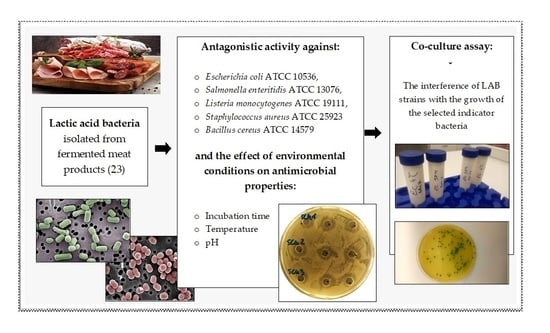
The Influence of Environmental Conditions on the Antagonistic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Meat Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Collection and Bacterial Growth Conditions
2.2. Antagonistic Activity
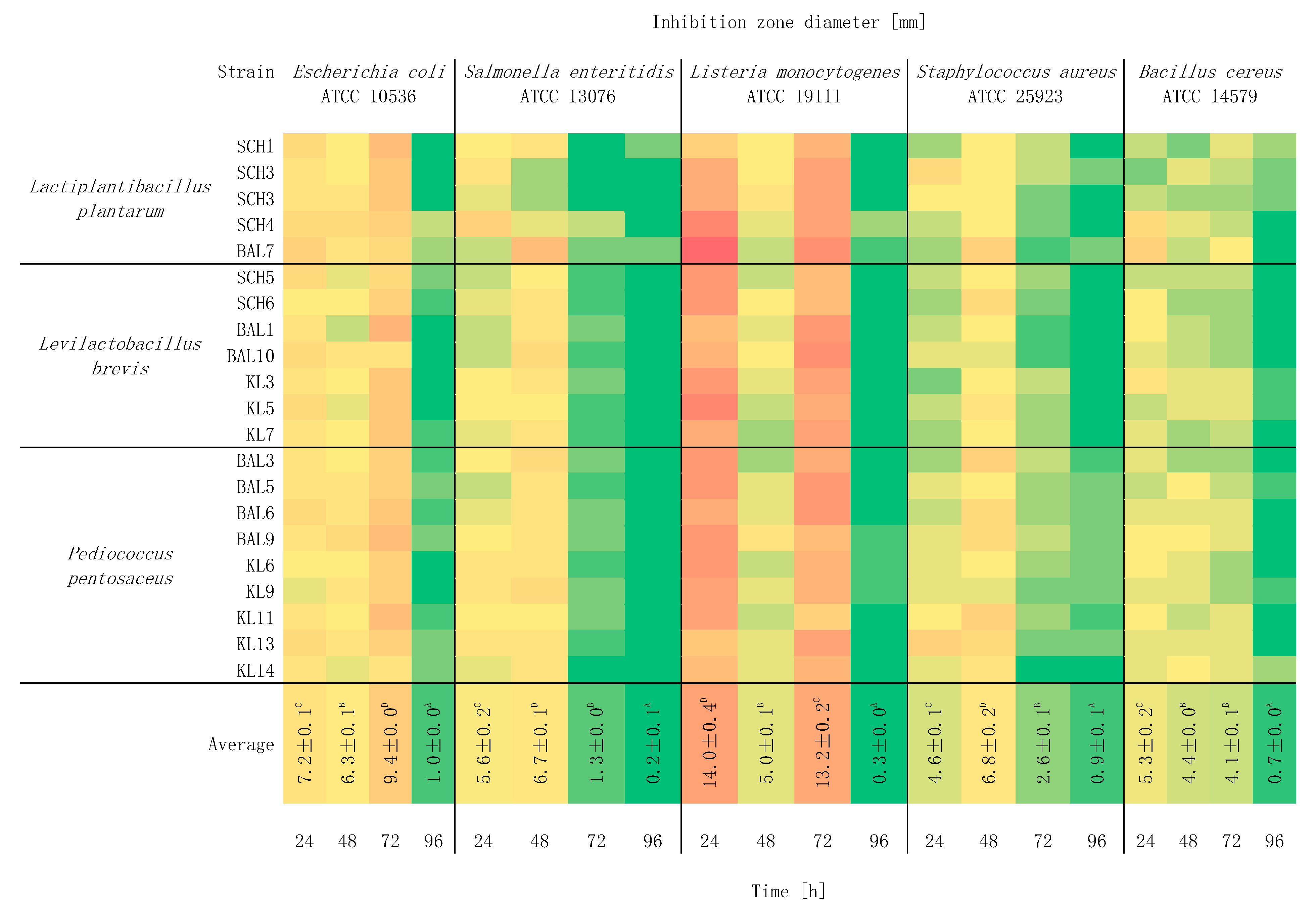
2.3. Study of the Effect of Incubation Time on Antagonistic Activity
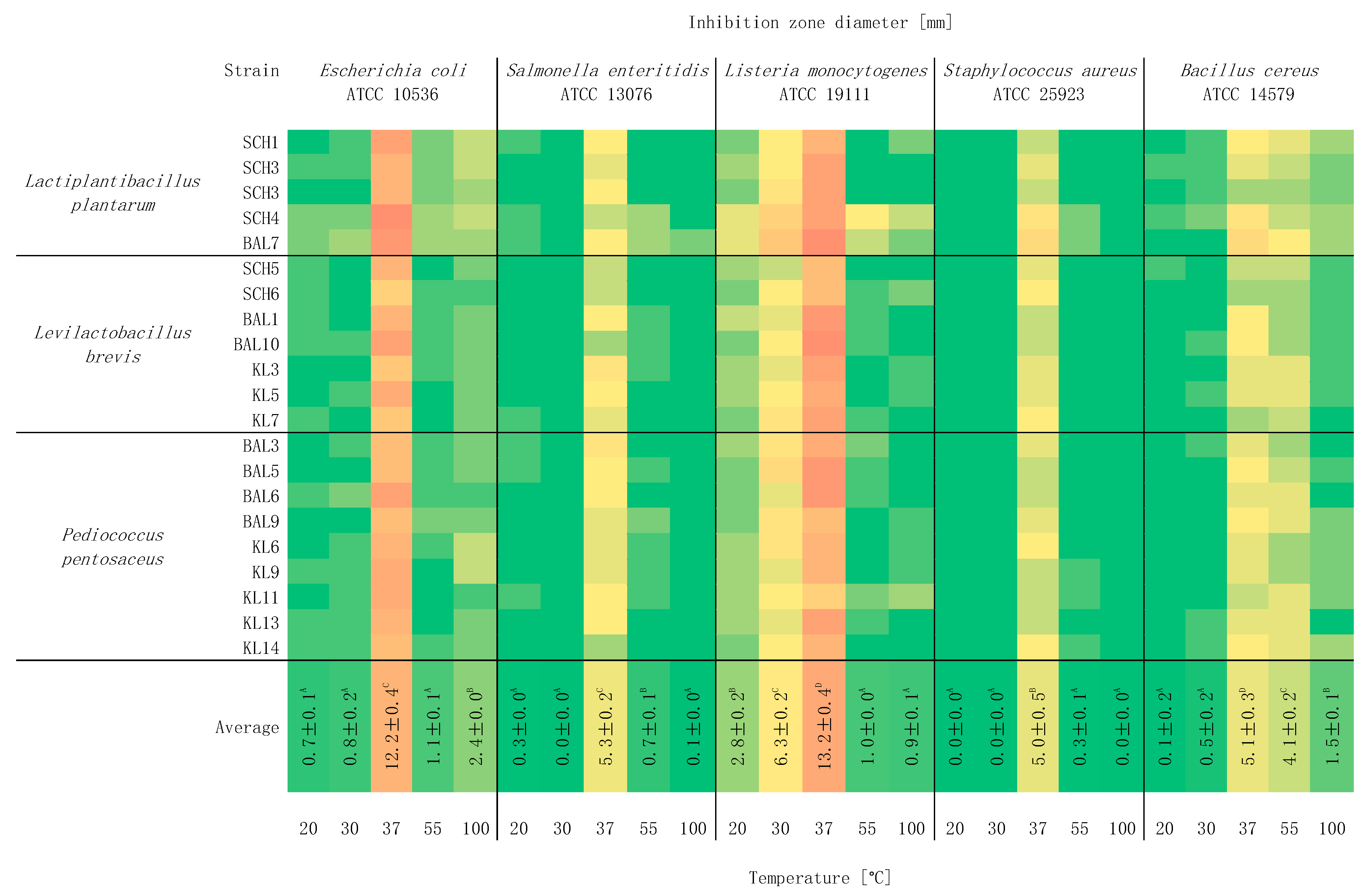
2.4. Study of the Effect of Temperature on Antagonistic Activity
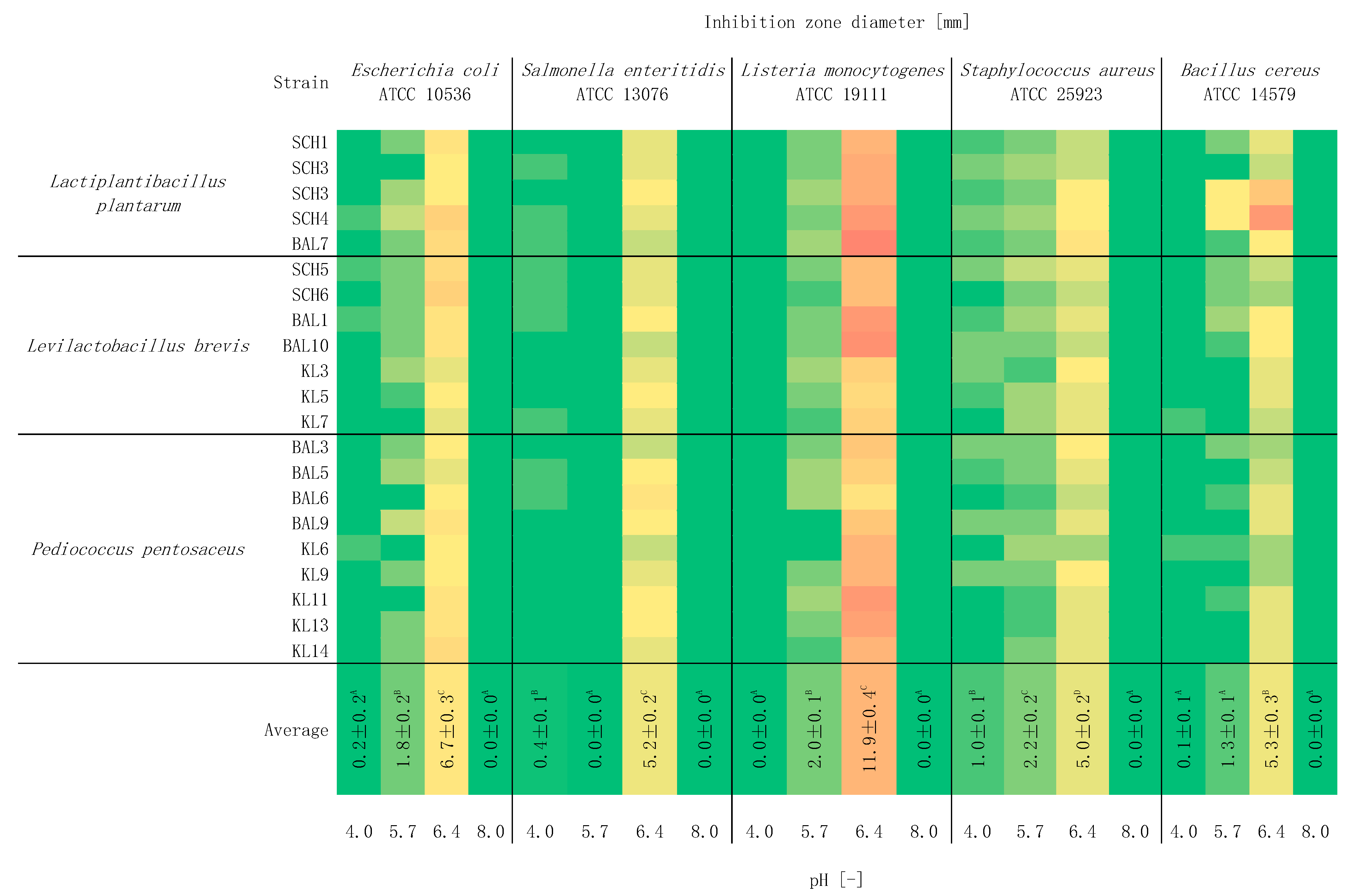
2.5. Study of the Effect of pH on Antagonistic Activity
2.6. Co-Culture Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
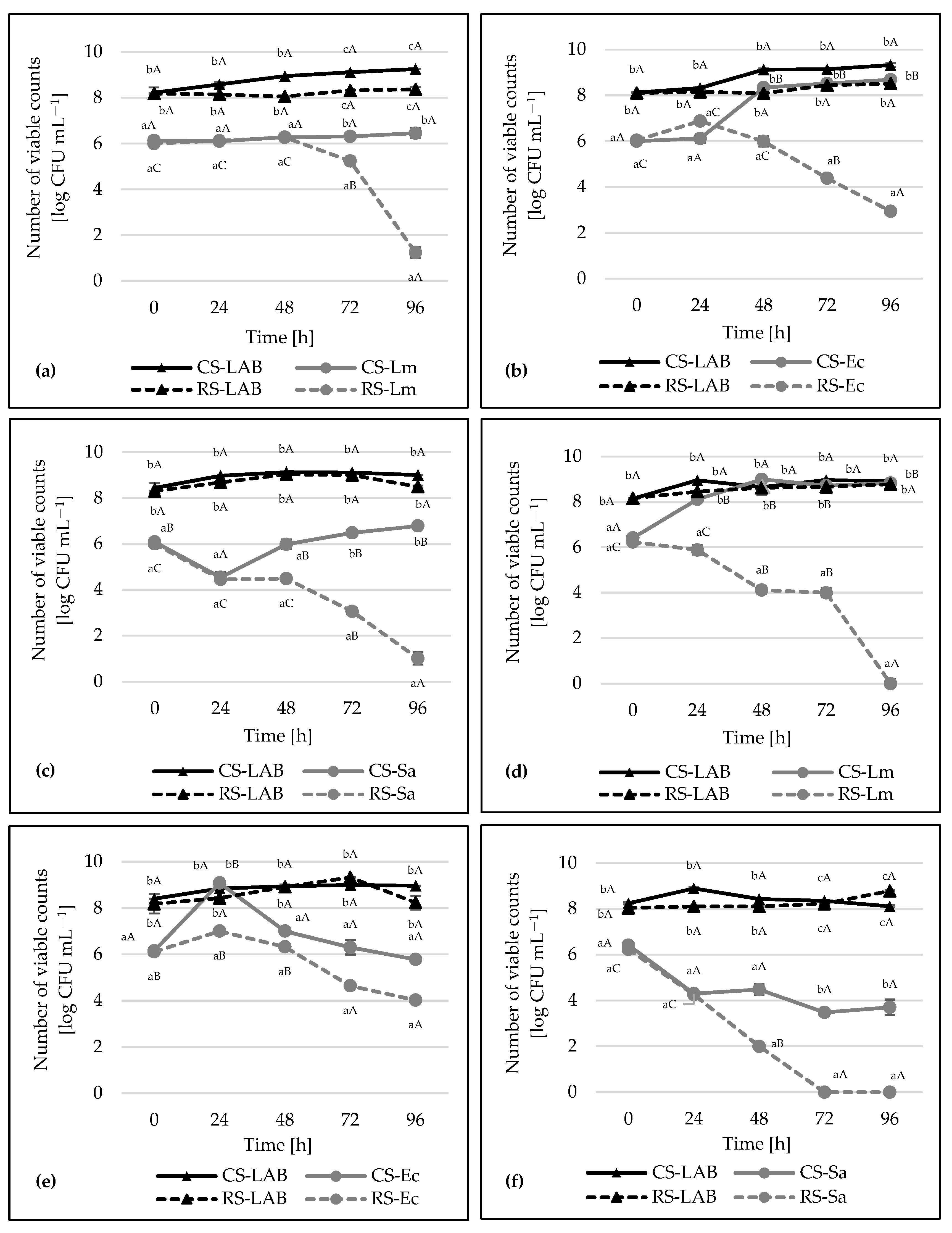
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bajpai, V.K.; Han, J.H.; Rather, I.A.; Park, C.; Lim, J.; Paek, W.K.; Lee, J.S.; Park, Y.H. Characterization and antibacterial potential of lactic acid bacterium Pediococcus pentosaceus 4I1 isolated from freshwater fish Zacco koreanus. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratajczak, K.; Piotrowska-Cyplik, A. Metabolites of lactic acid bacteria—Overview and industrial applications. Adv. Microbiol. 2017, 56, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Zoumpopoulou, G.; Foligné, B.; Alexandraki, V.; Kazou, M.; Pot, B.; Tsakalidou, E. Discovering probiotic microorganisms: In vitro, in vivo, genetic and omics approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Daim, A.; Hassouna, N.; Hafez, M.; Ashor, M.S.A.; Aboulwafa, M.M. Antagonistic activity of Lactobacillus isolates against Salmonella typhi in vitro. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 680605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontana, C.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Vignolo, G.; Saavedra, L. Occurrence of antilisterial structural bacteriocins genes in meat borne lactic acid bacteria. Food Control 2015, 47, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, V.; Khiabani, M.S.; Mokarram, R.R.; Hassanzadeh, A.M.; Ahmadi, E.; Gharenaghadeh, S.; Karimi, N.; Kafil, H.S. Lactobacillus plantarum as a probiotic potential from kouzeh cheese (traditional Iranian cheese) and its antimicrobial activity. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Cui, X.; Gu, S.; Yan, X.; Li, R.; Xia, S.; Chen, H.; Ge, J. Antioxidative and probiotic activities of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional artisanal milk cheese from Northeast China. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trush, E.A.; Poluektova, E.A.; Beniashvilli, A.G.; Shifrin, O.S.; Poluektov, Y.M.; Ivashkin, V.T. The Evolution of Human Probiotics: Challenges and Prospects. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbanwo, S.T.; Sanni, A.I.; Onilude, A.A. Influence of cultural conditions on the production of bacteriocin by Lactobacillus brevis OG1. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 2, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbosa, M.S.; Todorov, S.D.; Ivanova, I.V.; Belguesmia, Y.; Choiset, Y.; Rabesona, H.; Chobert, J.M.; Haertle, T.; Franco, B.D.G.M. Characterization of a two-peptide plantaricin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum MBSa4 isolated from Brazilian salami. Food Control 2016, 60, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mataragas, M.; Metaxopoulos, J.; Galiotou, M.; Drosinos, E.H. Influence of pH and temperature on growth and bacteriocin production by Leuconostoc mesenteroides L124 and Lactobacillus curvatus L442. Meat Sci. 2003, 64, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzepkowska, A.; Zielińska, D.; Ołdak, A.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. Safety assessment and antimicrobial properties of the lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from Polish raw fermented meat products. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2736–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.; Harris, H.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.M.; Chu, Y.C.; Hsiao, C.P.; Wu, J.S.; Hsieh, C.W.; Hou, C.Y. The Optimization of Plasma-Activated Water Treatments to Inactivate Salmonella Enteritidis (ATCC 13076) on Shell Eggs. Foods 2019, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ołdak, A.; Zielińska, D.; Rzepkowska, A.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. Comparison of antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from two different kinds of regional cheeses from Poland: Oscypek and Korycinski Cheese. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6820369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindbäck, T.; Granum, P.E. Bacillus cereus. In Food Microbiology: Fundamentals and Frontiers, 1st ed.; Doyle, M.P., Diez-Gonzalez, F., Hill, C., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.L.Y.; Forsythe, S.J.; El-Nezami, H. Probiotics interaction with foodborne pathogens: A potential alternative to