Abstract
The hydrogen sorption and electrochemical properties of the alloy Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 synthesized by ball milling under the protected atmosphere of argon for 50 h in a planetary ball mill are investigated. The significantly fast rate of absorption reaction is observed along with the hydrogen absorption capacity of 2.04 wt.% H2 at temperatures 200 and 300 °C and at a pressure of 1 MPa. Even at room temperature, the absorption capacity is relatively high, and it is about 1.6 wt.% H2. The alloy ball milled for 50 h and the alloy after cycling and hydrogenation were characterized by X-ray diffraction analyses, SEM, and TEM. The prepared alloy was tested as an anode in a Ni/MH battery in a 6 M KOH electrolyte. Galvanostatic and potentiostatic discharge modes were employed, revealing activation after the third cycle and giving a discharge capacity of 257 mAh/g.
1. Introduction
Hydrogen is an important and efficient future energy carrier, but its application remains challenging due to the safety issues related to its storage. Metal hydrides and especially Mg-based hydrides are good alternatives for solid-state hydrogen storage, because they provide reversibility, increased safety, and high volumetric densities and have an affordable price [1,2,3,4,5]. They can be used in various stationary and mobile applications, such as tanks for solid hydrogen storage, heat storage systems, fuel cells, and batteries. One advancing and powerful way of optimizing hydrogen storage alloys is the innovative method of machine learning [6]. However, as the authors in this study admitted, more efforts are necessary to achieve better predictive accuracy of the models. Preparing Mg-based alloys with other metals that are capable of storing hydrogen and also have high catalytic activity or better anti-corrosion resistance is an approach to improve their performance as hydrogen storage media and as anodes in Ni-MH batteries [2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Among the many hydrogen storage alloys that can be used as anodes in Ni-MH batteries, MgNi amorphous alloys prepared by ball milling are very promising because of their low cost and high hydrogen storage capacity. The main drawback of these alloys is the degradation rate of the electrochemical capacity, which inhibits their application. In some published results, it is shown that the most effective method to improve the cycling life and the capacity retention is partial substitution with various metals such as Al, Ni, V, Y, Ti, Cr, Zr, B, Co, Cr, Ta, Pd, and Ce [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. J. Huang et al. have proved that the fast degradation of electrochemical capacity of MgNi amorphous alloys is mainly attributed to hydrogen induced crystallization [16]. Adding other alloying metals to MgNi led to less hydrogen-induced crystallization and an improved capacity retention rate. The substitution of Mg by Ti seems to have a better effect on corrosion. It was claimed that the formation of titanium oxide can hinder further oxidation of Mg, which led to an improvement in electrochemical characteristics [17]. A comparable effect has the Al substitution for Mg in Mg1-xAlxNi alloys [19]. By these substitutions, the MgNi alloys have shown improvements in their electrochemical properties, particularly in their discharge capacity and cycling stability. Another approach to improving the electrochemical properties of the MgNi alloy is by adding some compounds such as FeB [23] or CoB [24]. The effect of Gd in the Mg-Ni alloys on the microstructural and electrochemical properties was investigated by Chen W. et al. [25]. The reported maximum discharge capacities of Mg71Ni29 and Mg72.6Ni25.3Gd1.1 are 134.3 mAh/g and 91.9 mAh/g, respectively. The substitution of Ni with Gd in the Mg-Ni alloy positively impacts cycling stability and corrosion resistance but lowers the electrochemical capacity and weakens characteristic peaks of Mg2Ni and strengthens those of MgNi2.
More detailed investigations of hydrogen storage properties of nanostructured multicomponent metal Mg-based alloys regarding higher storage capacity, fast absorption/ desorption kinetics at lower pressure, and better electrochemical properties as an anode in NiMH batteries are needed. Taking into consideration the published results discussed above, we aimed at obtaining a MgNi alloy with a BCC structure where nickel is partially substituted by vanadium, iron, and aluminum. The absence of rare-earth metals reduces cost and environmental concerns, while the use of abundant Mg increases the material’s practical relevance for large-scale applications. These results distinguish our work from prior studies on Mg–Ni substitutions, as the performance features observed here are directly related to the multicomponent design. The chosen method of synthesis is by grinding under argon in a planetary mill. This is not only because of the positive effects of ball milling but also because of the low evaporation temperature of magnesium, which makes it difficult to use melting. Therefore, the corresponding alloy with composition by the formula Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 was synthesized by ball milling in a planetary mill for 50 h under argon, and its hydrogen storage properties were studied at different temperatures. The phase composition of the alloy was monitored by X- ray diffraction, SEM, and TEM analyses. The electrochemical discharge capacity and capacity retention rate in 6 M KOH electrolyte of this alloy were also tested.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. X-Ray Diffraction Analyses
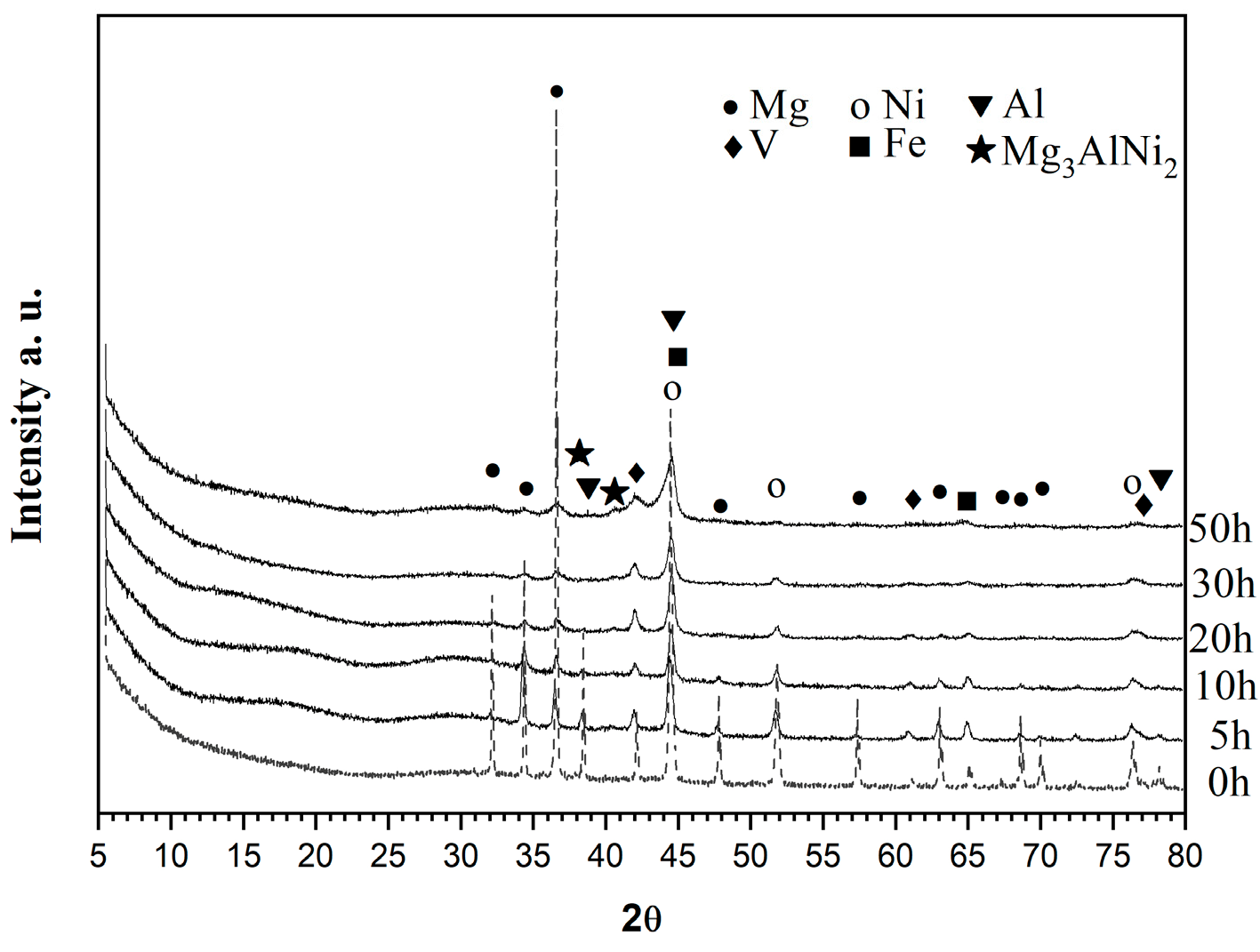
In Figure 1, X-ray diffraction patterns of the alloy are presented after 0, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 50 h of ball milling. Gradual broadening of the diffraction peaks combined with a decrease in the peaks’ intensity and also the disappearance of some of them, especially those of Mg, as well as those related to Al, V, and Fe metals, as a function of grinding time is observed. The ball-milled mixture after 50 h contains a Mg, Ni-type BCC structure and a V BCC-type structure and along with some traces of Mg3AlNi2, which is comparable to the background and starts to appear after 30 h of milling. The Mg2Ni phase is not observed even after 50 h of ball milling treatment.
