Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seed Protein–EGCG Conjugates: Covalent Bonding and Functional Research
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Extraction of HPI
2.3. Preparation of Covalent HPI-EGCG Complexes
2.4. Determination of Sulfhydryl Content
2.5. Determination of Free Amino Group Content
2.6. Determination of EGCG Content
2.7. Zeta Potential and Particle Size Determination
2.8. Circular Dichroism Analysis
2.9. Three-Dimensional Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.10. HPI-EGCG Conjugate Properties
2.10.1. Solubility
2.10.2. Emulsifying Properties
2.11. Cryo-Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of HPI and EGCG Covalent Reactive Groups and EGCG Content
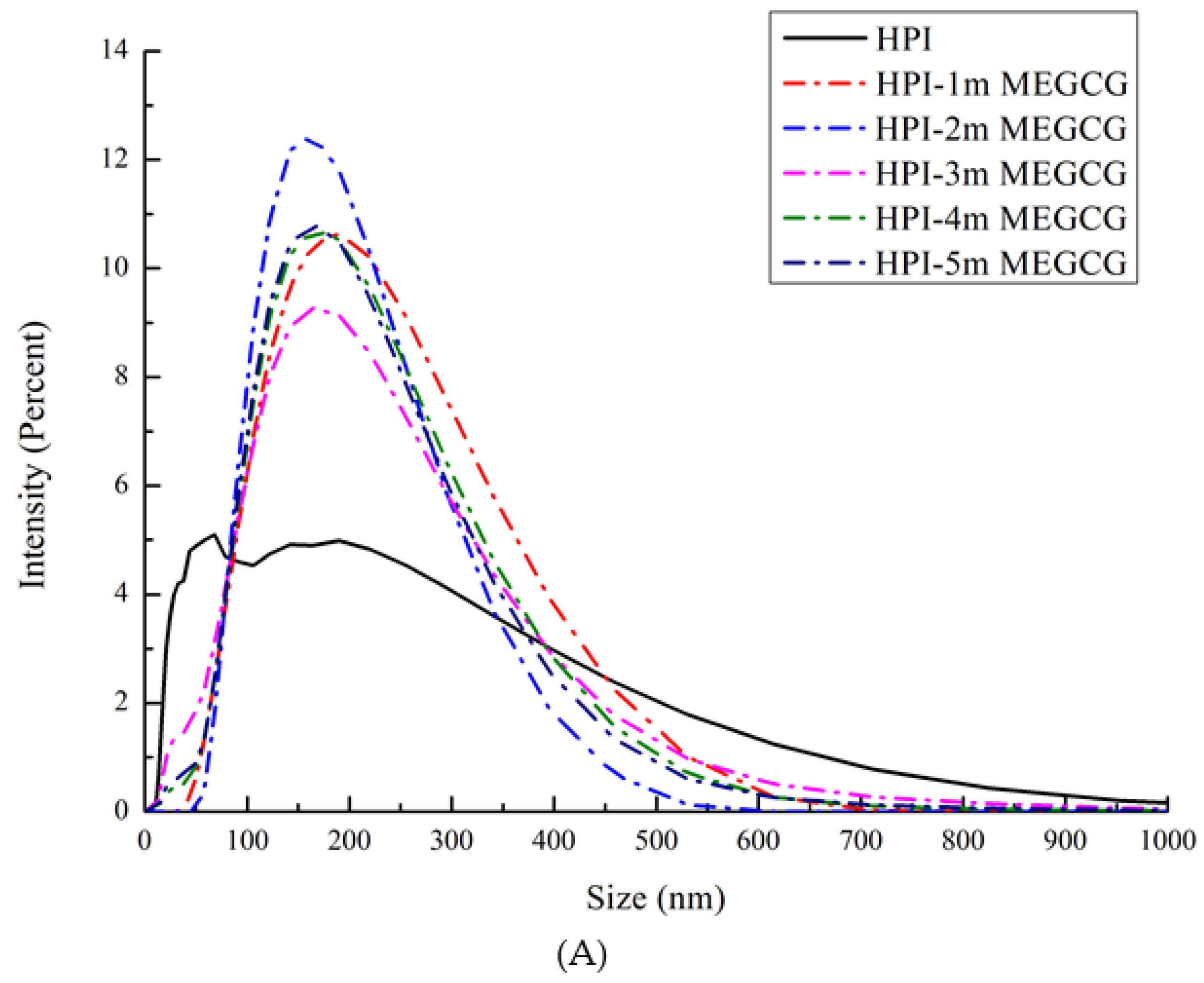
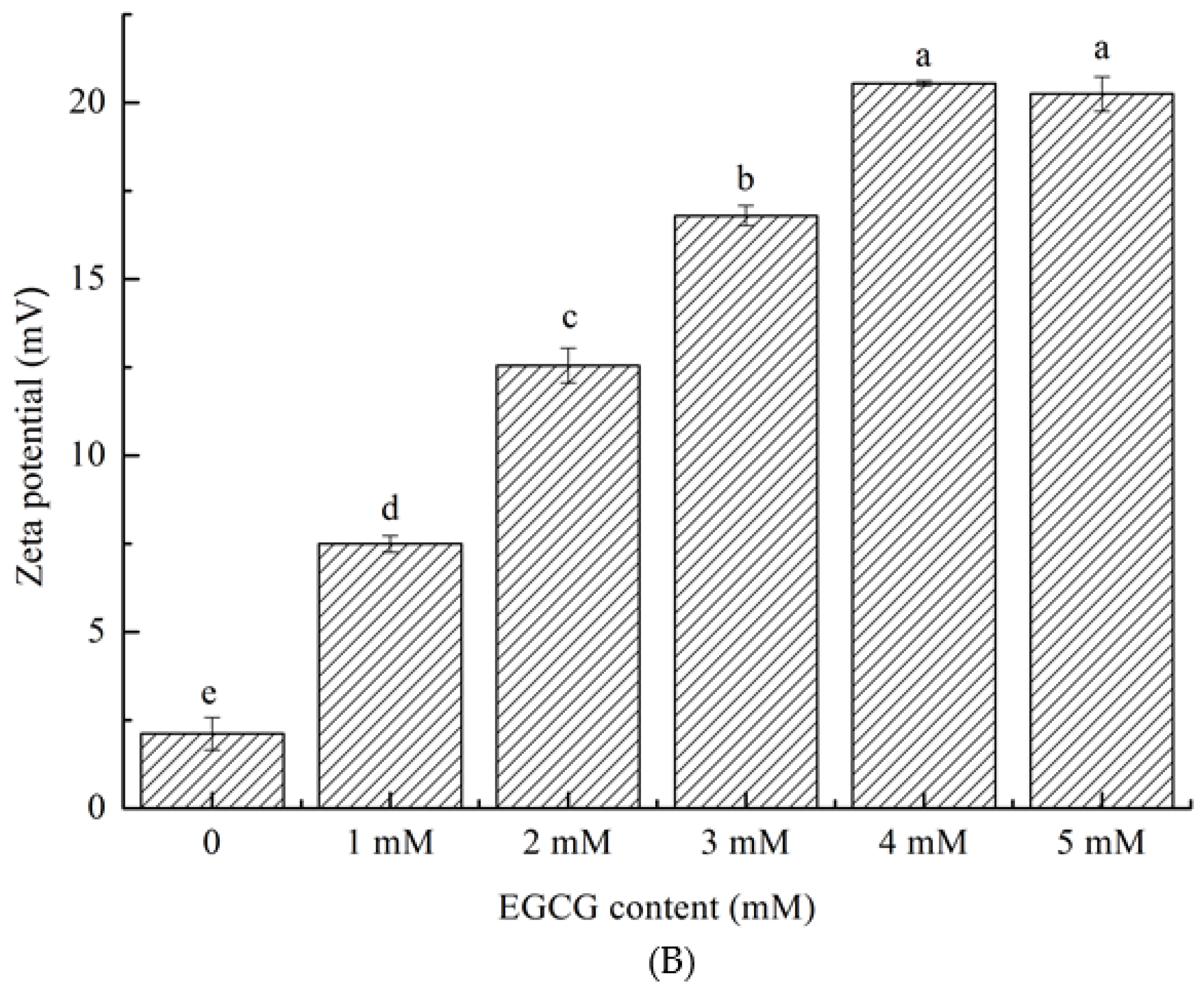
3.2. Particle Size Distribution and Zeta Potential Change Analysis
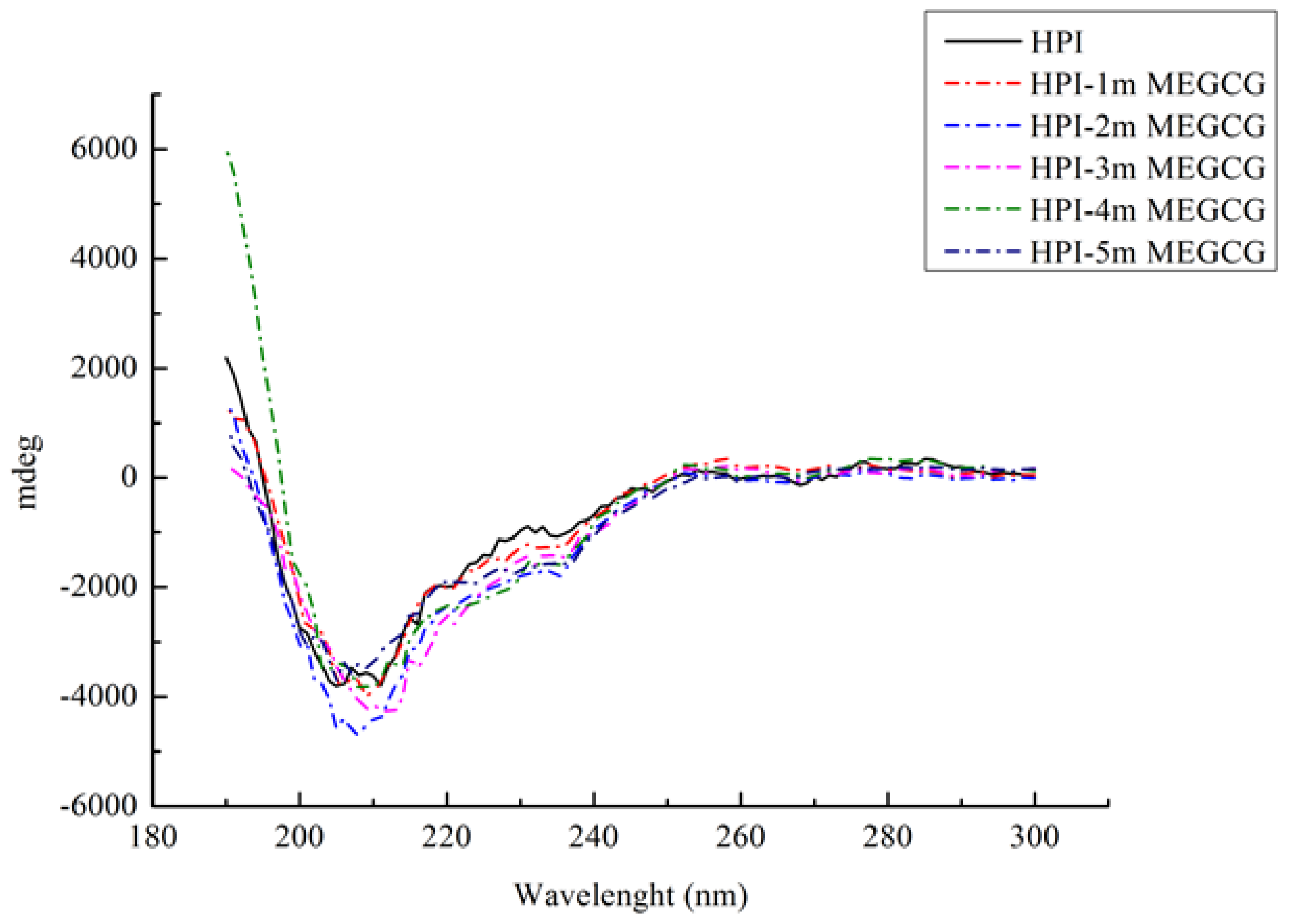
3.3. CD Spectroscopy
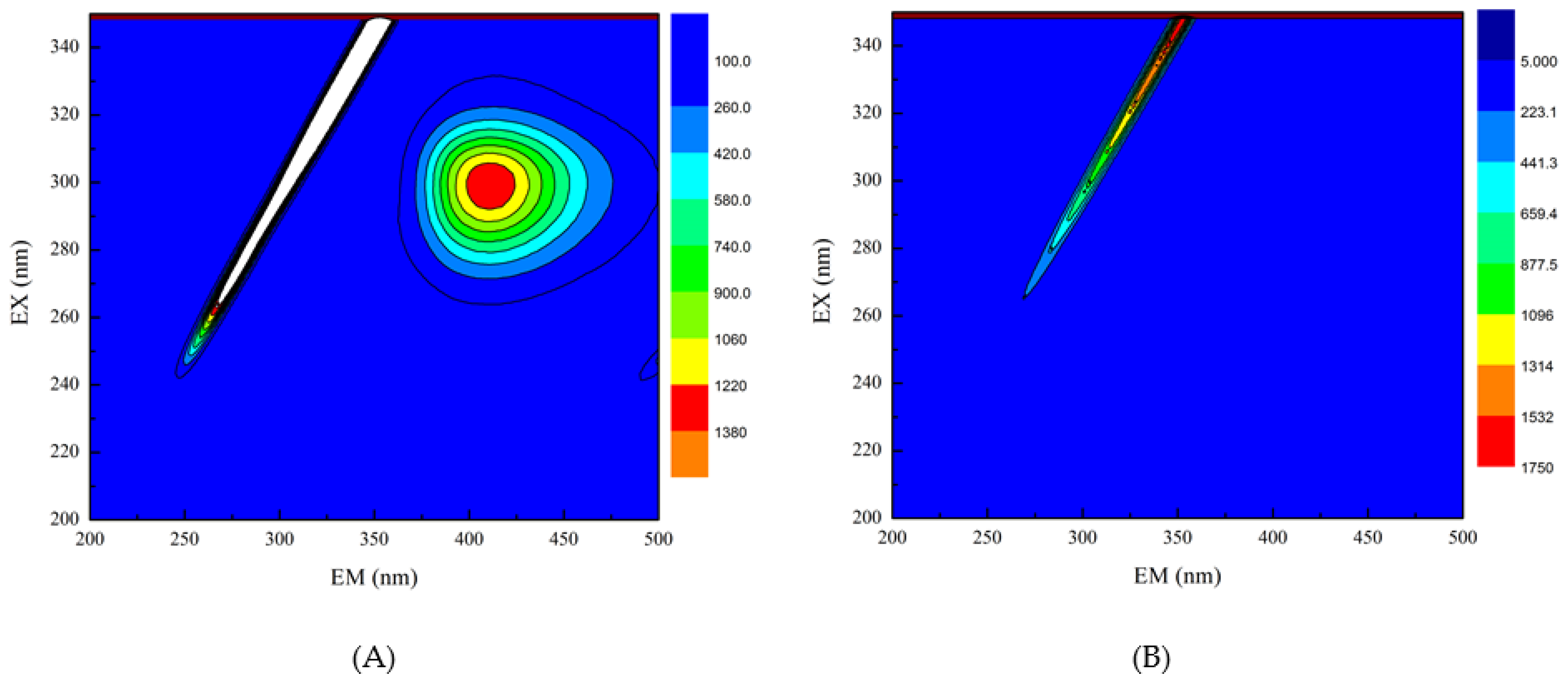
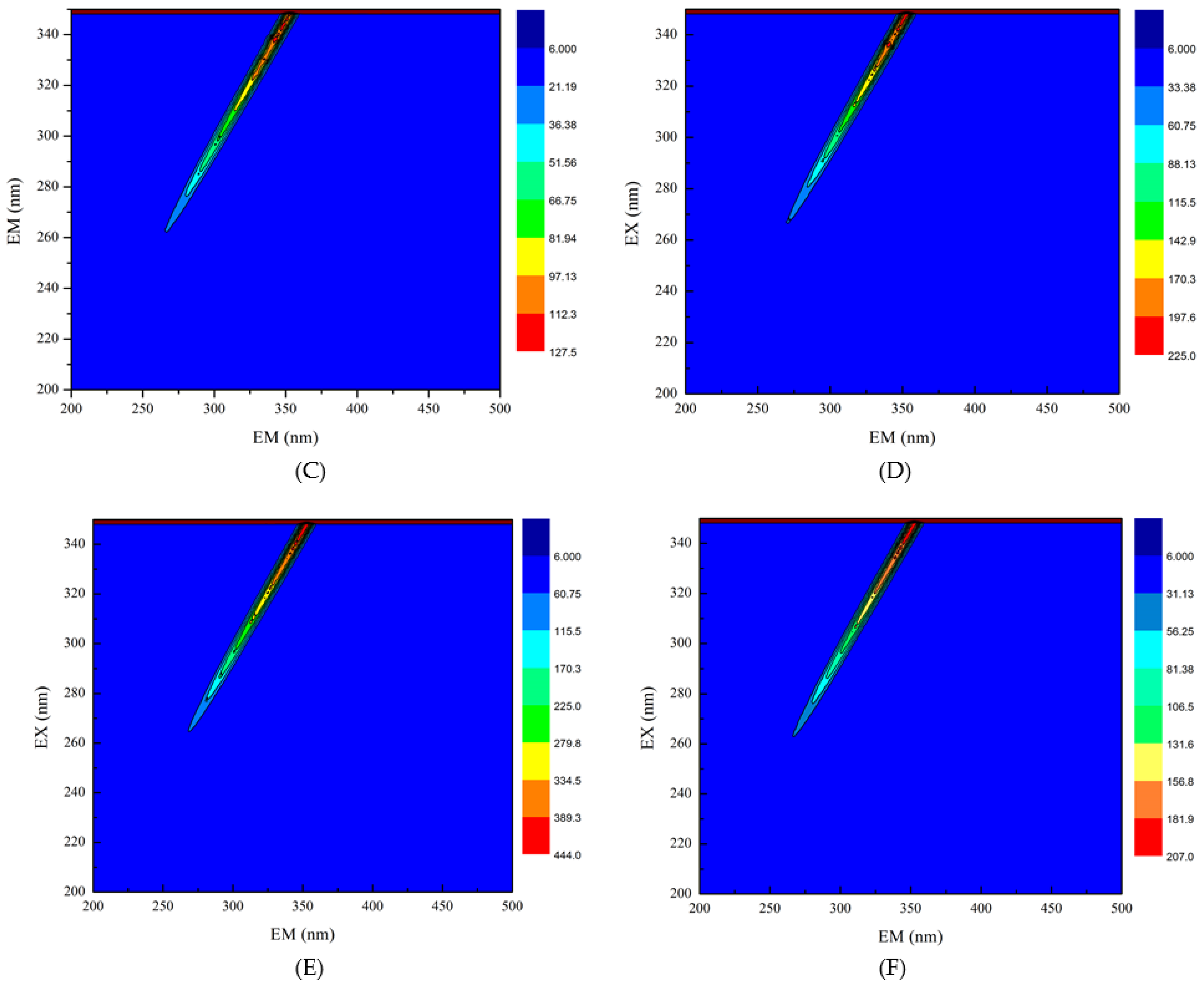
3.4. Three-Dimensional Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.5. Functional Properties of SPI-EGCG Conjugates
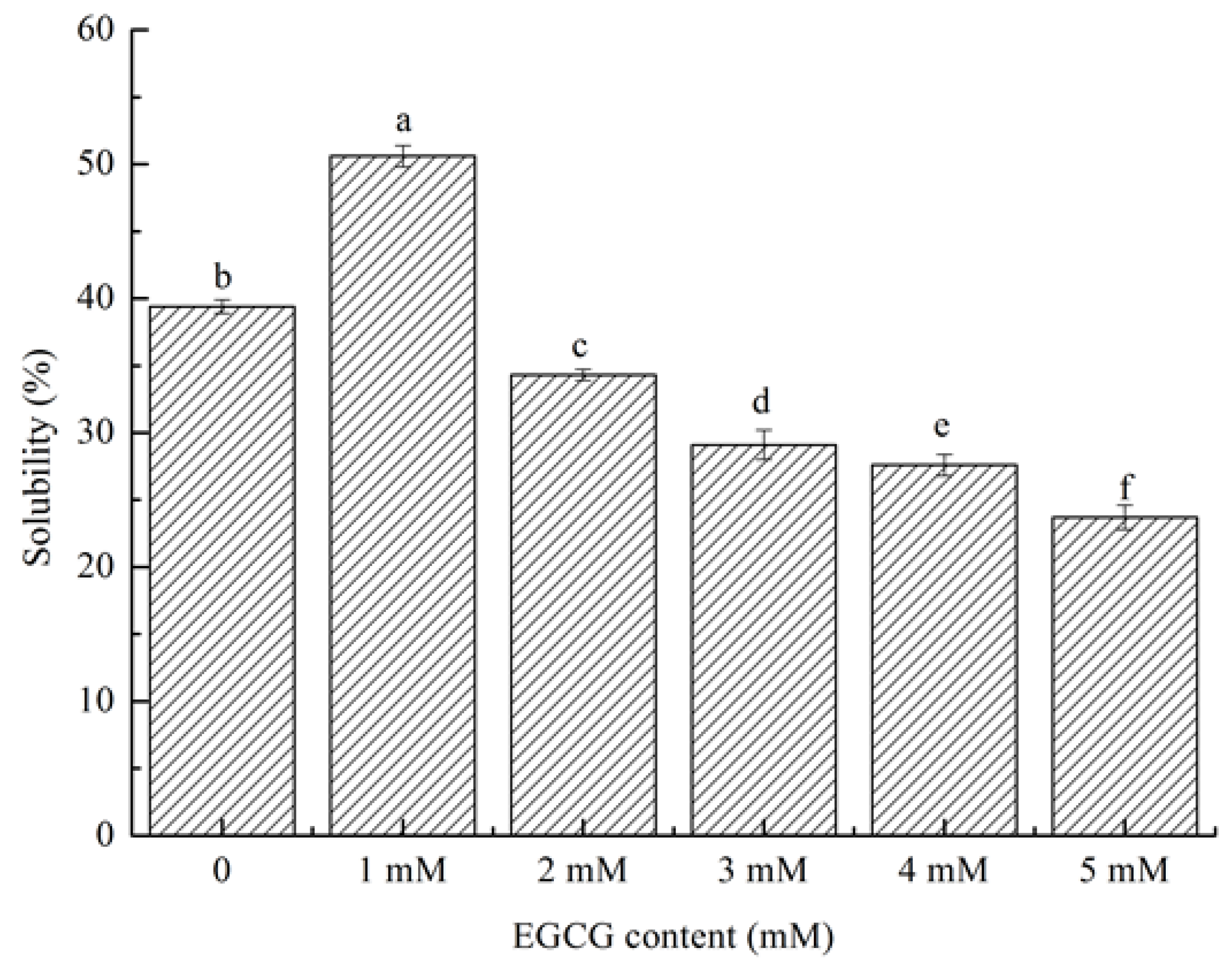
3.5.1. Solubility
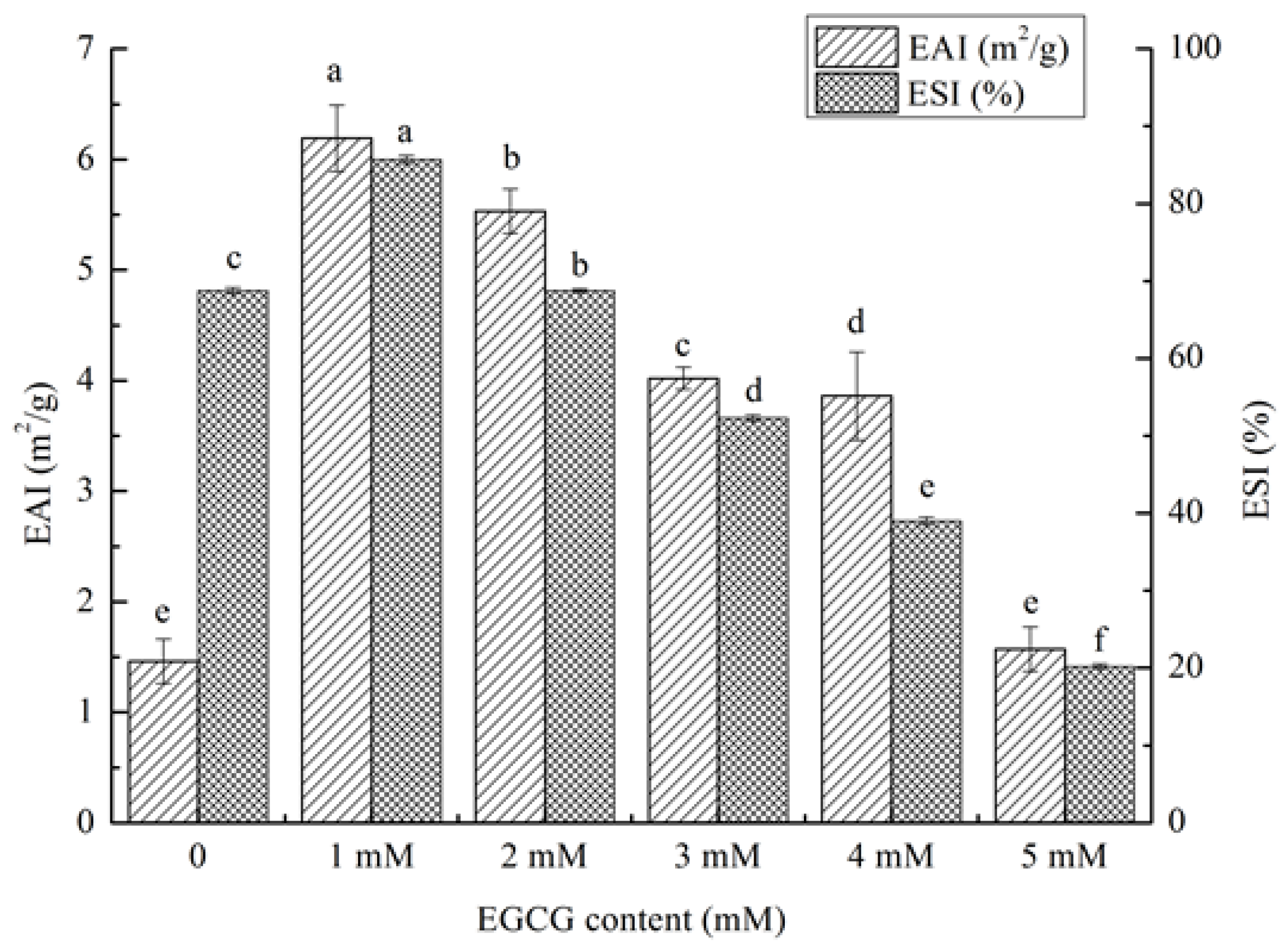
3.5.2. Emulsifying Properties of HPI-EGCG Conjugates
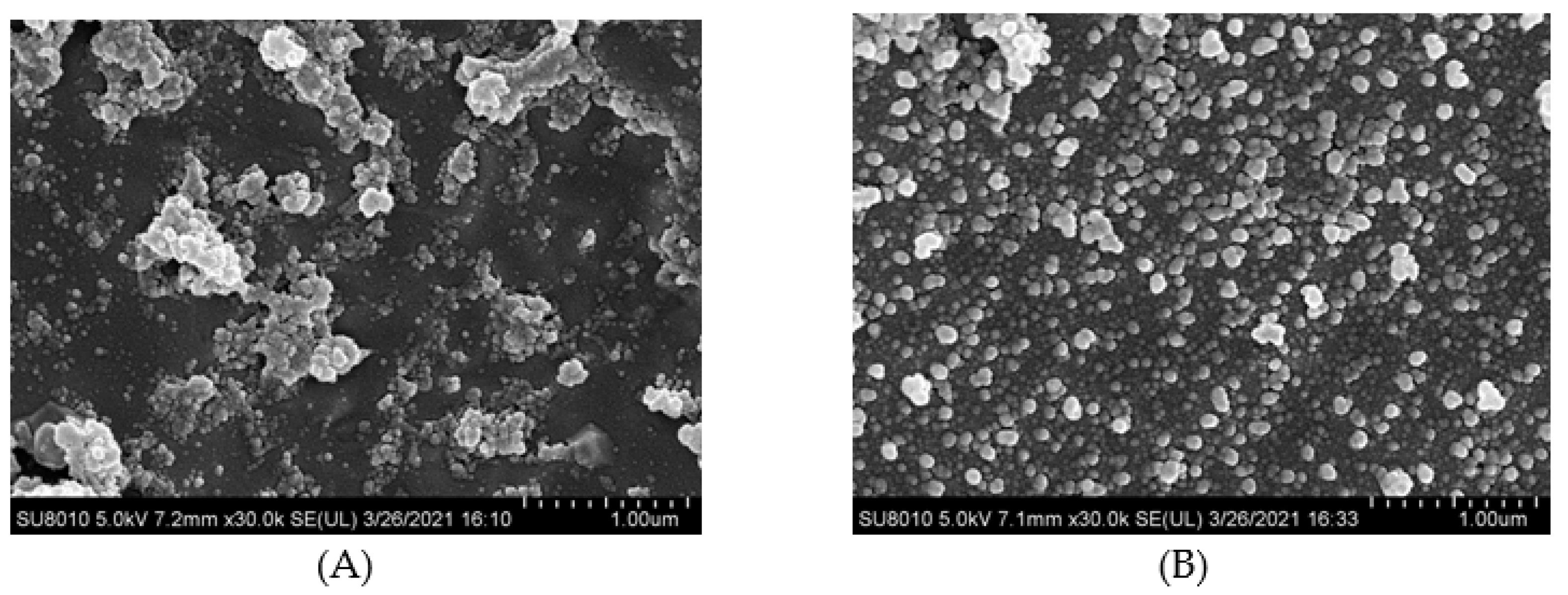
3.6. Cryo-Scanning Electron Microscopy Microstructure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blade, S.F. Industrial hemp in Alberta. In Alberta Hemp Symposia Proceedings; Blade, S., Ed.; Alberta Agriculture, Food and Rural Development: Red Deer, AB, Canada, 1998; pp. 2–11. [Google Scholar]
