Noble Metal Complexes in Cancer Therapy: Unlocking Redox Potential for Next-Gen Treatments
Abstract
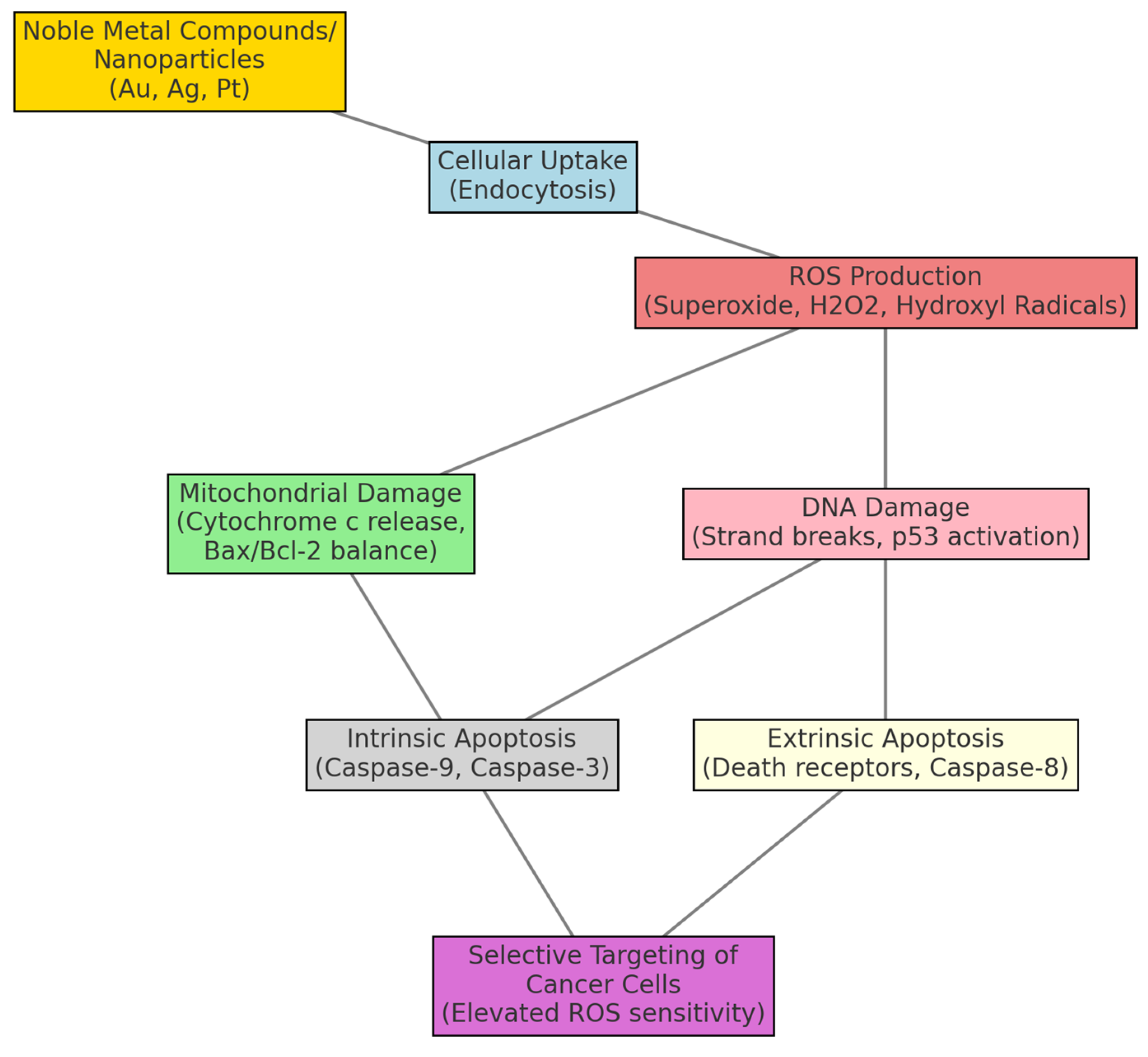
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
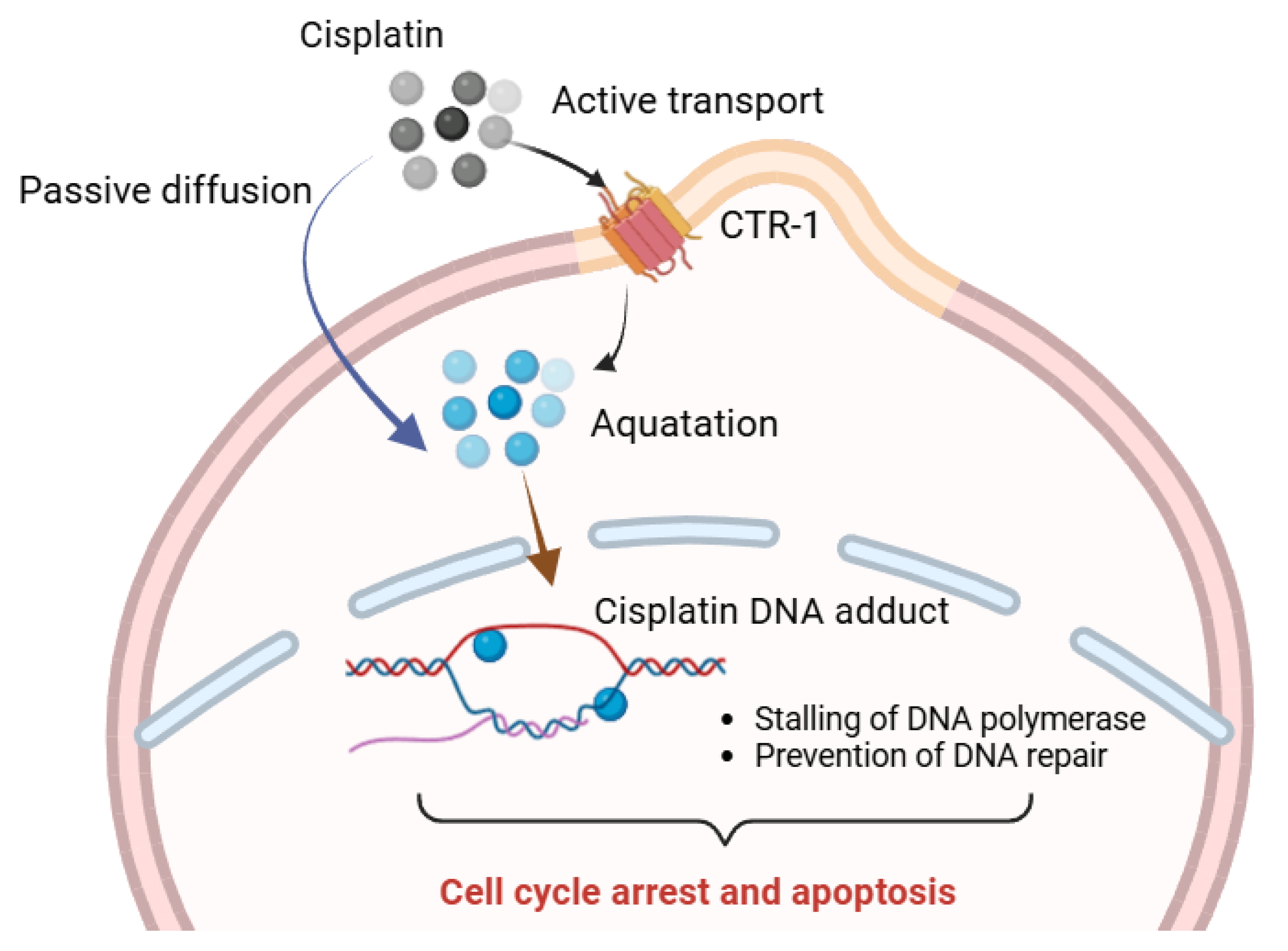
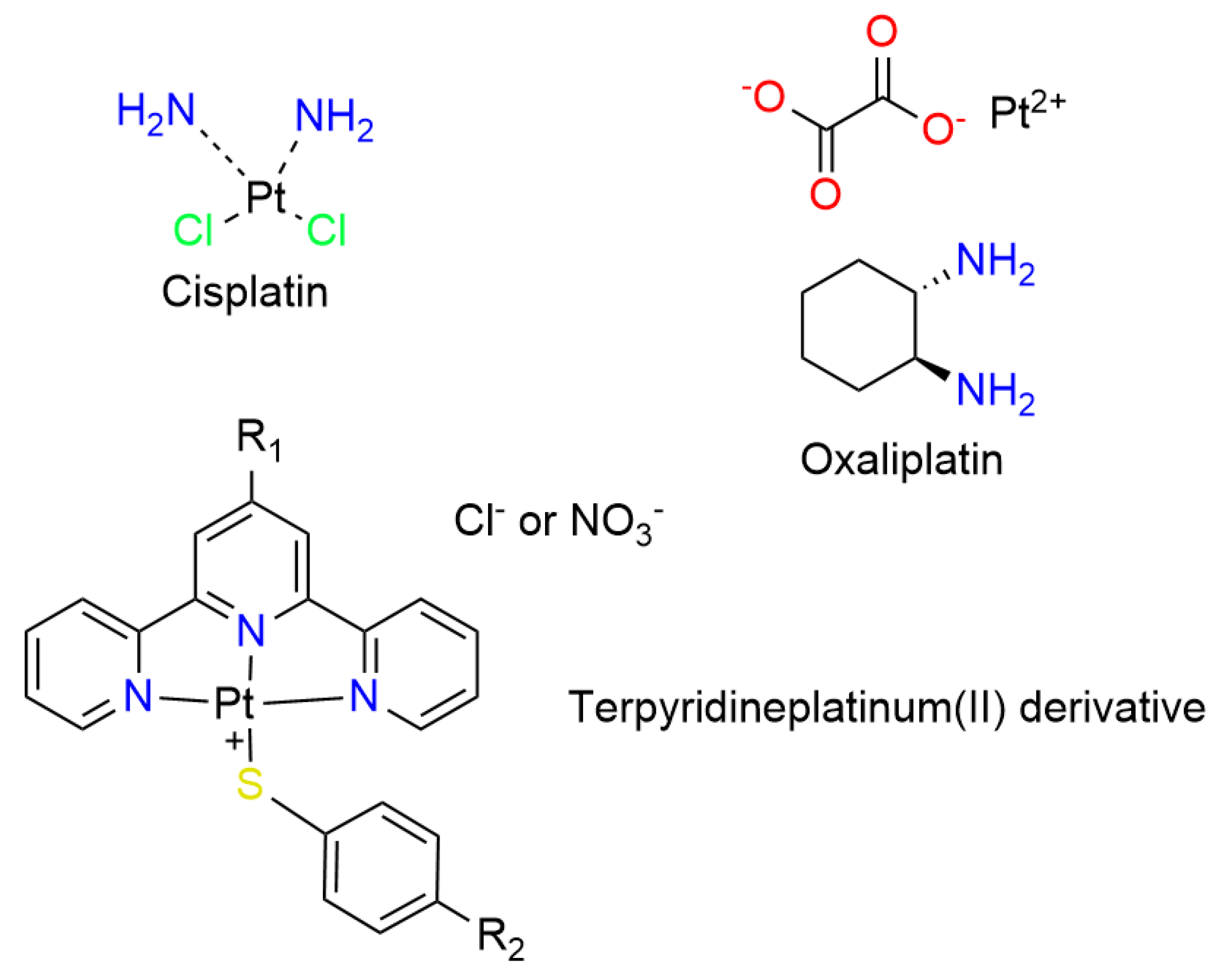
2.1. Platinum Complexes
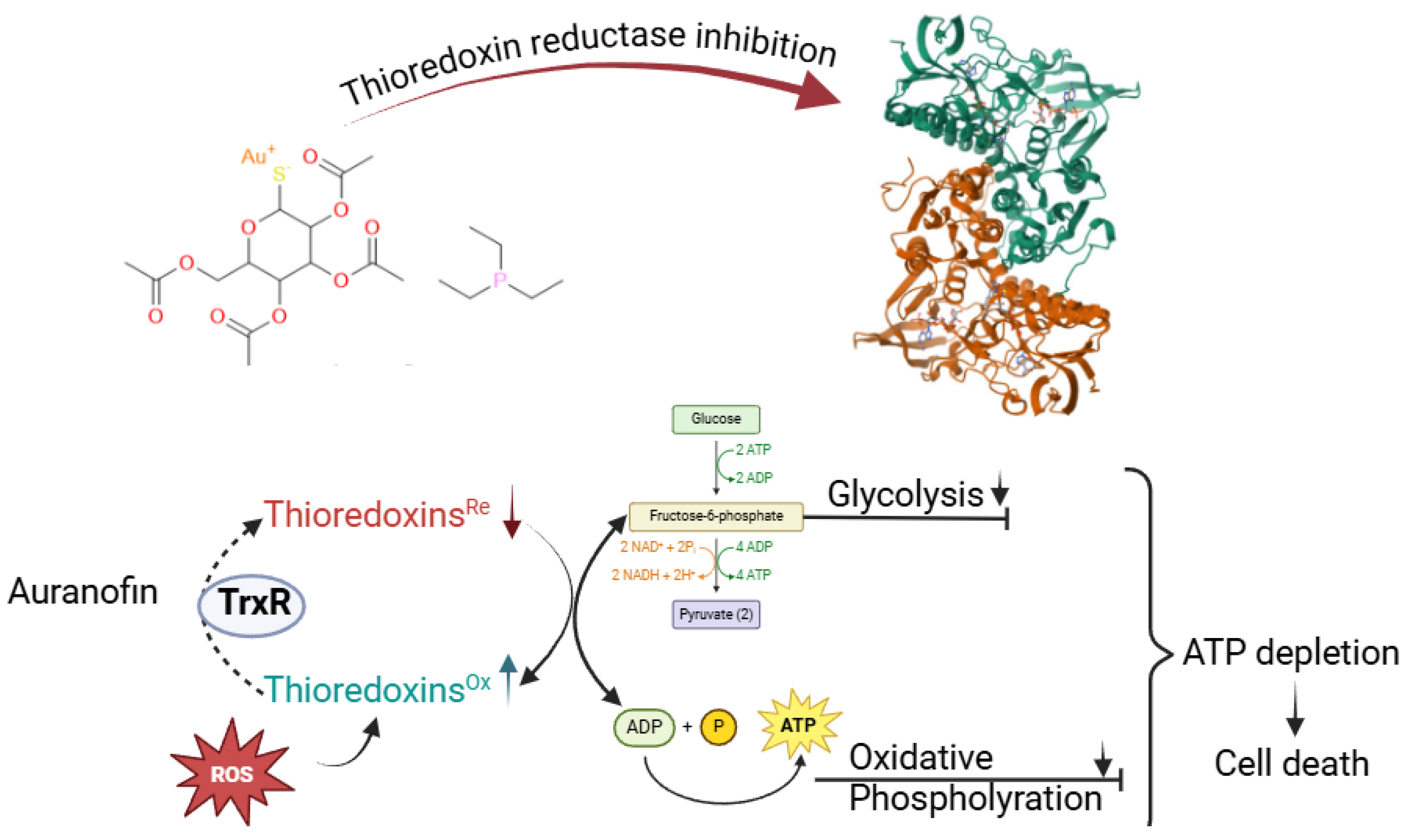
2.2. Gold Complexes: Targeting Redox Enzymes and Pathways
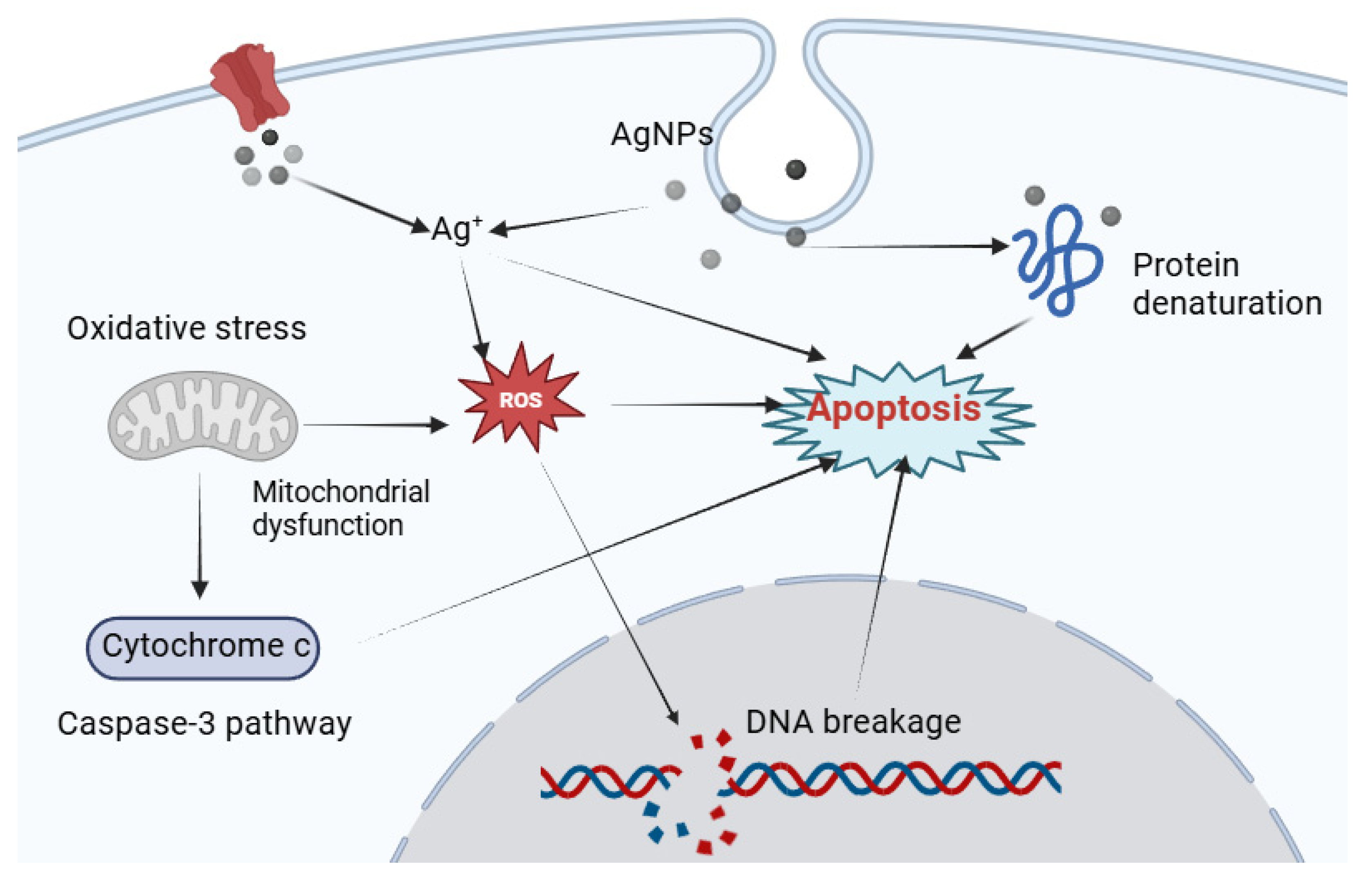
2.3. Silver Complexes: Exploiting Oxidative Stress
Ag+ + R-SH → R-S-Ag + H+
O2 + e− → O2•−
2 O2•− + 2 H+ → H2O2 + O2
H2O2 + Fe2+ → •OH + OH− + Fe3+
(Due to ROS) → Cytochrome c → Caspase activation
Caspase-9 → Caspase-3 → Apoptosis
DNA-P-Ag → DNA-P′ + Ag+ + free radicals (single-strand break in DNA)
DNA-P′ + DNA-P → DNA-P-P′ + Ag+ (double-strand break in DNA)
Ag+ + R-SH → R-S-Ag + H+
Oxidative Stress → Cellular Damage
Oxidative Damage → Caspase Activation → Apoptosis
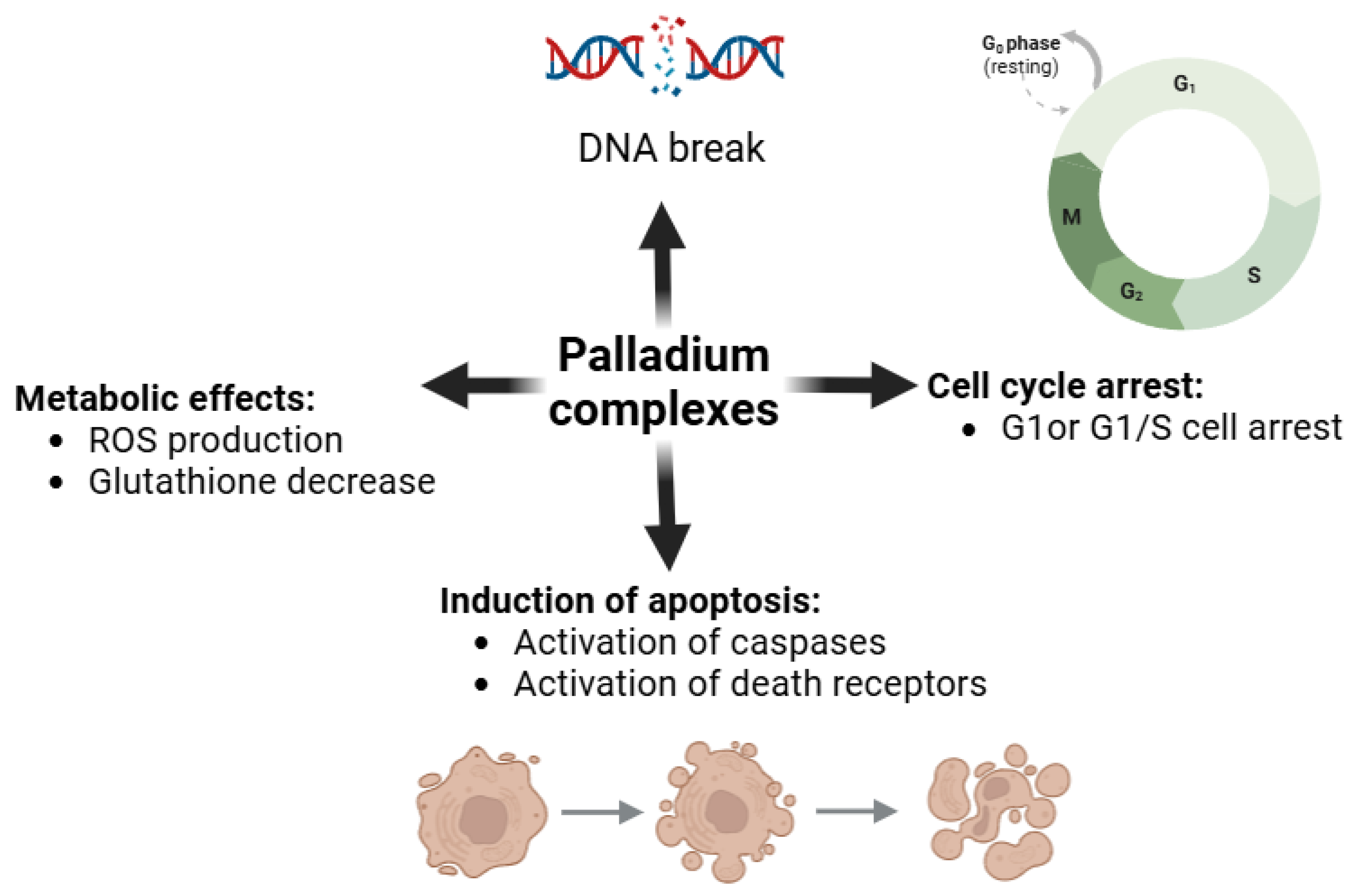
2.4. Palladium Complexes: Catalysts for Redox Disruption
3. Preparation Process—Literature Review
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahles, T.A.; Root, J.C.; Ryan, E.L. Cancer- and Cancer Treatment–Associated Cognitive Change: An Update on the State of the Science. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3675–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurhman, A.A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S. Hierarchical Nanostructured Noble Metal/Metal Oxide/Graphene-Coated Carbon Fiber: In Situ Electrochemical Synthesis and Use as