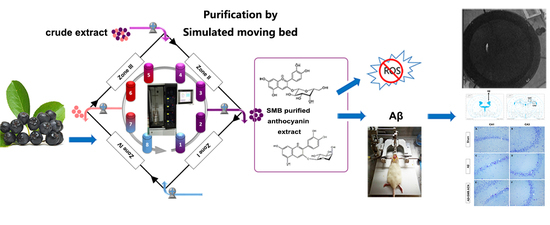
Isolation of Neuroprotective Anthocyanins from Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) against Amyloid-β-Induced Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Plants Material
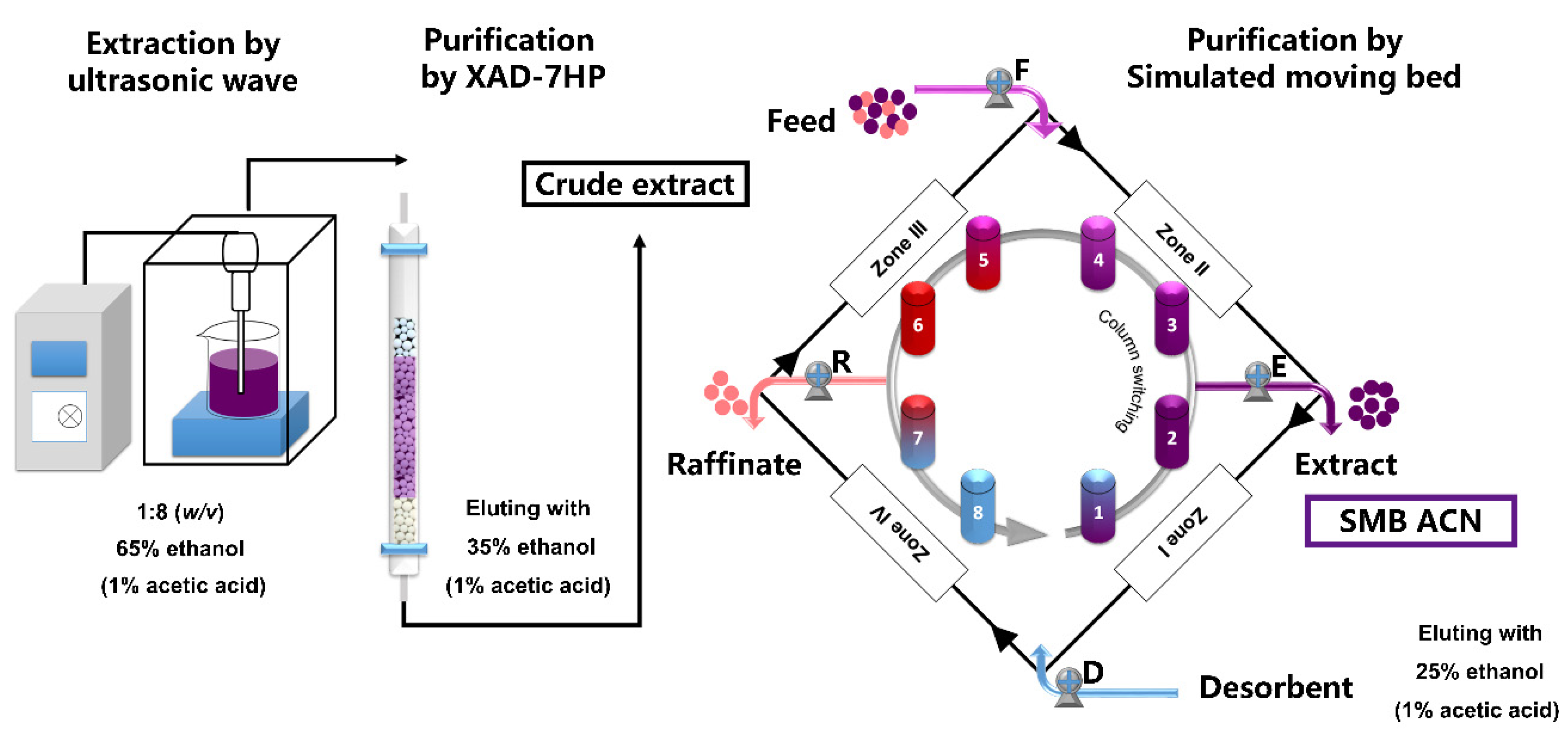
2.3. Extraction of Anthocyanins
2.4. Purification of Anthocyanins by SMB
2.5. HPLC-PDA and UPLC-QTOF-MS Analysis
2.6. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Assay
2.7. ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Assay
2.8. Experimental Animals
2.9. Preparation of Aβ-Induced Damage Rat Model
2.10. Morris Water Maze
2.11. Nissl Staining
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
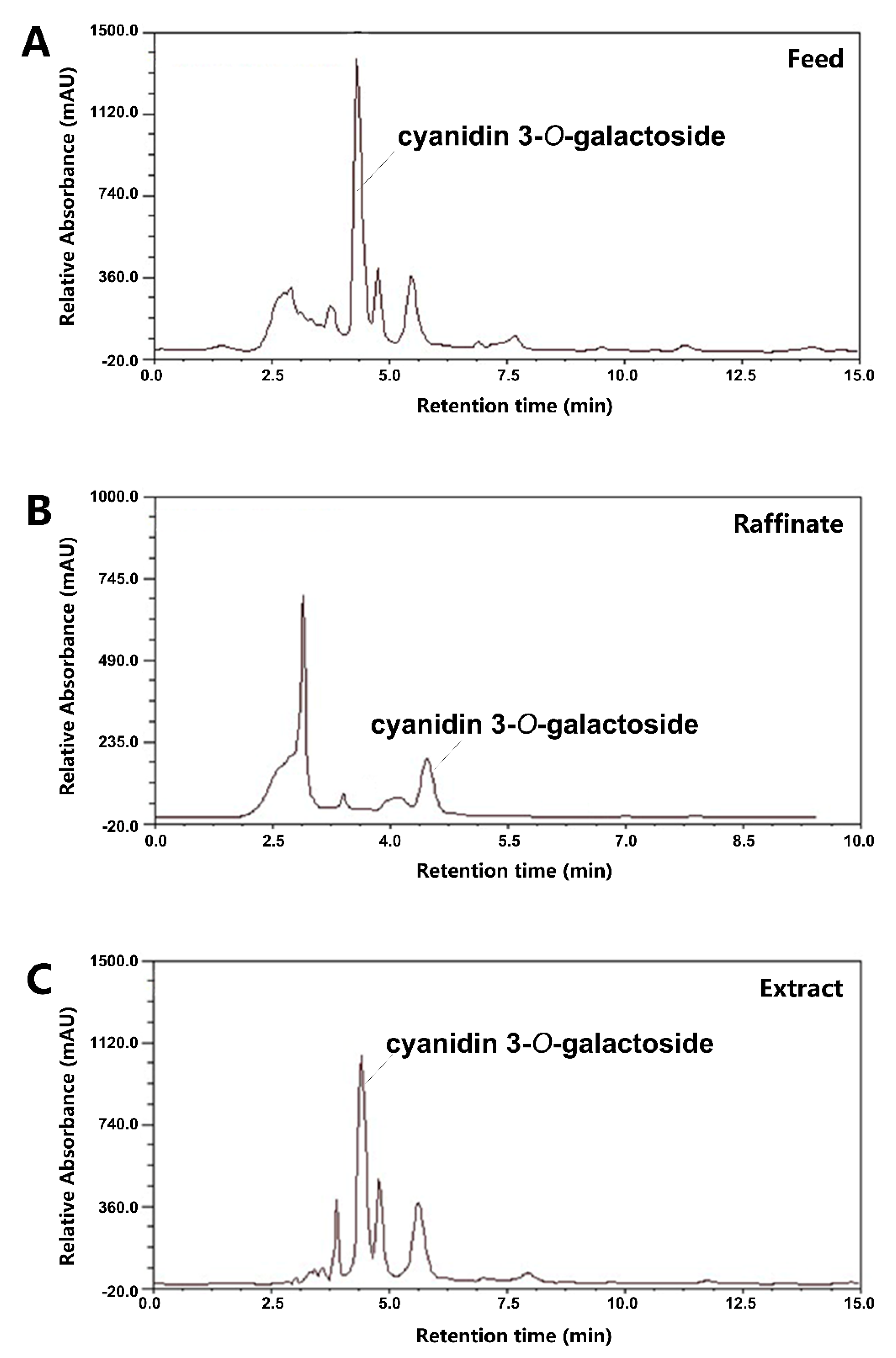
3.1. Isolation and Purification of Black Chokeberry Anthocyanins by SMB
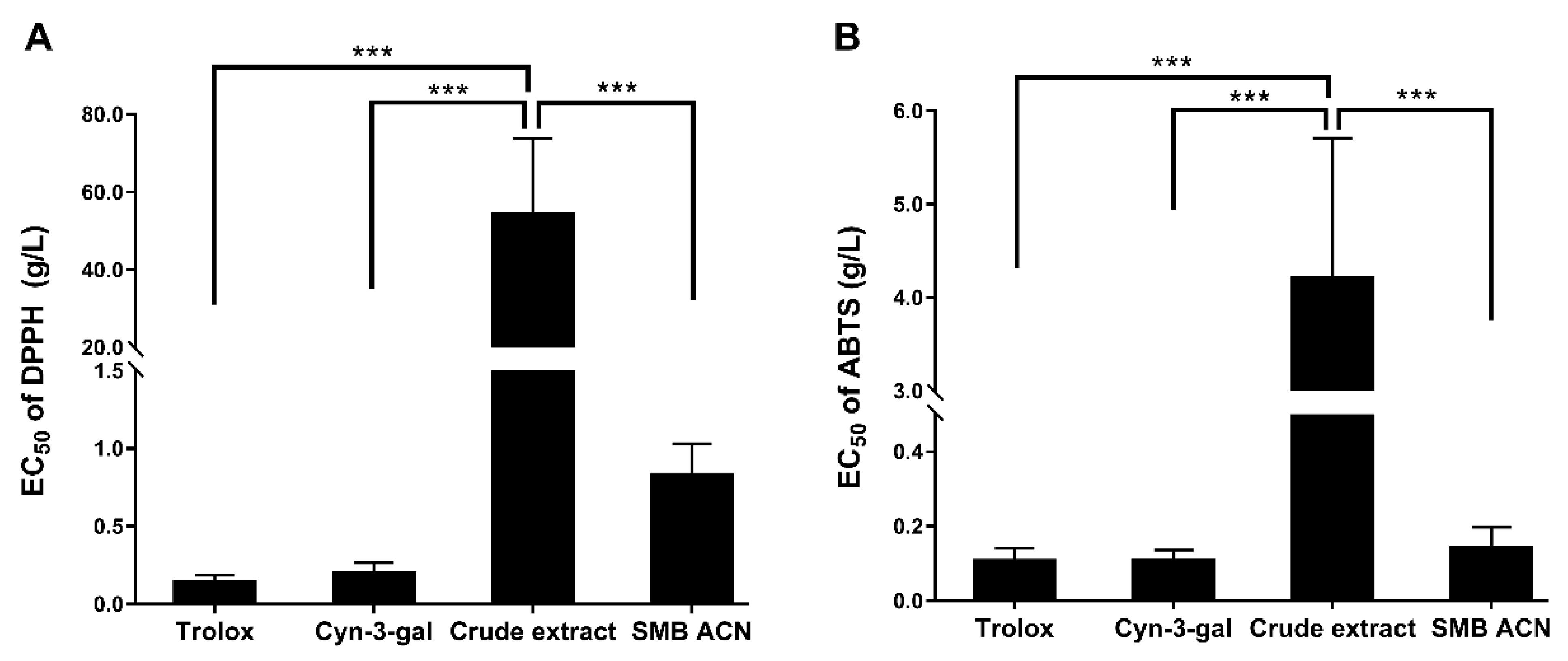
3.2. The Free Radical Scavenging Abilities of Black Chokeberry Anthocyanin Extracts
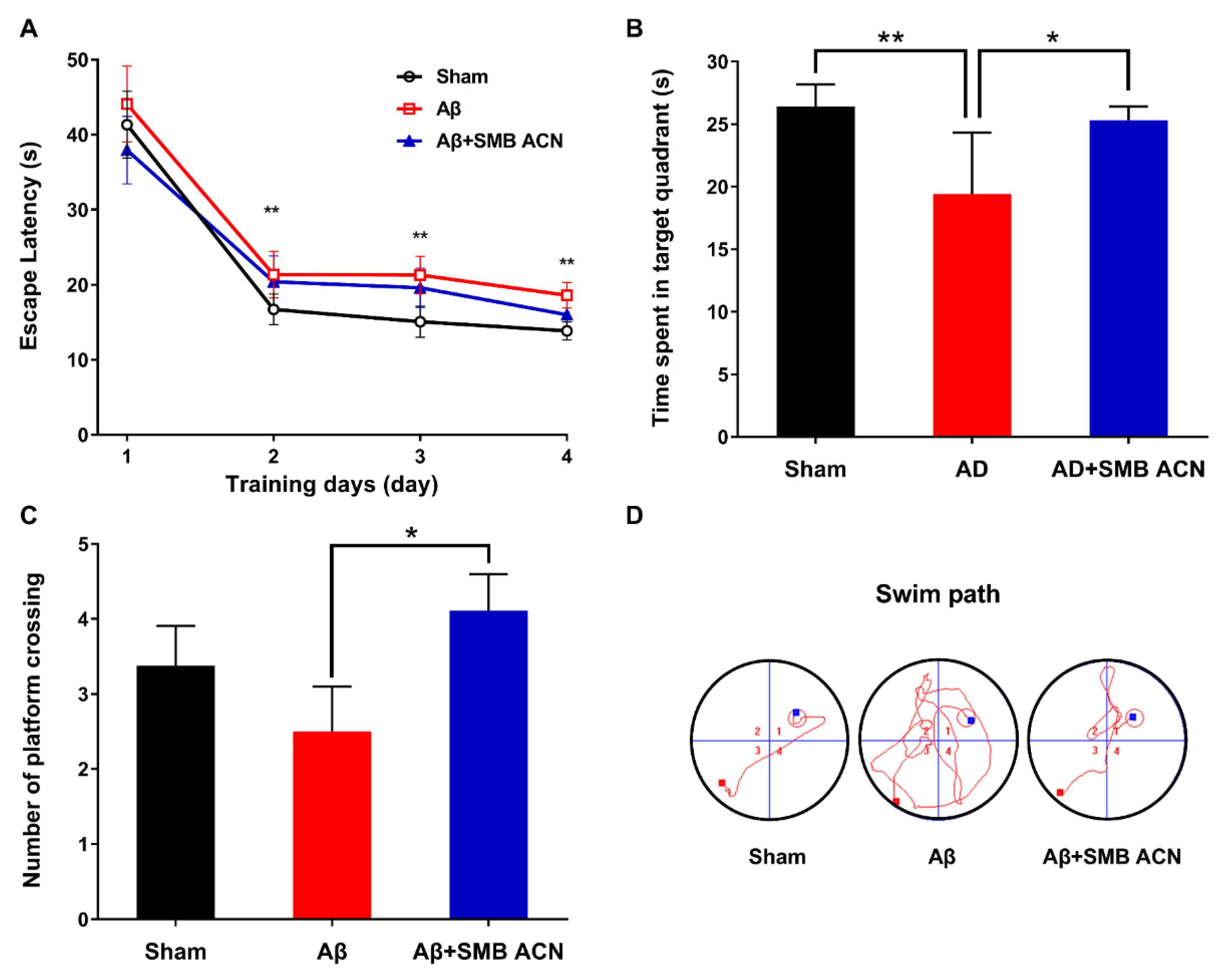
3.3. The Protection of Anthocyanins on Memory Impairment in Aβ-Induced Toxicity Rats
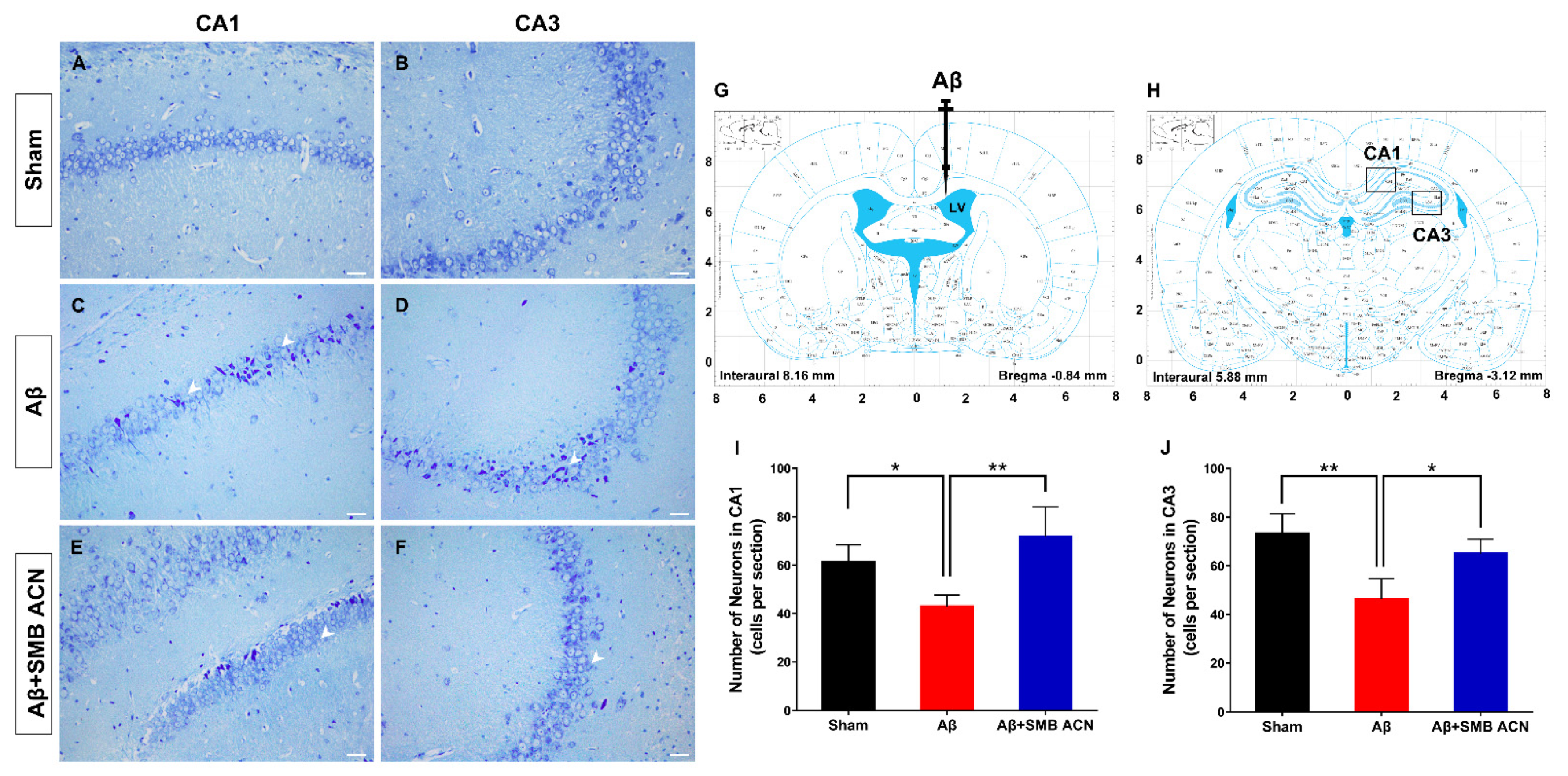
3.4. The Neuroprotective Effect of SMB Anthocyanins Extract in Rat Brain
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, B.; Ku, C.S.; Pham, T.X.; Park, Y.; Martin, D.A.; Xie, L.; Taheri, R.; Lee, J.; Bolling, B.W. Aronia melanocarpa (chokeberry) polyphenol-rich extract improves antioxidant function and reduces total plasma cholesterol in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanisavljević, N.; Samardžić, J.; Janković, T.; Šavikin, K.; Mojsin, M.; Topalović, V.; Stevanović, M. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activity of chokeberry juice phenolics during in vitro simulated digestion in the presence of food matrix. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denev, P.; Číž, M.; Kratchanova, M.; Blazheva, D. Black chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) polyphenols reveal different antioxidant, antimicrobial and neutrophil-modulating activities. Food Chem. 2019, 284, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaswant, M.; Shafie, S.R.; Mathai, M.L.; Mouatt, P.; Brown, L. Anthocyanins in chokeberry and purple maize attenuate diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. Nutrition 2017, 41, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thilavech, T.; Adisakwattana, S. Cyanidin-3-rutinoside acts as a natural inhibitor of intestinal lipid digestion and absorption. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, F.U.; Shah, S.A.; Badshah, H.; Khan, M.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanins encapsulated by PLGA@PEG nanoparticles potentially improved its free radical scavenging capabilities via p38/JNK pathway against Aβ1-42-induced oxidative stress. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Gao, J.; Fan, J.; Zhou, Z. Anthocyanins from Black Chokeberry (Aroniamelanocarpa Elliot) Delayed Aging-Related Degenerative Changes of Brain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5973–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.; Meireles, M.; Fernandes, I.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Gonzalez-Manzano, S.; Dueñas, M.; Freitas, V.; Mateus, N.; Calhau, C. Flavonoid metabolites transport across a human BBB model. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klisurova, D.; Petrova, I.; Ognyanov, M.; Georgiev, Y.; Kratchanova, M.; Denev, P. Co-pigmentation of black chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) anthocyanins with phenolic co-pigments and herbal extracts. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, C.L.; Bateman, R.; Blennow, K.; Rowe, C.C.; Sperling, R.A.; Cummings, J.L. Alzheimers disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, S.M.; Soares, M.S.P.; Gutierres, J.M.; Gerzson, M.F.B.; Carvalho, F.B.; Azambuja, J.H.