The Effect of Cold Press Chia Seed Oil By-Products on the Rheological, Microstructural, Thermal, and Sensory Properties of Low-Fat Ice Cream
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Experimental Design
2.2.2. Ice-Cream Preparation
2.2.3. Analysis of the Ice Cream Mix
Rheological Analyzes
Flow Behavior Rheological Properties
Dynamic Rheological Properties
3-ITT
Emulsion Stability Test
The Determination Particle Size
2.2.4. Analysis of the Ice Cream Samples
Overrun Measurement
Thermal Properties of Ice Cream Samples
Sensory Analysis of Ice Cream
Color Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Determination of Steady Shear Rheological Properties of Ice Cream Mix for the Formulation Optimization
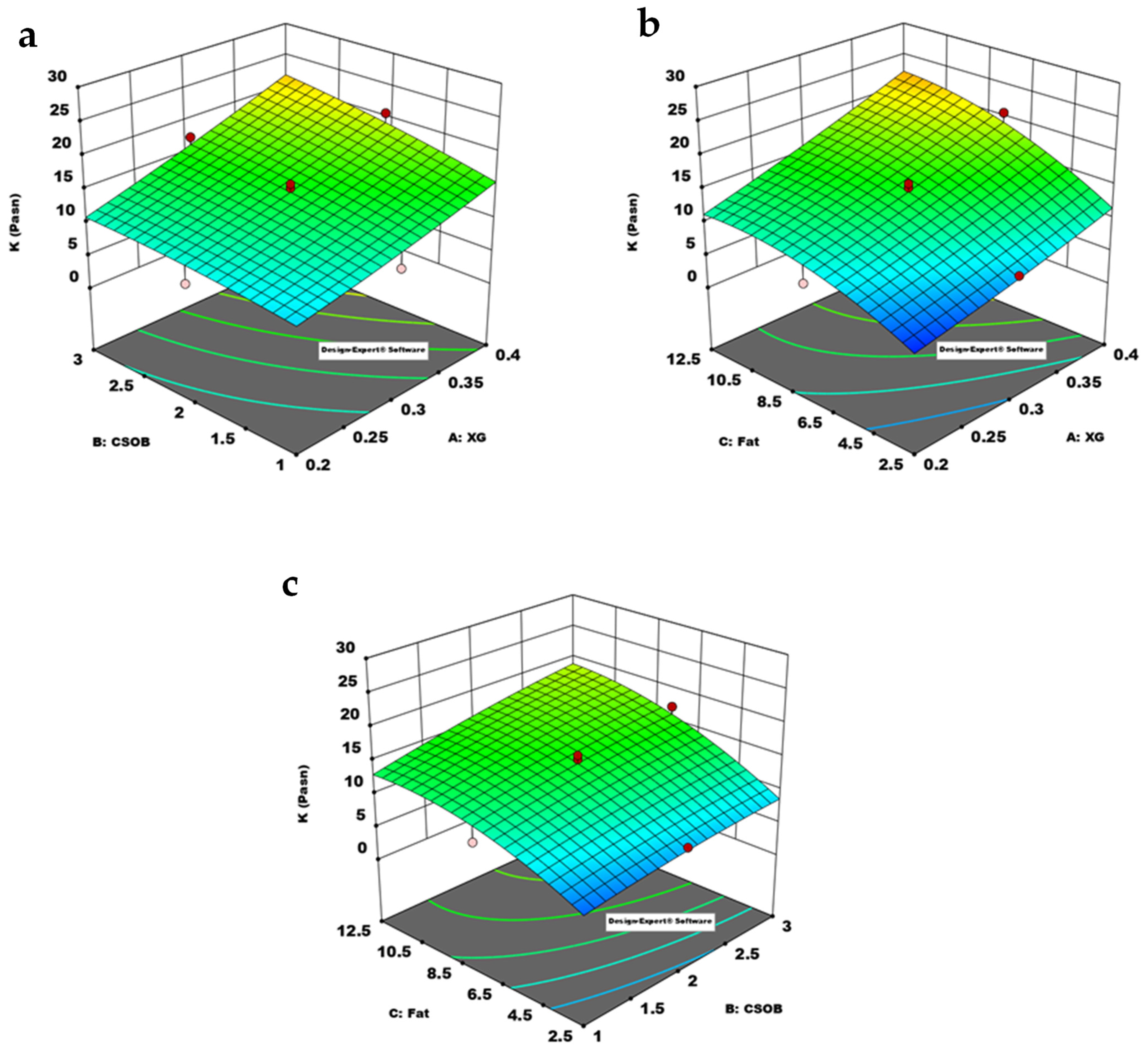
3.2. The Effect of Model Parameters on K and n Value and Determination Optimum Formulation
3.3. Rheological Properties of Optimum and Control Ice Cream Mixtures
3.4. Emulsion Stability and Microstructure Properties of Ice Cream Mixes
3.5. Quality Parameters of Ice Cream
3.5.1. Thermal Properties of Ice Cream
3.5.2. Overrun Properties of Ice Cream
3.5.3. Sensory and Color Quality of Ice Cream
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karaman, S.; Toker, Ö.S.; Yüksel, F.; Çam, M.; Kayacier, A.; Dogan, M. Physicochemical, bioactive, and sensory properties of persimmon-based ice cream: Technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution to determine optimum concentration. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marshall, R.T.; Goff, H.D.; Hartel, R.W. Ice Cream; Springer Science & Business Media: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, M.; Eskandari, M.H.; Davoudi, Z. Application and functions of fat replacers in low-fat ice cream: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, J. Fats, oils, and fat replacers. Food Technol. 1996, 50, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Góral, M.; Kozłowicz, K.; Pankiewicz, U.; Góral, D.; Kluza, F.; Wójtowicz, A. Impact of stabilizers on the freezing process, and physicochemical and organoleptic properties of coconut milk-based ice cream. LWT 2018, 92, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BahramParvar, M.; Goff, H.D. Basil seed gum as a novel stabilizer for structure formation and reduction of ice recrystallization in ice cream. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2013, 93, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baer, R.J.; Wolkow, M.D.; Kasperson, K.M. Effect of Emulsifiers on the Body and Texture of Low Fat Ice Cream1. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 3123–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, W.S. The Little Ice Cream Book; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Goff, H. On fat destabilization and composition of the air interface in ice cream containing saturated and unsaturated monoglyceride. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.N.; O’Connor, C.J.; Eyres, L. Application of emulsifiers/stabilizers in dairy products of high rheology. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 123, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Ali, N.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, W.Y.; Beh, B.K.; Tan, S.W.; Tan, S.G. The promising future of chia, Salvia hispanica L. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 171956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capitani, M.I.; Corzo-Rios, L.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Betancur-Ancona, D.; Nolasco, S.M.; Tomás, M.C. Rheological properties of aqueous dispersions of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) mucilage. J. Food Eng. 2015, 149, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-De La Rosa, G.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J.; Vernon-Carter, E.; Carrillo-Navas, H.; Pérez-Alonso, C. Viscoelasticity of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seed mucilage dispersion in the vicinity of an oil-water interface. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 49, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, V.; Gadhe, K.; Dipak, S.; Hingade, S. Studies on extraction and utilization of chia seed gel in ice cream as a stabilizer. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, B.E.; Ruivo, T.D.; da Silva Scapim, M.R.; Madrona, G.S.; Bergamasco, R.d.C. Optimization of the mucilage extraction process from chia seeds and application in ice cream as a stabilizer and emulsifier. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizi, R.; Goh, K.K.; Mutukumira, A.N. Effect of chia seed mucilage as stabiliser in ice cream. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 120, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ürkek, B. Effect of using chia seed powder on physicochemical, rheological, thermal, and texture properties of ice cream. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.A.; Piati, J.; Malacarne, L.T.; Gall, R.E.; Colla, E.; Bittencourt, P.R.; de Souza, A.H.; Gomes, S.T.; Matsushita, M. Extraction and application of chia mucilage (Salvia hispanica L.) and locust bean gum (Ceratonia siliqua L.) in goat milk frozen dessert. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 4148–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, J. Sugars and other sweeteners for ice cream and other frozen desserts. In Proceedings of the International Symposium, Athens, Greece, 18–19 September 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Akcicek, A.; Karasu, S. Utilization of cold pressed chia seed oil waste in a low-fat salad dressing as natural fat replacer. J. Food Process. Eng. 2018, 41, e12694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin-Cakmak, Z.H.; Karasu, S.; Kayacan-Cakmakoglu, S.; Akman, P.K. Investigation of potential use of by-products from cold-press industry as natural fat replacers and functional ingredients in a low-fat salad dressing. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 8, e15388. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, Z.H.; Karasu, S. Cold-pressed flaxseed oil by-product as a new source of fat replacers in low-fat salad dressing formulation: Steady, dynamic and 3-ITT rheological properties. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, F.S.; Tekin-Cakmak, Z.H.; Karasu, S.; Aksoy, A.S. Oxidative stability of the salad dressing enriched by microencapsulated phenolic extracts from cold-pressed grape and pomegranate seed oil by-products evaluated using OXITEST. Food Sci. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, S.; Karasu, S.; Tornuk, F.; Toker, O.S.; Gecgel, U.; Sagdic, O.; Ozcan, N.; Gül, O. Recovery potential of cold press byproducts obtained from the edible oil industry: Physicochemical, bioactive, and antimicrobial properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitani, M.I.; Spotorno, V.; Nolasco, S.M.; Tomás, M.C. Physicochemical and functional characterization of by-products from chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds of Argentina. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 45, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalın, A.S.; Karagözlü, C.; Ünal, G. Rheological properties of reduced-fat and low-fat ice cream containing whey protein isolate and inulin. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Sharma, H.K.; Kumar, N.; Kaur, M. The effect of inulin as a fat replacer on the quality of low-fat ice cream. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2015, 68, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilsay, T.Ö.; Yilmaz, L.; Bayizit, A.A. The effect of using a whey protein fat replacer on textural and sensory characteristics of low-fat vanilla ice cream. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 222, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, E.; Sahin, S.; Sumnu, G. Physicochemical, rheological, and sensory properties of low-fat ice cream designed by double emulsions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.; Al-Saleh, A.; Metwalli, A. Effect of inulin supplementation on rheological properties of low-fat ice cream. Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 1742–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, Z.H.; Avci, E.; Karasu, S.; Toker, O.S. Rapid determination of emulsion stability by rheology-based thermal loop test. LWT 2020, 122, 109037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Shyu, Y.-S.; Hsu, C.-K. Grape wine lees improves the rheological and adds antioxidant properties to ice cream. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukoulis, C.; Lebesi, D.; Tzia, C. Enrichment of ice cream with dietary fibre: Effects on rheological properties, ice crystallisation and glass transition phenomena. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloğlu, H.Ş.; Özcan, Y.; Karasu, S.; Çetin, B.; Sağdiç, O. Influence of transglutaminase treatment on the physicochemical, rheological, and melting properties of ice cream prepared from goat milk. Mljekarstvo 2018, 68, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Singh, A.K.; Yadav, D.N. Rheological properties of reduced fat ice cream mix containing octenyl succinylated pearl millet starch. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norton, I.T.; Spyropoulos, F.; Cox, P. Practical Food Rheology: An Interpretive Approach; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Olivos-Lugo, B.; Valdivia-López, M.; Tecante, A. Thermal and physicochemical properties and nutritional value of the protein fraction of Mexican chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.). Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2010, 16, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, D.; Arntfield, S.; Malcolmson, L.; Ryland, D. Textural analysis of fat reduced vanilla ice cream products. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, O.B.; GÜVEN, M.; Yasar, K.; Kaya, S.; Kahyaoglu, T. The functional, rheological and sensory characteristics of ice creams with various fat replacers. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2009, 62, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Wei, C.; Ye, X.; Shi, J.; Chen, S. Pectin from Citrus Canning Wastewater as Potential Fat Replacer in Ice Cream. Molecules 2018, 23, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurt, A.; Kahyaoglu, T. Rheological properties and structural characterization of salep improved by ethanol treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.S.; Sofian-Seng, N.-S.; Yusop, S.M.; Kasim, K.F.; Razali, N.S.M. Functionality of okra Gum as a novel carbohydrate-based fat replacer in ice cream. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2018, 24, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartel, R. Crystallization in Foods. In Handbook of Industrial Crystallization, 2nd ed.; Myerson, A.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 287–304. [Google Scholar]
