Barley Protein Properties, Extraction and Applications, with a Focus on Brewers’ Spent Grain Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
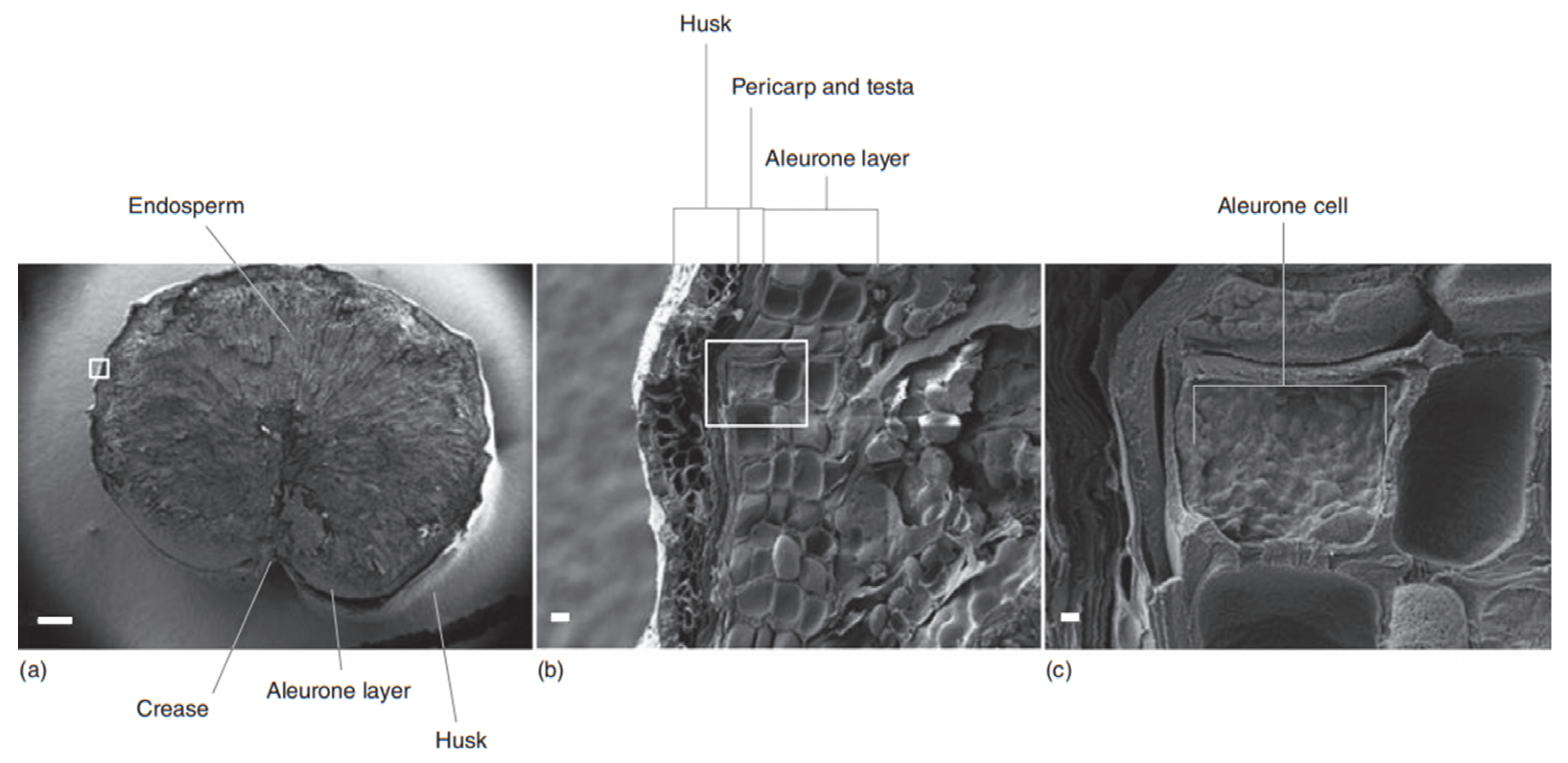
2. Barley Structure
3. Barley Proteins
3.1. Hordeins/Prolamins
3.2. Glutelin
3.3. Protein Z
3.4. Effect of Brewing Processes on Barley Proteins
3.4.1. Malting
3.4.2. Starch Degradation Inhibition
3.4.3. Mashing
3.4.4. Residual Beer Proteins
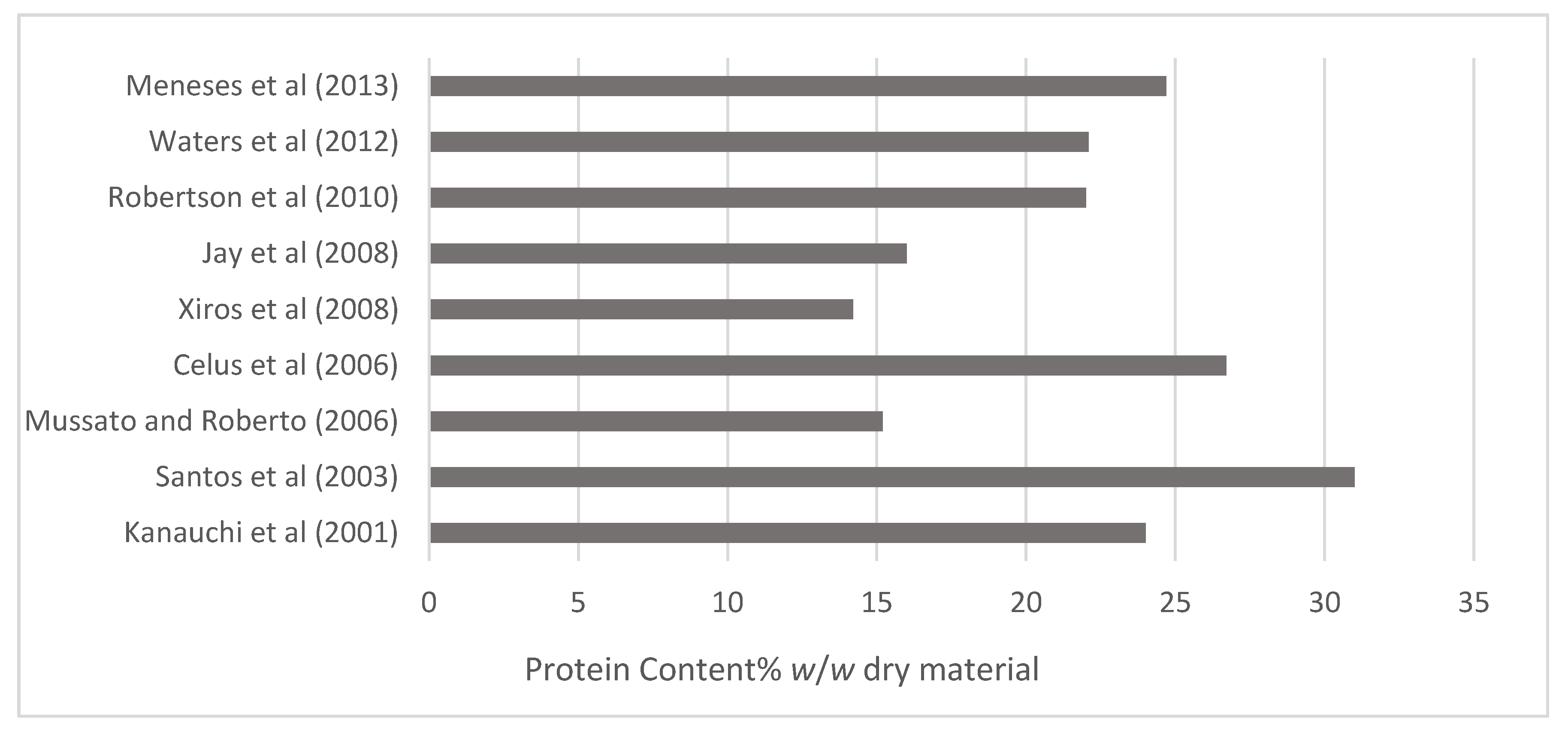
4. Overview of BSG
4.1. Adjuncts
4.2. Rice Protein
4.3. Maize Protein
5. Protein Extraction Methods
5.1. Innate Protein Extraction Methods
5.2. Extraction of Proteins from BSG
5.3. pH Shift Extraction Methods (Alkaline Extraction)
5.4. Filtration
5.5. Pre-Treatments
5.6. Enzymatic Treatment
5.7. Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction
5.8. Pulsed Electric Field
6. Applications
6.1. Animal Nutrition
6.2. Bio-Degradable Film
6.3. Food Applications
6.3.1. Biscuits
6.3.2. Bread
6.3.3. Snacks
6.3.4. Beverages
6.4. Barley Protein Hydrolysates
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mussatto, S.I. Brewer’ s Spent Grain: A Valuable Feedstock for Industrial Applications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martin, D.; Orive, M.; Iñarra, B.; Castelo, J.; Estévez, A.; Nazzaro, J.; Iloro, I.; Elortza, F.; Zufía, J. Brewers’ Spent Yeast and Grain Protein Hydrolysates as Second-Generation Feedstuff for Aquaculture Feed. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 5307–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, J.; Martin, D.S.; Perez-Vendrell, A.M.; Padrell, L.; Iñarra, B.; Orive, M.; Estévez, A. Apparent Digestibility Coefficients of Brewer’s by-Products Used in Feeds for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) and Gilthead Seabream (Sparus Aurata). Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccarthy, A.L.; Callaghan, Y.C.O.; Piggott, C.O.; Fitzgerald, R.J.; Brien, N.M.O. Postgraduate Symposium Brewers ’ Spent Grain; Bioactivity of Phenolic Component, Its Role in Animal Nutrition and Potential for Incorporation in Functional Foods: A Review. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2013, 72, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.L.; O’Callaghan, Y.C.; Neugart, S.; Piggott, C.O.; Connolly, A.; Jansen, M.A.K.; Krumbein, A.; Schreiner, M.; FitzGerald, R.J.; O’Brien, N.M. The Hydroxycinnamic Acid Content of Barley and Brewers’ Spent Grain (BSG) and the Potential to Incorporate Phenolic Extracts of BSG as Antioxidants into Fruit Beverages. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2567–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Dragone, G.; Roberto, I.C. Brewers ’ Spent Grain: Generation, Characteristics and Potential Applications. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, G.P. Chemical Composition in Barley Grains and Malt Quality; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 9783642012792. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, J.V.; Knox, R.B.; Pyliotis, N.A. The Structure and Composition of Aleurone Grains in the Barley Aleurone Layer. Planta 1971, 101, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, E.K.; Zannini, E. Cereal Grains for the Food and Beverage Industries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 9780857094131. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, K.M.; Steffen, E.J.; Arendt, E.K. Brewers’ Spent Grain: A Review with an Emphasis on Food and Health. J. Inst. Brew. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, R.C.; Bringhurst, T.A.; Brosnan, J.M.; Pearson, S. Potential of Hull-Less Barley Malt for Use in Malt and Grain Whisky Production. J. Inst. Brew. 2009, 115, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Gallaghar, E. Barley for Brewing: Characteristic Changes during Malting, Brewing and Applications of Its by-Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.; Rocha, M.A.M.; Coelho, E.; Pinho, O.; Saraiva, J.A.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Coimbra, M.A. Valuation of Brewer’s Spent Grain Using a Fully Recyclable Integrated Process for Extraction of Proteins and Arabinoxylans. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.C.; Zhang, G.P.; Zhou, M.X. Protein and Hordein Content in Barley Seeds as Affected by Nitrogen Level and Their Relationship to Beta-Amylase Activity. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, K.A.; Gayler, K.R.; Eagles, H.A.; Halloran, G.M. The Relationship between D Hordein and Malting Quality in Barley. J. Cereal Sci. 1996, 24, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagles, H.A.; Bedggood, A.G.; Panozzo, J.F.; Martin, P.J. Cultivar and Environmental Effects on Malting Quality in Barley. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, D.T.; Horsley, R.D.; Schwarz, P.B.; Goos, R.J. Nitrogen and Planting Date Effects on Low-Protein Spring Barley. Agron. J. 1993, 85, 1170–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Ding, S. Cultivar and Environmental Effects on (1 → 3, 1 → 4) β-D-Glucan and Protein Content in Malting Barley. J. Cereal Sci. 2001, 34, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Yu, G.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, G.; Jin, X. Grain Protein Content Variation and Its Association Analysis in Barley. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, R. Phenotypic, Physiological and Malt Quality Analyses of US Barley Varieties Subjected to Short Periods of Heat and Drought Stress. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 76, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R. Improving the Protein Content and Composition of Cereal Grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2007, 46, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, E.D. Hordein in Barley and Malt—A Review. J. Inst. Brew. 1981, 87, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Parmar, S.; Field, J.M. Two-dimensional Electrophoresis of Cereal Prolamins: Applications to Biochemical and Genetic Analyses. Electrophoresis 1988, 9, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Kreis, M.; Parmar, S.; Lew, E.J.L.; Kasarda, D.D. Identification of γ-Type Hordeins in Barley. FEBS Lett. 1985, 190, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tian, Z.; Chen, L. Effects of Deamidation on Aggregation and Emulsifying Properties of Barley Glutelin. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tian, Z.; Chen, L.; Temelli, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Functionality of Barley Proteins Extracted and Fractionated by Alkaline and Alcohol Methods. Cereal Chem. 2010, 87, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, C.; Thiele, F.; Arendt, E.K. Changes in the Protein Profile of Oats and Barley during Brewing and Fermentation. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2010, 68, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, F.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. Malt Derived Proteins: Effect of Protein Z on Beer Foam Stability. Food Biosci. 2018, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayashi, K.A.H.; To, K.A.I.; Ato, K.A.S.; Akeda, K.A.T. Novel Prediction Method of Beer Foam Stability Using Protein Z, Barley Dimeric r -Amylase Inhibitor-1 (BDAI-1) and Yeast Thioredoxin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 1, 8664–8671. [Google Scholar]