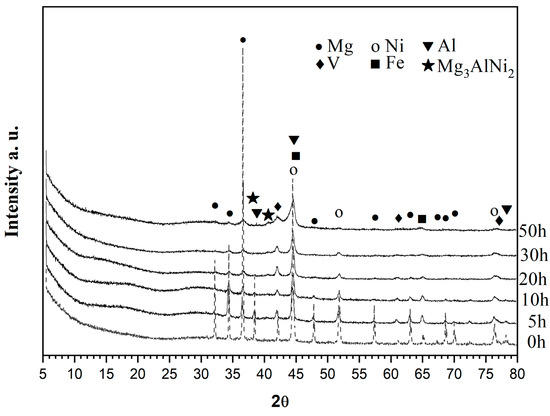
Figure 1.
XRD diffraction patterns of the Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 ball milled from bottom up 0, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 50 h under argon.
To determine the crystallite sizes of ball-milled powders, Scherrer’s formula is used. The crystallite sizes in nm after different times of ball milling are presented in Table 1. A significant decrease in the crystallite size is observed with the increase of ball milling time for all metals.

Table 1.
Crystallite size in nm calculated via Sherrer formula after different durations of ball milling.
The alloy Mg3AlNi2 can be synthesized by melting or ball milling and annealing [26,27,28] and absorbs hydrogen reversibly and faster and has better electrochemical properties than the Mg2Ni alloy electrode. A. Parente et al. [26] synthesized nanocrystalline materials MgmAlNin (m, n ≤ 3) by ball milling, made XRD Rietveld refinements in a thermodynamics study with PCT diagrams at different temperatures, and proposed a reaction for the disproportion of the Mg2AlNi2 phase with hydrogen. The resulting products are MgH2, Mg2NiH4, and Mg0.5AlNi1.5. These authors used a vibratory high energy mill Spex 8000 (SPEX samplePrep, Metuchen, NJ, USA) and the duration of their ball milling experiments was shorter and 30 h in total.
2.2. Gas Hydrogen Storage Properties
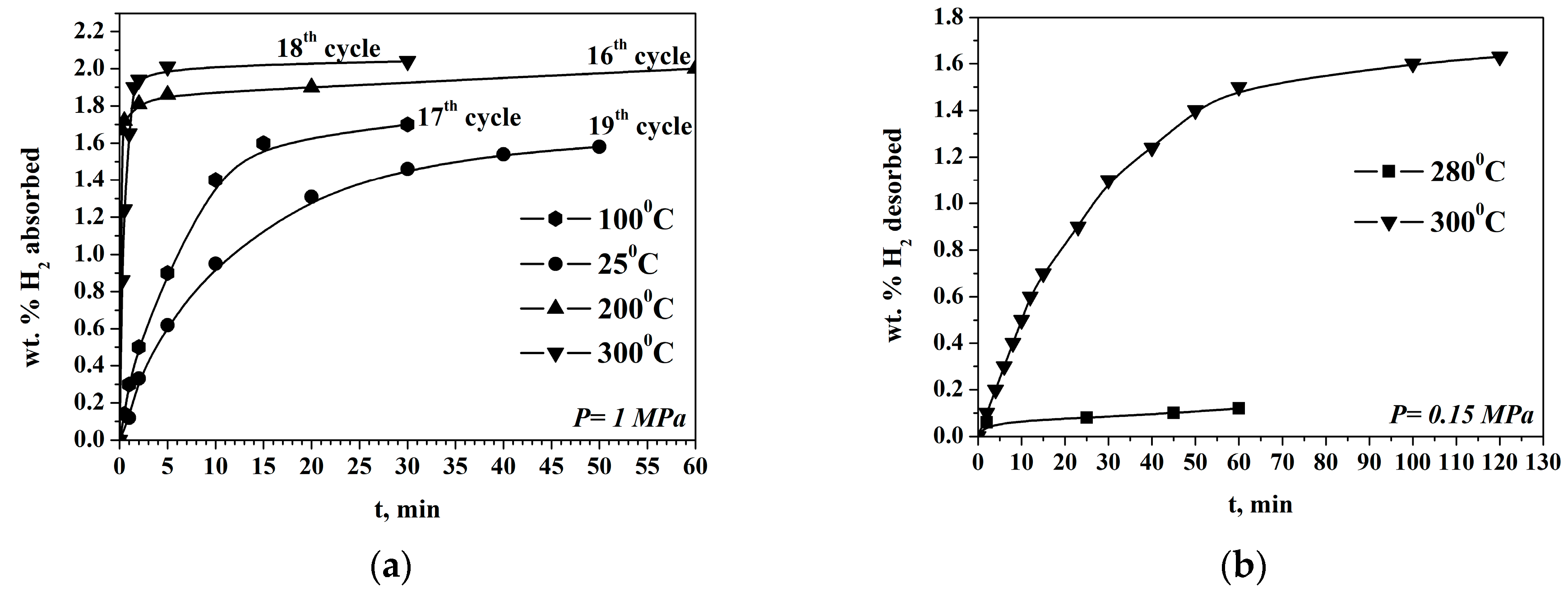
The first two cycles of hydrogenation are activation cycles during which slower kinetics and a capacity below 1 wt.% are detected. Usually, the Mg-based materials for hydrogen storage need activation, but the alloy prepared by us is activated relatively fast. The following cycles of hydrogenation/dehydrogenation showed that the Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 has a very rapid rate of absorption reaction at 200 and 300 °C with the maximum obtained hydrogen absorption capacity value of 2.04 wt.% H2. The alloy shows similar kinetics of the absorption reaction at both temperatures at the beginning of the process, but the reaction of hydrogen absorption is a bit faster at 200 °C after a very short period of up to 0.5 min. (Figure 2a). After that, with the progress of the absorption process, the rate at 200 °C is slower than at 300 °C. On the other hand, even at room temperature, the absorption capacity is quite high and around 1.6 wt.% H2. In fact, more than 90% of the maximum absorption capacity is obtained after 2 min of hydrogenation at 200 °C and 1 MPa. The alloy is subjected in total to 20 cycles of hydrogenation/ dehydrogenation at different temperatures.
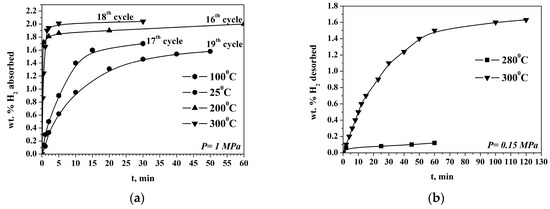
Figure 2.
Hydrogen absorption (a) and desorption (b) curves of the Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 ball milled 50 h under argon.
The obtained hydrogen absorption capacity is comparable with some published results of similar materials. The absorption capacity of Mg50Ni50 is 1.85 wt.% at 100 °C, and the composite Mg50Ni50- 25 wt.% Mg2Ni absorbs 1.47 wt.% H2 at 90 °C. The presented hydrogen absorption curves for these alloys showed faster kinetics, but at a hydrogen pressure of 2 MPa [29] and even a similar one at 3.3 MPa [30].
The desorption reaction is faster at 300 °C compared with that at 280 °C, but even after 2 h only 1.6 wt.% H2 is desorbed. Decreasing the temperature by only 20 degrees Celsius leads to even greater degradation in the desorption kinetics, and a very small amount of hydrogen is desorbed. At 260 °C and 0.15 MPa after 60 min., hydrogen desorption has not been detected (Figure 2b).