- Malomo, S.A.; He, R.; Aluko, R.E. Structural and Functional Properties of Hemp Seed Protein Products. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C1512–C1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.-H.; Wang, X.-S.; Yang, X.-Q. Enzymatic hydrolysis of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate by various proteases and antioxidant properties of the resulting hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.-R.; Qian, P.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, X.-H.; Chen, T.-P.; He, J.-F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J. Hempseed protein derived antioxidative peptides: Purification, identification and protection from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojić, M.; Mišan, A.; Sakač, M.; Dapčević Hadnađev, T.; Šarić, B.; Milovanović, I. Characterization of by-products originating from hemp oil processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12436–12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, M.; Guyomarc’H, F.; Legland, D.; Famelart, M.-H. Changing the isoelectric point of the heat-induced whey protein complexes affects the acid gelation of skim milk. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 23, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobek, L. Interactions of polyphenols with carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Ma, C.; Gao, Y.; McClements, D.J. Food-Grade Covalent Complexes and Their Application as Nutraceutical Delivery Systems: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurell, R.F.; Finot, P.A. Nutritional consequences of the reactions between proteins and oxidized polyphenolic acids. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1984, 177, 423–435. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, W.; Fan, R.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Evaluation of structural and functional properties of protein–EGCG complexes and their ability of stabilizing a model β-carotene emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phama, L.B.; Wang, B.; Zisuc, B.; Adhikaria, B. Covalent modification of flaxseed protein isolate by phenolic compounds and the structure and functional properties of the adducts. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.Y.; Xu, H.X.; Lu, Y.Q.; Zhang, T.T.; Li, S.M.; Lin, X.; Xu, B.Q.; Wu, X.L. Function, digestibility and allergenicity assessment of ovalbumin–EGCG conjugates. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 61, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.D.S. Tea: A new perspective on health benefits. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramza, A.; Korczak, J. Tea constituents (Camellia sinensis L.) as antioxidants in lipid systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram, S. Effects of Green Tea and EGCG on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Health. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 373S–388S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-H.; Ten, Z.; Wang, X.-S.; Yang, X.-Q. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Protein Isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8945–8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Ma, C.; McClements, D.J.; Gao, Y. A comparative study of covalent and non-covalent interactions between zein and polyphenols in ethanol-water solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, T.; Toma, S.J.; Nakai, S. Determination of SH-and SS-groups in some food proteins using Ellman’s reagent. J. Food Sci. 1974, 39, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, W.; Zhao, M. Effects of Malondialdehyde Modification on the In Vitro Digestibility of Soy Protein Isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 12139–12145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhou, L.; Jabbar, S.; Zeng, X. Effects of Oolong Tea Polyphenols, EGCG, and EGCG3″Me on Pancreatic α-Amylase Activity In Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9507–9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Ou, S.