Low Acrylamide Flatbreads Prepared from Colored Rice Flours and Relationship to Asparagine and Proximate Content of Flours and Flatbreads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Flatbread Preparation Process
2.4. Flatbread Proximate Composition Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Acrylamide Contents of Flatbreads
2.6. Analysis of Free Asparagine in Rice Flours and Flatbreads by Ion-Exchange Chromatography
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
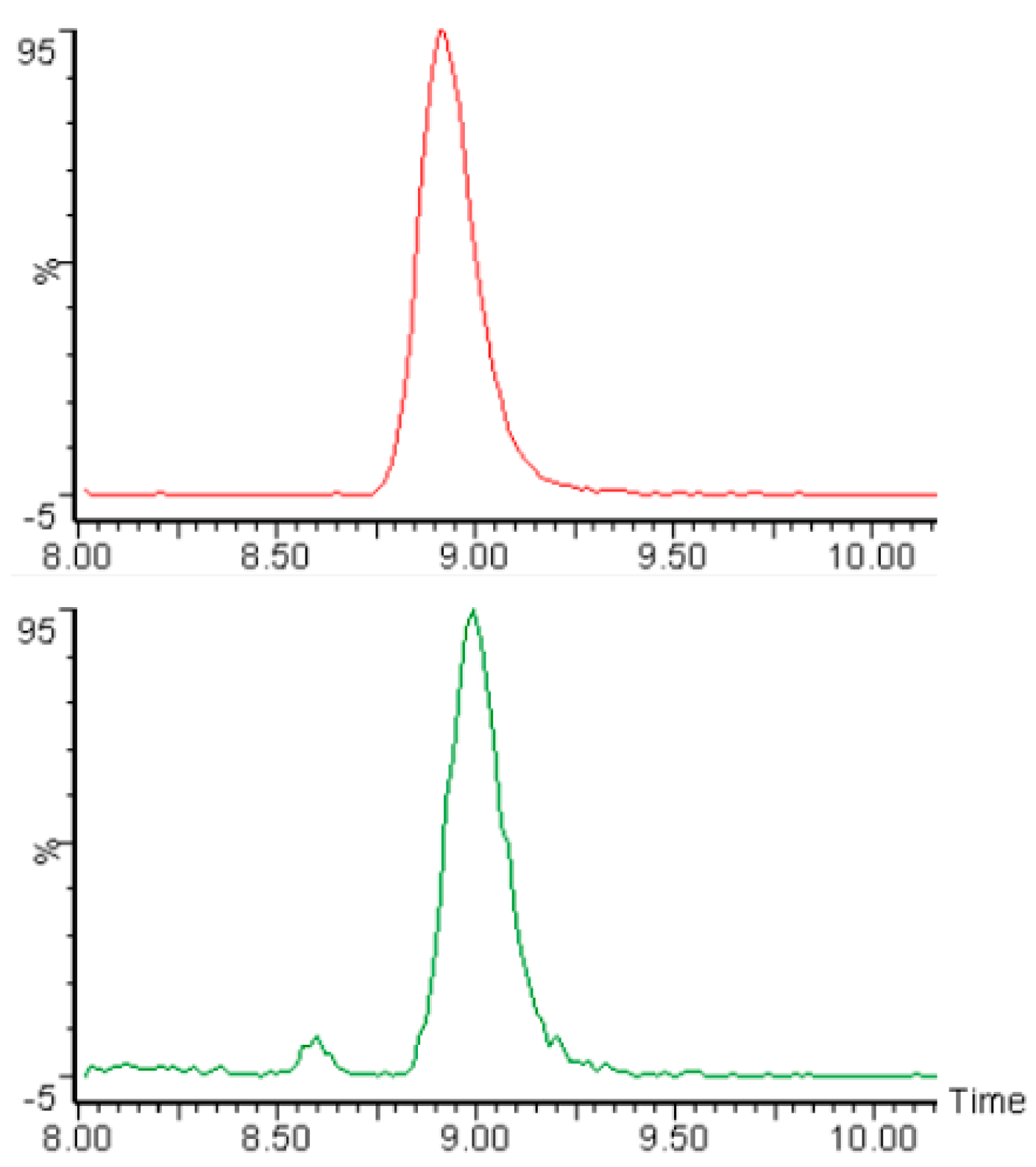
3.1. Accuracy, Precision, and Sensitivity of the Analytical Method for Acrylamide
3.2. Acrylamide Content of Flatbreads
3.3. Proximate Composition of Flatbreads—Relationship to Acrylamide Content
3.4. Acrylamide–Asparagine Relationships of Flatbreads
3.5. Health Benefits of Pigmented Rice and Its Components
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, M. Biological effects of Maillard browning products that may affect acrylamide safety in food. In Chemistry and Safety of Acrylamide in Food; Friedman, M., Mottram, D., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adani, G.; Filippini, T.; Wise, L.A.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Blaha, L.; Vinceti, M. Dietary intake of acrylamide and risk of breast, endometrial, and ovarian cancers: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hölzl-Armstrong, L.; Kucab, J.E.; Moody, S.; Zwart, E.P.; Loutkotová, L.; Duffy, V.; Luijten, M.; Gamboa da Costa, G.; Stratton, M.R.; Phillips, D.H.; et al. Mutagenicity of acrylamide and glycidamide in human TP53 knock-in (Hupki) mouse embryo fibroblasts. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 4173–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, M.; Dai, Y.; Fang, X.; Chen, K.; Liu, Q.; Xue, A.; Zhong, K.; Huang, Y.; et al. Acrylamide exposure represses neuronal differentiation, induces cell apoptosis and promotes tau hyperphosphorylation in hESC-derived 3D cerebral organoids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 144, 111643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayburn, J.R.; Friedman, M. L-Cysteine, N-acetyl-L-cysteine, and glutathione protect Xenopus laevis embryos against acrylamide-induced malformations and mortality in the Frog Embryo Teratogenesis Assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11172–11178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R.; Rayburn, J.R.; Cline, G.R.; Sauterer, R.; Friedman, M. The potential protective effect of L-cysteine against the toxicity of acrylamide and furan in exposed Xenopus laevis embryos: An interaction study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7927–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanski, F.; de Oliveira, V.M.; de Oliveira, I.M.; de Araújo Ramos, A.T.; de Oliveira Tonete, S.T.; de Oliveira Hykavei, G.; Bargi-Souza, P.; Schiessel, D.L.; Martino-Andrade, A.J.; Romano, M.A.; et al. Prepubertal acrylamide exposure causes dose-response decreases in spermatic production and functionality with modulation of genes involved in the spermatogenesis in rats. Toxicology 2020, 436, 152428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Lear, M.; Sedej, I.; Holstege, D.M.; Friedman, M.; McHugh, T.H.; Wang, S.C. Evaluation of thermal processing variables for reducing acrylamide in canned black ripe olives. J. Food Eng. 2016, 191, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crawford, L.M.; Kahlon, T.S.; Chiu, M.-C.M.; Wang, S.C.; Friedman, M. Acrylamide content of experimental and commercial flatbreads. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, L.M.; Kahlon, T.S.; Wang, S.C.; Friedman, M. Acrylamide content of experimental flatbreads prepared from potato, quinoa, and wheat flours with added fruit and vegetable peels and mushroom powders. Foods 2019, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Kahlon, T.; Wang, S.C.; Friedman, M. Low acrylamide flatbreads from colored corn and other flours. Foods 2021, 10, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed.; Horwitz, W., Ed.; AOAC International: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rombouts, I.; Lagrain, B.; Lamberts, L.; Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Wheat gluten amino acid analysis by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with integrated pulsed amperometric detection. In Amino Acid Analysis: Methods and Protocols; Alterman, M.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2030, pp. 381–394. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, F.; Velotto, S.; Rea, T.; Stasi, T.; Cirillo, T. Occurrence of acrylamide in Italian baked products and dietary exposure assessment. Molecules 2020, 25, 4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirot, V.; Hommet, F.; Tard, A.; Leblanc, J.C. Dietary acrylamide exposure of the French population: Results of the second French Total Diet Study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Cai, Y.Z.; Ke, J.; Corke, H. Dietary plant materials reduce acrylamide formation in cookie and starch-based model systems. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Jin, C.; Zhang, Y. Investigation of variations in the acrylamide and Nε-(carboxymethyl) lysine contents in cookies during baking. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, T1030–T1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, E.; Robin, L.P.; McGrath, S.; Srinivasan, J.; DiNovi, M.; Adachi, Y.; Chirtel, S. Acrylamide levels and dietary exposure from foods in the United States, an update based on 2011-2015 data. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 1475–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granby, K.; Nielsen, N.J.; Hedegaard, R.V.; Christensen, T.; Kann, M.; Skibsted, L.H. Acrylamide–asparagine relationship in baked/toasted wheat and rye breads. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2008, 25, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belkova, B.; Chytilova, L.; Kocourek, V.; Slukova, M.; Mastovska, K.; Kyselka, J.; Hajslova, J. Influence of dough composition on the formation of processing contaminants in yeast-leavened wheat toasted bread. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platat, C.; Habib, H.M.; Hashim, I.B.; Kamal, H.; AlMaqbali, F.; Souka, U.; Ibrahim, W.H. Production of functional pita bread using date seed powder. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6375–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bråthen, E.; Knutsen, S.H. Effect of temperature and time on the formation of acrylamide in starch-based and cereal model systems, flat breads and bread. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Nutritional value of proteins from different food sources. A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 6–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.; Finot, P.A. Nutritional improvement of bread with lysine and γ-glutamyllysine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdyk, N.; Rosén, J.; Andersson, R.; Åman, P. Effects of asparagine, fructose, and baking conditions on acrylamide content in yeast-leavened wheat bread. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2047–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreschi, F.; Kaack, K.; Granby, K. The effect of asparaginase on acrylamide formation in French fries. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Peters, R.J.; Van Boekel, M.A. Acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation during baking of biscuits: Part I: Effects of sugar type. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.I.; van Boekel, M. Acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation during biscuit baking. Part II: Effect of the ratio of reducing sugars and asparagine. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, X.; Nan, S.; Zeng, X.; Kang, L.; Liu, X.; Dai, Y. Inhibition kinetics and mechanism of glutathione and quercetin on acrylamide in the low-moisture Maillard systems. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıltırak, S.; Kocadağlı, T.; Çelik, E.E.; Özkaynak Kanmaz, E.; Gökmen, V. Effects of sprouting and fermentation on free asparagine and reducing sugars in wheat, einkorn, oat, rye, barley, and buckwheat and on acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation during heating. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9419–9433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivanti, V.; Finotti, E.; Friedman, M. Level of acrylamide precursors asparagine, fructose, glucose, and sucrose in potatoes sold at retail in Italy and in the United States. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C81–C85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulev, A.; Heckman, J.R.; Raskin, I.; Belanger, F.C. Tricin levels and expression of flavonoid biosynthetic genes in developing grains of purple and brown pericarp rice. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Rice brans, rice bran oils, and rice hulls: Composition, food and industrial uses, and bioactivities in humans, animals, and cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10626–10641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, V.C.; Lacerda, L.G. Black rice (Oryza sativa L.): A review of its historical aspects, chemical composition, nutritional and functional properties, and applications and processing technologies. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracassetti, D.; Pozzoli, C.; Vitalini, S.; Tirelli, A.; Iriti, M. Impact of cooking on bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of pigmented rice cultivars. Foods 2020, 9, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melini, V.; Acquistucci, R. Health-promoting compounds in pigmented Thai and wild rice. Foods 2017, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu, M.J.; Du, Y.M.; Liu, X.M.; Yan, N.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, Z.F. Extraction of proanthocyanidins from Chinese wild rice (Zizania latifolia) and analyses of structural composition and potential bioactivities of different fractions. Molecules 2019, 24, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vitalini, S.; Sardella, A.; Fracassetti, D.; Secli, R.; Tirelli, A.; Lodi, G.; Carrassi, A.; Varoni, E.M.; Iriti, M. Polyphenol bioavailability and plasma antiradical capacity in healthy subjects after acute intake of pigmented rice: A crossover randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, W.K.; Lee, H.W.; Shin, A.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, S.A.; Lee, J.E.; Kang, D. Multi-grain rice diet decreases risk of breast cancer in Korean women: Results from the health examinees study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Cheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Xue, M.; Liang, H. Red yeast rice ameliorates high-fat diet-induced atherosclerosis in Apoe(−/−) mice in association with improved inflammation and altered gut microbiota composition. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3880–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.-H.; Choi, S.H.; Kozukue, N.; Kim, H.