Antimicrobial Activity of Ethyl (2-(Methylcarbamoyl)phenyl)carbamate and Its Mixed Ligand Ni(II) and Co(II) Complexes
Abstract
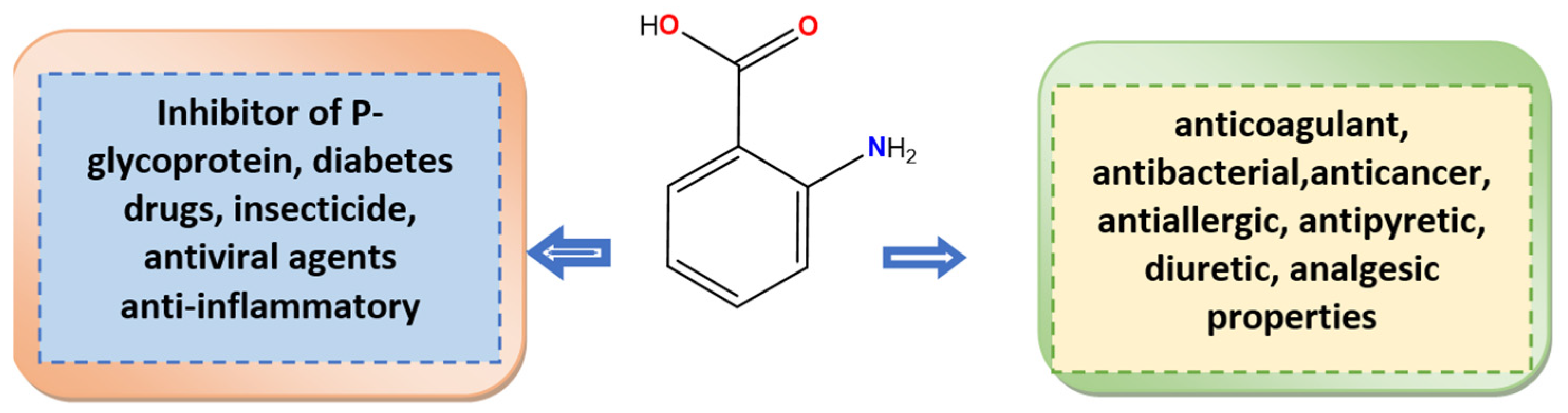
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
- Development of Safe Antimicrobial Agents
- 2.
- Adjunctive Therapies in Infection Management
- 3.
- Biomedical Coatings and Materials
- 4.
- Research into Selectivity Mechanisms
- 5.
- Applications in Chronic Infections
- 6.
- Food and Environmental Safety
- 7.
- Foundation for Structural Optimization
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
Microwave Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry (MP-AES) Determination of Co and Ni in the Complexes
3.2. Synthetic Methods Experimental Protocols
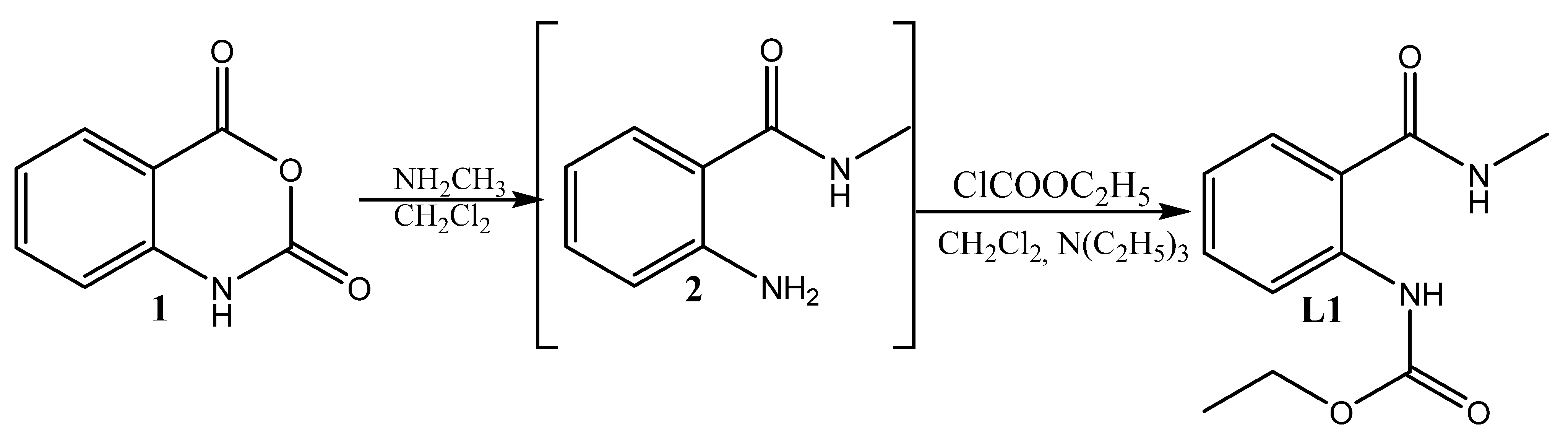
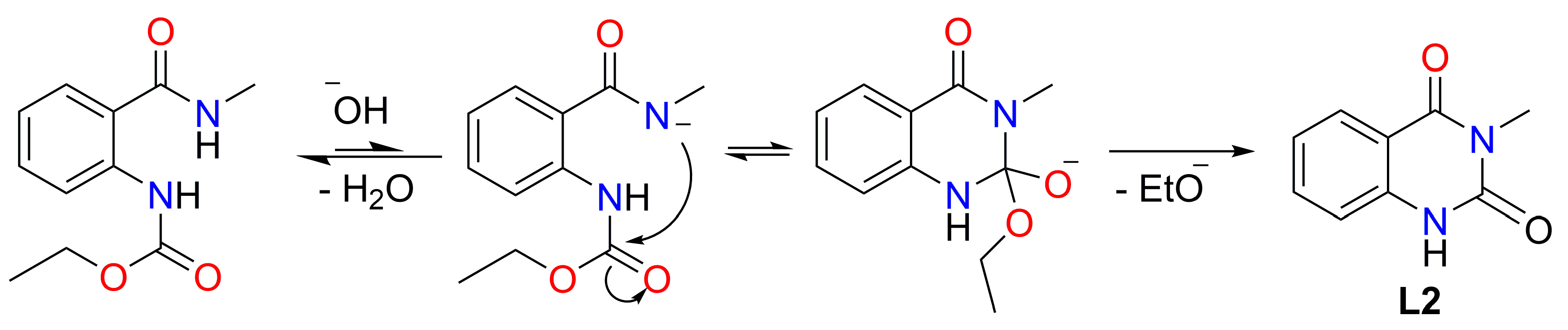
3.2.1. Synthesis of the Ligand—Ethyl (2-(Methylcarbamoyl)phenyl)carbamate L1
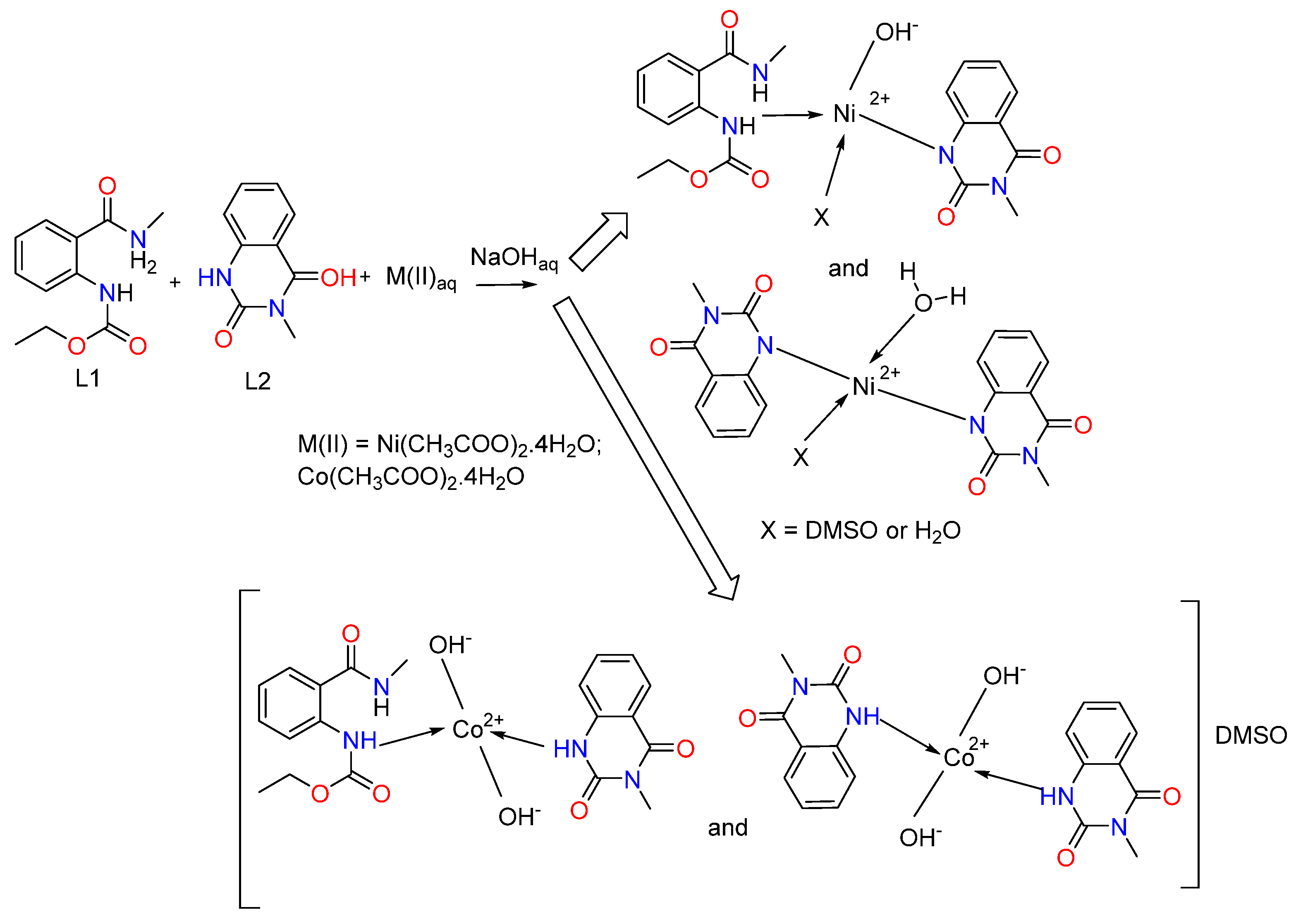
3.2.2. Synthesis of Ni(II) and Co(II) Complexes of Ethyl (2-(Methylcarbamoyl)phenyl)carbamate L1, M:L:OH− = 1:2:2
3.3. Microbiological Tests
3.3.1. Tested Microorganisms
Antimicrobial Activity Assay
3.3.2. Culture Media
3.4. Cytotoxic Activity
Cell Viability Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karygianni, L.; Ren, Z.; Koo, H.; Thurnheer, T. Biofilm Matrixome: Extracellular Components in Structured Microbial Communities. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, P. Extracellular Polymeric Substances, a Key Element in Understanding Biofilm Phenotype. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilhen, C.; Forestier, C.; Balestrino, D. Biofilm Dispersal: Multiple Elaborate Strategies for Dissemination of Bacteria with Unique Properties. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 105, 188–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, M.; Ahmad, W.; Andleeb, S.; Jalil, F.; Imran, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ali, M.; Rafiq, M.; Kamil, M.A. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuon, F.F.; Suss, P.H.; Telles, J.P.; Dantas, L.R.; Borges, N.H.; Ribeiro, V.S.T. Antimicrobial Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestby, L.K.; Grønseth, T.; Simm, R.; Nesse, L.L. Bacterial Biofilm and its Role in the Pathogenesis of Disease. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, Z.; McTiernan, C.D.; Suuronen, E.J.; Mah, T.-F.; Alarcon, E.I. Bacterial biofilm formation on implantable devices and approaches to its treatment and prevention. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; He, L.; Asiamah, T.K.; Otto, M. Colonization of medical devices by staphylococci. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 3141–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Tang, X.; Dong, W.; Sun, N.; Yuan, W. A Review of Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus aureus and Its Regulation Mechanism. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Bakker, H.C.; Fortes, E.D.; Wiedmann, M. Multilocus sequence typing of outbreak-associated Listeria monocytogenes isolates to identify epidemic clones. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, H.; Xue, L.; Lei, T.; Pang, R.; Wu, S.; Wu, H.; et al. Isolation, Potential Virulence, and Population Diversity of Listeria monocytogenes From Meat and Meat Products in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.; Jinneman, K.; Stelma, G.; Smith, B.G.; Lye, D.; Messer, J.; Ulaszek, J.; Evsen, L.; Gendel, S.; Bennett, R.W.; et al. Natural atypical Listeria innocua strains with Listeria monocytogenes pathogenicity island 1 genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4256–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlier, C.; Perrodeau, É.; Leclercq, A.; Cazenave, B.; Pilmis, B.; Henry, B.; Lopes, A.; Maury, M.M.; Moura, A.; Goffinet, F.; et al. Clinical features and prognostic factors of listeriosis: The MONALISA national prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoai-Tehrani, M.; Pilmis, B.; Maury, M.M.; Robineau, O.; Disson, O.; Jouvion, G.; Coulpier, G.; Thouvenot, P.; Bracq-Dieye, H.; Valès, G.; et al. Listeria monocytogenes-associated endovascular infections: A study of 71 consecutive cases. J. Infect. 2019, 79, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kong, X.; Niu, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, Q. Differences in Biofilm Formation of Listeria monocytogenes and Their Effects on Virulence and Drug Resistance of Different Strains. Foods 2024, 13, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochan, T.J.; Nozick, S.H.; Valdes, A.; Mitra, S.D.; Cheung, B.H.; Lebrun-Corbin, M.; Medernach, R.L.; Vessely, M.B.; Mills, J.O.; Axline, C.M.R.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates with Features of Both Multi-Drug-Resistance and Hypervirulence Have Unexpectedly Low Virulence. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, R.; Nair, A.V.; Parmar, K.; Rajmani, R.S.; Chakravortty, D.; Das, D. Combating Biofilm-Associated Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections Using a Bovine Microbial Enzyme. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: From the Natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Tong, Y.; Cheng, J.; Abbas, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Si, D.; Zhang, R. Biofilm and Small Colony Variants—An Update on Staphylococcus aureus Strategies toward Drug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Peng, C.T.; Chi, F.; Yu, C.D.; Yang, Q.L.; Li, Z.J. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities of Chlorogenic Acid against Yersinia enterocolitica. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 885092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, B.L.; Taylor, D.; Dix, B.A.; Cleeland, R. Method of Evaluating Effects of Antibiotics on Bacterial Biofilm. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1987, 31, 1502–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihmaid, S. Exploring the Dual Inhibitory Activity of Novel Anthranilic Acid Derivatives towards α-Glucosidase and Glycogen Phosphorylase Antidiabetic Targets: Design, In Vitro Enzyme Assay, and Docking Studies. Molecules 2018, 23, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-W.; Ma, L. Metal Complexes of Anthranilic Acid Derivatives: A New Class of Non-Competitive α-Glucosidase Inhibitors. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, T.M.; Aboshanab, A.M.; Abouzid, K.A.M.; Zaghary, W.A. Hands-on Synthetic Approaches and Biological Activities of Anthranilic Acid Derivatives: A Mini-Review. Egypt. J. Chem. 2023, 66, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasher, P.; Sharma, M. Medicinal Chemistry of Anthranilic Acid Derivatives: A Mini Review. Drug Dev. Res. 2021, 82, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Srivastava, V.K.; Kumar, A. Newer N-Substituted Anthranilic Acid Derivatives as Potent Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 37, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigato, P.A.; Peruzzo, V.; Tamburini, S. Acyclic and Cyclic Compartmental Ligands: Recent Results and Perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 953–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Noor, L.T.H.; Kakfm, A. Schiff Base and Ligand Metal Complexes of Some Amino Acids and Drug; LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-659-88556-3. [Google Scholar]
- Buvaylo, E.A.; Kokozay, V.N.; Vassilyeva, O.Y.; Skelton, B.W. Bis{2-[(pyridin-2-yl)methylideneamino]benzoato-κ3N,N′,O}chromium(III) nitrate monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. 2014, 70, m136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buvaylo, E.; Kokozay, V.; Rubini, K.; Vassilyeva, O.; Skelton, B. Unusual cocrystals made of a Schiff base metal complex and an organic molecule—Close-packing vs. hydrogen bond interactions. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1072, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Pal, S. Nickel(II) complexes with N,N,O-donor Schiff bases. Self-assembly to two-dimensional network via hydrogen bonding. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2005, 35, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buvaylo, E.A.; Kokozay, V.N.; Vassilyeva, O.Y.; Skelton, B.W. Crystal structure of bis(2-{[(pyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino}benzoato-k3N,N′,O)cobalt(II)N,N-dimethylformamide sesquisolvate. Acta Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-X.; Hojaghani, S.; Hu, M.-L.; Sadr, M.H.; Morsali, A. Sonochemical Synthesis and Characterization of New Nanostructures Cobalt(II) Metal-Organic Complexes Derived From the azo-coupling reaction of 4-Amino Benzoic Acid with Anthranilic acid, Salicylaldehyde and 2-Naphtol. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, M.; Abbasi, M.W.; Tariq, M.; Graham, J.P.; Al-Hagri, A.-R.S.; Elkarim, A.A.; Mohamed, M.E.; Nissapatorn, V.; Taha, M.; Hisaindee, S. Synthesis of Metal Anthranilate Complexes: Catalytic and Antipathogenic Studies. BMC Chem. 2022, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ajaily, M.M.; Morad, F.M. Studies on Cobalt(II) and Copper(II) Schiff Base Complexes. Asian J. Chem. 2007, 19, 4379–4384. Available online: https://asianpubs.org/index.php/ajchem/article/view/19941 (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Saghatforoush, L.A.; Khalilnezhad, R.; Ershad, S.; Ghammamy, S.; Hasanzadeh, M. Synthesis, Characterization and Electrochemical Properties of μ-Oxalato Copper(II) and Nickel(II) Complexes of Anthranilic Acid Schiff Base Ligands. Asian J. Chem. 2009, 21, 6326–6334. Available online: https://asianpubs.org/index.php/ajchem/article/view/12322/12303 (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Hossain, M.D.S.; Zakaria, C.M.; Kudrat-E-Zahan, M. Metal Complexes as Potential Antimicrobial Agent: A Review. Am. J. Heterocyc. Chem. 2018, 4, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, P.; Hristov, M. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel Complexes with Anthranilic Acid and Its Analogues. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, S.M.H.; Ghanim, F.H.; Al-Hamdani, A.A.S. Synthesis, Spectroscopic, Characterization and Biological Activities of Schiff Base Ligand and Metal Complexes of Some Metal (II) Salts with Anthranilic Acid. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Prasher, P.; Mudila, H.; Sharma, M.; Khati, B. Developmental Perspectives of the Drugs Targeting Enzyme-Instigated Inflammation: A Mini Review. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 417–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Prasher, P.; Dhillon, P.; Bhatti, R. Indole-Based Peptidomimetics as Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Hyperalgesic Agents: Dual Inhibition of 5-LOX and COX-2 Enzymes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuanfeng, N.; Zong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Bi, C.; Fan, Y. Synthesis, Structures, and Biological Activity of Novel Complexes with Trifluorinated Anthranilic Acid Derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1194, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalakshmi, R.T.; Bheeter, S.R.; Vasanth, N. Synthesis and Characterization of Biologically Active Metal Complexes of N-Phenyl Anthranilic Acid. ReTeLL 2015, 15, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, S.; Iqbal, Y.; Hussian, I.; Raza, M.; Shah, S.U.A.; Khan, A.; Taj, R.; Rauf, A. Synthesis of Anthranilic Acid and Phthalic Anhydride Ligand and Their Metal Complexes. Biochem. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 2, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Abid Obaid-Ur-Rahman; Rehman, W.; Kashif, M.; Zaman, R.; Ali, M.; Mir, S.; Qureshi, M.T. Ultrasonic Assisted Synthesis, Characterization and Bioactivity Assessment of Novel Piperonal Based Schiff Base and Its Metal Complexes. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2020, 39, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Oladipupo, O.E.; Ibukun, D.T.; Olalekan, T.E. Synthesis and Characterization of Mixed Ligand Dinuclear Metal(II) Complexes of Anthranilic Acid and Pyridine-2-aldoxime. Niger. J. Chem. Res. 2018, 23, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- El-Roudi, A.M.; Aly, A.A.M.; Abd El-Gaber, A.A.; El-Shabasy, M. Reactivity of Some Transition Metal Complexes of Anthranilic Acid with Leucine and Monochloroacetic Acid. Croat. Chem. Acta 1988, 61, 775–782. [Google Scholar]
- Lekaak, A.K.; Mahdi, S.H. Spectroscopic, Structural and Antibacterial Activity of Mixed Ligand Complexes from Schiff Base with Anthranilic Acid. IOP Conf. Ser. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1234, 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.-M.; Chang, L.-L.; Ying, M.-D.; Cao, J.; He, Q.-J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, B. Aldo–Keto Reductase AKR1C1–AKR1C4: Functions, Regulation, and Intervention for Anti-Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaarawy, R.F.M.; Janiak, C. Antibacterial susceptibility of new copper(II) N-pyruvoyl anthranilate complexes against marine bacterial strains—In search of new antibiofouling candidate. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, M.; Rajakumar, P. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Unsymmetrical Dendrimers With Indazole, Salicylates and Anthranilates as Surface Units. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2017, 54, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merk, D.; Lamers, C.; Weber, J.; Flesch, D.; Gabler, M.; Proschak, E.; Zsilavecz, M.S. Anthranilic acid derivatives as nuclear receptor modulators—Development of novel PPAR selective and dual PPAR/FXR ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrone, J.D.; Pelz, N.F.; Bates, B.S.; Souza-Fagundes, E.M.; Vangamudi, B.; Camper, D.V.; Kuznetsov, A.G.; Browning, C.F.; Feldkamp, M.D.; Frank, A.O.; et al. Identification and optimization of anthranilic acid based inhibitors of replication protein A. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, I.-S.; Kwak, J.H.; Pyo, S.; Lee, H.-W.; Kim, A.R.; Schmitz, F.J. Oscarellin an anthranilic acid derivative from a Philippine sponge, Oscarella stillans, as an inhibitor of inflammatory cytokines in macrophages. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrey, H.; Muller, F.J.; Harz, P.; Rupcic, Z.; Stadler, M.; Spiteller, P. Nematicidal anthranilic acid derivatives from Laccaria species. Phytochemistry 2019, 160, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teponno, R.B.; Noumeur, S.R.; Helaly, S.E.; Huttel, S.; Harzallah, D.; Stadler, M. Furanones and anthranilic acid derivatives from the endophytic fungus Dendrothyrium variisporum. Molecules 2017, 22, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, R.; Burgos, V.; Marín, V.; Camins, A.; Olloquequi, J.; González-Chavarría, I.; Ulrich, H.; Wyneken, U.; Luarte, A.; Ortiz, L.; et al. Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (CAPE): Biosynthesis, Derivatives and Formulations with Neuroprotective Activities. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, J.G.; Pressete, C.G.; Costa, A.V.; Martins, F.T.; de Almeida Lima, G.D.; Ionta, M.; Teixeira, R.R. Methoxylated Cinnamic Esters with Antiproliferative and Antimetastatic Effects on Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Life 2023, 13, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qandil, A.M. Prodrugs of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), More Than Meets the Eye: A Critical Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 17244–17274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludağ, M.O.; Ergün, B.Ç.; Alkan, D.A.; Ercan, N.; Özkan, G.Y.; Banoğlu, E. Stable Ester And Amide Conjugates Of Some Nsaids As Analgesic And Antiinflammatory compounds with improved biological activity. Turk. J. Chem. 2011, 35, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S. Research Progress in the Synthesis of Esters. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 440, 022019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevin, B.; Robert, W.; Iain, G.; Kevin, D. Design of ester prodrugs to enhance oral absorption of poorly permeable compounds: Challenges to the discovery scientist. Curr. Drug Metab. 