Cadmium Complexes—A Novel Family in the Coordination Chemistry of 1,2-bis(arylimino)acenaphthenes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
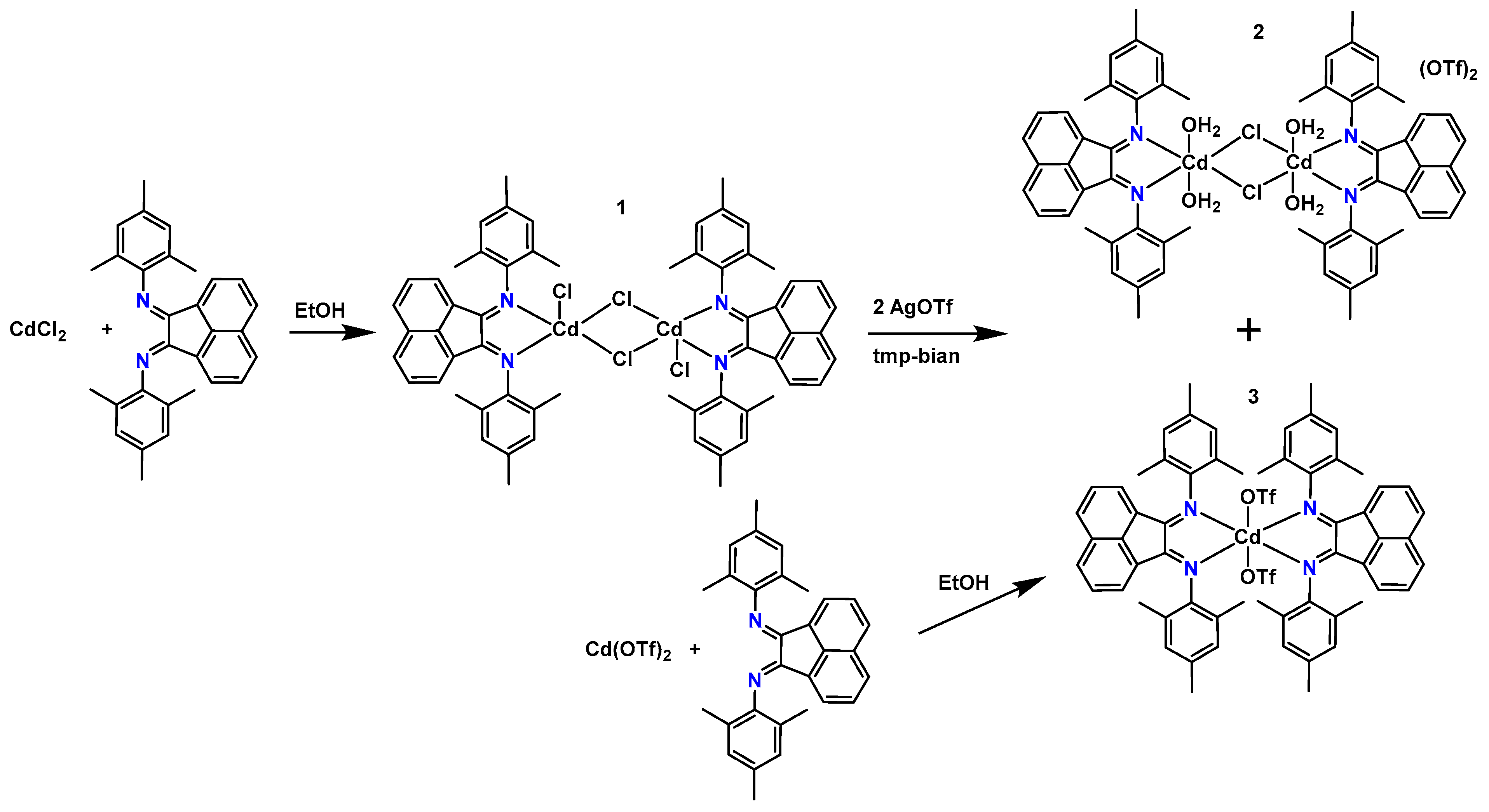
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. X-Ray Structure Description
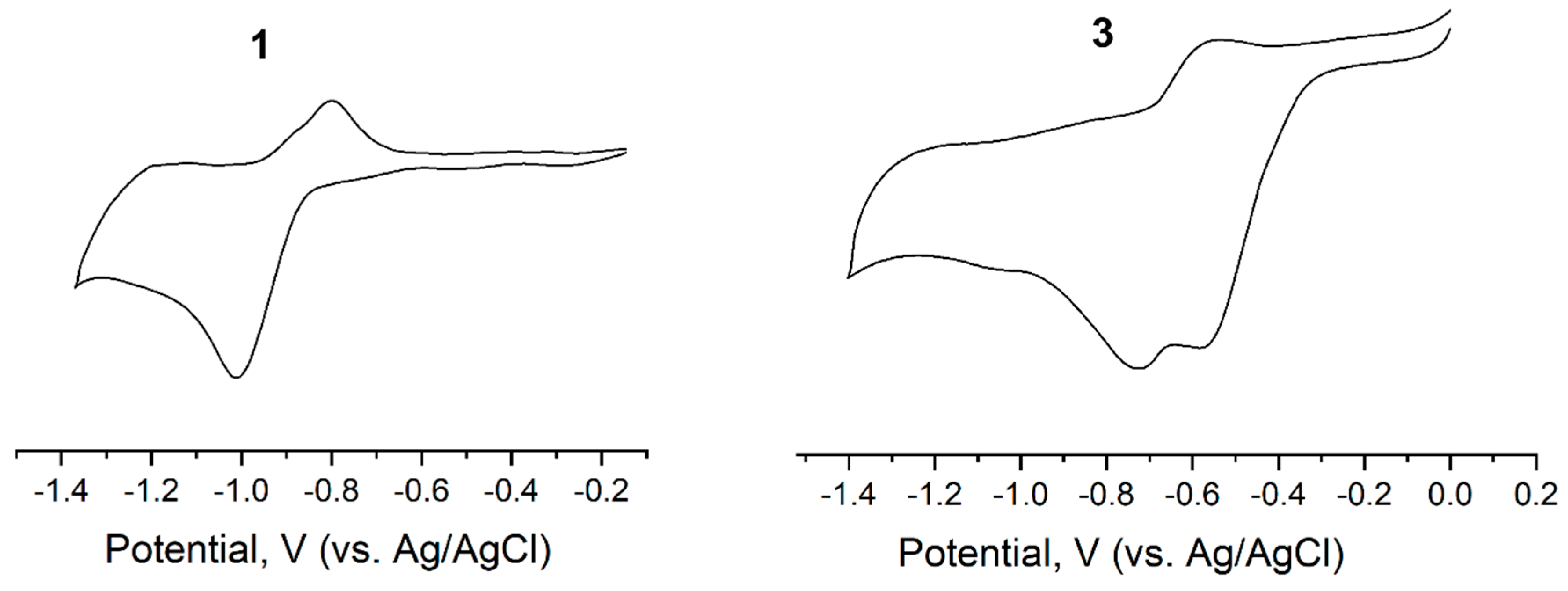
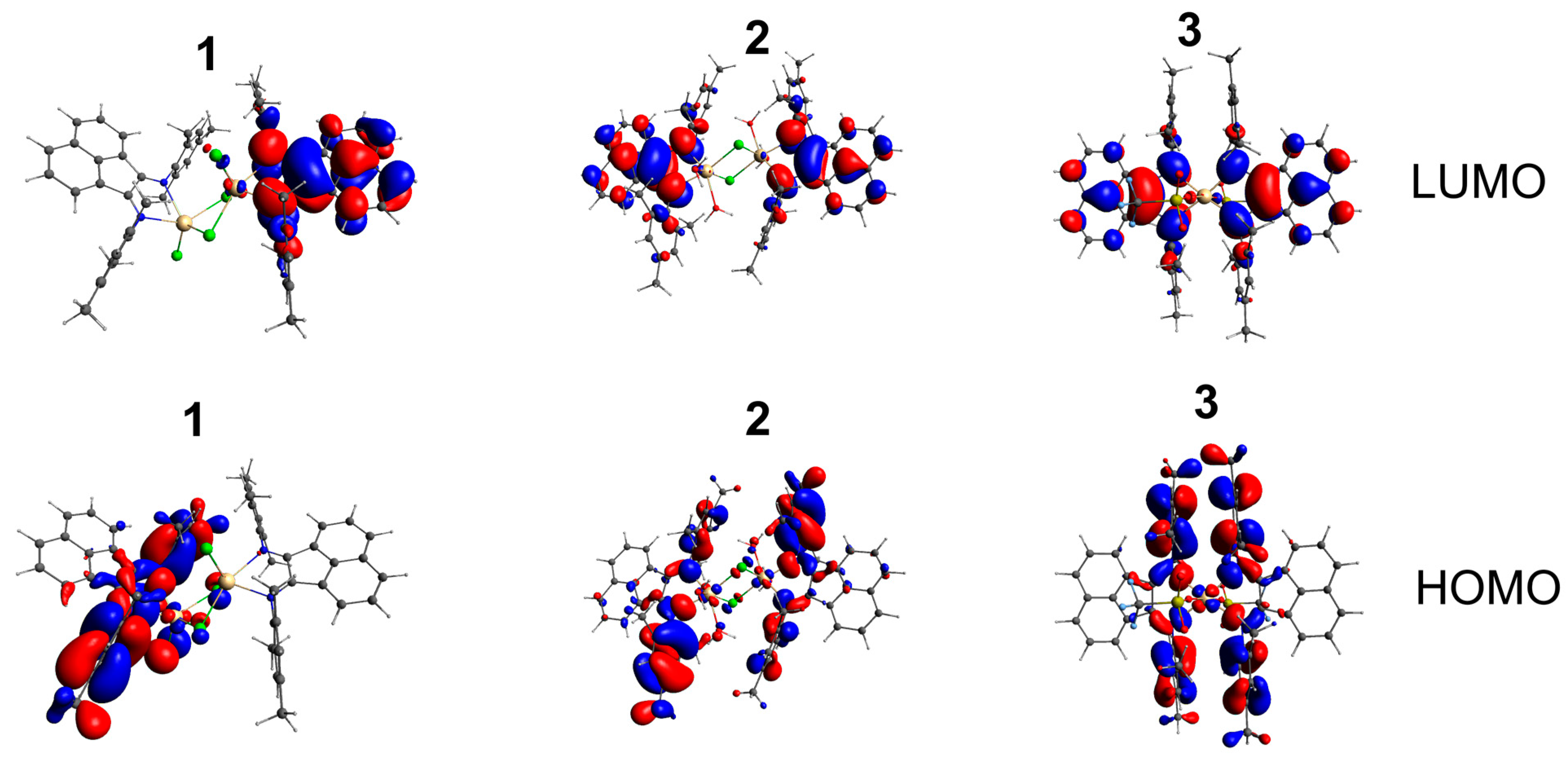
2.3. Electrochemical Properties
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
3.3. Quantum Chemical Calculations
3.4. Synthesis of [Cd2(tmp-bian)2Cl2(μ-Cl)2] (1)
3.5. Synthesis of [Cd(tmp-bian)2(OTf)2] (3)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fomenko, I.S.; Romashev, N.F.; Gushchin, A.L. Advances in the chemistry of redox-active bis(imino)acenaphthenes (BIAN): A case of transition metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 514, 215845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.J.; Vargas-Baca, I.; Cowley, A.H. Recent developments in the coordination chemistry of bis(imino)acenaphthene (BIAN) ligands with s- and p-block elements. J. Chem. Soc. Dalt. Trans. 2009, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, J.; Pölker, J.; Jacobi von Wangelin, A. Redox-active BIAN-based Diimine Ligands in Metal-Catalyzed Small Molecule Syntheses. ChemCatChem 2022, 14, e202101182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakumov, G.A.; Piskunov, A.V.; Cherkasov, V.K.; Fedushkin, I.L.; Ananikov, V.P.; Eremin, D.B.; Gordeev, E.G.; Beletskaya, I.P.; Averin, A.D.; Bochkarev, M.N.; et al. Organoelement chemistry: Promising growth areas and challenges. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2018, 87, 393–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yambulatov, D.S.; Nikolaevskii, S.A.; Kiskin, M.A.; Kholin, K.V.; Khrizanforov, M.N.; Budnikova, Y.G.; Babeshkin, K.A.; Efimov, N.N.; Goloveshkin, A.S.; Imshennik, V.K.; et al. Generation of a hetero spin complex from iron(Ii) iodide with redox active acenaphthene-1,2-diimine. Molecules 