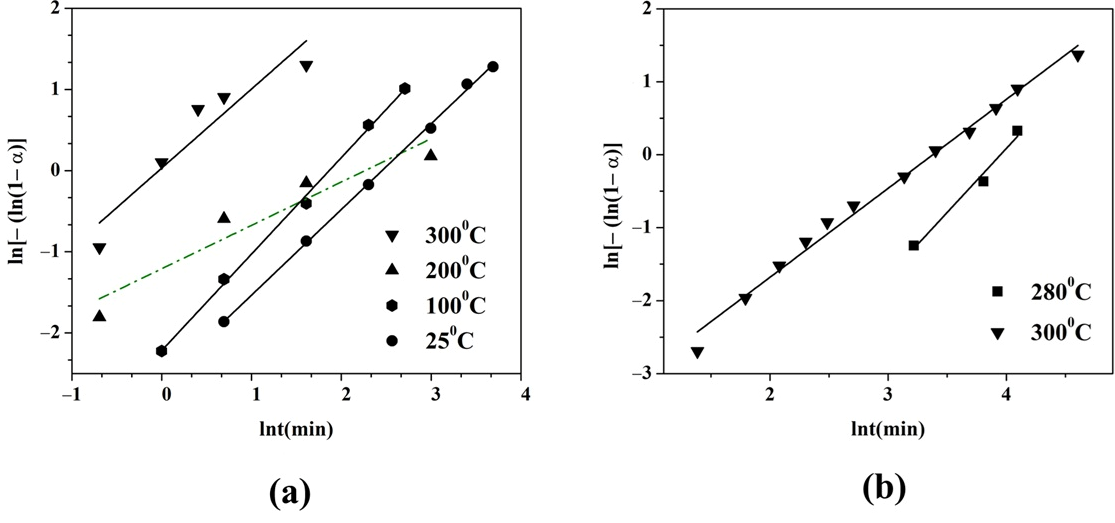
The hydrogen absorption and desorption were analyzed using the Johnson–Mehl- Avrami–Kolmogorov equation (JMAK). The constant n called the Avrami exponent reflects the constancy of the nucleation rate, the dimension of nuclei growth, and the rate controlling step. The Avrami exponent can be determined by the slope of the line described by ln[−ln(1 − α)] = lnt. The fraction of hydrogenation and dehydrogenation at a certain time α was transformed into normalized values (between 0 to 1). Figure 3a,b show the JMAK calculation results of the alloy’s hydrogen absorption and desorption at different temperatures. The R2 values of the JMAK curve fit for hydrogen absorption range from 0.87 to 0.99 and from 0.97 to 0.99 for hydrogen desorption. A good correlation of the fitting results indicates the values of R2 0.99 at 100 °C and 25 °C for hydrogen absorption. The lower value of R2 0.87 for the fits of the two faster absorption processes at higher temperatures at 300 °C and 200 °C has comparatively poor fits. The obtained values for the hydrogen absorption of the Avrami exponent n are 0.5, 0.9, 1.2, and 1 for 200°, 300°, 100°, and 25°, respectively. The fastest hydrogen absorption at the first stage of the reaction is observed at 200 °C, and n at this temperature has the lowest value indicating one dimensional diffusion-controlled growth with a decreasing nucleation rate. For the hydrogen desorption process, the values of the Avrami exponent are increased. The slower hydrogen desorption at 280 °C has a value of n 1.8, and at 300 °C the value is 1.2, indicating nucleation and a two-dimensional growth mechanism for desorption.
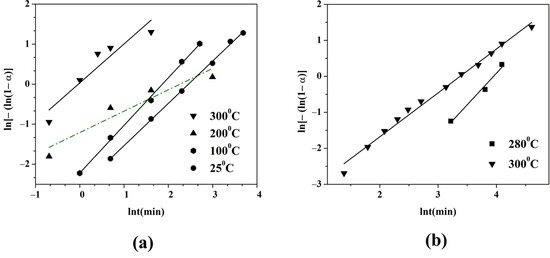
Figure 3.
JMFK fit curves of the Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5: (a) hydrogen absorption and (b) hydrogen desorption.
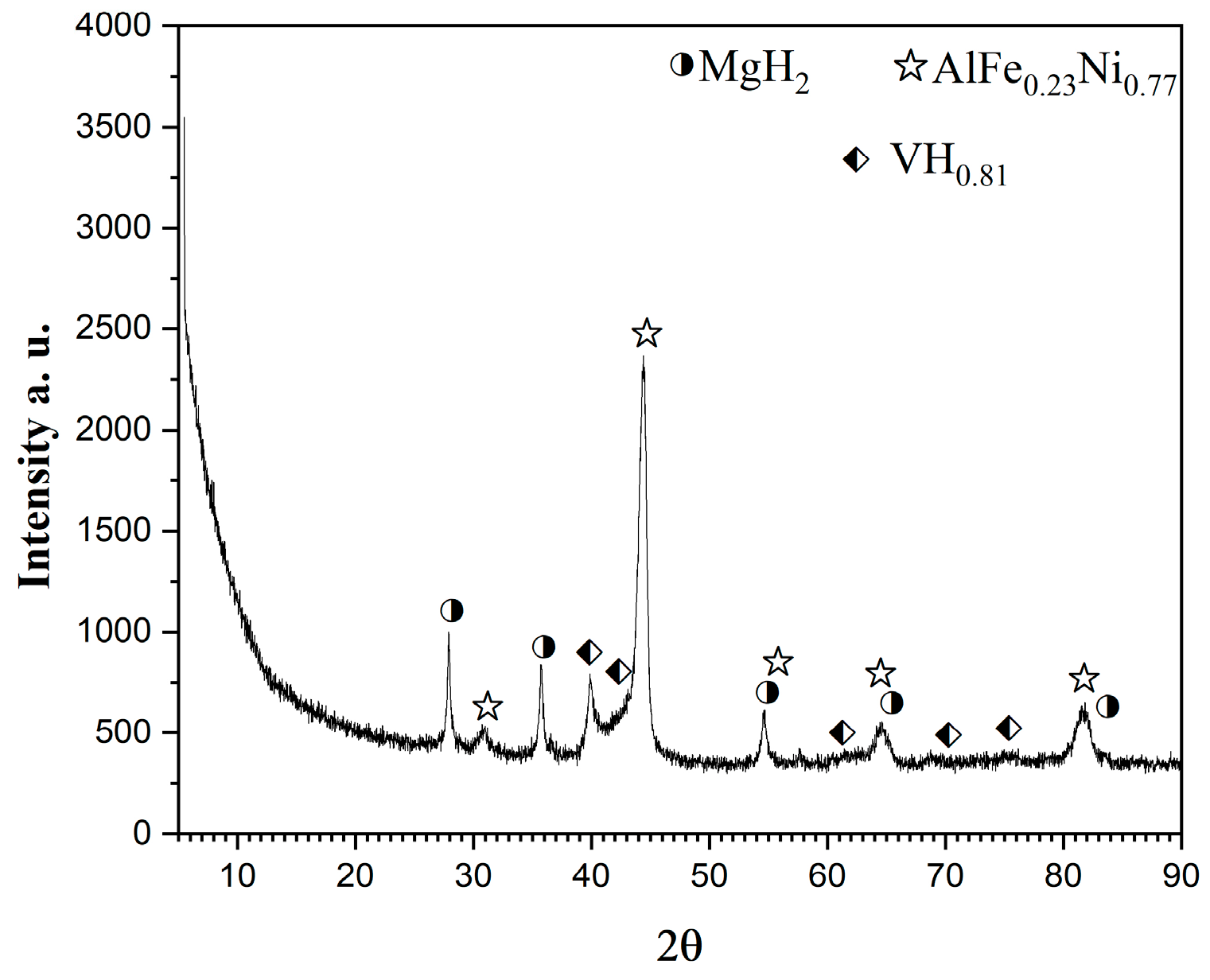
After hydrogenation at 200 °C and 1MPa for one hour, at the 20th cycle the sample is characterized by XRD and TEM. In Figure 4, the XRD diffraction patterns of the alloy after 50 h of ball milling and after hydrogenation are presented. The phase composition includes MgH2, VHx, and AlFe0.23Ni0.77 alloy. The ternary hydride Mg2NiH4 of the intermetallic Mg2Ni is not observed.
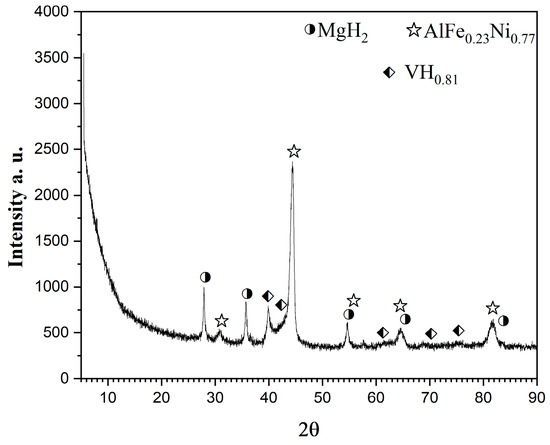
Figure 4.
XRD diffraction patterns of Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 ball milled 50 h under argon and after hydrogenation at 1 MPa and 200 °C.