- Fuangpaiboon, N.; Kijroongrojana, K. Sensorial and physical properties of coconut-milk ice creammodified with fat replacers. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Roos, Y.H. Mapping the Different States of Food Components Using State Diagrams. In Modern Biopolymer Science; Kasapis, S., Norton, I.T., Ubbink, J.B., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 261–276. [Google Scholar]
- Pintor-Jardines, A.; Arjona-Roman, J.L.; Totosaus-Sanchez, A.; Severiano-Perez, P.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, L.R.; Escalona-Buendia, H.B. The influence of agave fructans on thermal properties of low-fat, and low-fat and sugar ice cream. LTW Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 93, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, V.B.; Wolters, C.L.; Vodovotz, Y.; Ji, T. Physical Properties of Ice Cream Containing Milk Protein Concentrates. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykan, V.; Sezgin, E.; Guzel-Seydim, Z. Use of fat replacers in the production of reduced-calorie vanilla ice cream. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalın, A.S.; Kesenkas, H.; Dinkci, N.; Unal, G.; Ozer, E.; Kınık, O. Enrichment of probiotic ice cream with different dietary fibers: Structural characteristics and culture viability. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, A.I.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Elfaruk, M.S.; Alsaleem, K.A.; Hammam, A.R.A.; El-Derwy, Y.M.A. A novel process to improve the characteristics of low-fat ice cream using date fiber powder. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2836–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samakradhamrongthai, R.S.; Jannu, T.; Supawan, T.; Khawsud, A.; Aumpa, P.; Renaldi, G. Inulin application on the optimization of reduced-fat ice cream using response surface methodology. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanWees, S.R.; Rankin, S.A.; Hartel, R.W. The microstructural, melting, rheological, and sensorial properties of high-overrun frozen desserts. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, M.H.; Akbari, M. The effect of inulin on the physicochemical properties and sensory attributes of low-fat ice cream. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 57, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akın, M.B.; Akın, M.S.; Kırmacı, Z. Effects of inulin and sugar levels on the viability of yogurt and probiotic bacteria and the physical and sensory characteristics in probiotic ice-cream. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
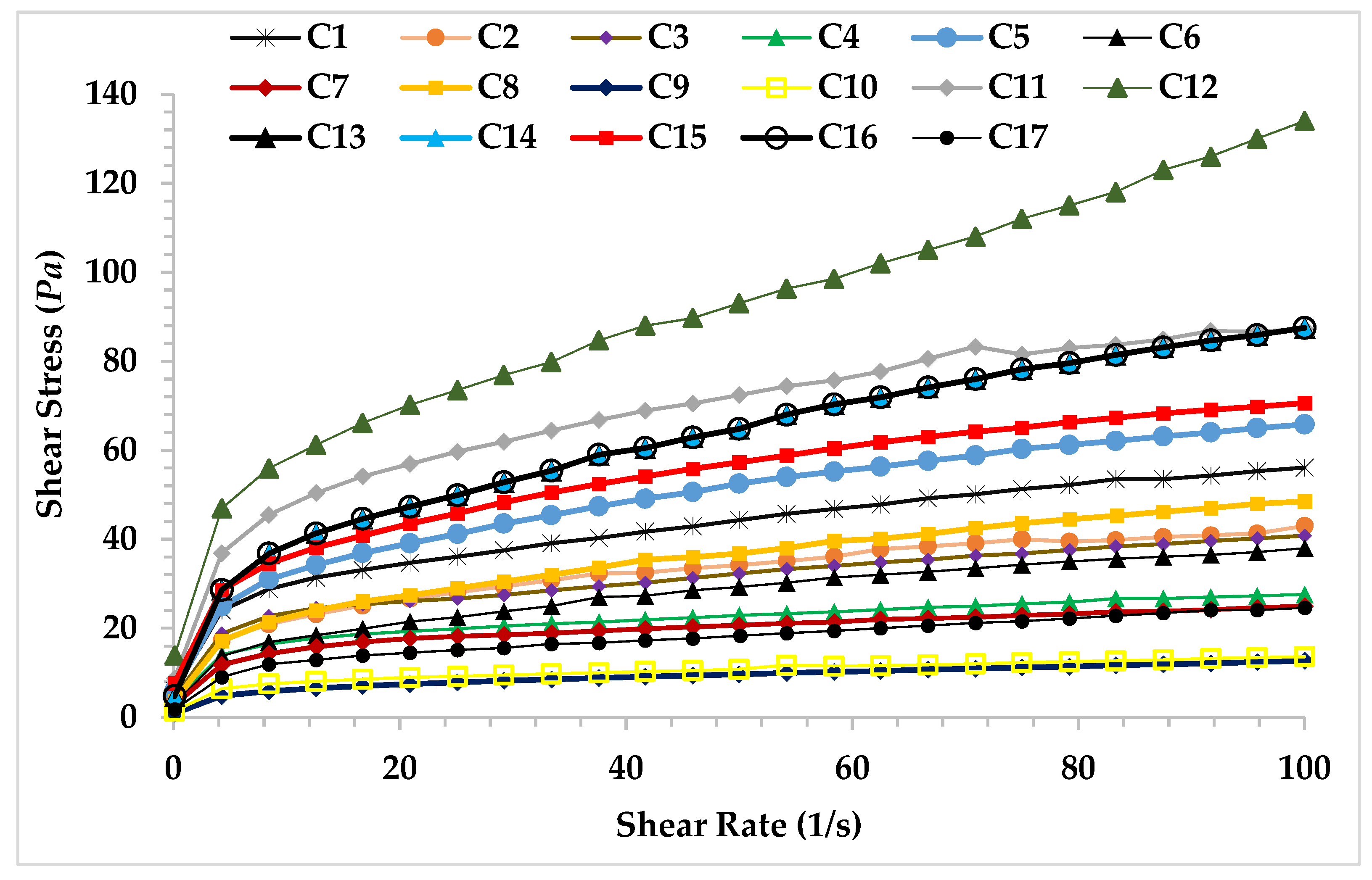