2021, 26, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komlyagina, V.I.; Romashev, N.F.; Kokovkin, V.V.; Gushchin, A.L.; Benassi, E.; Sokolov, M.N.; Abramov, P.A. Trapping of Ag+ into a Perfect Six-Coordinated Environment: Structural Analysis, Quantum Chemical Calculations and Electrochemistry. Molecules 2022, 27, 6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romashev, N.F.; Mirzaeva, I.V.; Bakaev, I.V.; Komlyagina, V.I.; Komarov, V.Y.; Fomenko, I.S.; Gushchin, A.L. Structure of a Binuclear Rhodium(I) Complex With the Acenaphthene- 1,2-Diimine Ligand. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 63, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komlyagina, V.I.; Bakaev, I.V.; Romashev, N.F.; Gushchin, A.L. Unusual Coordination Type of the Halogenated Bian Ligands in Silver(I) Complexes. Chem. Asian J. 2025, 20, e202401455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, V.; Laronha, H.; Gomes, C.S.B.; Cordas, C.M.; Brinco, J.; Freitas, F.; Gomes da Silva, M.D.R.; Avilés, T. Aerobic oxidation of benzylic alcohols catalysed by new (aryl-BIAN)copper(I) complexes: Their synthesis and structural characterization. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2023, 37, e7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Vélez, O.; O’Connor, K.S.; Lapointe, A.M.; Macmillan, S.N.; Coates, G.W. Switchable living nickel(ii) α-diimine catalyst for ethylene polymerisation. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 7607–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, X.; Luo, G.; Gao, W. Nickel complexes based on BIAN ligands: Transformation and catalysis on ethylene polymerization. Dalt. Trans. 2021, 50, 7356–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Fang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hor, T.S.A.; Weng, Z. Aryl-BIAN-ligated silver(i) trifluoromethoxide complex. Dalt. Trans. 