Despite the good hydrogen absorption rate, the absence of Mg2Ni after milling and Mg2NiH4 after hydrogenation has a negative effect on the desorption rate and temperature of the alloy. The intermetallic Mg2Ni improves the hydrogen sorption rate and lowers the desorption temperature, so it is of critical importance for the hydrogen storage properties of the Mg-based materials. To improve the hydrogen desorption properties, future experiments will consider adding some catalysts, an excess of magnesium, and changes in the production procedure of the alloy.
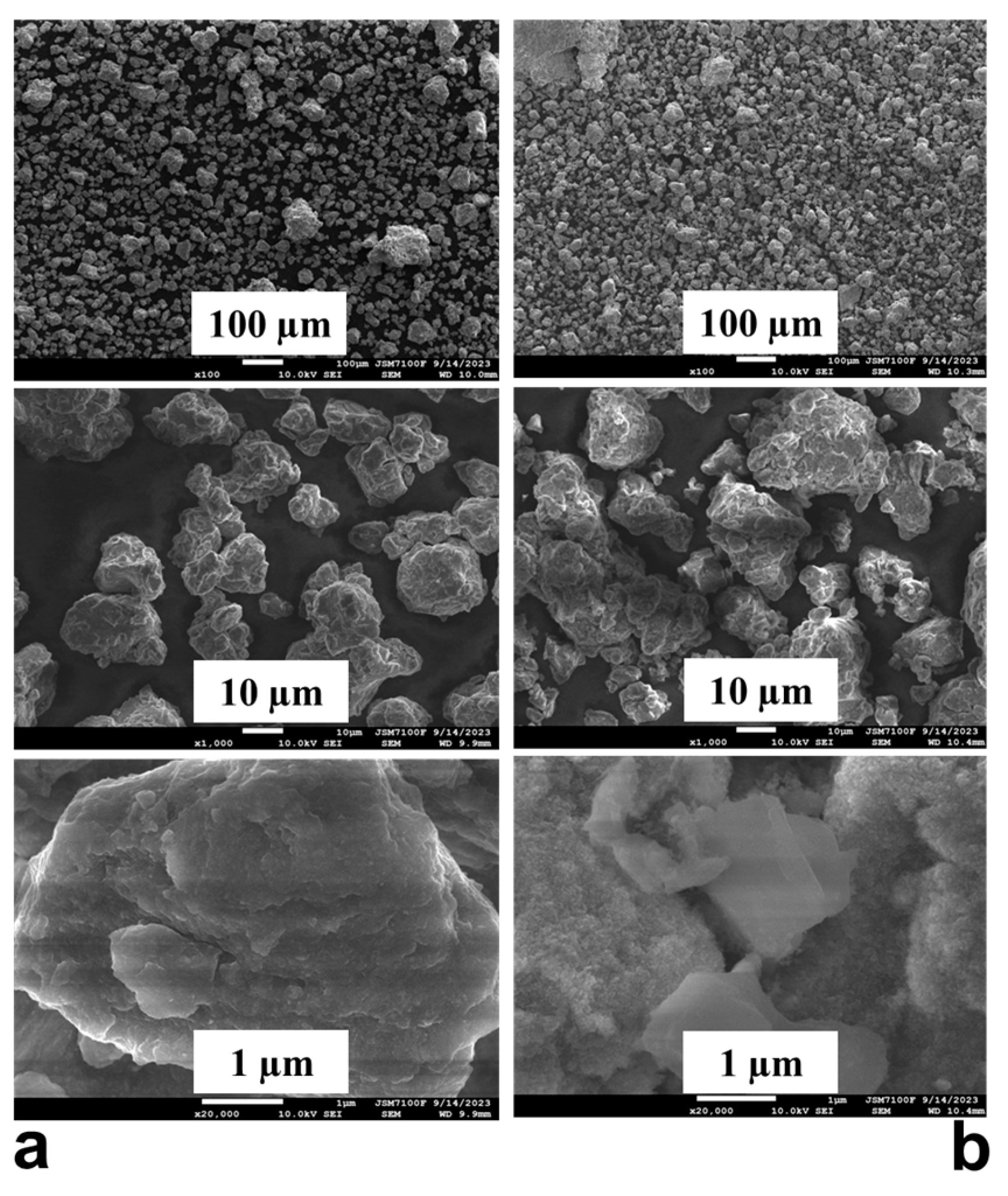
2.3. SEM and TEM Characterization of the Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 After Ball Milling and Hydrogenation
The SEM images are presented in Figure 5a,b. A higher fraction of small particles about a few micrometers in size is observed after hydrogenation. After ball milling for 50 h under argon, there are also some particles with a diameter of about 5 µm or even less than that size, but the majority of them are about 30–40 µm to 150 µm, and some agglomerates are also visible. From Figure 5, it can be concluded that the particles of the alloy ball milled for 50 h have a cracked non-smooth surface and irregular shapes. The process creates fine particles through mechanical fracturing but also causes these smaller particles to cold-weld and agglomerate into larger ones, resulting in a size distribution with both small and large particles. This mechanochemical process also generates strain and microstructural defects on the surface, but it may also promote oxidation and the formation of a magnesium oxide layer. After hydrogenation, the particles have a sponge-like surface and reduced size.
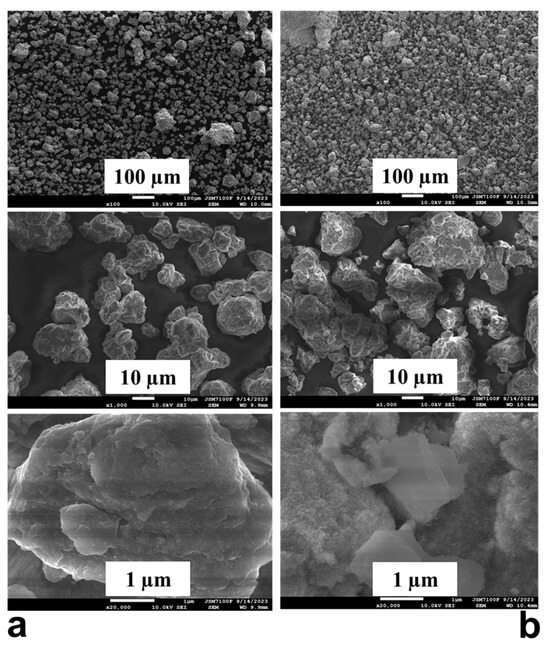

Figure 5.
SEM images of the Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5: (a) ball milled 50 h and (b) after hydrogenation at 200 °C and 1 MPa.
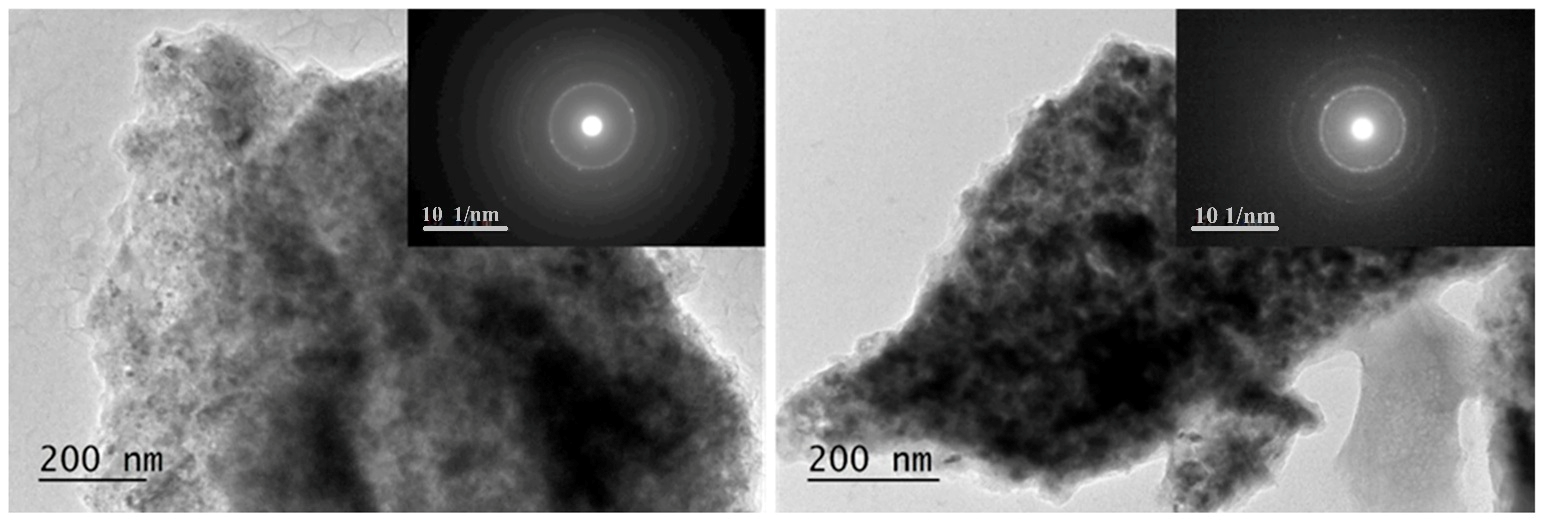
In Figure 6 and Figure 7, brightfield micrographs, SAED, and HRTEM for 50 h ball-milled powder under argon and after hydrogenation at 200 °C and 1 MPa are presented. TEM analyses confirm nanosized microstructures of both samples after milling and hydrogenation as well as the phase composition detected by X-ray diffraction analyses.