| Samples | XG (%) | Fat (%) | CSOB (%) | K (Pasn) | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.30 | 7.5 | 3 | 17.23 | 0.26 | 1.00 |
| C2 | 0.20 | 12.5 | 1 | 10.95 | 0.29 | 1.00 |
| C3 | 0.40 | 2.5 | 3 | 11.61 | 0.27 | 0.99 |
| C4 | 0.40 | 2.5 | 1 | 9.46 | 0.23 | 0.99 |
| C5 | 0.30 | 12.5 | 2 | 14.83 | 0.32 | 1.00 |
| C6 | 0.20 | 7.5 | 2 | 7.51 | 0.35 | 1.00 |
| C7 | 0.30 | 2.5 | 2 | 8.28 | 0.24 | 0.99 |
| C8 | 0.20 | 12.5 | 3 | 12.57 | 0.35 | 1.00 |
| C9 | 0.30 | 7.5 | 1 | 9.38 | 0.32 | 1.00 |
| C10 | 0.30 | 2.5 | 1 | 4.01 | 0.26 | 0.99 |
| C11 | 0.40 | 12.5 | 3 | 26.05 | 0.28 | 1.00 |
| C12 | 0.40 | 7.5 | 2 | 20.69 | 0.37 | 0.99 |
| C13 | 0.30 | 7.5 | 2 | 15.06 | 0.38 | 1.00 |
| C14 | 0.30 | 7.5 | 2 | 15.01 | 0.38 | 1.00 |
| C15 | 0.40 | 12.5 | 1 | 17.52 | 0.30 | 1.00 |
| C16 | 0.30 | 7.5 | 2 | 15.62 | 0.37 | 1.00 |
| C17 | 0.20 | 2.5 | 3 | 5.30 | 0.33 | 0.99 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Squares | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 529.67 | 9 | 58.85 | 56.29 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A-XG | 280.46 | 1 | 280.46 | 268.24 | <0.0001 | |
| B-CSOB | 86.69 | 1 | 86.69 | 82.91 | <0.0001 | |
| C-Fat | 138.80 | 1 | 138.80 | 132.75 | <0.0001 | |
| AB | 11.93 | 1 | 11.93 | 11.41 | 0.0118 | |
| AC | 2.29 | 1 | 2.29 | 2.19 | 0.1824 | |
| BC | 0.9184 | 1 | 0.9184 | 0.8783 | 0.3799 | |
| A² | 1.91 | 1 | 1.91 | 1.83 | 0.2183 | |
| B² | 0.0066 | 1 | 0.0066 | 0.0063 | 0.9391 | |
| C² | 7.74 | 1 | 7.74 | 7.41 | 0.0297 | |
| Residual | 7.32 | 7 | 1.05 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 7.09 | 5 | 1.42 | 12.18 | 0.0776 | not significant |
| R2 | 0.9864 | |||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9688 | |||||
| Predicted R2 | 0.8918 | |||||
| Adeq Precision | 30.5150 |
| Rheological Analysis | Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FF-IC | LF-IC | CBLF-IC | ||
| Steady shear | K (Pasn) | 5.66 ± 0.07 a | 3.46 ± 0.03 b | 5.53 ± 0.09 a |
| σ = K × γn | n | 0.32 ± 0.01 b | 0.36 ± 0.01 a | 0.30 ± 0.02 b |
| R2 | >0.99 | >0.99 | >0.99 | |
| Frequency | ||||
| = × (ω)n′ | K ′ | 23.41 ± 0.18 a | 3.09 ± 0.06 b | 23.09 ± 0.24 a |
| n′ | 0.268 ± 0.002 b | 0.535 ± 0.003 a | 0.268 ± 0.002 b | |
| R2 | 0.993 | 0.979 | 0.9878 | |
| = × (ω)n″ | K″ | 8.46 ± 0.12 a | 2.46 ± 0.02 b | 8.15 ± 0.35 a |
| n″ | 0.212 ± 0.001 c | 0.288 ± 0.002 a | 0.268 ± 0.003 b | |
| R2 | 0.979 | 0.983 | 0.978 | |
| 3-ITT | G0′ | 21.12 ± 0.08 a | 8.42 ± 0.04 c | 18.86 ± 0.05 b |
| Ge′ | 38.73 ± 0.15 a | 14.81 ± 0.08 c | 26.34 ± 0.11 b | |
| k | 0.027 ± 0.001 a | 0.011 ± 0.000 b | 0.025 ± 0.001 a | |
| Ge′/ G0′ | 1.834 | 1.760 | 1.397 | |
| k × 1000 | 27.00 | 11.10 | 25.33 | |
| R2 | 0.983 | 0.995 | 0.996 | |