2015, 44, 19682–19686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romashev, N.F.; Bakaev, I.V.; Komlyagina, V.I.; Sokolov, M.N.; Gushchin, A.L. Synthesis and Structure of Palladacyclopentadienyl Complex with Acenaphthene-1,2-Diimine Ligand. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 63, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jordan, R.F. Palladium-catalyzed dimerization of vinyl ethers to acetals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10254–10255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komlyagina, V.I.; Romashev, N.F.; Besprozvannykh, V.K.; Arakelyan, J.; Wu, C.; Chubarov, A.S.; Bakaev, I.V.; Soh, Y.K.; Abramov, P.A.; Cheung, K.L.; et al. Effects of Bis(imino)acenaphthene (Bian)-Derived Ligands on the Cytotoxicity, DNA Interactions, and Redox Activity of Palladium(II) Bipyridine Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 11541–11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluwer, A.M.; Koblenz, T.S.; Jonischkeit, T.; Woelk, K.; Elsevier, C.J. Kinetic and spectroscopic studies of the [palladium(Ar-bian)]-catalyzed semi-hydrogenation of 4-octyne. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15470–15480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-Teran, M.A.; Findlater, M. Redox-Active BIAN-Based Iron Complexes in Catalysis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 2022, e202200363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.A.; Vasudevan, K.; Hill, N.J.; Reeske, G.; Cowley, A.H. Facile routes to Alkyl-BIAN ligands. Chem. Commun. 2006, 2913–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.C.; Filgueiras, C.A.L.; Visentin, L.C.; Bordinhão, J.; Hörner, M. One-pot preparation, spectroscopic and structural characterization of mercury(II) complexes of bulky diimines with halides and pseudohalides. Zeitschrift Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2008, 634, 1896–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ayaan, U. Synthesis and structural studies of group 2B