Sustainable Semicrystalline/Nanocrystalline UiO-66-Type Zr-MOFs as Photodegraders of Rhodamine B
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
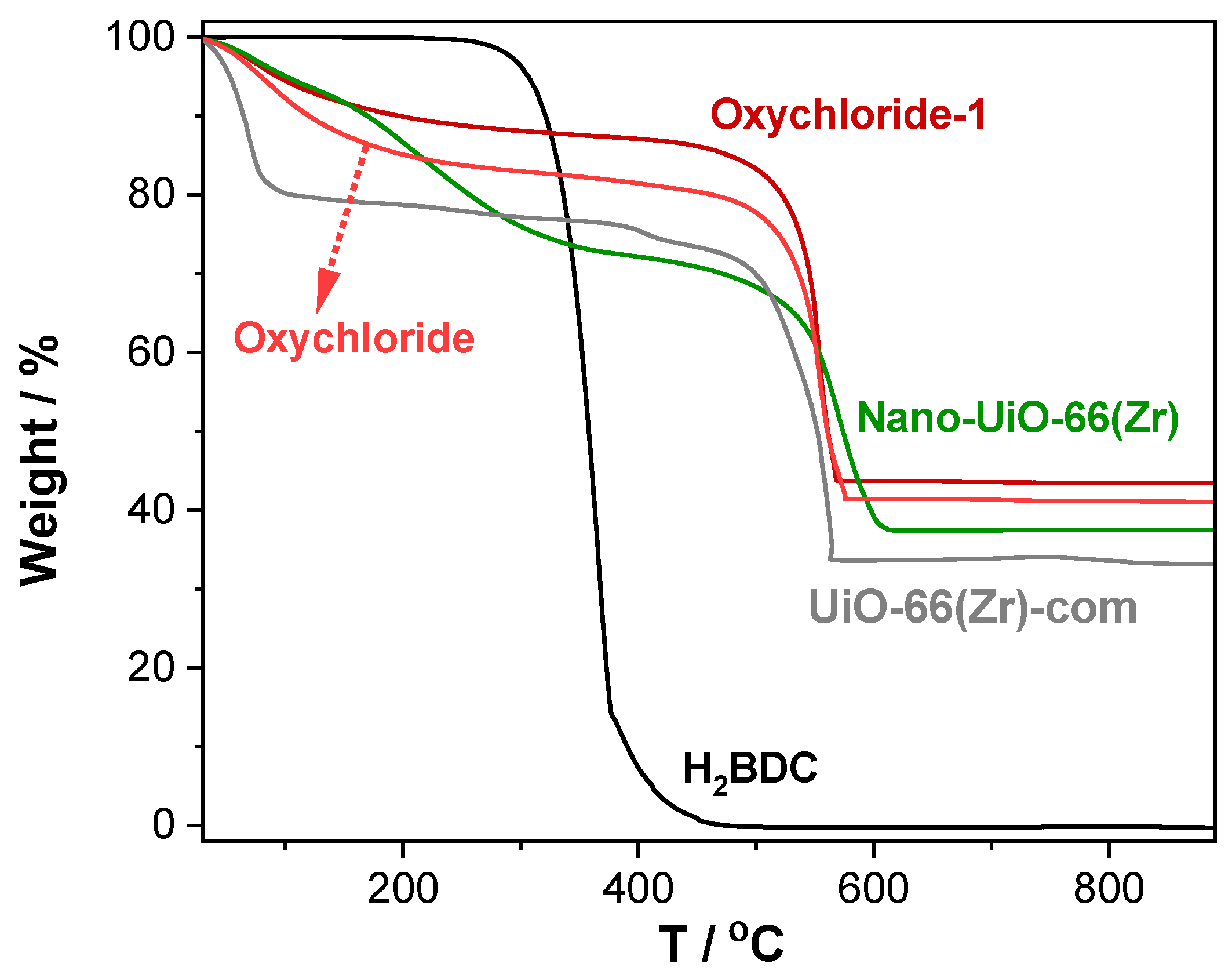
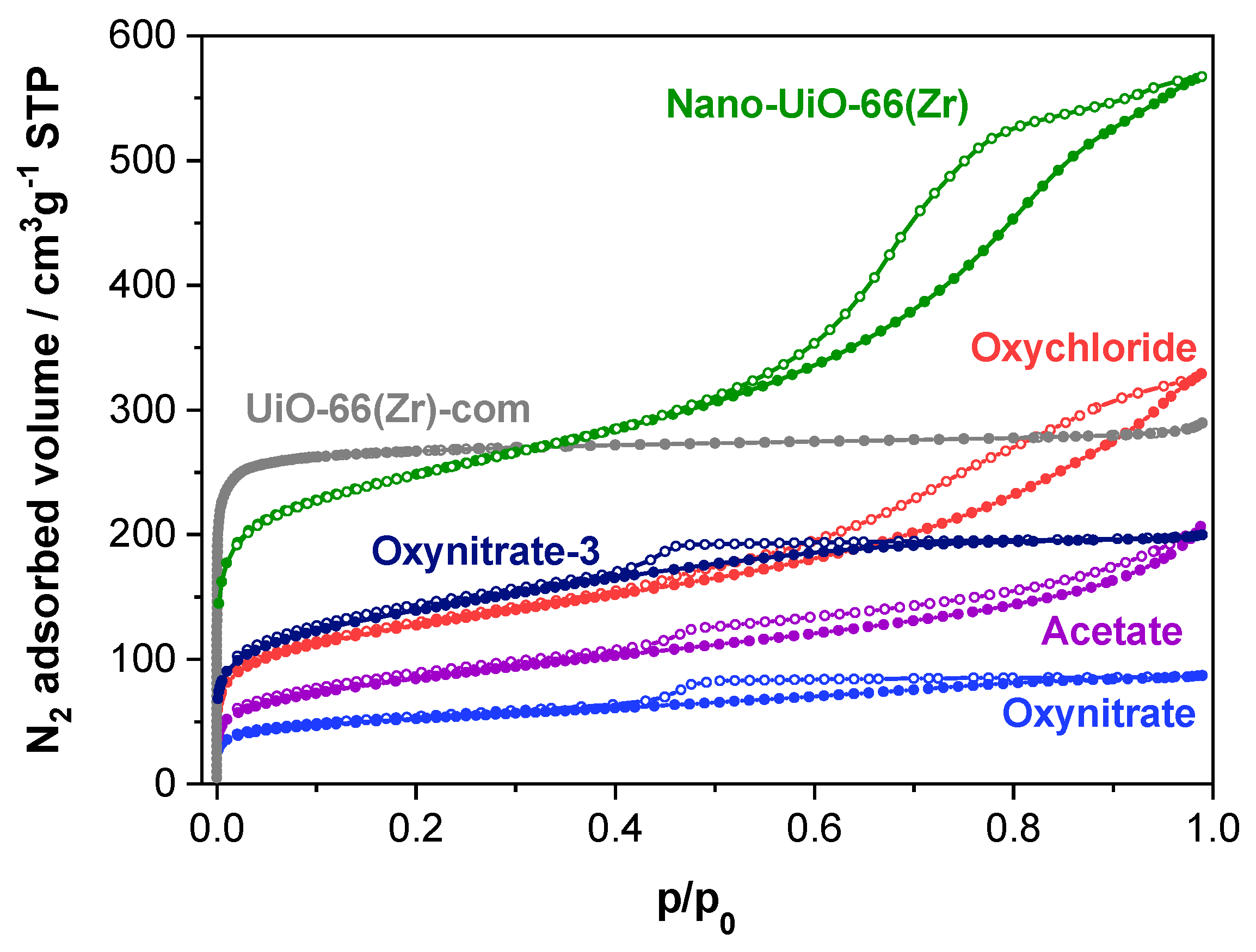
2.1. Characterization of the MOF Materials
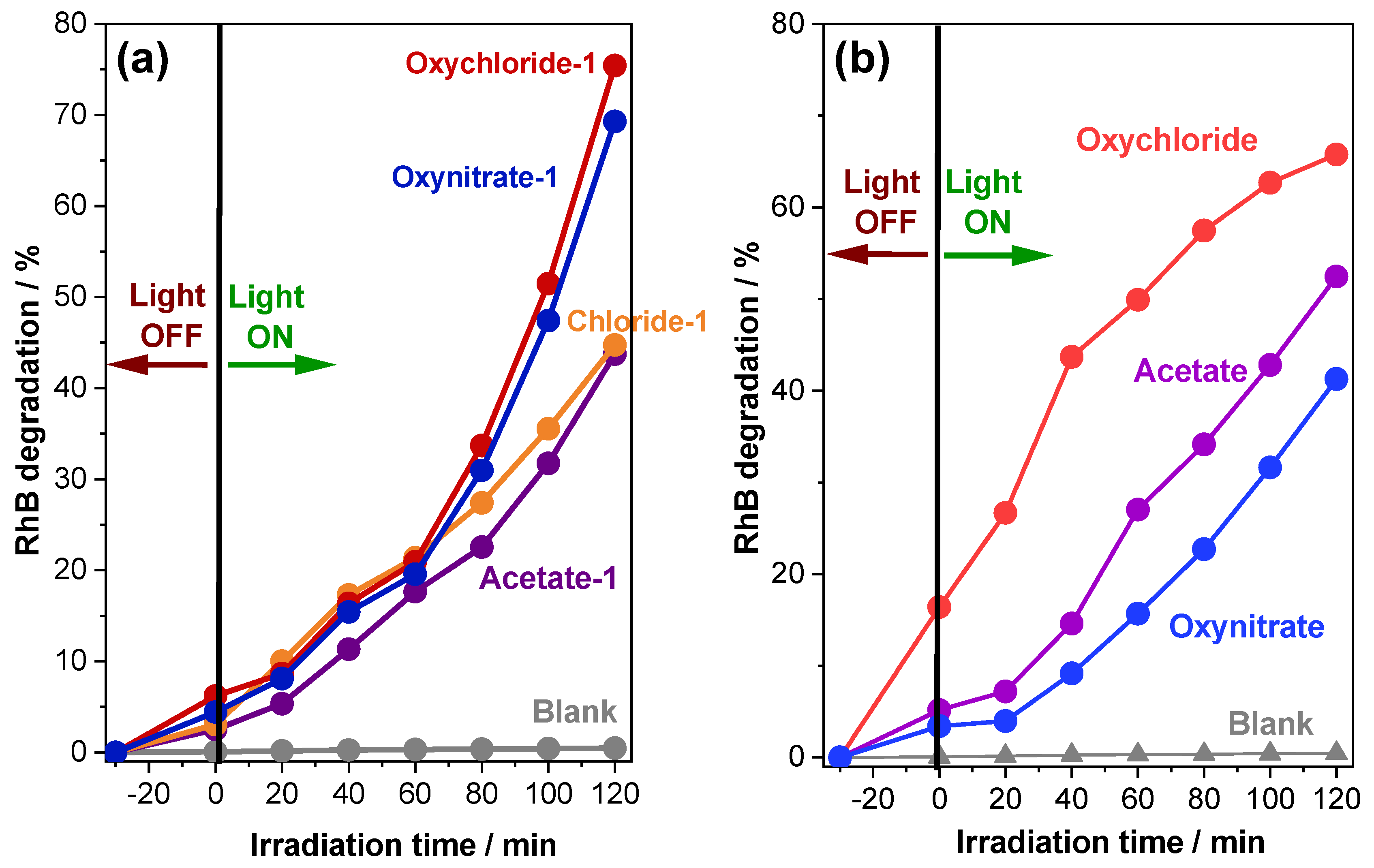
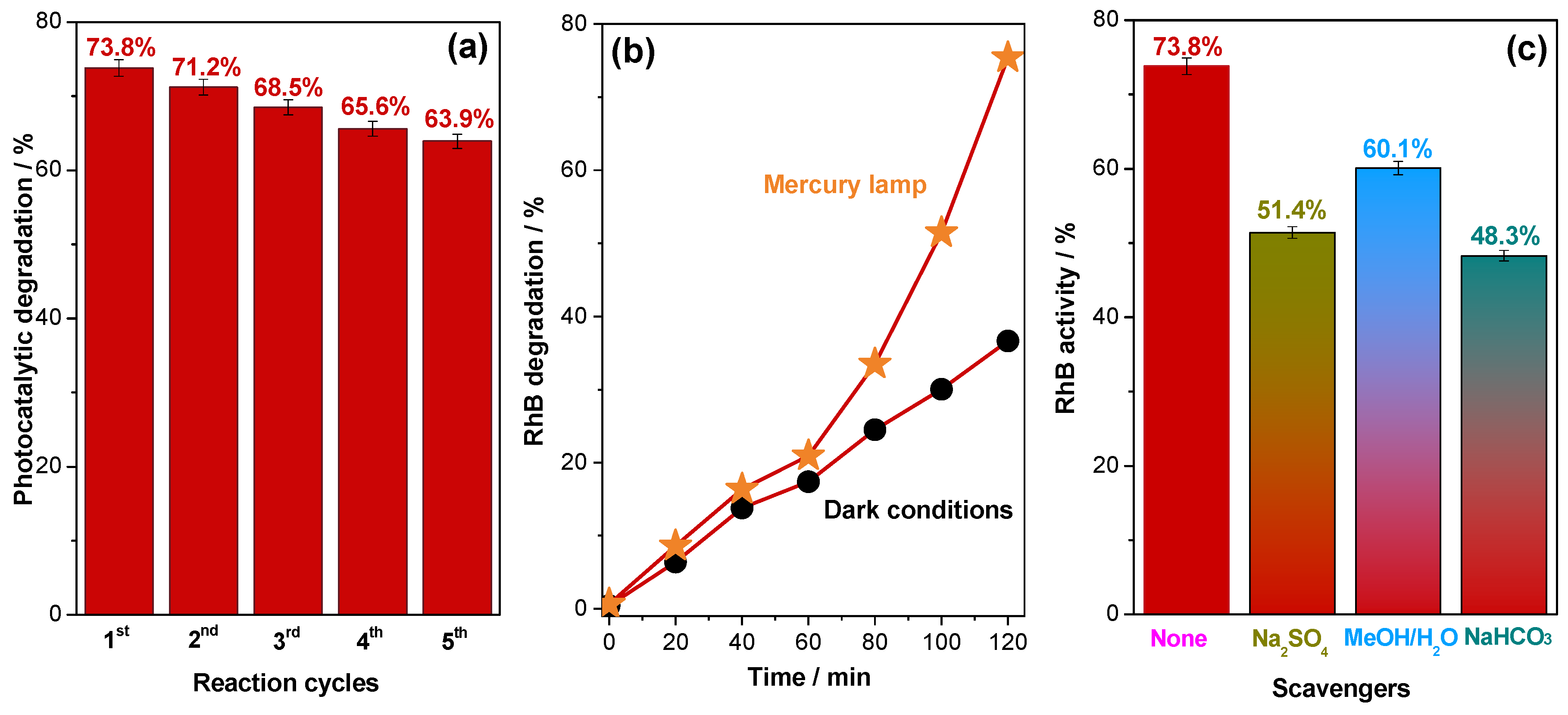
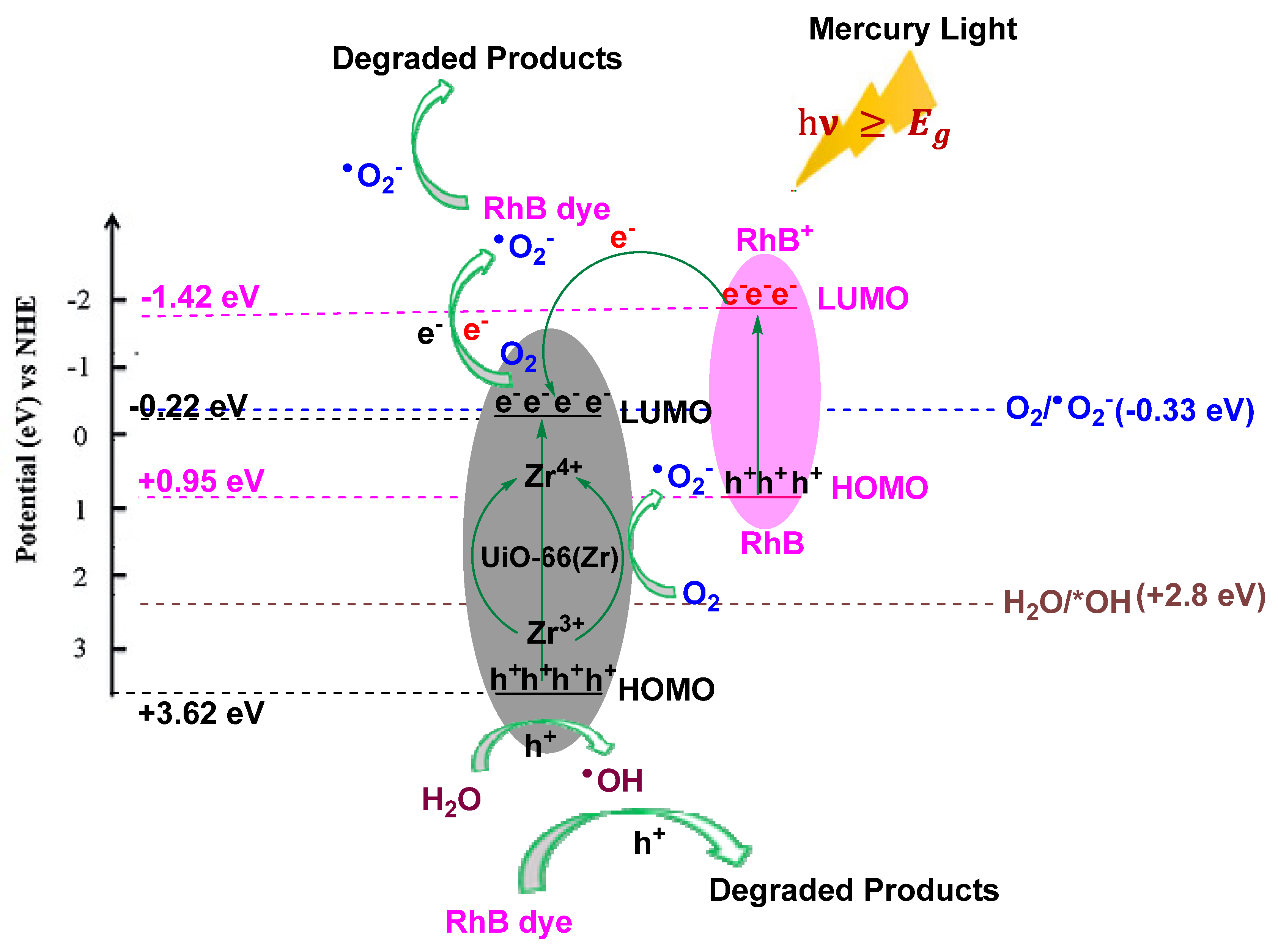
2.2. Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B Dye
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of MOFs
3.3. Materials Characterization
3.4. Photocatalytic Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavka, J.H.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Guillou, N.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K.P. A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13850–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendon, C.H.; Rieth, A.J.; Korzyński, M.D.; Dincă, M. Grand challenges and future opportunities for metal–organic frameworks. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Feng, L.; Wang, K.; Pang, J.; Bosch, M.; Lollar, C.; Sun, Y.; Qin, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, P. Stable metal–organic frameworks: Design, synthesis, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Kong, X.-J.; Li, J.-R. Chemically stable metal–organic frameworks: Rational construction and application expansion. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, F.; Tan, X.; Cai, Y.; Hu, B.; Huang, Q.; Fang, M.; Wang, X. Application of MOFs and COFs for photocatalysis in CO2 reduction, H2 generation, and environmental treatment. EnergyChem 2022, 4, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, G.; Fu, Y.; Li, N.; Hao, D.; Ma, S. Nanospace Engineering of Metal-Organic Frameworks for Heterogeneous Catalysis. ChemNanoMat 2022, 8, e202100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, J.M.; Taddesse, A.M.; Tsegaye, A.A.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M. CdS/g-C3N4/Sm-BDC MOF nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrodes as a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for malathion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 648, 158973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaye, M.; Taddesse, A.M.; Teju, E.; Sanchez-Sanchez, M.; Yassin, J.M. Preparation and adsorption behavior of Ce (III)-MOF for phosphate and fluoride ion removal from aqueous solutions. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 23860–23869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, R.; Donnadio, A.; Carta, M.; Sangregorio, C.; Tiana, D.; Vivani, R.; Taddei, M.; Costantino, F. Water-Based Synthesis and Enhanced CO2 Capture Performance of Perfluorinated Cerium-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks with UiO-66 and MIL-140 Topology. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, M.; Getachew, N.; Díaz, K.; Díaz-García, M.; Chebude, Y.; Díaz, I. Synthesis of metal–organic frameworks in water at room temperature: Salts as linker sources. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1500–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, H.-Q.; Jiao, L.; Jiang, H.-L. Metal-organic frameworks for catalysis: State of the art, challenges, and opportunities. EnergyChem 2019, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, M.R.; Islamoglu, T.; Garibay, S.J.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Room-temperature synthesis of UiO-66 and thermal modulation of densities of defect sites. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, J.M.; Taddesse, A.M.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M. Room temperature synthesis of high-quality Ce (IV)-based MOFs in water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 324, 111303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci-Camur, C.; Perez-Carvajal, J.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D. Metal acetylacetonates as a source of metals for aqueous synthesis of metal–organic frameworks. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14554–14560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chua, Y.S.; Krungleviciute, V.; Tyagi, M.; Chen, P.; Yildirim, T.; Zhou, W. Unusual and highly tunable missing-linker defects in zirconium metal–organic framework UiO-66 and their important effects on gas adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10525–10532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, A.U.; Trukhan, N.; Müller, U. Industrial applications of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, G.C.; Chavan, S.; Bordiga, S.; Svelle, S.; Olsbye, U.; Lillerud, K.P. Defect engineering: Tuning the porosity and composition of the metal–organic framework UiO-66 via modulated synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3749–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, W.; Wang, S.; Cho, D.; Auyeung, E.; Li, P.; Farha, O.K.; Mirkin, C.A. Role of modulators in controlling the colloidal stability and polydispersity of the UiO-66 metal–organic framework. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 33413–33418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillerm, V.; Gross, S.; Serre, C.; Devic, T.; Bauer, M.; Férey, G. A zirconium methacrylate oxocluster as precursor for the low-temperature synthesis of porous zirconium (IV) dicarboxylates. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Nouar, F.; Zhang, S.; Tissot, A.; Serre, C. One-Step Room-Temperature Synthesis of Metal (IV) Carboxylate Metal—Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 133, 4328–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerozal, R.T.; Pitt, T.A.; MacMillan, S.N.; Milner, P.J. High-Concentration Self-Assembly of Zirconium-and Hafnium-Based Metal–Organic Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 13273–13283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wu, Y.n. A showcase of green chemistry: Sustainable synthetic approach of zirconium-based MOF materials. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 9967–9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Kang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, D. A modulated hydrothermal (MHT) approach for the facile synthesis of UiO-66-type MOFs. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 4862–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Castano, I.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Qian, Y.; Chi, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, D. Modulator effects on the water-based synthesis of Zr/Hf metal–organic frameworks: Quantitative relationship studies between modulator, synthetic condition, and performance. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lam, I.T.Y.; Choi, S.-J.; Lu, D. Functionalized Metal–Organic Frameworks for Heavy Metal Ion Removal from Water. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 10189–10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Noh, H.; Ayoub, G.; Peterson, G.W.; Buru, C.T.; Islamoglu, T.; Farha, O.K. Scalable, room temperature, and water-based synthesis of functionalized zirconium-based metal–organic frameworks for toxic chemical removal. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z. Facile synthesis of NH2-UiO-66 modified low-cost loofah sponge for the adsorption of fluoride from water. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 929, 167270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaj, M.; Prosser, K.E.; Cohen, S.M. Room temperature aqueous synthesis of UiO-66 derivatives via postsynthetic exchange. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 8841–8845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yang, J.; Gu, J. Salting-in species induced self-assembly of stable MOFs. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 5743–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Tissot, A.; Serre, C. Metal-organic frameworks: From ambient green synthesis to applications. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2021, 94, 2623–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Vagin, S.; Kronast, A.; Rieger, B. Template mediated and solvent-free route to a variety of UiO-66 metal–organic frameworks. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102968–102971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamoglu, T.; Atilgan, A.; Moon, S.-Y.; Peterson, G.W.; DeCoste, J.B.; Hall, M.