- Kapp, G.R.; Bamforth, C.W. The Foaming Properties of Proteins Isolated from Barley. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 1281, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boba, J. Monitoring of Malting Process by Characterization of Glycation of Barley Protein Z. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. The Effects of Malting and Mashing on Barley Protein Extractability. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 44, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.M.; Coverdale, S.M.; Cole, N.; Hamilton, S.E.; de Jersey, J. Characterisation and Assessment of the Role of Barley Malt Endoproteases During Malting and Mashing1. J. Inst. Brew. 2002, 108, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, P.T.; Baxter, E.D.; Wainwright, T. Inhibition By Hordein of Starch Degradation. J. Inst. Brew. 1979, 85, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zou, W.; Dhital, S.; Wu, P.; Gidley, M.J.; Fox, G.P.; Gilbert, R.G. The Adsorption of α-Amylase on Barley Proteins Affects the in Vitro Digestion of Starch in Barley Flour. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.L.; Marinac, L. The Effect of Mashing on Malt Endoproteolytic Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, E.; Gastl, M.; Becker, T. Protein Changes during Malting and Brewing with Focus on Haze and Foam Formation: A Review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2011, 232, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonen, J.H.E.; Graveland, A.; Muts, G.C. The molecular structure of gelprotein from barley, its behaviour in wort—Filtration and analysis. J. Inst. Brew. 1987, 93, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Piggott, C.O.; Fitzgerald, R.J. Characterisation of Protein-Rich Isolates and Antioxidative Phenolic Extracts from Pale and Black Brewers’ Spent Grain. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skerritt, J.H.; Janes, P.W. Disulphide-Bonded ‘Gel Protein’ Aggregates in Barley: Quality-Related Differences in Composition and Reductive Dissociation. J. Cereal Sci. 1992, 16, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curioni, A.; Pressi, G.; Furegon, L.; Peruffo, A.D.B.; Agrarie, B.; Gradenigo, V. Major Proteins of Beer and Their Precursors in Barley: Electrophoretic and Immunological Studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 2620–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanauchi, O.; Araki, Y.; Andoh, A.; Mitsuyama, K. Prebiotic Treatment of Experimental Colitis with Germinated Barley Foodstuff: A Comparison with Probiotic or Antibiotic Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 1, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Xiros, C.; Topakas, E.; Katapodis, P.; Christakopoulos, P. Hydrolysis and Fermentation of Brewer’ s Spent Grain by Neurospora Crassa. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5427–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, A.J.; Parker, M.L.; Faulks, R.; Husband, F.; Wilde, P.; Smith, A.C.; Faulds, C.B.; Waldron, K.W. A Systematic Micro-Dissection of Brewers ’ Spent Grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.A.; Anson, K.J.A.I.; Treimo, J.; Faulds, C.B.; Brocklehurst, T.F.