A UHPLC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Meat Substitution by Nine Legume Species in Emulsion-Type Sausages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Chemical Material
2.1.2. Sample Material
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Sample Preparations for Mass Spectrometry
2.2.2. HPLC-MS/MS-Identification of Peptides for the Nine Legume Species
Liquid Chromatography—High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Data Analysis for Peptide Identification
2.2.3. Synthesis of Peptides
2.2.4. HPLC-MS/MS-Detection of Marker Peptides for the Nine Legume Species in Emulsion-Type Sausages
Liquid Chromatography—Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
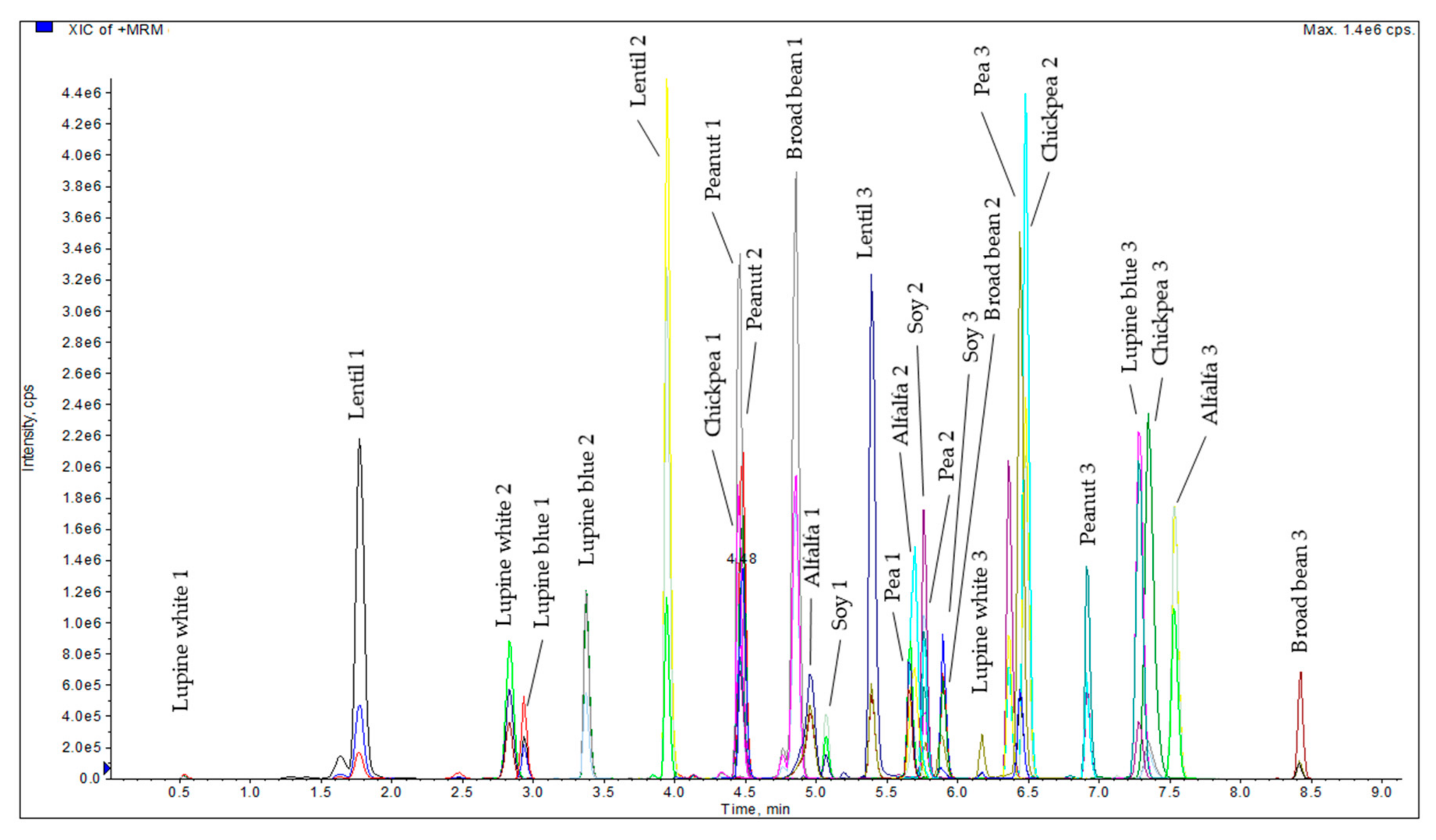
3.1. Determination of Suitable Marker Peptides for Alfalfa, Broad Bean, Chickpea, Lentil, Lupine Blue, Lupine White, Pea, Peanut, and Soy in Plant Material
3.2. Optimization of the Conditions of Protein Extraction and Tryptic Digestion in Meat Products with Added Legume Protein Flour
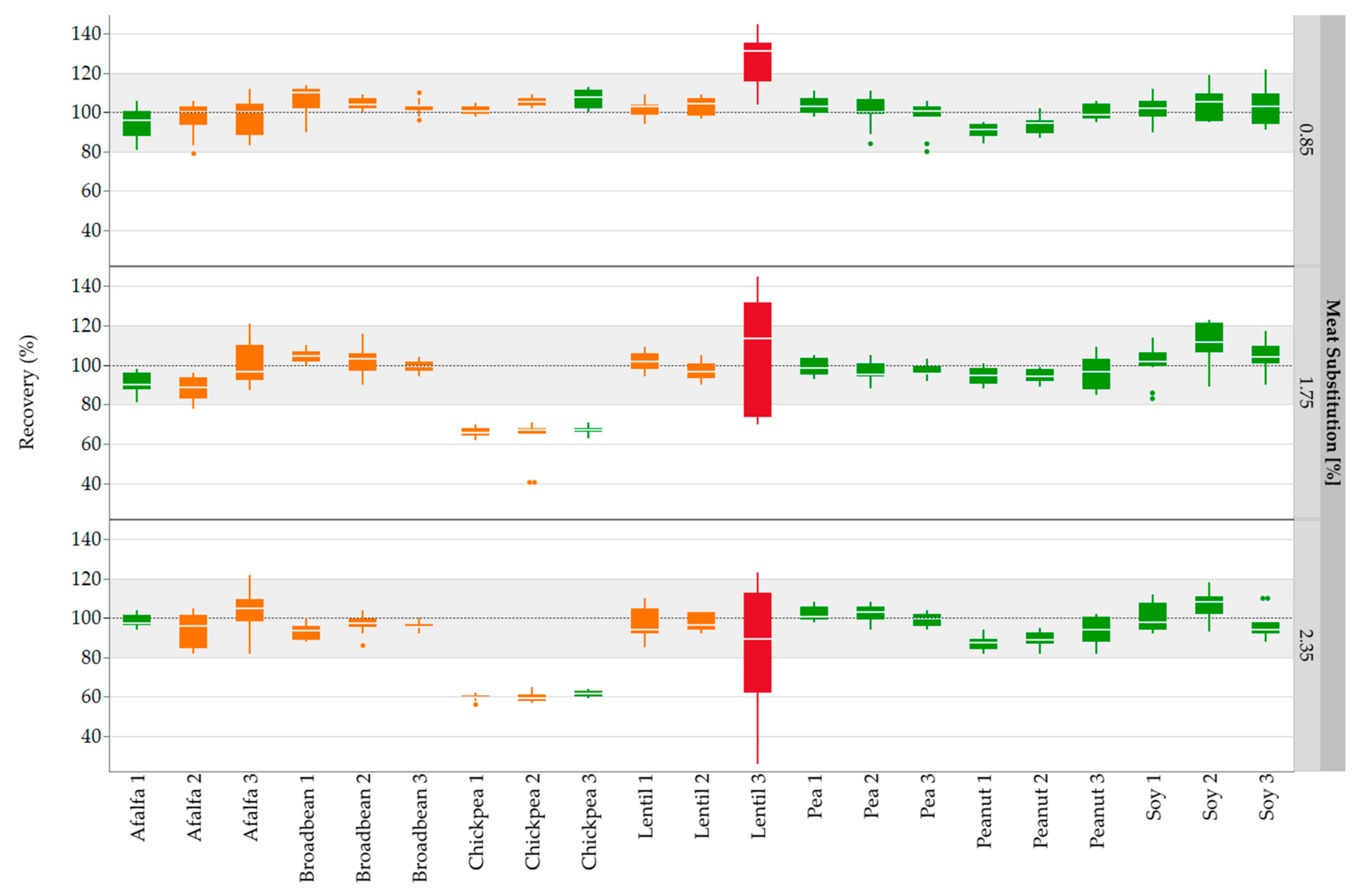
3.3. Detection of Legume Peptide Markers and Quantification of Meat Substitution by Legume Proteins in Emulsion-Type Sausages
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia Lopez, M.C.; Marina Alegre, M.L. Detection of adulterations: Addition of foreign proteins. In Safety Food Analysis of Food of Animal Origin; Nollet, L.M.L., Toldra, F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 155–187. [Google Scholar]
- (BMEL), Bundesministerium für Ernährung und Landwirtschaft. Leitsätze Für Fleisch Und Fleischerzeugnisse; BMEL: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and of the Council. Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the Provision of Food Information to Consumers, Amending Regulations (EC) No 1924/2006 and (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and Repealing Commission Directive 87/250/EEC, Council Directive 90/496/EEC, Commission Directive 1999/10/EC, Directive 2000/13/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Directives 2002/67/EC and 2008/5/EC and Commission Regulation (EC) No 608/2004 Text with EEA Relevance; European Union: Brussels, Belgium; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32011R1169 (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Belitz, H.-D.; Grosch, W.; Schieberle, P. Food Chemistry, 4th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ternes, W.; Täufel, A.; Tunger, L.; Zobel, M. (Eds.) Lexikon der Lebensmittel und der Lebensmittelchemie, 4th ed.; Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH: Stuttgart, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.C.; Liu, L.; Jiang, Y.R.; Faisal, S.; Wei, L.L.; Cao, C.J.; Yan, W.H.; Wang, Q. Converting peanut protein biomass waste into "double green" meat substitutes using a high-moisture extrusion process: A multiscale method to explore a process for forming a meat-like fibrous structure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10713–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahashon, S.N.; Kilonzo-Nthenge, A.K. Advances in soybean and soybean by-products in monogastric nutrition and health. In Soybean and Nutrition; El-Shemy, H., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; pp. 125–156. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Mielmann, A. The utilisation of lucerne (Medicago sativa): A review. Br. Food J. 2013, 115, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuders, F.K.G.; Dekkers, B.L.; Bodnar, I.; Erni, P.; Boom, R.M.; van der Goot, A.J. Comparing structuring potential of pea and soy protein with gluten for meat analogue preparation. J. Food Eng. 2019, 261, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, M.; Topfl, S.; Berger, R.G.; Hertel, C. Physico-chemical and nutritional properties of meat analogues based on Spirulina/lupin protein mixtures. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, A.; Sahar, A.; Sameen, A.; Saleem, A.; Tahir, A.T. Use of pea and rice protein isolates as source of meat extenders in the development of chicken nuggets. J. Food Process Preserv. 2018, 42, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulu, H. Effect of wheat flour, whey protein concentrate and soya protein isolate on oxidative processes and textural properties of cooked meatballs. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chempaka, M.Y.S.; Babji, A.S. Effect of non-meat proteins, soy protein isolate and sodium caseinate, on the textural properties of chicken bologna. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 1996, 47, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baune, M.C.; Baron, M.; Profeta, A.; Smetana, S.; Weiss, J.; Heinz, V.; Terjung, N. Impact of textured plant proteins on the technological and sensory properties of hybrid chicken nugget batters. Fleischwirtschaft 2020, 100, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Commission directive 2007/68/EC. In Official Journal of the European Union; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2007; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Senyuva, H.Z.; Jones, I.B.; Sykes, M.; Baumgartner, S. A critical review of the specifications and performance of antibody and DNA-based methods for detection and quantification of allergens in foods. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. 2019, 36, 507–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena-Torralba, A.; Pallas-Tamarit, Y.; Morais, S.; Maquieira, A. Recent advances and challenges in food-borne allergen detection. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 132, 116050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaci, L.; De Angelis, E.; Montemurro, N.; Pilolli, R. Comprehensive overview and recent advances in proteomics MS based methods for food allergens analysis. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 106, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilolli, R.; Nitride, C.; Gillard, N.; Huet, A.C.; van Poucke, C.; de Loose, M.; Tranquet, O.; Larre, C.; Adel-Patient, K.; Bernard, H.; et al. Critical review on proteotypic peptide marker tracing for six allergenic ingredients in incurred foods by mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planque, M.; Arnould, T.; Dieu, M.; Delahaut, P.; Renard, P.; Gillard, N. Liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry for detecting ten allergens in complex and incurred foodstuffs. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1530, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montowska, M.; Fornal, E. Detection of peptide markers of soy, milk and egg white allergenic proteins in poultry products by LC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montowska, M.; Fornal, E.; Piatek, M.; Krzywdzinska-Bartkowiak, M. Mass spectrometry detection of protein allergenic additives in emulsion-type pork sausages. Food Control 2019, 104, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montowska, M.; Fornal, E. Absolute quantification of targeted meat and allergenic protein additive peptide markers in meat products. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, B.; Munch, S.; Schwagele, F.; Neususs, C.; Jira, W. A sensitive HPLC-MS/MS screening method for the simultaneous detection of lupine, pea, and soy proteins in meat products. Food Control 2017, 71, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Office of Consumer Protection and Food Saftey. L 23.01-2 (12/2017) in: Amtliche Sammlung von Untersuchungsmethoden (ASU). Available online: https://www.methodensammlung-bvl.de/de (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- BMEL. Lebensmittel-und Futtermittelgesetzbuch in der Fassung der Bekanntmachung vom 3. Juni 2013 (BGBl. I S.1426), das zuletzt durch Artikel 97 der Verordnung vom 19. Juni 2020 (BGBl. I S. 1328) geändert worden ist"; BMEL: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jira, W.; Munch, S. A sensitive HPLC-MS/MS screening method for the simultaneous detection of barley, maize, oats, rice, rye and wheat proteins in meat products. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfner, L.; Kalkhof, S.; Jira, W. Authentication of nine poultry species using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 2021, 122, 107803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xin, L.; Shan, B.Z.; Chen, W.W.; Xie, M.J.; Yuen, D.; Zhang, W.M.; Zhang, Z.F.; Lajoie, G.A.; Ma, B. PEAKS DB: De novo sequencing assisted database search for sensitive and accurate peptide identification. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2012, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huschek, G.; Bonick, J.; Lowenstein, Y.; Sievers, S.; Rawel, H. Quantification of allergenic plant traces in baked products by targeted proteomics using isotope marked peptides. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, C.C.; Parker, C.H.; Jackson, L.S. A targeted LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous detection and quantitation of egg, milk, and peanut allergens in sugar cookies. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.Q.; Chen, N.N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, C.M.; Zhan, L.N.; Qu, L.; Cao, C.; Han, L.; Deng, X.J.; Ding, T.; et al. A rapid solid-phase extraction combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for simultaneous screening of multiple allergens in chocolates. Food Control 2018, 84, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heick, J.; Fischer, M.; Popping, B. First screening method for the simultaneous detection of seven allergens by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, T.; Clifford, R.; Oppermann, U. Simultaneous detection of 13 allergens in thermally processed food using targeted LC-MS/MS approach. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilolli, R.; De Angelis, E.; Monaci, L. In house validation of a high resolution mass spectrometry Orbitrap-based method for multiple allergen detection in a processed model food. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5653–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, R.; Brockmeyer, J. MRM3-based LC-MS multi-method for the detection and quantification of nut allergens. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7845–7855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planque, M.; Arnould, T.; Dieu, M.; Delahaut, P.; Renard, P.; Gillard, N. Advances in ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry for sensitive detection of several food allergens in complex and processed foodstuffs. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1464, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planque, M.; Arnould, T.; Delahaut, P.; Renard, P.; Dieu, M.; Gillard, N. Development of a strategy for the quantification of food allergens in several food products by mass spectrometry in a routine laboratory. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.E.; Baumgartner, S.; Aldick, T.; Bessant, C.; Giosafatto, V.; Heick, J.; Mamone, G.; O’Connor, G.; Poms, R.; Popping, B.; et al. Current perspectives and recommendations for the development of mass spectrometry methods for the determination of allergens in foods. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Bargen, C.; Dojahn, J.; Waidelich, D.; Humpf, H.U.; Brockmeyer, J. New sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of horse and pork in halal beef. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11986–11994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandjo, L.P.; Zingue, S.; Nascimento, M.; de Moraes, M.H.; Vicente, G.; Amoah, S.K.S.; Dalmarco, E.M.; Frode, T.S.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B.; Steindel, M. Cytotoxicity, antiprotozoal, and anti-inflammatory activities of eight curry powders and comparison of their UPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS chemical profiles. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2987–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desimoni, E.; Brunetti, B. About estimating the limit of detection by the signal to noise approach. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency, F.S. Adulteration of Food—Thresholds for Action and for Reporting. In Proceedings of the Food Standards Agency Board Meeting, London, UK, 18 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Thienes, C.P.; Masiri, J.; Benoit, L.A.; Barrios-Lopez, B.; Samuel, S.A.; Krebs, R.A.; Cox, D.P.; Dobritsa, A.P.; Nadala, C.; Samadpour, M. Quantitative detection of beef contamination in cooked meat products by ELISA. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Zhang, J.S.; Lai, S.Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.R.; Mo, W.M.; Ren, Y.P. Quantitative analysis of cow whole milk and whey powder adulteration percentage in goat and sheep milk products by isotopic dilution-ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyke, M.; Becker, R.; Brockmeyer, J.; Jira, W.; Popping, B.; Uhlig, S.; Wittke, S. German Government Official Methods Board Points the Way Forward: Launch of a New Working Group for Mass Spectrometry for Protein Analysis to Detect Food Fraud and Food Allergens. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, H.V.; Arias, A.; Simons, E.; Gerdts, J.; Povolo, B.; Rothney, J.; Protudjer, J.L.P. Adult and Pediatric Food Allergy to Chickpea, Pea, Lentil, and Lupine: A Scoping Review. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Processing Series 1 | Processing Series 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | Test Sausages | C2 | Standard Sausages | Unknown Sausages | |||||||||||||||
| 0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | 0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | |
| Formulations (%) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pork | 54 | 53.98 | 53.9 | 53.8 | 51.6 | 50 | 44.15 | 44.15 | 44.15 | 44.15 | 44.15 | 44.15 | 44.15 | 44.15 | 44.15 | 45.05 | 44.63 | 44.50 | 44.35 |
| Back fat | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| Curing salt | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Phosphate | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Ice | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 24 | 27.30 | 26.89 | 26.75 | 26.36 | 26.31 | 27.00 | 26.45 | 26.99 | 27.31 | 26.50 | 26.24 | 26.64 | 26.96 |
| LFM | - | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.4 | - | 2.55 | 2.96 | 3.10 | 3.49 | 3.54 | 2.85 | 3.40 | 2.86 | 2.54 | 2.45 | 3.14 | 2.86 | 2.69 |
| Legume Flour (%) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Alfalfa | - | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.03 | 0.27 | - | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.26 | 0.34 | 0.42 | 0.50 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 0.62 | - | 0.22 | 0.46 |
| Broad bean | - | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.04 | 0.40 | - | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.85 | 0.96 | 0.04 | 0.67 | 0.91 | - | 0.33 |
| Chickpea | - | 0.005 | 0.018 | 0.04 | 0.46 | - | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.13 | 0.75 | 0.89 | 0.21 | 1.17 | 0.05 | 0.19 | - | 0.40 | 0.82 | 1.10 |
| Lentil | - | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.04 | 0.40 | - | 0.37 | 0.47 | 0.16 | 0.69 | 0.80 | 0.91 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.64 | 0.86 | - |
| Lupine blue | - | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.02 | 0.23 | - | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.39 | 0.52 | - |
| Lupine white | - | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.02 | 0.25 | - | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.21 | 0.62 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.32 | - | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.59 |
| Pea | - | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.13 | - | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.29 | - | 0.10 | 0.21 |
