NMR in the Service of Wine Differentiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Application of NMR in Wine Analysis
2.1. Diversity of NMR Experiments in Wine Analysis
2.2. Some Features of NMR Wine Analysis and Data Handling
2.3. NMR as a Powerful Tool for Identification of the Geographical Origin
3. SNIF-NMR
3.1. Features of Deuterium Nuclei and Deuterium NMR
3.2. The Principle of SNIF-NMR for Food Authentication
3.3. Application of SNIF-NMR in Food Analysis
4. SNIF-NMR in Wine Authenticity
4.1. Detection of Wine Chaptalization
4.2. SNIF-NMR in Wine Authentication
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebeler, S.E. Analytical chemistry: Unlocking the secrets of wine flavor. Food Rev. Int. 2001, 17, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, B.C. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR). In Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology—Analytical Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 5, pp. 701–720. [Google Scholar]
- Van Duynhoven, J.P.M. Food and Nutritional Science, Applications of Magnetic Resonance. In Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry, 2nd ed.; Lindon, J.C., Tranter, G.E., Eds.; Elsevier/Acad. Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, K.; Maltese, F.; Fortes, A.M.; Pais, M.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Monitoring biochemical changes during grape berry development in Portuguese cultivars by NMR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.E.; Gaudillere, J.-P.; Van Leeuwen, C.; Hilbert, G.; Lavialle, O.; Maucourt, M.; Deborde, C.; Moing, A.; Rolin, D. 1H NMR and Chemometrics to Characterize Mature Grape Berries in Four Wine-Growing Areas in Bordeaux, France. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6382–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, P.; Celano, G.; Palese, A.M.; Lardo, E.; Drosos, M.; Piccolo, A. HRMAS-NMR metabolomics of Aglianicone grapes pulp to evaluate terroir and vintage effects, and, as assessed by the Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) technique, spatial variability of vineyard soils. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picone, G.; Trimigno, A.; Tessarin, P.; Donnini, S.; Rombolà, A.D.; Capozzi, F. 1H NMR foodomics reveals that the biodynamic and the organic cultivation managements produce different grape berries (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Sangiovese). Food Chem. 2016, 213, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brescia, M.A.; Caldarola, V.; De Giglio, A.; Benedetti, D.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Sacco, A. Characterization of the geographical origin of Italian red wines based on traditional and nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometric determinations. Analytica Chimica Acta 2002, 458, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rituerto, E.; Savorani, F.; Avenoza, A.; Busto, J.H.; Peregrina, J.M.; Engelsen, S.B. Investigations of La Rioja terroir for wine production using 1H NMR metabolomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3452–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amargianitaki, M.; Spyros, A. NMR-Based metabolomics in wine quality control and authentication. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2017, 4, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yue, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, W.; Zhang, F.; Hardie, J.W. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Spectroscopic Discrimination of Wines Reflects Genetic Homology of Several Different Grape (V. vinifera L.) Cultivars. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascellani, A.; Hoca, G.; Babisz, M.; Krska, P.; Kloucek, P.; Havlik, J. 1H NMR chemometric models for classification of Czech wine type and variety. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godelmann, R.; Fang, F.; Humpfer, E.; Schütz, B.; Bansbach, M.; Schäfer, H.; Spraul, M. Targeted and nontargeted wine analysis by 1H NMR spectroscopy combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Differentiation of important parameters: Grape variety, geographical origin, year of vintage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5610–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, P.; Francesca, N.; Moschetti, G.; Piccolo, A. NMR spectroscopy evaluation of direct relationship between soils and molecular composition of red wines from Aglianico grapes. Analytica Chimica Acta 2010, 673, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papotti, G.; Bertelli, D.; Graziosi, R.; Silvestri, M.; Bertacchini, L.; Durante, C.; Plessi, M. Application of one- and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy for the characterization of Protected Designation of Origin Lambrusco wines of Modena. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imparato, G.; Di Paolo, E.; Braca, A.; Lamanna, R. Nuclear magnetic resonance profiling of wine blends. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avenoza, A.; Busto, J.H.; Canal, N.; Peregrina, J.M. Time course of the evolution of malic and lactic acids in the alcoholic and malolactic fermentation of grape must by quantitative 1H NMR (qHNMR) spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4715–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, S.; Barnett, N.W.; Adams, M.; Cook, I.B.; Dyson, G.A.; Johnston, G. Monitoring a commercial fermentation with proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy with the aid of chemometrics. Analytica Chimica Acta 2006, 563, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.-S.; Hwang, G.-S.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, E.-Y.; van den Berg, F.; Park, W.-M.; Lee, C.-H.; Hong, Y.-S. 1H NMR-Based metabolomic approach for understanding the fermentation behaviors of wine yeast strains. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.M.; Ferreira, A.C.S.; de Pinho, P.G.; Silva, A.M.S. New qualitative approach in the characterization of antioxidants in white wines by antioxidant free radical scavenging and NMR techniques. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10326–10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Maltese, F.; Zyprian, E.; Rex, M.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR metabolic fingerprinting based identification of grapevine metabolites associated with downy mildew resistance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9599–9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-S.; Cilindre, C.; Liger-Belair, G.; Jeandet, P.; Hertkorn, N.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Metabolic influence of Botrytis cinerea infection in champagne base wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7237–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhong, Q.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Pfister, M.K.H.; Horn, B.; Huang, Z. Classification of Chinese wine varieties using 1H NMR spectroscopy combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Food Control 2018, 88, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadi, M.; Zira, A.; Magiatis, P.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Mikros, E. 1H NMR-based metabonomics for the classification of Greek wines according to variety, region, and vintage. Comparison with HPLC data. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 11067–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves Filho, E.G.; Silva, L.M.A.; Ribeiro, P.R.V.; de Brito, E.S.; Zocolo, G.J.; Souza-Leão, P.C.; Marques, A.T.B.; Quintela, A.L.; Larsen, F.H.; Canuto, K.M. 1H NMR and LC-MS-based metabolomic approach for evaluation of the seasonality and viticultural practices in wines from São Francisco River Valley, a Brazilian semi-arid region. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pascali, S.A.; Coletta, A.; Del Coco, L.; Basile, T.; Gambacorta, G.; Fanizzi, F.P. Viticultural practice and winemaking effects on metabolic profile of Negroamaro. Food Chem. 2014, 161, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, P.; Spaccini, R.; Francesca, N.; Moschetti, G.; Piccolo, A. Metabolomic by 1H NMR spectroscopy differentiates “Fiano di Avellino” white wines obtained with different yeast strains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10816–10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skogerson, K.; Runnebaum, R.; Wohlgemuth, G.; de Ropp, J.; Heymann, H.; Fiehn, O. Comparison of gas chromatography-coupled time-of-flight mass spectrometry and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy metabolite identification in white wines from a sensory study investigating wine body. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6899–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochfort, S.; Ezernieks, V.; Bastian, S.E.P.; Downey, M.O. Sensory attributes of wine influenced by variety and berry shading discriminated by NMR metabolomics. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, R.; Cagliani, L.R.; Guantieri, V.; Simonato, B. Identification of metabolic content of selected Amarone wine. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Oliveira, A.S.; Azevedo, J.; Freitas, D.V.; Lopes, P.; Roseira, I.; Cabral, M.; Guedes de Pinho, P. Assessment of oxidation compounds in oaked Chardonnay wines: A GC-MS and 1H NMR metabolomics approach. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baderschneider, B.; Winterhalter, P. Isolation and characterization of novel benzoates, cinnamates, flavonoids, and lignans from Riesling wine and screening for antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2788–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guebailia, H.A.; Chira, K.; Richard, T.; Mabrouk, T.; Furiga, A.; Vitrac, X.; Monti, J.-P.; Delaunay, J.-C.; Mérillon, J.-M. Hopeaphenol: The first resveratrol tetramer in wines from North Africa. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9559–9564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forino, M.; Gambuti, A.; Moio, L. NMR-Based systematic analysis of bioactive phytochemicals in red wine. First determination of xanthurenic and oleanic acids. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Rivas-Gonzalo, J.C.; Freitas, D.V. Identification of anthocyanin-flavanol pigments in red wines by NMR and mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, N.; Carvalho, E.; Carvalho, A.R.F.; Melo, A.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Silva, A.M.S.; Freitas, D.V. Isolation and structural characterization of new acylated anthocyanin-vinyl-flavanol pigments occurring in aging red wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitrac, X.; Bornet, A.; Vanderlinde, R.; Valls, J.; Richard, T.; Delaunay, J.-C.; Mérillon, J.-M.; Teissédre, P.-L. Determination of stilbenes (δ-viniferin, trans-astringin, trans-piceid, cis- and trans-resveratrol, ε-viniferin) in Brazilian wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5664–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, M.; Winterhalter, P. Novel Aged Anthocyanins from Pinotage Wines: Isolation, Characterization, and Pathway of Formation. In Red Wine Color; Waterhouse, A.L., Kennedy, J.A., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Mateus, N.; Oliveira, J.; Pissarra, J.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Rivas-Gonzalo, J.C.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Silva, A.M.S.; Freitas, D.V. A new vinylpyranoanthocyanin pigment occurring in aged red wine. Food Chem. 2006, 97, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Iturmendi, N.; Grelard, A.; Moine, V.; Dufourc, E. Quantitative analysis of Bordeaux red wine precipitates by solid-state NMR: Role of tartrates and polyphenols. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, E.J.; Peng, Z.; Pocock, K.F.; Jones, G.P.; Clarke, P.; Williams, P.J. Solid-State 13C NMR investigation into insoluble deposits adhering to the inner glass surface of bottled red wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Plaza, C.; Beaver, J.W.; Miller, K.V.; Lerno, L.; Dokoozlian, N.; Ponangi, R.; Blair, T.; Block, D.E.; Oberholster, A. Cell Wall—Anthocyanin Interactions during Red Wine Fermentation-Like Conditions. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2020, 71, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnländer, B.; Baderschneider, B.; Messerer, M.; Winterhalter, P. Isolation of Two Novel Terpenoid Glucose Esters from Riesling Wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Oliveira, J.; Silva, A.M.S.; Mateus, N.; Freitas, D.V. Oxovitisins: A new class of neutral pyranone-anthocyanin derivatives in red wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8814–8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glabasnia, A.; Hofmann, T. Sensory-Directed identification of taste-active ellagitannins in American (Quercus alba L.) and European oak wood (Quercus robur L.) and quantitative analysis in bourbon whiskey and oak-matured red wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3380–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchal, A.; Waffo-Téguo, P.; Génin, E.; Mérillon, J.-M.; Dubourdieu, D. Identification of new natural sweet compounds in wine using centrifugal partition chromatography-gustatometry and Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9629–9637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, C.; Bayonove, C.L. Interactions between wine polyphenols and aroma substances. An insight at the molecular level. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolantonaki, M.; Jourdes, M.; Shinoda, K.; Teissedre, P.-L.; Quideau, S.; Darriet, P. Identification of adducts between an odoriferous volatile thiol and oxidized grape phenolic compounds: Kinetic study of adduct formation under chemical and enzymatic oxidation conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolantonaki, M.; Magiatis, P.; Waterhouse, A.L. Direct Analysis of Free and Sulfite-Bound Carbonyl Compounds in Wine by Two-Dimensional Quantitative Proton and Carbon Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 10799–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, M.; Dauphin, B.; La Guerche, S.; Pons, A.; Lavigne-Cruege, V.; Shinkaruk, S.; Bunner, D.; Richard, T.; Monti, J.-P.; Darriet, P. Identification of impact odorants contributing to fresh mushroom off-flavor in wines: Incidence of their reactivity with nitrogen compounds on the decrease of the olfactory defect. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3264–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy-Tanneau, S.; Le Guernevé, C.; Meudec, E.; Cheynier, V. Characterization of a colorless anthocyanin-flavan-3-ol dimer containing both carbon-carbon and ether interflavanoid linkages by NMR and mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3592–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Mateus, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; Freitas, D.V. Equilibrium forms of vitisin B pigments in an aqueous system studied by NMR and visible spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 11352–11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Barathieu, K.; Laguerre, M.; Schmitter, J.-M.; Fouquet, E.; Pianet, I.; Dufourc, E.J. Three-Dimensional structure and dynamics of wine tannin-saliva protein complexes. A multitechnique approach. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 10385–10395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cala, O.; Pinaud, N.; Simon, C.; Fouquet, E.; Laguerre, M.; Dufourc, E.J.; Pianet, I. NMR and molecular modeling of wine tannins binding to saliva proteins: Revisiting astringency from molecular and colloidal prospects. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Duarte, I.F.; Almeida, C.; Delgadillo, I.; Goodfellow, B.J.; Gil, A.M.; Morris, G.A. High-Resolution NMR and diffusion-ordered spectroscopy of port wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3736–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobieski, D.N.; Mulvihill, G.; Broz, J.S.; Augustine, M.P. Towards rapid throughput NMR studies of full wine bottles. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2006, 29, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weekley, A.J.; Bruins, P.; Sisto, M.; Augustine, M.P. Using NMR to study full intact wine bottles. J. Magn. Reson. 2003, 161, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Košir, I.J.; Kidrič, J. Identification of amino acids in wines by one- and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Schäfer, H.; Humpfer, E.; Spraul, M.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Application of automated eightfold suppression of water and ethanol signals in 1H NMR to provide sensitivity for analyzing alcoholic beverages. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defernez, M.; Colquhoun, I.J. Factors affecting the robustness of metabolite fingerprinting using 1H NMR spectra. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esslinger, S.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Wittkowski, R. Authentication of Wine by 1H-NMR Spectroscopy: Opportunities and Challenges. In Advances in Wine Research; Ebeler, S.B., Sacks, G., Vidal, S., Winterhalter, P., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 85–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, A.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Dieterle, F.; Senn, H. NMR Spectroscopy Techniques for Application in Metabonomics. In The Handbook of Metabonomics and Metabolomics; Lindon, J.C., Nicholson, J.K., Holmes, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 55–112. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, F.H.; van den Berg, F.; Engelsen, S.B. An exploratory chemometric study of 1H NMR spectra of table wines. J. Chemom. 2006, 20, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Daszykowski, M.; Walczak, B.; Sweatman, B.C.; Connor, S.C.; Haselden, J.N.; Crowther, D.J.; Gill, R.W.; Lutz, M.W. Peak alignment of urine NMR spectra using fuzzy warping. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2006, 46, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csenki, L.; Alm, E.; Torgrip, R.J.O.; Aberg, K.M.; Nord, L.I.; Schuppe-Koistinen, I.; Lindberg, J. Proof of principle of a generalized fuzzy Hough transform approach to peak alignment of one-dimensional 1H NMR data. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, G.; van den Berg, F.; Andersson, C. Correlation optimized warping and dynamic time warping as preprocessing methods for chromatographic data. J. Chemom. 2004, 18, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselkov, K.A.; Lindon, J.C.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Crockford, D.; Volynkin, V.V.; Holmes, E.; Davies, D.B.; Nicholson, J.K. Recursive segment-wise peak alignment of biological 1H NMR spectra for improved metabolic biomarker recovery. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savorani, F.; Tomasi, G.; Engelsen, S.B. Icoshift: A versatile tool for the rapid alignment of 1D NMR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 2010, 202, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Godelmann, R.; Hermann, A.; Kuballa, T.; Cannet, C.; Schäfer, H.; Spraul, M.; Rutledge, D.N. Synergistic effect of the simultaneous chemometric analysis of 1H NMR spectroscopic and stable isotope (SNIF-NMR, 18O, 13C) data: Application to wine analysis. Analytica Chimica Acta 2014, 833, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.E.; Watling, J.; Lee, G. The multi-element determination and regional discrimination of Australian wines. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagra, E.; Santos, L.S.; Vaz, B.G.; Eberlin, M.N.; Felipe, L.V. Varietal discrimination of Chilean wines by direct injection mass spectrometry analysis combined with multivariate statistics. Food Chem. 2012, 31, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danezis, G.P.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Camin, F.; Brusic, V.; Georgiou, C.A. Food authentication: Techniques, trends & emerging approaches. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalvez, A.; Armenta, S.; de la Guardia, M. Trace-Element composition and stable-isotope ratio for discrimination of foods with protected designation of origin. Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1295–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldahl, K.; Bro, R. Some common misunderstandings in chemometrics. J. Chemom. 2010, 24, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spraul, M.; Link, M.; Schaefer, H.; Fang, F.; Schuetz, B. Wine analysis to check quality and authenticity by fully-automated 1H-NMR. BIO Web Conf. 2015, 5, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, J.T.W.E.; Tas, A.C.; van den Berg, F.; van der Greef, J. A new method for classification of wines based on proton and carbon-13NMR spectroscopy in combination with pattern recognition techniques. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1993, 21, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brescia, M.A.; Košir, I.J.; Caldarola, V.; Kidrič, J.; Sacco, A. Chemometric classification of Apulian and Slovenian wines using 1H NMR and ICP-OES together with HPICE data. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, E.; Foca, G.; Vignali, M.; Tassi, L.; Ulrici, A. Adulteration of the anthocyanin content of red wines: Perspectives for authentication by Fourier Transform-Near InfraRed and 1H NMR spectroscopies. Analytica Chimica Acta 2011, 701, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.Y.; Bai, G.Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.L. Classification of wines based on combination of 1H NMR spectroscopy and principal component analysis. Chin. J. Chem. 2007, 25, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougeon, L.; Da Costa, G.; Le Mao, I.; Ma, W.; Teissedre, P.L.; Guyon, F.; Richard, T. Wine Analysis and Authenticity Using 1H-NMR Metabolomics Data: Application to Chinese Wines. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 3425–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougeon, L.; da Costa, G.; Richard, T.; Guyon, F. Wine Authenticity by Quantitative 1H NMR Versus Multitechnique Analysis: A Case Study. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.S.; Ki, M.K.; Van Den Berg, F.; Hwang, G.S.; Park, W.M.; Lee, C.H.; Hong, Y.S. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic characterization of wines by grape varieties and production areas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8007–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viggiani, L.; Morelli, M.A.C. Characterization of wines by nuclear magnetic resonance: A work study on wines from the Basilicata region in Italy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8273–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jézéquel, T.; Joubert, V.; Giraudeau, P.; Remaud, G.S.; Akoka, S. The new face of isotopic NMR at natural abundance. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2017, 55, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayle, K.; Grand, M.; Chaintreau, A.; Robins, R.J.; Fieber, W.; Sommer, H.; Akoka, S.; Remaud, G.S. Internal Referencing for 13C Position-Specific Isotope Analysis Measured by NMR Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 7550–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.J.; Sun, X.Y.; Guillou, C.; Martin, M.L. NMR determination of absolute site-specific natural isotope ratios of hydrogen in organic molecules. Analytical and mechanistic applications. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.J.; Zhang, B.L.; Naulet, N.; Martin, M.L. Deuterium transfer in the bioconversion of glucose to ethanol studied by specific labeling at the natural abundance level. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 5116–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aursand, M.; Mabon, F.; Martin, G.J. Characterization of farmed and wild salmon (Salmo salar) by a combined use of compositional and isotopic analyses. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remaud, G.S.; Silvestre, V.; Akoka, S. Traceability in quantitative NMR using an electronic signal as working standard. Accred. Qual. Assur. 2005, 10, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignali, C.; Caligiani, A.; Palla, G. Quantitative 2H NMR spectroscopy with 1H lock extender. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 187, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesot, P.; Courtieu, J. Natural abundance deuterium NMR spectroscopy: Developments and analytical applications in liquids, liquid crystals and solid phases. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Recon. Spectrosc. 2009, 55, 128–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantsch, H.H.; Saito, H.; Smith, I.C.P. Deuterium magnetic resonance, applications in chemistry, physics and biology. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Recon. Spectrosc. 1977, 11, 211–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidrič, J. NMR Study of Beverages. Annu. Rep. Nucl. Magn. Recon. Spectrosc. 2008, 64, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.J.; Martin, M.L.; Mabon, F.; Michon, M.J. A new method for the identification of the origin of ethanols in grain and fruit spirits: High field quantitative deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance at the natural abundance level. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1983, 31, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, C. L’analyse isotopique des vins. Analysis 1991, 19, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Botosoa, E.P.; Caytan, E.; Silvestre, V.; Robins, R.J.; Akoka, S.; Remaud, G.S. Unexpected fractionation in site-specific 13C isotopic distribution detected by quantitative 13C NMR at natural abundance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.L.; Martin, G.J. Site-Specific isotope effects and origin inference. Isot. Anal. 1999, 27, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martin, G.J.; Martin, M.L. The Site-Specific Natural Isotope Fractionation-NMR Method Applied to the Study of Wines. In Modern Methods of Plant Analysis, 1st ed.; Linskens, H.-F., Jackson, J.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; Volume 6, pp. 258–275. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.G.; Wood, R.; Martin, G.J. Detection of added beet sugar in concentrated and single strength fruit juices by deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance (SNIF-NMR method): Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 1996, 79, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet, C.; Said, R.; Rabiller, C.; Martin, M.L. Natural Abundance Isotopic Fractionation in the Fermentation Reaction: Influence of the Nature of the Yeast. Bioorg. Chem. 1996, 24, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-L.Y.; Vallet, C.; Martin, Y.-L.; Martin, M.L. Natural Abundance Isotopic Fractionation in the Fermentation Reaction: Influence of the Fermentation Medium. Bioorg. Chem. 1997, 25, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauhl, C.; Wittkowski, R. Oenological influences on the D/H ratios of wine ethanol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3979–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Guzzon, R.; Simoni, M.; Malacarne, M.; Larcher, R.; Camin, F. The effect of stopping alcoholic fermentation on the variability of H, C and O stable isotope ratios of ethanol. Food Control 2014, 40, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.G.; Hanote, V.; Lees, M.; Martin, Y.-L. Interpretation of Combined 2H SNIF/NMR and 13C SIRA/MS Analyses of Fruit Juices to Detect Added Sugar. J. AOAC Int. 1996, 79, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billault, I.; Robins, R.; Akoka, S. Determination of deuterium isotope ratios by quantitative 2H NMR spectroscopy: The ERETIC method as a generic reference signal. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5902–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Grand, F.; George, G.; Akoka, S. How to reduce the experimental time in isotopic 2H NMR using the ERETIC method. J. Magn. Reson. 2005, 174, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.J.; Martin, M.L. Flavor Chemistry: 30 Years of Progress, 1st ed.; Teranishi, R., Wick, E.L., Hornstein, I., Eds.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, B. Food Authentication, 1st ed.; Ashurst, P.R., Dennis, M.J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 60–107. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, F.; Jamin, E. 2H NMR and 13C-IRMS analyses of acetic acid from vinegar, 18O-IRMS analysis of water in vinegar: International collaborative study report. Analytica Chimica Acta 2009, 649, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, F.; Randet, C.; Gilbert, A.; Silvestre, V.; Jamin, E.; Akoka, S.; Remaud, G.; Segebarth, N.; Guillou, C. Improved characterization of the botanical origin of sugar by carbon-13SNIF-NMR applied to Ethanol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11580–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, V.; Silvestre, V.; Grand, M.; Loquet, D.; Ladroue, V.; Besacier, F.; Akoka, S.; Remaud, G.S. Full spectrum isotopic 13C NMR using polarization transfer for position-specifc isotope analysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8692–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Diehl, B.W. Authentication of the origin of sucrose-based sugar products using quantitative natural abundance 13C NMR. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayle, K.; Akoka, S.; Remaud, G.S.; Robins, R.J. Nonstatistical 13C distribution during carbon transfer from glucose to ethanol during fermentation is determined by the catabolic pathway exploited. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 4118–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caer, V.; Trierweiler, M.; Martin, G.J.; Martin, M.L. Determination of site-specifc carbon isotope ratios at natural abundance by carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 2306–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.L.; Trierweiler, M.; Jouitteau, C.; Martin, G.J. Consistency of NMR and Mass Spectrometry Determinations of Natural-Abundance Site-Specific Carbon Isotope Ratios. The Case of Glycerol. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2301–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caytan, E.; Remaud, G.; Tenailleau, E.; Akoka, S. Precise and accurate quantitative 13C NMR with reduced experimental time. Talanta 2007, 71, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, F.; Van Leeuwen, C.; Gaillard, L.; Grand, M.; Akoka, S.; Remaud, G.S.; Sabathie, N.; Salagoity, M.