transition metal complexes with the bulky nitrogen ligand bis[N-(2,6-diisopropylphenyl) imino]acenaphthene. Monatshefte Chem. 2004, 135, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.A.; Lee, L.M.; Vargas-Baca, I.; Cowley, A.H. Photophysical tuning of the aggregation-induced emission of a series of para-substituted aryl bis(imino)acenaphthene zinc complexes. Dalt. Trans. 2015, 44, 11984–11996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Chen, C. Influence of Backbone Substituents on the Ethylene (Co)polymerization Properties of α-diimine Pd(II) and Ni(II) Catalysts. Organometallics 2016, 35, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundil, R.; Sokolohorskyj, A.; Hošek, J.; Cvačka, J.; Císařová, I.; Kvíčala, J.; Merna, J. Nickel and palladium complexes with fluorinated alkyl substituted α-diimine ligands for living/controlled olefin polymerization. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, A.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Liang, T.; Sun, W.H. Attaining highly branched polyethylene elastomers by employing modified α-diiminonickel(II) catalysts: Probing the effects of enhancing fluorine atom on the ligand framework towards mechanical properties of polyethylene. Polymer 2020, 187, 122089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.R.; Gomes, P.T.; Costa, S.I.; Duarte, M.T.; Branquinho, R.; Fernandes, A.C.; Chien, J.C.W.; Singh, R.P.; Marques, M.M. Highly active new α-diimine nickel catalyst for the polymerization of α-olefins. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerr, A.M.; Curry, M.R.; Chapleski, R.C.; Burroughs, J.M.; Lander, E.K.; Roy, S.; Long, B.K. Redox Potential as a Predictor of Polyethylene Branching Using Nickel α-Diimine Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Kong, S.; Shi, Q.; Mao, J.; Guo, C.; Yi, J.; Liang, T.; Sun, W.H. Enhancing the activity and thermal stability of nickel complex precatalysts using 1-[2,6-bis(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl)-4-methyl phenylimino]-2-aryliminoacenaphthylene derivatives. Organometallics 2015, 34, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldanis, R.J.; Wood, J.S.