-Y.; Tang, C.-H. Core–Shell Soy Protein–Soy Polysaccharide Complex (Nano)particles as Carriers for Improved Stability and Sustained Release of Curcumin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5053–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Esposito, D.; Lila, M.A.; Foegeding, E.A. Formation of whey protein–polyphenol meso-structures as a natural means of creating functional particles. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakis, C.; Hasni, I.; Bourassa, P.; Tarantilis, P.; Polissiou, M.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.-A. Milk β-lactoglobulin complexes with tea polyphenols. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Jiang, N.; Poias, V.; Zhang, X.; Qi, B.; Li, A.; Wang, Z. Interaction of soybean protein isolate and phosphatidylcholine in nanoemulsions: A fluorescence analysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 814–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, V.M.; Lopez, A.M.; Hayes, M. Assessment of the functional properties of protein extracted from the brown seaweed Himanthalia elongata (Linnaeus) S. F. Gray. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Li, X.M.; Chen, F.L.; Piekoszewski, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.L.; Guan, H.N.; Shi, Y.G.; Zhang, N. The effect of extreme acid-induced soybean glycinin molten globules state on foaming ability. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105819–105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkevičius, M.; Allred, S.; Velev, O.D.; Velikov, K.P. Stabilization of oil continuous emulsions with colloidal particles from water-insoluble plant proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 8, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Sun, C.; Gao, Y. Influence of polysaccharides on the physicochemical properties of lactoferrin–polyphenol conjugates coated β-carotene emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Hatasa, Y.; Kawamura, S.; Shibata, T.; Akagawa, M.; Uchida, K. Identification of Polyphenol-Specific Innate Epitopes That Originated from a Resveratrol Analogue. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 4701–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, A.; Coupland, J.N. The effect of surfactants on the solubility, zeta potential, and viscosity of soy protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhou, C.; Fu, F.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Q. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on particle size and film properties of soy protein isolate. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 43, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.-D.; Lin, Y.-F.; Xu, X.; Meng, L.; Dong, M.-S. Effect of non-covalent and covalent complexation of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate with soybean protein isolate on protein structure and in vitro digestion characteristics. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Sun, C.; McClements, D.J.; Gao, Y. Utilization of interfacial engineering to improve physicochemical stability of beta-carotene emulsions: Multilayer coatings formed using protein and protein-polyphenol conjugates. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, Y.H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Matsumura, Y. Effects of Enzymatic Deamidation by Protein-Glutaminase on Structure and Functional Properties of Wheat Gluten. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6034–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Damodaran, S. Heat-induced conformational changes in whey protein isolate and its relation to foaming properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Sun, H.; Qi, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Functional and conformational changes to soy proteins accompanying anthocyanins: Focus on covalent and non-covalent interactions. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Zheng, M.; Tao, F.; Chen, W.; Huang, G.; Jiang, J. Effect of covalent modification by (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on physicochemical and functional properties of whey protein isolate. LWT 2016, 66, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshadrai, S.R.; Rawel, M.; Kroll, J. Influence of a sugar moiety (rhamnosylgluco-side) at 3-O position on the reactivity of quercetin with whey proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2003, 32, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E.; Altay, F. A review on protein–phenolic interactions and associated changes. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.H.; Benjakul, S.; Sae-leaw, T.; Balange, A.K.; Maqsood, S. Protein–polyphenol conjugates: Antioxidant property, functionalities and their applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, W.; Xiao, L. Functional properties of protein isolates from soybeans stored under various conditions. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, M.A.; van Vliet, T. Interfacial rheological properties of adsorbed protein layers and surfactants: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 91, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, E.; Bizot, H.; Cathala, B.; Capron, I. Chitin Nanocrystals for Pickering High Internal Phase Emulsions. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3766–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Wu, N.; Wu, F.; Yu, D.; Elfalleh, W. Effects of (+)-catechin on a rice bran protein oil-in-water emulsion: Droplet size, zeta-potential, emulsifying properties, and rheological behavior. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos Díaz, C.; Wandersleben, T.; Marqués, A.M.; Rubilar, M. Multilayer emulsions stabilized by vegetable proteins and polysaccharides. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 25, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; Zhu, G.; Huang, G.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. A novel pickering emulsion produced using soy protein-anthocyanin complex nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gunasekaran, S. Effects of protein concentration and oil-phase volume fraction on the stability and rheology of menhaden oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein isolate with xanthan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, S.; Kazuhiro, M.; Nakauma, M.; Funami, T.; Nambu, Y.; Matsumiya, K.; Matsumura, Y. Stabilization of whey protein isolate-based emulsions via complexation with xanthan gum under acidic conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Sulfhydryl Groups (μmol/g Protein) | Free Amino Groups (μmol/g Protein) | EGCG Content (μmol/g Protein) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HPI | 28.41 ± 0.06 a | 225.33 ± 0.7 a | — |
| HPI-1 mM EGCG | 17.48 ± 0.13 b | 202.02 ± 5.1 b | 23.08 ± 1.1 c |
| HPI-2 mM EGCG | 14.58 ± 0.14 c | 196.02 ± 1.9 c | 55.79 ± 1.8 c |
| HPI-3 mM EGCG | 12.53 ± 0.08 d | 173.39 ± 1.2 d | 87.38 ± 3.0 bc |
| HPI-4 mM EGCG | 9.14 ± 0.01 e | 84.39 ± 2.3 e | 100.15 ± 0.9 b |