| Peanut | - | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.02 | 0.21 | - | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.37 | 0.50 | - | 0.18 |
| Soy | - | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.12 | - | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.25 | - | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.27 |
| Meat Substitution (%) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Alfalfa | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 1.30 | 1.60 | 1.90 | 2.20 | 2.50 | 2.35 | - | 0.85 | 1.75 |
| Broad bean | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.40 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 1.30 | 1.60 | 1.90 | 2.20 | 2.50 | 0.10 | 1.75 | 2.35 | - | 0.85 |
| Chickpea | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.70 | 1.00 | 1.30 | 1.60 | 1.90 | 2.20 | 2.50 | 0.10 | 0.40 | - | 0.85 | 1.75 | 2.35 |
| Lentil | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | 1.30 | 1.60 | 1.90 | 2.20 | 2.50 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 1.75 | 2.35 | - |
| Lupine blue | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.30 | 1.60 | 1.90 | 2.20 | 2.50 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 1.75 | 2.35 | - |
| Lupine white | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.60 | 1.90 | 2.20 | 2.50 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 1.30 | - | 0.85 | 1.75 | 2.35 |
| Pea | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.90 | 2.20 | 2.50 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 1.30 | 1.60 | 2.35 | - | 0.85 | 1.75 |
| Peanut | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.20 | 2.50 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 1.30 | 1.60 | 1.90 | 1.75 | 2.35 | - | 0.85 |
| Soy | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.50 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 1.30 | 1.60 | 1.90 | 2.20 | - | 0.85 | 1.75 | 2.35 |
| Total | - | - | - | - | - | - | 11.70 | 11.70 | 11.70 | 11.70 | 11.70 | 11.70 | 11.70 | 11.70 | 11.70 | 9.90 | 10.75 | 11.00 | 11.30 |
| Marker Peptide | tR [Min] | DP [V] | m/z (Charge State) | Product Ions | CE [V] | CXP [V] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfalfa 1 | VEGGLSIMSPPER | 4.91 ± 0.02 | 71 | 686.4 (+2) | 498.3 (y4), 585.3 (y5), 716.3 (y6) | 27/29/31 | 26/26/24 |
| Alfalfa 2 | FNLEAGDIMR | 5.75 ± 0.02 | 56 | 583.3 (+2) | 662.3 (y6), 419.2 (y3), 591.3 (y5) | 29/39/27 | 32/24/30 |
| Alfalfa 3 | ISDVNSLTLPILR | 7.60 ± 0.01 | 60 | 720.9 (+2) | 498.3 (y4), 712.5 (y6), 316.2 (b3) | 35/35/35 | 36/36/36 |
| Broad bean 1 | EDVLSLAPK | 4.77 ± 0.02 | 36 | 486.3 (+2) | 515.3 (y5), 315.2 (y3), 628.4 (y6) | 23/21/25 | 24/16/32 |
| Broad bean 2 | FNLEEGDLIR | 5.90 ± 0.01 | 16 | 603.3 (+2) | 702.4 (y6), 401.3 (y3), 573.3 (y5) | 31/43/31 | 28/22/26 |
| Broad bean 3 | LSPGDVLVIPAGYPVAIK | 8.47 ± 0.01 | 16 | 603.7 (+3) | 458.3 (y92+), 527.4 (y5), 514.8 (y102+) | 21/35/15 | 24/36/36 |
| Chickpea 1 | GGLSFISPSEK | 4.44 ± 0.02 | 11 | 561.3 (+2) | 547.3 (y5), 460.2 (y4), 660.4 (y6) | 27/37/27 | 28/30/30 |