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Stefanello, F.M.; Spanevello, R.M. Anthocyanins as a potential pharmacological agent to manage memory deficit, oxidative stress and alterations in ion pump activity induced by experimental sporadic dementia of Alzheimers type. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 56, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hao, W.; Qin, Y.; Decker, Y.; Wang, X.; Burkart, M.; Schoetz, K.; Menger, M.D.; Fassbender, K.; Liu, Y. Long-term treatment with Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 improves symptoms and pathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 46, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimidt, H.L.; Garcia, A.; Martins, A.; Mello-Carpes, P.B.; Carpes, F.P. Green tea supplementation produces better neuroprotective effects than red and black tea in Alzheimer-like rat model. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Banerjee, S.; Sil, P.C. The beneficial role of curcumin on inflammation, diabetes and neurodegenerative disease: A recent update. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 83, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Fu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Gu, L.; Li, J. Antioxidant Activity and Neuroprotective Activity of Stilbenoids in Rat Primary Cortex Neurons via the PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres-Lacueva, C.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Galli, R.L.; Jauregui, O.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Joseph, J.A. Anthocyanins in aged blueberry-fed rats are found centrally and may enhance memory. Nutr. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.B.; Choi, J.H.; Chang, Y.K.; Mun, S. Production of high-purity fucose from the seaweed of Undaria pinnatifida through acid-hydrolysis and simulated-moving bed purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumi, A.; Engell, S.; Diehl, M.; Bock, H.G.; Schlöder, J. Efficient optimization of simulated moving bed processes. Chem. Eng. Process. 