Implant Soft-Tissue Attachment Using 3D Oral Mucosal Models—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Source
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Materials
- TiZr-SLA: titanium–zirconium alloy, which underwent sandblasting and acid etching (SLA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol, and was gamma sterilized;
- TiZr-M: as-machined TiZr (gamma sterilized);
- ZrO2-M: as-machined ZrO2 (zirconia), which was ethylene oxide-sterilized;
- PEEK-M: as-machined PEEK (polyether ether ketone), which was steam sterilized.
2.4. 3D Oral Mucosa Models
2.5. Implant/Abutment Insertion
2.6. Stimulation of the 3D Oral Mucosa Models to Induce Inflammation
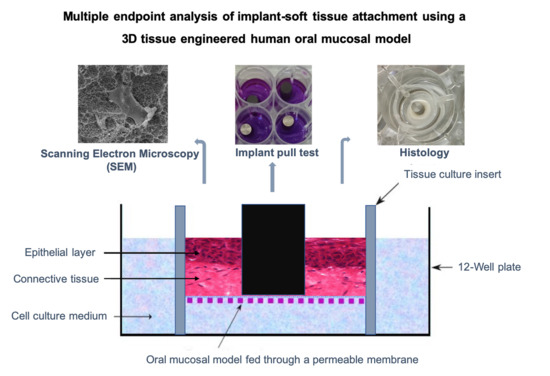
2.7. Multiple Endpoint Analyses
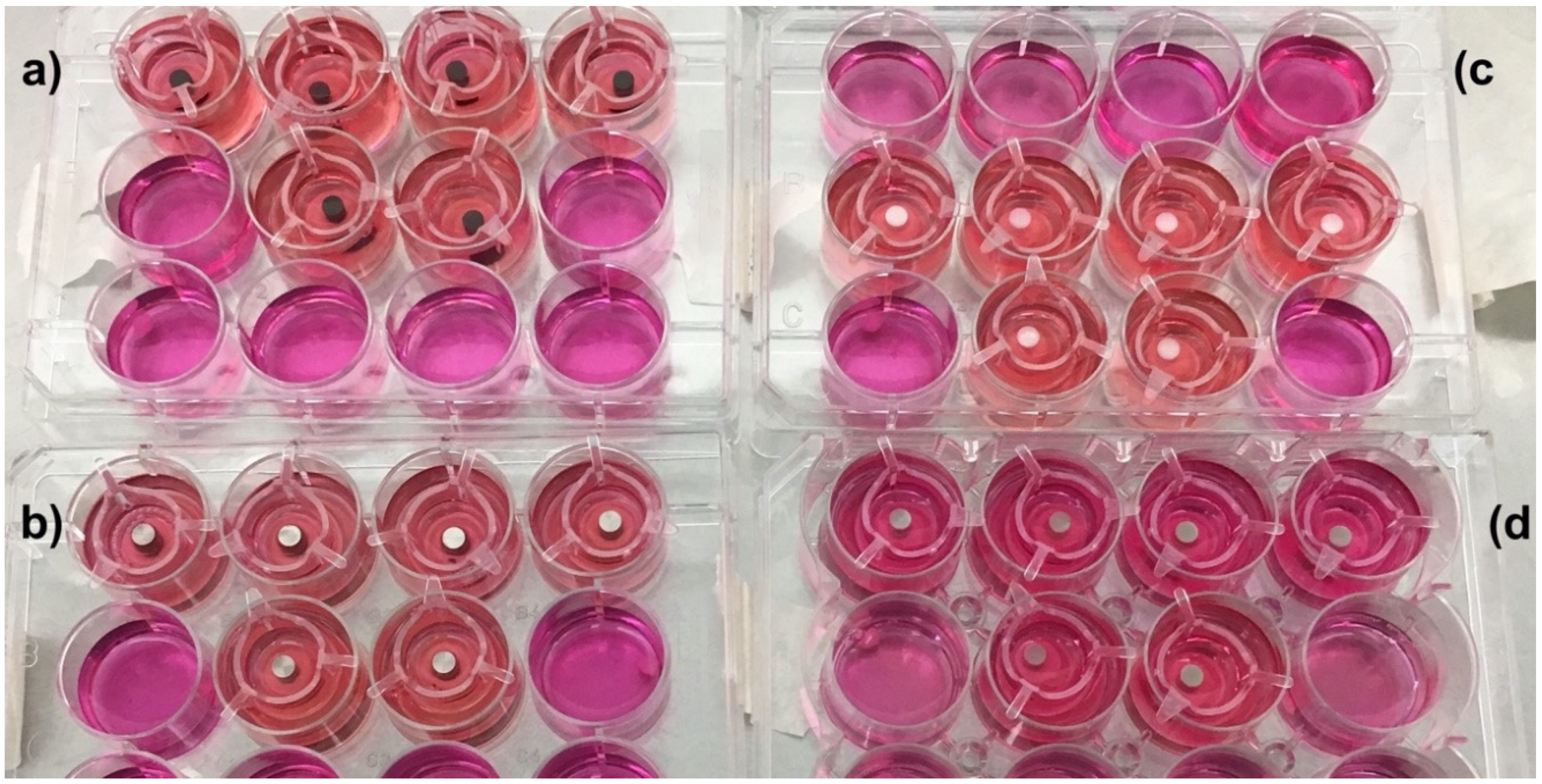
2.7.1. Tissue Viability Pull Test
2.7.2. Histological Processing
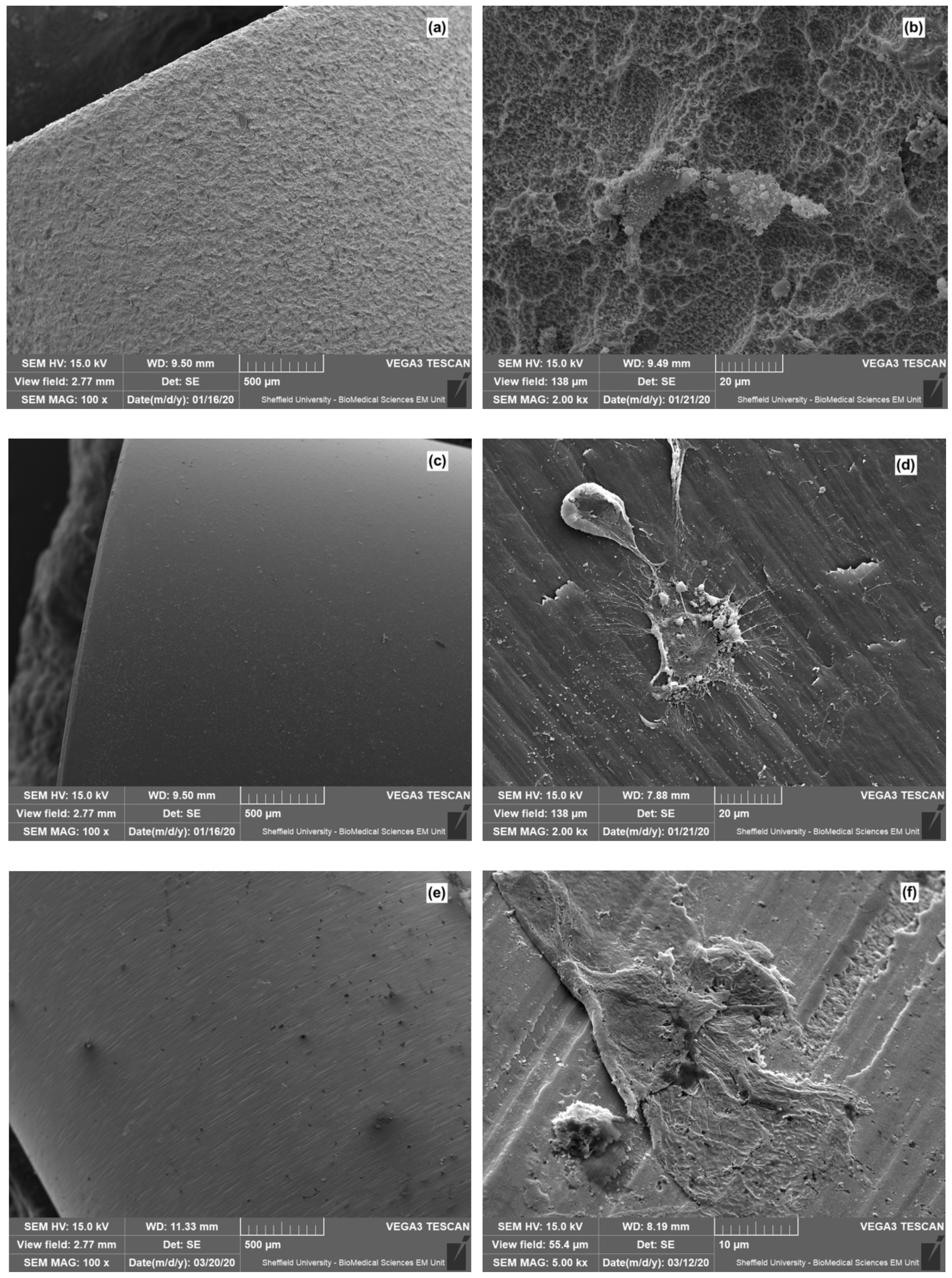
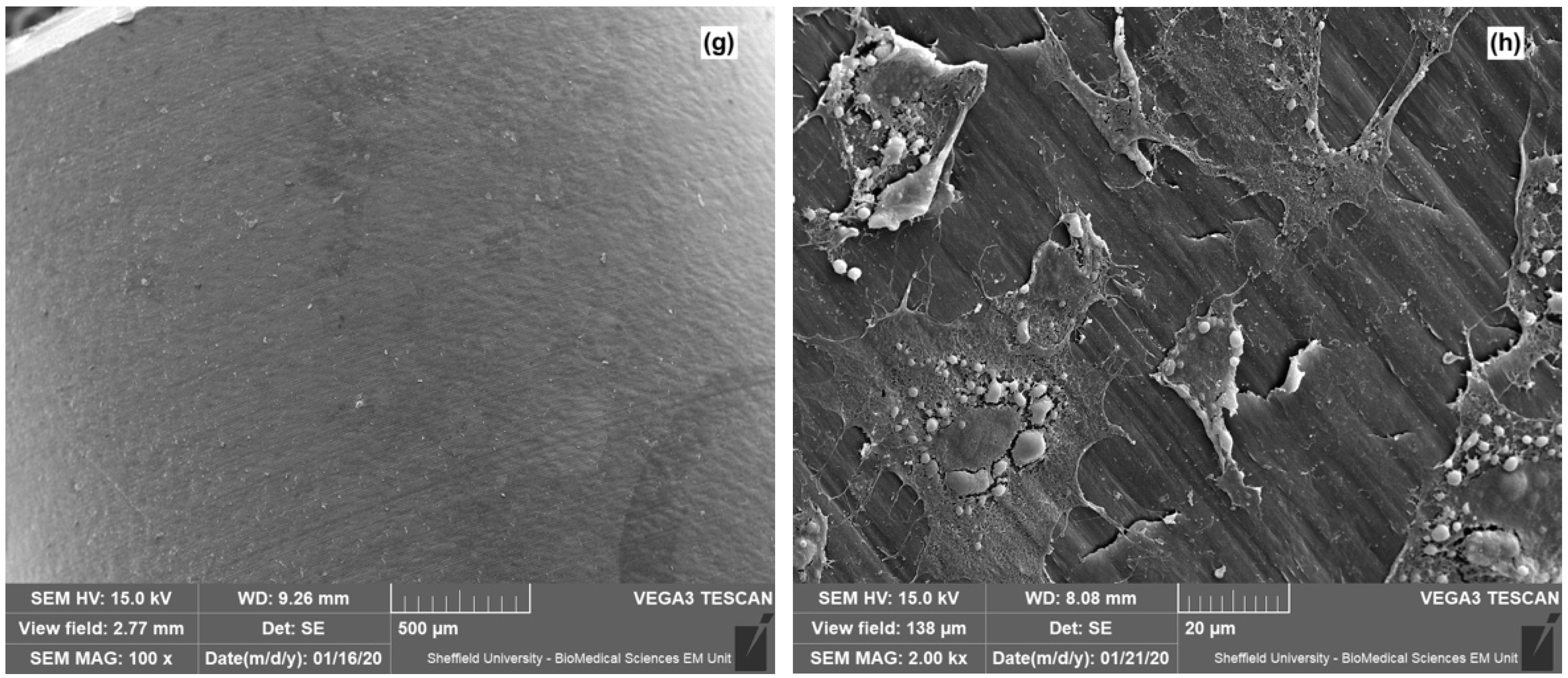
2.7.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.7.4. Statistical Analysis
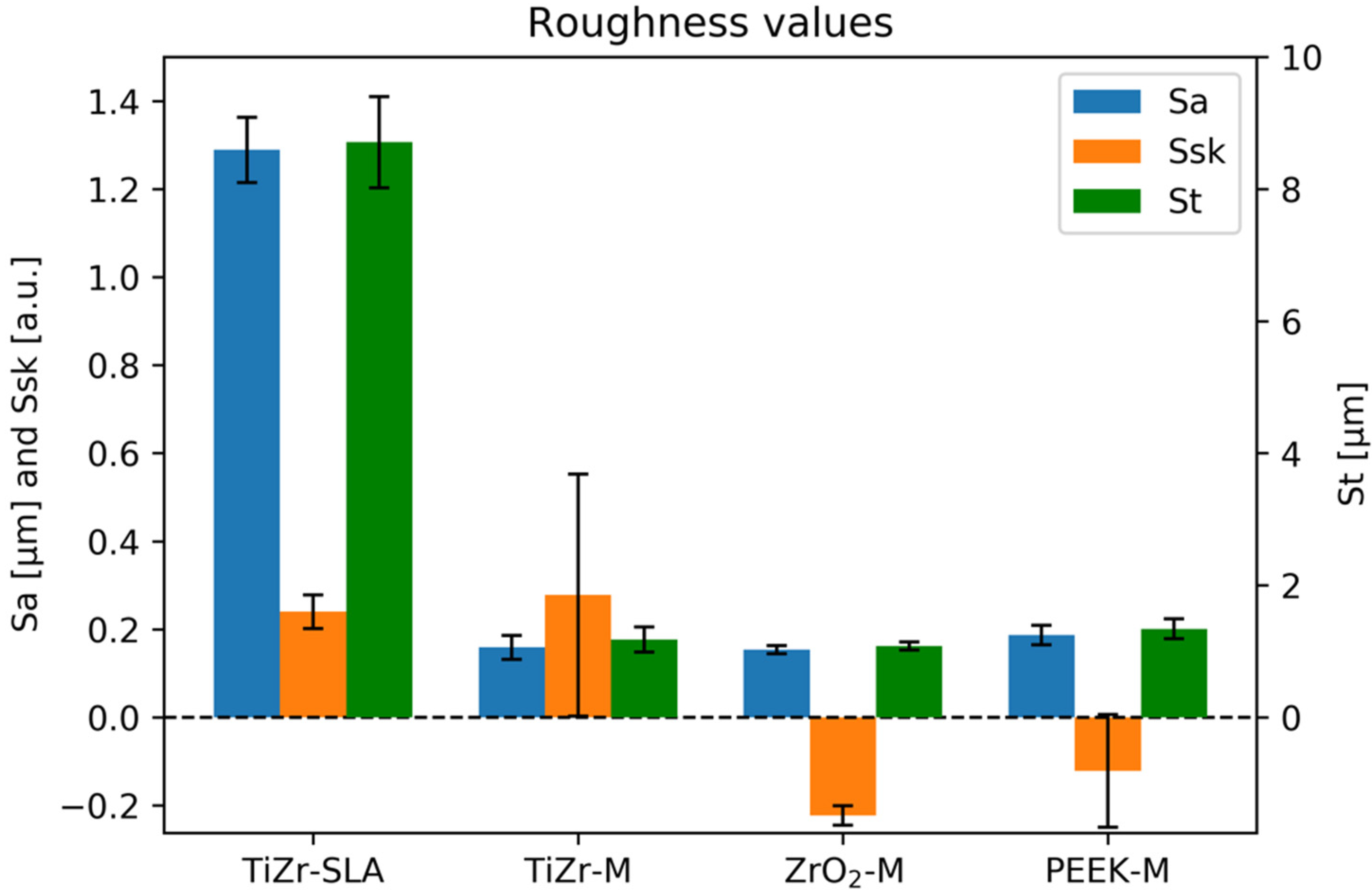
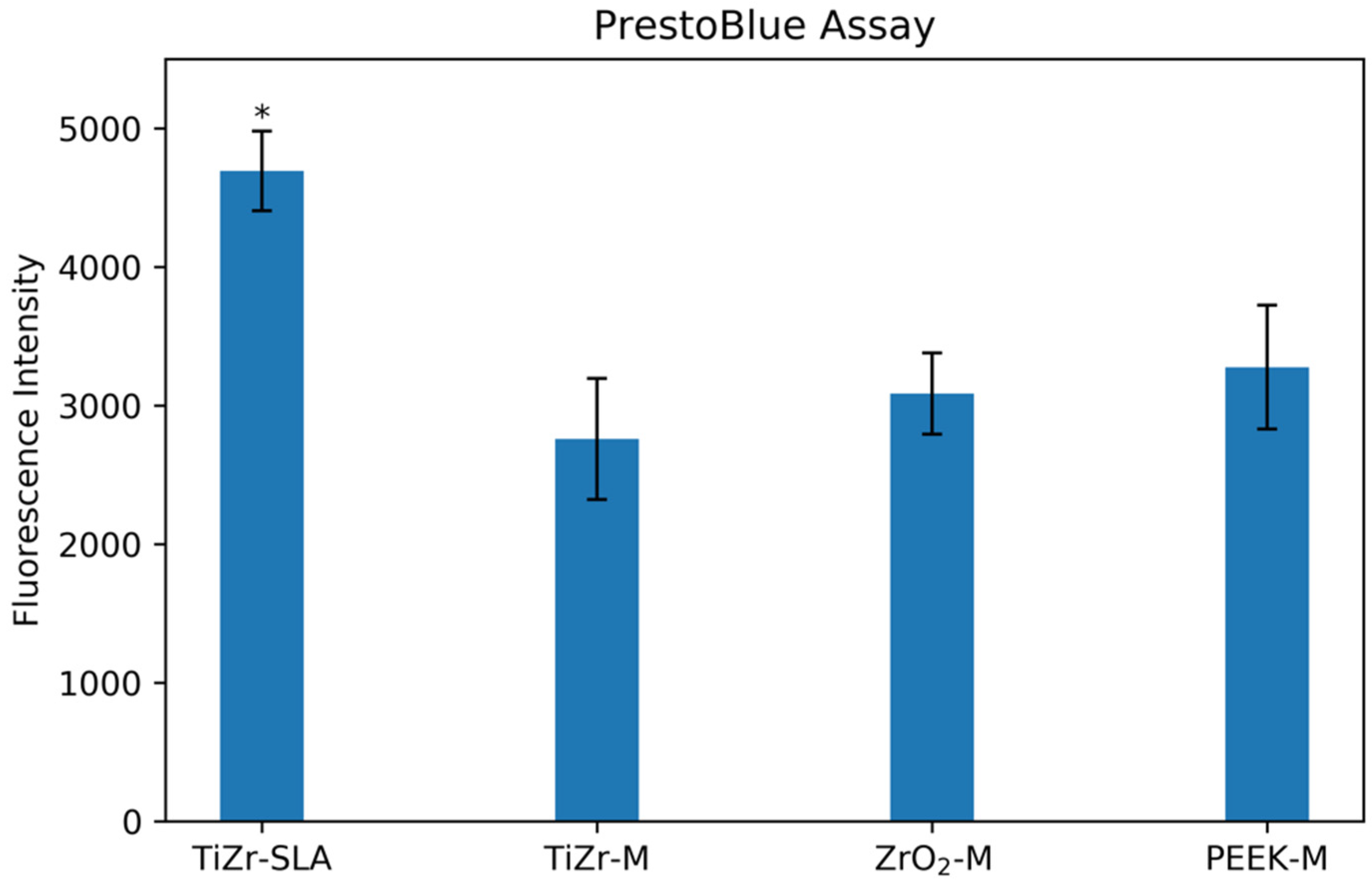
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cochran, D.L. A comparison of endosseous dental implant surfaces. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 1523–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, W.; Moharamzadeh, K.; Brook, I.; Vannoort, R. A review of histomorphometric analysis techniques for assessing implant-soft tissue interface. Biotech. Histochem. 2011, 86, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheideler, L.; Rupp, F.; Wendel, H.P.; Sathe, S.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. Photocoupling of fibronectin to titanium surfaces influences keratinocyte adhesion, pellicle formation and thrombogenicity. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, G.; Wiedmann-Al-Ahmad, M.; Otten, J.E.; Hubner, U.