A Comparison of Fresh Pork Colour Measurements by Using Four Commercial Handheld Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measuring Canadian Pork Colour Standards
2.2. Instrumental Measurements of Commercial Pork
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Instrumental Comparison on Canadian Colour Standard
3.2. Instrumental Comparison on Retail Meat Samples
3.3. Instrumental Measurements and Subjective Standards
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, D.A.; Shackelford, S.D.; Wheeler, T.L. Use of visible and near-infrared spectroscopy to predict pork longissimus lean color stability. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 4195–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ngapo, T.M. Consumer preferences for pork chops in five Canadian provinces. Meat Sci. 2017, 129, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngapo, T.M.; Martin, J.F.; Dransfield, E. International preferences for pork appearance: II. Factors influencing consumer choice. Food Qual. Prefer. 2007, 18, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrer, B.M.; Boler, D.D. REVIEW: Subjective pork quality evaluation may not be indicative of instrumental pork quality measurements on a study-to-study basis. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2017, 33, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIE. Recommendations on Uniform Color Spaces—Color-Difference Equations, Psychometric Color Terms = Recommandations Sur Les Espaces Chromatiques Uniformes—Les Formules de Difference de Couleur, Les Termes Psychometriques de la Couleur; Bureau Central de la CIE: Paris, France, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Tapp, W.N.; Yancey, J.W.S.; Apple, J.K. How is the instrumental color of meat measured? Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NPPC. Official Color and Marbling Standards; The Pork Producers Council: Des Moines, IA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Holman, B.W.B.; Collins, D.; Kilgannon, A.K.; Hopkins, D.L. The effect of technical replicate (repeats) on Nix Pro Color Sensor™ measurement precision for meat: A case-study on aged beef colour stability. Meat Sci. 2018, 135, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, B.W.B.; Hopkins, D.L. A comparison of the Nix Colour Sensor Pro™ and HunterLab MiniScan™ colorimetric instruments when assessing aged beef colour stability over 72 h display. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, B.W.B.; Kerr, M.J.; Morris, S.; Hopkins, D.L. The identification of dark cutting beef carcasses in Australia, using Nix Pro Color Sensor™ colour measures, and their relationship to bolar blade, striploin and topside quality traits. Meat Sci. 2019, 148, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Bohrer, B.; Lopez-Campos, O.; Prieto, N.; Uttaro, B.; Juarez, M. Comparing Nix sensor and Minolta colourimeter to measure instrumental colour in fresh pork. In Proceedings of the Banff Pork Seminar, University of Alberta, Banff, AB, Canada, 7–9 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, D.S.; Buhler, J.F.; Stafford, C.D.; Keele, N.E.; Esco, A.N.; Yang, J.; Matarneh, S. Color muse colorimeter as an alternative method for measuring color in meat. In Proceedings of the 73rd Reciprocal Meat Conference, Virtual, 3–6 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Maignel, L.; Fortier, M.P.; Lambert, P.; Riendeau, L.; Wyss, S.; Sullivan, B. Defining carcass and meat quality standards for Canadian pork: Meat colour. In Proceedings of the 58th International Congress of Meat Science and Technology, Montreal, QC, Canada, 12–17 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, H.; Saito, F.; Ikeda, T.; Ando, S.; Kamatsu, A. Standard models of pork-colour. Bull. Natl. Inst. Anim. Ind. 1975, 29, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, M.S.; Novakofski, J.; Freise, K. Instrumental evaluation of pH effects on ability of pork chops to bloom. Meat Sci. 2006, 72, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Variable Inc. Introducing Spectro 1 Pro. Available online: https://variableinc.com/spectro-1-pro.html (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Nix Sensor Ltd. Nix Hardware Comparison. Available online: https://www.nixsensor.com/compare-nixes/ (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Mason, R.L.; Gunst, R.F.; Hess, J.L. Statistical Design and Analysis of Experiments: With Applications to Engineering and Science; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 474. [Google Scholar]
- Girolami, A.; Napolitano, F.; Faraone, D.; Braghieri, A. Measurement of meat color using a computer vision system. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, B.W.B.; Ponnampalam, E.N.; van de Ven, R.J.; Kerr, M.G.; Hopkins, D.L. Lamb meat colour values (HunterLab CIE and reflectance) are influenced by aperture size (5 mm v. 25 mm). Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giavarina, D. Understanding Bland Altman analysis. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, M.S.; Zhu, L.G.; Bidner, B.; Meisinger, D.J.; McKeith, F.K. Measuring pork color: Effects of bloom time, muscle, pH and relationship to instrumental parameters. Meat Sci. 2001, 57, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D. A Practical Guide to Machine Vision Lighting. Available online: https://www.advancedillumination.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/A-Practical-Guide-to-Machine-Vision-Lighting-v.-4-Generic.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2020).