| Chickpea 2 | IVDLAIPINTPAK | 6.53 ± 0.01 | 26 | 682.9 (+2) | 740.4 (y7), 328.2 (b3), 625.4 (b6) | 29/35/25 | 42/22/30 |
| Chickpea 3 | SSNPFTFLVPPR | 7.46 ± 0.01 | 91 | 681.8 (+2) | 369.2 (y3), 468.3 (y4), 581.4 (y5) | 25/33/33 | 24/22/32 |
| Lentil 1 | VILEDQEQEPQHR | 1.87 ± 0.03 | 31 | 540.9 (+3) | 704.8 (y112+), 648.3 (y102+), 470.2 (y113+) | 23/21/23 | 40/42/24 |
| Lentil 2 | FFEVTPEK | 3.93 ± 0.01 | 66 | 498.8 (+2) | 702.4 (y6), 373.2 (y3), 573.3 (y5) | 21/35/25 | 34/28/32 |
| Lentil 3 | VVDFVISLNRPGK | 5.41 ± 0.03 | 101 | 481.9 (+3) | 623.4 (y112+), 301.2 (y3), 884.5 (y8) | 19/37/27 | 44/20/40 |
| Lupine blue 1 | QQEQQLEGELEK [25] | 2.48 ± 0.02 | 36 | 729.9 (+2) | 389.2 (y3), 386.2 (b3), 575.3 (y5) | 37/35/33 | 29/18/28 |
| Lupine blue 2 | NTLEATFNTR [25,31] | 3.35 ± 0.01 | 31 | 583.8 (+2) | 838.4 (y7), 709.4 (y6), 458.2 (b4) | 31/31/21 | 50/40/26 |
| Lupine blue 3 | ISSVNSLTLPILR [25] | 7.11 ± 0.01 | 45 | 706.9 (+2) | 498.3 (y4), 712.5 (y6), 359.2 (a4) | 33/31/35 | 22/30/24 |
| Lupine white 1 | NPYHFSSQR [31] | 0.49 ± 0.06 | 21 | 379.2 (+3) | 341.2 (y83+), 373.7 (b62+), 390.2 (y3) | 17/13/23 | 20/24/20 |
| Lupine white 2 | DKPSQSGPFNLR | 2.83 ± 0.02 | 46 | 449.2 (+3) | 323.7 (y52+), 646.4 (y5), 549.3 (y4) | 19/21/27 | 16/30/40 |
| Lupine white 3 | AVNELTFPGSAEDIER | 5.90 ± 0.01 | 46 | 583.3 (+3) | 487.2 (y92+), 560.8 (y102+), 417.2 (y3) | 21/15/41 | 22/40/22 |
| Pea 1 | ELTFPGSVQEINR [25] | 5.68 ± 0.02 | 41 | 745.4 (+2) | 999.5 (y9), 500.3 (y92+), 491.3 (b4) | 37/37/29 | 48/28/26 |
| Pea 2 | LSSGDVFVIPAGHPVAVK [25] | 5.72 ± 0.02 | 120 | 598.3 (+3) | 438.3 (y92+), 513.3 (y5), 363.2 (y113+) | 27/37/43 | 34/24/24 |
| Pea 3 | LTPGDVFVIPAGHPVAVR [25] | 6.57 ± 0.01 | 36 | 615.7 (+3) | 544.3 (y163+), 541.3 (y5), 452.3 (y92+) | 21/35/33 | 28/38/14 |
| Peanut 1 | GTGNLELVAVR [32,33,34,35,36] | 4.45 ± 0.02 | 96 | 564.8 (+2) | 345.2 (y3), 557.4 (y5), 686.4 (y6) | 29/33/31 | 24/28/38 |
| Peanut 2 | FNLAGNHEQEFLR [32,33,37,38] | 4.45 ± 0.02 | 61 | 525.6 (+3) | 262.1 (b2), 657.3 (y112+), 600.8 (y102+) | 23/23/23 | 14/40/16 |
| Peanut 3 | WLGLSAEYGNLYR [32,34] | 7.02 ± 0.01 | 16 | 771.4 (+2) | 272.2 (a2), 300.2 (b2), 357.2 (b3) | 39/35/39 | 14/18/18 |
| Soy 1 | SQSDNFEYVSFK [23,34,36] | 5.02 ± 0.04 | 31 | 725.8 (+2) | 381.2 (y3), 643.3 (y5), 1235.6 (y10) | 35/35/29 | 26/46/52 |
| Soy 2 | EAFGVNMQIVR [25,34,38,39] | 5.77 ± 0.02 | 61 | 632.3 (+2) | 760.4(y6), 387.3 (y3), 532.3 (y92+) | 29/29/27 | 38/22/34 |
| Soy 3 | FYLAGNQEQEFLK [22,23,25,36] | 6.00 ± 0.01 | 36 | 793.9 (+2) | 311.1 (b2), 424.2 (b3), 638.8 (y112+) | 41/35/33 | 18/26/38 |
| Extraction Buffer | Time (Min) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | TE | TP | TA | |||||||||||
| 100 | 50/50 | 50/50 | 60/40 | 70/30 | 50/50 | 60/40 | 70/30 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 150 | 180 | |
| Alfalfa 1 | 79 | 88 | 72 | 54 | 58 | 65 | 92 | 100 | 69 | 86 | 97 | 42 | 100 | 44 |
| Alfalfa 2 | 14 | 35 | 41 | 52 | 45 | 67 | 100 | 75 | 93 | 89 | 66 | 92 | 91 | 100 |
| Alfalfa 3 | 3 | 57 | 59 | 58 | 41 | 100 | 98 | 42 | 100 | 90 | 39 | 97 | 97 | 84 |
| Broad bean 1 | 30 | 90 | 72 | 76 | 49 | 72 | 100 | 88 | 100 | 96 | 83 | 94 | 96 | 98 |
| Broad bean 2 | 26 | 76 | 63 | 72 | 51 | 74 | 100 | 96 | 100 | 96 | 84 | 87 | 85 | 92 |