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Rausch, M.D.; Chien, J.C.W. The formation and polymerization behavior of Ni(II) α-diimine complexes using various aluminum activators. J. Organometalic Chem. 2002, 645, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrizanforova, V.V.; Fayzullin, R.R.; Musina, E.I.; Karasik, A.A.; Budnikova, Y.H. Electrochemical and catalytic properties of nickel(II) complexes with bis(imino)acenaphthene and diazadiphosphacyclooctane ligands. Mendeleev Commun. 2020, 30, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lopes, P.S.; Figueira, C.A.; Gomes, C.S.B.; Duarte, M.T.; Rosa, V.; Fliedel, C.; Avilés, T.; Gomes, P.T. Cationic and neutral (Ar-BIAN)copper(I) complexes containing phosphane and arsane ancillary ligands: Synthesis, molecular structure and catalytic behaviour in cycloaddition reactions of azides and alkynes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1404–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laricheva, Y.A.; Guan, C.; Kuratieva, N.V.; Romashev, N.F.; Gushchin, A.L. Synthesis and Structure of Manganese Complexes with N,N′-bis[(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)imino]acenaphthene. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. Khimiya 2024, 50, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ayaan, U.; Murata, F.; El-Derby, S.; Fukuda, Y. Synthesis, structural and solvent influence studies on solvatochromic mixed-ligand copper(II) complexes with the rigid nitrogen ligand: Bis[N-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)imino]acenaphthene. J. Mol. Struct. 2004, 692, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS Program for Scaling and Correction of Area Detector Data; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübschle, C.B.