- Goni, V.; Indurain, G.; Hernandez, B.; Beriain, M.J. Measuring muscle color in beef using an instrumental method versus visual color scales. J. Muscle Foods 2008, 19, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khliji, S.; Van de Ven, R.; Lamb, T.; Lanza, M.; Hopkins, D.J.M.S. Relationship between consumer ranking of lamb colour and objective measures of colour. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, B.W.B.; van de Ven, R.J.; Mao, Y.; Coombs, C.E.O.; Hopkins, D.L. Using instrumental (CIE and reflectance) measures to predict consumers’ acceptance of beef colour. Meat Sci. 2017, 127, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
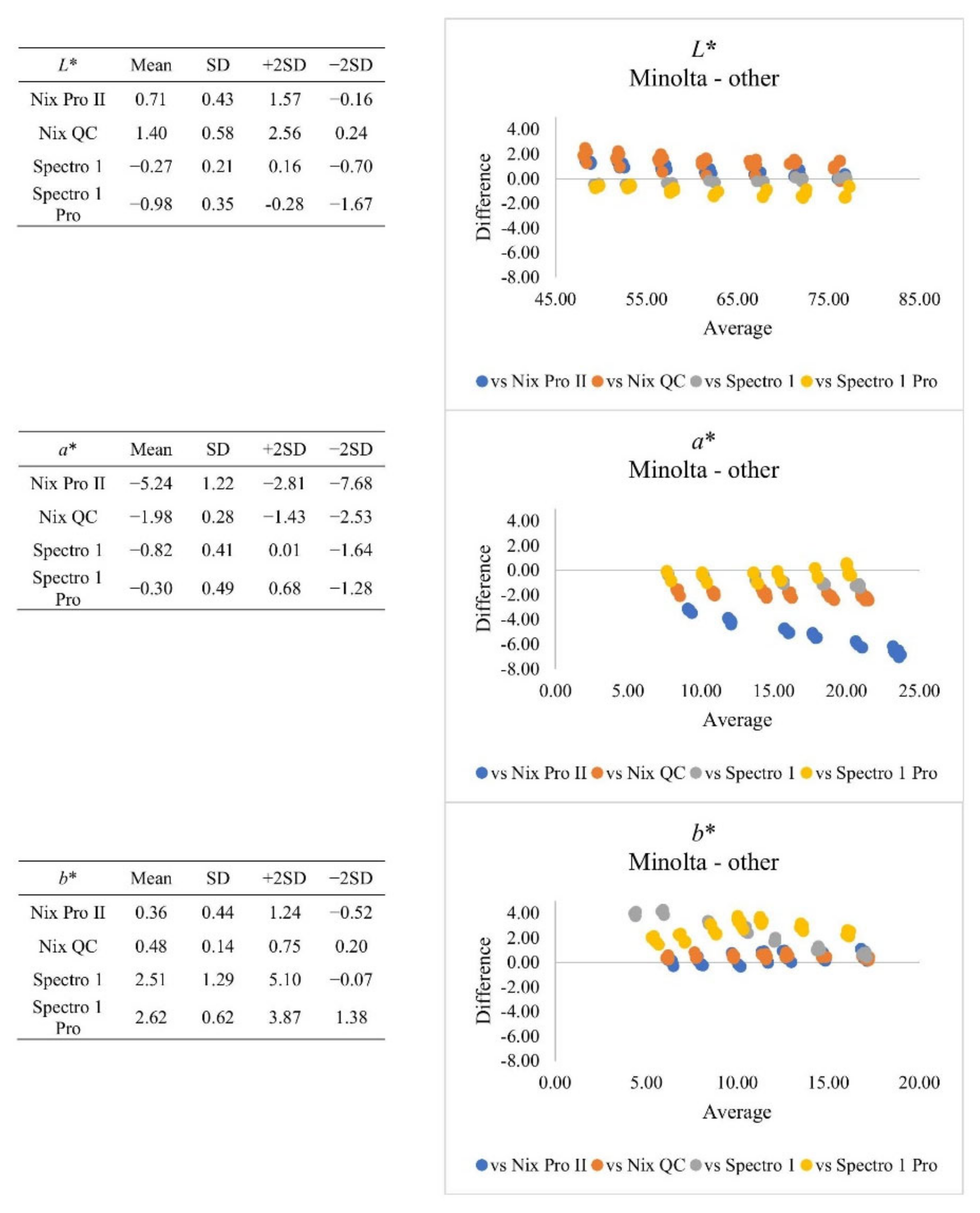
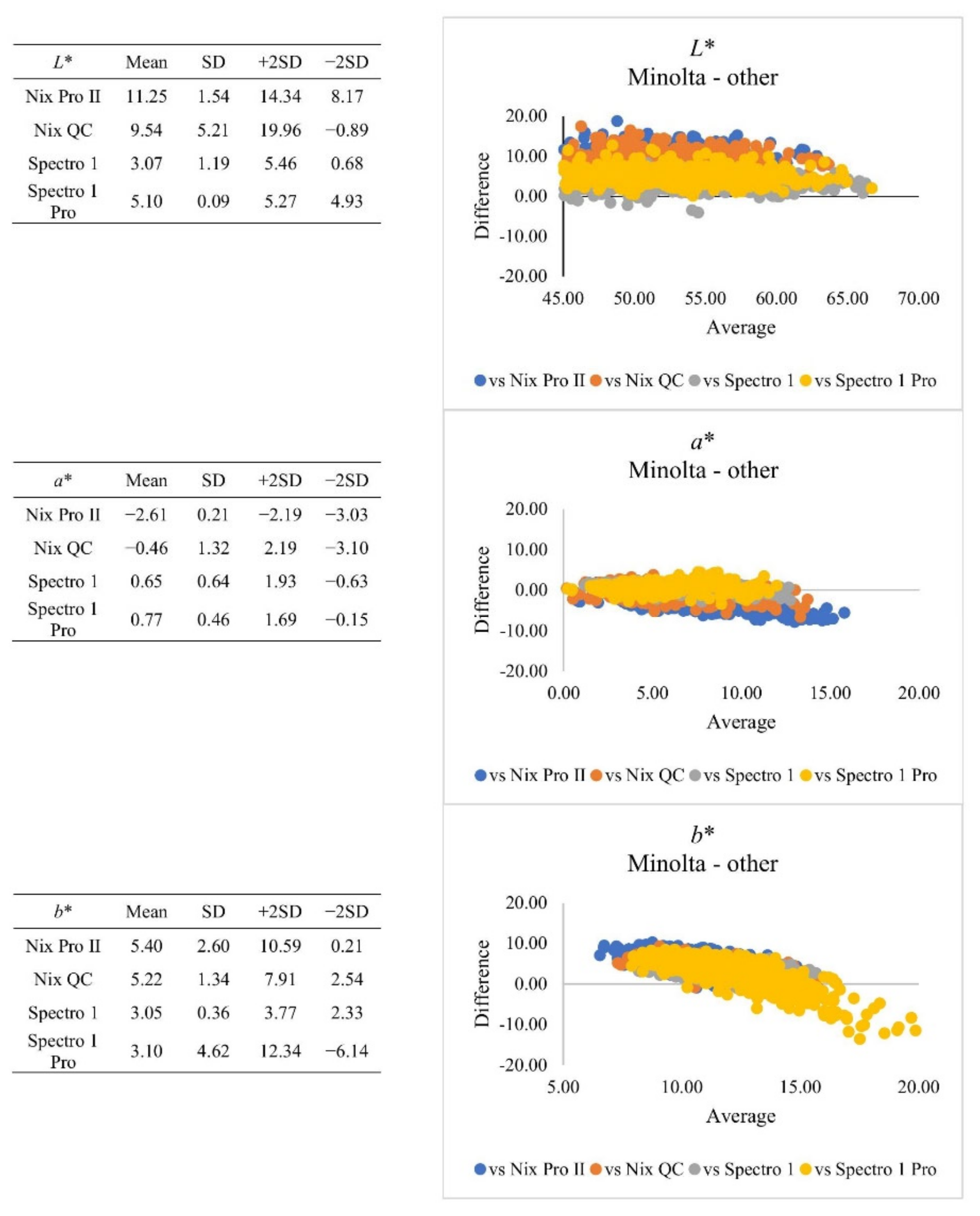
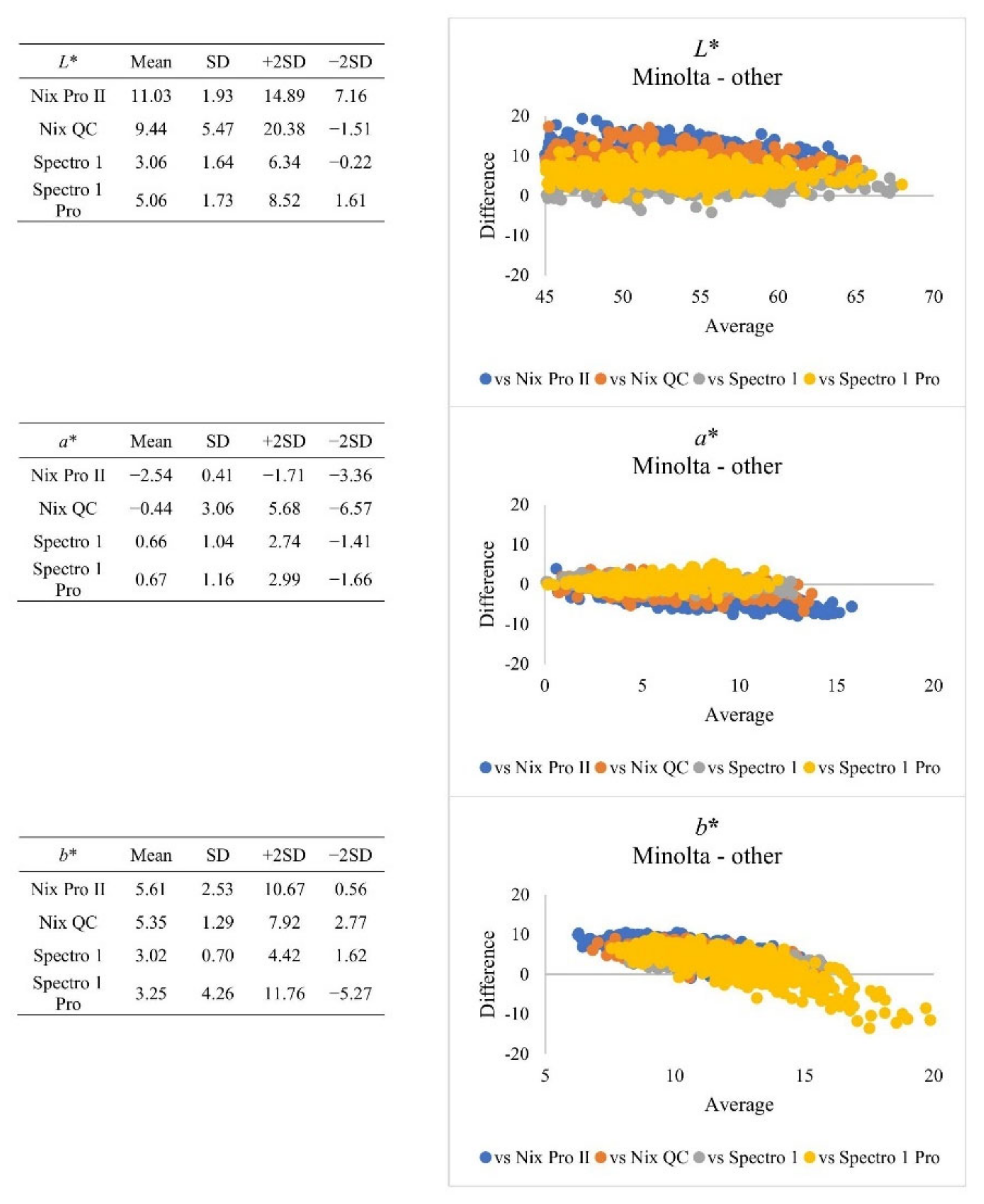
| Subjective Colour Score | Minolta | Nix Pro II | Nix QC | Spectro 1 | Spectro 1 Pro | SEM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | 0 | 76.78 b | 76.33 c | 75.51 d | 75.28 e | 77.57 a | 0.06 |
| 1 | 71.88 b | 71.35 c | 70.57 d | 70.04 e | 72.93 a | 0.05 | |
| 2 | 67.49 b | 66.94 c | 66.20 d | 65.55 e | 68.55 a | 0.04 | |
| 3 | 62.13 b | 61.43 c | 60.75 d | 60.16 e | 63.21 a | 0.04 | |