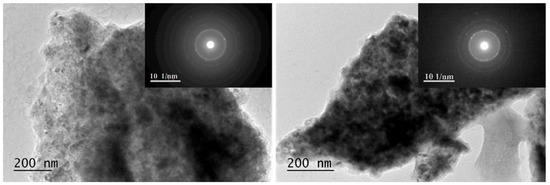
Figure 6.
Brightfield micrographs and SAED are presented for Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 left— ball- milled for 50 h and right—after hydrogenation at 200 °C and 1 MPa.
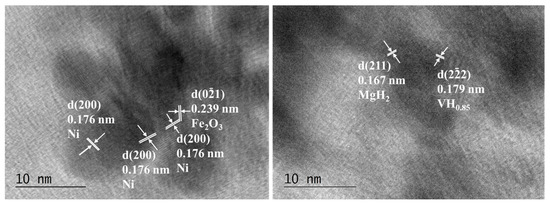
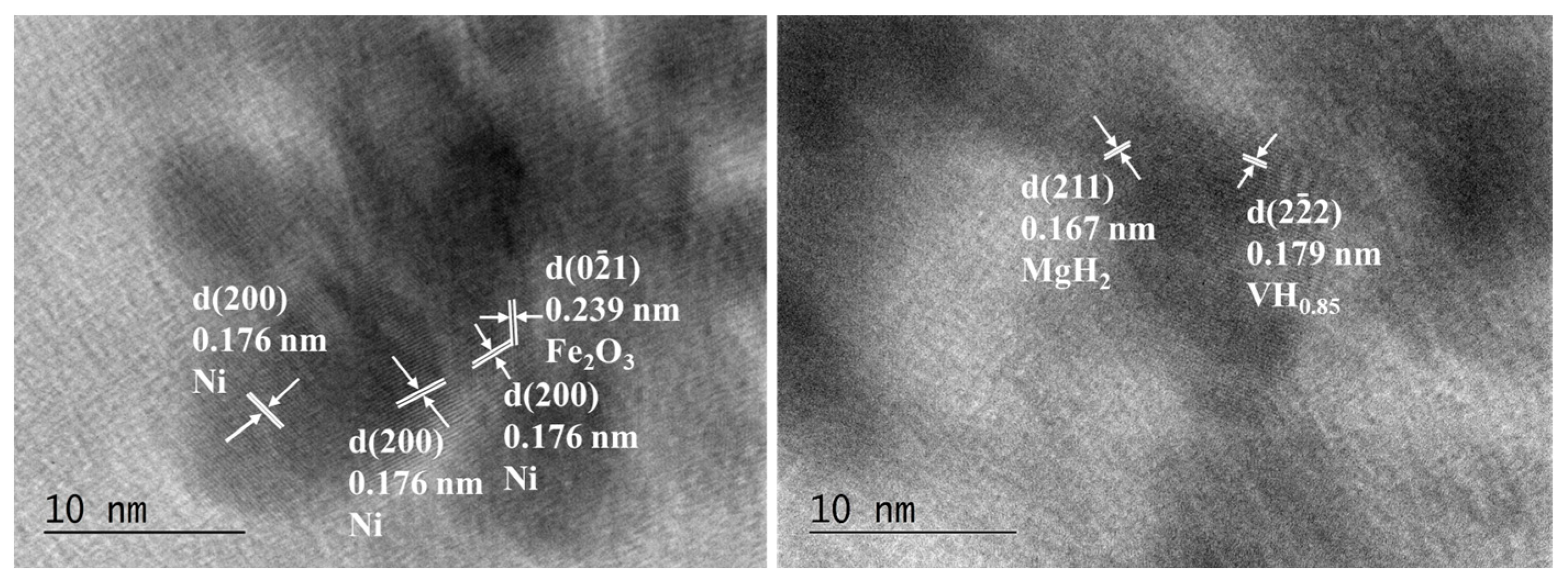
Figure 7.
HTREM images of Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 after 50 h ball milling on the left and after hydrogenation at 200 °C and 1 MPa on the right.
The particles have an irregular shape and are overlapping. Some nanocrystalline areas are observed (Figure 6). The SAED patterns after 50 h of ball milling in Figure 6 are associated with the metals Mg, Ni, Fe, Al, and V. All patterns observed after hydrogenation by SAED in Figure 6 on the right belong to MgH2. In the HTREM image for the 50 h ball-milled sample, the interplanar distance of the lattice fringes of 0.176 nm belongs to the (200) planes of Ni. Another lattice fringe is that of Fe2O3 d (021) = 0.179 nm (Figure 7 left). The right HTREM image in Figure 7 is for the alloy after hydrogenation, and the lattice fringes of 0.167 nm belong to (211) of MgH2 and d (222) = 0.179 nm of VHx. In other obtained SAED results for the alloy after hydrogenation, the patterns of AlFe0.23Ni0.77 alloy and MgO are also observed.
Some oxidized areas, e.g., MgO and Fe2O3 phases, are detected by TEM in both powders after 50 h of ball milling and hydrogenation, but this could be explained by the copper grid preparation and transfer into the TEM holder when the samples are exposed briefly to air. The phase Mg3AlNi2 is not observed by TEM characterization probably because of its low amount and the locality of this method, and after hydrogenation, if the disproportionation reaction occurs as proposed by A. Parente et al. [26], it would be difficult to detect such traces of the phases.
2.4. Electrochemical Properties and Cycle Stability
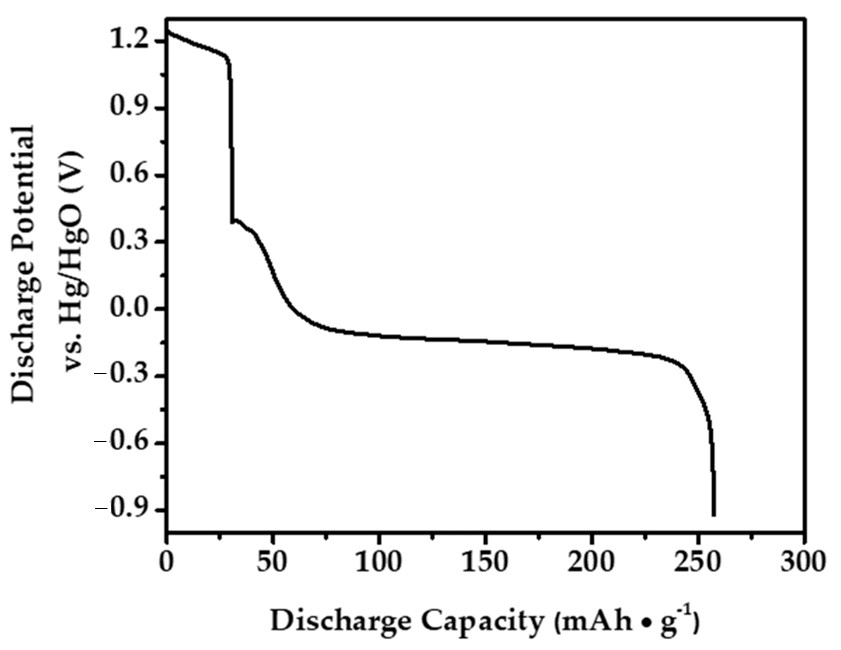
In this study, to optimize the performance of the anode material that we prepared for Ni-MH batteries, determine a safe charge–discharge range, and ensure its stability during this process, an extensive literature review was conducted initially to understand the electrochemical behavior of similar materials [31,32,33,34,35]. The primary aim of this literature review was to identify the potential ranges based on the data obtained to prevent damage to the alloy electrode during overcharging or discharging. Subsequently, the electrochemical stability limits of our alloy electrode were determined at a cutoff potential of −0.9 V using techniques such as Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) through these comprehensive approaches. These methods enable the identification of potential ranges where stable electrochemical reactions occur without triggering undesirable side reactions or electrode degradation. To evaluate the electrochemical characteristics of the Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 alloy electrode synthesized through a 50 h ball milling process, galvanostatic and potentiostatic discharge modes were employed. The galvanostatic discharge curve, presented in Figure 8, shows the electrode’s performance when charged at a 1C rate and discharged at a 0.2 C rate, resulting in a maximum discharge capacity of 257 mAh/g.
