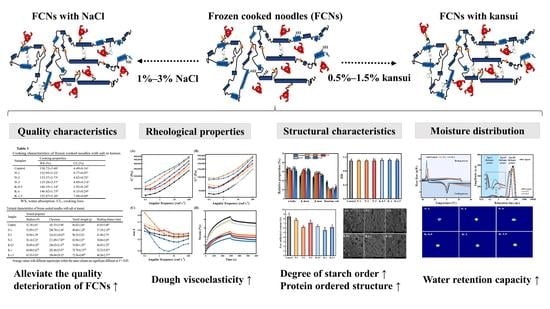
Moisture Distribution and Structural Properties of Frozen Cooked Noodles with NaCl and Kansui
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Sampling of FCNs
2.3. Rheological Properties Tests
2.3.1. Dynamic Frequency Sweep
2.3.2. Creep Recovery Measurement
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.5. Freezable Water Content
2.6. Measurement of Protons Migration and Distribution
2.7. Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) Analysis
2.8. Measurement of Free Sulfhydryl Content
2.9. Cooking Properties and Texture Analysis of FCNs
2.10. Organoleptic Evaluation
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rheological Properties Analysis
3.1.1. Dynamic Frequency Sweep
3.1.2. Creep and Recovery Measurements
3.2. Morphological Characteristics
3.3. Freezable Water Content
3.4. Water Distribution and Migration
3.4.1. Water Distribution
3.4.2. Water Migration
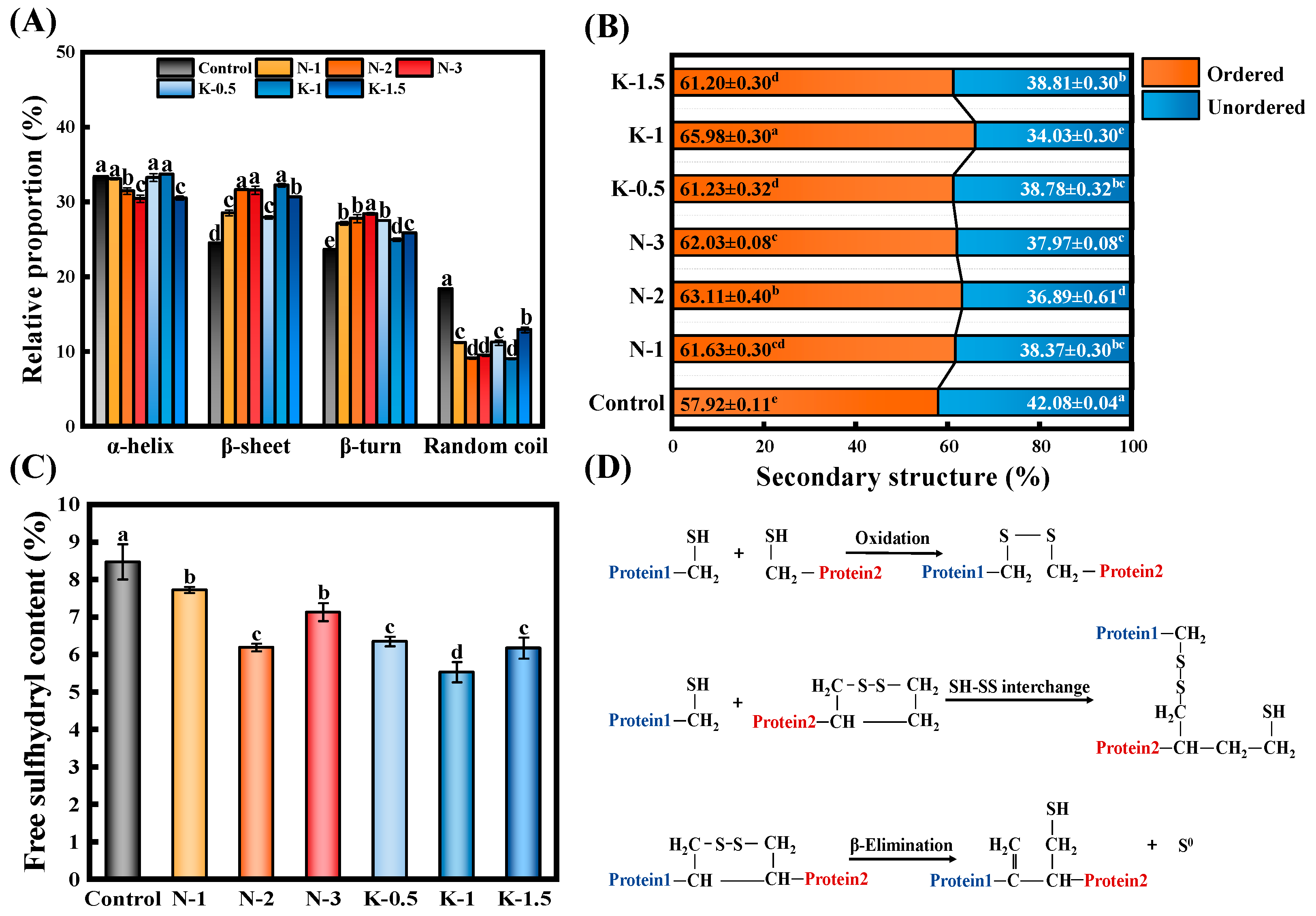
3.5. Gluten Secondary Structure
3.6. Changes of Free Sulfhydryl (-SH) Contents
3.7. Quality Characteristics
3.7.1. Cooking Properties
3.7.2. Texture Properties
3.8. Organoleptic Properties
3.9. Network Reinforcement Mechanism by NaCl and Kansui after Freezing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obadi, M.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Xu, B. Factors affecting frozen cooked noodle quality: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Frozen steamed breads and boiled noodles: Quality affected by ingredients and processing. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Nishijima, N.; Oda, Y.; Handa, A.; Zhang, Y. Utilization of egg white solids to improve the texture and cooking quality of cooked and frozen pasta. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 109031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, X.N.; Zhu, K.X. Effects of frozen storage on the quality characteristics of frozen cooked noodles. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, X.J. Effect of kansui addition on dough rheology and quality characteristics of chickpea-wheat composite flour-based noodles and the underlying mechanism. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.X. Asian noodles: History, classification, raw materials, and processing. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Roach, R.R.; Hoseney, R.C. Effect of nonchaotropic salts on flour bread-making properties. Cereal Chem. 1992, 69, 366–371. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.P.; Fu, F.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, M.; Ai, Z.L.; Bian, K. Effect of NaCl on rheological properties of dough and noodle quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 93, 102936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.W.; Ma, M.; Yang, T.B.; Li, M.; Sun, Q.J. Heat mediated physicochemical and structural changes of wheat gluten in the presence of salt and alkali. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia, N.; Dhaka, V.; Khatkar, B.S. Instant Noodles: Processing, Quality, and Nutritional Aspects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1386–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, Q.J.; Han, C.W.; Chen, H.H.; Tang, W.T. Comparative study of the quality characteristics of fresh noodles with regular salt and alkali and the underlying mechanisms. Food Chem. 2017, 246, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.Y.; Wang, J.R.; Sun, L.N.; Zhou, X.N.; Cheng, J.J.; Sun, Y.X. Effect of kansui on the physicochemical, structural, and quality characteristics of adlay seed flour-fortified wheat noodles. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 146, 111458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, S.Y.; Lubowa, M.; Tan, T.C.; Murad, M.; Easa, A.M. The use of salt-coating to effect textural, mechanical, cooking and sensory properties of air-dried yellow alkaline noodles. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, T.; Ma, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, L.; Xu, D.; Wu, F.; Xu, X. Understanding the influence of pullulan on the quality changes, water mobility, structural properties and thermal properties of frozen cooked noodles. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Mu, T.H.; Sun, H.N. Effects of starch from five different botanical sources on the rheological and structural properties of starch-gluten model doughs. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Y.; Ke, C.X.; Li, L. Physicochemical, rheological and digestive characteristics of soy protein isolate gel induced by lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Eng. 2020, 292, 110243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.R.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Y.L. Effect of boiling and steaming on the surface tackiness of frozen cooked noodles. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 130, 109747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, M.C.; Ma, S.P.; Wang, H.S. Physicochemical characterization of rice, potato, and pea starches, each with different crystalline pattern, when incorporated with Konjac glucomannan. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, S.A.; Singh, J.; Chhikara, N.; Panghal, A.; Gat, Y. Quality characterization of gluten free noodles enriched with chickpea protein isolate. Food Biosci. 2020, 36, 100626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.L.; Tan, T.C.; Mat, E.A. Comparative study of cooking quality, microstructure, and textural and sensory properties between fresh wheat noodles prepared using sodium chloride and salt substitutes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 97, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.F.; Guo, X.N.; Li, M.; Zhu, K.X. Effect of different mixing and kneading process on the quality characteristics of frozen cooked noodle. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 101, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, T.H.; Day, L. Effect of sodium chloride on gluten network formation, dough microstructure and rheology in relation to breadmaking. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Suo, W.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Dong, S.; Guo, P.; Chen, S.; Li, H. Influence of emulsifiers and enzymes on dough rheological properties and quality characteristics of steamed bread enriched with potato pulp. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.Y.; Mu, T.H.; Zhang, M.; Ma, M.M. Effects of ionic polysaccharides and egg white protein complex formulations on dough rheological properties, structure formation and in vitro starch digestibility of wet sweet potato vermicelli. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Rasheed, M.; Gu, S.; Guo, B. Effect of freezing rate and frozen storage on the rheological properties and protein structure of non-fermented doughs. J. Food Eng. 2021, 293, 110377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.R.; Xu, F.; Li, Z.K. Effects of water addition and noodle thickness on the surface tackiness of frozen cooked noodles. J. Food Process Preserv. 2020, 44, e14717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Yang, Z.; Guo, X.N.; Xing, J.J.; Zhu, K.X. Effect of NaHCO3 and freeze-thaw cycles on frozen dough: From water state, gluten polymerization and microstructure. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombouts, I.; Jansens, K.; Lagrain, B.; Delcour, J.A.; Zhu, K.X. The impact of salt and alkali on gluten polymerization and quality of fresh wheat noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, L.J.; Guo, X.N.; Zhu, K.X. Effect of steaming on the quality characteristics of frozen cooked noodles. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Qu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J. Further interpretation of the strengthening effect of curdlan on frozen cooked noodles quality during frozen storage: Studies on water state and properties. Food Chem. 2020, 346, 128908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Ren, T.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, B.; Hu, X. Interpreting the correlation between repeated sheeting process and wheat noodle qualities: From water molecules movement perspective. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, J.E.; Damodaran, S. Bran-induced changes in water structure and gluten conformation in model gluten dough studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Luo, Z.G.; Yang, Q.Y.; Xiao, Z.G.; Lu, X.X. Effect of quinoa flour on baking performance, antioxidant properties and digestibility of wheat bread. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanga, S.K.; Wang, J.; Orsat, V.; Raghavan, V. Effect of pulsed ultrasound, a green food processing technique, on the secondary structure and in-vitro digestibility of almond milk protein. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, G.; Ran, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Kan, J. Adlay starch-gluten composite gel: Effects of adlay starch on rheological and structural properties of gluten gel to molecular and physico-chemical characteristics. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, P.S.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Grant, A.; Wellner, N.; Field, J.M.; Shewry, P.R.; Tatham, A.S. FTIR and NMR studies on the hydration of a high-Mr subunit of glutenin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1995, 17, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Xu, D.; Wu, F.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of Na2CO3 on quality and volatile compounds of steamed bread fermented with yeast or sourdough. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, L.; Nikoo, M.; Ocen, D.; Wu, F.F.; Yang, N.; Jin, Z.Y.; Xu, X.M. Effect of frozen storage on the conformational, thermal and microscopic properties of gluten: Comparative studies on gluten-, glutenin- and gliadin-rich fractions. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 Control,
Control,  N-1,
N-1,  N-2,
N-2,  N-3,
N-3, 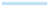 K-0.5,
K-0.5,  K-1,
K-1,  K-1.5.
K-1.5.
 Control,
Control,  N-1,
N-1,  N-2,
N-2,  N-3,
N-3,  K-0.5,
K-0.5,  K-1,
K-1,  K-1.5.