| HPI-5 mM EGCG | 9.96 ± 0.03 e | 65.29 ± 2.8 f | 109.80 ± 3.3 a |
| Sample | α-Helix (%) | β-Sheet (%) | β-Turn (%) | Random Coil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPI | 1.79 | 82.79 | 0 | 15.50 |
| HPI-1mMEGCG | 1.87 | 71.16 | 0 | 27.30 |
| HPI-2mMEGCG | 3.33 | 66.86 | 2.33 | 27.76 |
| HPI-3mMEGCG | 3.90 | 66.67 | 3.40 | 25.53 |
| HPI-4mMEGCG | 5.41 | 69.60 | 0 | 24.43 |
| HPI-5mMEGCG | 1.94 | 70.67 | 1.43 | 25.67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, X.-H.; Yang, Y.; Bian, X.; Wang, B.; Ren, L.-K.; Liu, L.-L.; Yu, D.-H.; Yang, J.; Guo, J.-C.; Wang, L.; et al. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seed Protein–EGCG Conjugates: Covalent Bonding and Functional Research. Foods 2021, 10, 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071618
Pang X-H, Yang Y, Bian X, Wang B, Ren L-K, Liu L-L, Yu D-H, Yang J, Guo J-C, Wang L, et al. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seed Protein–EGCG Conjugates: Covalent Bonding and Functional Research. Foods. 2021; 10(7):1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071618
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Xin-Hui, Yang Yang, Xin Bian, Bing Wang, Li-Kun Ren, Lin-Lin Liu, De-Hui Yu, Jing Yang, Jing-Chun Guo, Lei Wang, and et al. 2021. "Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seed Protein–EGCG Conjugates: Covalent Bonding and Functional Research" Foods 10, no. 7: 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071618
APA StylePang, X.-H., Yang, Y., Bian, X., Wang, B., Ren, L.-K., Liu, L.-L., Yu, D.-H., Yang, J., Guo, J.-C., Wang, L., Zhang, X.-M., Yu, H.-S., & Zhang, N. (2021). Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seed Protein–EGCG Conjugates: Covalent Bonding and Functional Research. Foods, 10(7), 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071618