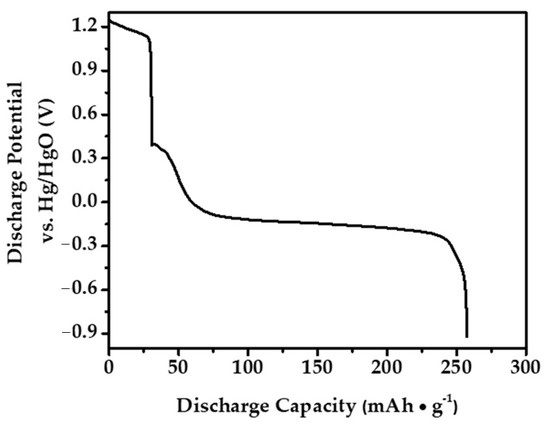
Figure 8.
The maximum discharge capacity of the Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 alloy electrode at the 4th cycle.
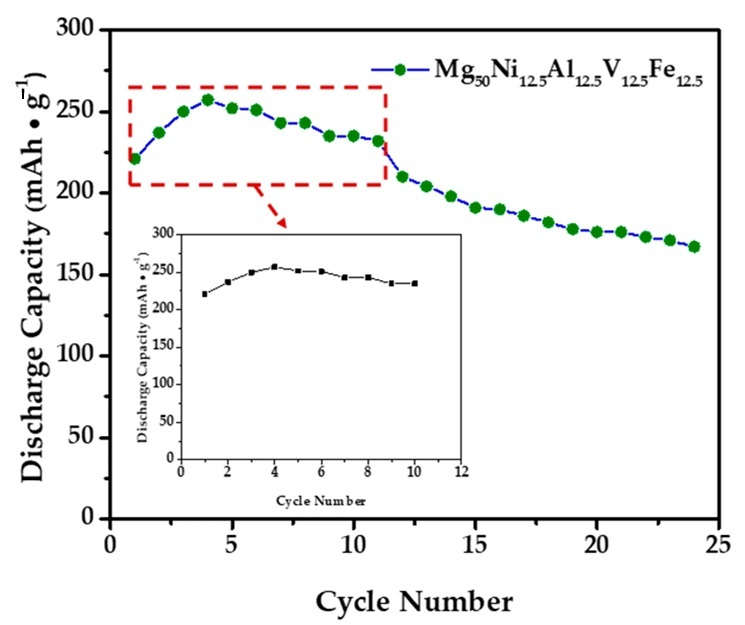
Electrochemical cycling tests were performed on three independently prepared electrodes to ensure reproducibility. The maximum discharge capacities obtained for the first cycle were 257.0, 256.5, and 255.5 mAh g−1, respectively. These values are in close agreement, giving an average of 256.3 ± 0.8 mAh g−1 (SD, n = 3) with a maximum deviation of only 1.5 mAh g−1. This narrow variation confirms the high reproducibility of the electrochemical performance. Accordingly, the capacities presented in Figure 9 and Figure 10 represent the mean values of three electrodes, and the corresponding error bars indicate ± standard deviation.
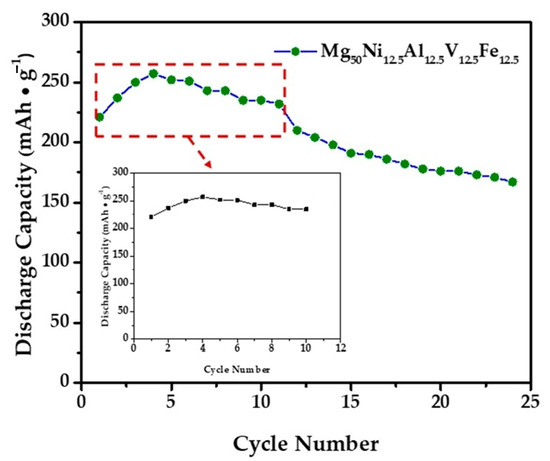
Figure 9.
The maximum discharge capacity Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 alloy electrode at the 4th cycle. The dashed red box marks the activation region (cycles 1–4).
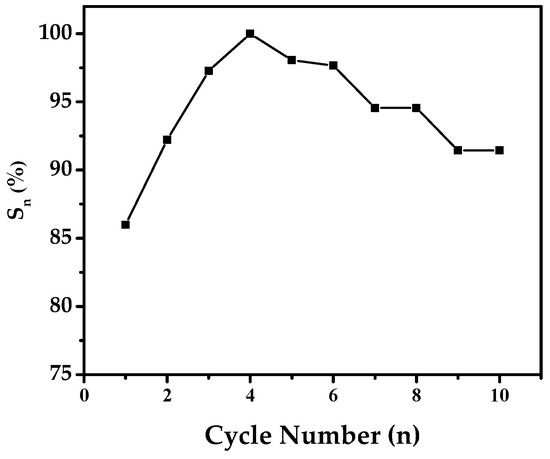
Figure 10.
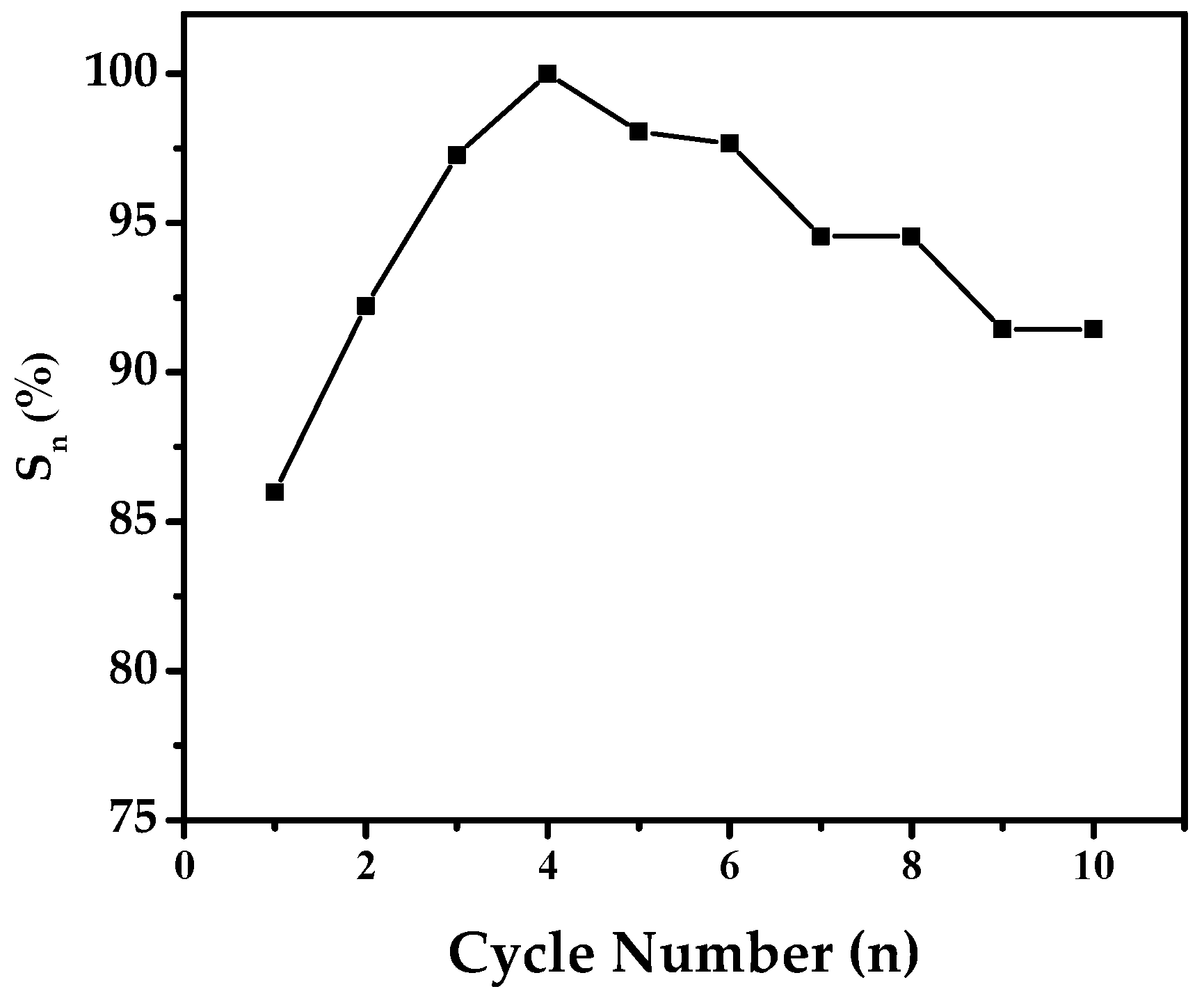
Capacity retention rate (Sn) and cycle number (n) of Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 after 50 h of ball milling.