2007, 46, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strube, J.; Jupke, A.; Epping, A.; Schmidt-Traub, H.; Schulte, M.; Devant, R. Design, optimization, and operation of SMB chromatography in the production of enantiomerically pure pharmaceuticals. Chirality 1999, 11, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Yin, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, J. Isolation of high-purity anthocyanin mixtures and monomers from blueberries using combined chromatographic techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1327, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyło, A.; Nowicka, P. Anticholinergic effects of Actinidia arguta fruits and their polyphenol content determined by liquid chromatography-photodiode array detector-quadrupole/time of flight-mass spectrometry (LC-MS-PDA-Q/TOF). Food Chem. 2019, 271, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wen, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Z.; Li, J. The influence of ripening stage and region on the chemical compounds in mulberry fruits (Morus atropurpurea Roxb.) based on UPLC-QTOF-MS. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensor, L.L.; Menezes, F.S.; Leitão, G.G.; Reis, A.S.; Santos, T.C.; Coube, C.S.; Leitão, S.G. Screening of Brazilian plant extracts for antioxidant activity by the use of DPPH free radical method. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Bio. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C. DHA-PC and DHA-PS improved Aβ1–40 induced cognitive deficiency uncoupled with an increase in brain DHA in rats. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 22, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, M.; Xu, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C. Eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids improve Aβ1–40-induced cognitive deficiency in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohanaki, H.; Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Nikbakht, F.; Roghani, M. Pelargonidin improves memory deficit in amyloid β25-35 rat model of Alzheimer’s disease by inhibition of glial activation, cholinesterase, and oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, L.; Zeng, X.-A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Sleep deprivation accelerates the progression of alzheimer’s disease by influencing Aβ-related metabolism. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 650, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.-B.; Su, B.-G.; Yang, Y.-W.; Ren, Q.-L.; Wu, P.-D. Simulated moving bed separation of tocopherol homologues: Simulation and experiments. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2009, 10, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oszmianski, J.; Sapis, J.C. Anthocyanins in fruits of Aronia melanocarpa (chokeberry). J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 1241–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, S. Separation of epigallocatechin gallate from tea polyphenol by simulated moving bed chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1265, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Li, B.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Meng, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, N. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside attenuates amyloid-beta (Aβ1-40)-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells through a Nrf2 mechanism. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Magnuson, B.A.; Giusti, M.M. Analysis of anthocyanins in rat intestinal contents--impact of anthocyanin chemical structure on fecal excretion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2859–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel-Hidalgo, J.J.; Cacabelos, R. β-Amyloid (1–40)-induced neurodegeneration in the rat hippocampal neurons of the CA1 subfield. Acta Neuropathol. 