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Dittrich, B. ShelXle: A Qt graphical user interface for SHELXL. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spek, A.L. PLATON SQUEEZE: A tool for the calculation of the disordered solvent contribution to the calculated structure factors. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. Single-crystal structure validation with the program PLATON. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F.; Wennmohs, F.; Becker, U.; Riplinger, C. The ORCA quantum chemistry program package. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 224108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. Software update: The ORCA program system—Version 5.0. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2022, 12, e1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeweyher, E.; Ehlert, S.; Hansen, A.; Neugebauer, H.; Spicher, S.; Bannwarth, C.; Grimme, S. A generally applicable atomic-charge dependent London dispersion correction. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 150, 154122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrae, D.; Häußermann, U.; Dolg, M.; Stoll, H.; Preuß, H. Energy-adjusted ab initio pseudopotentials for the second and third row transition elements. Theor. Chim. Acta 1990, 77, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. An Improvement of the Resolution of the Identity Approximation for the Formation of the Coulomb Matrix. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F. Accurate Coulomb-fitting basis sets for H to Rn. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
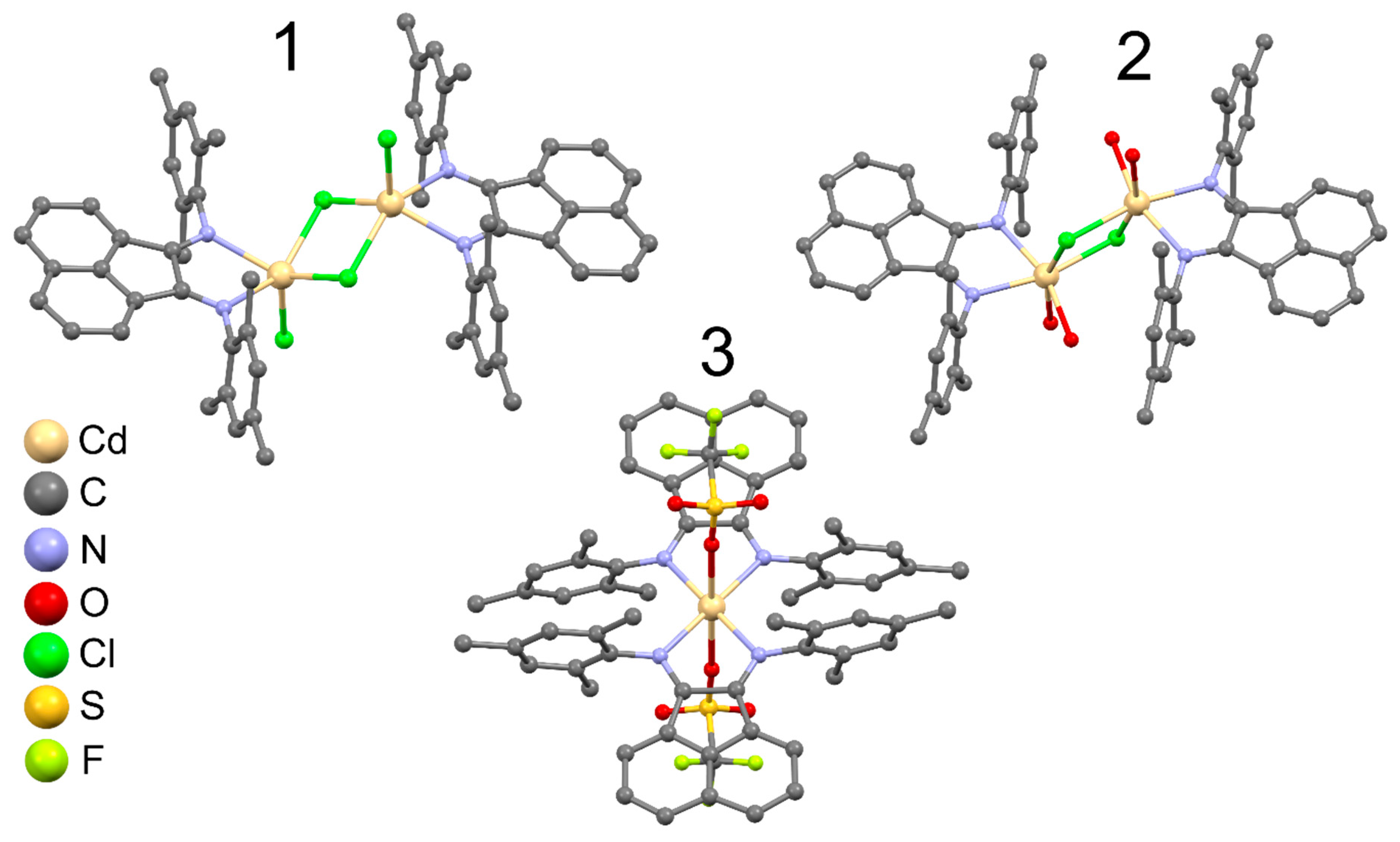
| 1•2(C2H5)2O | Distance, Å | 2 | Distance, Å | 3•1.2CH2Cl2 | Distance, Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd–N | 2.354(2) 2.427(2) | Cd–N | 2.375(3) 2.362(2) | Cd–N | 2.314(2) 2.391(3) |
| Cd–(μ-Cl) | 2.5944(8) 2.5100(7) | Cd–(μ-Cl) | 2.559(1) 2.6000(9) | Cd–O | 2.381(2) |