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Waldron, K.W. LWT—Food Science and Technology Profiling Brewers ’ Spent Grain for Composition and Microbial Ecology at the Site of Production. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, C. Mussatto Chemical Characterization and Liberation of Pentose Sugars from Brewer’ s Spent Grain. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process. Environ. Clean Technol. 2006, 274, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.; Jimenez, J.; Bartolome, B.; Gomez-Cordoves, C.; Del Nozal, M. Variability of Brewer’ s Spent Grain within a Brewery. Food Chem. 2003, 80, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, D.M.; Jacob, F.; Titze, J.; Arendt, E.K.; Zannini, E. Fibre, Protein and Mineral Fortification of Wheat Bread through Milled and Fermented Brewer ’ s Spent Grain Enrichment. Eur. Food Res.Technol. 2012, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, N.G.T.; Martins, S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mussatto, S.I. Influence of Extraction Solvents on the Recovery of Antioxidant Phenolic Compounds from Brewer’ s Spent Grains. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 108, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, P.; Kordialik-bogacka, E. Trends in Food Science & Technology Alternatives to Malt in Brewing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorke, J.; Cook, D.; Ford, R. Brewing with Unmalted Cereal Adjuncts: Sensory and Analytical Impacts on Beer Quality. Beverages 2021, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, B.W.J.W. Amount of Starch or Sugar from the Agricultural Source. Hydrate Source38 Other than Malted Barley Which Contributes Case of Extraction and the Amount of Nitrogenous Materials Using Isothermal Conversion. J. Inst. Brew 1986, 92, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatthar, J.; Heinisch, J.; Senn, T. Unmalted Triticale Cultivars as Brewing Adjuncts: Effects of Enzyme Activities and Composition on Beer Wort Quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 654, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, R.C. A Comparison of Maize, Sorghum and Barley as Brewing Adjuncts. J. Inst. Brew. 2002, 108, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzenbaumer, B.; Kerpes, R.; Titze, J.; Jacob, F.; Arendt, E. Impact of Various Levels of Unmalted Oats (Avena sativa L.) on the Quality and Processability of Mashes. Worts, and Beers. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2012, 70, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, O.; Sileoni, V.; Marconi, O.; Sileoni, V.; Ceccaroni, D.; Perretti, G. The Use of Rice in Brewing. Adv. Int. Rice Res. 2017, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Robards, K.; Helliwell, S.; Blanchard, C. Review Composition and Functional Properties of Rice. Int. J. food Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 849–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.R.N.; Dlamini, B.C.; Kruger, J. 125 Th Anniversary Review: The Science of the Tropical Cereals Sorghum, Maize and Rice in Relation to Lager Beer Brewing. J. Inst. Brew. 2013, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Bechtel, D.B. Properties of Whole and Undigested Fraction of Protein Bodies of Milled Rice Preparations Had Higher Fat Content than Whole PB Preparation. Endosperm Protein of Rice Exists Mainly as That the Protein Fraction Rendered Undigested. Agric. Biol. Chem. 2015, 42, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S. Description, development, structure, and composition of the corn kernel. In Corn: Chemistry and Technology; American Association of Cereal Chemists: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2003; pp. 69–106. ISBN 1891127330. [Google Scholar]