K-1.5.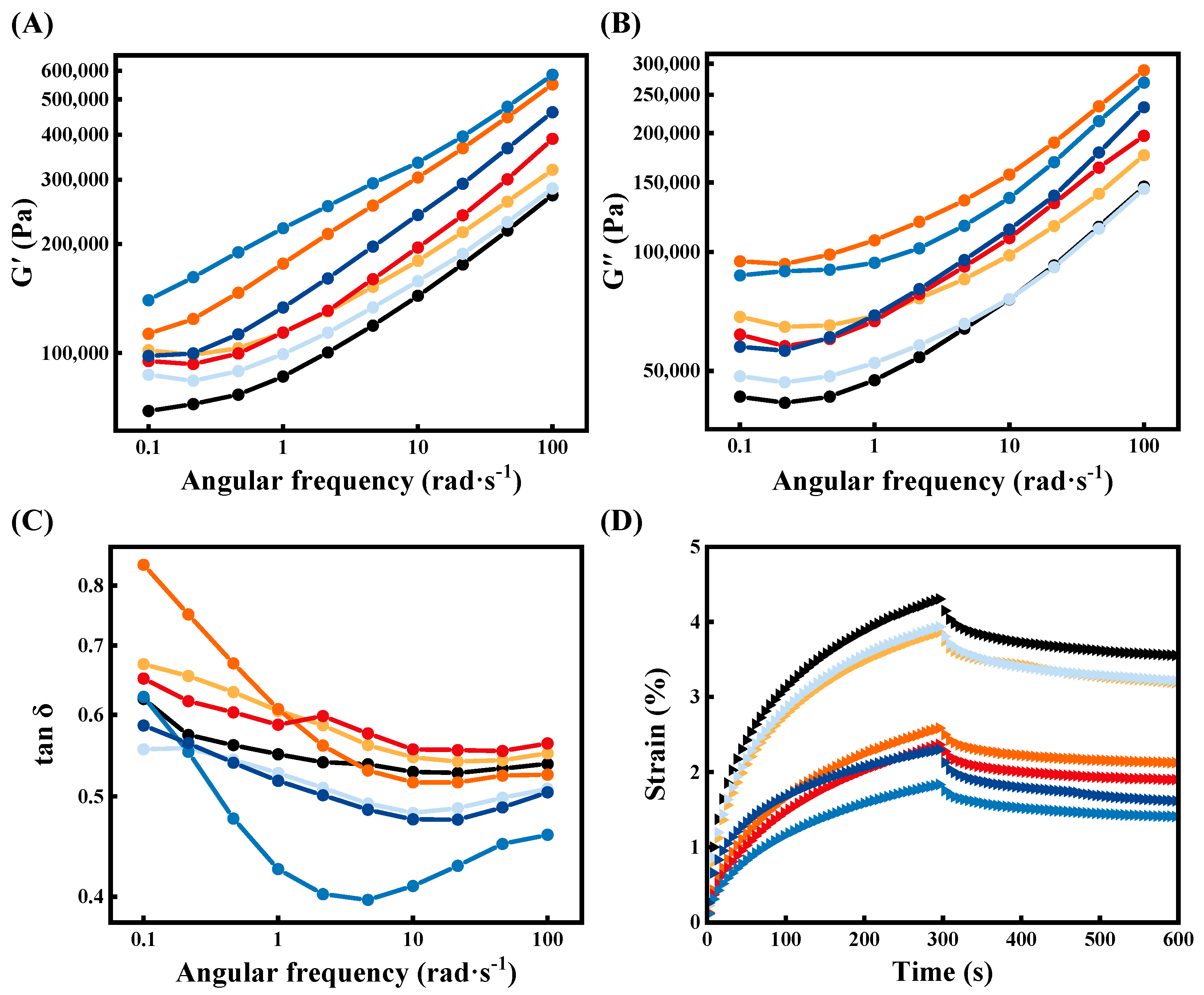


 Control,
Control,  N-1,
N-1,  N-2,
N-2,  N-3,
N-3,  K-0.5,
K-0.5,  K-1,
K-1,  K-1.5.
K-1.5.
 Control,
Control,  N-1,
N-1,  N-2,
N-2,  N-3,
N-3,  K-0.5,
K-0.5,  K-1,
K-1,  K-1.5.
K-1.5.