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Cerium (IV) vs zirconium (IV) based metal–organic frameworks for detoxification of a nerve agent. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 2672–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.K.; Le, V.N.; Yoo, K.S.; Song, M.; Kim, D.; Kim, J. Facile synthesis of UiO-66 (Zr) using a microwave-assisted continuous tubular reactor and its application for toluene adsorption. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 4949–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shen, K.; Li, Y. Greening the processes of metal–organic framework synthesis and their use in sustainable catalysis. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 3165–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, J.M.; Taddesse, A.M.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M. Sustainable synthesis of semicrystalline Zr-BDC MOF and heterostructural Ag3PO4/Zr-BDC/g-C3N4 composite for photocatalytic dye degradation. Catal. Today 2022, 390, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakamorė, I.; Rousseau, J.; Rousseau, C.; Monflier, E.; Szilágyi, P.Á. An ambient-temperature aqueous synthesis of zirconium-based metal–organic frameworks. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 5292–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, H.; Mouchaham, G.; Steunou, N.; Devic, T.; Serre, C. Titanium coordination compounds: From discrete metal complexes to metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3431–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, N.; Chebude, Y.; Diaz, I.; Sanchez-Sanchez, M. Room temperature synthesis of metal organic framework MOF-2. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, M.; Mayoral, A.; Diaz, I.; Sanchez-Sanchez, M. Nanoscaled M-MOF-74 materials prepared at room temperature. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 2479–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Lo, W.-S.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Chen, W.-J.; Lin, C.-H.; Shieh, F.-K. Green and rapid synthesis of zirconium metal–organic frameworks via mechanochemistry: UiO-66 analog nanocrystals obtained in one hundred seconds. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5818–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Xu, X.; Ni, B.; Wang, H.; Long, Y.; Hu, W.; Wang, X. Fast and scalable synthesis of uniform zirconium-, hafnium-based metal–organic framework nanocrystals. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 19209–19215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddei, M.; Dümbgen, K.C.; van Bokhoven, J.A.; Ranocchiari, M. Aging of the reaction mixture as a tool to modulate the crystallite size of UiO-66 into the low nanometer range. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 6411–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botas, J.A.; Calleja, G.; Sanchez-Sanchez, M.; Orcajo, M.G. Effect of Zn/Co ratio in MOF-74 type materials containing exposed metal sites on their hydrogen adsorption behaviour and on their band gap energy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2011, 36, 10834–10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Guo, X.; He, C.; Duan, C. Metal–organic frameworks: Versatile materials for heterogeneous photocatalysis. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7935–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousov, A.S.; Fukina, D.G.; Koryagin, A.V. Metal–organic framework-based heterojunction photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation: Design, construction, and performances. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 2675–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvaro, M.; Carbonell, E.; Ferrer, B.; Llabrés i Xamena, F.X.; Garcia, H. Semiconductor behavior of a metal-organic framework (MOF). Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 5106–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Yao, J. Modified metal-organic frameworks as photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 231, 317–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Sharma, V.K.; Ma, X.; Zhou, H.-C. Metal-organic frameworks for environmental applications. Cell Reports Phys. Sci. 2021, 2, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Du, L.; Li, B.; Xiao, S.; Wang, G.; Yang, X. Modified UiO-66 as photocatalysts for boosting the carbon-neutral energy cycle and solving environmental remediation issues. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 458, 214428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, T.; Taddesse, A.M.; Geresu, G.; Diaz, I.; Yassin, J.M. Boosted photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of polyaniline supported tandem nn ternary CdS-ZnO-Ag3PO4 composite under visible light irradiation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, A.; Cabrero-Antonino, M.; Navalón, S.; Álvaro, M.; Ferrer, B.; García, H. Enhancing visible-light photocatalytic activity for overall water splitting in UiO-66 by controlling metal node composition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 278, 119345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, X.-B.; Shi, Z.; Feng, S. Visible-light-responsive UiO-66 (Zr) with defects efficiently promoting photocatalytic CO2 reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 28977–28984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Cai, C. Cerium-based UiO-66 metal-organic framework for synergistic dye adsorption and photodegradation: A discussion of the mechanism. Dyes Pigm. 2021, 185, 108957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, R.; Shen, Q.; Wei, L.; Hao, D.; Li, N.; Zhou, J. Hybrid BiOBr/UiO-66-NH2 composite with enhanced visible-light driven photocatalytic activity toward RhB dye degradation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadeniz, B.; Howarth, A.J.; Stolar, T.; Islamoglu, T.; Dejanović, I.; Tireli, M.; Wasson, M.C.; Moon, S.