Combination of Acid and Base Activation of Montmorillonite Clay and Its Impact on the Basic Blue-41 Removal Properties: Regeneration and Single Batch Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Composition (XRF Data)
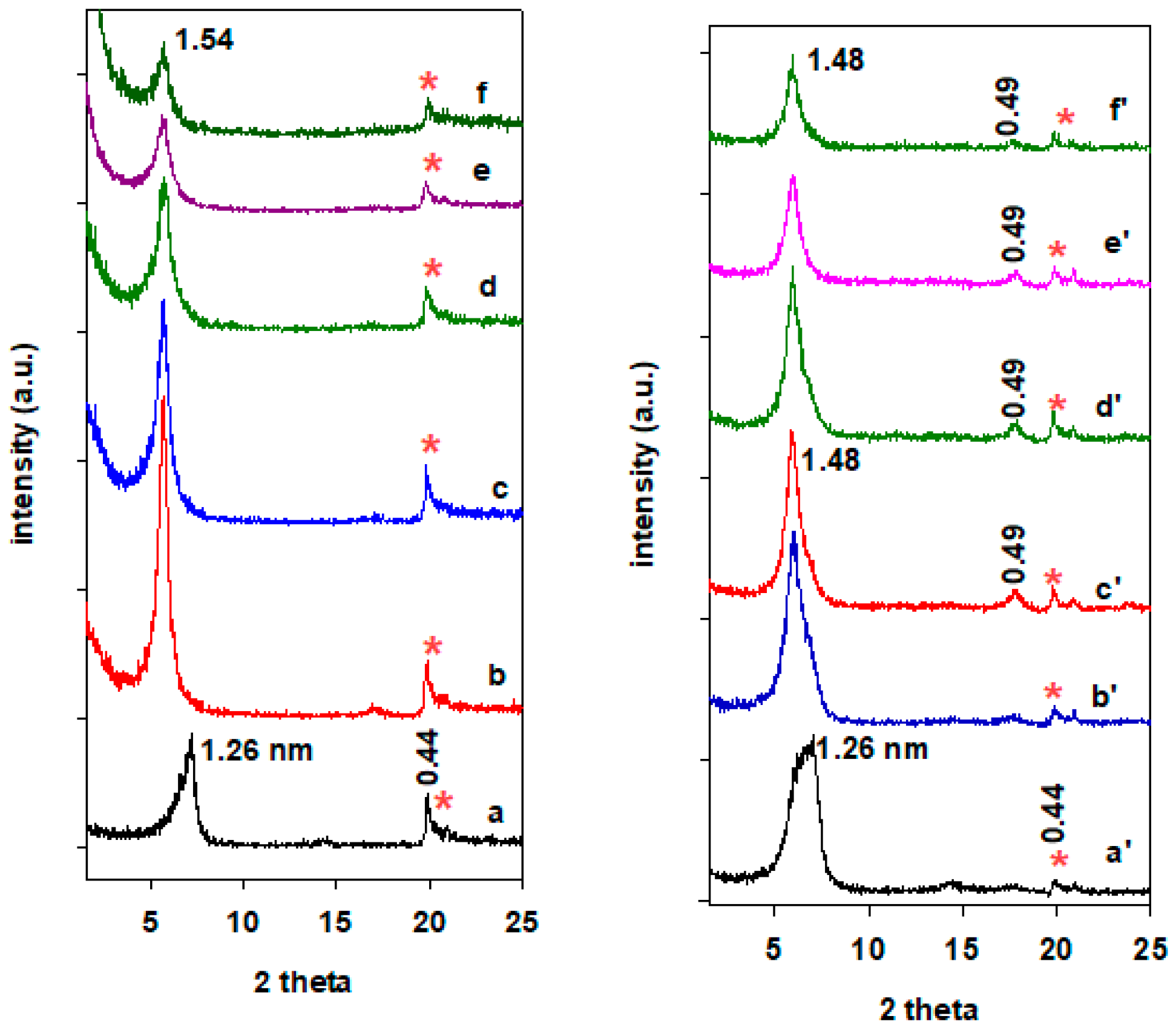
2.2. XRD Data
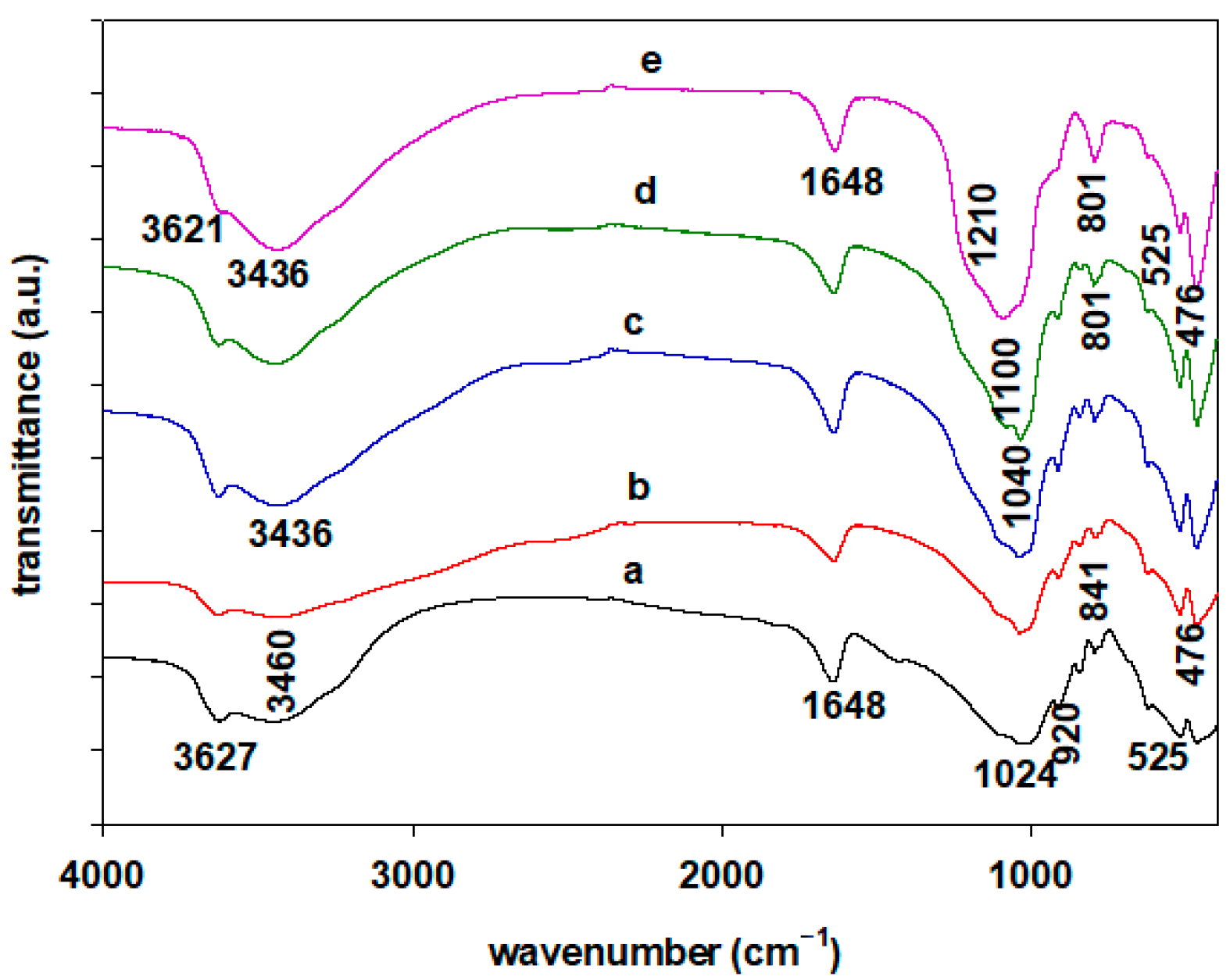
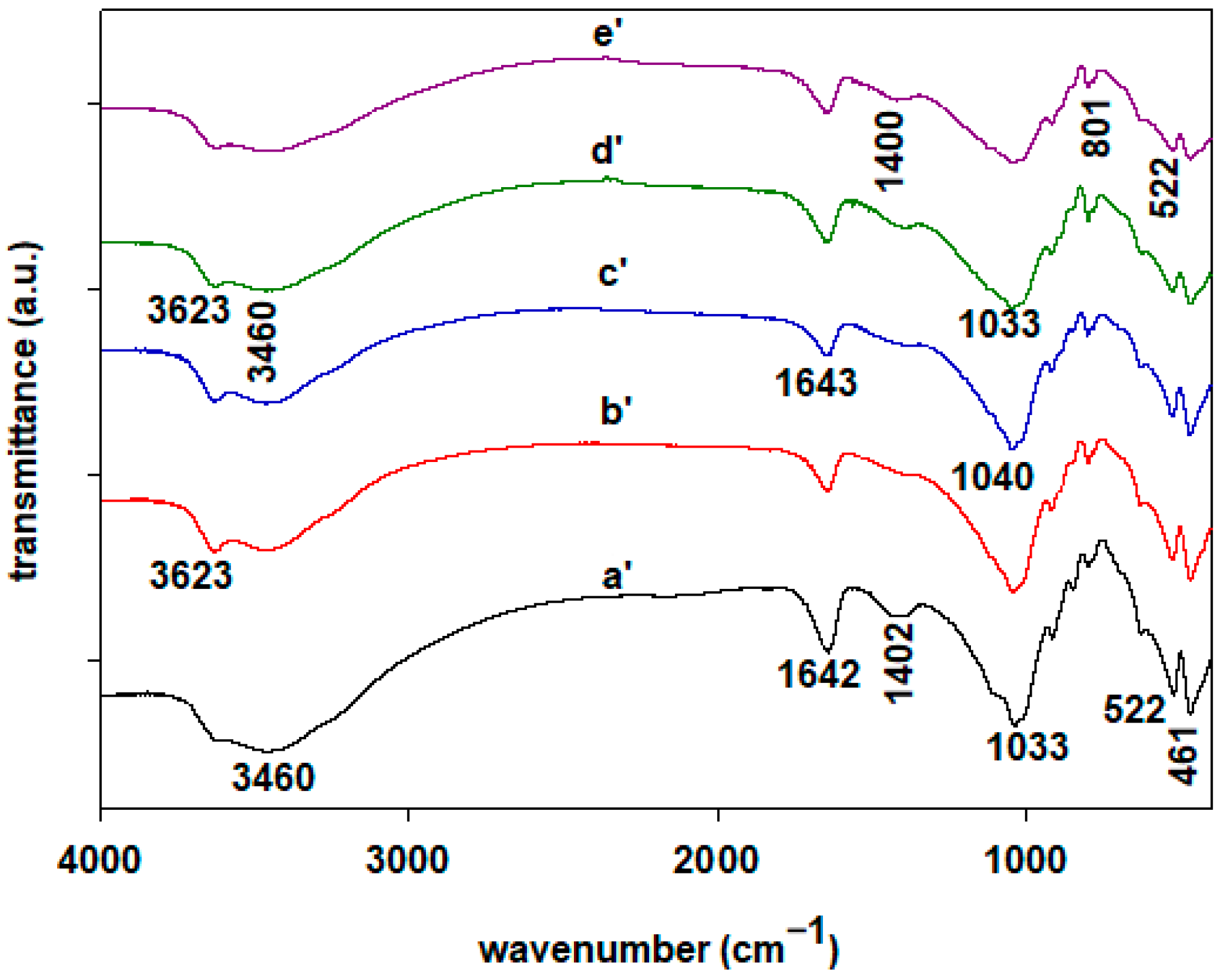
2.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
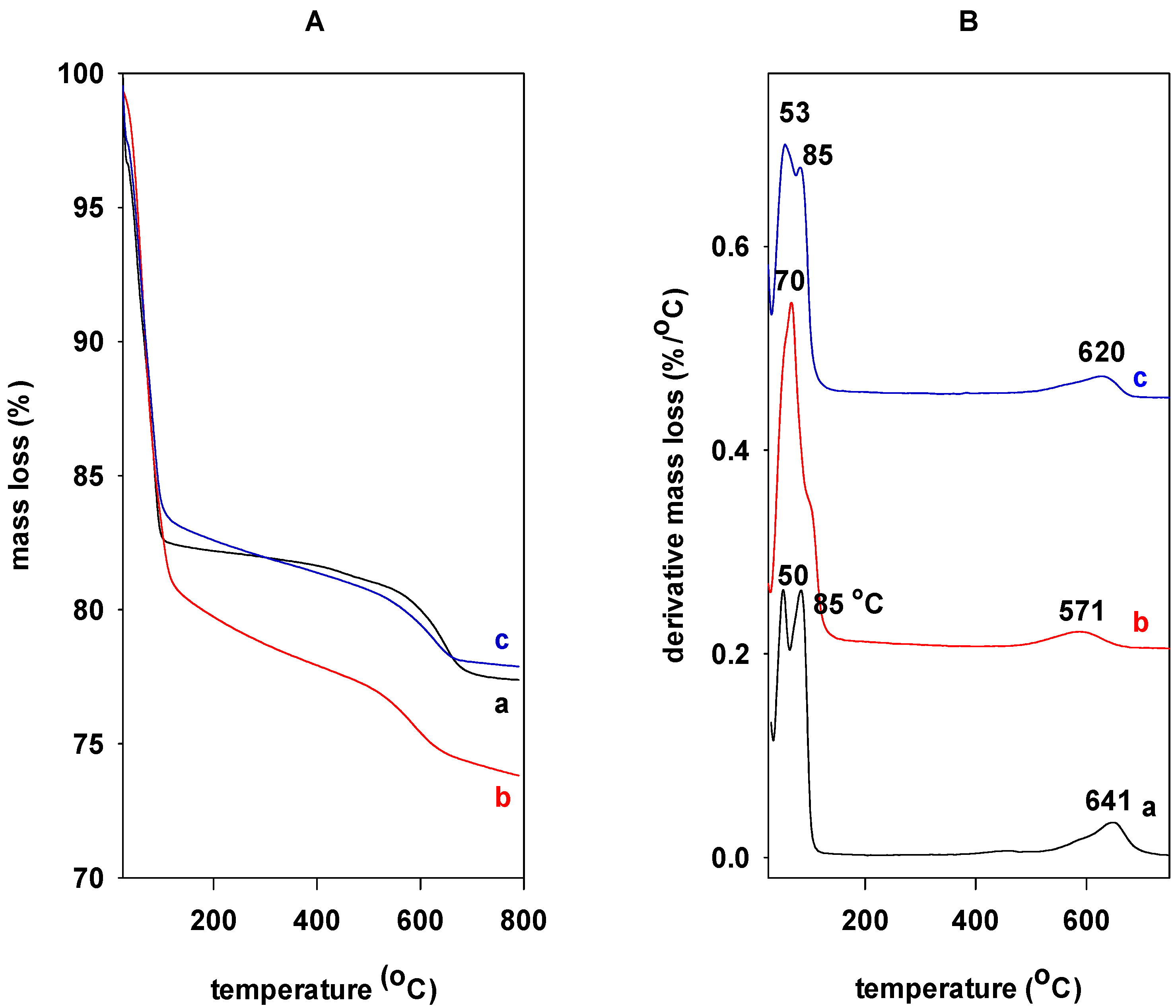
2.4. TGA Data
2.5. 29Si MAS NMR Data
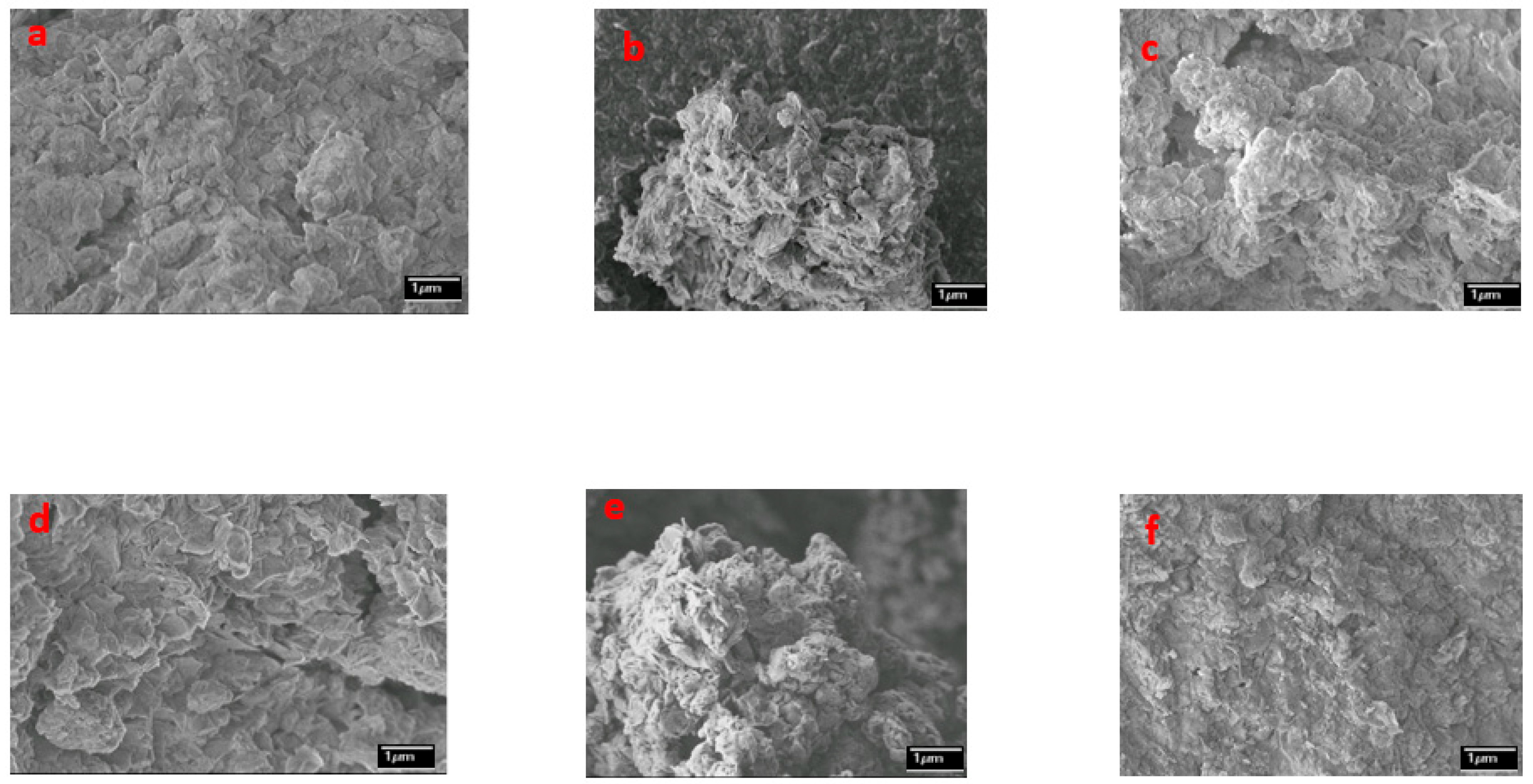
2.6. Microtextural Properties
3. Basic Blue-41 Removal Experiments
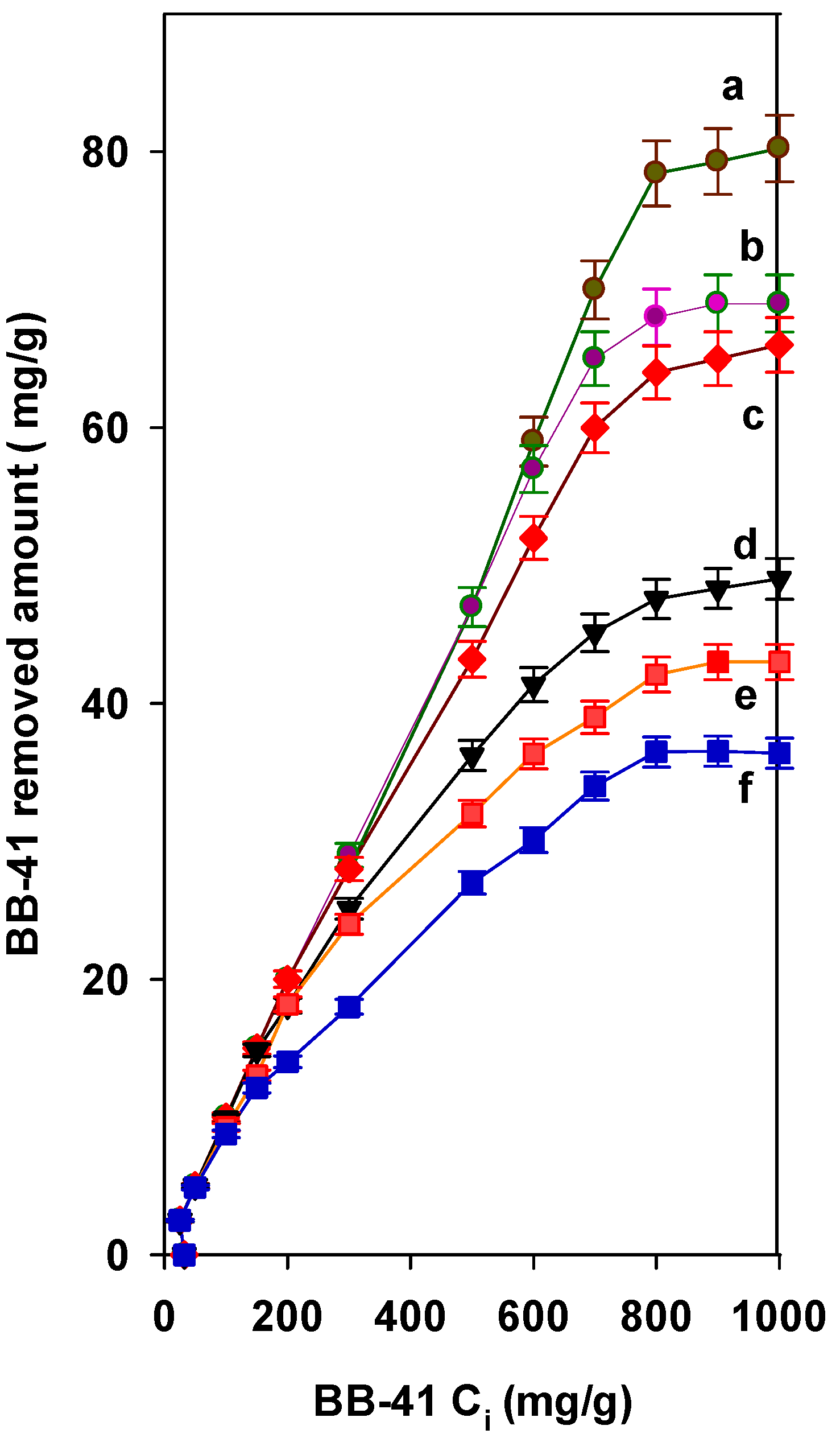
3.1. Effect of Initial Concentration
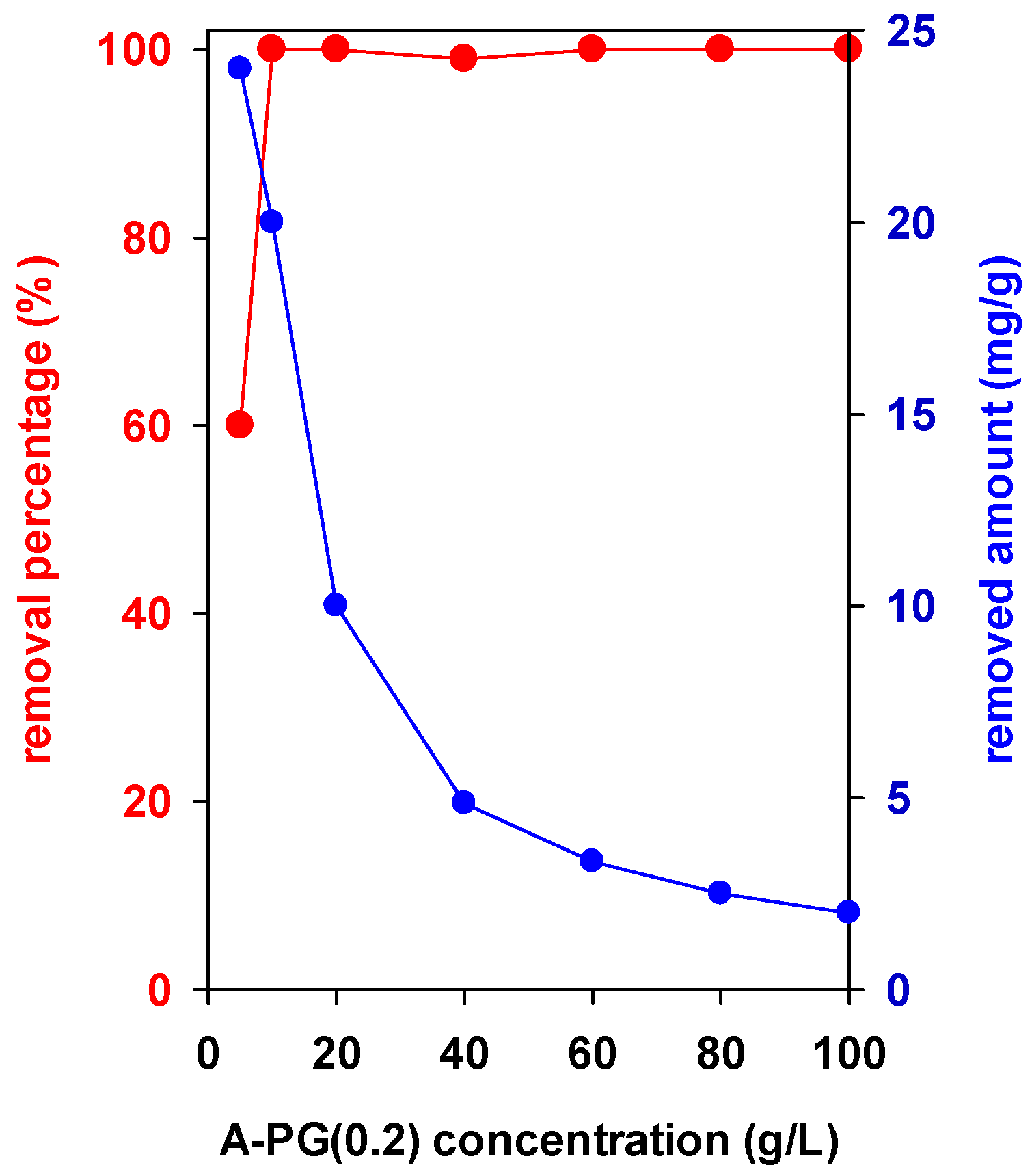
3.2. Effect of Used Masses
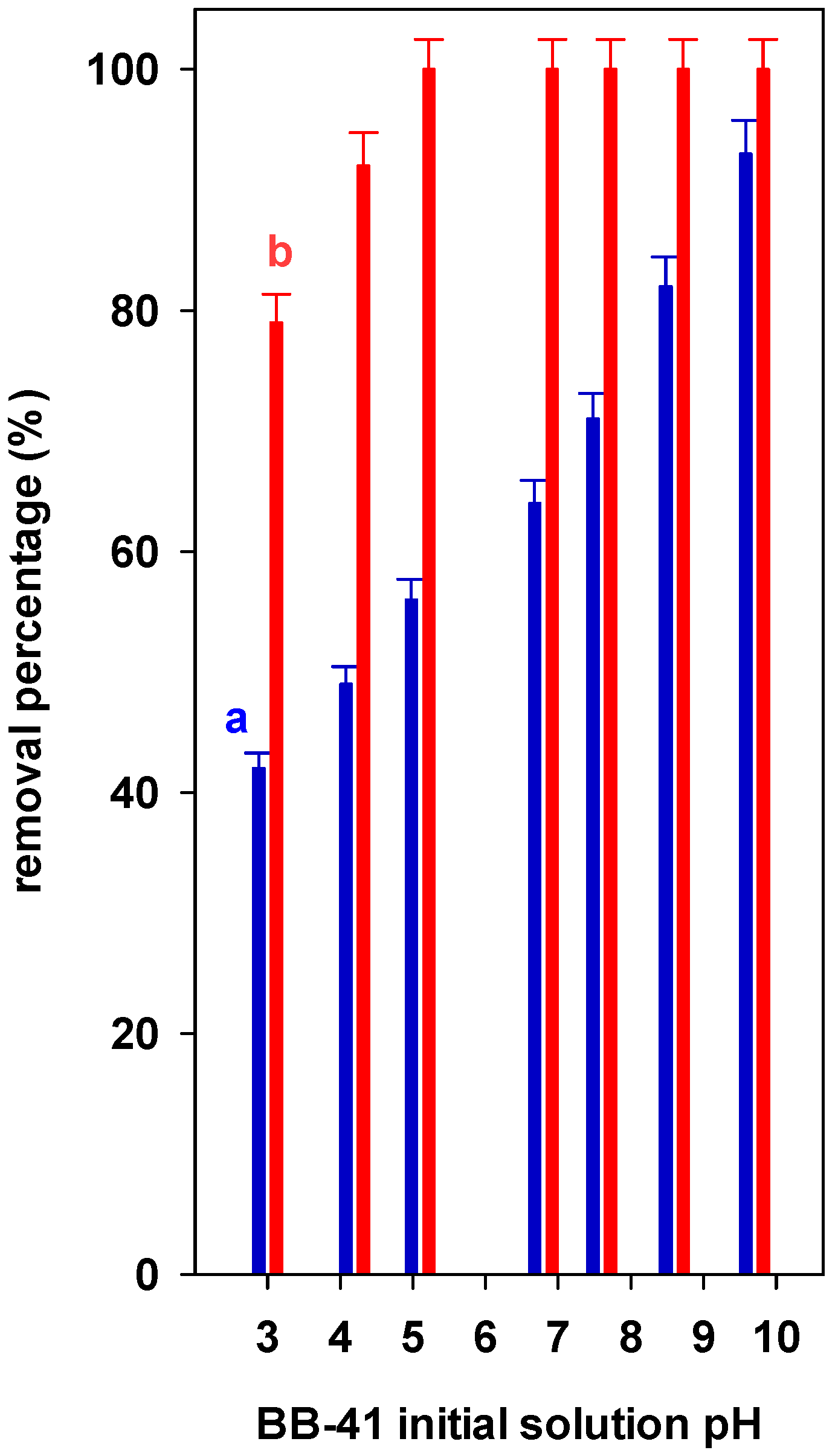
3.3. Effect of Environmental Factor: Effect of Initial pH
3.4. Effect of Acid and Base Activation
3.5. Estimation of Maximum Removal Capacity
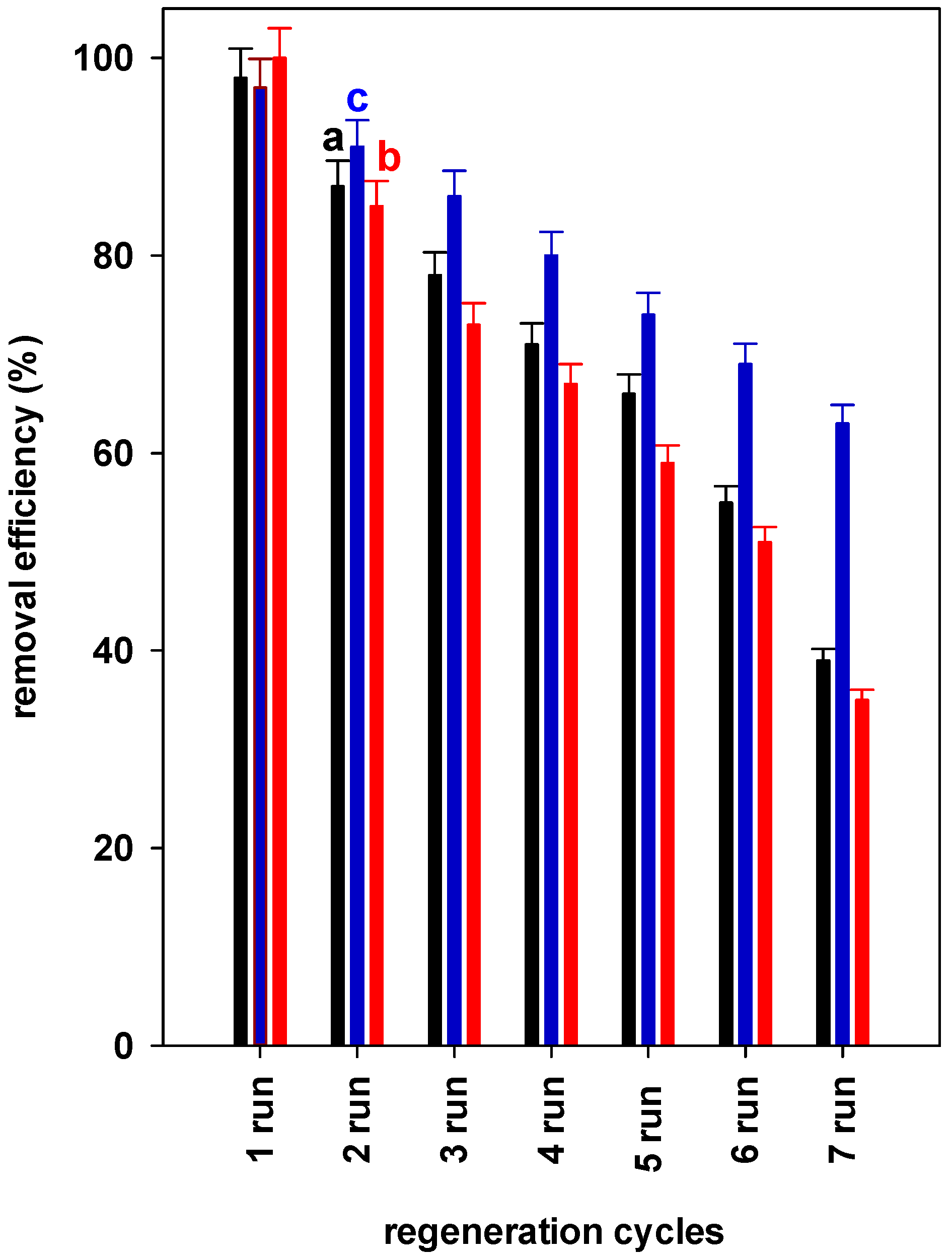
3.6. Regeneration Tests
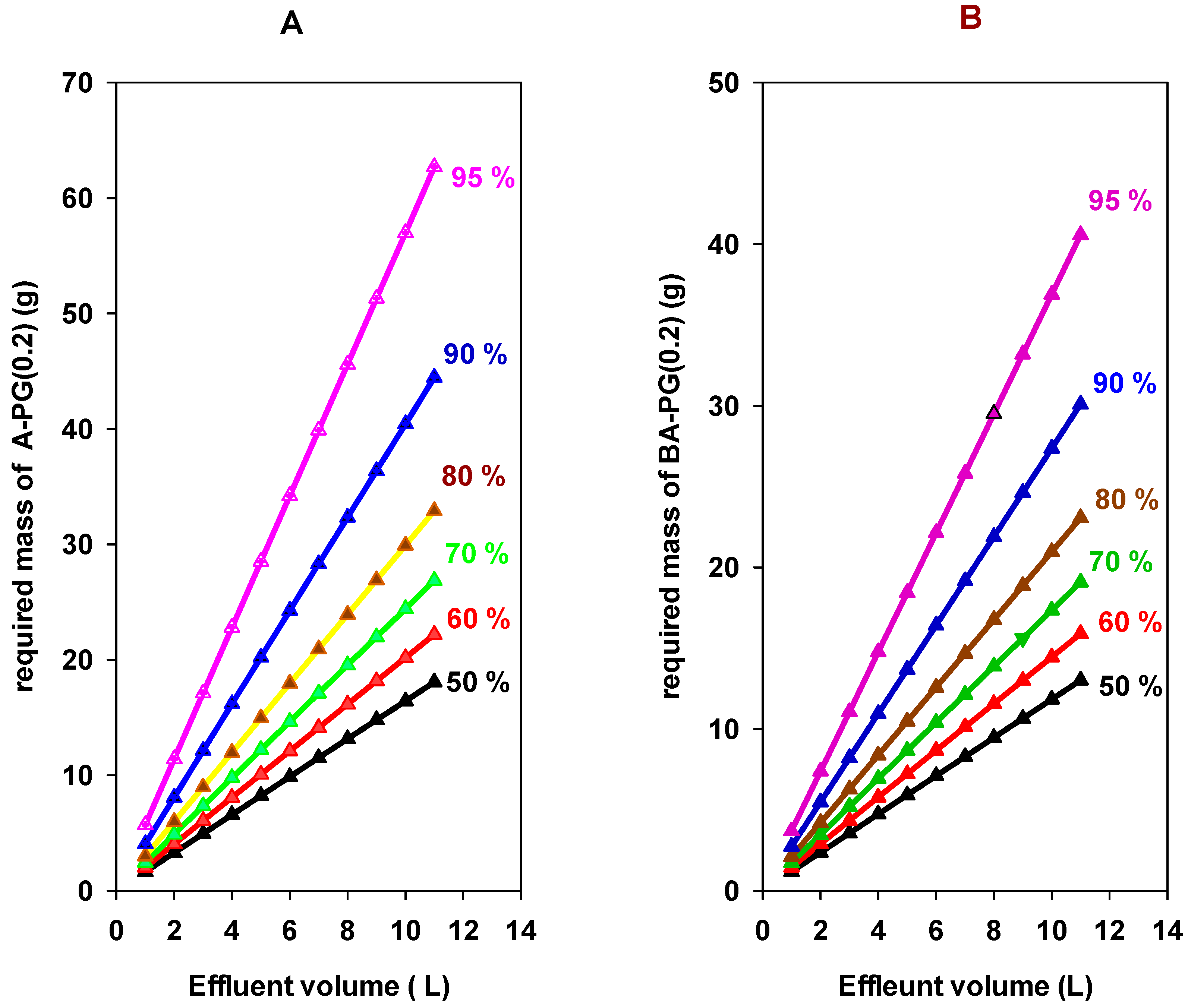
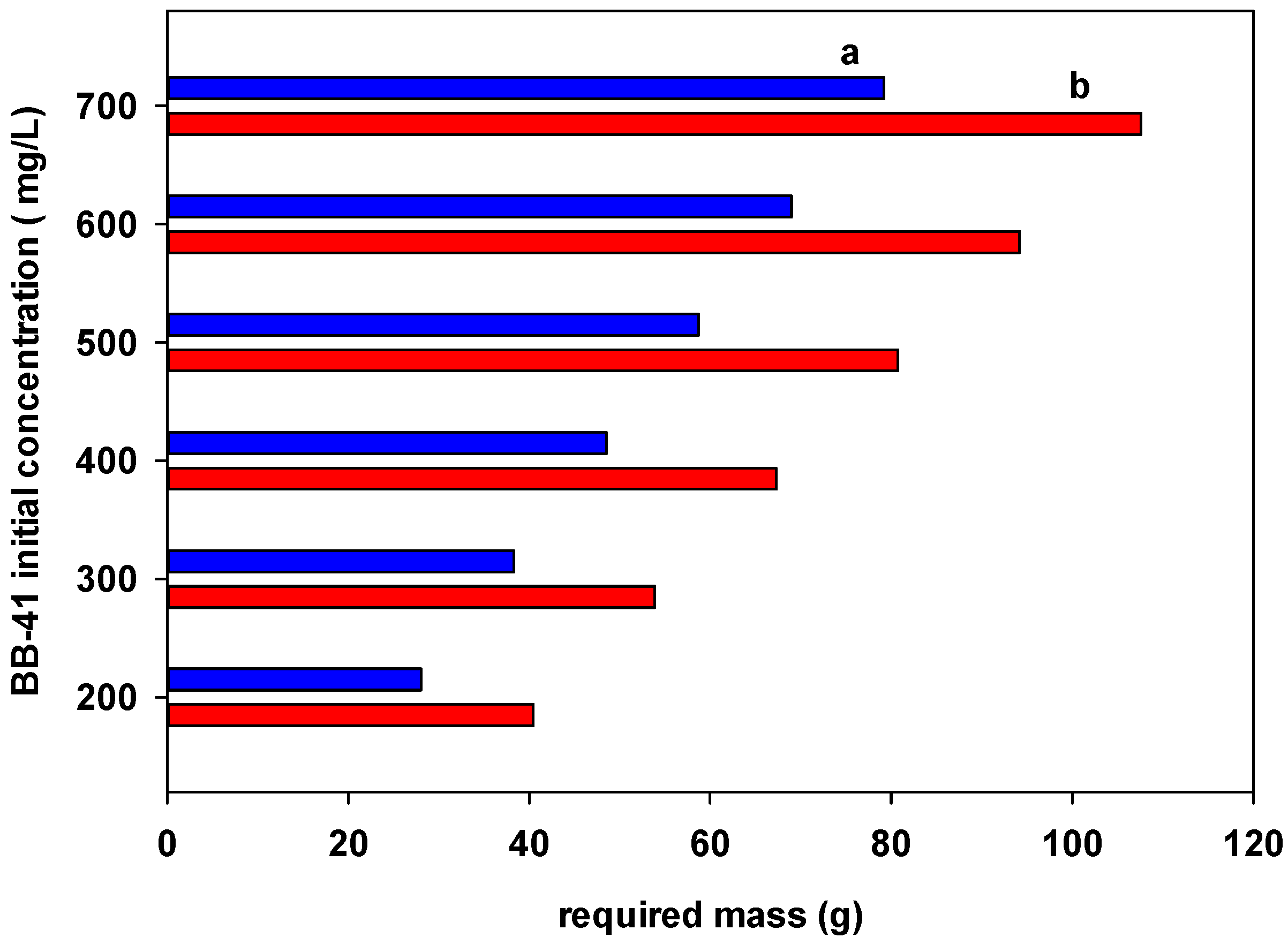
3.7. Single Batch Design Process
4. Experimental
4.1. Materials
4.2. Acid Activation Process
4.3. Base Activation
4.4. Basic Blue-41 Removal Procedure
4.5. Regeneration Runs
4.6. Characterization Techniques
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babuji, P.; Thirumalaisamy, S.; Duraisamy, K.; Periyasamy, G. Human health risks due to exposure to water pollution: A review. Water 2023, 15, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ye, W.; Xie, M.; Seo, D.H.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y.; Van der Bruggen, B. Environmental impacts and remediation of dye-containing wastewater. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 785–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.; Nemr, A. Health and environmental impacts of dyes: Mini review. Amer. J. Environ. Sci. Engin. 2017, 1, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kant, R. Textile dyeing industry an environmental hazard. Nat. Sci. 2012, 4, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, I.; Butnaru, R. Wastewater characteristics in textile finishing mills. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2008, 7, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amte, G.K.; Mhaskar, T.V. Impact of textile-dyeing industry effluent on some haematological parameters of freshwater fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2013, 12, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa, M.L.; de Moraes, P.B.; Lopes, P.R.M.; Montagnolli, R.N.; de Angelis, D.D.F.; Bidoia, E.D. Contamination by remazol red brilliant dye and its impact in aquatic photosynthetic microbiota. Environ. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 1, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Piaskowski, K.; Świderska-Dąbrowska, R.; Zarzycki, P.K. Dye removal from water and wastewater using various physical, chemical, and biological processes. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, R.; Mulky, L. Adsorption of dyes from wastewater: A comprehensive review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2023, 10, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solayman, H.; Hossen, M.A.; Abd Aziz, A.; Yahya, N.Y.; Leong, K.H.; Sim, L.C.; Monir, M.U.; Zoh, K.D. Performance evaluation of dye wastewater treatment technologies: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Rabbi, M.R.; Abu Sufian, M.; Mahjebin, S. Review Effects of textile dyeing effluent on the environment and its treatment: A review. Eng. Appl. Sci. Lett. 2022, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngulube, T.; Gumbo, J.R.; Masindi, V.; Maity, A. An update on synthetic dyes adsorption onto clay based minerals: A state-of-art review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 191, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.N.M.A.; Sultana, N.; Sayem, A.S.M.; Smriti, S.A. Sustainable adsorbents from plant-derived agricultural wastes for anionic dye removal: A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, N.; Mao, L.; Qiu, M.; Hu, B.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; et al. Orderly porous covalent organic frameworks-based materials: Superior adsorbents for pollutants removal from aqueous solutions. Innovation 2021, 2, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, G.; Bendre, A.; Mariappan, E.; Altalhi, T.; Kigga, M.; Ching, Y.C.; Jung, H.-Y.; Bhaduri, B.; Kurkuri, M. Recent trends in the application of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for the removal of toxic dyes and their removal mechanism-a review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 31, e00378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, L. Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemo, A.A.; Adeoye, I.O.; Bello, O.S. Adsorption of dyes using different types of clay: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Ramos, R.; Jacobo-Azuara, A.; Martínez-Costa, J.I. Organoclays. Fundamentals and Applications for Removing Toxic Pollutants from Water Solution. In Porous Materials. Engineering Materials; Moreno-Piraján, J.C., Giraldo-Gutierrez, L., Gómez-Granados, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rápó, E.; Tonk, S. Factors affecting synthetic dye adsorption; desorption studies: A Review of Results from the Last Five Years (2017–2021). Molecules 2021, 26, 5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombacz, E.; Szekeres, M. Colloidal behavior of aqueous montmorillonite suspensions: The specific role of pH in the presence of indifferent electrolytes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 27, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F.; Yan, L.; Al-Faze, R.; Al-Sehimi, A. Removal enhancement of basic blue 41 by waste brick from an aqueous solution. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.M.; Al Dmour, H.; Popoola, S.A.; Oudghiri Hassani, H.; Rakass, S.; Al-Faze, R.; Kooli, F. Parameters Synthesis of Na-magadiite materials for water treatment and removal of basic blue-41: Properties and single-batch design adsorber. Inorganics 2023, 11, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakan, S.; Aghazadeh, V. The advantages of clay mineral modification methods for enhancing adsorption efficiency in wastewater treatment: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 2572–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, M.; Brown, D. Surface acidities and catalytic activities of acid-activated clays. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2004, 212, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.-P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahranowski, K.; Klimek, A.; Gaweł, A.; Olejniczak, Z.; Serwicka, E.M. Rehydration Driven Acid Impregnation of Thermally Pretreated Ca-Bentonite—Evolution of the Clay Structure. Materials 2022, 15, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komadel, P. Acid activated clays: Materials in continuous demand. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 131, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrado, K.A.; Komadel, P. Acid Activation of Bentonites and Polymer-Clay Nanocomposites. Elements 2009, 5, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.; Berger, G. Kaolinite and smectite dissolution rate in high molar KOH solutions at 35° and 80 °C. Appl. Geochem. 1998, 13, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, A.; Heath, A.; Patureau, P.; Evernden, M.; Walker, P. Alkali activation behaviour of un-calcined montmorillonite and illite clay minerals. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 166, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahranowski, K.; Klimek, A.; Gaweł, A.; Serwicka, E.M. Rehydration Driven Na-Activation of Bentonite—Evolution of the Clay Structure and Composition. Materials 2021, 14, 7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foletto, E.L.; Volzone, C.; Porto, L.M. Performance of an Argentinian acid-activated bentonite in the bleaching of soybean oil. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2003, 20, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidis, G.E.; Scott, P.W.; Dunham, A.C. Acid activation and bleaching capacity of bentonites from the islands of Milos and Chios, Aegean, Greece. Appl. Clay Sci. 1997, 12, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrage, E.; Lanson, B.; Sakharov, B.A.; Geoffroy, N.; Jacquot, E.; Drits, V.A. Investigation of dioctahedral smectite hydration properties by modeling of X-ray diffraction profiles: Influence of layer charge and charge location. Am. Mineral. 2007, 92, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, B.; Chudasama, C.D.; Jasra, R.V. Determination of structural modification in acid activated montmorillonite clay by FT IR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2006, 64, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F.; Liu, Y.; Tan, S.X.; Zheng, J. Organoclays from alkaline-treated acid-activated clays. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, P.W.; Bouazza, A. Bentonite transformations in strongly alkaline solutions. Geotext. Geomembr. 2010, 28, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozefaciuk, G.; Sarzynska, D.M. Effect of acid treatment and alkali treatment on nanopore properties of selected minerals. Clays Clay Miner. 2006, 54, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Chaker, Y.; Belarbi, E.H.; Abbas, O.; Chotard, J.N.; Abassi, H.B.; Nguyen Van Nhien, A.; El Hadri, M.; Bresson, S. XRD and ATR/FTIR investigations of various montmorillonite clays modified by monocationic and dicationic imidazolium ionic liquids. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1173, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejová, J. FTIR techniques in clay mineral studies. Vib. Spectrosc. 2003, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horri, N.; Sanz-Pérez, E.S.; Arencibia, A.; Sanz, R.; Frini-Srasra, N.; Srasra, E. Effect of acid activation on the CO2 adsorption capacity of montmorillonite. Adsorption 2020, 26, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioğlan, S.; Yüzer, H.; Koral, M. Acid activation and bleaching performance of Turkish (somas) bentonite in crude soybean oil. Part. Sci. Technol. 2010, 28, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglar, B.; Afsin, B.; Koksal, E.; Tabak, A.; Eren, E. Characterization of Unye bentonite after treatment with sulfuric acid. Quim. Nova 2012, 36, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Guo, J.; Xie, X.; Lin, H.; Li, L. A microstructural study of acid-activated montmorillonite from Choushan, China. Clay Miner. 2002, 37, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón, E.; Alba, M.D. Swelling layered minerals applications: A solid state NMR overview. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2021, 124–125, 99–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lellou, S.; Kadi, S.; Ouadjenia, F.; Benhebal, H.; Schott, J.; Marouf, R. Synthesis and application of montmorillonite nanocomposites/phenolic resins for the elimination of Basic Blue 41. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 218, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kassimi, A.; Boutouil, A.; El Himri, M.; Laamari, M.R.; El Haddad, M. Selective and competitive removal of three basic dyes from single, binary and ternary systems in aqueous solutions: A combined experimental and theoretical study. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Madanat, O.Y.; Popoola, S.A.; Al Dmour, H.; Al-Faze, R.; Kooli, F. Na-Kenyaite as Efficient Basic Blue-41 Dye Removal: Synthesis and Regeneration Studies. Water 2024, 16, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwosu, F.O.; Ajala, O.J.; Owoyemi, R.M.; Raheem, B.G. Preparation and characterization of adsorbents derived from bentonite and kaolin clays. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, C.; El Kurdi, R.; Patra, D. Effect of pH on the removal of anionic and cationic dyes using zinc curcumin oxide nano-particles as adsorbent. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 277, 125504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olakitan Ijagbemi, C.; Baek, M.H.; Kim, D.S. Montmorillonite surface properties and sorption characteristics for heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodoo, D.; Fynn, G.E.; Yawson, E.S.C.; Appiah, G.; Suleiman, N.; Yaya, A. Eco-efficient treatment of hazardous bauxite liquid-residue using acid-activated clays. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmani, Y.; Franco, D.S.P.; Georgin, J.; Lamhasni, T.; Brahmi, Y.; Oukhrib, R.; Mustapha, B.; Moussout, H.; Ouallal, H.; Sadik, A. Comparison of phenol adsorption property and mechanism onto different moroccan clays. Water 2023, 15, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.M.; Jefri, G.A.M.; Al-Faze, R.; Kooli, F. Organo acid-activated clays for water treatment as removal agent of Eosin-Y: Properties, regeneration, and single batch design absorber. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amari, A.; Gannouni, H.; Khan, M.I.; Almesfer, M.K.; Elkhaleefa, A.M.; Gannouni, A. Effect of structure and chemical activation on the adsorption properties of green clay minerals for the removal of cationic dye. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Hu, X.; Wan, Y.; Wang, S.; Gao, B. Removal of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel from aqueous solutions by alkali-modified biochar: Batch and column tests. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Kan, H.; Zheng, Y. Preparation of Acid- and Alkali-Modified Biochar for Removal of Methylene Blue Pigment. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30906–30922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Keihankhadiv, S.; Suhas; Tyagi, I.; Karri, R.R.; Chaudhary, M.; Mubarak, N.M.; Chaudhary, S.; Kumar, P.; Singh, P. Comparison and interpretation of isotherm models for the adsorption of dyes, proteins, antibiotics, pesticides and heavy metal ions on different nanomaterials and nonnano materials—A comprehensive review. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2023, 13, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, S.A.; Al Dmour, H.; Rakass, S.; Fatimah, I.; Liu, Y.; Mohmoud, A.; Kooli, F. Enhancement properties of Zr modified porous clay heterostructures for adsorption of basic-blue 41 dye: Equilibrium, regeneration, and single batch design adsorber. Materials 2022, 15, 5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F.; Liu, Y.; Abboudi, M.; Oudghiri Hassani, H.; Rakass, S.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Al Wadaani, F. Waste bricks applied as removal agent of Basic Blue 41 from aqueous solution: Base treatment and their regeneration efficiency. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humelnicu, I.; Baiceanu, A.; Ignat, M.; Dulman, V. The removal of Basic Blue 41 textile dye from aqueous solution by ad-sorption onto natural zeolitic tuff: Kinetics and thermodynamics. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 105, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougazeh, M.; Kooli, F.; Buhl, J.-C. Removal efficiency of basicblue41 by three zeolites prepared from natural Jordanian kaolinite. Clays Clay Miner. 2019, 67, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul, A.R.; Aldemir, A.; Koyuncu, H. An investigation of natural and modified diatomite performance for adsorption of Basic Blue 41: Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 229, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dmour, H.; Kooli, F.; Mohmoud, A.; Liu, Y.; Popoola, S.A. Al and Zr Porous Clay Heterostructures as Removal Agents of Basic Blue-41 Dye from an Artificially Polluted Solution: Regeneration Properties and Batch Design. Materials 2021, 14, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Messaoudi, N.; El Khomri, M.; El Mouden, A.; Bouich, A.; Jada, A.; Lacherai, A.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Mulla, S.I.; Kumar, V.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P. Regeneration and reusability of non-conventional low-cost adsorbents to remove dyes from wastewaters in multiple consecutive adsorption–desorption cycles: A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 11739–11756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momina Shahadat, M.; SuIsamil, S. Regeneration performance of clay-based adsorbents for the removal of industrial dyes: A review. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 24571–24587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Deng, S.; Shen, L.; Shan, D.; Liu, D.; Yu, G. Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents for eliminating dyes from aqueous solutions. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2017, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilzadeh Shirazi, E.; Metzger, J.W.; Fischer, K.; Hassani, A.H. Design and cost analysis of batch adsorber systems for removal of dyes from contaminated groundwater using natural low-cost adsorbents. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2020, 11, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Maheshwari, V.; Rastogi, K.; Singh, K.; Kumar, S.; Kapoor, A.; Sastry, S. Treatment of textile dyes using modified banyan leaf-based biosorbent using batch and intensified batch process: Kinetic and isotherm studies. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Batch sorber design using equilibrium and contact time data for the removal of lead. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2000, 124, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakouta, S.M.E.; Salemb, N.A.; Abdeltawab, A.A. Single and two-stage batch adsorber design for efficient uranium removal by activated carbon. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 98, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | SiO2/Al2O3 | CEC * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PG (BPG) | 5.4 (4.05) | 3.1 (2.19) | 21.4 (18.1) | 59.7 (51.2) | 2.1 (1.55) | 2.79 (2.84) | 140 |
| A-PG(0.1) (B-APG(0.1)) | 0.0 (4.34) | 2.6 (2.73) | 18.2 (21.2) | 54.7 (43.8) | 2.1 (2.13) | 3.00 (2.82) | 120 |
| A-PG(0.2) (BA-PG(0.2)) | 00 (4.65) | 2.3 (2.18) | 16.6 (16.8) | 58.9 (42.4) | 1.8 (1.39) | 3.54 (3.0) | 102 |
| A-PG(0.3) (BA-PG(0.3)) | 0.0 (4.82) | 2.0 (2.46) | 14.5 (16.9) | 66.5 (48.9) | 1.7 (1.95) | 4.58 (2.91) | 89 |
| A-PG(0.4) (BA-PG(0.4)) | 0.0 (6.25) | 1.8 (1.81) | 12.7 (13.8) | 72.1 (42.1) | 1.5 (1.58) | 5.67 (3.05) | 78 |
| A-PG(0.5) (BA-PG(0.5)) | 0.0 (7.48) | 1.0 (1.54) | 8.1 (12.7) | 83.6 (46.7) | 0.96 (1.49) | 10.32 (3.05) | 65 |
| Samples | SBET (m2/g) | T.P.V. (cc/g) | A.P.S (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PG (BPG) | 5 (3) | 0.031 (0.016) | 26.7 (22.3) |
| APG-0.1 (BAPG-0.1) | 127 (4) | 0.126 (0.031) | 4.0 (35.8) |
| APG-0.2 (BAPG-0.2) | 151 (6) | 0.224 (0.097) | 5.9 (23.3) |
| APG-0.3 (BAPG-0.3) | 216 (8) | 0.227 (0.03) | 4.2 (16.2) |
| APG-0.4 (BAPG-0.4) | 234 (10) | 0.350 (0.053) | 6.3 (20.1) |
| APG-0.5 (BAPG-0.5) | 273 (4) | 0.458 (0.02) | 6.7 (18.9) |
| Samples | qmax (mg/g) | KL (g/L) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PG (BPG) * | 81 (108) | 0.0775 (0.2066) | 0.9923 (0.9997) |