| Samples | z′ | K × 105 | R2 | Creep Phase | Recovery Phase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jmax × 10−4 (1/Pa) | ƞ0 × 109 (Pa·s) | Je/Jmax (%) | Jv/Jmax (%) | ||||
| Control | 0.261 ± 0.017 a | 0.992 ± 0.037 e | 0.952 ± 0.049 | 1.24 ± 0.09 a | 15.96 ± 0.92 a | 54.75 ± 3.68 d | 45.26 ± 3.68 a |
| N-1 | 0.246 ± 0.052 a | 1.055 ± 0.049 de | 0.995 ± 0.002 | 1.09 ± 0.11 bc | 11.52 ± 1.12 b | 63.15 ± 2.03 c | 36.85 ± 2.03 b |
| N-2 | 0.246 ± 0.015 a | 1.184 ± 0.062 bc | 0.968 ± 0.046 | 0.97 ± 0.07 cd | 8.74 ± 0.77 c | 73.57 ± 1.34 b | 26.43 ± 1.34 c |
| N-3 | 0.257 ± 0.007 a | 1.071 ± 0.025 de | 0.977 ± 0.001 | 0.95 ± 0.05 d | 9.33 ± 0.63 c | 72.72 ± 3.06 b | 27.28 ± 3.06 c |
| K-0.5 | 0.254 ± 0.003 a | 1.114 ± 0.073 cd | 0.982 ± 0.010 | 1.11 ± 0.04 b | 7.55 ± 0.25 d | 65.95 ± 3.17 c | 34.05 ± 3.17 b |
| K-1 | 0.244 ± 0.004 a | 2.118 ± 0.031 a | 0.993 ± 0.004 | 0.77 ± 0.03 e | 6.92 ± 0.35 d | 78.27 ± 1.22 a | 21.73 ± 1.22 d |
| K-1.5 | 0.251 ± 0.006 a | 1.254 ± 0.077 b | 0.980 ± 0.009 | 0.93 ± 0.09 d | 7.34 ± 0.50 d | 74.23 ± 0.72 b | 25.77 ± 0.72 c |
| Samples | Cooking Properties | Textural Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS (%) | CL (%) | Hardness (N) | Chewiness | Tensile Strength (g) | Breaking Distance (mm) | |
| Control | 130.73 ± 5.40 c | 4.49 ± 0.16 c | 52.74 ± 3.81 c | 183.35 ± 15.96 c | 66.82 ± 2.64 e | 43.03 ± 5.00 d |
| N-1 | 132.95 ± 3.22 c | 4.77 ± 0.07 c | 55.89 ± 3.57 c | 208.70 ± 11.94 c | 80.60 ± 1.18 bc | 57.18 ± 2.19 ab |
| N-2 | 133.37 ± 2.73 c | 4.82 ± 0.22 c | 56.94 ± 1.59 c | 216.81 ± 19.63 bc | 90.35 ± 2.81 a | 61.94 ± 2.75 a |
| N-3 | 135.28 ± 2.57 c | 4.89 ± 0.36 c | 56.14 ± 2.52 c | 211.89 ± 17.85 bc | 82.96 ± 2.87 b | 54.86 ± 3.03 b |
| K-0.5 | 146.35 ± 1.24 b | 5.92 ± 0.24 b | 58.89 ± 4.26 bc | 246.83 ± 21.87 b | 74.88 ± 1.58 cd | 46.45 ± 1.52 d |
| K-1 | 146.42 ± 1.75 b | 6.35 ± 0.24 b | 65.55 ± 3.83 a | 296.04 ± 28.52 a | 78.79 ± 6.13 bcd | 52.32 ± 3.91 bc |
| K-1.5 | 155.87 ± 5.36 a | 7.88 ± 0.09 a | 64.00 ± 3.62 ab | 282.48 ± 23.47 a | 72.56 ± 4.89 de | 48.56 ± 2.37 cd |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, M.; Cui, T.; Peng, Z.; Cheng, J. Moisture Distribution and Structural Properties of Frozen Cooked Noodles with NaCl and Kansui. Foods 2021, 10, 3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123132
Wang J, Ding Y, Wang M, Cui T, Peng Z, Cheng J. Moisture Distribution and Structural Properties of Frozen Cooked Noodles with NaCl and Kansui. Foods. 2021; 10(12):3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123132
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiarong, Yangyue Ding, Mingyang Wang, Tianqi Cui, Zeyu Peng, and Jianjun Cheng. 2021. "Moisture Distribution and Structural Properties of Frozen Cooked Noodles with NaCl and Kansui" Foods 10, no. 12: 3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123132
APA StyleWang, J., Ding, Y., Wang, M., Cui, T., Peng, Z., & Cheng, J. (2021). Moisture Distribution and Structural Properties of Frozen Cooked Noodles with NaCl and Kansui. Foods, 10(12), 3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123132