| 4 | 57.40 b | 56.43 c | 55.81 d | 55.25 e | 58.24 a | 0.04 | |
| 5 | 52.81 b | 51.61 c | 50.96 d | 50.66 e | 53.34 a | 0.04 | |
| 6 | 49.31 b | 47.88 c | 47.27 d | 47.17 e | 49.88 a | 0.04 | |
| a* | 0 | 7.95 d | 10.78 a | 9.23 b | 7.71 e | 8.02 c | 0.02 |
| 1 | 11.04 c | 14.00 a | 11.77 b | 9.71 e | 10.53 d | 0.02 | |
| 2 | 15.10 c | 18.31 a | 15.31 b | 13.34 e | 14.04 d | 0.03 | |
| 3 | 17.07 b | 20.42 a | 17.12 b | 15.44 d | 15.62 c | 0.02 | |
| 4 | 20.11 b | 23.90 a | 19.93 c | 18.65 d | 18.00 e | 0.03 | |
| 5 | 22.73 b | 26.68 a | 22.31 c | 21.34 d | 20.04 e | 0.03 | |
| 6 | 22.70 b | 26.80 a | 22.38 c | 21.41 d | 20.05 e | 0.03 | |
| b* | 0 | 16.97 b | 16.62 d | 16.88 c | 17.20 a | 14.90 e | 0.02 |
| 1 | 14.56 ab | 14.37 c | 14.50 b | 14.60 a | 12.10 d | 0.02 | |
| 2 | 12.59 a | 12.40 b | 12.41 b | 11.83 c | 9.65 d | 0.03 | |
| 3 | 11.41 a | 11.31 b | 11.24 b | 9.80 c | 8.51 d | 0.02 | |
| 4 | 9.75 b | 9.84 a | 9.54 c | 7.05 e | 7.30 d | 0.03 | |
| 5 | 7.76 b | 7.91 a | 7.48 c | 3.96 e | 6.00 d | 0.03 | |
| 6 | 6.19 b | 6.35 a | 5.96 c | 2.66 e | 4.55 d | 0.03 |
| RSD % | Colour | Instrument Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coordinate | Minolta | Nix Pro II | Nix QC | Spectro 1 | Spectro 1 Pro | |
