Formulation Optimization of Sucrose-Free Hard Candy Fortified with Cudrania tricuspidata Extract
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Natural flavorings: Cudrania tricuspidata fruit extract (prepared by decoction according to Section 2.3.1); 65 Brix lemon extract (Serim Food, Bucheon, Korea); 64 Brix ginger extract (ES Food, Seoul, Korea).
- Sucrose-free hard candy: isomalt (Palatinit Subungsmittel GmbH, Mannheim,, Germany); maltitol syrup (Samyangcorp quone, Korea); xylitol (Danisco Sweeteners Oy, Sokeritehtaantie, Finland); water.
- Traditional hard candy (control): refined granulated sucrose (Samyangcorp quone, Seoul, Korea); 70 DE glucose syrup (Ottogi, Seoul, Korea); water.
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Determination of the Addition Level of Cudrania tricuspidata Fruit Extract
2.2.2. Determination of Sugar-Free Candy Formulation by D-Optimal Mixture Design
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.3.1. Manufacturing of Cudrania tricuspidata Fruit Extract
2.3.2. Preparation of Traditional Hard Candies
2.3.3. Preparation of Sucrose-Free Hard Candies
2.4. Physicochemical Analysis
2.5. Color Analysis
2.6. Hardness Analysis
2.7. Sensory Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization Study
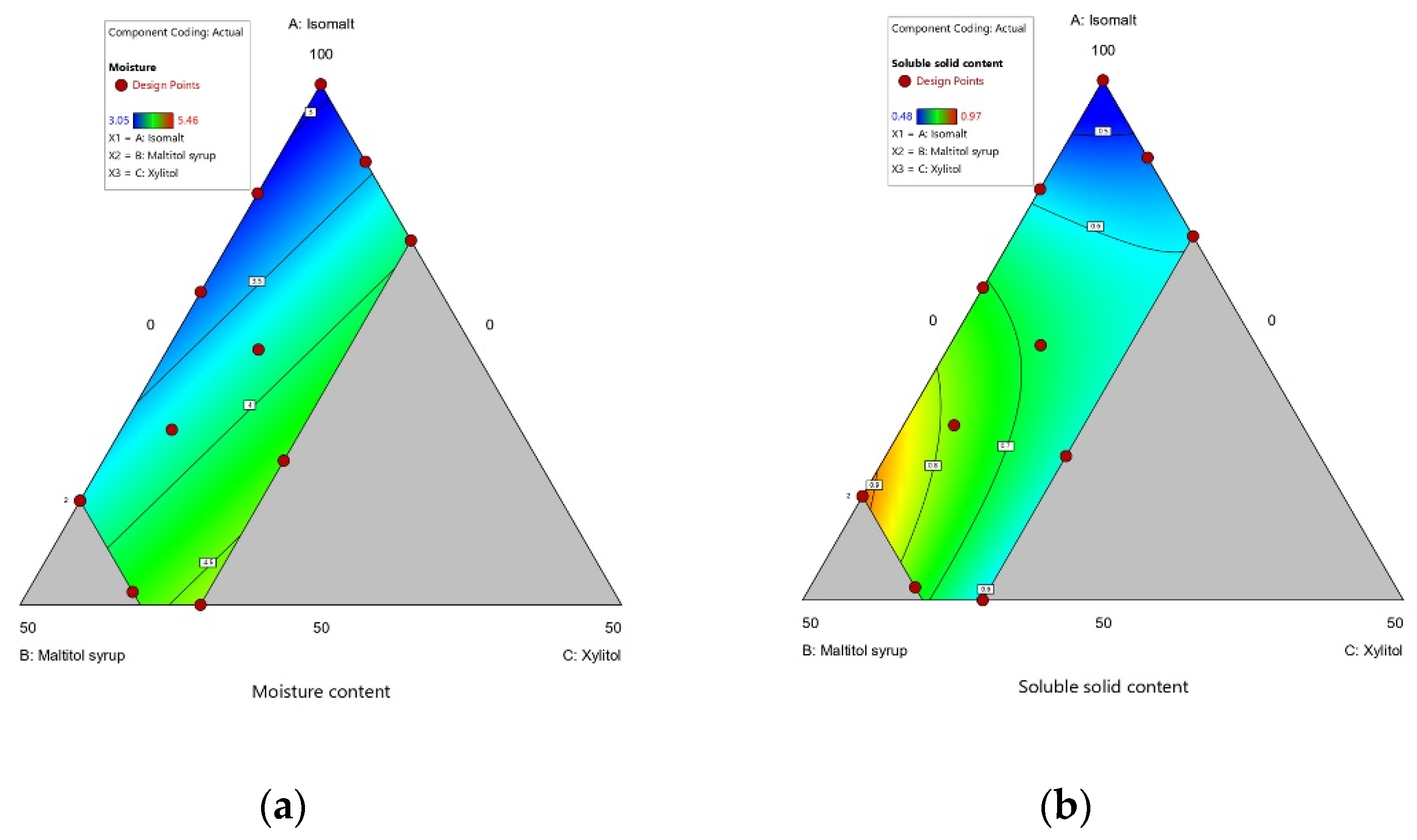
3.1.1. Physicochemical Properties
3.1.2. Color
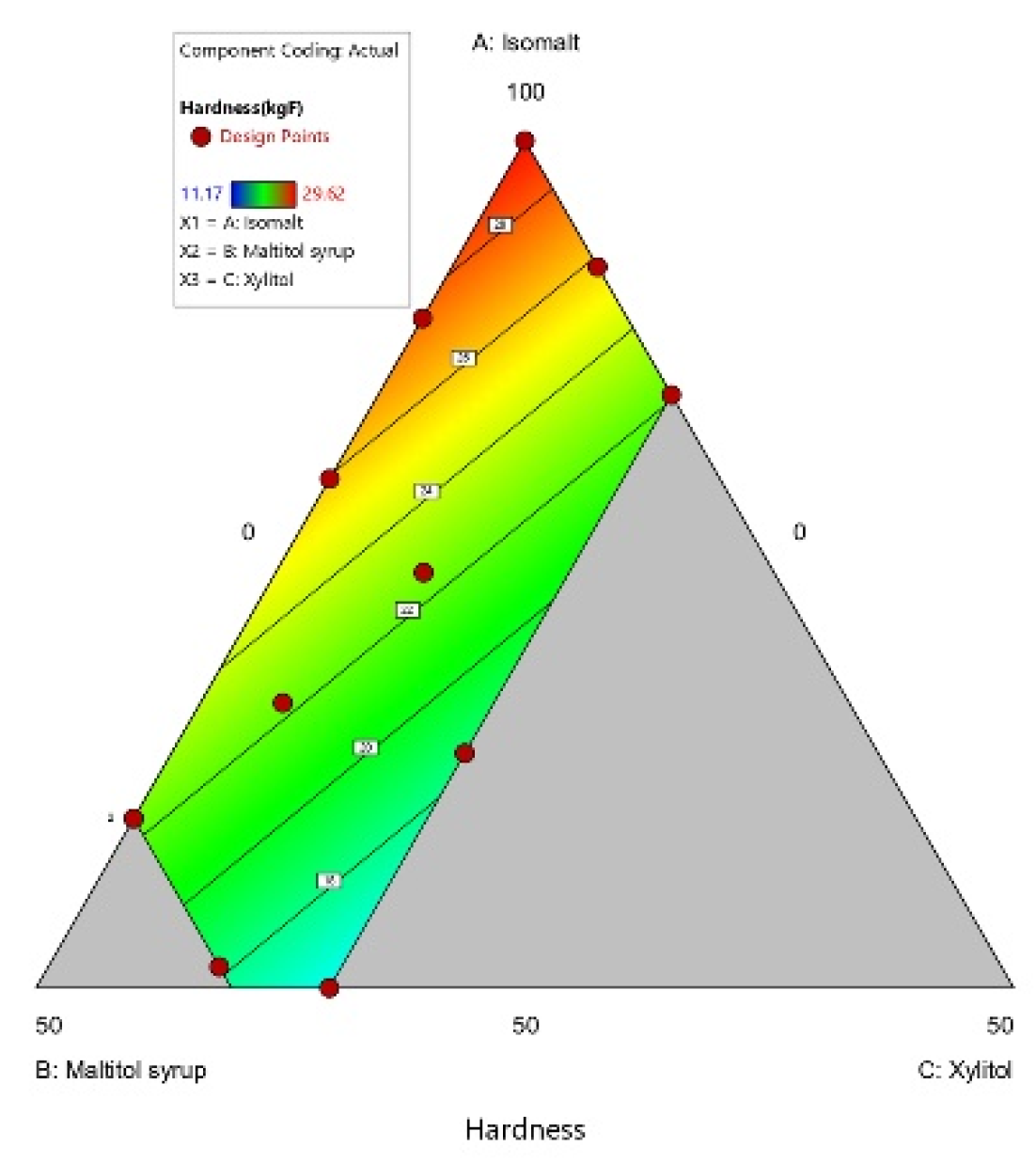
3.1.3. Hardness
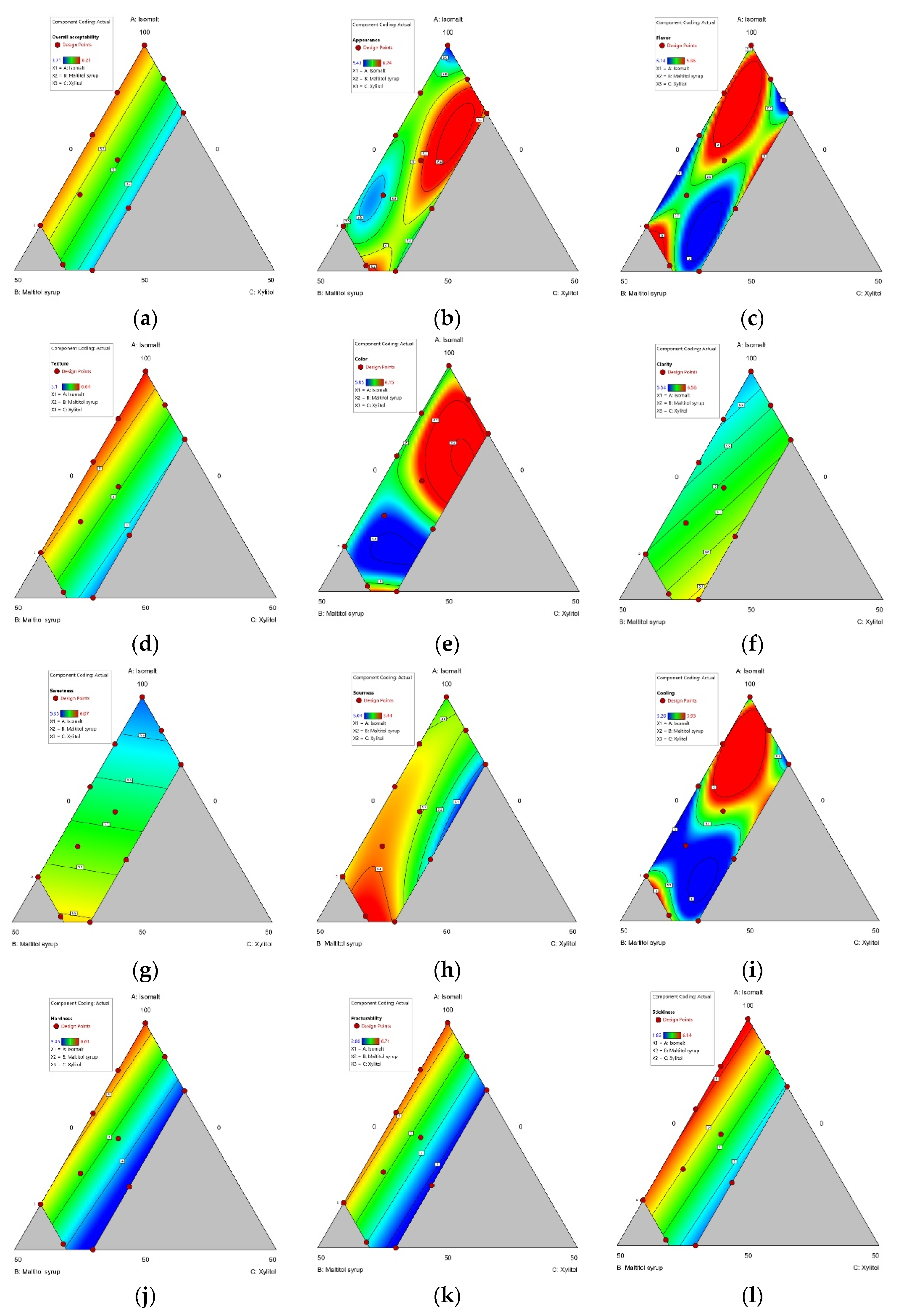
3.1.4. Sensory Properties
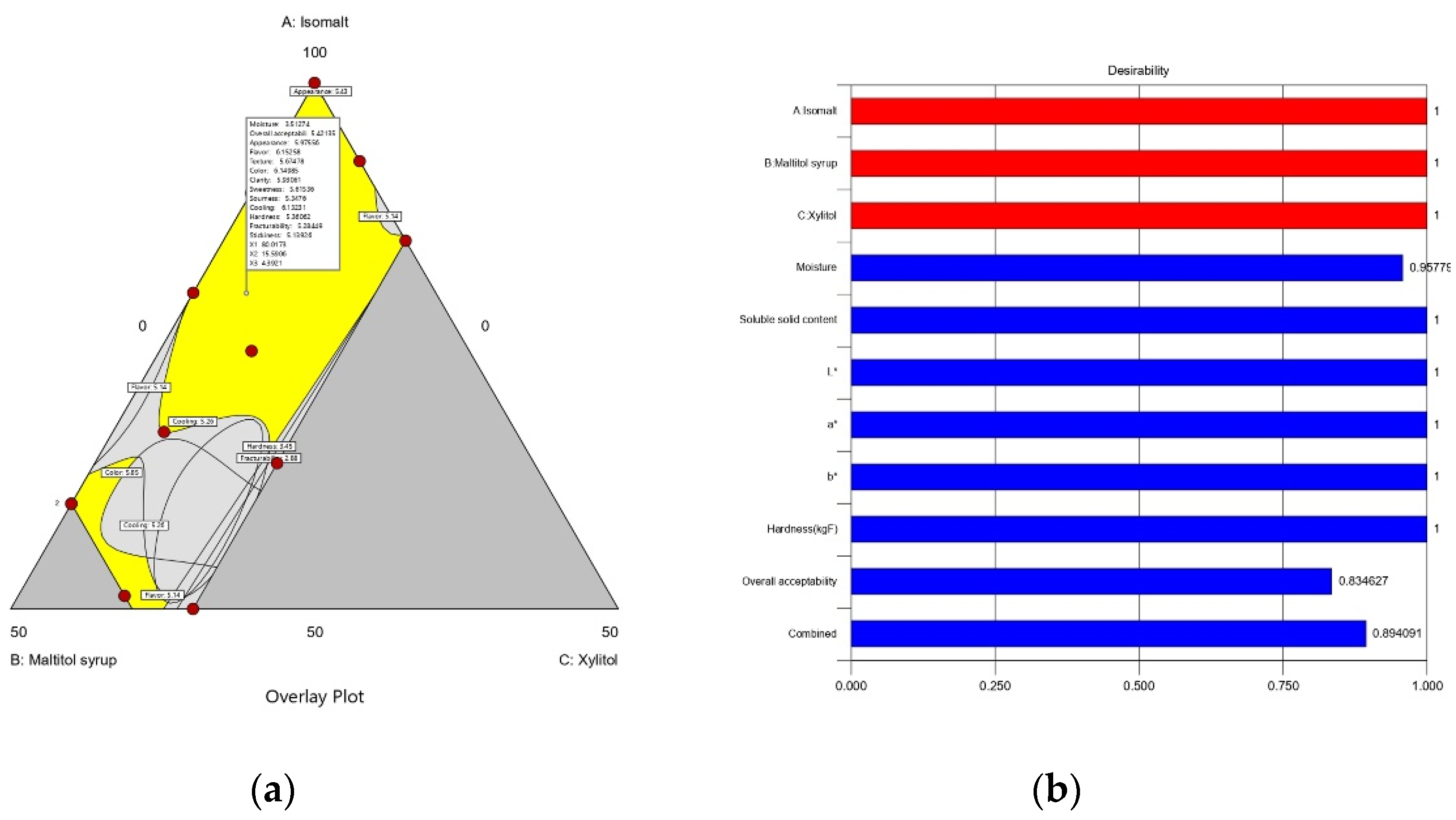
3.1.5. Hard Candy Formulation Optimization
3.2. Precursory Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, C.; Sher, A.; Rousset, P.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Formulation of food emulsions using natural emulsifiers: Utilization of quillaja saponin and soy lecithin to fabricate liquid coffee whiteners. J. Food Eng. 2017, 209, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino, M.; Veiga, M.; Sousa, P.; Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Pintado, M. Agro-food byproducts as a new source of natural food additives. Molecules 2019, 24, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Çoban, B.; Bilgin, B.; Yurt, B.; Kopuk, B.; Atik, D.S.; Palabiyik, I. Utilization of the barberry extract in the confectionery products. LWT 2021, 145, 111362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersen, L.; Strømdahl, L.D.; Olsen, K.; Skibsted, L.H. Heat and light stability of three natural blue colorants for use in confectionery and beverages. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 220, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ibarbia, L.; Majdanski, T.; Schubert, S.; Windhab, N.; Schubert, U.S. Safety and regulatory review of dyes commonly used as excipients in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanarek, R.B. Artificial food dyes and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylewski, S.; Jacobson, M.F. Toxicology of food dyes. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2012, 18, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, D.; Barba, F.J.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Cruz, A.G.; Putnik, P. Functional foods: Product development, technological trends, efficacy testing, and safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jędrusek-Golińska, A.; Górecka, D.; Buchowski, M.; Wieczorowska-Tobis, K.; Gramza-Michałowska, A.; Szymandera-Buszka, K. Recent progress in the use of functional foods for older adults: A narrative review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 835–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.I.L.; Silva, E.K.; Meireles, M.A.A. Natural blue food colorants: Consumer acceptance, current alternatives, trends, challenges, and future strategies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chranioti, C.; Nikoloudaki, A.; Tzia, C. Saffron and beetroot extracts encapsulated in maltodextrin, gum Arabic, modified starch and chitosan: Incorporation in a chewing gum system. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, I.d.O.; Passos, T.S.; Chiapinni, C.; Silveira, G.K.; Souza, J.C.; Coca-Vellarde, L.G.; Deliza, R.; de Lima Araújo, K.G. Colour evaluation of a phycobiliprotein-rich extract obtained from Nostoc PCC9205 in acidic solutions and yogurt. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, J.; Stolyhwo, A. Application of carbon dioxide in subcritical state (LCO2) for extraction/fractionation of carotenoids from red paprika. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.I.L.; Silva, E.K.; Meireles, M.A.A. Trends and challenges in the industrialization of natural colorants. Food Public Health 2019, 9, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Ding, Y.; Forrest, B.; Oh, J.; Boussert, S.M.; Hamann, M.T. Lemon yellow# 15 a new highly stable, water soluble food colorant from the peel of Citrus limon. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Sun, J.; Ran, G.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Tian, L. Bioactive compounds from Cudrania tricuspidata: A natural anticancer source. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 494–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.-N.; Park, D.-H.; Park, J.-Y.; Song, S.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Yoon, G.; Moon, H.-S.; Oh, D.-S.; Rhee, S.-H.; Im, E.-O. Tyrosinase inhibition antioxidant effect and cytotoxicity studies of the extracts of Cudrania tricuspidata fruit standardized in chlorogenic acid. Molecules 2019, 24, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, W.; Yoon, C.-S.; Kim, K.-W.; Lee, H.; Kim, N.; Woo, E.-R.; Kim, Y.-C.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, H. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of Kuwanon C from Cudrania tricuspidata are mediated by heme oxygenase-1 in HT22 hippocampal cells, RAW264. 