-J.; Friedman, M. Growth-inhibitory effects of pigmented rice bran extracts and three red bran fractions against human cancer cells: Relationships with composition and antioxidative activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9151–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.P.; Kang, M.Y.; Nam, S.H.; Friedman, M. Dietary rice bran component γ-oryzanol inhibits tumor growth in tumor-bearing mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.P.; Kim, S.P.; Nam, S.H.; Friedman, M. Antitumor effects of dietary black and brown rice brans in tumor-bearing mice: Relationship to composition. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.P.; Lee, S.J.; Nam, S.H.; Friedman, M. The composition of a bioprocessed shiitake (Lentinus edodes) mushroom mycelia and rice bran formulation and its antimicrobial effects against Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium strain SL1344 in macrophage cells and in mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, P.; Li, J.; Gao, S.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, L.; Shi, J. Network pharmacology-based and experimental identification of the effects of quercetin on Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 589588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Ullah, H.; Aschner, M.; Cheang, W.S.; Akkol, E.K. Neuroprotective effects of quercetin in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira-Caro, G.; Watanabe, S.; Crozier, A.; Fujimura, T.; Yokota, T.; Ashihara, H. Phytochemical profile of a Japanese black-purple rice. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.P.; Lee, J.R.; Kwon, K.S.; Jang, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Yu, K.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Friedman, M. A bioprocessed black rice bran glutathione-enriched yeast extract protects rats and mice against alcohol-induced hangovers. Food Nutr. Sci. 2021, 12, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheang, I.; Liao, S.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Yao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. Association of acrylamide hemoglobin biomarkers with serum lipid levels in general US population: NHANES 2013–2016. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemgesberg, M.; Stegmüller, S.; Cartus, A.; Hemmer, S.; Püttmann, M.; Stockis, J.P.; Schrenk, D. Acrylamide-derived DNA adducts in human peripheral blood mononuclear cell DNA: Correlation with body mass. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 157, 112575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Flatbread | Rice Flour (g) | Guar Gum (g) | Salt (g) | Olive Oil (mL) | Water (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black Japonica Rice | 47.82 | 1.91 | 0.53 | 1.91 | 47.82 |
| Chinese Black Rice | 41.82 | 1.67 | 0.46 | 1.67 | 54.37 |
| French Camargue Rice | 47.82 | 1.91 | 0.53 | 1.91 | 47.82 |
| Himalayan Red Rice | 47.82 | 1.91 | 0.53 | 1.91 | 47.82 |
| Long Grain Brown Rice | 47.82 | 1.91 | 0.53 | 1.91 | 47.82 |
| Purple Sticky Rice | 46.71 | 1.87 | 0.51 | 1.87 | 49.04 |
| Short Grain Brown Rice | 47.82 | 1.91 | 0.53 | 1.91 | 47.82 |
| Wehani Rice (red-brown) | 46.71 | 1.87 | 0.51 | 1.87 | 49.04 |
| Wild Rice (broken; black) | 43.65 | 1.75 | 0.48 | 1.75 | 52.38 |
| Indian Brown Basmati Rice | 47.82 | 1.91 | 0.53 | 1.91 | 47.82 |
| Organic Brown Jasmine Rice | 47.82 | 1.91 | 0.53 | 1.91 | 47.82 |
| Organic Jade Pearl Rice (green) | 41.82 | 1.67 | 0.46 | 1.67 | 54.37 |
| Flour Type | Acrylamide * (µg/kg) |
|---|---|
| Black Japonica Rice | 50.5 ± 6.1 a |
| Chinese Black Rice | 50.8 ± 8.8 a |
| French Camargue Rice | 24.45 ± 0.66 f |
| Himalayan Red Rice | 7.1 ± 1.1 h |
| Long Grain Brown Rice ** | 4.9 ± 1.4 h |
| Purple Sticky Rice | 7.5 ± 1.7 h |