The alloy electrode can become fully activated after the 3rd cycle, as shown in Figure 9. The variations in the discharge capacities of Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 alloys with the cycle number are illustrated in Figure 9, indicating that the alloy can attain its maximum discharge capacities at the fourth cycle. The reason for such easy activation of this multicomponent system can be attributed to the formation of phase boundaries, which are essential diffusion tunnels for hydrogen atoms [36]. Therefore, the easy attainment of the maximum capacity after the third cycle can be attributed to the beneficial effects of these multicomponent and multiphase structures.
The electrochemical test results for the Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 alloy electrode’s 24-cycle performance show that the alloy achieved a maximum discharge capacity of 257 mAh/g at the fourth cycle. As can be seen in Figure 9, at the 10th cycle, the alloy electrode provided a maximum discharge capacity of 235 mAh/g, and at the end of the 24th cycle, the discharge capacity of our alloy electrode is 167 mAh/g. This value corresponds to an approximate capacity retention rate of 65%.
Although the alloy maintains a stable discharge capacity during the first 10 cycles, a pronounced decline occurs thereafter, leading to ~65% retention at cycle 24. This trend is consistent with the behavior reported by Iwakura et al. [37], where post-cycling degradation of Mg–Ni alloys was attributed to oxidation of the Mg-rich surface and structural instability of the hydride phase. Their results (Figure 9) [35] demonstrate that a rapid drop in capacity can occur even in the absence of direct surface analysis such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), underscoring the intrinsic susceptibility of Mg-based alloys to corrosion in an alkaline environment. Therefore, the retention loss observed in our Mg–Ni–Al–V–Fe can be rationalized within this well-established degradation framework.
The cycle stability of the electrode is an important factor in understanding how well the battery holds up after activation. A critical factor here is the capacity retention rate (Sn), calculated as Sn = Cn/Cmax × 100%. In this formula, Cmax is the highest discharge capacity, and Cn is the capacity at a certain number of charge/discharge cycles.
Figure 10 shows the capacity retention rates (Sn) in percent for the alloy electrode against cycle numbers. The fluctuating curves offer insights into how the discharge capacity undergoes changes due to oxidation during charge/discharge cycles.
Remarkably, the alloy demonstrates a strong cycle stability of 91.43% by the 10th cycle. It is worth highlighting that our observed capacity retention rate stands out compared to findings in the literature. For instance, in the study by Y. Zhang et al. [36], where they explored the electrochemical properties of a distinct alloy electrode specifically, Mg50-xTixNi45Al3Co2, they noted a capacity retention rate of 73% at the 10th cycle. This observed capacity loss was attributed to the formation of Mg (OH)2 on the surface of the electrode. The capacity fading observed during cycling can be reasonably attributed to pulverization and oxidation-driven surface degradation. Although no direct surface analysis was conducted in this study, the interpretation is consistent with well-documented corrosion mechanisms of Mg-based alloys in an alkaline environment. Similar oxidation-induced particle fragmentation and capacity attenuation have been reported by Jain et al. [3]. Therefore, the degradation pathway proposed here should be regarded as a possible explanation supported by established literature rather than direct experimental verification.
In the literature, the discharge capacity of Mg-Ni-based alloys has been reported over a wide range with a substantial decrease during cycling (Table 2). For example, Huang et al. achieved a discharge capacity of 488.65 mAh/g in the Mg55Ni45 alloy, although this value decreased to around 110 mAh/g after cycling [20]. The La1.5Mg0.5Ni7 alloy, produced by mechanical alloying, exhibited a remarkable discharge capacity of 304 mAh/g [38]. In this study, the Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 demonstrated a discharge capacity of 257 mAh/g, which is competitive within the mid-range when compared to the literature.

Table 2.
Comparison between the received electrochemical capacity and performance in this study and some published data of other Mg-based materials.
3. Materials and Methods
Argon with a purity of 99.999% and hydrogen with a purity of 99.99% were used for these experiments. Mg was purchased from Strem chemicals (Newburyport, MA 01950-4098, USA) with a purity of 99% and of size 50 mesh. Other metals were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) as follows: Ni powder 150 μm with a purity of 99.9%, V powder 325 mesh with a 99.5% purity, Al powder 60 μm with a purity of 99.9%, and Fe powder 60 μm with a purity of 99%. The metal mixture of 3 g with a composition corresponding to the formula Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 was milled under argon in a planetary mono mill Pulverisette 6 Fritsch (Fritsch, Idar-Oberstein, Germany) with a rotation speed of 300 rpm, stainless steel balls with diameters 10 mm, and a ball to powder weight ratio of 15:1 for a total duration of 50 h. After 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 h of ball milling, the stainless steel vial with a volume of 80 mL was opened in a glove box under argon and some amount of the powder was taken for X-ray diffraction analyses using a Powder X-ray Diffractometer Bruker D8 Advance with a LynxEye detector and Cu kα radiation (Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany). After 50 h of ball milling under argon and after hydrogenation at 200 °C and 1 MPa, the samples were characterized by TEM HR STEM JEOL JEM 2100 with a GATAN Orius 832 SC1000 CCD Camera (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were obtained with a JEOL JSM 7100 F microscope(JEOL, Tokyo, Japan).
The hydrogen sorption properties of the alloy were studied at 25, 100, 200, and 300 °C and a pressure of 1 MPa for absorption and 0.15 MPa for desorption and at 300, 280, and 260 °C using a volumetric Sievert’s type apparatus.
The electrochemical properties and kinetics characteristics were studied by using a three-electrode system. The working electrode was made by mixing the alloy powder ground under 30–60 microns with high purity nickel powder at a ratio of 3:1 and then cold pressing it into 10 mm diameter pellets under 15 MPa. The electrode pellets then were wrapped with foam nickel. Finally, the electrodes were immersed in a 6 M KOH solution for 1 day to be completely wetted before the electrochemical measurement. The Ni(OH)2 counter electrode and a Hg/HgO reference electrode were used to set up a three-electrode cell in the 6 M KOH solution. The amount of nickel hydroxide was four times the weight of the alloy placed as the working electrode. The discharge capacity of the working electrode was calculated based on the theoretical capacity of (NiOH)2, reported to be 289 mAh/g [39]. The discharge capacity was calculated using the amount of the active material. Electrochemical measurements were carried out on three independently fabricated electrodes under identical conditions. The discharge capacities reported in this work are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). The three-electrode cell was monitored by a Bio-Logic SP-300 galvanostat/potentiostat (Seyssinet-Pariset, France). The system was charged/discharged at a 0.2 C rate in order to fully activate the electrodes. After activation, each electrode was charged at a 1 C rate for 5 h followed by 30 min rest and then discharged at a 0.25 C rate to the cut-off potential of −0.9 V vs. the Hg/HgO reference electrode.
4. Conclusions
The X-ray diffraction patterns of the ball-milled alloy Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 for 50 h under argon showed the presence of Mg, Al, Ni, Fe, and some minor quantity of the partially disordered CsCl-type cubic structure Mg3AlNi2 phase. TEM analyses confirmed the results from X-ray diffraction analyses and revealed nanosized microstructures for the ball-milled alloy and for the hydrogenated one. After hydrogenation of this alloy, MgH2, VHx, Fe, Al, and Ni were detected. Mg2Ni was not formed after ball milling nor was Mg2NiH4 formed after hydrogenation. The reversible hydrogen storage capacity of this nanosized material Mg50Ni12.5Al12.5V12.5Fe12.5 was due mainly to magnesium. The nonstoichiometric vanadium hydride and other metals along with Mg3AlNi2 favor the hydrogen sorption properties. This metallic powder showed very fast absorption kinetics and resistance to oxidation, which is confirmed by the results from the electrochemical testing. It appears that the effects of ball milling such as decreasing particles size and introducing many defects also contributed to these good absorption kinetics properties. The kinetics of desorption was not as fast, and only a small quantity of hydrogen was desorbed at the lower temperature 280 °C. To improve the desorption characteristics of this type of alloy in order for it to be more attractive for hydrogen storage applications, changes in the conditions of synthesis and optimization of the composition are being considered for the future.