| Broad bean 3 | 94 | 76 | 48 | 55 | 56 | 90 | 100 | 92 | 93 | 96 | 97 | 93 | 96 | 100 |
| Chickpea 1 | 47 | 36 | 62 | 71 | 65 | 87 | 98 | 100 | 91 | 88 | 88 | 100 | 95 | 92 |
| Chickpea 2 | 16 | 22 | 72 | 72 | 38 | 87 | 100 | 82 | 100 | 86 | 88 | 89 | 97 | 81 |
| Chickpea 3 | 27 | 23 | 60 | 47 | 27 | 100 | 100 | 77 | 97 | 88 | 88 | 89 | 100 | 95 |
| Lentil 1 | 12 | 20 | 76 | 74 | 39 | 87 | 100 | 79 | 79 | 88 | 90 | 94 | 100 | 96 |
| Lentil 2 | 10 | 18 | 63 | 65 | 36 | 87 | 100 | 80 | 83 | 90 | 89 | 96 | 100 | 98 |
| Lentil 3 | 7 | 14 | 36 | 67 | 36 | 83 | 100 | 78 | 92 | 89 | 92 | 100 | 100 | 98 |
| Lupine blue 1 | 38 | 42 | 74 | 84 | 77 | 100 | 98 | 98 | 100 | 90 | 75 | 83 | 87 | 86 |
| Lupine blue 2 | 19 | 17 | 45 | 54 | 40 | 92 | 100 | 89 | 100 | 100 | 70 | 83 | 81 | 80 |
| Lupine blue 3 | 15 | 6 | 37 | 48 | 36 | 82 | 100 | 90 | 100 | 88 | 54 | 96 | 96 | 100 |
| Lupine white 1 | 38 | 42 | 74 | 84 | 77 | 100 | 98 | 98 | 99 | 95 | 95 | 100 | 94 | 89 |
| Lupine white 2 | 19 | 17 | 45 | 54 | 40 | 92 | 100 | 89 | 89 | 95 | 97 | 98 | 100 | 95 |
| Lupine white 3 | 15 | 11 | 37 | 48 | 35 | 82 | 100 | 90 | 80 | 88 | 90 | 95 | 100 | 96 |
| Pea 1 | 21 | 35 | 85 | 84 | 72 | 83 | 100 | 85 | 89 | 100 | 100 | 93 | 80 | 95 |
| Pea 2 | 28 | 24 | 66 | 73 | 68 | 85 | 100 | 89 | 94 | 100 | 100 | 90 | 94 | 91 |
| Pea 3 | 22 | 21 | 54 | 62 | 58 | 86 | 100 | 85 | 99 | 100 | 94 | 93 | 95 | 95 |
| Peanut 1 | 69 | 43 | 71 | 70 | 61 | 98 | 100 | 87 | 100 | 86 | 81 | 71 | 61 | 56 |
| Peanut 2 | 70 | 24 | 57 | 49 | 39 | 100 | 91 | 60 | 100 | 90 | 94 | 82 | 91 | 92 |
| Peanut 3 | 73 | 59 | 81 | 71 | 72 | 100 | 82 | 59 | 100 | 83 | 85 | 72 | 79 | 80 |
| Soy 1 | 29 | 29 | 67 | 67 | 58 | 96 | 100 | 93 | 100 | 80 | 77 | 77 | 73 | 68 |
| Soy 2 | 6 | 16 | 52 | 43 | 27 | 100 | 98 | 68 | 100 | 95 | 87 | 94 | 88 | 77 |
| Soy 3 | 28 | 33 | 77 | 60 | 53 | 95 | 100 | 86 | 100 | 92 | 89 | 92 | 86 | 75 |
| Mean | 31 | 35 | 61 | 64 | 50 | 88 | 98 | 83 | 95 | 91 | 85 | 89 | 91 | 87 |
| Maxima (N) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 19 | 2 | 13 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spörl, J.; Speer, K.; Jira, W. A UHPLC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Meat Substitution by Nine Legume Species in Emulsion-Type Sausages. Foods 2021, 10, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10050947
Spörl J, Speer K, Jira W. A UHPLC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Meat Substitution by Nine Legume Species in Emulsion-Type Sausages. Foods. 2021; 10(5):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10050947
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpörl, Johannes, Karl Speer, and Wolfgang Jira. 2021. "A UHPLC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Meat Substitution by Nine Legume Species in Emulsion-Type Sausages" Foods 10, no. 5: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10050947
APA StyleSpörl, J., Speer, K., & Jira, W. (2021). A UHPLC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Meat Substitution by Nine Legume Species in Emulsion-Type Sausages. Foods, 10(5), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10050947