7 macrophage, and BV2 microglia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-H.; Park, S.-E.; Yeo, S.-H.; Kim, S. Anti-inflammatory and cytotoxicity effects of Cudrania tricuspidata fruits vinegar in a co-culture system with RAW264.7 macrophages and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Foods 2020, 9, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.S.; Yang, J.H.; Seo, K.H.; Shin, S.M.; Park, E.Y.; Cho, S.S.; Jo, G.U.; Eo, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Oh, D.S. Cudrania Tricuspidata Extract and Its Major Constituents Inhibit Oxidative Stress-Induced Liver Injury. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, Y. Comparison of proximate composition of Curdrania tricuspidata Bureau fruit. J. Agric. Life Sci. 2015, 46, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, G.-R.; Gebru, Y.A.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, D.-H.; Han, H.-A.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, M.-K. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Steam-Distilled Essential Oil and Glycosidically Bound Volatiles from Maclura Tricuspidata Fruit. Foods 2019, 8, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.-N.; Choi, E.-H.; Yoo, S.-S. Quality Characteristics of Sulgidduk added with Cudrania tricuspidata Fruit Puree. Food Serv. Ind. J. 2017, 13, 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.-J.; Kim, M.-H.; Choi, S.-R.; Kim, Y.-K.; Jin, H.-H. Quality Characteristics of Fresh Noodle with Freeze-dried Mulberry (Cudrania tricuspidata) Powder. East Asian Soc. Diet. Life 2018, 28, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-N.; Choi, E.-H. Quality Characteristics of Julpyun added with Cuccibbong (Cudrania tricuspidata) Fruit Puree. Food Serv. Ind. J. 2019, 15, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Cappa, C.; Lavelli, V.; Mariotti, M. Fruit candies enriched with grape skin powders: Physicochemical properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongia, G. Fruit ingredients in confectionery applications. Manuf. Confect. 2014, 94, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings, S.C.; Low, J.Y.; Keast, R.S. Sugar reduction without compromising sensory perception. An impossible dream? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2287–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumbe, A.; Lee, A.; Storey, D. Polyols in confectionery: The route to sugar-free, reduced sugar and reduced calorie confectionery. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 85, S31–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, P.; Conn, H. Carbohydrate Substitutes. WO 2005/006981, 27 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Aidoo, R.P.; Depypere, F.; Afoakwa, E.O.; Dewettinck, K. Industrial manufacture of sugar-free chocolates—Applicability of alternative sweeteners and carbohydrate polymers as raw materials in product development. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 32, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilara, A. The Shelf Life of Ice Cream and Frozen Desserts. Dev. Food Sci. 1993, 33, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Willibald-Ettle, I.; Schiweck, H. Advances in Sweeteners; Grenby, T.H., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 134–149. ISBN 978-1-4612-8522-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sentko, A.; Willibald-Ettle, I. Isomalt. In Sweeteners and Sugar Alternatives in Food Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 243–274. [Google Scholar]
- Kearsley, M.W.; Deis, R.C. 12 Maltitol and Maltitol Syrups. In Sweeteners and Sugar Alternatives in Food Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- Sträter, P. Palatinit-technological and processing characteristics. Altern. Sweeten. 1986, 83, 217–244. [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga, G.; Li-Chan, E.; Nakai, S.; Cofrades, S.; Jimenez-Colmenero, F. Ingredient interaction effects on protein functionality: Mixture design approach. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutcosky, S.D.; Grossmann, M.V.E.; Silva, R.S.S.; Welsch, A.K. Combined sensory optimization of a prebiotic cereal product using multicomponent mixture experiments. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, S.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Kayacier, A. Simplex lattice mixture design approach on the rheological behavior of glucomannan based salep-honey drink mixtures: An optimization study based on the sensory properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannarswamy, A.; Munson-McGee, S.H.; Andersen, P.K. D-optimal designs for the Cross viscosity model applied to guar gum mixtures. J. Food Eng. 2010, 97, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanemberg, F.E.; Korzenowski, A.L.; Sellitto, M.A. Effects of sugar composition on shelf life of hard candy: Optimization study using D-optimal mixture design of experiments. J. Food Process. Eng. 2019, 42, e13213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hagbani, T.; Altomare, C.; Salawi, A.; Nazzal, S. D-optimal mixture design: Formulation development, mechanical characterization, and optimization of curcumin chewing gums using oppanol® B 12 elastomer as a gum-base. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 553, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Tian, M.; Chen, L.; Ma, D.; Cui, X.; Meng, J. Probiotic goat milk tablets: Formulation optimization and stability evaluation. LWT 2020, 119, 108862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.B.; Queiroz, M.B.; Fadini, A.L.; da Fonseca, R.C.; Germer, S.P.; Efraim, P. Chewy candy as a model system to study the influence of polyols and fruit pulp (açai) on texture and sensorial properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, A.H.; Pirouzian, H.R.; Konar, N.; Toker, O.S.; Polat, D.G. Effects of polyols on the quality characteristics of sucrose-free milk chocolate produced in a ball mill. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29676–29688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rad, A.H.; Pirouzian, H.R.; Toker, O.S.; Konar, N. Application of simplex lattice mixture design for optimization of sucrose-free milk chocolate produced in a ball mill. LWT 2019, 115, 108435. [Google Scholar]