-H. Comparative study of 13C composition in ethanol and bulk dry wine using isotope ratio monitoring by mass spectrometry and by nuclear magnetic resonance as an indicator of vine water status. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 9053–9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, A.; Silvestre, V.; Segebarth, N.; Tcherkez, G.; Guillou, C.; Robins, R.J.; Akoka, S.; Remaud, G.S. The intramolecular 13C-distribution in ethanol reveals the influence of the CO2-fixation pathway and environmental conditions on the site-specific 13C variation in glucose. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camin, F.; Simoni, M.; Hermann, A.; Thomas, F.; Perini, M. Validation of the 2H-SNIF NMR and IRMS Methods for Vinegar and Vinegar Analysis: An International Collaborative Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.-W.; Li, P.-H.; Cheng, J.-Y.; Ma, J.-T. Using SNIF-NMR method to identify the adulteration of molasses spirit vinegar by synthetic acetic acid in rice vinegar. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Paolini, M.; Simoni, M.; Bontempo, L.; Vrhovsek, U.; Sacco, M.; Thomas, F.; Jamin, E.; Hermann, A.; Camin, F. Stable isotope ratio analysis for verifying the authenticity of balsamic and wine vinegar. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8197–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.; Jamin, E.; Remaud, G.; Martin, Y.-L.; Martin, G.G.; Martin, M.L. Authentication of Lemon Juices and Concentrates by a Combined Multi-isotope Approach Using SNIF-NMR and IRMS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2200–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-L.; Lees, M.; Martin, G.J. Stable Isotope Fractionation in Fruit Juice Concentrates: Application to the Authentication of Grape and Orange Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 2411–2417. [Google Scholar]
- Perini, M.; Giongo, L.; Grisenti, M.; Bontempo, L.; Camin, F. Stable isotope ratio analysis of different European raspberries, blackberries, blueberries, currants and strawberries. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrinc, N.; Bat, K.; Košir, I.J.; Golob, T.; Kokkinofta, R. Characterization of commercial Slovenian and Cypriot fruit juices using stable isotopes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6764–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudon, S.; Danzart, M.; Merle, M.H. Deuterium Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Stable Carbon Isotope Ratio Analysis/Mass Spectrometry of Certain Monofloral Honeys. J. AOAC Int. 2000, 83, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotte, J.F.; Casabianca, H.; Lhéritier, J.; Perrucchietti, C.; Sanglar, C.; Waton, H.; Grenier-Loustalot, M.F. Study and validity of 13C stable carbon isotopic ratio analysis by mass spectrometry and 2H site-specific natural isotopic fractionation by nuclear magnetic resonance isotopic measurements to characterize and control the authenticity of honey. Analytica Chimica Acta 2007, 582, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdas, D.A.; Guyon, F.; Puscas, R.; Vigouroux, A.; Gaillard, L.; Dehelean, A.; Feher, I.; Cristea, G. Applications of emerging stable isotopes and elemental markers for geographical and varietal recognition of Romanian and French honeys. Food Chem. 2021, 334, 127599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.G.; Martin, Y.-L.; Naulet, N.; McManus, H.J.D. Application of 2H SNIF-NMR and 13C SIRA-MS Analyses to Maple Syrup: Detection of Added Sugars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 3206–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, Z.; Vallet, C.; Martin, G.J. Stable isotope characterization of milk components and whey ethanol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4693–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remaud, G.S.; Martin, Y.-L.; Martin, G.G.; Martin, G.J. Detection of Sophisticated Adulterations of Natural Vanilla Flavors and Extracts: Application of the SNIF-NMR Method to Vanillin and p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamin, E.; Martin, F.; Martin, G.G. Determination of Site-Specific (Deuterium/Hydrogen) Ratios in Vanillin by 2H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometry: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2007, 90, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royer, A.; Naulet, N.; Mabon, F.; Lees, M.; Martin, G.J. Stable isotope characterization of olive oils: II-deuterium distribution in fatty acids studied by nuclear magnetic resonance (SNIF-NMR). J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, P.A.; Remaud, G.S.; Jamin, E.; Martin, Y.-L. Geographic origin determination of heroin and cocaine using site-specific isotopic ratio deuterium NMR. J. Forensic Sci. 2000, 45, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertino, A.; Barge, A.; Cravotto, G.; Genzini, L.; Gobetto, R.; Vincenti, M. Natural origin of ascorbic acid: Validation by 13C NMR and IRMS. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.J.; Danho, D.; Vallet, C. Natural isotope fractionation in the discrimination of sugar origins. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 1991, 56, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.J.; Guillou, C.; Martin, M.L.; Cabanis, M.T.; Tep, Y.; Aerny, J. Natural factors of isotope fractionation and the characterization of wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Failoni, A.; Simoni, M.; Tonon, A.; Camin, F. Influence of Fermentation Water on Stable Isotopic D/H Ratios of Alcohol Obtained from Concentrated Grape Must. Molecules 2020, 25, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, M.P.; Zhang, B.; Martin, G.J. Determination of the geographical origin of wine using joint analysis of elemental and isotopic composition. II—Differentiation of the principal production zones in France for the 1990 vintage. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 1995, 67, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Comission of the European Communities. Regulation EC No. 555/2008. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2008, L170, 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann, A. Determination of site-specific D/H isotope ratios of glycerol from different sources by 2H-NMR spectroscopy. Zeitschrift Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und -Forschung A 1999, 208, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Camin, F. δ18O of ethanol in wine and spirits for authentication purposes. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.; Santos, H. NMR Studies of Wine Chemistry and Wine Bacteria. Annu. Rep. Nucl. Magn. Recon. Spectrosc. 1999, 37, 179–202. [Google Scholar]