| ζ-potential (mV) | −39.13 ± 1.041 a | −32.03 ± 1.464 b | −28.90 ± 1.058 c | |
| d32 (µm) | 1.305 ± 0.044 a | 0.877 ± 0.024 b | 0.494 ± 0.012 c | |
| PdI | 0.741 ± 0.127 a | 0.493 ± 0.167 a | 0.534 ± 0.174 a | |
| Sample | T0 (°C) | Tend (°C) | Tf (°C) | ΔT (°C) | ΔHf (J/g) | Wf (%) | Overrun (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FF-IC | −11.67 ± 0.06 C | 5.39 ± 0.04 A | −3.66 ± 0.02 B | 17.06 ± 0.05 A | 166.01 ± 2.68 B | 49.72 ± 0.28 B | 75.41 ± 0.18 B |
| LF-IC | −11.0 ± 0.15 B | 4.95 ± 0.01 B | −3.35 ± 0.05 A | 15.95 ± 0.08 B | 199.32 ± 2.45 A | 59.51 ± 1.05 A | 71.23 ± 0.31 C |
| CBLF-IC | −10.18 ± 0.04 A | 3.23 ± 0.02 C | −3.98 ± 0.03 C | 14.16 ± 0.10 C | 146.85 ± 1.25 C | 43.95 ± 0.74 C | 86.31 ± 0.62 A |
| Sample | Color and Appearance | Icy Structure and Consistency | Foreign Taste and Smell | Cream Taste | Melting Resistance | General Acceptance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FF-IC | 7.90 ± 1.10 A | 7.01 ± 1.10 A | 7.20 ± 1.40 A | 7.00 ± 2.26 A | 7.15 ± 2.08 A | 7.44 ± 1.50 A |
| LF-IC | 6.75 ± 1.25 B | 5.01 ± 1.73 B | 6.10 ± 1.73 A,B | 5.70 ± 1.51 A | 5.13 ± 1.45 B | 5.72 ± 1.85 B |
| CBLF-IC | 6.21 ± 0.92 B | 6.00 ± 1.42 A,B | 5.50 ± 2.51 A,B | 6.40 ± 1.25 A | 6.11 ± 1.10 A,B | 6.12 ± 1.35 A,B |
| Sample | L* | a* | b* |
|---|---|---|---|
| FF-IC | 83.42 ± 0.23 A | 4.93 ± 0.02 A | 15.41 ± 0.08 A |
| LF-IC | 79.07 ± 0.43 B | 4.81 ± 0.12 A | 15.11 ± 0.15 A |
| CBLF-IC | 77.08 ± 0.58 C | 4.23 ± 0.15 B | 13.63 ± 0.01 B |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atik, I.; Tekin Cakmak, Z.H.; Avcı, E.; Karasu, S. The Effect of Cold Press Chia Seed Oil By-Products on the Rheological, Microstructural, Thermal, and Sensory Properties of Low-Fat Ice Cream. Foods 2021, 10, 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102302
Atik I, Tekin Cakmak ZH, Avcı E, Karasu S. The Effect of Cold Press Chia Seed Oil By-Products on the Rheological, Microstructural, Thermal, and Sensory Properties of Low-Fat Ice Cream. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102302
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtik, Ilker, Zeynep Hazal Tekin Cakmak, Esra Avcı, and Salih Karasu. 2021. "The Effect of Cold Press Chia Seed Oil By-Products on the Rheological, Microstructural, Thermal, and Sensory Properties of Low-Fat Ice Cream" Foods 10, no. 10: 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102302
APA StyleAtik, I., Tekin Cakmak, Z. H., Avcı, E., & Karasu, S. (2021). The Effect of Cold Press Chia Seed Oil By-Products on the Rheological, Microstructural, Thermal, and Sensory Properties of Low-Fat Ice Cream. Foods, 10(10), 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102302