| A-PG(0.1) | 72 (99) | 0.056 (0.1084) | 0.9992 (0.9997) |
| A-PG(0.2) | 67 (91) | 0.099 (0.1305) | 0.9997 (0.9998) |
| A-PG(0.3) | 51 (86) | 0.0461 (0.105) | 0.9982 (0.9992) |
| A-PG(0.4) | 43 (81) | 0.0134 (0.0936) | 0.9802 (0.9992) |
| A-PG(0.5) | 37 (82) | 0.0072 (0.0951) | 0.9901 (0.9995) |
| Samples | 1/n | KF (mg/g) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PG (BPG) * | 0.2553 (0.0912) | 3.1652 (3.2087) | 0.8836 (0.8126) |
| A-PG(0.1) | 0.3622 (0.1675) | 2.2498 (3.7395) | 0.8912 (0.7682) |
| A-PG(0.2) | 0.2970 (0.1289) | 2.6024 (3.7750) | 0.8725 (0.9390) |
| A-PG(0.3) | 0.2512 (0.1153) | 3.6633 (3.3.7733) | 0.9134 (0.9134) |
| A-PG(0.4) | 0.3971 (0.1179) | 1.1885 (3.7132) | 0.9321 (0.9098) |
| A-PG(0.5) | 0.5618 (0.08388) | 1.1352 (3.8389) | 0.9274 (0.9274) |
| Samples | qmax (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Montmorillonite (Mt)+ | 55 | [59] |
| Saudi Local clays | 50–70 | [25] |
| Brick wastes | 60–70 | [21,60] |
| Natural zeolite | 60–70 | [61] |
| Sodalite zeolite | 39 | [62] |
| Mn-modified diatomite | 77 | [63] |
| Bentonite * | 173 | [46] |
| Alumina pillared clay | 88 | [34] |
| Zirconia pillared clay | 114 | [64] |
| Acid-activated PGs (A-PG) | 43–88 | This study |
| Base–acid-activated PGs (BA-PGs) | 92–110 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alraddadi, T.S.; Al-Faze, R.; Popoola, S.A.; Alam, M.G.; Rakass, S.; Al Dmour, H.; Kooli, F. Combination of Acid and Base Activation of Montmorillonite Clay and Its Impact on the Basic Blue-41 Removal Properties: Regeneration and Single Batch Design. Inorganics 2025, 13, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13070228
Alraddadi TS, Al-Faze R, Popoola SA, Alam MG, Rakass S, Al Dmour H, Kooli F. Combination of Acid and Base Activation of Montmorillonite Clay and Its Impact on the Basic Blue-41 Removal Properties: Regeneration and Single Batch Design. Inorganics. 2025; 13(7):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13070228
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlraddadi, Thamer S., Rawan Al-Faze, Saheed A. Popoola, Mohd Gulfam Alam, Souad Rakass, Hmoud Al Dmour, and Fethi Kooli. 2025. "Combination of Acid and Base Activation of Montmorillonite Clay and Its Impact on the Basic Blue-41 Removal Properties: Regeneration and Single Batch Design" Inorganics 13, no. 7: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13070228
APA StyleAlraddadi, T. S., Al-Faze, R., Popoola, S. A., Alam, M. G., Rakass, S., Al Dmour, H., & Kooli, F. (2025). Combination of Acid and Base Activation of Montmorillonite Clay and Its Impact on the Basic Blue-41 Removal Properties: Regeneration and Single Batch Design. Inorganics, 13(7), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13070228