- Giese, H.; Hejgaard, J. Synthesis of Salt-Soluble Proteins in Barley. Pulse-Labeling Study of Grain Filling in Liquid-Cultured Detached Spikes. Planta 1984, 161, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Ellis, J.R.S.; Pratt, H.M.; Miflin, B.J. A Comparison of Methods for the Extraction and Separation of Hordein Fractions from 29 Barley Varieties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1978, 29, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavonius, L.R.; Albers, E.; Undeland, I. PH-Shift Processing of Nannochloropsis Oculata Microalgal Biomass to Obtain a Protein-Enriched Food or Feed Ingredient. ALGAL 2015, 11, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Brewers’ Spent Grain Proteins and Technofunctional Properties of the Resulting Hydrolysates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8703–8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bals, B.; Balan, V.; Dale, B. Bioresource Technology Integrating Alkaline Extraction of Proteins with Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Cellulose from Wet Distiller’ s Grains and Solubles. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5876–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diptee, R.; Smith, J.P.; Alli, I.; Khanizadeh, S. Application of response surface methodology in protein extraction studies from brewer’s spent grain. J. Food Process. Preserv. 1989, 13, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templin, T.L.; Johnston, D.B.; Singh, V.; Tumbleson, M.E.; Belyea, R.L.; Rausch, K.D. Membrane Separation of Solids from Corn Processing Streams. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.S.; Yin, G.M.; He, Y.Z.; Hu, S.Q.; Li, B.; Li, L.; Liang, H.L.; Borthakur, D. Recovery of Protein from Brewer’s Spent Grain by Ultrafiltration. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 48, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Cermeno, M.; Crowley, D.; O’Callaghan, Y.; O’Brien, N.M.; Fitzgerald, R.J. Characterisation of the in Vitro Bioactive Properties of Alkaline and Enzyme Extracted Brewers’ Spent Grain Protein Hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Johansen, A.Z.; Mussatto, S.I. Evaluation of Different Pretreatment Strategies for Protein Extraction from Brewer’s Spent Grains. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, P.; Martins, D.; Buchert, J.; Faulds, C.B. Pre-Hydrolysis with Carbohydrases Facilitates the Release of Protein from Brewer’s Spent Grain. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommi, K.; Niemi, P.; Kemppainen, K.; Kruus, K. Impact of Thermochemical Pre-Treatment and Carbohydrate and Protein Hydrolyzing Enzyme Treatment on Fractionation of Protein and Lignin from Brewer’s Spent Grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treimo, J.; Aspmo, S.I.