| Intra-day i | L* | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| a* | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.18 | |
| b* | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.41 | 0.46 | |
| Inter-day ii | L* | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.09 |
| a* | 0.21 | 0.55 | 0.98 | 0.31 | 0.33 | |
| b* | 0.50 | 1.11 | 0.86 | 0.69 | 1.59 | |
| Intra-model iii | L* | 0.50 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.21 |
| a* | 0.56 | 1.03 | 0.93 | 0.41 | 2.35 | |
| b* | 0.53 | 2.69 | 0.75 | 1.93 | 2.84 | |
| Minolta | Nix Pro II | Nix QC | Spectro 1 | Spectro 1 Pro | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | 55.07 a ± 5.20 | 43.83 e ± 5.83 | 45.69 d ± 5.68 | 52.00 b ± 5.12 | 49.97 c ± 5.33 |
| a* | 5.05 c ± 2.42 | 7.66 a ± 3.35 | 5.48 b ± 2.52 | 4.40 d ± 2.72 | 4.27 d ± 2.01 |
| b* | 13.53 a ± 1.29 | 8.13 c ± 2.29 | 8.19 c ± 1.94 | 10.48 b ± 1.38 | 10.43 b ± 3.36 |
| Nix Pro II | Nix QC | Spectro 1 | Spectro 1 Pro | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Muscle | L* | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.90 |
| a* | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.88 | |