2003, 4, 461–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, M.; Milusheva, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Stefanova, I.; Todorova, M.; Kircheva, N.; Angelova, S.; Pencheva, M.; Stojnova, K.; Tsoneva, S.; et al. Spasmolytic Activity and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Novel Mebeverine Derivatives. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milusheva, M.; Stoyanova, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Stefanova, I.; Todorova, M.; Pencheva, M.; Stojnova, K.; Tsoneva, S.; Nedialkov, P.; Nikolova, S. 2-Amino-N-Phenethylbenzamides for Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment. Molecules 2024, 29, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milusheva, M.; Todorova, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Stefanova, I.; Feizi-Dehnayebi, M.; Pencheva, M.; Nedialkov, P.; Tumbarski, Y.; Yanakieva, V.; Tsoneva, S.; et al. Novel Anthranilic Acid Hybrids—An Alternative Weapon against Inflammatory Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milusheva, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Stefanova, I.; Feizi-Dehnayebi, M.; Mihaylova, R.; Nedialkov, P.; Cherneva, E.; Tumbarski, Y.; Tsoneva, S.; Todorova, M.; et al. Synthesis, Molecular Docking, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Anthranilic Acid Hybrid and Its Diamides as Antispasmodics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Ma, N.; Tian, J.; Sun, H.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, C. Synthesis of N-Unsubstituted and N3-Substituted Quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones from o-Aminobenzamides and CO2 at Atmospheric Pressure and Room Temperature. Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 2471–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, J.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Karimi, A.R. An Efficient One-Pot Procedure for Preparation of 2,4(1H,3H)-Quinazolinediones and 2-Thioxoquinazolinone Derivatives Under Microwave Irradiation. Synth. Commun. Int. J. Rapid Commun. Synth. Org. Chem. 2003, 33, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirode, P.R. A study of mixed ligand complexes of anthranilic acidsemicarbazone and benzaldehyde with Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II). World J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 7, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, P.E.; Tsoneva, S.H.; Nikolova, S.A.; Ivanov, I.I. Novel complexes of n-substituted-4,5-dimethoxy-phenylethyl-2-arylketoamides with metal ions. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 51, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Alwan, A.H.M. Spectroscopic and Magnetic Study of Mixed Ligand Complexes with Divalent Transition Metals Using Azo-Azomethine Ligands. Univ. Thi-Qar J. 2025, 20, 1–19. Available online: https://jutq.utq.edu.iq/index.php/main/article/view/397 (accessed on 28 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Al-Noor, T.H.; AL-Jeboori, A.T.; Ghanim, F.H. Synthesis and characterization of the mixed ligand complexes (L-alanine and anthranilic acid) with some transition Ions. Diyala J. Pure Sci. 2010, 6, 103–110. Available online: https://iasj.rdd.edu.iq/journals/uploads/2024/12/05/ab9ac4b3982c30c3ded242649e575b1f.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Mohamed, A.; Dayo, M.; Alahmadi, S.; Ali, S. Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Green-Synthesized Using Extracts of Different Plants. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, B.K.; Vidyarthi, S.N.; Prakash, O.; Baluni, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) Coordination Compounds with Nitrogen, Oxygen Containing Schiff Base. Orient. J. Chem. 2013, 29, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Noor, T.H.; Ali, K.F.; Jarad, A.J.; Kindeel, A.S. Synthesis, Spectral and Antimicrobial Activity of Mixed Ligand Complexes of Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) with Anthranilic Acid and Tributylphosphine. Chem. Mater. Res. 2013, 3, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Jayachandiran, K.; Esha, S.; Lakshmi, M.S.; Mahalakshmi, S.; Arockiasamy, S. Synthesis and Structural Insights of Bis(2-Methoxy-6-{[(2-Methylpropyl)imino]methyl}phenolato) Nickel(II) Complex through DFT and Docking Investigations. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, T.O.; Oluwarinde, B.O.; Montso, P.K.; Ateba, C.N.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Antimicrobial Activities of Cu(II), In(III), and Sb(III) Complexes of N-Methyl-N–Phenyl Dithiocarbamate Complexes. Results Chem. 2021, 3, 100241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


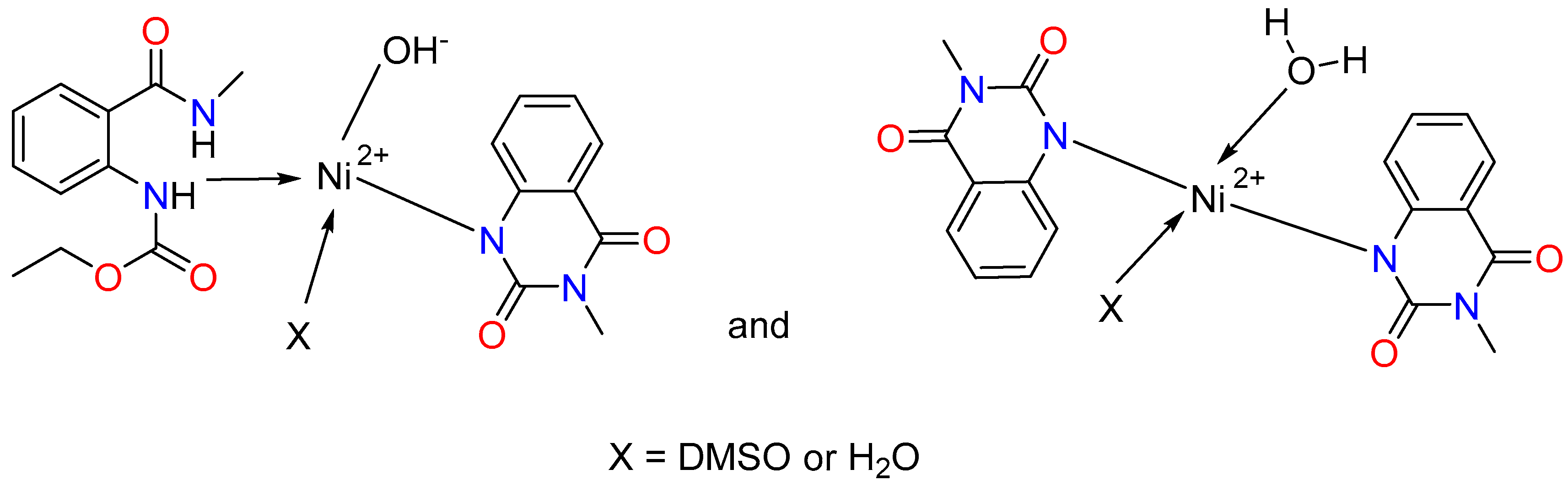
| Complexes | Colour | Solubility | Yield (%) | Melting Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | colorless | soluble in DMSO and CHCl3 | 80 | 136–137 |
| Ni(II) | bright green | insoluble in H2O, THF, CH3COCH3, EtOH, EtOAc and cyclohexane and soluble in DMSO | 31 | 245–247 |
| Co(II) | purple | 33 | 240–241 |
| Atom | δ (1H) ppm (L1) | δ (1H) ppm L2 [68] | δ (1H) ppm Ni(II) | δ (1H) ppm Co(II) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH(COO) | 10.96 (s) | 11.43 (s) | 10.95 * - | 10.99 * 11.43 ** |
| NHCH3 | 8.72 (q) | 8.71 * | 8.72 * | |
| CH | 8.19 (dd) | 7.93 (d) | 8.19 (d) * 7.92 (d) ** | 8.19 * 7.92 ** |
| CH | 7.70 (dd) | 7.64–7.66 (m) | 7.69 (d) * 7.63 ** | 7.70 * 7.64 ** |
| CH | 7.48 (ddd) | 7.17–7.21 (m) | 7.48 * 7.18 ** | 7.48 * 7.18 ** |
| CH | 7.08 (ddd) | 7.17–7.21 (m) | 7.07 * 7.18 ** | 7.09 * 7.18 ** |
| NHCH3 | 2.78 (d) | 3.26 (s) | 2.77 * 3.25 ** | 2.77 * 3.25 ** |
| CH2 | 4.12 (q) | 4.12 (q) * | 4.12 * | |
| CH3 | 1.23 (t) | 1.23 (t) * | 1.24 * | |
| DMSO | - | - | 2.54 | 2.53 |
| Atom | δ (13C) ppm (L1) | δ (13C) ppm (L2) [68] | δ (13C) ppm Ni(II) | δ (13C) ppm Co(II) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C=O(NCH3) | 169.16 | 162.6 | 169.16 * 162.66 ** | 169.15 * 162.65 ** |
| C=O(NH) | 153.37 | 150.8 | 153.37 * 150.88 ** | 153.40 * 150.85 ** |
| C | 139.67 | 139.8 | 139.67 * 139.91 ** | 139.70 * 139.83 ** |
| CH | 132.53 | 135.3 | 132.52 * 135.28 ** | 132.52 * 135.28 ** |
| CH | 128.40 | 127.7 | 128.40 * 127.71 ** | 128.39 * 127.72 ** |
| CH | 122.16 | 122.9 | 122.15 * 122.82 ** | 122.17 * 122.86 ** |
| C | 120.03 | 114.1 | 120.02 * 114.15 ** | 120.08 * 114.14 ** |
| CH | 119.05 | 115.5 | 119.05 * 115.60 ** | 119.05 * 115.55 ** |
| CH2CH3 | 61.04 | - | 61.04 * | 61.03 * |
| NHCH3 | 26.68 | 27.5 | 26.67 * 27.46 ** | 26.67 * 27.46 ** |
| CH2CH3 | 14.85 | - | 14.85 * | 14.84 * |
| DMSO | - | - | 40.88 | 40.90 |
| Assignment | L1 | L2 [69] | Ni(II) | Co(II) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ν(OH) | - | 3436 | 3442 | |
