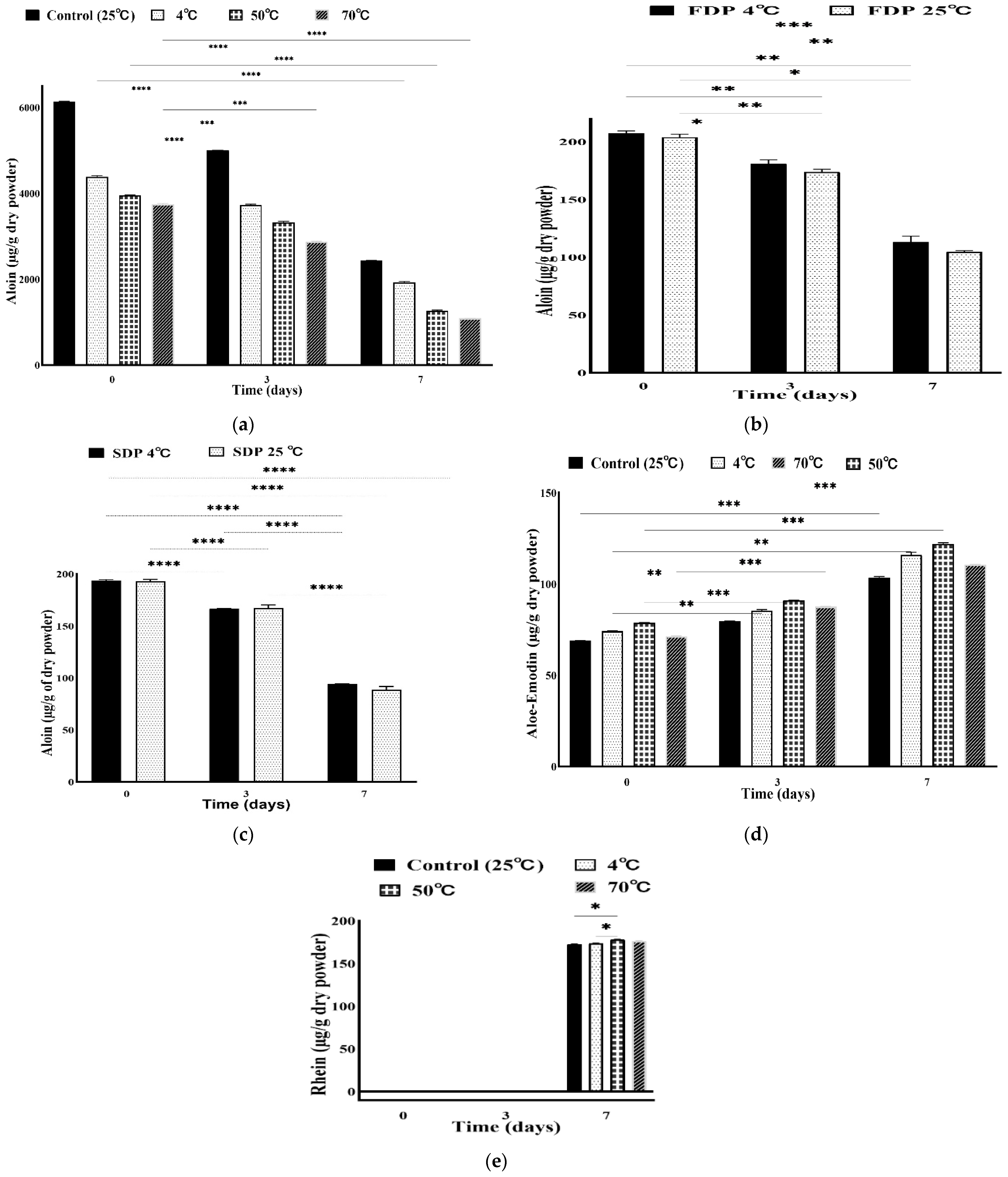
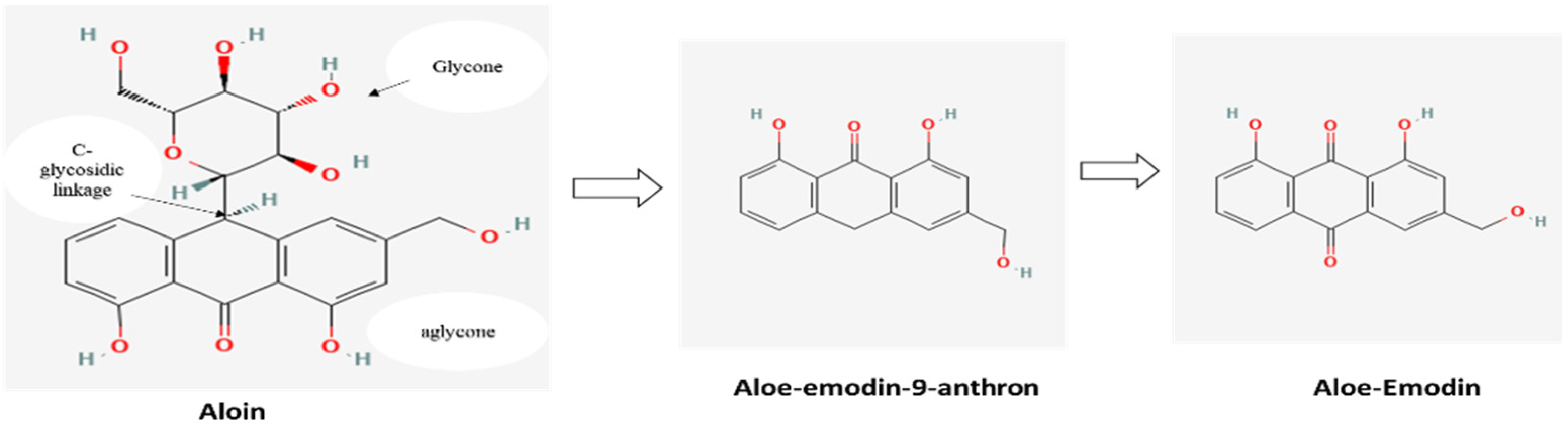
3.3. Stability of Anthraquinones at Different Temperatures
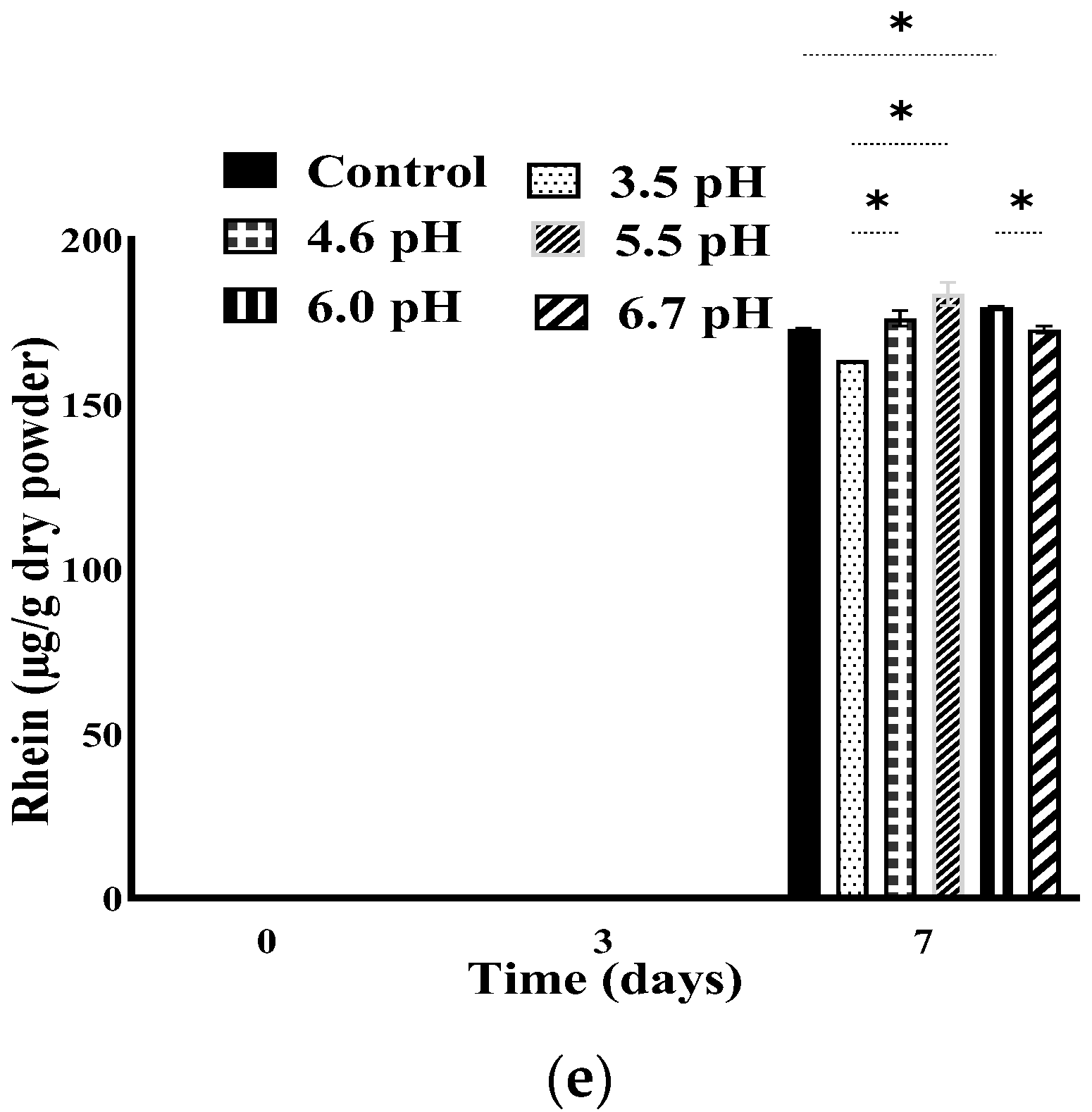
3.4. Stability of Anthraquinones at Different pH Adjustments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atherton, P. Aloe vera revisited. Br. J. Phytother. 1997, 4, 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Urch, D. Aloe Vera-Nature’s Gift; Blackdown Publications: Bristol, UK, 1999; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Eshun, K.; He, Q. Aloe vera: A valuable ingredient for the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, M.D.; Olson, G.R.; Tryndyak, V.P.; Bryant, M.S.; Felton, R.P.; Beland, F.A. From the cover: Aloin, a component of the aloe vera plant leaf, induces pathological changes and modulates the composition of microbiota in the large intestines of f344/N male rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 158, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drudi, D.; Tinto, D.; Ferranti, D.; Fiorelli, F.; Pozzo, M.D.; Capitani, O. Aloe barbadensis miller versus silver sulfadiazine creams for wound healing by secondary intention in dogs and cats: A randomized controlled study. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 117, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges-Argáez, R.; Chan-Balan, R.; Cetina-Montejo, L.; Ayora-Talavera, G.; Sansores-Peraza, P.; Gómez-Carballo, J.; Cáceres-Farfán, M. In vitro evaluation of anthraquinones from Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) roots and several derivatives against strains of influenza virus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 132, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremić, S.; Amić, A.; Stanojević-Pirković, M.; Marković, Z. Selected Anthraquinones as Potential Free Radical Scavengers and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 1890–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, L.T.; Mazumder, A.; Dwivedi, A.; Gerber, M.; du Plessis, J.; Hamman, J.H. In vitro wound healing and cytotoxic activity of the gel and whole-leaf materials from selected aloe species. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 200, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sosa, K.; Villarreal-Alvarez, N.; Lübben, P.; Peña-Rodríguez, L.M. Chrysophanol, an antimicrobial anthraquinone from the root extract of Colubrina greggii. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2006, 50, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Xing, F.; Zhu, G.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; Qu, J.; Lee, I.; Pan, L. Rhein antagonizes P2X7 receptor in rat peritoneal macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Yadav, M.; Yadav, A.; Rohilla, P.; Yadav, J.P. Antiplasmodial potential and quantification of aloin and aloe-emodin in Aloe vera collected from different climatic regions of India. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 310–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, K.; Kuepper, U.; Musshoff, F.; Madea, B.; Reusch, H.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Quality control of Aloe vera beverages. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 4, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Salah, F.; Ghoul, Y.E.; Mahdhi, A.; Majdoub, H.; Jarroux, N.; Sakli, F. Effect of the deacetylation degree on the antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of acemannan from Aloe vera. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 103, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhao, X.; Yue, L.; Liu, L. Main anthraquinone components in Aloe vera and their inhibitory effects on the formation of advanced glycation end-products. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, X.B.; Yu, Q.M.; Luo, Q.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z. Synergistic cancer growth-inhibitory effect of emodin and low-dose cisplatin on gastric cancer cells In vitro. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, W.J.; Wu, X.F.; Zhong, J.S.; Wan, J.Z. Effects of temperature, pH and light on the stability of aloin A and characterisation of its major degradation products. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wei, Y.; Ashokkumar, M.; Qin, J.; Han, N.; Wang, Y. Effect of ultrasound on binding interaction between emodin and micellar casein and its microencapsulation at various temperatures. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 62, 104861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-M.; Xie, W.-G.; Wen, T.-T.; Zhao, X. Thermal behavior of five free anthraquinones from rhubarb. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 100, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Jadhav, A.; Kadam, V. Forced degradation studies of aloe emodin and emodin by HPTLC. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaparakou, E.H.; Kanakis, C.D.; Gerogianni, M.; Maniati, M.; Vekrellis, K.; Skotti, E.; Tarantilis, P.A. Quantitative determination of aloin, antioxidant activity, and toxicity of Aloe vera leaf gel products from Greece. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Machado, D.I.; López-Cervantes, J.; Mariscal-Domínguez, M.F.; Cruz-Flores, P.; Campas-Baypoli, O.N.; Cantú-Soto, E.U.; Sanches-Silva, A. An HPLC Procedure for the Quantification of Aloin in Latex and Gel from Aloe barbadensis Leaves. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 55, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.L.