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Schilli, W. The titanium surface texture effects adherence and growth of human gingival keratinocytes and human maxillar osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 2799–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Brook, I.M.; Van Noort, R.; Scutt, A.M.; Thornhill, M.H. Tissue-engineered oral mucosa: A review of the scientific literature. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Colley, H.; Murdoch, C.; Hearnden, V.; Chai, W.L.; Brook, I.M.; Thornhill, M.H.; MacNeil, S. Tissue-engineered oral mucosa. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Brook, I.M.; Van Noort, R.; Scutt, A.M.; Smith, K.G.; Thornhill, M.H. Development, optimization and characterization of a full-thickness tissue engineered human oral mucosal model for biological assessment of dental biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Brook, I.M.; Scutt, A.M.; Thornhill, M.H.; Van Noort, R. Mucotoxicity of dental composite resins on a tissue-engineered human oral mucosal model. J. Dent. 2008, 36, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Franklin, K.L.; Brook, I.M.; van Noort, R. Biologic assessment of antiseptic mouthwashes using a three-dimensional human oral mucosal model. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.L.; Moharamzadeh, K.; Brook, I.M.; Emanuelsson, L.; Palmquist, A.; van Noort, R. Development of a novel model for the investigation of implant-soft tissue interface. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, F.; Moharamzadeh, K.; Tayebi, L. Three-Dimensional In Vitro Oral Mucosa Models of Fungal and Bacterial Infections. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, W.L.; Brook, I.M.; Palmquist, A.; van Noort, R.; Moharamzadeh, K. The biological seal of the implant-soft tissue interface evaluated in a tissue-engineered oral mucosal model. J. R. Soc. Interface/R. Soc. 2012, 9, 3528–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.L.; Moharamzadeh, K.; van Noort, R.; Emanuelsson, L.; Palmquist, A.; Brook, I.M. Contour analysis of an implant—Soft tissue interface. J. Periodontal Res. 2013, 48, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, W.L.; Brook, I.M.; Emanuelsson, L.; Palmquist, A.; van Noort, R.; Moharamzadeh, K. Ultrastructural analysis of implant-soft tissue interface on a three dimensional tissue-engineered oral mucosal model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinnock, A.; Murdoch, C.; Moharamzadeh, K.; Whawell, S.; Douglas, C.W. Characterisation and optimisation of organotypic oral mucosal models to study Porphyromonas gingivalis invasion. Microbes Infection/Inst. Pasteur 2014, 16, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Franklin, K.L.; Smith, L.E.; Brook, I.M.; Van Noort, R. Evaluation of the effects of ethanol on monolayer and 3D models of human oral mucosa. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 5, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almela, T.; Al-Sahaf, S.; Bolt, R.; Brook, I.M.; Moharamzadeh, K. Characterization of Multilayered Tissue-Engineered Human Alveolar Bone and Gingival Mucosa. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2018, 24, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almela, T.; Brook, I.M.; Moharamzadeh, K. Development of three-dimensional tissue engineered bone-oral mucosal composite models. J. Mater. Sci. Mater Med. 2016, 27, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almela, T.; Al-Sahaf, S.; Brook, I.M.; Khoshroo, K.; Rasoulianboroujeni, M.; Fahimipour, F.; Tahriri, M.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Bolt, R.; Tayebi, L.; et al. 3D printed tissue engineered model for bone invasion of oral cancer. Tissue Cell 2018, 52, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binaljadm, T.; Moorehead, R.; Almela, T.; Franklin, K.L.; Tayebi, L.; Moharamzadeh, K. Biomodification of a Class-V Restorative Material by Incorporation of Bioactive Agents. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, Z.N.; Alqahtani, A.; Almela, T.; Franklin, K.L.; Tayebi, L.; Moharamzadeh, K. Effects of electronic cigarette liquid on monolayer and 3D tissue-engineered models of human gingival mucosa. J. Adv. Periodontol. Implant. Dent. 2019, 11, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingendoh-Tsakmakidis, A.; Mikolai, C.; Winkel, A.; Szafranski, S.P.; Falk, C.S.; Rossi, A.; Walles, H.; Stiesch, M. Commensal and pathogenic biofilms differently modulate peri-implant oral mucosa in an organotypic model. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Deng, D.; Buskermolen, J.K.; Janus, M.M.; Krom, B.P.; Roffel, S.; Waaijman, T.; van Loveren, C.; Crielaard, W.; Gibbs, S. Multi-species oral biofilm promotes reconstructed human gingiva epithelial barrier function. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roffel, S.; Wu, G.; Nedeljkovic, I.; Meyer, M.; Razafiarison, T.; Gibbs, S. Evaluation of a novel oral mucosa in vitro implantation model for analysis of molecular interactions with dental abutment surfaces. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21 (Suppl. 1), 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannoort, R. Titanium—The implant material of today. J. Mater. Sci. 1987, 22, 3801–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinemann, S.G. Titanium—The material of choice? Periodontology 2000 1998, 17, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.F. Titanium for medical applications. In Titanium in Medicine; Brunette, D., Tengvall, P., Textor, M., Thomson, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nawas, B.; Bragger, U.; Meijer, H.J.; Naert, I.; Persson, R.; Perucchi, A.; Quirynen, M.; Raghoebar, G.M.; Reichert, T.E.; Romeo, E.; et al. A double-blind randomized controlled trial (RCT) of titanium-13 zirconium versus titanium grade IV small-diameter bone level implants in edentulous mandibles—Results from a 1-year observation period. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, E.; Lops, D.; Amorfini, L.; Chiapasco, M.; Ghisolfi, M.; Vogel, G. Clinical andradiographic evaluation of small-diameter (3.3 mm) implants followed for 1–7 years: Alongitudinal study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2006, 17, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinsli, B.; Sagesser, T.; Mericske, E.; Mericske-Stern, R. Clinical evaluation of small-diameter ITI implants: A prospective study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2004, 19, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Allum, S.R.; Tomlinson, R.A.; Joshi, R. The impact of loads on standard diameter, small diameter and mini implants: A comparative laboratory study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, M.S. Mechanical complications of dental implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2000, 11, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, G.R.; Gardner, L.K.; Toth, R.W. Titanium—The mystery metal of implant Dentistry-Dental materials aspects. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1985, 54, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Williams, R.L.; Williams, D.F. Conjoint corrosion and wear in titanium alloys. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.I.; Han, J.H.; Lee, I.S.; Lee, K.H.; Shin, M.C.; Choi, B.B. New titanium alloys for biomaterials: A study of mechanical and corrosion properties and cytotoxicity. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 1997, 7, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Chai, F.; Hornez, J.C.; Li, C.L.; Zhao, Y.M.; Traisnel, M.; Hildebrand, H.F. The corrosion and biological behaviour of titanium alloys in the presence of human lymphoid cells and MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, N.; Berner, S.; De Wild, M.; Wieland, M. The binary TiZr alloy—A newly developed Ti alloy for use in dental implants. Forum Implantol. 2009, 5, 530–539. [Google Scholar]
- Chiapasco, M.; Casentini, P.; Zaniboni, M.; Corsi, E.; Anello, T. Titanium-zirconium alloy narrow-diameter implants (Straumann Roxolid®) for the rehabilitation of horizontally deficient edentulous ridges: Prospective study on 18 consecutive patients. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barter, S.; Stone, P.; Bragger, U. A pilot study to evaluate the success and survival rate of titanium-zirconium implants in partially edentulous patients: Results after 24 months of follow-up. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitalla, A.; Muller, W.D. PEEK Dental Implants: A Review of the literature. J. Oral Implant. 2013, 39, 39743–39749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.M.; Ingalhalikar, A.; Highsmith, J.M.; Vaccaro, A.R. Biomechanical rigidity of an all-polyetheretherketone anterior thoracolumbar spinal reconstruction construct: An in vitro corpectomy model. Spine J. 2009, 9, 330335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Shepherd, D.; Dearn, K. Strength of poly-etheretherketone: Effects of sterilization and thermal ageing. Polym Test. 2013, 32, 10011005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, J.; Adler, S.; Kisttler, F. The use of plastics in fixed prosthetic implant restoration. ZWR-German Dent. J. 2013, 122, 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.; Bohner, L.; Hanisch, M.; Kleinheinz, J.; Sielker, S. Influence of Implant Material and Surface on Mode and Strength of Cell/Matrix Attachment of Human Adipose Derived Stromal Cell. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorkhan, M.; Yucel-Lindberg, T.; Hall, J.; Svensater, G.; Davies, J.R. Adherence of human oral keratinocytes and gingival fibroblasts to nano-structured titanium surfaces. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannasi, C.; Pagni, G.; Polenghi, C.; Niada, S.; Manfredi, B.; Brini, A.T.; Rasperini, G. Impact of Dental Implant Surface Modifications on Adhesion and Proliferation of Primary Human Gingival Keratinocytes and Progenitor Cells. Int J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2018, 38, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Hu, X.; Yu, X.; Wan, S.; Wu, F.; Ouyang, J.; Deng, F. Micro-/nano-topography of selective laser melting titanium enhances adhesion and proliferation and regulates adhesion-related gene expressions of human gingival fibroblasts and human gingival epithelial cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5045–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Diaz, L.; Dedavid, B.A.; Gehrke, S.A. Evaluation of Fibroblasts Cells Viability and Adhesion on Six Different Titanium Surfaces: An in vitro Experimental Study. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2018, 12, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigolin, M.S.M.; Barbugli, P.A.; Jorge, J.H.; Reis, M.R.D.; Adabo, G.L.; Casemiro, L.A.; Martins, C.H.G.; de Lima, O.J.; Mollo Junior, F.A. Effect of the aging of titanium and zirconia abutment surfaces on the viability, adhesion, and proliferation of cells and the adhesion of microorganisms. J. Prosthet Dent. 2019, 122, 564 e1–564 e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsuta, I.; Ayukawa, Y.; Furuhashi, A.; Ogino, Y.; Moriyama, Y.; Tsukiyama, Y.; Koyano, K. In vivo and in vitro studies of epithelial cell behavior around titanium implants with machined and rough surfaces. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deporter, D.A.; Watson, P.A.; Pilliar, R.M.; Howley, T.P.; Winslow, J. A histological evaluation of a functional endosseous, porous-surfaced, titanium alloy dental implant system in the dog. J. Dent. Res. 1988, 67, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.; van der Zypen, E.; Stich, H.; Sutter, F. The reactions of bone, connective tissue, and apithelium to endosteal implants with titanium-sprayed surfaces. J. Maxxilofac. Surg. 1981, 9, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swope, E.; James, R. A longitudinal study on hemidesmosome formation at the dental-tissue overflow. J. Oral Implantol. 1981, 9, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sculean, A.; Gruber, R.; Bosshardt, D.D. Soft tissue wound healing around teeth and dental implants. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41 (Suppl. 15), S6–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barker, E.; AlQobaly, L.; Shaikh, Z.; Franklin, K.; Moharamzadeh, K. Implant Soft-Tissue Attachment Using 3D Oral Mucosal Models—A Pilot Study. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj8030072
Barker E, AlQobaly L, Shaikh Z, Franklin K, Moharamzadeh K. Implant Soft-Tissue Attachment Using 3D Oral Mucosal Models—A Pilot Study. Dentistry Journal. 2020; 8(3):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj8030072
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarker, Emilia, Lina AlQobaly, Zahab Shaikh, Kirsty Franklin, and Keyvan Moharamzadeh. 2020. "Implant Soft-Tissue Attachment Using 3D Oral Mucosal Models—A Pilot Study" Dentistry Journal 8, no. 3: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj8030072
APA StyleBarker, E., AlQobaly, L., Shaikh, Z., Franklin, K., & Moharamzadeh, K. (2020). Implant Soft-Tissue Attachment Using 3D Oral Mucosal Models—A Pilot Study. Dentistry Journal, 8(3), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj8030072