1998, 95, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Hidalgo, J.J.; Alvarez, X.A.; Cacabelos, R.; Quack, G. Neuroprotection by memantine against neurodegeneration induced by β-amyloid (1–40). Brain Res. 2002, 958, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbishegi, M.; Heidari, Z.; Mahmoudzadeh-Sagheb, H.; Valizadeh, M.; Doostkami, M. Neuroprotective effects of Withania coagulans root extract on CA1 hippocampus following cerebral ischemia in rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2016, 6, 399–409. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Xu, H.; Meng, X.; Qi, J.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L. Potential use of hyperoxygenated solution as a treatment strategy for carbon monoxide poisoning. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Rehman, S.U.; Amin, F.U.; Kim, M.O. Enhanced neuroprotection of anthocyanin-loaded PEG-gold nanoparticles against Aβ1-42-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration via the NF-KB /JNK/GSK3β signaling pathway. Nanomed. NBM 2017, 13, 2533–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Run | Flow Rates (mL/min) | Switch Time ts (s) | Purity (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QE | QR | QD | QF | |||
| A | 1.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 | 0.45 | 135 | 68.7 |
| B | 1.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 | 0.45 | 140 | 78.2 |
| C | 1.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 | 0.40 | 140 | 73.1 |
| D | 1.5 | 8.0 | 4.5 | 0.42 | 141 | 71.4 |
| E | 3.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 | 0.45 | 141 | 70.3 |
| F | 1.5 | 6.0 | 4.5 | 0.42 | 141 | 77.5 |
| G | 1.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 | 0.45 | 141 | 78.3 |
| H | 1.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 | 0.42 | 141 | 85.1 |