- Rasouli-Pirouzian, H.; Peighambardoust, S.H.; Azadmard-Damirchi, S. Rheological properties of sugar-free milk chocolate: Comparative Study and optimisation. Czech J. Food Sci. 2017, 35, 440–448. [Google Scholar]
- Sokmen, A.; Gunes, G. Influence of some bulk sweeteners on rheological properties of chocolate. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohner, S.; de Gaudry, D.K.; Toews, I.; Ferenci, T.; Meerpohl, J.J. Non-nutritive sweeteners for diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 5, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, J.-L.; Jeong, H.-C. Quality characteristics of pound cake with added Rubus coreanus Miquel concentrate. J. East Asian Soc. Diet. Life 2013, 23, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, W.D. Hard candy: Cooking. Manuf. Confect. 1995, 75, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bunce, M.G. Anthocyanin and Tea Extract Enriched Hard Candy to Increase Visual Appeal and Total Phenolics. Master’s Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hartel, R.W.; Joachim, H.; Elbe, V.; Hofberger, R. Fats, Oils and Emulsifiers. In Confectionery Science and Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 85–124. ISBN 978-33-1987-150-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Lee, S.; Shin, Y. Effect of heating conditions on physical properties of model hard candy. Food Eng. Prog. 2006, 10, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gok, S.; Toker, O.S.; Palabiyik, I.; Konar, N. Usage possibility of mannitol and soluble wheat fiber in low calorie gummy candies. LWT 2020, 128, 109531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikzade, V.; Tehrani, M.M.; Saadatmand-Tarzjan, M. Optimization of low-cholesterol–low-fat mayonnaise formulation: Effect of using soy milk and some stabilizer by a mixture design approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarteshnizi, R.A.; Hosseini, H.; Bondarianzadeh, D.; Colmenero, F.J. Optimization of prebiotic sausage formulation: Effect of using β-glucan and resistant starch by D-optimal mixture design approach. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ergun, R.; Lietha, R.; Hartel, R. Moisture and shelf life in sugar confections. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 162–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cock, P. Erythritol. In Sweeteners and Sugar Alternatives in Food Technology, 2nd ed.; Kay O’Donnell, M.W.K., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 213–241. ISBN 978-11-1837-394-1. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; Choi, H. Sweeteners Handbook; Hyoil Books: Seoul, Korea, 2002; pp. 13–277. ISBN 978-89-8489-048-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nowakowski, C.; Hartel, R. Moisture sorption of amorphous sugar products. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidoo, R.P.; Afoakwa, E.O.; Dewettinck, K. Optimization of inulin and polydextrose mixtures as sucrose replacers during sugar-free chocolate manufacture–Rheological, microstructure and physical quality characteristics. J. Food Eng. 2014, 126, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.G.; Bozza, F.T.; Thomazini, M.; Favaro-Trindade, C.S. Microencapsulation of xylitol by double emulsion followed by complex coacervation. Food Chem. 2015, 171, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovina, K.; Prabakaran, P.P.; Siddiquee, S.; Shaarani, S.M. Methods for the analysis of Sunset Yellow FCF (E110) in food and beverage products-a review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.-S.; Tai, N.D. Quality characteristics and antioxidant activities of aronia jam replacing sucrose with different sugar substances. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2014, 27, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taskinen, S. Hard Candies Containing Xylitol and Other Sugar Alcohols Having Reduced Tack. U.S. Patent 5,223,303, 23 June 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Di Monaco, R.; Miele, N.A.; Cabisidan, E.K.; Cavella, S. Strategies to reduce sugars in food. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 19, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabandi, K.; Jafari, S.M.; Mahoonak, A.S.; Mohammadi, A. Application of gum Arabic and maltodextrin for encapsulation of eggplant peel extract as a natural antioxidant and color source. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, N.; Iritani, S.; Miyake, T. Hard Candy with a Relatively-High Moisture and Hardness, and Process of the Same. U.S. Patent 6,455,096B1, 23 April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Arcaño, Y.D.; García, O.D.V.; Mandelli, D.; Carvalho, W.A.; Pontes, L.A.M. Xylitol: A review on the progress and challenges of its production by chemical route. Catal. Today 2020, 344, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabors, L.O.B.; Gelardi, R.C. Alternative sweeteners: An overview. In Alternative Sweeteners, 4th ed.; O’Brien-Nabors, L., Ed.; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-05-8540-704-3. [Google Scholar]
- Saint-Eve, A.; Déléris, I.; Panouillé, M.; Dakowski, F.; Cordelle, S.; Schlich, P.; Souchon, I. How texture influences aroma and taste perception over time in candies. Chemosens. Percept. 2011, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazic, Z.R. Design of Experiments in Chemical Engineering: A Practical Guide; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; ISBN 978-35-2760-416-6. [Google Scholar]