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Z. Effects of heat treatments on the stabilities of polysaccharides substances and barbaloin in gel juice from Aloe vera Miller. J. Food Eng. 2006, 75, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzoni, M.; Molinari, G.P.; Lucini, L. Stability of the main Aloe fractions and Aloe-based commercial products under different storage conditions. Agrochimica 2011, 55, 288–296. [Google Scholar]
- Minjares-Fuentes, R.; Femenia, A.; Comas-Serra, F.; Rosselló, C.; Rodríguez-González, V.; González-Laredo, R.; Gallegos-Infante, J.; Medina-Torres, L. Effect of different drying procedures on physicochemical properties and flow behavior of Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) gel. LWT 2016, 74, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, G.J.; Dobson, P.; Jordan-Mahy, N. Effect of different cooking regimes on rhubarb polyphenols. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, G.-C.; Chung, D.-Y. Antioxidant Effects of Extracts from Cassia t ora L. Prepared under Different Degrees of Roasting on the Oxidative Damage to Biomolecules. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wamer, W.G.; Vath, P.; Falvey, D.E. In vitro studies on the photobiological properties of aloe emodin and aloin A. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, M.; Park, J.; Kim, N.Y.; Shin, Y.G.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.K. Analysis of 13 phenolic compounds in Aloe species by high performance liquid chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. Int. J. Plant Chem. Biochem. Tech. 1998, 9, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindroth, R.; Pajutee, M. Chemical analysis of phenolic glycosides: Art, facts, and artifacts. Oecologia 1987, 74, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, A.A.; Lević, S.M.; Pavlović, V.B.; Marković, S.B.; Pjanović, R.V.; Đorđević, V.B.; Nedović, V.; Bugarski, B.M. Freeze vs. Spray drying for dry wild thyme (Thymus serpyllum L.) extract formulations: The impact of gelatin as a coating material. Molecules 2021, 26, 3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, F.; Vatanara, A.; Park, E.J.; Na, D.H. Drying technologies for the stability and bioavailability of biopharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jawade, N.R.; Chavan, A.R. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of aloin from aloe vera gel. Procedia Eng. 2013, 51, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.S.; Yang, T.-J.; Park, S.U.; Baek, J.H.; Wu, S.; Lim, K.-B. Induction and Proliferation of Adventitious Roots from’Aloe vera’Leaf Tissues for’in vitro’Production of Aloe-emodin. Plant Omics 2011, 4, 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H. Free radical scavenging and leukemia cell growth inhibitory properties of onion powders treated by different heating processes. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, SNQ50–SNQ54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagne, E.; Bisrat, D.; Viljoen, A.; Van Wyk, B. Chemistry of Aloe species. Curr. Org. Chem. 2000, 4, 1055–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grun, M.; Franz, G. Studies on the biosynthesis of aloins in aloe-arborescens mill. Arch. Der. Pharm. 1982, 315, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-S.; Van der Heijden, R.; Verpoorte, R. Biosynthesis of anthraquinones in cell cultures of the Rubiaceae. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2001, 67, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardsadegh, B.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Aloe vera leaf extract mediated green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their in vitro antimicrobial activity against spoilage fungi and pathogenic bacteria strains. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.X.; Cheong, K.Y. Effects of drying temperature and ethanol concentration on bipolar switching characteristics of natural Aloe vera-based memory devices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 26833–26853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamlang, S.; Buranut, T.; Niansiri, A.; Sirivat, A. Controlled aloin release from crosslinked polyacrylamide hydrogels: Effects of mesh size, electric field strength and a conductive polymer. Materials 2013, 6, 4787–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Wilkanowicz, S.; Melendez-Rodriguez, B.; Lagaron, J.M. Nanoencapsulation of Aloe vera in Synthetic and Naturally Occurring Polymers by Electrohydrodynamic Processing of Interest in Food Technology and Bioactive Packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem 2017, 65, 4439–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.M.; Barot, A.A.; Kumar Sinha, V. Sequential liquefaction of Nicotiana tabacum stems biomass by crude polyhydric alcohols for the production of polyols and rigid polyurethane foams. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejatzadeh-Barandozi, F.; Enferadi, S.T. FT-IR study of the polysaccharides isolated from the skin juice, gel juice, and flower of Aloe vera tissues affected by fertilizer treatment. Org. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valverde, J.M.; Valero, D.; Martínez-Romero, D.; Guillén, F.; Castillo, S.; Serrano, M. Novel edible coating based on Aloe vera gel to maintain table grape quality and safety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7807–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierhalz, A.C.K.; Lopes, S.A.; Pires, A.L.R.; Moraes, Â.M. Development of polysaccharide-based membranes incorporating the bioactive compound aloin. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2017, 66, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guin, P.S.; Das, S.; Mandal, P. Electrochemical reduction of quinones in different media: A review. Int. J. Electrochem. 2011, 2011, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Femenia, A.; García-Pascual, P.; Simal, S.; Rosselló, C. Effects of heat treatment and dehydration on bioactive polysaccharide acemannan and cell wall polymers from Aloe barbadensis Miller. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 51, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriariyakul, W.; Swasdisevi, T.; Devahastin, S.; Soponronnarit, S. Drying of aloe vera puree using hot air in combination with far-infrared radiation and high-voltage electric field: Drying kinetics, energy consumption and product quality evaluation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokboribal, J.; Tachaboonyakiat, W.; Sangvanich, P.; Ruangpornvisuti, V.; Jettanacheawchankit, S.; Thunyakitpisal, P. Deacetylation affects the physical properties and bioactivity of acemannan, an extracted polysaccharide from Aloe vera. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, F.; Bogoni, P.; Masotti, P.; Micali, G. High-performance liquid chromatographic profiles of aloe constituents and determination of aloin in beverages, with reference to the EEC regulation for flavouring substances. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 718, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, E.T.; da Silva, M.M.; de Andrade, S.J.; Cardoso, M.P.; Silva, L.A.; de Andrade, J.B. Evaluation of thermal stability of quinones by thermal analysis techniques. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 529, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, K.; Ganora, L.; Yarnell, E. The effect of freeze-drying and its implications for botanical medicine: A review. Phytother.Res. Int. J. Devoted Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Nat. Prod. Deriv. 2005, 19, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, K.; Uehara, S.-i.; Takano, I.; Shindo, T.; Nishijima, M. Stability of barbaloin in aqueous solution. Food Preserv. Sci. 2000, 26, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, I.; Winters, W.D.; Scott, M.; Kousoulas, K. An in vitro and in vivo toxicologic evaluation of a stabilized aloe vera gel supplement drink in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomer, J.L.; Stagliano, K.W.; Gazzillo, J.A. Preparation of functionalized juglone acetates and juglones via 1,4-dimethoxynaphthalene derivatives: Synthesis of anthraquinones related to rhein and aloe-emodin. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 7906–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, R.; Simonsen, J. Experiments on the constitution of the aloins. Part III. J. Chem. Soc. 1932, 382, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Viesca, F.; Gómez, R. The mechanism of nitric acid degradation of the C-glycoside Aloin to Aloe-emodin. Am. J. Chem. 2020, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Assary, R.S.; Kim, T.; Low, J.J.; Greeley, J.; Curtiss, L.A. Glucose and fructose to platform chemicals: Understanding the thermodynamic landscapes of acid-catalysed reactions using high-level ab initio methods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 16603–16611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korth, H.-G.; Mulder, P. Anthrone and related hydroxyarenes: Tautomerization and hydrogen bonding. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 7674–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauwald, H.W. Naturally occurring quinones and their related reduction forms: Analysis and analytical methods. PZ Wiss 1990, 3, 169–181. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, H.-M.; Lin, Y.-T.; Hsiao, P.-L.; Su, Y.-H.; Tsao, H.-T.; Wen, K.-C. Determination of marked components—aloin and aloe-emodin—in Aloe vera before and after hydrolysis. J. Food Drug Anal. 2012, 20, 646–652. [Google Scholar]


| Sample (µg/g of Dry Powder) | Aloin | Aloe-Emodin | Rhein |
|---|---|---|---|
| WLAG | 6134.0 ± 15.0 a | 69.0 ± 0.0 a | 172.7 ± 0.4 a |
| FDP | 223.1 ± 3.9 b | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| SDP | 220.0 ± 0.2 b | 18.2 ± 0.0 c | 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadiq, U.; Gill, H.; Chandrapala, J. Temperature and pH Stability of Anthraquinones from Native Aloe vera Gel, Spray-Dried and Freeze-Dried Aloe vera Powders during Storage. Foods 2022, 11, 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11111613
Sadiq U, Gill H, Chandrapala J. Temperature and pH Stability of Anthraquinones from Native Aloe vera Gel, Spray-Dried and Freeze-Dried Aloe vera Powders during Storage. Foods. 2022; 11(11):1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11111613
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadiq, Uzma, Harsharn Gill, and Jayani Chandrapala. 2022. "Temperature and pH Stability of Anthraquinones from Native Aloe vera Gel, Spray-Dried and Freeze-Dried Aloe vera Powders during Storage" Foods 11, no. 11: 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11111613
APA StyleSadiq, U., Gill, H., & Chandrapala, J. (2022). Temperature and pH Stability of Anthraquinones from Native Aloe vera Gel, Spray-Dried and Freeze-Dried Aloe vera Powders during Storage. Foods, 11(11), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11111613