| Short Grain Brown Rice | 19.5 ± 3.0 g |
| Wehani Rice | 33.9 ± 2.8 e |
| Wild Rice (broken) | 45.0 ± 4.6 b |
| Indian Brown Basmati Rice | 37.7 ± 6.5 d |
| Organic Brown Jasmine Rice | 37.7 ± 2.5 d |
| Organic Jade Pearl Rice | 41.9 ± 5.1 c |
| Flatbreads | Protein ** (N × 5.95) (g) | Crude Fat (g) | Ash (g) | Total Carbohydrates (g) | Dry Matter (DM) (g) | Water (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black Japonica Rice | 4.512 ± 0.071 b | 10.13 ± 0.33 a | 2.355 ± 0.010 a | 47.73 ± 0.52 d | 63.87 ± 0.43 | 36.13 ± 0.43 |
| Chinese Black Rice | 3.107 ± 0.040 h | 7.55 ± 0.30 d | 2.048 ± 0.030 g | 44.76 ± 1.3 h | 56.6 ± 1.1 | 43.4 ± 1.1 |
| French Camargue Rice | 3.665 ± 0.050 f | 8.92 ± 0.42 b | 2.3260 ± 0.0067 b | 47.90 ± 0.62 c | 61.93 ± 0.68 | 38.06 ± 0.68 |
| Himalayan Red Rice | 3.637 ± 0.010 f | 9.78 ± 0.24 a | 1.9850 ± 0.0093 f | 48.06 ± 0.18 c | 62.73 ± 0.47 | 37.27 ± 0.47 |
| Long Grain Brown Rice | 3.685 ± 0.027 f | 9.70 ± 0.68 a | 2.297 ± 0.013 bc | 47.60 ± 0.24 d | 62.42 ± 0.50 | 37.58 ± 0.50 |
| Purple Sticky Rice | 4.027 ± 0.20 d | 10.13 ± 0.62 a | 2.2300 ± 0.0048 d | 46.81 ± 0.94 f | 62.36 ± 0.17 | 37.63 ± 0.17 |
| Short Grain Brown Rice | 3.037 ± 0.51 i | 9.09 ± 0.18 b | 2.233 ± 0.010 d | 48.68 ± 0.50 a | 62.199 ± 0.055 | 37.801 ± 0.055 |
| Wehani Rice | 3.818 ± 0.53 e | 9.30 ± 0.78 b | 2.400 ± 0.014 b | 46.08 ± 0.50 g | 60.6 ± 1.2 | 39.4 ± 1.2 |
| Wild Rice (broken) | 4.836 ± 0.72 a | 6.12 ± 0.64 f | 2.268 ± 0.019 e | 46.14 ± 0.28 g | 58.42 ± 0.32 | 41.58 ± 0.32 |
| Indian Brown Basmati Rice | 4.417 ± 0.84 c | 8.91 ± 0.48 bc | 2.164 ± 0.040 e | 47.42 ± 2.31 e | 62.1 ± 1.5 | 37.9 ± 1.5 |
| Organic Brown Jasmine Rice | 3.256 ± 0.11 g | 7.77 ± 0.56 d | 2.047 ± 0.010 f | 48.56 ± 1.3 a | 60.83 ± 0.62 | 39.16 ± 0.62 |
| Organic Jade Pearl Rice | 3.247 ± 0.069 g | 7.23 ± 0.54 de | 1.391 ± 0.029 h | 48.26 ± 1.4 b | 59.5 ± 1.7 | 40.5 ± 1.7 |
| Flour Asparagine | Flatbread Asparagine | |
|---|---|---|
| 507.0 ± 9.9 | 458.5 ± 6.4 | |
| Chinese Black Rice | 1179 ± 32 | 1085 ± 17 |
| French Camargue Rice | 427 ± 15 | 377 ± 16 |
| Himalayan Red Rice | 218 ± 11 | 205.50 ± 0.71 |
| Long Grain Brown Rice | 146.5 ± 2.1 | 173.0 ± 8.5 |
| Purple Sticky Rice | 116.0 ± 8.5 | 120.0 ± 2.8 |
| Short Grain Brown Rice | 284.0 ± 2.8 | 251.5 ± 4.9 |
| Wehani Rice | 382 ± 13 | 304 ± 18 |
| Wild Rice (broken) | 130.5 ± 3.5 | 147.0 ± 2.8 |
| Indian Brown Basmati Rice | 405.0 ± 4.2 | 367.0 ± 4.2 |
| Organic Brown Jasmine Rice | 216.0 ± 2.8 | 211.50 ± 0.71 |
| Organic Jade Pearl Rice | 93.0 ± 1.4 | 94.5 ± 3.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Kahlon, T.; Wang, S.C.; Friedman, M. Low Acrylamide Flatbreads Prepared from Colored Rice Flours and Relationship to Asparagine and Proximate Content of Flours and Flatbreads. Foods 2021, 10, 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122909
Li X, Kahlon T, Wang SC, Friedman M. Low Acrylamide Flatbreads Prepared from Colored Rice Flours and Relationship to Asparagine and Proximate Content of Flours and Flatbreads. Foods. 2021; 10(12):2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122909
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xueqi, Talwinder Kahlon, Selina C. Wang, and Mendel Friedman. 2021. "Low Acrylamide Flatbreads Prepared from Colored Rice Flours and Relationship to Asparagine and Proximate Content of Flours and Flatbreads" Foods 10, no. 12: 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122909
APA StyleLi, X., Kahlon, T., Wang, S. C., & Friedman, M. (2021). Low Acrylamide Flatbreads Prepared from Colored Rice Flours and Relationship to Asparagine and Proximate Content of Flours and Flatbreads. Foods, 10(12), 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122909