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Horn, S.J. Enzymatic Solubilization of Proteins in Brewer’s Spent Grain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5359–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.S.; Tian, Y.J.; He, Y.Z.; Li, L.; Hu, S.Q.; Li, B. Optimisation of Ultrasonic-Assisted Protein Extraction from Brewer’s Spent Grain. Czech J. Food Sci. 2010, 28, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, H.; Emilia, T.; Zhao, H. Modification of Structural and Functional Characteristics of Brewer’s Spent Grain Protein by Ultrasound Assisted Extraction. LWT 2020, 139, 110582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Keefe, S.F.O.; Neilson, A.P.; Feng, H.; Wang, Z. Original Article Recovery of Protein Hydrolysates from Brewer ’ s Spent Grain Using Enzyme and Ultrasonication. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Tiwari, B.K.; Hossain, M.B.; Brunton, N.P.; Rai, D.K. Recent Advances on Application of Ultrasound and Pulsed Electric Field Technologies in the Extraction of Bioactives from Agro-Industrial By-Products. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, R.N.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Roobab, U.; Munir, M.A.; Naderipour, A.; Qureshi, M.I.; Bekhit, A.; Liu, Z.W.; Aadil,, R.M. Pulsed Electric Field: A Potential Alternative towards a Sustainable Food Processing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachovska, T.K.; Ngadi, M.O.; Raghavan, G.S.V. Pulsed Electric Field Assisted Juice Extraction from Alfalfa. Can. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 48, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, B.; Tiwari, B.K.; Walsh, D.; Griffin, T.P.; Islam, N.; Lyng, J.G.; Brunton, N.P.; Rai, D.K.; Biosciences, F.; Food, T.; et al. Impact of Pulsed Electric Field Pre-Treatment on Nutritional and Polyphenolic Contents and Bioactivities of Light and Dark Brewer ’ s Spent Grains. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 54, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselló-soto, E.; Barba, F.J.; Parniakov, O.; Galanakis, C.M. High Voltage Electrical Discharges, Pulsed Electric Field, and Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Protein and Phenolic Compounds from Olive Kernel. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 8, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belibasakis, N.G.; Tsirgogianni, D. Effects of Wet Brewers Grains on Milk Yield, Milk Composition and Blood Components of Dairy Cows in Hot Weather. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996, 57, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getu, K. Supplementary Value of Ensiled Brewers Spent Grain Used as Replacement to Cotton Seed Cake in the Concentrate Diet of Lactating Crossbred Dairy Cows. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 3675–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, S.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Composition and Nutrient Value Proposition of Brewers Spent Grain. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukasafari, M.A.; Ambula, M.K.; Karege, C.; King, A.M. Effects of Substituting Sow and Weaner Meal with Brewers’ Spent Grains on the Performance of Growing Pigs in Rwanda. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 50, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakugh, I.D.I.; Tegbe, B. Replacement Value of Brewers ’ Dried Grain for Maize on Performance of Pigs. J. Sci. Food 1994, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.C.S.; Chngt, A.L.; Jesudason, R.B. Incorporation of Microbiologically Treated Spent Brewery Grains into Broiler Rations. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1991, 13, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolome, B.; Santos, M.; Jime, J.J.; Nozal, M.J.; Go, C. Pentoses and Hydroxycinnamic Acids in Brewer’ s Spent Grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 36, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, H.J.; Song, K. Bin Preparation and Characterization of Brewer’s Spent Grain Protein-Chitosan Composite Films. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 7549–7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Shin, Y.J.; Song, K. Bin Preparation of a Barley Bran Protein—Gelatin Composite Film Containing Grapefruit Seed Extract and Its Application in Salmon Packaging. J. Food Eng. 2012, 113, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojceska, V.; Ainsworth, P. The Effect of Different Enzymes on the Quality of High-Fibre Enriched Brewer’ s Spent Grain Breads. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ktenioudaki, A.; Crofton, E.; Scannell, A.G.M.; Hannon, J.A.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Gallagher, E. Sensory Properties and Aromatic Composition of Baked Snacks Containing Brewer’s Spent Grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.Y.; Bian, M.H.; Li, L.; Qiang, L.; Luo, H. Study of Protein Cookies with Brewer’s Grains. J. Sichuan Univ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 4, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ktenioudaki, A.; Shea, N.O.; Gallagher, E. Rheological Properties of Wheat Dough Supplemented with Functional By-Products of Food Processing: Brewer ’ s Spent Grain and Apple Pomace. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojceska, V.; Ainsworth, P.; Plunkett, A.; Ibanoǧlu, S. The Recycling of Brewer’s Processing by-Product into Ready-to-Eat Snacks Using Extrusion Technology. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojceska, V.; Ainsworth, P.; Plunkett, A.; Ibanoǧlu, Ş. The Effect of Extrusion Cooking Using Different Water Feed Rates on the Quality of Ready-to-Eat Snacks Made from Food by-Products. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, P.; Ibanoǧlu, Ş.; Plunkett, A.; Ibanoǧlu, E.; Stojceska, V. Effect of Brewers Spent Grain Addition and Screw Speed on the Selected Physical and Nutritional Properties of an Extruded Snack. J. Food Eng. 2007, 81, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Mandal, R.; Shojaei, M.; Singh, A.; Kowalczewski, P.L.; Ligaj, M.; Pawlicz, J.; Jarzebski, M. Novel Drying Methods for Sustainable Upcycling of Brewers’ Spent Grains as a Plant Protein Source. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, E.; Çelik, S.; İbanoğlu, E. Foaming Properties of Barley Protein Isolates and Hydrolysates. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, S.; Zhang, H.; Ahmed, M.S.; Wang, J. Ultrasonic Pretreatment Improved the Antioxidant Potential of Enzymatic Protein Hydrolysates from Highland Barley Brewer’s Spent Grain (BSG). J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanput, W.; Theerakulkait, C.; Nakai, S. Antioxidative Properties of Partially Purified Barley Hordein, Rice Bran Protein Fractions and Their Hydrolysates. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 49, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, E.; Bamdad, F.; Chen, L. Metal Solubility Enhancing Peptides Derived from Barley Protein. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Barley | Malt | BSG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total protein (% w/w) | 9.65 | 8.52 | 22.13 |
