Development of Antioxidant-Fortified Oleogel and Its Application as a Solid Fat Replacer to Muffin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Oleogels
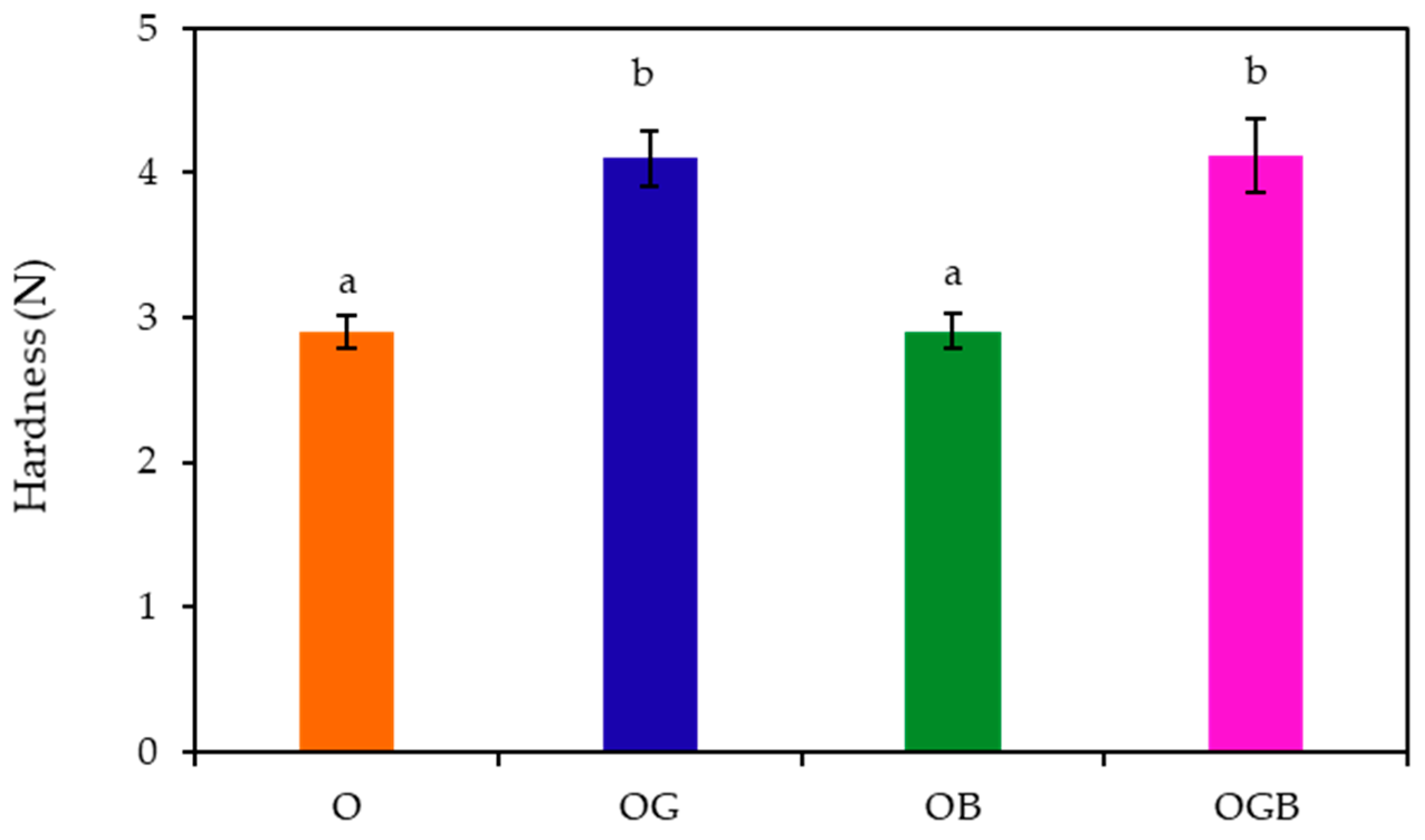
2.2. Textural Measurement of Oleogels
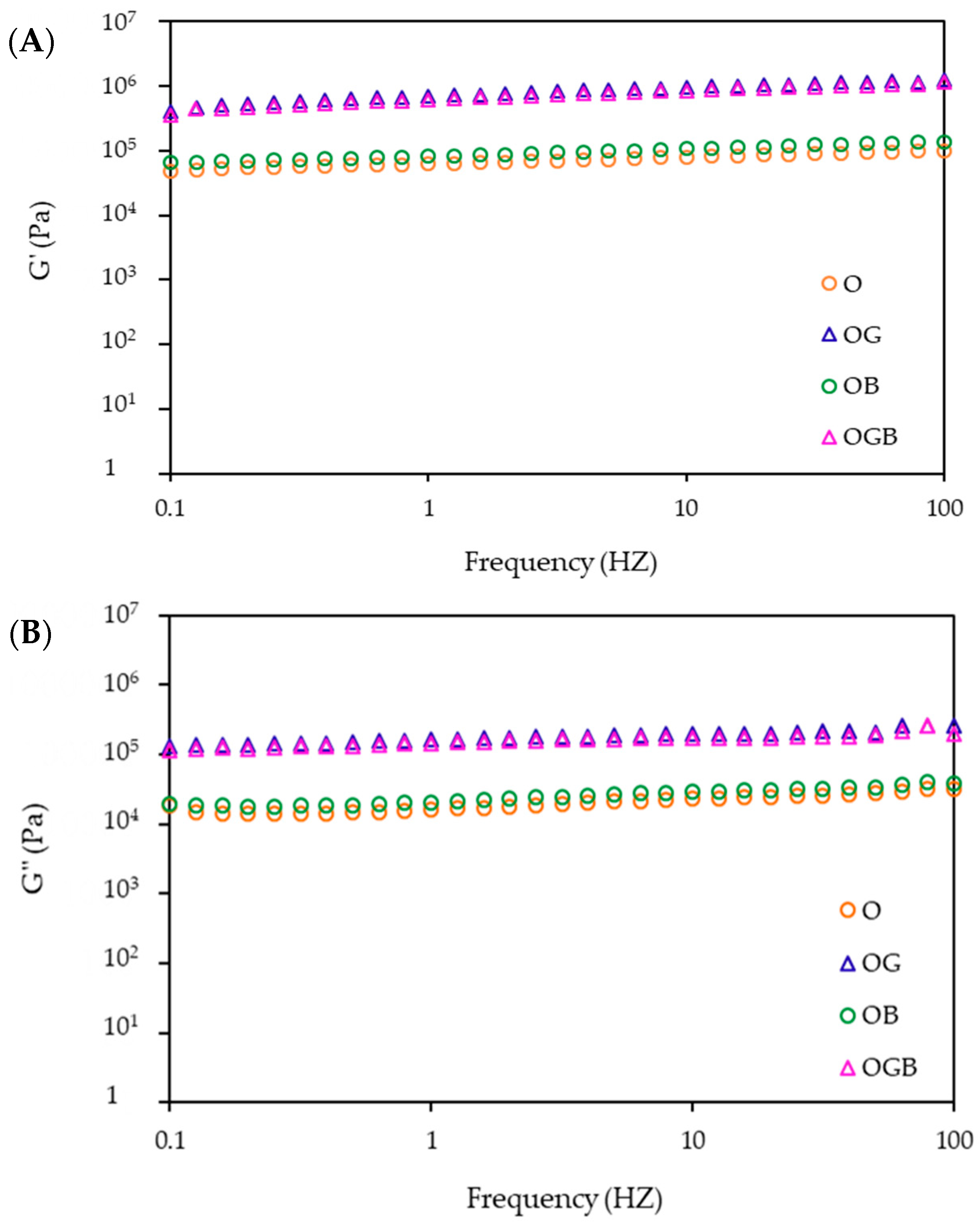
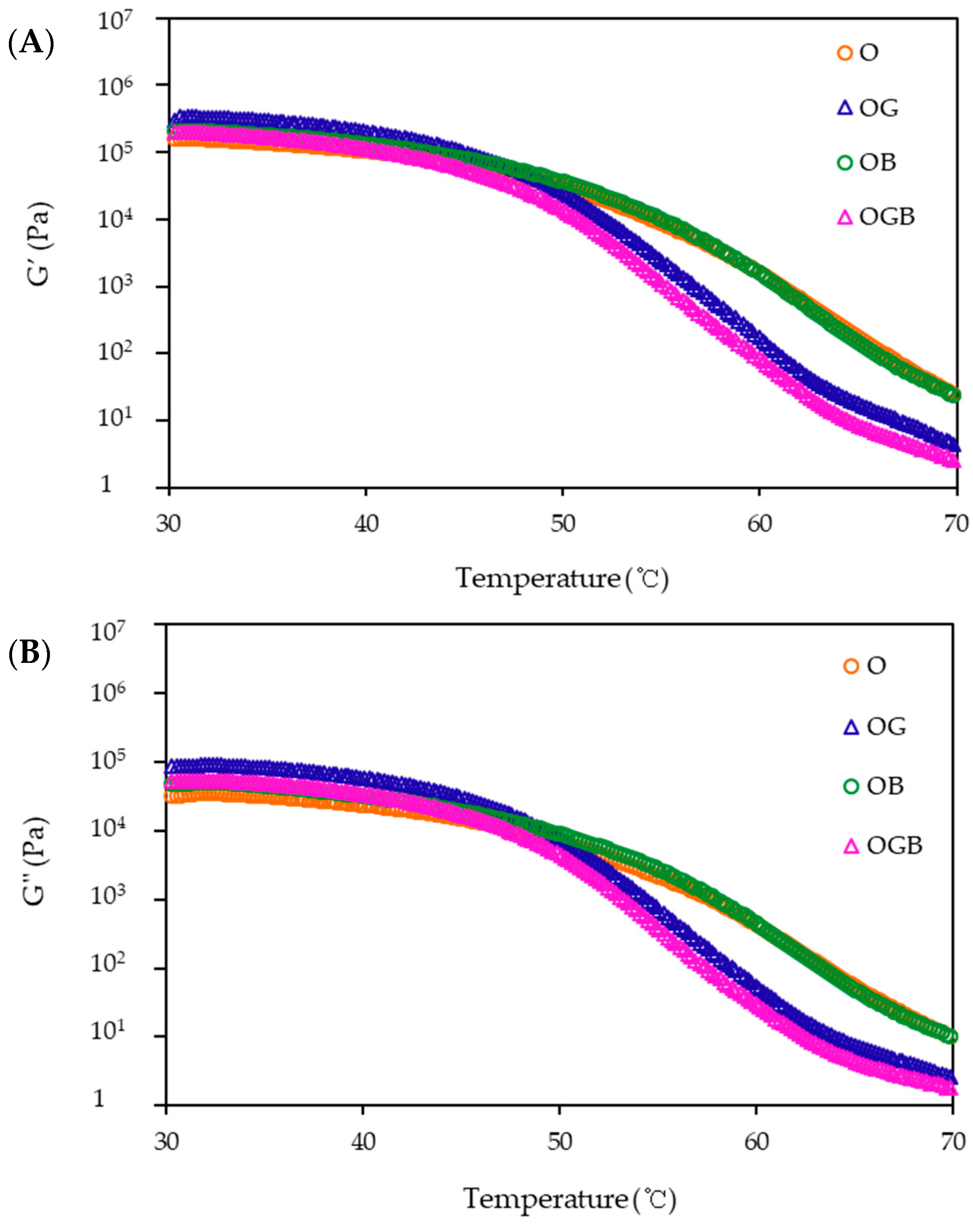
2.3. Rheological Measurement
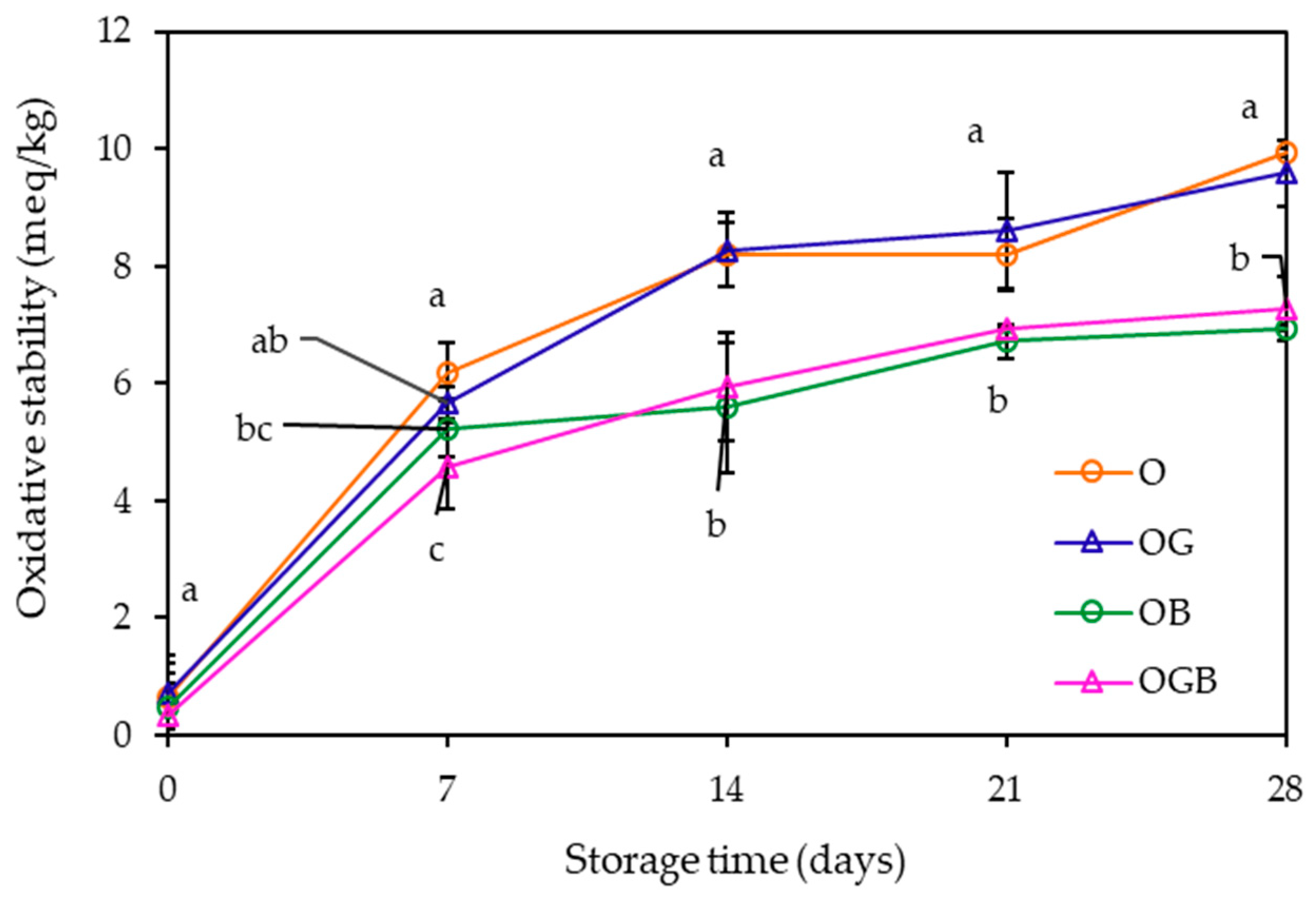
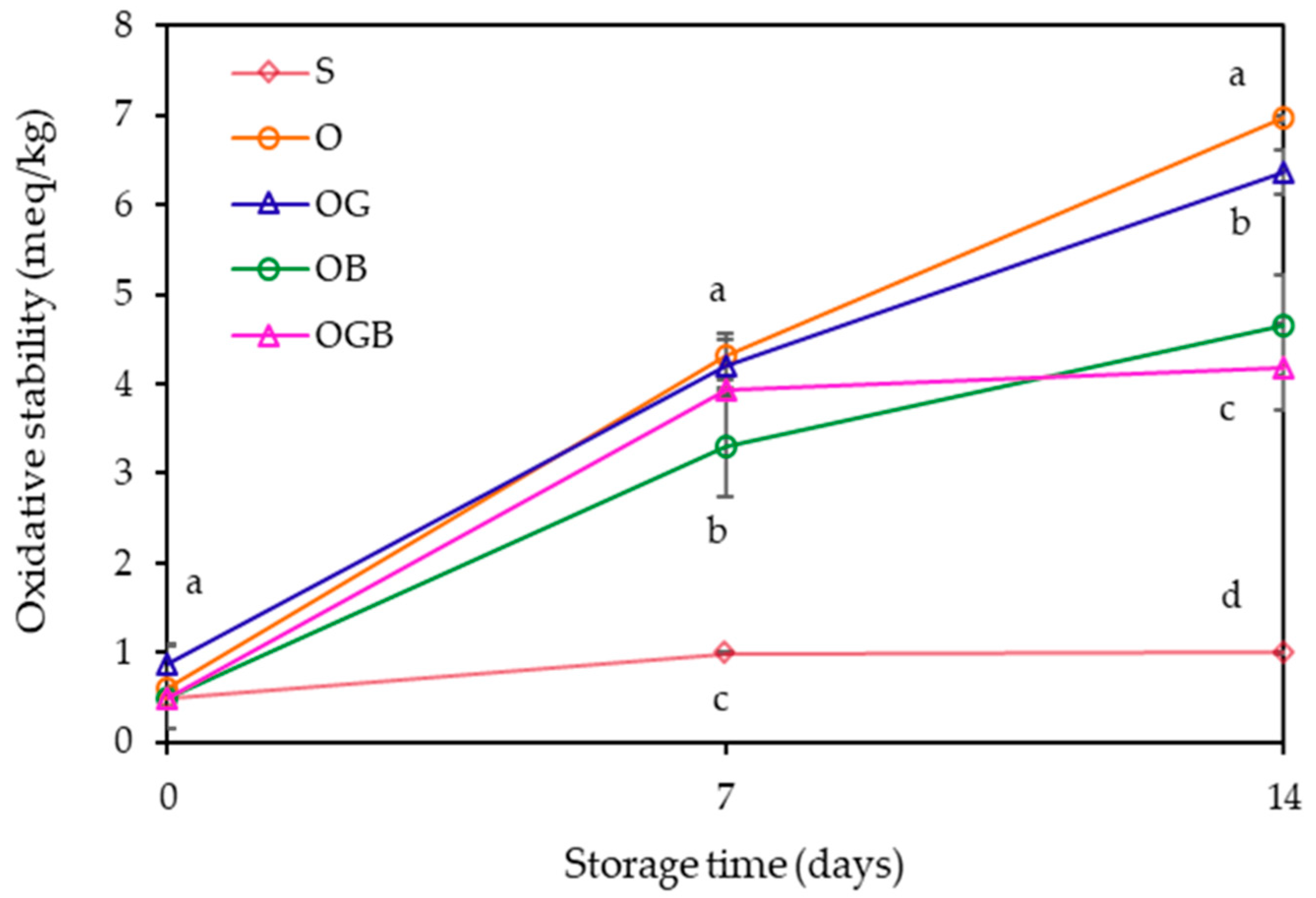
2.4. Oxidative Stability Measurement during Storage
2.5. Preparation of Muffins
2.6. Specific Gravity of Muffin Batter
2.7. Specific Volume of Muffin
2.8. Tomographic Analysis of Muffin Crumb
2.9. Textural Measurement
2.10. Color Measurement of Muffin
2.11. Oxidation Stability Measurement of Muffins
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Barbut, S.; Marangoni, A.G. The role of surfactants on ethylcellulose oleogel structure and eechanical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Co, E.; Marangoni, A. Organogels: An alternative edible oil-structuring method. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 749–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, I.K.; Amoah, C.; Lim, J.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S. Assessing the effectiveness of wax-based sunflower oil oleogels in cakes as a shortening replacer. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 86, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, B.; Demirkesen, I. Reducing saturated fat with oleogel/shortening blends in a baked product. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, I.K.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.G.; Lee, S. Feasibility of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose oleogel as an animal fat replacer for meat patties. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.J.