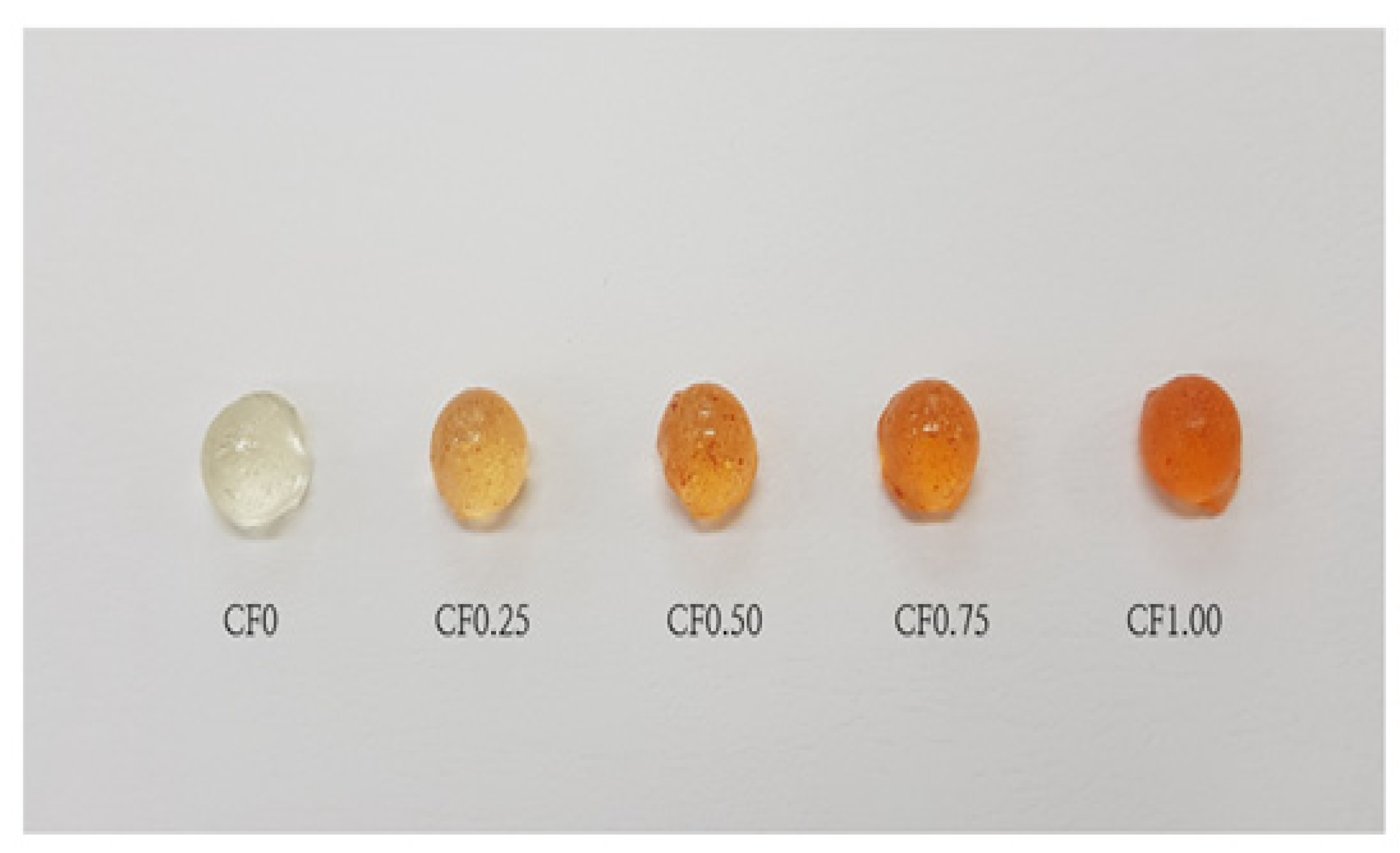


| Figure Ingredients (g) | Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF0 1 | CF0.25 2 | CF0.50 3 | CF0.75 4 | CF1.00 5 | |
| Glucose syrup | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Sucrose | 59.20 | 58.95 | 58.70 | 58.45 | 58.20 |
| Cudrania tricuspidata fruit extract | 0.00 (0.00%) | 0.25 (0.25%) | 0.50 (0.50%) | 0.75 (0.75%) | 1.00 (1.00%) |
| Ginger extract | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Lemon extract | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Mint flavoring | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Sample | UnCoded Values | Real Values | Sucrose | Glucose Syrup | Cudrania tricuspidata Fruit Extract | Ginger Extract | Lemon Extract | Mint Flavor | Water | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 1 | B 2 | C 3 | Isomalt | Maltitol Syrup | Xylitol | |||||||||
| 1 | 0.850 | 0 | 0.150 | 83.68 | 0 | 14.77 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 2 | 0.600 | 0.400 | 0 | 59.07 | 39.38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 3 | 0.639 | 0.211 | 0.150 | 62.91 | 20.77 | 14.77 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 4 | 0.500 | 0.350 | 0.150 | 49.22 | 34.46 | 14.77 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 5 | 1.00 | 0 | 0 | 98.45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 6 | 0.668 | 0.290 | 0.042 | 65.79 | 28.52 | 4.14 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 7 | 0.513 | 0.400 | 0.088 | 50.46 | 39.38 | 8.61 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 8 | 0.600 | 0.400 | 0 | 59.07 | 39.38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 9 | 0.801 | 0.199 | 0 | 78.82 | 19.63 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 10 | 0.926 | 0 | 0.074 | 91.12 | 0 | 7.33 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 11 | 0.895 | 0.105 | 0 | 88.14 | 10.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 12 | 0.745 | 0.179 | 0.076 | 73.36 | 17.64 | 7.45 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 13 (control) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 58.45 | 40 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| 14 (control) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 58.45 | 40 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 30 | 130 |
| Sample | Moisture (g/100g) | SSC | L* | a* | b* | Hardness (kgF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | ||||||
| 3 | ||||||
| 4 | ||||||
| 5 | ||||||
| 6 | ||||||
| 7 | ||||||
| 8 | ||||||
| 9 | ||||||
| 10 | ||||||
| 11 | ||||||
| 12 | ||||||
| 13 (control) | ||||||
| 14 (control) | ||||||
| Model | Linear | Quadratic | Cubic | Quadratic | Linear | Linear |
| p-value | 0.0055 | 0.0062 | 0.4097 | 0.0388 | 0.0496 | 0.0053 |
| R2 | 0.6851 | 0.8979 | 0.8895 | 0.9644 | 0.4871 | 0.6878 |
| Adjusted-R2 | 0.6152 | 0.8128 | 0.392 | 0.8769 | 0.3731 | 0.6184 |