- Thiem, I.; Luepke, M.; Seifert, H. Factors influencing the 18O/16O-ratio in meat juices. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2004, 40, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyon, F.; Douet, C.; Colas, S.; Salagoïty, M.-H.; Medina, B. Effects of must concentration techniques on wine isotopic parameters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9918–9923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Rolle, L.; Franceschi, P.; Simoni, M.; Torchio, F.; Di Martino, V.; Marianella, R.M.; Gerbi, V.; Camin, F. H, C, and O Stable Isotope Ratios of Passito Wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5851–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, A. Determination of stable isotope ratios in food analysis. Food Rev. Int. 2001, 17, 347–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Miralles, J.E.; Salazar, D.M.; Solana, I. Regional Origin Assignment of Red Wines from Valencia (Spain) by 2H NMR and 13C IRMS Stable Isotope Analysis of Fermentative Ethanol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 2645–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordevic, N.; Wehrens, R.; Postma, G.J.; Buydens, L.M.C.; Camin, F. Statistical methods for improving verification of claims of origin for Italian wines based on stable isotope ratios. Analytica Chimica Acta 2012, 757, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camin, F.; Dordevic, N.; Wehrens, R.; Neteler, M.; Delucchi, L.; Postma, G.; Buydens, L. Climatic and geographical dependence of the H, C and O stable isotope ratios of Italian wine. Analytica Chimica Acta 2015, 853, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Košir, I.J.; Kocjan, M.; Ogrinc, N.; Kidrič, J. Use of SNIF-NMR and IRMS in combination with chemometric methods for the determination of chaptalisation and geographical origin of wines (the example of Slovenian wines). Analytica Chimica Acta 2001, 429, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versini, G.; Monetti, A.; Reniero, F. Monitoring Authenticity and Regional Origin of Wines by Natural Stable Isotope Ratios Analysis. In Wine Nutritional and Therapeutic Benefits; Watkins, T.R., Ed.; ACS Symposium Series; Americal Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 113–130. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Xue, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L. The application of SNIF-NMR and IRMS combined with C, H and O isotopes for detecting the geographical origin of Chinese wines. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2014, 50, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinofta, R.; Fotakis, C.; Zervou, M.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Savvidou, C.; Poulli, K.; Louka, C.; Economidou, N.; Tzioni, E.; Damianou, K.; et al. Isotopic and Elemental Authenticity Markers: A Case Study on Cypriot Wines. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3902–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrinc, N.; Košir, I.J.; Kocjančič, M.; Kidrič, J. Determination of Authenticy, Regional Origin, and Vintage of Slovenian Wines Using a Combination of IRMS and SNIF-NMR Analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pîrnău, A.; Bogdan, M.; Măgdaş, D.A.; Stătescu, D. Isotopic Analysis of some Romanian Wines by 2H NMR and IRMS. Food Biophys. 2013, 8, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghemo, C.; Albertino, A.; Gobetto, R.; Spanna, F. Correlation between isotopic and meteorological parameters in Italian wines: A local-scale approach. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2088–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejjani, J.; Balaban, M.; Rizk, T. A sharper characterization of the geographical origin of Lebanese wines by a new interpretation of the hydrogen isotope ratios of ethanol. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, C.; Bertacchini, L.; Bontempo, L.; Camin, F.; Manzini, D.; Lambertini, P.; Marchetti, A.; Paolini, M. From soil to grape and wine: Variation of light and heavy elements isotope ratios. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monetti, A.; Versini, G.; Dalpiaz, G.; Reniero, F. Sugar Adulterations Control in Concentrated Rectified Grape Musts by Finite Mixture Distribution Analysis of the myo- and scyllo-Inositol Content and the D/H Methyl Ratio of Fermentative Ethanol. J. Agric. Food Chem 1996, 44, 2194–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, A.; Reniero, F.; Moussa, I.; Schmidt, H.L.; Versini, G.; Merle, M.H. Stable oxygen isotope content of water of EU data-bank wines from Italy, France and Germany. Zeitschrift Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und -Forschung A 1999, 208, 400–407. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.J.; Mazure, M.; Jouitteau, C.; Martin, Y.L.; Aguile, L.; Allain, P. Characterization of the Geographic Origin of Bordeaux Wines by a Combined Use of Isotopic and Trace Element Measurements. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1999, 50, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Geana, E.I.; Popescu, R.; Costinel, D.; Dinca, O.R.; Ionete, R.E.; Stefanescu, I.; Artem, V.; Bala, C. Classification of red wines using suitable markers coupled with multivariate statistic analysis. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monetti, A.; Versini, G.; Reniero, F. Classification of Italian wines on a regional scale by means of a multi-isotopic analysis. Dev. Food Sci. 1995, 37, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.J.; Koziet, J.; Rossmann, A.; Dennis, J. Site-Specific natural isotope fractionation in fruit juices determined by deuterium NMR an European inter-laboratory comparison study. Analytica Chimica Acta 1996, 321, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Košir, I.; Kocjančič, M.; Kidrič, J. Wine analysis by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy. Analusis 1998, 26, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Košir, I.J.; Kidrič, J. Use of modern nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in wine analysis: Determination of minor compounds. Analytica Chimica Acta 2002, 458, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremaud, G.; Quaile, S.; Piantini, U.; Pfammatter, E.; Corvi, C. Characterization of Swiss vineyards using isotopic data in combination with trace elements and classical parameters. Eur. Food Res. Tech. 2004, 219, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