antibiotics and future challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3320–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, N.A.; Kermanshahi, R.K.; Yakhchali, B.; Sattari, T.N. Antagonistic activity of probiotic lactobacilli against Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 2169–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settanni, L.; Valmorri, S.; Suzzi, G.; Corsetti, A. The role of environmental factors and medium composition on bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances (BLIS) production by Enterococcus mundtii strains. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetanková, J.; Hladíková, Z.; Valach, F.; Zimanová, M.; Kohajdová, Z.; Greif, G.; Greifová, M. Influence of aerobic and anaerobic conditions on the growth and metabolism of selected strains of Lactobacillus plantarum. Acta Chim. Slovaca 2012, 5, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, K.; Liu, M.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, T.; Fan, M.; Wei, X. Antibacterial activity of selenium-enriched lactic acid bacteria against common food-borne pathogens in vitro. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 1930–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, H.S.; Meng, X.C.; Wang, H. Plantaricin MG active against Gram-negative bacteria produced by Lactobacillus plantarum KLDS1. 0391 isolated from “Jiaoke”, a traditional fermented cream from China. Food Control 2010, 21, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarela, M.; Rantala, M.; Hallamaa, K.; Nohynek, L.; Virkajärvi, I.; Mättö, J. Stationary-phase acid and heat treatments for improvement of the viability of probiotic lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Settachaimongkon, S.; van Valenberg, H.J.; Gazi, I.; Nout, M.R.; van Hooijdonk, T.C.; Zwietering, M.H.; Smid, E.J. Influence of Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 on post-acidification, metabolite formation and survival of starter bacteria in set-yoghurt. Food Microbiol. 2016, 59, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mıdık, F.; Tokatlı, M.; Elmacı, S.B.; Özçelik, F. Influence of different culture conditions on exopolysaccharide production by indigenous lactic acid bacteria isolated from pickles. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.T.; Hsieh, P.S.; Ho, H.H.; Hsieh, S.H.; Kuo, Y.W.; Yang, S.F.; Lin, C.W. Antibacterial activity of viable and heat-killed probiotic strains against oral pathogens. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareb, R.; Bernardeau, M.; Gueguen, M.; Vernoux, J.P. In vitro characterization of aggregation and adhesion properties of viable and heat-killed forms of two probiotic Lactobacillus strains and interaction with foodborne zoonotic bacteria, especially Campylobacter jejuni. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, D.; Łepecka, A.; Ołdak, A.; Długosz, E.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. Growth and adhesion inhibition of pathogenic bacteria by live and heat-killed food-origin Lactobacillus strains or their supernatants. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2021, 368, fnab024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, M.P.; Capozzi, V.; Longo, A.; Russo, P.; Rieu, A.; Guzzo, J.; Fiocco, D. The phenotypic analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum shsp mutants reveals a potential role for hsp1 in cryotolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, S.D.; Franco, B.D.G.D.M. Lactobacillus plantarum: Characterization of the species and application in food production. Food Rev. Int. 2010, 26, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, X.; Luo, T.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z. Cold-stress response of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum K25 by iTRAQ proteomic analysis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoudia, N.; Rieu, A.; Briandet, R.; Deschamps, J.; Chluba, J.; Jego, G.; Garrido, C.; Guzzo, J. Biofilms of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus fermentum: Effect on stress responses, antagonistic effects on pathogen growth and immunomodulatory properties. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duar, R.M.; Lin, X.B.; Zheng, J.; Martino, M.E.; Grenier, T.; Pérez-Muñoz, M.E.; Leulier, F.; Gänzle, M.; Walter, J. Lifestyles in transition: Evolution and natural history of the genus Lactobacillus. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, S27–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseini Nezhad, M.; Hussain, M.A.; Britz, M.L. Stress responses in probiotic Lactobacillus casei. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2015, 55, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosu-Tudor, S.S.; Brown, L.; Hebert, E.M.; Brezeanu, A.; Brinzan, A.; Fadda, S.; Mozzi, F.; Zamfir, M. S-layer production by Lactobacillus acidophilus IBB 801 under environmental stress conditions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4573–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zotta, T.; Parente, E.; Ricciardi, A. Aerobic metabolism in the genus Lactobacillus: Impact on stress response and potential applications in the food industry. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moradi, M.; Mardani, K.; Tajik, H. Characterization and application of postbiotics of Lactobacillus spp. on Listeria monocytogenes in vitro and in food models. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 111, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, W.P.; Hertel, C.; Genus, I. Lactobacillus. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; Vos, P., Garrity, G., Jones, D., Krieg, N.R., Ludwig, W., Rainey, F.A., Schleifer, K.-H., Whitman, W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 3, pp. 465–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Singh, B.P.; Thakur, N.; Gulati, S.; Gupta, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Panwar, H. Antibacterial effects of Lactobacillus isolates of curd and human milk origin against food-borne and human pathogens. 3 Biotech. 2017, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.H.; Ren, L.Q.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, B.C. Characterization of antimicrobial activity of three Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from Chinese traditional dairy food. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ołdak, A.; Zielińska, D.; Łepecka, A.; Długosz, E.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. Lactobacillus plantarum Strains Isolated from Polish Regional Cheeses Exhibit Anti-Staphylococcal Activity and Selected Probiotic Properties. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 12, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eddine, S.D.; Yasmine, S.; Fatima, G.; Amina, Z.; Battache, G.; Mebrouk, K. Antifungal and antibacterial activity of some lactobacilli isolated from camel’s milk biotope in the south of Algeria. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2020, 9, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Patel, A.; Ambalam, P.; Holst, O.; Ljungh, A.; Prajapati, J. Determination of an antimicrobial activity of Weissella confusa, Lactobacillus fermentum, and Lactobacillus plantarum against clinical pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in co-culture. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabasco, R.; García-Cayuela, T.; Peláez, C.; Requena, T. Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5 increases lactacin B production when it senses live target bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 132, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Lim, H.S.; Oh, J.S.; Lim, Y.J.; Wuertz-Kozak, K.; Harro, J.M.; Shirtliff, M.E.; Achermann, Y. Antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus salivarius and Lactobacillus fermentum against Staphylococcus aureus. Path. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohestani, M.; Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Badali, A. Effects of cell-free supernatant of Lactobacillus acidophilus LA5 and Lactobacillus casei 431 against planktonic form and biofilm of Staphylococcus aureus. Vet. Res. Forum 2018, 9, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, I.M.; Møretrø, T.; Katla, T.; Axelsson, L.; Storrø, I. Influence of complex nutrients, temperature and pH on bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus sakei CCUG 42687. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 53, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, V.; Quiberoni, A.; Reinheimer, J.; Suárez, V. Functional properties of Lactobacillus plantarum strains: A study in vitro of heat stress influence. Food Microbiol. 2016, 54, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlindungan, E.; Lugli, G.A.; Ventura, M.; van Sinderen, D.; Mahony, J. Lactic Acid Bacteria Diversity and Characterization of Probiotic Candidates in Fermented Meats. Foods 2021, 10, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Tested LAB Strains [12] | GenBank Accession [12] | New Nomenclature of LAB [13] |
|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus plantarum SCH1 | KX 014848 | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SCH1 |
| Lactobacillus plantarum SCH2 | KX 014847 | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SCH2 |
| Lactobacillus plantarum SCH3 | KX 021365 | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SCH3 |
| Lactobacillus plantarum SCH4 | KX 021366 | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SCH4 |
| Lactobacillus plantarum BAL7 | KX 021348 | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BAL7 |
| Lactobacillus brevis SCH5 | KX 021367 | Levilactobacillus brevis SCH5 |
| Lactobacillus brevis SCH6 | KX 021368 | Levilactobacillus brevis SCH6 |
| Lactobacillus brevis BAL1 | KX 021369 | Levilactobacillus brevis BAL1 |