The alloy exhibited a maximum electrochemical discharge capacity of 257 mAh/g. Despite not surpassing the elevated values reported in previous studies for similar materials [10,11,12,13,21], this capacity is comparable to results from other sources [23,24,25,38] and showed a better capacity retention rate than the materials published in [9,10,16,20,22] and a comparable retention rate to that in [18]. Notably, the alloy demonstrated stability during electrochemical cycling, making it a promising candidate for Ni-MH battery applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.G. and G.Ç.; methodology, E.G. and P.M.; validation, E.G. and G.Ç.; formal analysis, E.G. and G.Ç.; investigation, E.G., G.Ç., H.Y., and P.M.; resources, E.G. and G.Ç.; data curation, E.G.; writing—original draft preparation, E.G.; writing—review and editing, G.Ç., H.Y., and P.M.; visualization, E.G., G.Ç., H.Y., and P.M.; supervision, E.G. and G.Ç.; project administration, E.G. and G.Ç.; funding acquisition, E.G. and G.Ç. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences under the project IC-TR/02/2022-2023 and TUBITAK (The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey) project № 121N774 for the support of this work. Some research equipment of Distributed Research Infrastructure INFRAMAT, part of Bulgarian National Roadmap for Research Infrastructures, supported by Bulgarian Ministry of Education and Science under project D01-322/30.11.2023 were used for this investigation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Loïc Joanny and Francis Gouttefangeas for SEM experiments at CMEBA platform (ScanMAT, UAR 2025 University of Rennes-CNRS).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rampai, M.M.; Mtshali, C.B.; Seroka, N.S.; Khotseng, L. Hydrogen production, storage, and transportation: Recent advances. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 6699–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yartys, V.A.; Lototskyy, M.V.; Akiba, E.; Albert, R.; Antonov, V.E.; Ares, J.R.; Zhu, M. Magnesium based materials for hydrogenbased energy storage: Past, present and future. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 7809–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, I.P.; Lal, C.; Jain, A. Hydrogen storage in Mg: A most promising material. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 5133–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Wu, P.; Ding, Z. Magnesium-Based Hydrogen Storage Alloys: Advances, Strategies, and Future Outlook for Clean Energy Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhu, W.; Lu, C.; Ding, W.; Zou, J. Nanostructuring of Mg-based hydrogen storage materials: Recent advances for promoting key applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, A.B. An innovative study on high entropy energy storage Mg-Y-Ni-cu systems: Machine learning-driven optimization of electrical cycling in Ni-MH battery alloys. J. Energy Storage 2025, 107, 114958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, X.; Peng, X.; Chen, D.; Pan, F. Research advances of magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide in 2021. J. Magnes. Alloys 2022, 10, 863–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Pistidda, C.; Gizer, G.; Klassen, T.; Dornheim, M. Mg-based materials for hydrogen storage. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 1837–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, S.; Roue, L.; Huot, J.; Schulz, R.; Aymard, L.; Tarascon, J.M. Properties of mechanically alloyed Mg-Ni-Ti ternary hydrogen storage alloys for Ni-MH batteries. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Inoue, S.; Mu, D.; Hatano, Y.; Watanabe, K. Electrochemical studies of the effect of surface modification of amorphous MgNi electrodes by carbon or Ni. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 349, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anik, M. Effect of Titanium additive element on the discharging behavior of MgNi Alloy electrode. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 15075–15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anik, M.; Özdemir, G.; Kücükdeveci, N.; Baksan, B. Effect of Al, B, Ti and Zr additive elements on the electrochemical hydrogen storage performance of MgNi alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Wan, N.; Li, L. The effects of Pd and/or Zr additives on the structures and cyclic stabilities of Mg50Ni50-based electrode alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 2768–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçküdeveci, N.; Erdoğan, I.A.; Aybar, A.B. Effects of Zr addition on electrochemical characteristics of MgTiMnNi hydrogen storage alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 18753–18760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, W.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, L.; Zhu, M. Promoting the cycling stability of amorphous MgNi-based alloy electrodes by mitigating hydrogen-induced crystallization. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 6701–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M.; Fang, F.; Sun, D. Hydrogenation and crystallization of amorphous phase: A new mechanism for the electrochemical capacity and its decay in milled MgNi alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 305, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-C.; Lee, P.S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Züttel, A.; Schlapbach, L. Effects of Ti on the cycle life of amorphous MgNi-based alloy prepared by ball milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 306, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükdeveci, N.; Akay Erdoğan, I.; Binal Aybar, A.; Anik, M. Electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of mechanically alloyed Mg0.8Ti0.2-xMnxNi (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1) type alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Ding, P.D.; Gao, S.; Pan, F.S.; Tang, A. Effect of Al content on hydrogen storage properties of amorphous Mg1-xAlxNi (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3) alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2009, 610–613, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongeat, C.; Grosjean, M.H.; Ruggeri, S.; Dehmas, M.; Bourlot, S.; Marcotte, S.; Roué, L. Evaluation of different approaches for improving the cycle life of MgNi-based electrodes for Ni-MH batteries. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M. Reducing the electrochemical capacity decay of milled Mg-Ni alloys: The role of stabilizing amorphous phase by Ti-substitution. J. Power Sources 2019, 438, 226984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, S. Enhancing the cycle stability of milled Mg-Ni alloys: The role of Pd substitution on reversible electrochemical hydrogenation/dehydrogenation reactions. Electrochem. Commun. 2025, 170, 107860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Feng, Y.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, X.; Jang, M.-B. Preparation and electrochemical characteristics of MgNi-FeB alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 3915–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, L. Improving hydrogen-induced crystallization and electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of MgNi amorphous alloy with CoB addition. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 588, 121646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Sha, J.; Li, L.; Bao, J.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, M.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Z.J. The effect of Gd on the microstructure and electrochemical properties of Mg-Ni-based alloys. Alloys Compd. 2024, 981, 173638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, A.; Nale, A.; Catti, M.; Kopnin, E.; Caracino, P. Hydrogenation properties of Mg2AlNi2 and mechanical alloying in the Mg-Al-Ni system. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 477, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, T.; Li, L. Effect of partial substitution of Ti for Al on the phase structure and electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of Mg3AlNi2 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 746, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng- Long, L.; Fu- Kai, H.; Wen- Chi, C.; Chih- Kuang, L.; Jing- Chie, L. Influence of Mg3AlNi2 content on the cycling stability of Mg2Ni-Mg3AlNi2 hydrogen storage alloy electrodes. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, D.; Ordoñez, S.; Fernández, J.F.; Sánchez, C.; Serafini, D.; Rojas, P.A.; Aguilar, C.; Tapia, P. Effect of amorphous Mg50Ni50 on hydriding and dehydriding behavior of Mg2Ni alloy. Mater. Charact. 2011, 62, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Asano, K.; Enoki, H.; Akiba, E. Preparation and hydrogen storage properties of nano-structured Mg-Ni BCC alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 477, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.-X.; Lei, Y.-Q.; Wang, Q.-D. The reduction of cycling capacity degradation of Mg–Ni-based electrode alloys by Fe substitution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2002, 27, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Fetcenko, M.A.; Li, F.; Ouchi, T. Structural, thermodynamic, and electrochemical properties of TixZr1−x(VNiCrMnCoAl)2 C14 Laves phase alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 464, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etiemble, A.; Rousselot, S.; Guo, W.; Idrissi, H.; Roué, L. Influence of Pd addition on the electrochemical performance of Mg-Ni-Ti-Al-based metal hydride for Ni-MH batteries. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 7169–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Shen, Y.; Onur Şahin, E.; Noréus, D.; Öztürk, T. Activation behavior of an AB2 type metal hydride alloy for NiMH batteries. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 9948–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Young, K.; Meng, T.; Ouchi, T.; Yasuoka, S. Partial substitution of cobalt for nickel in mixed rare earth metal based superlattice hydrogen absorbing alloy–Part 1 structural, hydrogen storage and electrochemical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 660, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Gao, J.; Hu, F.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, D. Electrochemical hydrogen storage behaviors of as-milled Mg-Ti-Ni-Co-Al-based alloys applied to Ni-MH battery. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 342, 136123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, H.; Inoue, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Tamura, S. Electrochemical and structural properties of Mg–Ni hydrogen storage alloys. J. Less-Common Met. 1991, 172–174, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Werwiński, M.; Szajek, A.; Marczyńska, A.; Smardz, L.; Novak, M.; Jurczyk, M. Effect of substitution La by Mg on electrochemical and electronic properties in La2−xMgxNi7 alloys: A combined experimental and ab initio studies. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 763, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, B.; Nalajala, V.S.; Popuri, A.K.; Subbaiah, T.; Minakshi, M. Perspectives on nickel hydroxide electrodes suitable for rechargeable batteries: Electrolytic vs. chemical synthesis routes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).