| Predicted-R2 | 0.3499 | 0.4733 | −22.8968 | −1.2748 | −0.0356 | 0.3044 |
| Adeq Precision | 8.9203 | 10.3742 | 3.962 | 10.285 | 4.6499 | 9.073 |
| Sample | Overall Acceptance | Appearance | Flavor | Texture | Color | Clarity | Sweetness | Sourness | Cooling | Hardness | Fracturability | Stickiness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||||
| 10 | ||||||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||||||
| 13 (control) | ||||||||||||
| 14 (control) | ||||||||||||
| Model | Linear | Cubic | Cubic | Linear | Special Quartic | Linear | Linear | Special Cubic | Cubic | Linear | Linear | Linear |
| p-value | 0.0001 | 0.2987 | 0.5516 | <0.0001 | 0.0393 | 0.0319 | 0.0482 | 0.0961 | 0.0331 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| R2 | 0.8611 | 0.9242 | 0.8368 | 0.9354 | 0.9547 | 0.5348 | 0.4904 | 0.8069 | 0.9925 | 0.8939 | 0.9161 | 0.9038 |
| Adj.R2 | 0.8303 | 0.583 | 0.1021 | 0.921 | 0.834 | 0.4314 | 0.3771 | 0.5753 | 0.959 | 0.8703 | 0.8974 | 0.8825 |
| Pred.R2 | 0.7286 | −14.3311 | −43.7979 | 0.8705 | −18.2426 | 0.158 | 0.11 | −0.802 | 0.7835 | 0.8231 | 0.8672 | 0.8395 |
| Adeq Precision | 11.1297 | 5.79 | 3.1224 | 19.348 | 8.7539 | 6.5206 | 5.1557 | 6.4978 | 15.7647 | 14.6211 | 15.6455 | 15.2314 |
| Sensory Property | Samples | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF0 1 | CF0.25 2 | CF0.50 3 | CF0.75 4 | CF1.00 5 | F-value | |
| Overall acceptance | abc | ab | bc | c | a | 4.401 *** |
| Appearance acceptance | c | b | b | b | a | 11.751 *** |
| Flavor acceptance | 1.104 | |||||
| Texture acceptance | bc | ab | c | c | a | 8.567 *** |
| Color acceptance | c | b | b | b | a | 9.860 *** |
| Clarity acceptance | c | b | bc | b | a | 7.884 *** |
| Sweetness acceptance | 2.168 | |||||
| Sourness acceptance | 0.811 | |||||
| Cooling acceptance | a | ab | ab | b | b | 3.183 ** |
| Hardness acceptance | b | a | b | b | ab | 3.525 ** |
| Fracturability acceptance | ab | a | b | b | ab | 3.062 ** |
| Stickiness acceptance | c | b | b | bc | a | 5.019 *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, Y.; Oh, J.; Cho, M.S. Formulation Optimization of Sucrose-Free Hard Candy Fortified with Cudrania tricuspidata Extract. Foods 2021, 10, 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102464
Jeon Y, Oh J, Cho MS. Formulation Optimization of Sucrose-Free Hard Candy Fortified with Cudrania tricuspidata Extract. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102464
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Yoowha, Jieun Oh, and Mi Sook Cho. 2021. "Formulation Optimization of Sucrose-Free Hard Candy Fortified with Cudrania tricuspidata Extract" Foods 10, no. 10: 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102464
APA StyleJeon, Y., Oh, J., & Cho, M. S. (2021). Formulation Optimization of Sucrose-Free Hard Candy Fortified with Cudrania tricuspidata Extract. Foods, 10(10), 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102464