| ν(NH, -C(=O)-NH-CH3) | 3345 | 3345 | 3345 | |
| ν(NH, -NH-C(=O)OCH2CH3) | 3258 | 3165 | - | 3189 |
| ν(Csp2-H, -Ph) | 3072 | 3060 | 3058 | |
| ν(C=O) | 1739 | 1715 | 1718 | 1717 |
| δ(NH) + ν(C=O), -C(=O)-NH-CH3) | 1664 | 1662 | 1666 | 1665 |
| δ(NH) + ν(C=O), -NH-C(=O)OCH2CH3) | 1633 | 1645 | 1645 |
| Metal Complex | Composition * | Formulae | Mr g/mol | W(M)% calc./exp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co(II) | [L1.3L2.4(OH−).2Co].DMSO | C40H48N8O14SCo2 | 997.78 | 11.6/11.9 ± 0.6 |
| Ni(II) | [L1.3L2-3H.DMSO.2H2O(OH−).2Ni] | C40H46N8O13SNi2 | 996.29 | 11.8/11.8 ± 0.6 |
| Tested Microorganisms | Inhibition Zones, mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| L | Ni(II) | Co(II) | |
| Candida albicans NBIMCC 74 | 8 | - | - |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATCC 9763 | 9 | - | - |
| Aspergillus niger ATCC 1015 | 8 | 9 | 9 |
| Aspergillus flavus | 8 | - | - |
| Penicillium chrysogenum | 9 | - | - |
| Rhizopus sp. | 8 | 8 | - |
| Fusarium moniliforme ATCC 38932 | 8 | 8 | - |
| Salmonella enteritidis ATCC 13076 | - | - | 11 |
| Salmonella typhimurium NBIMCC 1672 | - | - | 11 |
| Klebsiella pneumonia ATCC 13883 | - | 12 | 13 |
| Proteus vulgaris ATCC 6380 | - | - | 13 |
| Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 4BCL-YT-- | 8 | - | 10 |
| Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 | - | - | 9 |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | - | - | 13 |
| Listeria monocytogenes NBIMCC 8632 | - | - | 15 |
| Micrococcus luteus 2YC-YT | 8 | - | 20 |
| Compound | Cell Lines | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| K-562 | LAMA-84 | CCL-1 | |
| Co(II) complex | 115.6 ± 8.2 | 120.7 ± 11.5 | 130.6 ± 10.5 |
| Ni(II) complex | >200 | 105.1 ± 7.3 | >200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsoneva, S.; Milusheva, M.; Burdzhiev, N.; Marinova, P.; Varbanova, E.; Tumbarski, Y.; Mihaylova, R.; Cherneva, E.; Nikolova, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Ethyl (2-(Methylcarbamoyl)phenyl)carbamate and Its Mixed Ligand Ni(II) and Co(II) Complexes. Inorganics 2025, 13, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13080267
Tsoneva S, Milusheva M, Burdzhiev N, Marinova P, Varbanova E, Tumbarski Y, Mihaylova R, Cherneva E, Nikolova S. Antimicrobial Activity of Ethyl (2-(Methylcarbamoyl)phenyl)carbamate and Its Mixed Ligand Ni(II) and Co(II) Complexes. Inorganics. 2025; 13(8):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13080267
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsoneva, Slava, Miglena Milusheva, Nikola Burdzhiev, Petya Marinova, Evelina Varbanova, Yulian Tumbarski, Rositsa Mihaylova, Emiliya Cherneva, and Stoyanka Nikolova. 2025. "Antimicrobial Activity of Ethyl (2-(Methylcarbamoyl)phenyl)carbamate and Its Mixed Ligand Ni(II) and Co(II) Complexes" Inorganics 13, no. 8: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13080267
APA StyleTsoneva, S., Milusheva, M., Burdzhiev, N., Marinova, P., Varbanova, E., Tumbarski, Y., Mihaylova, R., Cherneva, E., & Nikolova, S. (2025). Antimicrobial Activity of Ethyl (2-(Methylcarbamoyl)phenyl)carbamate and Its Mixed Ligand Ni(II) and Co(II) Complexes. Inorganics, 13(8), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13080267









