Homoleptic Lanthanide Complexes Containing a Redox-Active Ligand and the Investigation of Their Electronic and Photophysical Properties
Abstract
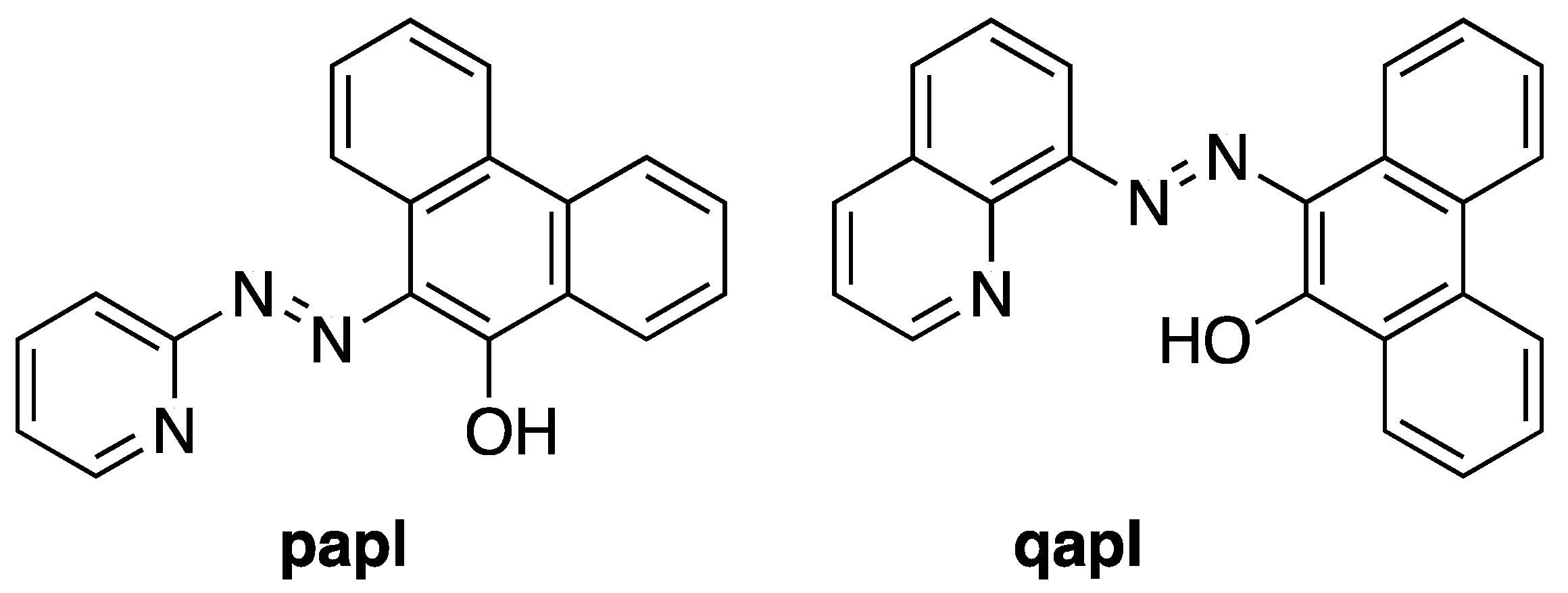
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
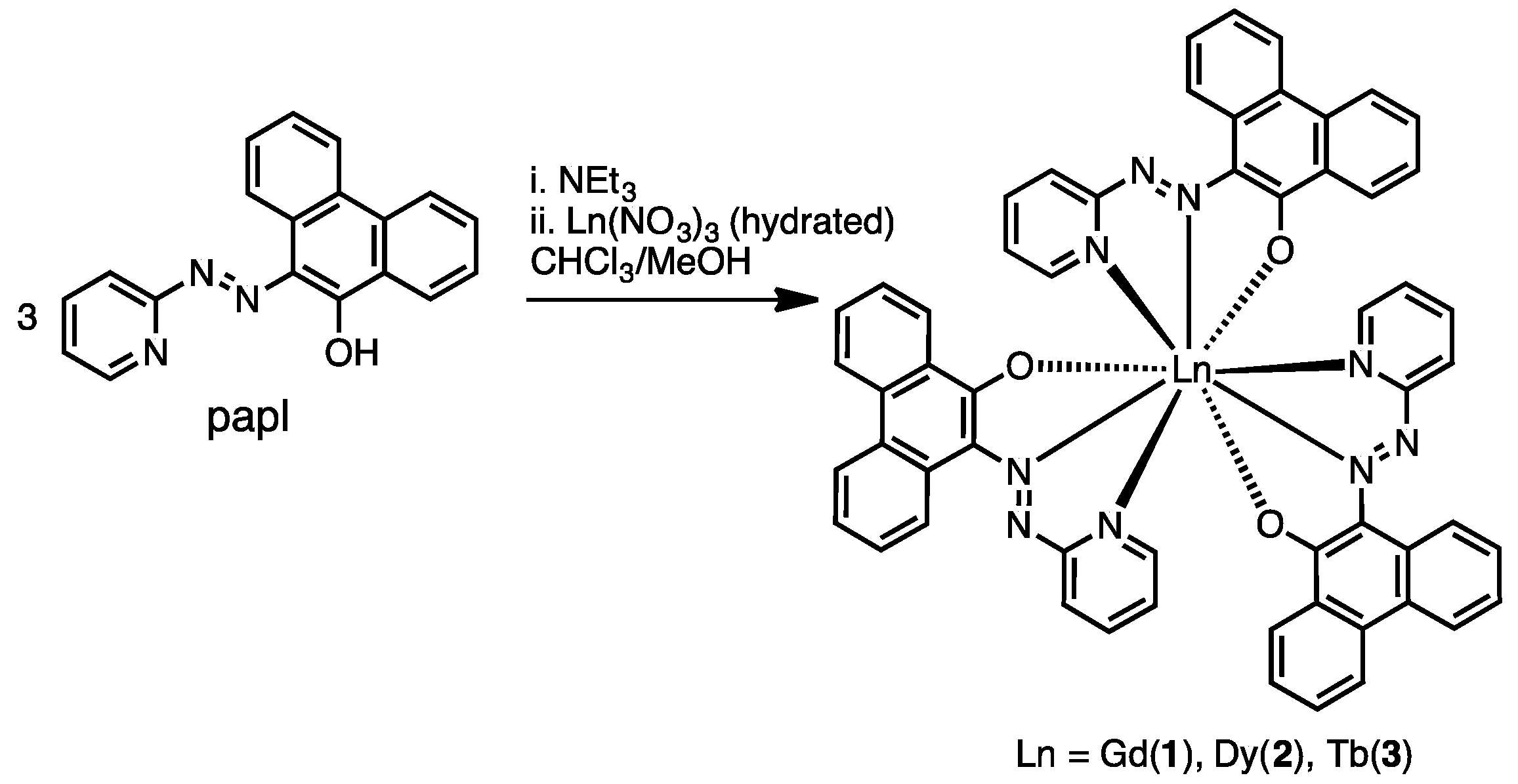
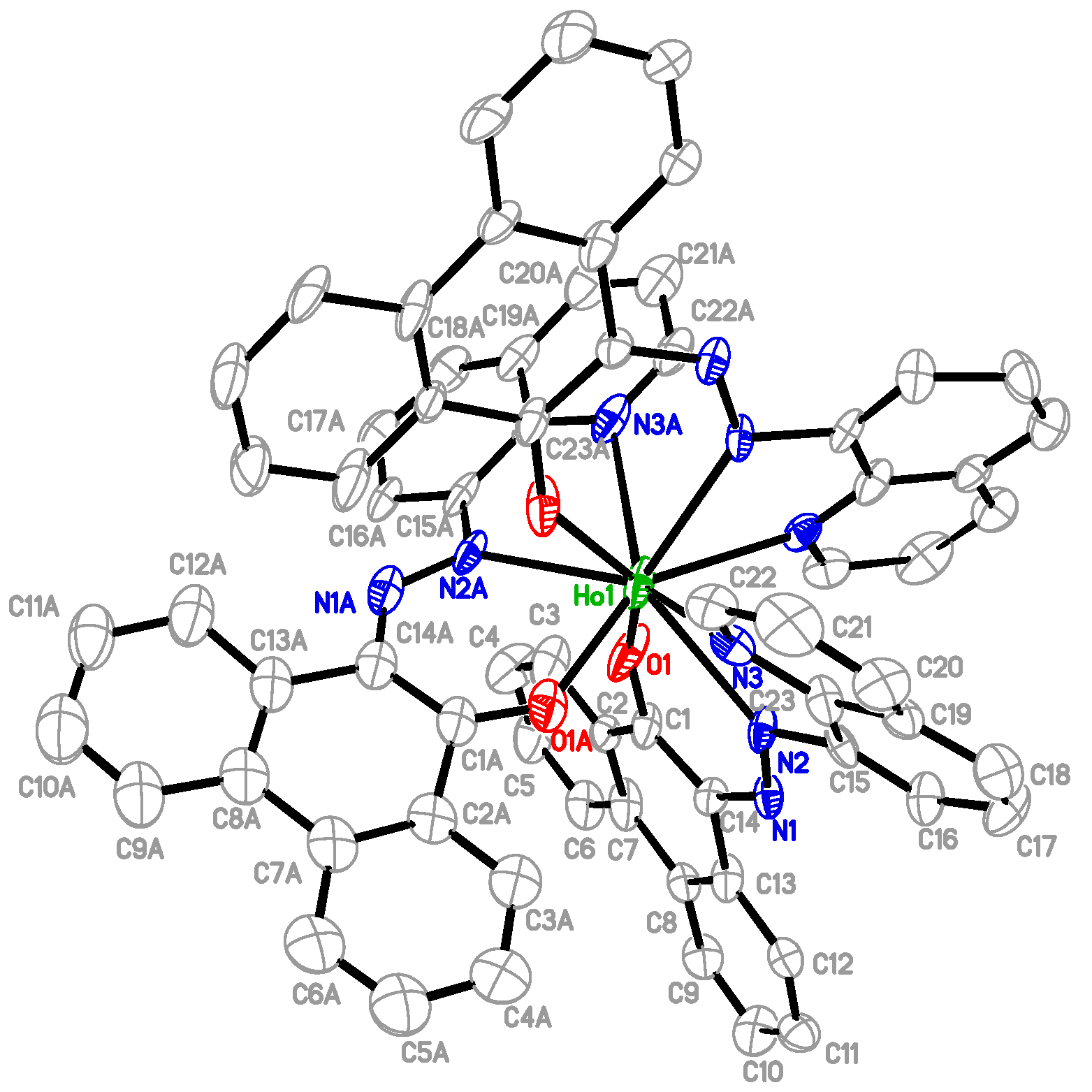
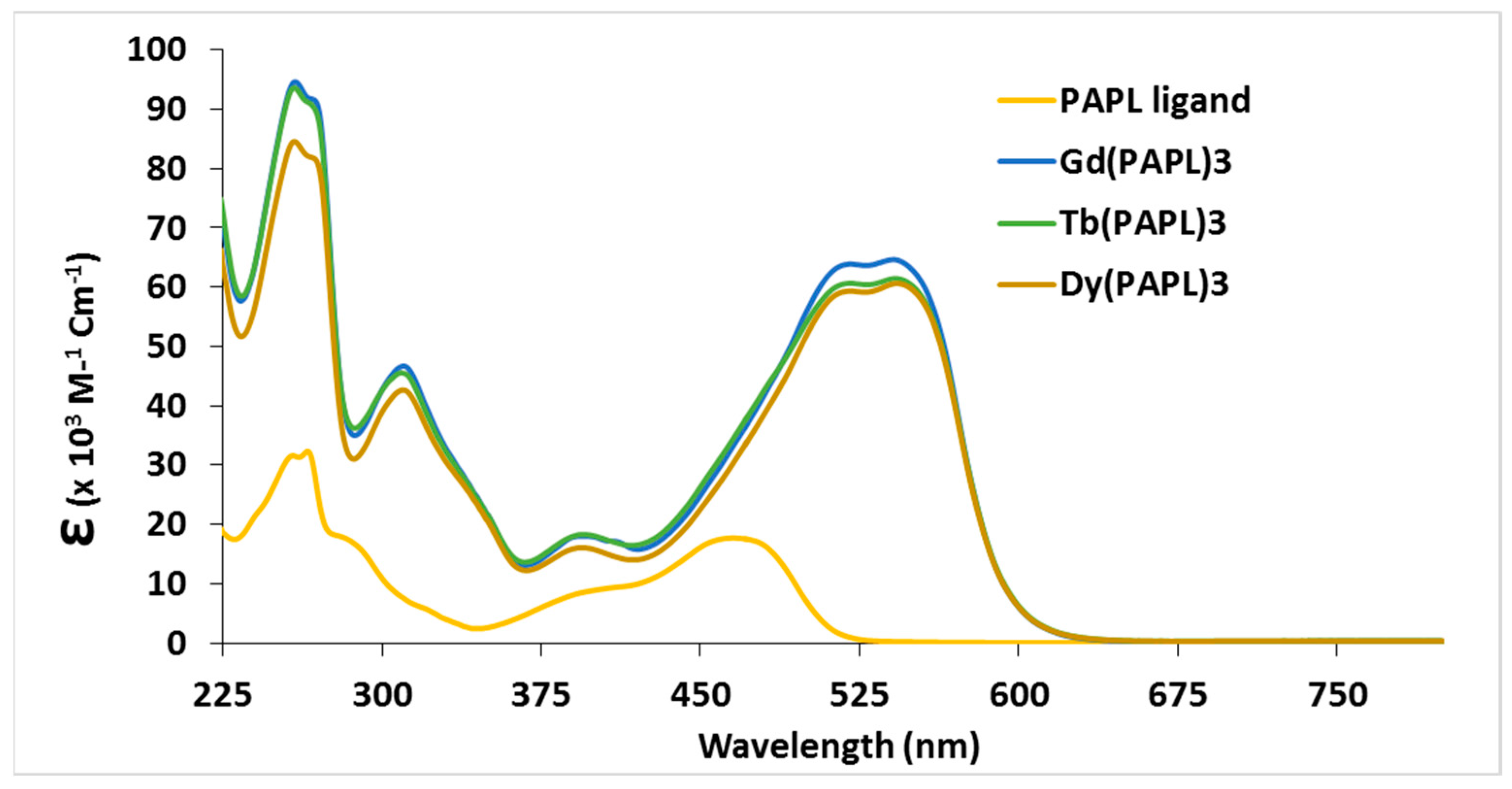
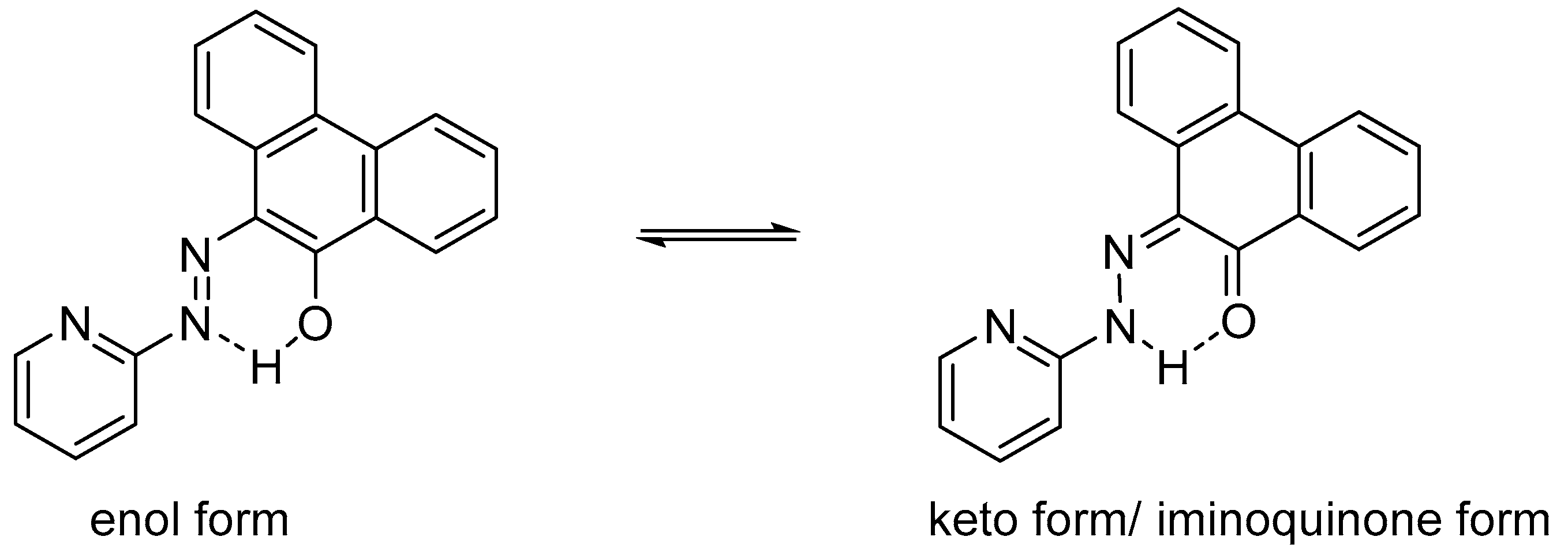
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Ln(papl)3 Ln = Gd, Tb, Dy and Ho(qapl)3 Complexes
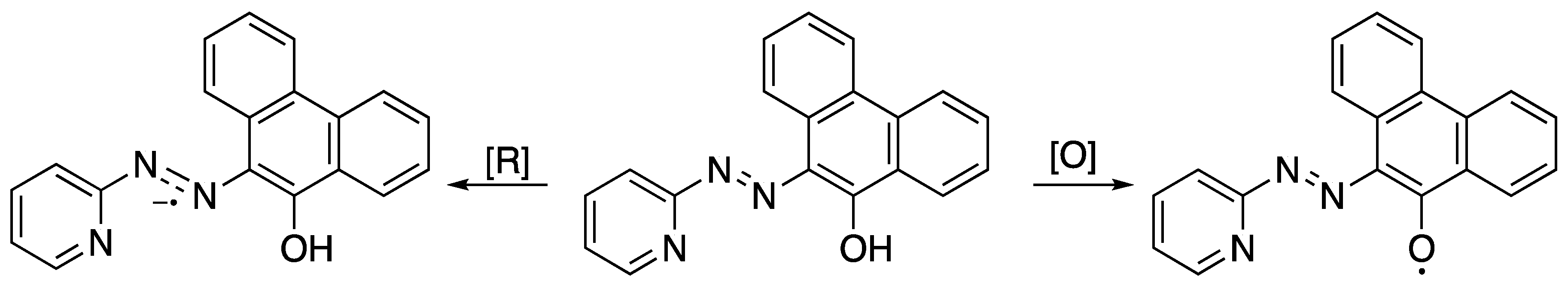
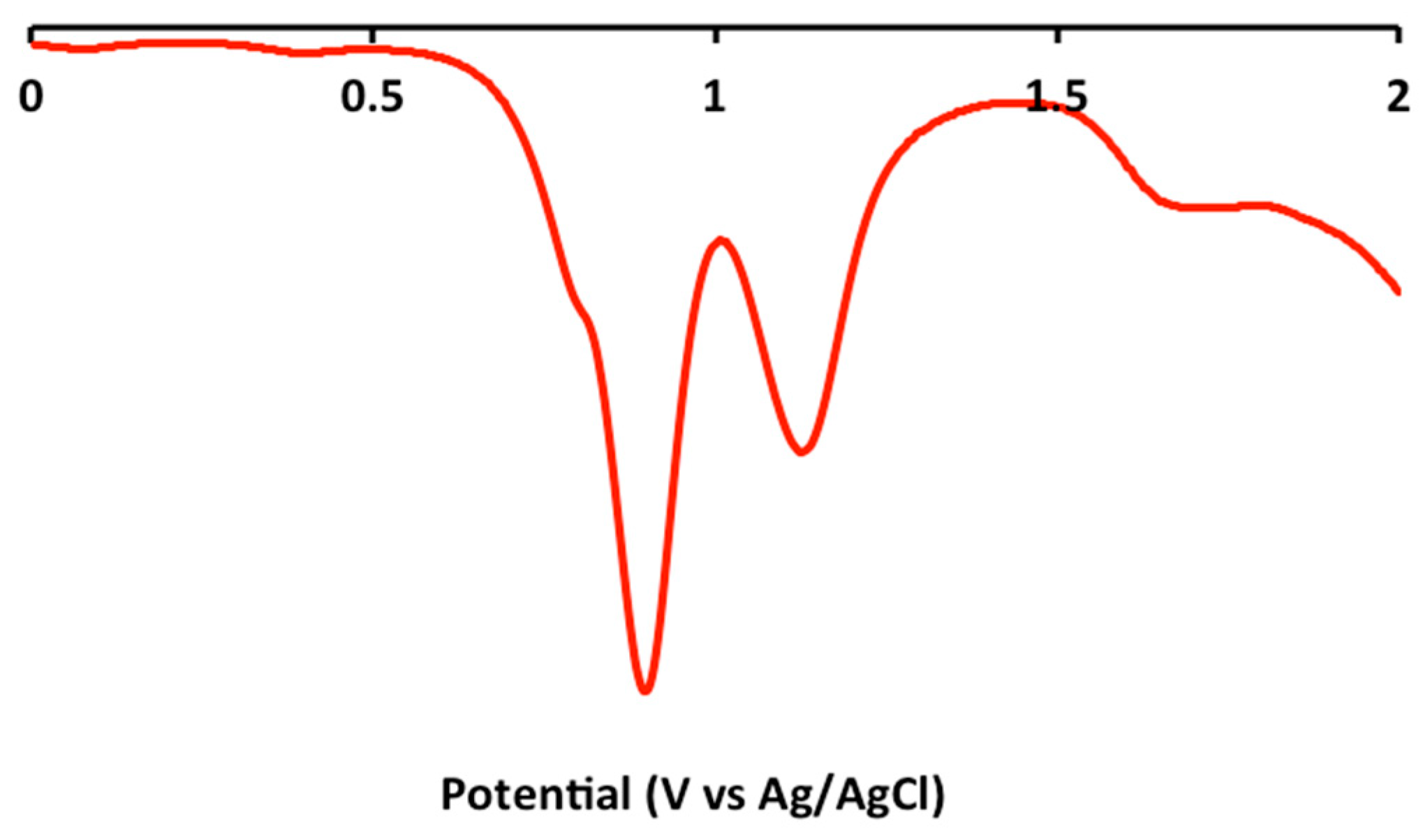
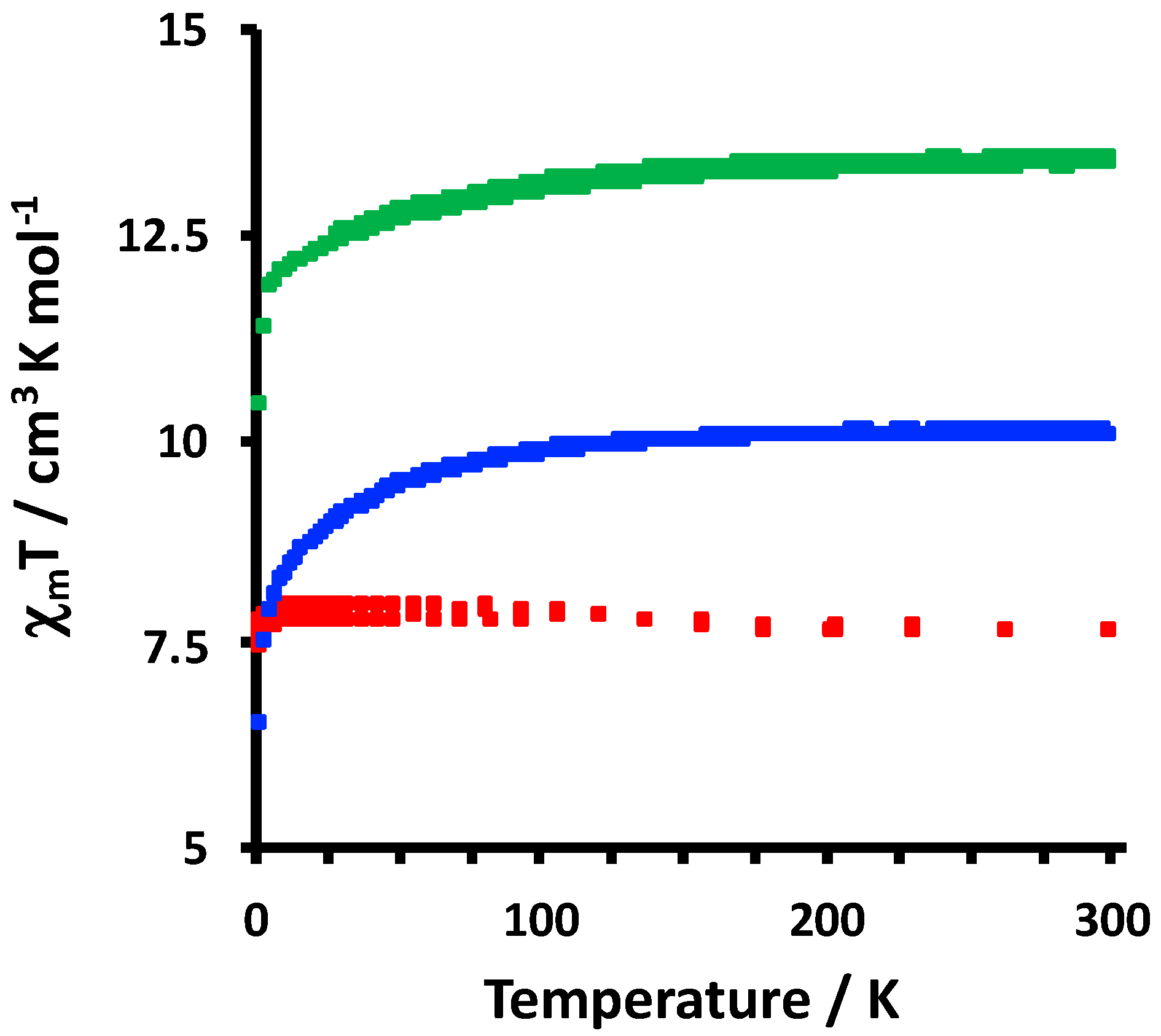
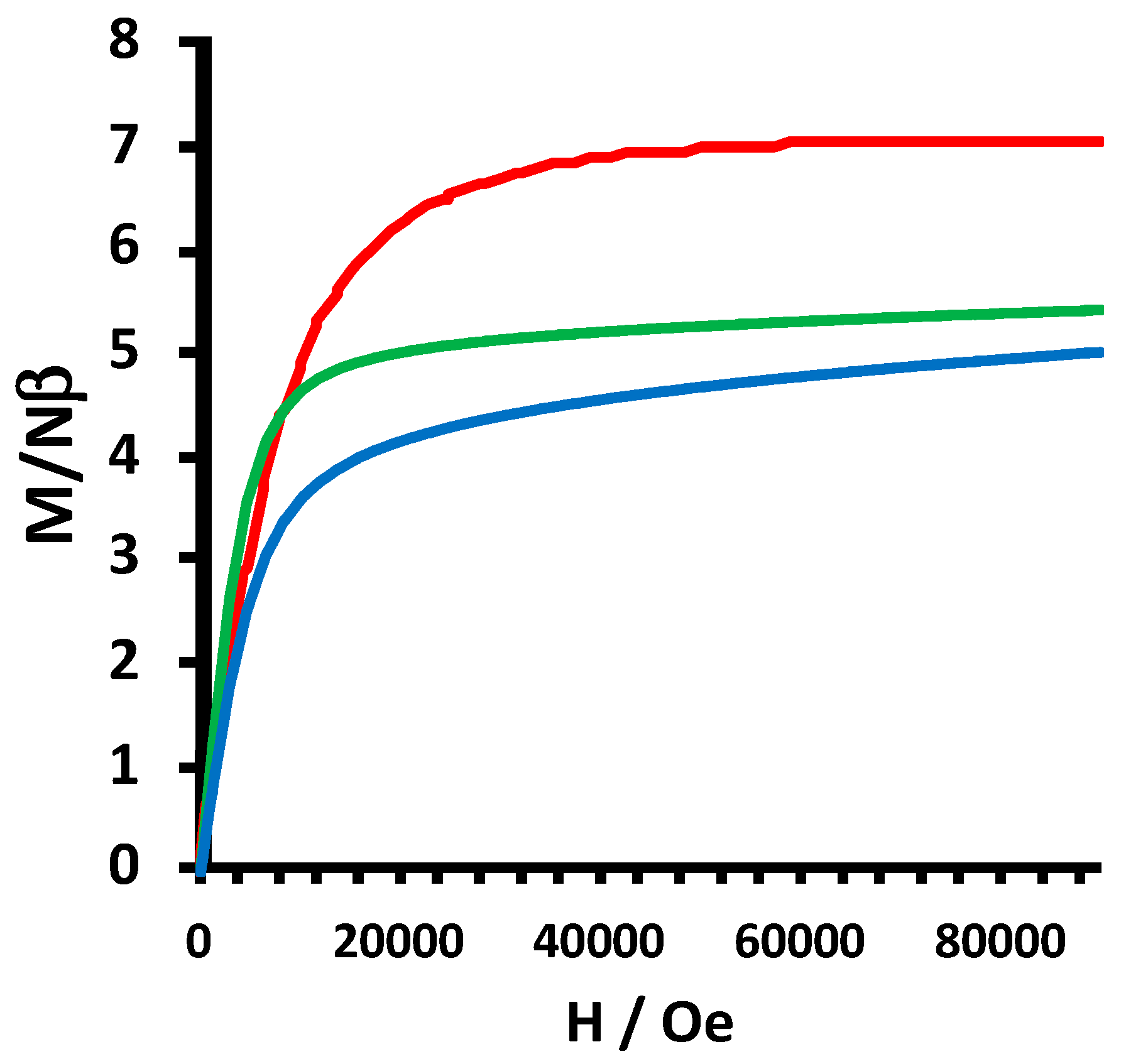
2.2. Electrochemical and Variable Temperature Magnetic Susceptibility Data
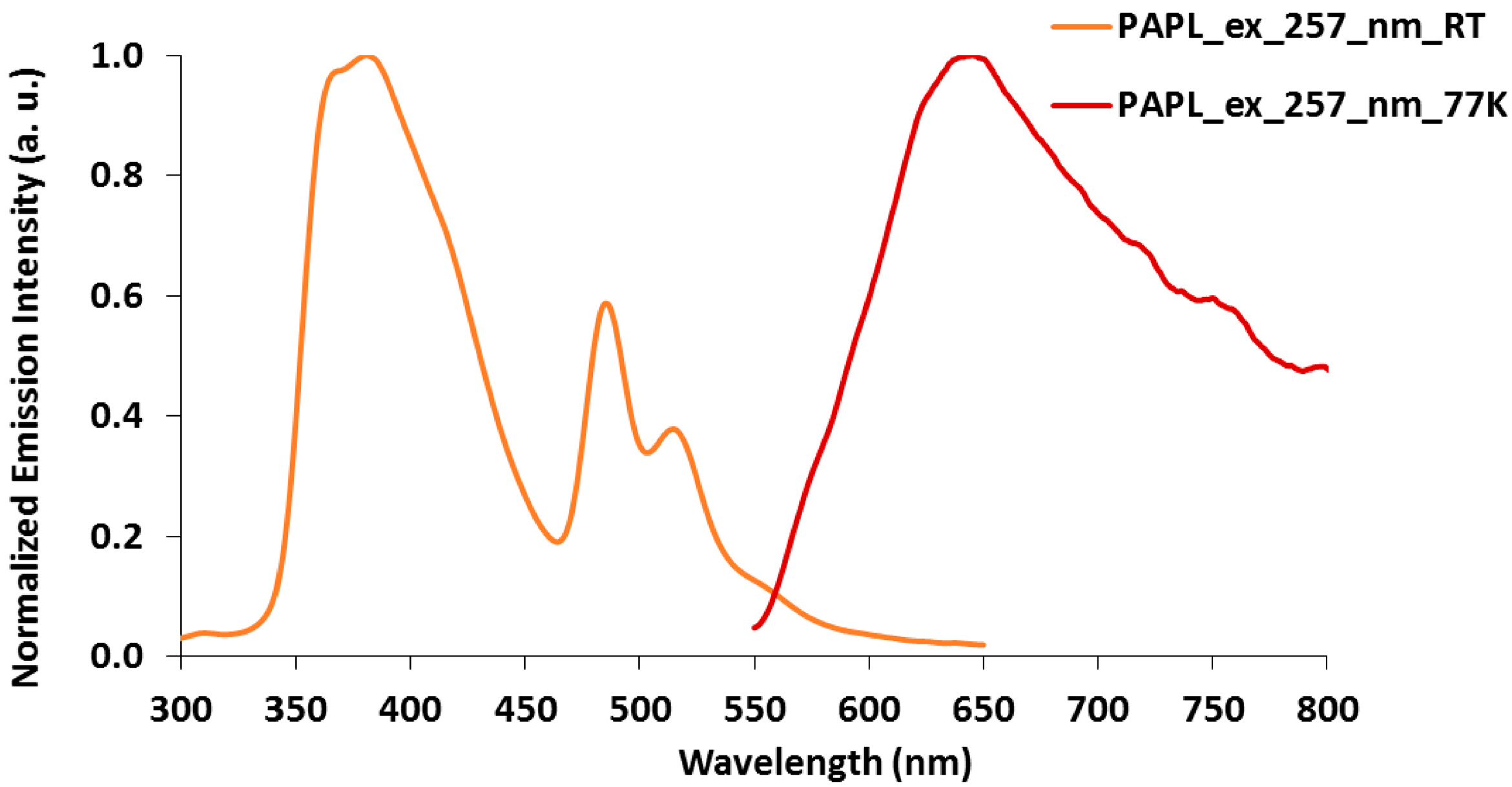
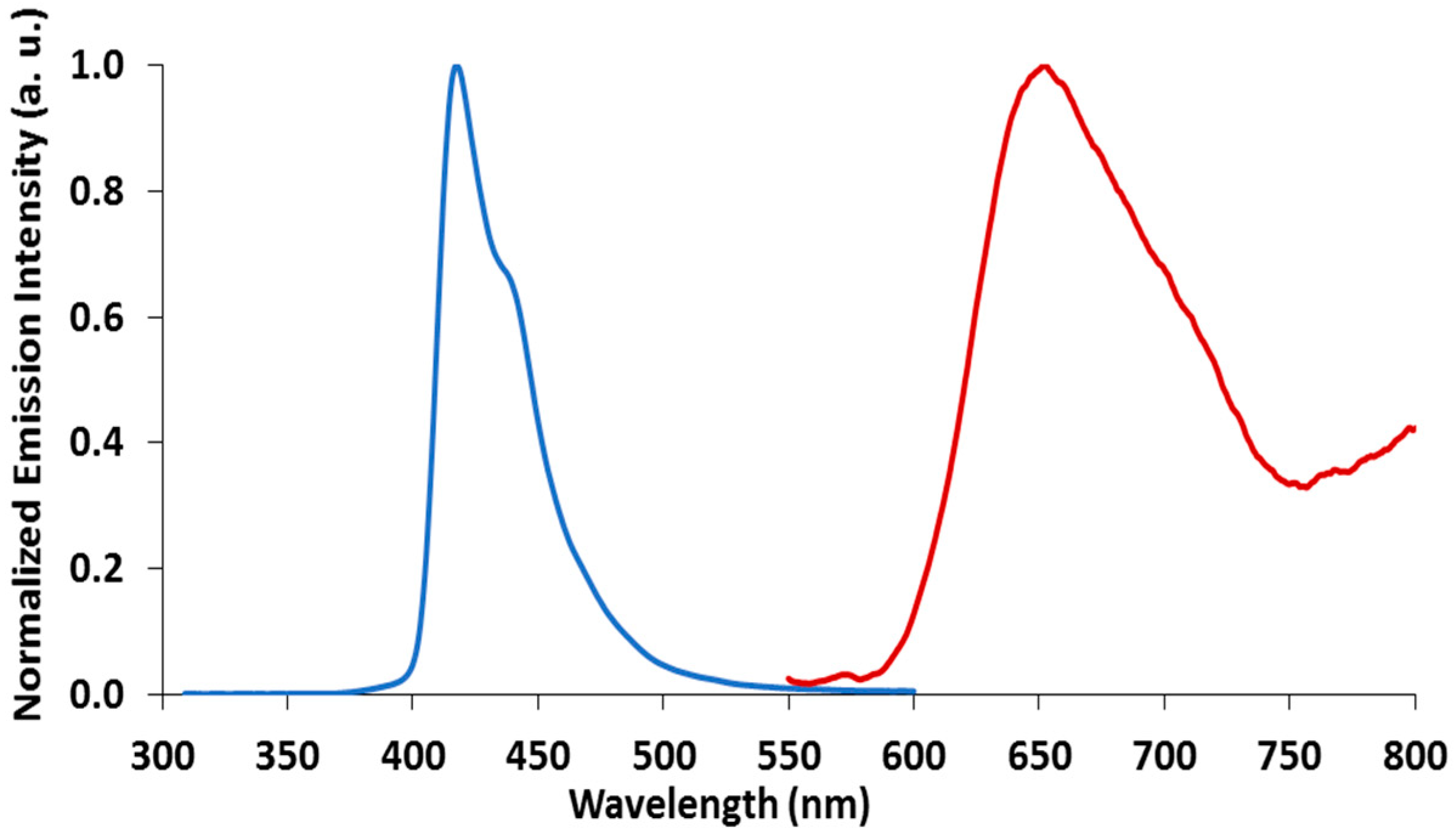
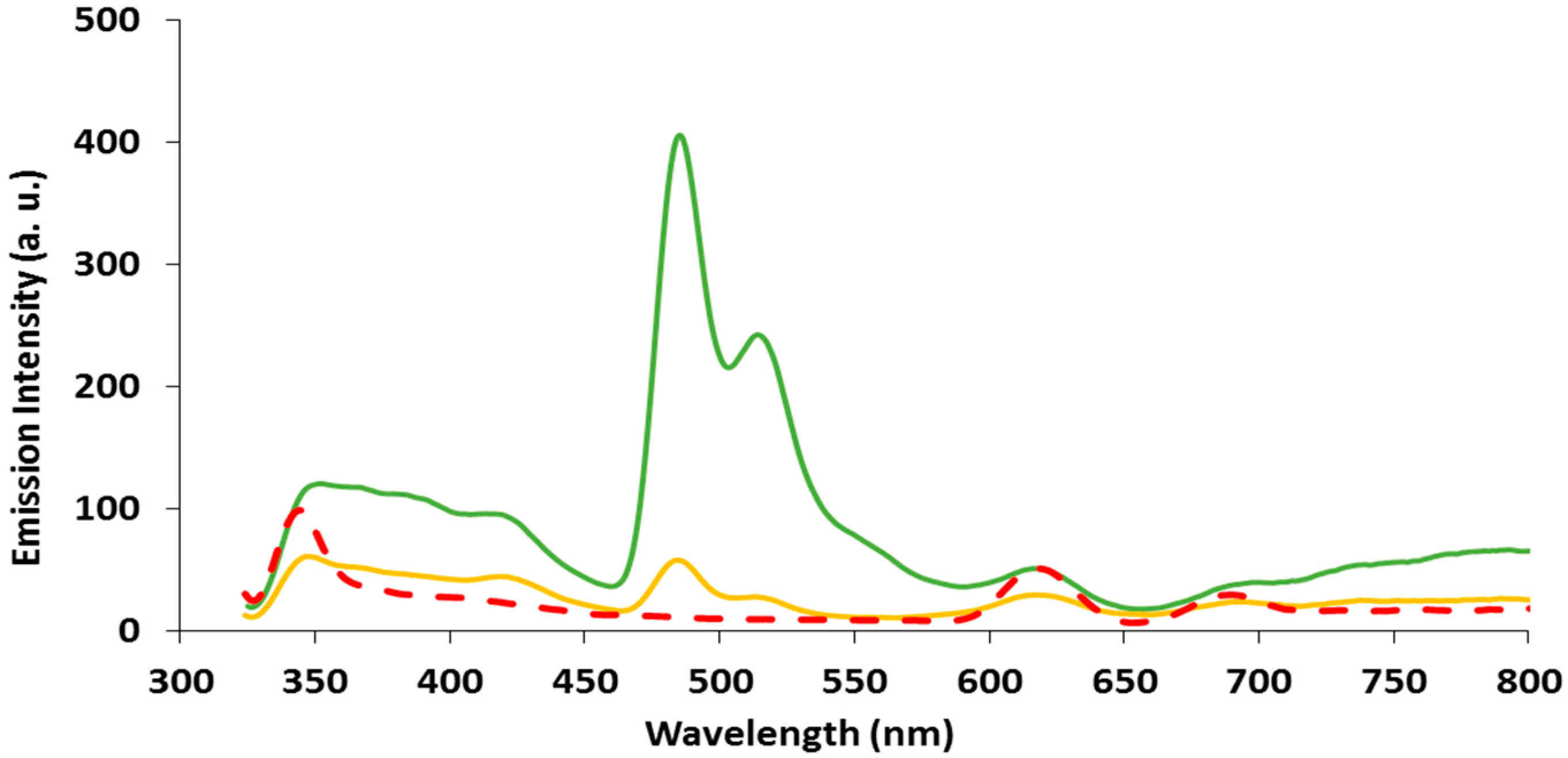
2.3. Emission Spectroscopy of papl and 1–3
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Electrochemical Measurements
3.3. DC Variable Temperature Magnetic Susceptibility Measurements