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Cunha, R.L.; Vicente, A.A. Fortified beeswax oleogels: Effect of β-carotene on the gel structure and oxidative stability. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4241–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, S.; Martini, S. Physical characterization of crystalline networks formed by binary blends of waxes in soybean oil. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callau, M.; Sow-Kébé, K.; Nicolas-Morgantini, L.; Fameau, A.-L. Effect of the ratio between behenyl alcohol and behenic acid on the oleogel properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 560, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirkesen, I.; Mert, I.D. Recent developments of oleogel utilizations in bakery products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 60, 2460–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-Ramírez, D.; Lobato-Calleros, C.; Vernon-Carter, E.J.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J. Cooling rate, sorbitan and glyceryl monostearate gelators elicit different microstructural, viscoelastic and textural properties in chia seed oleogels. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Pramanik, K.; Ray, S.S.; Pal, K. Development and Characterization of Sorbitan Monostearate and Sesame Oil-Based Organogels for Topical Delivery of Antimicrobials. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 16, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barroso, N.G.; Okuro, P.K.; Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Cunha, R.L. Tailoring properties of mixed-component oleogels: Wax and monoglyceride interactions towards flaxseed oil structuring. Gels 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.O.; Hwang, H.S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, S. The thermal, rheological, and structural characterization of grapeseed oil oleogels structured with binary blends of oleogelator. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3432–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.J.; Nan, Y.; Liu, G.Q. The effects of oil type and crystallization temperature on the physical properties of vitamin C-loaded oleogels prepared by an emulsion-templated approach. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8028–8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Xu, X.; Qian, Z.; Cheng, H.; Shen, X.; Chen, S.; Ye, X. Xanthan gum-assisted fabrication of stable emulsion-based oleogel structured with gelatin and proanthocyanidins. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masotta, N.E.; Höcht, C.; Contin, M.; Lucangioli, S.; Rojas, A.M.; Tripodi, V.P. Bioavailability of coenzyme Q10 loaded in an oleogel formulation for oral therapy: Comparison with a commercial-grade solid formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 582, 119315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Pintado, T.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Cofrades, S. The effect of household storage and cooking practices on quality attributes of pork burgers formulated with PUFA- and curcumin-loaded oleogels as healthy fat substitutes. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 119, 108909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, K.; Tak, A.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, P.; Yousuf, B.; Wani, A.A. Chemistry, encapsulation, and health benefits of β-carotene—A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2015, 11, 1018696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chloe, M.; Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Wright, A.J.; Barbut, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Ethylcellulose oleogels for lipophilic bioactive delivery–effect of oleogelation on in vitro bioaccessibility and stability of beta-carotene. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1438–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; Fu, S.Y.; Hou, J.J.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.M.; Yang, X.Q. Zein based oil-in-glycerol emulgels enriched with β-carotene as margarine alternatives. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lim, J.; Lee, J.; Hwang, H.-S.; Lee, S. Utilization of Oleogels as a Replacement for Solid Fat in Aerated Baked Goods: Physicochemical, Rheological, and Tomographic Characterization. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, A.I.; Marangoni, A.G. The effect of shear on the microstructure and oil binding capacity of wax crystal networks. Food Biophys. 2015, 10, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y. Extraction of rutin from tartary buckwheat milling fractions and evaluation of its thermal stability in an instant fried noodle system. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association of Cereal Chemists (AACC). Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, 10th ed.; Cereals & Grains Association: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000; Available online: https://www.cerealsgrains.org/resources/Methods/Pages/10BakingQuality.aspx (accessed on 18 October 2021).
- Franco, D.; Martins, A.J.; López-Pedrouso, M.; Purriños, L.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Vicente, A.A.; Pastrana, L.M.; Zapata, C.; Lorenzo, J.M. Strategy towards replacing pork backfat with a linseed oleogel in frankfurter sausages and its evaluation on physicochemical, nutritional, and sensory characteristics. Foods 2019, 8, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kupiec, M.; Zbikowska, A.; Marciniak-Lukasiak, K.; Kowalska, M. Rapeseed Oil in New Application: Assessment of Structure of Oleogels Based on their Physicochemical Properties and Microscopic Observations. Agriculture 2020, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, T.L.T.; Chaves, K.F.; Fernandes, G.D.; Rodrigues, J.B.; Bolini, H.M.A.; Arellano, D.B. Sensory and Technological Evaluation of Margarines With Reduced Saturated Fatty Acid Contents Using Oleogel Technology. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Mao, L.; Lu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Effect of monoglyceride content on the solubility and chemical stability of β-carotene in organogels. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 106, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Tang, L.; Dong, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Effect of oleogelation on physical properties and oxidative stability of camellia oil-based oleogels and oleogel emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Bemer, H.L.; Maleky, F. Oxidative Stability of Rice Bran Wax Oleogels and an Oleogel Cream Cheese Product. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulp, K.; Loewe, R.; Lorenz, K.; Gelroth, J. Batters and Breadings in Food Processing, 2nd ed.; Cereals & Grains Association: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-891127-71-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wilderjans, E.; Luyts, A.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Ingredient functionality in batter type cake making. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 30, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Bae, I.Y.; Park, H.-G.; Lee, H.; Lee, S. (1-3)(1-6)-β-Glucan-Enriched Materials from Lentinus Edodes Mushroom as a High-Fibre and Low-Calorie Flour Substitute for Baked Foods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsaragkou, K.; Papantoniou, M.; Mandala, I. Rheological, physical, and sensory attributes of gluten-free rice cakes containing resistant starch. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donis-Gonzalez, I.R.; Guyer, D.E.; Pease, A.; Barthel, F. Internal characterisation of fresh agricultural products using traditional and ultrafast electron beam X-ray computed tomography imaging. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 117, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, L.; Williams, P.; du Plessis, A.; Manley, M. X-ray micro-computed tomography (microCT) for non-destructive characterisation of food microstructure. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 47, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OH, I.K.; Lee, S. Utilization of foam structured hydroxypropyl methylcellulose for oleogels and their application as a solid fat replacer in muffins. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Cludts, N.; Sintang, M.D.B.; Lesaffer, A.; Dewettinck, K. Edible oleogels based on water soluble food polymers: Preparation, characterization and potential application. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| S | O | OG | OB | OGB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific gravity of batter | 0.97 ± 0.00 b | 1.13 ± 0.00 a | 1.13 ± 0.01 a | 1.13 ± 0.01 a | 1.12 ± 0.01 a |
| Specific volume of muffin (mL g−1) | 1.71 ± 0.02 a | 1.58 ± 0.11 bc | 1.62 ± 0.01 abc | 1.52 ± 0.06 c | 1.65 ± 0.02 ab |
| Cross-sectional micro-CT image of muffin | 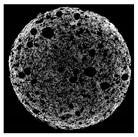 | 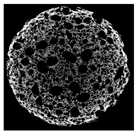 | 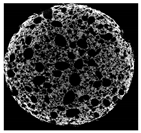 | 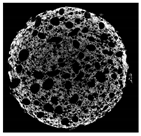 | 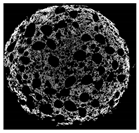 |
| Total porosity (%) | 63.91 ± 2.85 a | 62.89 ± 1.90 a | 62.79 ± 1.28 a | 62.45 ± 1.43 a | 62.16 ± 1.80 a |
| Visual Appearance of Muffin | S 1 | O | OG | OB | OGB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 day (before storage) |  |  |  |  |  |
| 14 day (after storage) |  |  |  |  |  |
