Utilization of Nanotechnology to Improve the Handling, Storage and Biocompatibility of Bioactive Lipids in Food Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bioactive Lipids
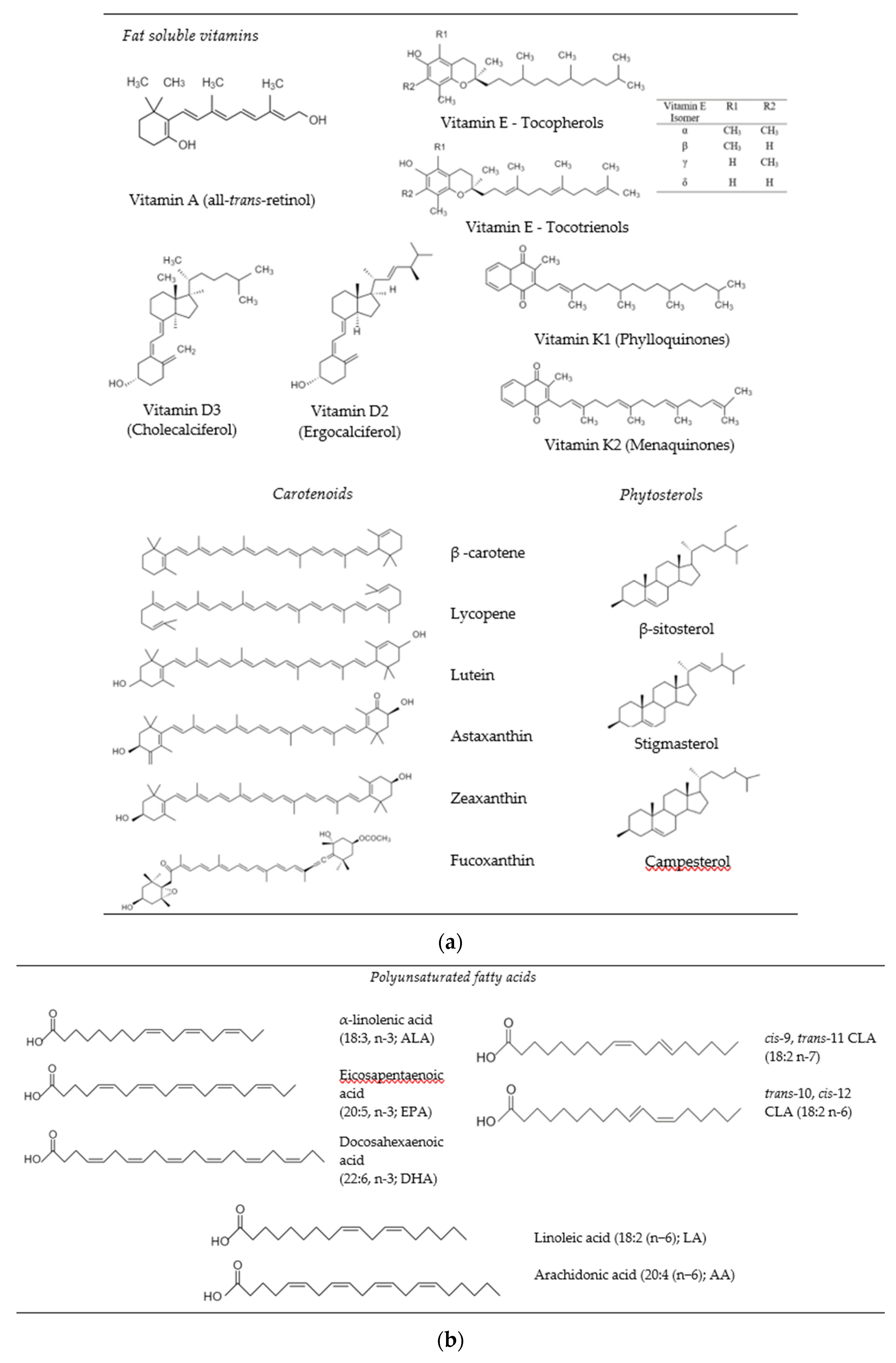
2.1. Fat Soluble Vitamins
2.2. Carotenoids
2.3. Phytosterols
2.4. Essential Fatty Acids (Omega-3s and CLA)
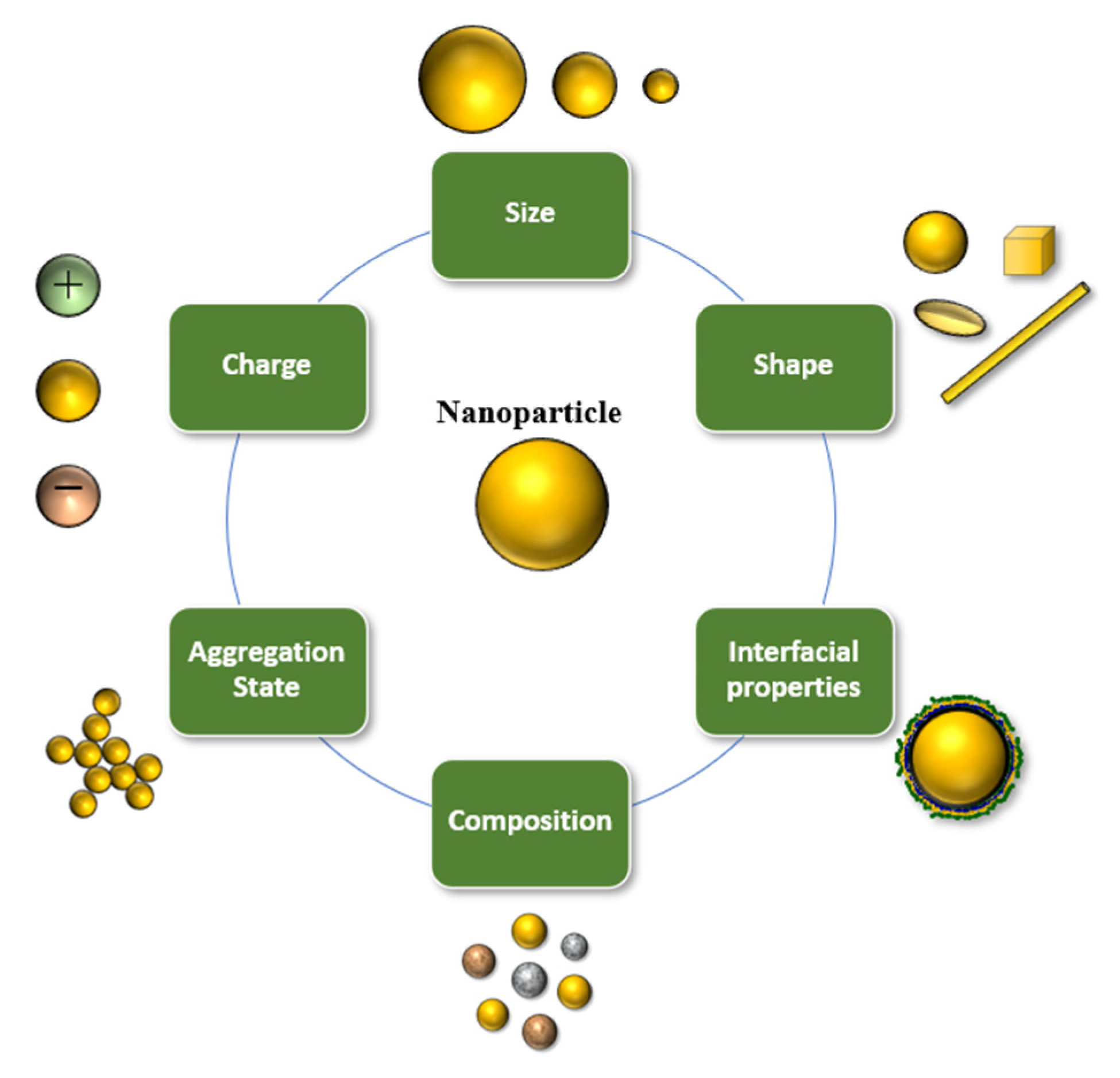
3. Nanoscale Delivery Systems for Encapsulation of Bioactive Lipids
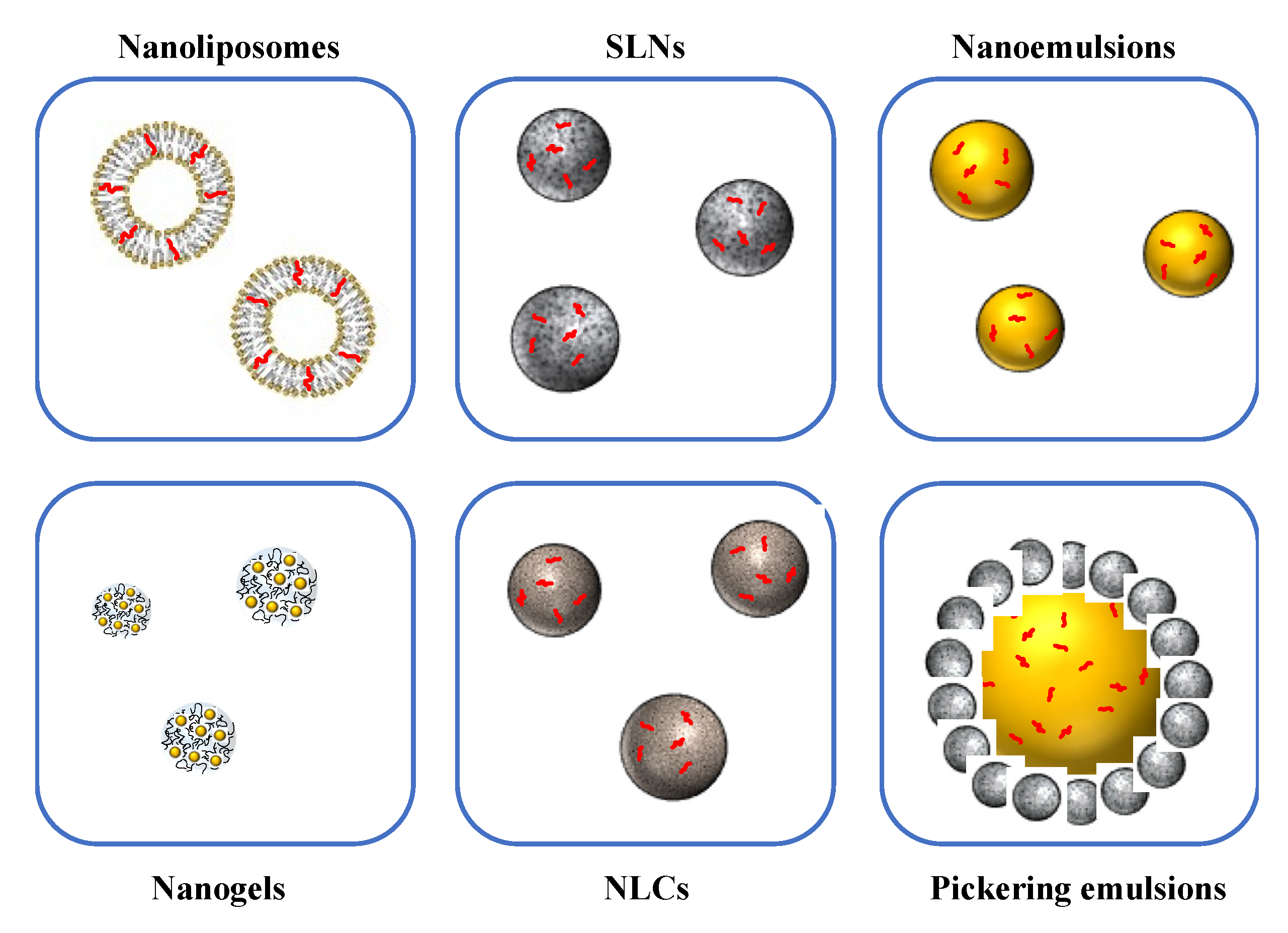
3.1. Nanoemulsions
3.2. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers
3.3. Nanoliposomes
3.4. Biopolymer Nanogels and Nanofibers
3.5. Nanoparticle-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions
3.6. Nanoparticle Formation Methods
4. Improved Food Matrix Compatibility and Handling
5. Enhanced Stability
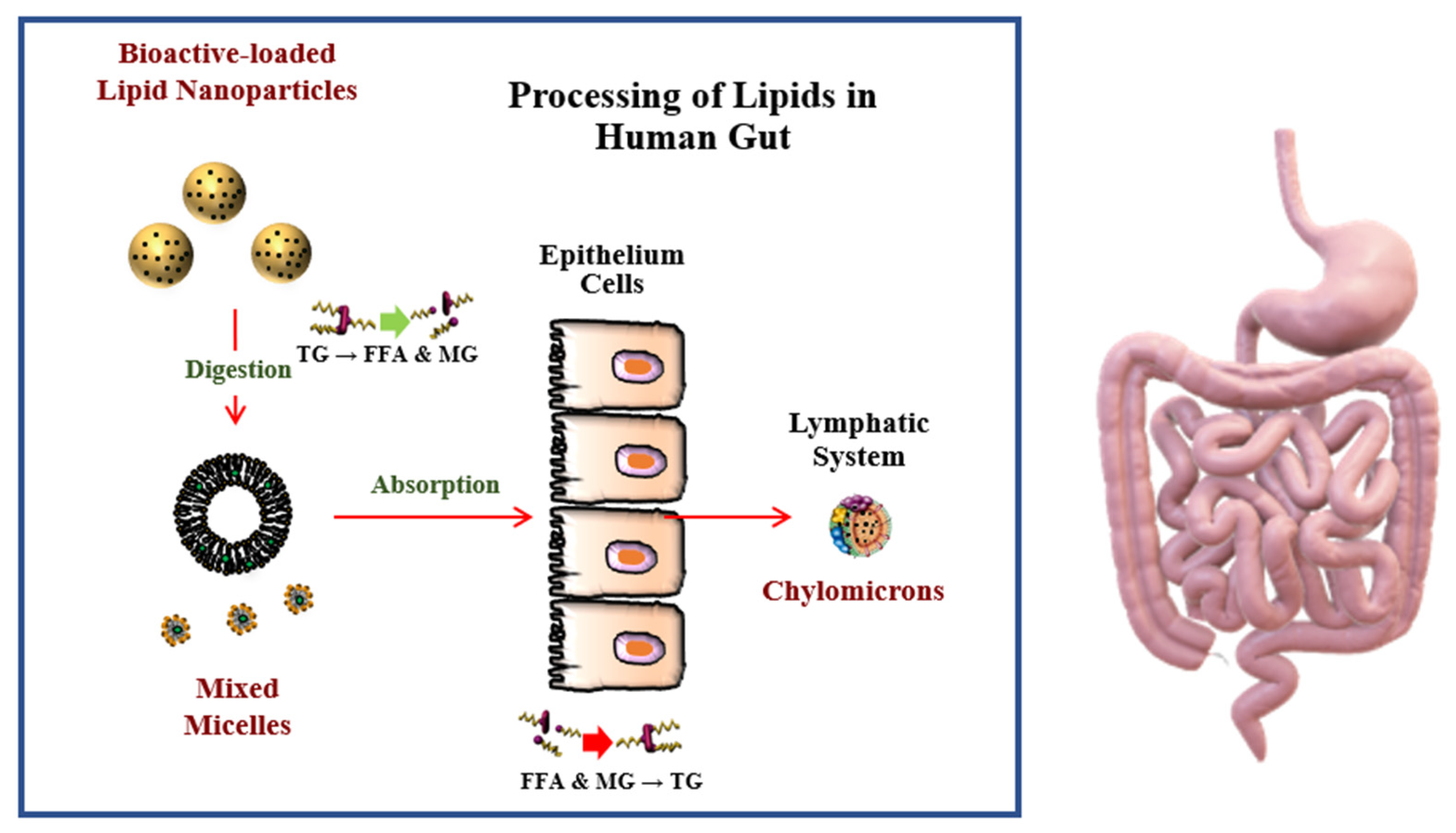
6. Enhanced Bioavailability
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sankar, R.; Ravisankar, P.; Reddy, A.A.; Nagalakshmi, B.; Koushik, O.S.; Vijaya Kumar, B.; Anvith, P.S. The comprehensive review on fat soluble vitamins. IOSR J. Pharm. 2015, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar]
- Eggersdorfer, M.; Wyss, A. Carotenoids in Human Nutrition and Health. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 652, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautwein, E.A.; Demonty, I. Phytosterols: Natural Compounds with Established and Emerging Health Benefits. Oléagineux Corps Gras Lipides 2007, 14, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, D.; Block, R.; Mousa, S.A. Omega-3 Fatty Acids EPA and DHA: Health Benefits throughout Life. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Design of Foods with Bioactive Lipids for Improved Health. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, L.; Corzo-Martínez, M.; Arranz-Martínez, P.; Barroso, E.; Reglero, G.; Torres, C. Bioactive Lipids. In Bioactive Molecules in Food. Reference Series in Phytochemistry; Mérillon, J.M., Ramawat, K.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 467–527. [Google Scholar]
- Das, U.N. Bioactive Lipids in COVID-19-Further Evidence. Arch. Med. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogero, M.M.; Leão, M.D.C.; Santana, T.M.; Pimentel, M.V.D.M.; Carlini, G.C.; Da Silveira, T.F.; Gonçalves, R.C.; Castro, I.A. Potential Benefits and Risks of Omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation to Patients with COVID-19. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 156, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bistrian, B.R. Parenteral Fish-Oil Emulsions in Critically Ill COVID-19 Emulsions. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, D.O.; Best, T.J.; Zhang, H.; Vokes, T.; Arora, V.; Solway, J. Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics with COVID-19 Test Results. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2019722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.S. Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Dietary Sources, Metabolism, and Significance—A Review. Life Sci. 2018, 203, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.A.; Nyström, L.; Whitaker, B.D.; Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Baer, D.J.; Gebauer, S.K.; Hicks, K.B. Phytosterols and Their Derivatives: Structural Diversity, Distribution, Metabolism, Analysis, and Health-Promoting Uses. Prog. Lipid Res. 2018, 70, 35–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiani, G.; Castón, M.J.P.; Catasta, G.; Toti, E.; Cambrodón, I.G.; Bysted, A.; Granado-Lorencio, F.; Olmedilla-Alonso, B.; Knuthsen, P.; Valoti, M.; et al. Carotenoids: Actual Knowledge on Food Sources, Intakes, Stability and Bioavailability and Their Protective Role in Humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 194–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibian, M.; Torbati, M.; Mogaddam, M.R.A.; Mirlohi, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Mohtadinia, J. Evaluation of Vitamin D3 and D2 Stability in Fortified Flat Bread Samples during Dough Fermentation, Baking and Storage. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Chaudhuri, U.R.; Chakraborty, R. Structure, Health Benefits, Antioxidant Property and Processing and Storage of Carotenoids. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Nanoscale Nutrient Delivery Systems for Food Applications: Improving Bioactive Dispersibility, Stability, and Bioavailability. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, N1602–N1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, H.; Gömmel, C.; Leuenberger, B.H.; Weiss, J. Influence of Encapsulated Functional Lipids on Crystal Structure and Chemical Stability in Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Towards Bioactive-Based Design of Delivery Systems. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; McClements, D.J.; Xiao, H. Improving Oral Bioavailability of Nutraceuticals by Engineered Nanoparticle-Based Delivery Systems. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T.; Park, H.J. Recent Developments in Nanoformulations of Lipophilic Functional Foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahrani, A.A.; Greaves, R.F. Fat-Soluble Vitamins: Clinical Indications and Current Challenges for Chromatographic Measurement. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2016, 37, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clagett-Dame, M.; Knutson, D. Vitamin a in Reproduction and Development. Nutrients 2011, 3, 385–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prietl, B.; Treiber, G.; Pieber, T.R.; Amrein, K. Vitamin D and Immune Function. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2502–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borel, P.; Desmarchelier, C. Annual Review of Nutrition Bioavailability of Fat-Soluble Vitamins and Phytochemicals in Humans: Effects of Genetic Variation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeer, C. Vitamin K: The Effect on Health beyond Coagulation—An Overview. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 56, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, C.S.; McClements, D.J.; Weiss, J.; Decker, E.A. Factors Influencing the Chemical Stability of Carotenoids in Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Ma, C.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Advances in Research on Bioactivity, Metabolism, Stability and Delivery Systems of Lycopene. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carpena, M.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Pereira, A.G.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Scientific Approaches on Extraction, Purification and Stability for the Commercialization of Fucoxanthin Recovered from Brown Algae. Foods 2020, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yuan, J.P.; Wu, C.F.; Wang, J.H. Fucoxanthin, a Marine Carotenoid Present in Brown Seaweeds and Diatoms: Metabolism and Bioactivities Relevant to Human Health. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1806–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Dash, R.; Haque, M.N.; Mohibbullah, M.; Oktaviani, D.F.; Hossain, M.T.; Choi, H.J.; Moon, I.S. Phytosterols of Marine Algae: Insights into the Potential Health Benefits and Molecular Pharmacology. Phytomedicine 2020, 69, 153201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, L.; Symington, A.M. Algal-Oil Supplements Are a Viable Alternative to Fish-Oil Supplements in Terms of Docosahexaenoic Acid (22:6n-3; DHA). J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.J.; Miles, E.A.; Burdge, G.C.; Yaqoob, P.; Calder, P.C. Metabolism and Functional Effects of Plant-Derived Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Humans. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 64, 30–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugasini, D.; Lokesh, B.R. Uptake of α-Linolenic Acid and Its Conversion to Long Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Rats Fed Microemulsions of Linseed Oil. Lipids 2012, 47, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, S.; Spener, F. Conjugated Linoleic Acids as Functional Food: An Insight into Their Health Benefits. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, S.; Assadpour, E.; Katouzian, I.; Jafari, S.M. Lipid Nano Scale Cargos for the Protection and Delivery of Food Bioactive Ingredients and Nutraceuticals. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 74, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadpour, E.; Mahdi Jafari, S. A Systematic Review on Nanoencapsulation of Food Bioactive Ingredients and Nutraceuticals by Various Nanocarriers. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3129–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakamasundari, S.K.; Leena, M.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Formulation and Applications in Food Bioactive Delivery. In Innovative Food Processing Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 580–604. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J.; Rao, J. Food-Grade Nanoemulsions: Formulation, Fabrication, Properties, Performance, Biological Fate, and Potential Toxicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 285–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Khalid, N.; Chen, Z.; Neves, M.A.; Barrow, C.J.; Nakajima, M. Formulation and Characterization of Astaxanthin-Enriched Nanoemulsions Stabilized Using Ginseng Saponins as Natural Emulsifiers. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, B.; McClements, D.J. Progress in Natural Emulsifiers for Utilization in Food Emulsions. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaiko, J.; McClements, D.J. Low-Energy Formation of Edible Nanoemulsions by Spontaneous Emulsification: Factors Influencing Particle Size. J. Food Eng. 2015, 146, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; McClements, D.J. Formation of Nanoemulsions Stabilized by Model Food-Grade Emulsifiers Using High-Pressure Homogenization: Factors Affecting Particle Size. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Nanoemulsions versus Microemulsions: Terminology, Differences, and Similarities. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J.; Kristbergsson, K.; Helgason, T.; Awad, T. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Delivery Systems for Bioactive Food Components. Food Biophys. 2008, 3, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katouzian, I.; Faridi Esfanjani, A.; Jafari, S.M.; Akhavan, S. Formulation and Application of a New Generation of Lipid Nano-Carriers for the Food Bioactive Ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjidi, F.; Shahedi, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Nasirpour, A. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): A Potential Delivery System for Bioactive Food Molecules. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, S.; Danaei, M.; Mozafari, M.R. Nanoliposome Technology for the Food and Nutraceutical Industries. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Abbas, S.; Feng, B.; Zhang, X.; Xia, S. Modulation of the Carotenoid Bioaccessibility through Liposomal Encapsulation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthil Muthu Kumar, T.; Senthil Kumar, K.; Rajini, N.; Siengchin, S.; Ayrilmis, N.; Varada Rajulu, A. A Comprehensive Review of Electrospun Nanofibers: Food and Packaging Perspective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamabadi, H.; Assadpour, E.; Tabarestani, H.S.; Falsafi, S.R.; Jafari, S.M. Electrospinning Approach for Nanoencapsulation of Bioactive Compounds; Recent Advances and Innovations. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Ahmad, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H. A Review of Recent Progress on High Internal-Phase Pickering Emulsions in Food Science. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, W.W.; Lim, H.P.; Low, L.E.; Tey, B.T.; Chan, E.S. Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions for Encapsulation and Delivery of Bioactives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, B. Novel Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Tea Water-Insoluble Protein Nanoparticles from Tea Residues. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tan, Y.; Lv, S.; Liu, J.; Muriel Mundo, J.L.; Bai, L.; Rojas, O.J.; McClements, D.J. Nanochitin-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions: Influence of Nanochitin on Lipid Digestibility and Vitamin Bioaccessibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Su, E.; Liu, X.; Wan, Z.; Yang, X. Self-Assembled Egg Yolk Peptide Micellar Nanoparticles as a Versatile Emulsifier for Food-Grade Oil-in-Water Pickering Nanoemulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11728–11740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, H.; Ankenbrand, J.; Zeeb, B.; Badolato Bönisch, G.; Schäfer, C.; Kohlus, R.; Weiss, J. Influence of Spray Drying on the Stability of Food-Grade Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejrapha, P.; Min, S.G.; Surassmo, S.; Choi, M.J. Physicothermal Properties of Freeze-Dried Fish Oil Nanocapsules Frozen under Different Conditions. Dry. Technol. 2010, 28, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökmen, V.; Mogol, B.A.; Lumaga, R.B.; Fogliano, V.; Kaplun, Z.; Shimoni, E. Development of Functional Bread Containing Nanoencapsulated Omega-3 Fatty Acids. J. Food Eng. 2011, 105, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Messery, T.M.; Altuntas, U.; Altin, G.; Özçelik, B. The Effect of Spray-Drying and Freeze-Drying on Encapsulation Efficiency, in Vitro Bioaccessibility and Oxidative Stability of Krill Oil Nanoemulsion System. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Wagner, G. Vitamin E Nanoparticle for Beverage Applications. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2004, 82, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780429154034. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbanzade, T.; Jafari, S.M.; Akhavan, S.; Hadavi, R. Nano-Encapsulation of Fish Oil in Nano-Liposomes and Its Application in Fortification of Yogurt. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyasoglu, H.; El, S.N. Nanoencapsulation of EPA/DHA with Sodium Caseinate-Gum Arabic Complex and Its Usage in the Enrichment of Fruit Juice. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 56, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojagh, S.M.; Hasani, S. Characteristics and Oxidative Stability of Fish Oil Nano-Liposomes and Its Application in Functional Bread. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, F.S.; Farzadnia, F.; Aghajani, A.; Ahmadzadeh NobariAzar, F.; Pezeshki, A. Conjugated Linoleic Acid Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier as a Potential Antioxidant Nanocarrier for Food Applications. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4185–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anarjan, N.; Tan, C.P. Chemical Stability of Astaxanthin Nanodispersions in Orange Juice and Skimmed Milk as Model Food Systems. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campo, C.; Queiroz Assis, R.; Marques da Silva, M.; Haas Costa, T.M.; Paese, K.; Stanisçuaski Guterres, S.; de Oliveira Rios, A.; Hickmann Flôres, S. Incorporation of Zeaxanthin Nanoparticles in Yogurt: Influence on Physicochemical Properties, Carotenoid Stability and Sensory Analysis. Food Chem. 2019, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.K.D.O.C.; de Carvalho Gomes, C.; de Araújo Amaral, M.L.Q.; de Medeiros, L.D.G.; Medeiros, I.; Porto, D.L.; Aragão, C.F.S.; Maciel, B.L.L.; de AraújoMorais, A.H.; SouzaPassos, T. Nanoencapsulation Improved Water Solubility and Color Stability of Carotenoids Extracted from Cantaloupe Melon (Cucumis Melo L.). Food Chem. 2019, 270, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoond Zardini, A.; Mohebbi, M.; Farhoosh, R.; Bolurian, S. Production and Characterization of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers and Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Lycopene for Food Fortification. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopde, S.; Datir, R.; Deshmukh, G.; Dhotre, A.; Patil, M. Nanoparticle Formation by Nanospray Drying & Its Application in Nanoencapsulation of Food Bioactive Ingredients. J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 2, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, V.K.; Aggarwal, M. Fabrication of Nano-Structured Lipid Carrier for Encapsulation of Vitamin D3 for Fortification of ‘Lassi’; A Milk Based Beverage. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Dai, T.; Muriel Mundo, J.L.; Tan, Y.; Bai, L.; McClements, D.J. The Gastrointestinal Fate of Inorganic and Organic Nanoparticles in Vitamin D-Fortified Plant-Based Milks. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.O.; Ha, T.V.A.; Choi, Y.J.; Ko, S. Optimization of Homogenization-Evaporation Process for Lycopene Nanoemulsion Production and Its Beverage Applications. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewen, A.; Chan, B.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Optimization of Vitamins A and D3 Loading in Re-Assembled Casein Micelles and Effect of Loading on Stability of Vitamin D3 during Storage. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syama, M.A.; Arora, S.; Gupta, C.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, V. Enhancement of Vitamin D 2 Stability in Fortified Milk during Light Exposure and Commercial Heat Treatments by Complexation with Milk Proteins. Food Biosci. 2019, 29, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, N.; Ranjan, S.; Mundra, S.; Ramalingam, C.; Kumar, A. Fabrication of Food Grade Vitamin E Nanoemulsion by Low Energy Approach, Characterization and Its Application. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherpour, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Hamishehkar, H. Preparation and Characterization of Betasitosterol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Butter Enrichment. Food Biosci. 2017, 20, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubeyitogullari, A.; Ciftci, O.N. In Vitro Bioaccessibility of Novel Low-Crystallinity Phytosterol Nanoparticles in Non-Fat and Regular-Fat Foods. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, D.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Reis, S. Nanoencapsulation Approaches for Oral Delivery of Vitamin A. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Gao, J.; Ye, H.; Ren, G.; Ma, X.; Xie, H.; Fang, S.; Lei, Q.; Fang, W. Development of Ovalbumin-Pectin Nanocomplexes for Vitamin D3 Encapsulation: Enhanced Storage Stability and Sustained Release in Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.; Arora, S.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, V. Evaluation of Effective Storage Conditions and In-Vitro Bioaccessibility of Vitamin A from Native and Modified Sodium Caseinate-Vitamin A Complexes. LWT 2019, 111, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, V.K.; Aggarwal, M. A Phase Inversion Based Nanoemulsion Fabrication Process to Encapsulate Vitamin D3 for Food Applications. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 190, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahafi, S.M.; Goli, S.A.H.; Kadivar, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Shirvani, A. Pomegranate Seed Oil Nanoemulsion Enriched by α-Tocopherol; the Effect of Environmental Stresses and Long-Term Storage on Its Physicochemical Properties and Oxidation Stability. Food Chem. 2021, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hategekimana, J.; Chamba, M.V.M.; Shoemaker, C.F.; Majeed, H.; Zhong, F. Vitamin E Nanoemulsions by Emulsion Phase Inversion: Effect of Environmental Stress and Long-Term Storage on Stability and Degradation in Different Carrier Oil Types. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 483, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Gu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, H.; McClements, D.J. Vitamin e Encapsulation in Plant-Based Nanoemulsions Fabricated Using Dual-Channel Microfluidization: Formation, Stability, and Bioaccessibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10532–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, C.M.; Tavares, M.N.; Macedo, L.P.; Araújo, G.S.; Furlong, E.B.; Dora, C.L.; Burkert, J.F.M. Physical and Chemical Stability of β-Carotene Nanoemulsions during Storage and Thermal Process. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat Doost, A.; Afghari, N.; Abbasi, H.; Nikbakht Nasrabadi, M.; Dewettinck, K.; van der Meeren, P. Nano-Lipid Carriers Stabilized by Hydrophobically Modified Starch or Sucrose Stearate for the Delivery of Lutein as a Nutraceutical Beverage Model. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimet, P.; Rosenberg, D.; Livney, Y.D. Re-Assembled Casein Micelles and Casein Nanoparticles as Nano-Vehicles for ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimet, P.; Livney, Y.D. Beta-Lactoglobulin and Its Nanocomplexes with Pectin as Vehicles for ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, C.; Liu, E.; Zhang, F.; Meng, X.; Liu, B. Effect of Environmental Stresses on Physicochemical Properties of ALA Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion System Prepared by Emulsion Phase Inversion. Food Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, B.; Jinap, S.; Mozafari, M.R.; Yazid, A.M. Comparative Study of the Oxidative and Physical Stability of Liposomal and Nanoliposomal Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Prepared with Conventional and Mozafari Methods. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2761–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Xia, N.; Xia, Q. Nanostructured Lipid Carrier (NLC) as a Strategy for Encapsulation of Quercetin and Linseed Oil: Preparation and in Vitro Characterization Studies. J. Food Eng. 2017, 215, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Lobato, K.B.; Paese, K.; Forgearini, J.C.; Guterres, S.S.; Jablonski, A.; de Oliveira Rios, A. Evaluation of Stability of Bixin in Nanocapsules in Model Systems of Photosensitization and Heating. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B. Chitosan Hydrochloride/Carboxymethyl Starch Complex Nanogels Stabilized Pickering Emulsions for Oral Delivery of β-Carotene: Protection Effect and in Vitro Digestion Study. Food Chem. 2020, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zou, L.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, W. One-Step Preparation of High Internal Phase Emulsions Using Natural Edible Pickering Stabilizers: Gliadin Nanoparticles/Gum Arabic. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Díaz, C.; Opazo-Navarrete, M.; Soto-Añual, M.; Leal-Calderón, F.; Bustamante, M. Food-Grade Pickering Emulsion as a Novel Astaxanthin Encapsulation System for Making Powder-Based Products: Evaluation of Astaxanthin Stability during Processing, Storage, and Its Bioaccessibility. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaconia, M.A.; dos Passos Ramos, S.; Pereira, C.F.; Lemes, A.C.; de Rosso, V.V.; Braga, A.R.C. Overcoming Restrictions of Bioactive Compounds Biological Effects in Food Using Nanometer-Sized Structures. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105939. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, M.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J. Delivery of Lipophilic Bioactives: Assembly, Disassembly, and Reassembly of Lipid Nanoparticles. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 53–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Jiang, P.; Chai, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D.; Bao, W.; Liu, B.; Liu, B.; Norde, W.; Li, Y. The Delivery of Sensitive Food Bioactive Ingredients: Absorption Mechanisms, Influencing Factors, Encapsulation Techniques and Evaluation Models. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guri, A.; Gülseren, I.; Corredig, M. Utilization of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Enhanced Delivery of Curcumin in Cocultures of HT29-MTX and Caco-2 Cells. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsou, E.; Dupin, A.; Sassi, A.H.; Monteil, J.; Sotiroudis, G.T.; Leal-Calderon, F.; Xenakis, A. Hydroxytyrosol Encapsulated in Biocompatible Water-in-Oil Microemulsions: How the Structure Affects in Vitro Absorption. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasa-Falcon, A.; Arranz, E.; Odriozola-Serrano, I.; Martín-Belloso, O.; Giblin, L. Delivery of β-Carotene to the in Vitro Intestinal Barrier Using Nanoemulsions with Lecithin or Sodium Caseinate as Emulsifiers. LWT 2021, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inapurapu, S.P.; Ibrahim, A.; Kona, S.R.; Pawar, S.C.; Bodiga, S.; Bodiga, V.L. Development and Characterization of ω-3 Fatty Acid Nanoemulsions with Improved Physicochemical Stability and Bioaccessibility. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, R.; Engelberg, S.; Fahoum, L.; Meyron-Holtz, E.G.; Livney, Y.D. Potato Protein- Based Carriers for Enhancing Bioavailability of Astaxanthin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Arora, S.; Gupta, C.; Kapila, S. Effect of Sodium Caseinate and Vitamin A Complexation on Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Vitamin A in Caco-2 Cells. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Garcia, C. v.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Development of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for the Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Vitamin D3. Food Chem. 2017, 225, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, B.; Argin, S.; Ozilgen, M.; McClements, D.J. Nanoemulsion Delivery Systems for Oil-Soluble Vitamins: Influence of Carrier Oil Type on Lipid Digestion and Vitamin D3 Bioaccessibility. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; McClements, D.J. Vitamin E Bioaccessibility: Influence of Carrier Oil Type on Digestion and Release of Emulsified α-Tocopherol Acetate. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Pandya, J.K.; Chung, C.; McClements, D.J.; Kinchla, A.J. Emulsions as Delivery Systems for Gamma and Delta Tocotrienols: Formation, Properties and Simulated Gastrointestinal Fate. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D. Fabrication and Characterization of Lutein-Loaded Nanoparticles Based on Zein and Sophorolipid: Enhancement of Water Solubility, Stability, and Bioaccessibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, T.V.A.; Kim, S.; Choi, Y.; Kwak, H.S.; Lee, S.J.; Wen, J.; Oey, I.; Ko, S. Antioxidant Activity and Bioaccessibility of Size-Different Nanoemulsions for Lycopene-Enriched Tomato Extract. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Wang, D.; Gan, L.; Shao, P.; Jiang, L.; Sun, P. Preparation and Characterization of Zein/Pectin-Based Phytosterol Nanodispersions and Kinetic Study of Phytosterol Release during Simulated Digestion in Vitro. LWT 2020, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcclements, D.J.; Xiao, H. Excipient Foods: Designing Food Matrices That Improve the Oral Bioavailability of Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1320–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; McClements, D.J. Enhancement of Lycopene Bioaccessibility from Tomato Juice Using Excipient Emulsions: Influence of Lipid Droplet Size. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Lam, T.I.; Yokoyama, W.; Cheng, L.W.; Zhong, F. Cellular Uptake of β-Carotene from Protein Stabilized Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Prepared by Homogenization-Evaporation Method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T. kumar; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, M.; Koley, H.; Dhar, P. Comparative Study of Gastrointestinal Absorption of EPA & DHA Rich Fish Oil from Nano and Conventional Emulsion Formulation in Rats. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuasal, B.S.; Lucas, C.; Peyton, B.; Alayoubi, A.; Nazzal, S.; Sylvester, P.W.; Kaddoumi, A. Enhancement of Intestinal Permeability Utilizing Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Increases γ-Tocotrienol Oral Bioavailability. Lipids 2012, 47, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bioactive Lipid | Nanocarrier System | Food Application | Benefits | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyunsaturated omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids | ||||
| Flax seed oil (high in ALA) | Starch nanocomplexes | Bread | Reduced lipid oxidation, reduced HMF and acrylamide during baking | [57] |
| Fish oil (EPA-DHA) | Nanoliposomes | Yogurt | Increased bioactive retention, reduced lipid oxidation, high sensory score | [61] |
| Fish oil (EPA-DHA) | Sodium caseinate/gum arabic nanocomplexes | Fruit juice | Acceptable taste scores, high bioaccessibility | [62] |
| Fish oil (EPA-DHA) | Nanoliposomes | Bread | Improved oxidative stability, good textural and sensory quality | [63] |
| CLA | Nanostructured lipid carriers | Low fat milk | Improved physical, oxidative and thermal stability | [64] |
| Carotenoids | ||||
| Astaxanthin | Nanodispersions | Orange juice, skimmed milk | Improved storage stability, high in vitro cellular uptake | [65] |
| Zeaxanthin | Nanoparticles, nanoemulsions | Yogurt | High storage stability in food matrix, in vitro controlled release | [66] |
| Carotenoid extract (high in β-carotene) | Nanoemulsion | Yogurt | Increased dispersibility, high storage stability | [67] |
| Lycopene | Solid lipid nanoparticles, nanostructured lipid carriers | Orange drink | Increased dispersibility, better aftertaste scores, high overall acceptance | [68] |
| Lycopene | Nanoemulsion | Model beverage | Improved storage stability | [72] |
| Fat soluble vitamins | ||||
| Vitamin D3 | Nanostructured lipid carrier | ‘Lassi’ Yogurt based beverage | High sensory acceptance, sustained release in simulated intestinal fluid | [70] |
| Vitamin D3 | Organic nanoparticles (Nanoemulsion, Nanocellulose), inorganic nanoparticle (TiO2) | Plant-based milks | Improved viscosity and color | [71] |
| Vitamin A, D3 | Reassembled casein micelle | Skim milk | Improved storage stability | [73] |
| Vitamin D2 | Na-caseinate nanocomplexes | Milk | Improved storage and thermal stability | [74] |
| Vitamin E | Nanoemulsion | Fruit juice | Increased shelf life | [75] |
| Phytosterols | ||||
| β-sitosterol | Nanostructured lipid carriers | Butter | Improved storage stability, high antioxidant activity | [76] |
| Phytosterols | Nanoporous starch aerogels | Granola bars, pudding | Improved bioaccessibility | [77] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McClements, D.J.; Öztürk, B. Utilization of Nanotechnology to Improve the Handling, Storage and Biocompatibility of Bioactive Lipids in Food Applications. Foods 2021, 10, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020365
McClements DJ, Öztürk B. Utilization of Nanotechnology to Improve the Handling, Storage and Biocompatibility of Bioactive Lipids in Food Applications. Foods. 2021; 10(2):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020365
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcClements, David Julian, and Bengü Öztürk. 2021. "Utilization of Nanotechnology to Improve the Handling, Storage and Biocompatibility of Bioactive Lipids in Food Applications" Foods 10, no. 2: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020365
APA StyleMcClements, D. J., & Öztürk, B. (2021). Utilization of Nanotechnology to Improve the Handling, Storage and Biocompatibility of Bioactive Lipids in Food Applications. Foods, 10(2), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020365