| Cd–Cl | 2.4211(8) | Cd–O | 2.329(2) 2.349(3) | С–N | 1.275(4) 1.288(4) |
| С–N | 1.280(3) 1.269(3) | С–N | 1.278(4) 1.271(5) | С–С | 1.515(5) |
| С–С | 1.514(3) | С–C | 1.528(5) |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HOMO | |||
| tmp-bian | 74.8% | 86.7% | 89.4% |
| Cd | 9.2% | 1.0% | 3.0% |
| Cl | 9.9% | 0.60% | - |
| LUMO | |||
| tmp-bian | 93.1% | 91.4% | 88.8% |
| Cd | 1.0% | 0.5% | 1.3% |
| Cl | 0.5% | 0.1% | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chekhov, E.V.; Bakaev, I.V.; Gukova, A.K.; Shaposhnikov, N.O.; Komlyagina, V.I.; Appazova, S.; Diyarova, B.; Darmagambet, K.; Appazov, N.; Romashev, N.F.; et al. Cadmium Complexes—A Novel Family in the Coordination Chemistry of 1,2-bis(arylimino)acenaphthenes. Inorganics 2025, 13, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13050145
Chekhov EV, Bakaev IV, Gukova AK, Shaposhnikov NO, Komlyagina VI, Appazova S, Diyarova B, Darmagambet K, Appazov N, Romashev NF, et al. Cadmium Complexes—A Novel Family in the Coordination Chemistry of 1,2-bis(arylimino)acenaphthenes. Inorganics. 2025; 13(5):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13050145
Chicago/Turabian StyleChekhov, Egor V., Ivan V. Bakaev, Alisa K. Gukova, Nikolay O. Shaposhnikov, Veronika I. Komlyagina, Saltanat Appazova, Banu Diyarova, Klara Darmagambet, Nurbol Appazov, Nikolai F. Romashev, and et al. 2025. "Cadmium Complexes—A Novel Family in the Coordination Chemistry of 1,2-bis(arylimino)acenaphthenes" Inorganics 13, no. 5: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13050145
APA StyleChekhov, E. V., Bakaev, I. V., Gukova, A. K., Shaposhnikov, N. O., Komlyagina, V. I., Appazova, S., Diyarova, B., Darmagambet, K., Appazov, N., Romashev, N. F., & Gushchin, A. L. (2025). Cadmium Complexes—A Novel Family in the Coordination Chemistry of 1,2-bis(arylimino)acenaphthenes. Inorganics, 13(5), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13050145