| Texture | S 1 | O | OG | OB | OGB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (N) | 2.34 ± 0.48 d 2,3 | 10.16 ± 0.38 b | 7.92 ± 0.87 c | 11.49 ± 1.01 a | 7.89 ± 0.71 c |
| Springiness (mm) | 0.86 ± 0.01 a | 0.85 ± 0.03 a | 0.78 ± 0.01 b | 0.86 ± 0.01 a | 0.81 ± 0.02 b |
| Cohesiveness | 0.78 ± 0.07 a | 0.65 ± 0.02 b | 0.53 ± 0.02 c | 0.64 ± 0.01 b | 0.58 ± 0.01 c |
| Chewiness (J) | 1.84 ± 0.29 e | 6.50 ± 0.29 b | 3.69 ± 0.52 d | 7.87 ± 0.52 a | 4.40 ± 0.34 c |
| Color | S 1 | O | OG | OB | OGB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | 61.63 ± 0.49 d 2,3 | 63.22 ± 0.37 b | 63.84 ± 0.46 a | 60.97 ± 0.27 e | 62.54 ± 0.31 c |
| a* | 9.79 ± 0.30 b | 9.31 ± 0.22 c | 9.51 ± 0.28 bc | 11.19 ± 0.26 a | 10.95 ± 0.28 a |
| b* | 28.01 ± 0.37 c | 27.85 ± 0.42 c | 26.86 ± 0.31 d | 50.06 ± 0.47 a | 47.86 ± 0.14 b |
| C* | 29.67 ± 0.44 c | 29.60 ± 0.43 c | 28.50 ± 0.32 d | 51.30 ± 0.52 a | 49.09 ± 0.09 b |
| H° | 70.75 ± 0.33 c | 71.51 ± 0.39 b | 70.51 ± 0.53 c | 77.40 ± 0.18 a | 77.11 ± 0.35 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.; Lee, S.; Oh, I. Development of Antioxidant-Fortified Oleogel and Its Application as a Solid Fat Replacer to Muffin. Foods 2021, 10, 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123059
Jeong S, Lee S, Oh I. Development of Antioxidant-Fortified Oleogel and Its Application as a Solid Fat Replacer to Muffin. Foods. 2021; 10(12):3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123059
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Sohui, Suyoung Lee, and Imkyung Oh. 2021. "Development of Antioxidant-Fortified Oleogel and Its Application as a Solid Fat Replacer to Muffin" Foods 10, no. 12: 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123059
APA StyleJeong, S., Lee, S., & Oh, I. (2021). Development of Antioxidant-Fortified Oleogel and Its Application as a Solid Fat Replacer to Muffin. Foods, 10(12), 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123059