3.4. Preparation of Complexes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bottrill, M.; Kwok, L.; Long, N.J. Lanthanides in magnetic resonance imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, P.; Kuprov, I.; Parker, D. Lanthanide complexes as paramagnetic probes for 19F magnetic resonance. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitovich, P.B.; Burns, P.J.; McKay, A.M.; Morrow, J.R. Redox-activated MRI contrast agents based on lanthanide and transition metal ions. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 133, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Qu, Z.B.; Han, C.M.; Lu, L.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhou, T.; Shi, G. Time-resolved probes and oxidase-based biosensors using terbium(III)-guanosine monophosphate-mercury(II) coordination polymer nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12855–12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bünzli, J.-C.G. Lanthanide Luminescence for Biomedical Analyses and Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2729–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, D.N.; Winpenny, R.E.P.; Layfield, R.A. Lanthanide single-molecule magnets. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 5110–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorace, L.; Benelli, C.; Gatteschi, D. Lanthanides in molecular magnetism: Old tools in a new field. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3092–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinehart, J.; Long, J. Exploiting single-ion anisotropy in the design of f-element single-molecule magnets. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 2078–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Ghosh, P.; Goswami, S. Recent advances on the chemistry of transition metal complexes of 2-(arylazo)pyridines and its arylamino derivatives. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 2213–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiswell, B.; Lions, F.; Tomlinson, M.L. Tridentate Chelate Compounds. IV. Metal Complexes from a-Diketone Mono-a-pyridylhydrazone Type Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 1961, 611, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, N.; Lough, A.J.; Gorelsky, S.I.; Lemaire, M.T. Molecular and electronic structures of complexes containing 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-phenanthrol (PAPL): Revisiting a redox-active ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 13021–13028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.A.; Lough, A.J.; Lemaire, M.T. Spin-crossover in a homoleptic cobalt(II) complex containing a redox-active NNO ligand. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Kawamukai, K.; Okai, M.; Mochida, T.; Sakurai, T.; Ohta, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Einaga, Y.; Shiota, Y.; Yoshizawa, K. A New Family of Anionic FeIII Spin Crossover Complexes Featuring a Weak-Field N2O4 Coordination Octahedron. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreiadis, E.S.; Imbert, D.; Pécaut, J.; Demadrille, R.; Mazzanti, M. Self-assembly of highly luminescent lanthanide complexes promoted by pyridine-tetrazolate ligands. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.A.; Bonanno, N.M.; Mirza, D.; Lough, A.J.; Lemaire, M.T. A trivalent cobalt complex with the new redox-active ligand 10-(8-quinolylazo)-9-phenanthrol (qapl). Polyhedron 2017, 131, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, N.M.; van Damme, N.; Lough, A.J.; Lemaire, M.T. Transition metal complexes containing a ditopic redox active ligand featuring very intense visible absorption bands. Dyes Pigment. 2015, 123, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L.; Xu, Y.H.; Jin, X.X.; Xiao, S.; Yi, H.B.; Yan, J. Synthesis and characterization of luminescent zinc complexes containing redox-active 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-acenaphthequinol ligands with nonlinear optical property. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2016, 64, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Kong, X.; Sheng, C.; Wang, R.; Peyghambarian, N.; Norwood, R.A.; Zheng, Z. A dinuclear europium(III) complex with thenoyltrifluoroacetonato and 1-(2-pyridylzao)-2-naphtholato ligands and its optical properties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2011, 370, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.D.S.; Descalzo, R.R.; Gonçalves, P.F.B.; Benvenutti, E.V.; Rodembusch, F.S. Evidence for excited state intramolecular charge transfer in benzazole-based pseudo-stilbenes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 10994–11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuvaev, S.; Utochnikova, V.; Marciniak, Ł.; Freidzon, A.; Sinev, I.; Van Deun, R.; Freire, R.O.; Zubavichus, Y.; Grünert, W.; Kuzmina, N. Lanthanide complexes with aromatic o-phosphorylated ligands: Synthesis, structure elucidation and photophysical properties. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 3121–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bünzli, J.-C.G.; Piguet, C. Taking advantage of luminescent lanthanide ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 1048–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.U.; Slanina, T.; Heckel, A.; König, B. Lanthanide Ions Coupled with Photoinduced Electron Transfer Generate Strong Reduction Potentials from Visible Light. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 7900–7904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pointillart, F.; le Guennic, B.; Cador, O.; Maury, O.; Ouahab, L. Lanthanide Ion and Tetrathiafulvalene-Based Ligand as a “magic” Couple toward Luminescence, Single Molecule Magnets, and Magnetostructural Correlations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2834–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
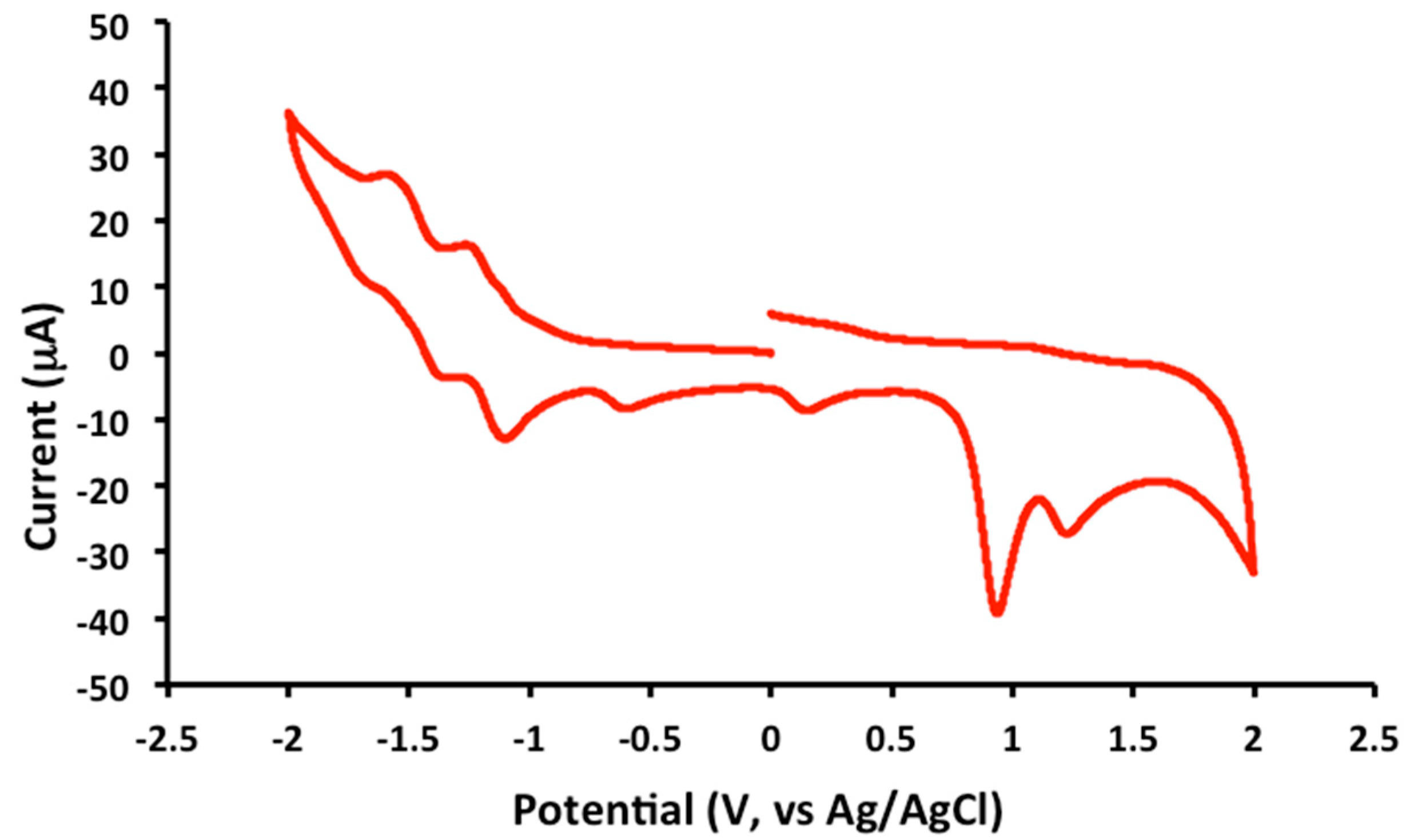
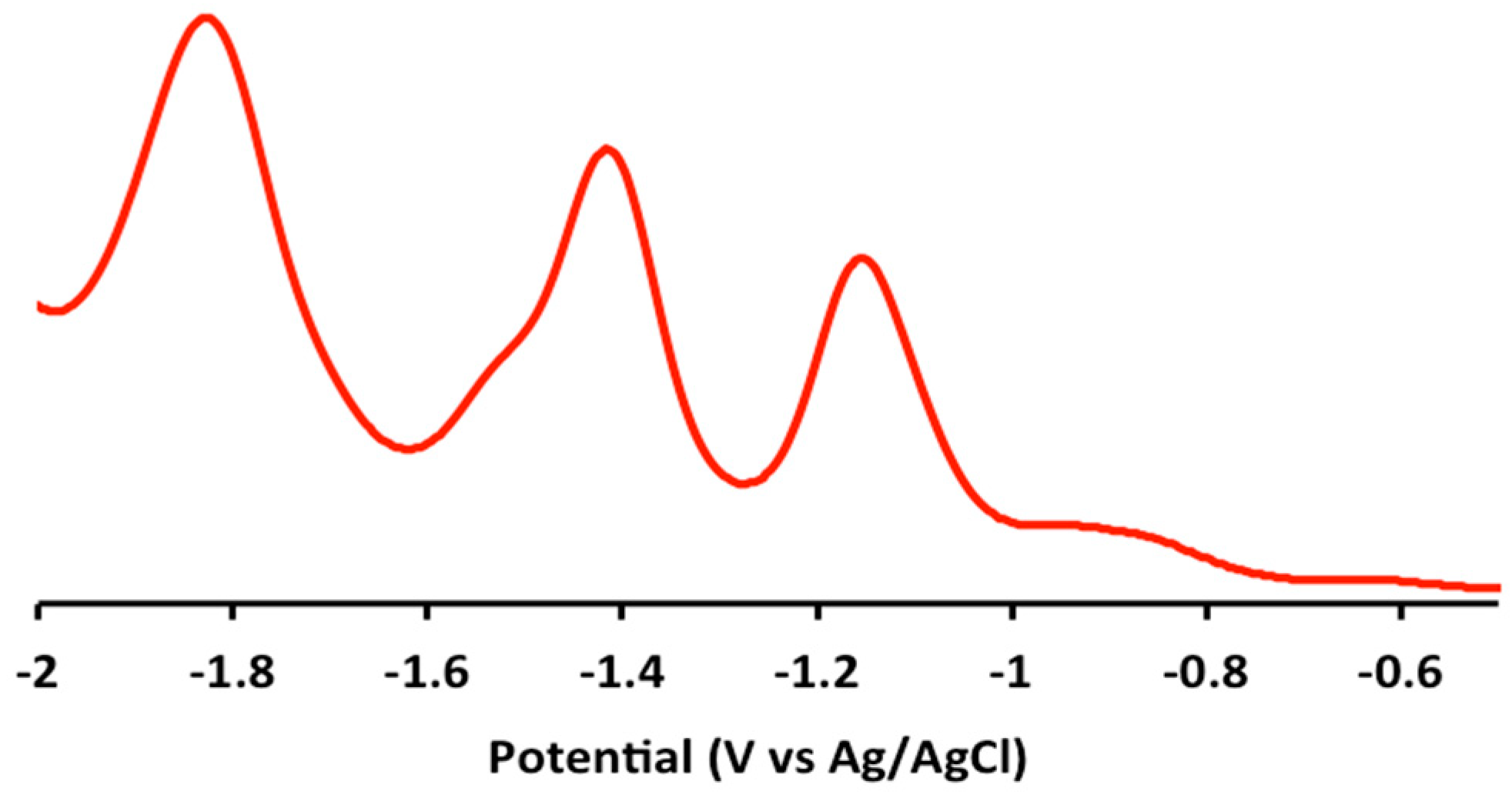
| Compound | E1/2 (Anodic) | E1/2 (Cathodic) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.2 (irr), 0.9 (irr) | −1.2 (qr), −1.5 (qr), −1.8 (irr) |
| 2 | 1.2 (irr), 0.9 (irr) | −1.2 (qr), −1.4 (qr) |
| 3 | 1.2 (irr), 1.0 (irr) | −1.2 (qr), −1.5 (qr), −1.9 (irr) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taylor, R.A.; Bonanno, N.M.; Cibian, M.; Yadav, J.; Silverstein, H.J.; Wiebe, C.R.; Mauws, C.; Lough, A.J.; Lemaire, M.T. Homoleptic Lanthanide Complexes Containing a Redox-Active Ligand and the Investigation of Their Electronic and Photophysical Properties. Inorganics 2018, 6, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020056
Taylor RA, Bonanno NM, Cibian M, Yadav J, Silverstein HJ, Wiebe CR, Mauws C, Lough AJ, Lemaire MT. Homoleptic Lanthanide Complexes Containing a Redox-Active Ligand and the Investigation of Their Electronic and Photophysical Properties. Inorganics. 2018; 6(2):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020056
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaylor, Robin A., Nico M. Bonanno, Mihaela Cibian, Jeetkia Yadav, Harlyn J. Silverstein, Christopher R. Wiebe, Cole Mauws, Alan J. Lough, and Martin T. Lemaire. 2018. "Homoleptic Lanthanide Complexes Containing a Redox-Active Ligand and the Investigation of Their Electronic and Photophysical Properties" Inorganics 6, no. 2: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020056
APA StyleTaylor, R. A., Bonanno, N. M., Cibian, M., Yadav, J., Silverstein, H. J., Wiebe, C. R., Mauws, C., Lough, A. J., & Lemaire, M. T. (2018). Homoleptic Lanthanide Complexes Containing a Redox-Active Ligand and the Investigation of Their Electronic and Photophysical Properties. Inorganics, 6(2), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020056