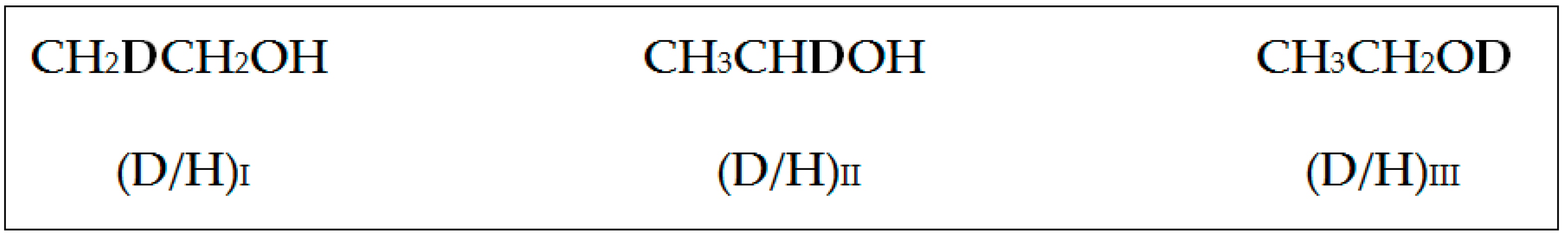
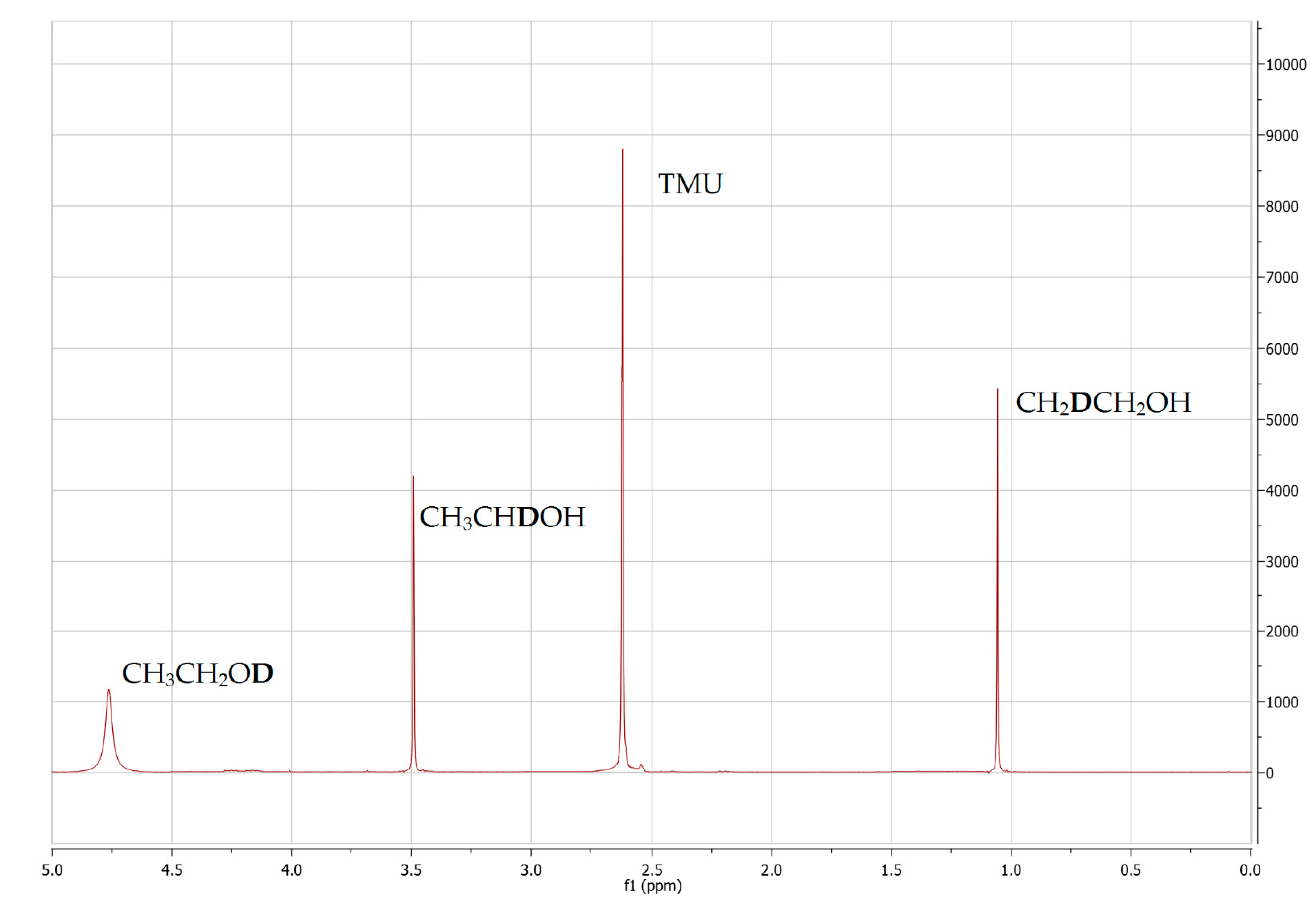
| Discriminative Factor Investigated by NMR Metabolomics/Aim of NMR Study | Chemometric Method | NMR Technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grape berries; variety, harvesting time | PCA, PLS, OPLS | 1H, J-res, COSY, HMBC, HSQC | [4] |
| Grape berries; variety, terroir | ANOVA, PCA | 1H | [5] |
| Grape berries; cultivation practices | PCA | 1H | [7] |
| Grape pulp; terroir, vintage | PCA, ANOVA, PLS-DA | HR-MAS, COSY, TOCSY, J-res, HSQC, HMBC | [6] |
| Geographical origin | PCA, HCA, DA | 1H | [8] |
| PCA, PLS-DA | 1H, 13C, HMBC, HSQC | [15] | |
| Terroir | PCA, ECVA | 1H | [9] |
| PCA, DA, HCA | 1H, COSY, TOCSY, HSQC | [14] | |
| Variety | PCA, PLS, HCA | 1H, COSY | [11] |
| PCA, PLS, HCA, ANOVA, RF | 1H, 13C, J-res, COSY, HSQC | [12] | |
| PCA, LDA | 1H | [23] | |
| Cultivation technique | PCA, OPLS-DA | 1H | [26] |
| PCA, PLS | 1H, 13C, COSY, HSQC, HMBC | [25] | |
| Variety, geographical origin, and vintage | PCA, PLS-DA | 1H | [24] |
| PCA, LDA, MANOVA, MC | 1H | [13] | |
| Yeast strain applied in fermentation | PCA, HCA, DA, ANOVA | 1H, COSY, TOCSY, HSQC, HMBC | [27] |
| Fermentation monitoring | - | 1H | [17] |
| PCA | 1H | [18] | |
| PCA, PLS-DA, OPLS-DA | 1H, TOCSY, HMBC, HSQC | [19] | |
| Infection by plant pathogen | PCA, PLS-DA, HCA | 1H, J-res, COSY, HMBC, HSQC | [21] |
| PCA, OPLS-DA | 1H, TOCSY, COSY, HMBC, HSQC | [22] | |
| Sensoric profile | ANOVA, PLS | 1H, COSY, HSQC | [28] |
| Sensoric profile, variety, cultivation practices | PCA, PLS-DA | 1H | [29] |
| Vintage, ageing | PCA, PLS-DA | 1H, TOCSY, HSQC | [30] |
| Ageing | - | 1H, COSY, TOCSY, HSQC, DOSY | [55] |
| PCA, PLS-DA, ANOVA | 1H, TOCSY, HSQC | [31] | |
| Wine blending | LDA, ANN | 1H | [16] |
| Assessment of wine antioxidative potential and influence of aging conditions | - | 1H, 13C, COSY, HSQC, HMBC | [20] |
| Identification and characterization of minor wine components with sensoric or bioactive role | Always a combination of some of the following techniques: 1H, 13C, COSY, NOESY, TOCSY, ROESY, HMBC, HSQC, HMQC | [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,43,44,45,46,52] | |
| Interactions between wine components with sensoric role | CP-MAS NMR | [42] | |
| 1H | [47] | ||
| 1H, 13C, HMQC, HMBC, COSY | [48] |
| Purpose | Samples and Varieties | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adulteration detection | 354 samples; multiple varieties | Italy | [160] |
| Geographical discrimination, adulteration detection-watering | 30 samples; multiple varieties | Italy, Germany, France | [161] |
| Adulteration detection-glycerol | - | Germany | [141] |
| Adulteration detection-sugar, Geographical discrimination | 50 samples; 17 varieties | Slovenia | [151] |
| Geographical discrimination, Adulteration detection | 5 varieties; Feteasca Regala, Feteasca Alba, Merlot, Cabernet Sauvignon | Romania | [156] |
| Adulteration detection-watering | 69 samples; multiple varieties | Italy | [142] |
| Influence of must concentration on isotope ratios | 42 must samples | France | [145] |
| Influence of fermentation stopping on isotope ratios | 126 must samples, 18 commercial wines | Italy | [103] |
| Influence of grape withering on the isotope ratios | 78 samples; Passito wines | Italy | [146] |
| Geographical discrimination | 1383 samples; 14 varieties | Germany | [69] |
| 33 samples, 17 varieties | Slovenia, southern Italy | [77] | |
| 166 samples; multiple varieties | France | [139] | |
| 96 samples; Bobal, Tempranillo, Monastrell | Spain | [148] | |
| 5220 samples; multiple varieties | Italy | [149] | |
| 3948 samples; multiple varieties | Italy | [150] | |
| 1496 samples; multiple varieties | Italy | [152] | |
| 100 samples; Merlot, Cabernet Sauvignon, Riesling, Chardonnay, and Italian Riesling | China | [153] | |
| 76 samples; Xynisteri, Maratheftiko, Cabernet Sauvignon, and Shiraz | Cyprus | [154] | |
| 102 samples; multiple varieties | Slovenia | [155] | |
| 54 samples; Nebbiolo, barbera | Northern Italy | [157] | |
| 78 samples; Mourvedre, Rolle, and Syrah | Lebanon | [158] | |
| 206 samples; Lambrusco, Trentodoc | Italy | [159] | |
| 259 samples; multiple varieties | France | [162] | |
| 56 samples; Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Feteasca Neagra, Pinot Noir, and Mamaia | Romania | [163] | |
| 445 samples; multiple varieties | Italy | [164] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viskić, M.; Bandić, L.M.; Korenika, A.-M.J.; Jeromel, A. NMR in the Service of Wine Differentiation. Foods 2021, 10, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010120
Viskić M, Bandić LM, Korenika A-MJ, Jeromel A. NMR in the Service of Wine Differentiation. Foods. 2021; 10(1):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010120
Chicago/Turabian StyleViskić, Marko, Luna Maslov Bandić, Ana-Marija Jagatić Korenika, and Ana Jeromel. 2021. "NMR in the Service of Wine Differentiation" Foods 10, no. 1: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010120
APA StyleViskić, M., Bandić, L. M., Korenika, A.-M. J., & Jeromel, A. (2021). NMR in the Service of Wine Differentiation. Foods, 10(1), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010120