| b* | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.32 | |
| Central Area | L* | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.92 |
| a* | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.89 | |
| b* | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.78 | 0.30 |
| Minolta | Nix Pro II | Nix QC | Spectro 1 | Spectro 1 Pro | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Muscle | L* | −0.68 | −0.85 | −0.85 | −0.80 | −0.78 |
| a* | 0.47 | 0.69 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.60 | |
| b* | −0.14 | 0.31 | 0.32 | −0.39 | 0.41 | |
| Central Area | L* | −0.76 | −0.86 | −0.84 | −0.80 | −0.78 |
| a* | 0.59 | 0.69 | 0.64 | 0.67 | 0.59 | |
| b* | −0.13 | 0.31 | 0.31 | −0.35 | 0.42 |
| Minolta | Nix Pro II | Nix QC | Spectro 1 | Spectro 1 Pro | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Muscle | 1 L* | −0.68 | −0.83 | −0.84 | −0.79 | −0.77 |
| a* | 0.47 | 0.68 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.58 | |
| b* | −0.13 | 0.25 | 0.29 | −0.39 | 0.41 | |
| Central Area | L* | −0.75 | −0.83 | −0.83 | −0.78 | −0.76 |
| a* | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.57 | |
| b* | −0.12 | 0.26 | 0.29 | −0.35 | 0.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Lam, S.; Bohrer, B.M.; Uttaro, B.; López-Campos, O.; Prieto, N.; Larsen, I.L.; Juárez, M. A Comparison of Fresh Pork Colour Measurements by Using Four Commercial Handheld Devices. Foods 2021, 10, 2515. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112515
Wei X, Lam S, Bohrer BM, Uttaro B, López-Campos O, Prieto N, Larsen IL, Juárez M. A Comparison of Fresh Pork Colour Measurements by Using Four Commercial Handheld Devices. Foods. 2021; 10(11):2515. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112515
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xinyi, Stephanie Lam, Benjamin M. Bohrer, Bethany Uttaro, Oscar López-Campos, Nuria Prieto, Ivy L. Larsen, and Manuel Juárez. 2021. "A Comparison of Fresh Pork Colour Measurements by Using Four Commercial Handheld Devices" Foods 10, no. 11: 2515. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112515
APA StyleWei, X., Lam, S., Bohrer, B. M., Uttaro, B., López-Campos, O., Prieto, N., Larsen, I. L., & Juárez, M. (2021). A Comparison of Fresh Pork Colour Measurements by Using Four Commercial Handheld Devices. Foods, 10(11), 2515. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112515