| Lactobacillus brevis BAL10 | KX 021350 | Levilactobacillus brevis BAL10 |
| Lactobacillus brevis KL3 | KX 021351 | Levilactobacillus brevis KL3 |
| Lactobacillus brevis KL5 | KX 021352 | Levilactobacillus brevis KL5 |
| Lactobacillus brevis KL7 | KX 021354 | Levilactobacillus brevis KL7 |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus BAL3 | KX 021370 | Unchanged name |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus BAL5 | KX 021346 | Unchanged name |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus BAL6 | KX 021347 | Unchanged name |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus BAL9 | KX 021349 | Unchanged name |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus KL6 | KX 021353 | Unchanged name |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus KL9 | KX 021361 | Unchanged name |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus KL11 | KX 021362 | Unchanged name |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus KL13 | KX 021363 | Unchanged name |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus KL14 | KX 021364 | Unchanged name |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łepecka, A.; Szymański, P.; Rutkowska, S.; Iwanowska, K.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. The Influence of Environmental Conditions on the Antagonistic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Meat Products. Foods 2021, 10, 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102267
Łepecka A, Szymański P, Rutkowska S, Iwanowska K, Kołożyn-Krajewska D. The Influence of Environmental Conditions on the Antagonistic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Meat Products. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102267
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁepecka, Anna, Piotr Szymański, Sylwia Rutkowska, Kinga Iwanowska, and Danuta Kołożyn-Krajewska. 2021. "The Influence of Environmental Conditions on the Antagonistic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Meat Products" Foods 10, no. 10: 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102267
APA StyleŁepecka, A., Szymański, P., Rutkowska, S., Iwanowska, K., & Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. (2021). The Influence of Environmental Conditions on the Antagonistic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Meat Products. Foods, 10(10), 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102267