| (% of total) | |||
| Aspartic acid | 0.19 | 0.17 | 4.81 |
| Glutamic acid | 0.85 | 0.75 | 16.59 |
| Asparagine | 0.23 | 0.33 | 1.47 |
| Serine | 0.12 | 0.07 | 3.77 |
| Glutamine | ND | ND | 0.07 |
| Histidine | 1.59 | 1.9 | 26.27 |
| Glycine | 0.08 | 0.06 | 1.74 |
| Arginine | 0.21 | 0.23 | 4.51 |
| Alanine | 0.22 | 0.23 | 4.12 |
| γ- aminobutyric acid | 2.56 | 0.01 | 0.26 |
| Tyrosine | 0.14 | 0.14 | 2.57 |
| Valine | 2.56 | 0.24 | 4.61 |
| Threonine | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.71 |
| Methionine | 0.03 | ND | ND |
| Tryptophan | 0.01 | ND | 0.14 |
| Phenylalanine | 0.2 | 0.21 | 4.64 |
| Isoleucine | 0.17 | 0.17 | 3.31 |
| Leucine | 0.3 | 0.29 | 6.12 |
| Lysine | 2.52 | 3.69 | 14.31 |
| Patent Number | Title | Area of Usage | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
| WO/2018/033521 | A process for preparing a beverage or beverage component, beverage or beverage component prepared by such process and use of brewers’ spent grains for preparing such beverage or beverage component. | Food/beverage ingredient | Process of preparing a beverage or beverage component obtained by the fermentation of brewers’ spent grain and a process of preparing such beverage and other foodstuffs. |
| WO/2018/033522 | A process for preparing a beverage or beverage component from brewers’ spent grains. | Food/beverage ingredient | Process of preparing a beverage or beverage component obtained by the enzymatic saccharification and fermentation of brewers’ spent grain and a process of preparing such beverage, as well as other foodstuffs. |
| WO/2019/034567 | A process for microbial stabilization of brewers’ spent grain, microbiologically stabilized brewers’ spent grain and use thereof. | Food/beverage ingredient | Process for treating brewers’ spent grains (BSG) obtained from the brewing process such that the growth of microbes in said grains and subsequent production of microbial toxins are kept below specified levels. |
| WO/2019/158755 | A process for recovering proteinaceous and/or fibrous material from brewers’ spent grains and use thereof. | Food/beverage ingredient | Process of extracting or purifying proteinaceous material and/or fibraceous material from brewers’ spent grain, as well as the use of these materials. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaeger, A.; Zannini, E.; Sahin, A.W.; Arendt, E.K. Barley Protein Properties, Extraction and Applications, with a Focus on Brewers’ Spent Grain Protein. Foods 2021, 10, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061389
Jaeger A, Zannini E, Sahin AW, Arendt EK. Barley Protein Properties, Extraction and Applications, with a Focus on Brewers’ Spent Grain Protein. Foods. 2021; 10(6):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061389
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaeger, Alice, Emanuele Zannini, Aylin W. Sahin, and Elke K. Arendt. 2021. "Barley Protein Properties, Extraction and Applications, with a Focus on Brewers’ Spent Grain Protein" Foods 10, no. 6: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061389
APA StyleJaeger, A., Zannini, E., Sahin, A. W., & Arendt, E. K. (2021). Barley Protein Properties, Extraction and Applications, with a Focus on Brewers’ Spent Grain Protein. Foods, 10(6), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061389