-Y.; Farha, O.K.; Friščić, T. Benign by design: Green and scalable synthesis of zirconium UiO-metal–organic frameworks by water-assisted mechanochemistry. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15841–15849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Fang, Y. Facile synthesis of rGO@ In2S3@ UiO-66 ternary composite with enhanced visible-light photodegradation activity for methyl orange. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2019, 384, 112025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Lin, H.; Chang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, G. A series of Anderson-type polyoxometalate-based metal–organic complexes: Their pH-dependent electrochemical behaviour, and as electrocatalysts and photocatalysts. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 12465–12478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chao, F.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Ren, J.; Guo, Y.; Lou, Y. Synthesis of flower-like CuS/UiO-66 composites with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 104, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, J.M.; Taddesse, A.M.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M. Sustainable synthesis of a new semiamorphous Ti-BDC MOF material and the photocatalytic performance of its ternary composites with Ag3PO4 and g-C3N4. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 578, 151996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddesse, A.M.; Bekele, T.; Diaz, I.; Adgo, A. Polyaniline supported CdS/CeO2/Ag3PO4 nanocomposite: An “AB” type tandem nn heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2021, 406, 113005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorovski, S.; Strekowski, R.; Barbati, S.; Vione, D. Environmental implications of hydroxyl radicals (•OH). Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13051–13092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, F.A.; Majid, K. Enhancement of the photocatalytic performance and thermal stability of an iron based metal–organic-framework functionalised by Ag/Ag3PO4. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.; Faulkner, L. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals an d Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Xia, J.; Li, L.; Lv, Q.; Zhao, K.; Ahmad, M.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, S.; Ye, F.; Zhang, Q. Comprehensive enhancement of photocatalytic H2O2 generation and antibacterial efficacy on carbon nitride through a straightforward polydopamine coating strategy. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 56, 105566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumanal, M.; Ortega-Guerrero, A.; Jablonka, K.M.; Smit, B.; Tavernelli, I. Charge Separation and Charge Carrier Mobility in Photocatalytic Metal-Organic Frameworks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-P.; Gagliardi, L.; Truhlar, D.G. Cerium metal–organic framework for photocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7904–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Feng, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, H.-C.; Sharma, V.K.; Ma, X. Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) as photocatalysts for the degradation of agricultural pollutants in water. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 804–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Li, J.-R.; Lv, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Guo, G. Photocatalytic organic pollutants degradation in metal–organic frameworks. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2831–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsenis, A.D.; Puškarić, A.; Štrukil, V.; Mottillo, C.; Julien, P.A.; Užarević, K.; Pham, M.-H.; Do, T.-O.; Kimber, S.A.; Lazić, P. In situ X-ray diffraction monitoring of a mechanochemical reaction reveals a unique topology metal-organic framework. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Užarević, K.; Wang, T.C.; Moon, S.-Y.; Fidelli, A.M.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K.; Friščić, T. Mechanochemical and solvent-free assembly of zirconium-based metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2133–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, P.A.; Mottillo, C.; Friščić, T. Metal–organic frameworks meet scalable and sustainable synthesis. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 2729–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Farha, O.K.; Roberts, J.; Scheidt, K.A.; Nguyen, S.T.; Hupp, J.T. Metal–organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, O.M.; O’Keeffe, M.; Ockwig, N.W.; Chae, H.K.; Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J. Reticular synthesis and the design of new materials. Nature 2003, 423, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploskonka, A.M.; Marzen, S.E.; DeCoste, J.B. Facile synthesis and direct activation of zirconium based metal–organic frameworks from acetone. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Flores, A.M.; Sánchez-Martínez, D.; del Rocío Hernández-Romero, M.; Zarazúa-Morín, M.E.; Torres-Martínez, L.M. Visible-light-driven BaBiO3 perovskite photocatalysts: Effect of physicochemical properties on the photoactivity towards water splitting and the removal of rhodamine B from aqueous systems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2019, 368, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, H.; Chen, C.; Han, F.; Wen, C. Protonated graphitic carbon nitride coated metal-organic frameworks with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for contaminants degradation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 441, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, T.; Jia, M.; Yang, J.; Zhao, P.; Cai, K.; Ma, W.; Huang, Y. Resin modified MIL-53 (Fe) MOF for improvement of photocatalytic performance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, K.; Vinothkumar, K.; Teja, Y.; Al-Shehri, B.M.; Selvaraj, M.; Sakar, M.; Balakrishna, R.G. Ligand-mediated band structure engineering and physiochemical properties of UiO-66 (Zr) metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for solar-driven degradation of dye molecules. Colloids Surf. APhysicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 653, 129992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Jiang, J.; Chao, F.; Lou, Y.; Chen, J. Ligand modification of UiO-66 with an unusual visible light photocatalytic behavior for RhB degradation. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Z.; Wu, J. Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance of BiOBr/UiO-66 (Zr) composite for dye degradation with the assistance of UiO-66. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 39592–39600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cheng, W.; Yu, Z.; Ge, S.; Shao, Q.; Pan, D.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z. Microwave hydrothermally synthesized WO3/UiO-66 nanocomposites toward enhanced photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 1330–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yassin, J.M.; Taddesse, A.M.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M. Sustainable Semicrystalline/Nanocrystalline UiO-66-Type Zr-MOFs as Photodegraders of Rhodamine B. Inorganics 2025, 13, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13050131
Yassin JM, Taddesse AM, Sánchez-Sánchez M. Sustainable Semicrystalline/Nanocrystalline UiO-66-Type Zr-MOFs as Photodegraders of Rhodamine B. Inorganics. 2025; 13(5):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13050131
Chicago/Turabian StyleYassin, Jemal M., Abi M. Taddesse, and Manuel Sánchez-Sánchez. 2025. "Sustainable Semicrystalline/Nanocrystalline UiO-66-Type Zr-MOFs as Photodegraders of Rhodamine B" Inorganics 13, no. 5: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13050131
APA StyleYassin, J. M., Taddesse, A. M., & Sánchez-Sánchez, M. (2025). Sustainable Semicrystalline/Nanocrystalline UiO-66-Type Zr-MOFs as Photodegraders of Rhodamine B. Inorganics, 13(5), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13050131