| Peak | RT HPLC | Compound | Molecular Formula | ESI(+)MS/MS2 | Crude Extract | SMB ACN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (min) | (m/z) | (mg/100 g FW) | (mg/g DW) | |||
| 1 | 4.809 | cyanidin 3-O-galactoside | C21H21O11 | 449.1089([M]+) 287.0560([M-gal]+) | 500.4 ± 38.7 | 449.1 ± 30.8 |
| 2 | 5.169 | cyanidin 3-O-glucoside | C21H21O11 | 449.1088([M]+) 287.0558([M-glu]+) | 18.6 ± 1.8 | ND |
| 3 | 5.923 | cyanidin 3-O-arabinoside | C20H19O10 | 419.0975([M]+) 287.0557([M-arab]+) | 144.2 ± 14.0 | 161.2 ± 33.8 |
| 4 | 8.219 | cyanidin 3-O-xyloside | C20H19O10 | 419.0975([M]+) 287.0556([M-xyl]+) | 23.4 ± 1.8 | ND |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, H.; Cui, H.; Tian, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Ramassamy, C.; Li, J. Isolation of Neuroprotective Anthocyanins from Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) against Amyloid-β-Induced Cognitive Impairment. Foods 2021, 10, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010063
Wen H, Cui H, Tian H, Zhang X, Ma L, Ramassamy C, Li J. Isolation of Neuroprotective Anthocyanins from Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) against Amyloid-β-Induced Cognitive Impairment. Foods. 2021; 10(1):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010063
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Haichao, Hui Cui, Hehe Tian, Xiaoxu Zhang, Liyan Ma, Charles Ramassamy, and Jingming Li. 2021. "Isolation of Neuroprotective Anthocyanins from Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) against Amyloid-β-Induced Cognitive Impairment" Foods 10, no. 1: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010063
APA StyleWen, H., Cui, H., Tian, H., Zhang, X., Ma, L., Ramassamy, C., & Li, J. (2021). Isolation of Neuroprotective Anthocyanins from Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) against Amyloid-β-Induced Cognitive Impairment. Foods, 10(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010063