Microelectrode for Real-Time Molecular Detection of Cancer Cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8129–8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruebo, M.; Vilaboa, N.; Sáez-Gutierrez, B.; Lambea, J.; Tres, A.; Valladares, M.; González-Fernández, Á. Assessment of the Evolution of Cancer Treatment Therapies. Cancers 2011, 3, 3279–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debela, D.T.; Muzazu, S.G.; Heraro, K.D.; Ndalama, M.T.; Mesele, B.W.; Haile, D.C.; Kitui, S.K.; Manyazewal, T. New Approaches and Procedures for Cancer Treatment: Current Perspectives. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 20503121211034366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.K.; Bundy, B.; Wenzel, L.; Huang, H.Q.; Baergen, R.; Lele, S.; Copeland, L.J.; Walker, J.L.; Burger, R.A. Intraperitoneal Cisplatin and Paclitaxel in Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghipour, I.; Moghbeli, M. Matrix Metalloproteinases as the Critical Regulators of Cisplatin Response and Tumor Cell Invasion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 982, 176966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Sharma, A.S.; Ahmad, W.; Zareef, M.; Hassan, M.M.; Viswadevarayalu, A.; Jiao, T.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Noble Metals Based Bimetallic and Trimetallic Nanoparticles: Controlled Synthesis, Antimicrobial and Anticancer Applications. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 51, 454–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreaden, E.C.; El-Sayed, M.A. Detecting and Destroying Cancer Cells in More than One Way with Noble Metals and Different Confinement Properties on the Nanoscale. In Nanomaterials and Neoplasms; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Lan, W.-J.; Chen, C.-H. Redox Preparation of Mixed-Valence Cobalt Manganese Oxide Nanostructured Materials: Highly Efficient Noble Metal-Free Electrocatalysts for Sensing Hydrogen Peroxide. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindoli, A.; Rigobello, M.P.; Scutari, G.; Gabbiani, C.; Casini, A.; Messori, L. Thioredoxin Reductase: A Target for Gold Compounds Acting as Potential Anticancer Drugs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 1692–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhao, G. Recent Advances in the Development of Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Kumar, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy of Human Cancers. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2019, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in Cancer Therapy: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Senovilla, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Martins, I.; Kepp, O.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Molecular Mechanisms of Cisplatin Resistance. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, S.D. Platinum Complexes of Terpyridine: Interaction and Reactivity with Biomolecules. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 1495–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Yu, C.; Ba, L.; Liu, Q.; Qian, Y.; Yang, B.; Gao, C. Anticancer Platinum-based Complexes with Non-classical Structures. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluccia, M.; Natile, G. Trans-Platinum Complexes in Cancer Therapy. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem.-Anti-Cancer Agents) 2007, 7, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause-Heuer, A.M.; Grünert, R.; Kühne, S.; Buczkowska, M.; Wheate, N.J.; Le Pevelen, D.D.; Boag, L.R.; Fisher, D.M.; Kasparkova, J.; Malina, J.; et al. Studies of the Mechanism of Action of Platinum(II) Complexes with Potent Cytotoxicity in Human Cancer Cells. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5474–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callari, M.; Aldrich-Wright, J.R.; de Souza, P.L.; Stenzel, M.H. Polymers with Platinum Drugs and Other Macromolecular Metal Complexes for Cancer Treatment. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1614–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-Y.; Chen, M.-H.; Kuo, W.-T.; Sun, Y.-J.; Lin, F.-H. The Characterization and Evaluation of Cisplatin-Loaded Magnetite–Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles (mHAp/CDDP) as Dual Treatment of Hyperthermia and Chemotherapy for Lung Cancer Therapy. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 2399–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The First Metal Based Anticancer Drug. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Livingston, M.J.; Safirstein, R.; Dong, Z. Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity: New Insights and Therapeutic Implications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcindor, T.; Beauger, N. Oxaliplatin: A Review in the Era of Molecularly Targeted Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2011, 18, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cersosimo, R.J. Oxaliplatin-Associated Neuropathy: A Review. Ann. Pharmacother. 2005, 39, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göschl, S.; Schreiber-Brynzak, E.; Pichler, V.; Cseh, K.; Heffeter, P.; Jungwirth, U.; Jakupec, M.A.; Berger, W.; Keppler, B.K. Comparative Studies of Oxaliplatin-Based Platinum (IV) Complexes in Different in Vitro and in Vivo Tumor Models. Metallomics 2017, 9, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dowd, P.D.; Sutcliffe, D.F.; Griffith, D.M. Oxaliplatin and Its Derivatives–An Overview. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 497, 215439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.; Arnold, D. Oxaliplatin: A Review of Approved Uses. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2012, 13, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei Chin, C.; Yuan Qiang Wong, D.; Jothibasu, R.; Han Ang, W. Anticancer Platinum (IV) Prodrugs with Novel Modes of Activity. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 2602–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, D. Platinum (IV) Anticancer Prodrugs–Hypotheses and Facts. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 12983–12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Han, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, F. Multicomponent Assembled Systems Based on Platinum(II) Terpyridine Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2719–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefer, D.; Cseh, K.; Hejl, M.; Roller, A.; Jakupec, M.A.; Galanski, M.S.; Keppler, B.K. Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxic Activity, and 19F NMR Spectroscopic Investigations of (OC-6-33)-Diacetato (Ethane-1, 2-Diamine) Bis (3, 3, 3-Trifluoropropanoato) Platinum (IV) and Its Platinum (II) Counterpart. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 490, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Bai, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Peng, J. N-Heterocyclic Carbene Platinum Complexes Functionalized with a Polyether Chain and Silyl Group: Synthesis and Application as a Catalyst for Hydrosilylation. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2017, 192, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.-C.; Ko, T.-P.; Su, W.-C.; Su, T.-L.; Wang, A.H.-J. Terpyridine–Platinum (II) Complexes Are Effective Inhibitors of Mammalian Topoisomerases and Human Thioredoxin Reductase 1. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; He, M.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Xue, P. Platinum–Titania Schottky Junction as Nanosonosensitizer, Glucose Scavenger, and Tumor Microenvironment-Modulator for Promoted Cancer Treatment. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 12118–12133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchenko, N. Ligand Effects on the Properties of Ultra-Small Platinum-Based Nanoparticles. Ph.D. Thesis, INSA de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. The Next Generation of Platinum Drugs: Targeted Pt(II) Agents, Nanoparticle Delivery, and Pt(IV) Prodrugs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3436–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalbari, F.H.; Telleria, C.M. The Gold Complex Auranofin: New Perspectives for Cancer Therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2021, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, R.; Burini, A.; Ricci, S.; Pellei, M.; Rigobello, M.P.; Citta, A.; Dolmella, A.; Gandin, V.; Marzano, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Azolate Gold (I) Phosphane Complexes as Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibiting Antitumor Agents. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 5307–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Ma, X.; Chang, X.; Liang, Z.; Lv, L.; Shan, M.; Lu, Q.; Wen, Z.; Gust, R.; Liu, W. Recent Development of Gold (I) and Gold (III) Complexes as Therapeutic Agents for Cancer Diseases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5518–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thota, S.; Crans, D.C. Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Pharmaceutical Sciences; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gamberi, T.; Chiappetta, G.; Fiaschi, T.; Modesti, A.; Sorbi, F.; Magherini, F. Upgrade of an Old Drug: Auranofin in Innovative Cancer Therapies to Overcome Drug Resistance and to Increase Drug Effectiveness. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1111–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capparelli, E.V.; Bricker-Ford, R.; Rogers, M.J.; McKerrow, J.H.; Reed, S.L. Phase I Clinical Trial Results of Auranofin, a Novel Antiparasitic Agent. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01947-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlos Lima, J.; Rodriguez, L. Phosphine-Gold (I) Compounds as Anticancer Agents: General Description and Mechanisms of Action. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem.-Anti-Cancer Agents) 2011, 11, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Mirsadeghi, H.A.; Abedanzadeh, S.; Yazdani, A.; Alamdarlou, A.; Babaghasabha, M.; Almansaf, Z.; Faghih, Z.; McConnell, Z.; Shahsavari, H.R. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Thiolate Gold (i) Complexes as Thioredoxin Reductase (TrxR) and Glutathione Reductase (GR) Inhibitors. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 13173–13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichibu, Y.; Negishi, Y.; Tsukuda, T.; Teranishi, T. Large-Scale Synthesis of Thiolated Au25 Clusters via Ligand Exchange Reactions of Phosphine-Stabilized Au11 Clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 13464–13465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.W.-Y.; Lok, C.-N.; Fong, T.T.-H.; Li, C.K.-L.; Yang, Z.F.; Zou, T.; Siu, A.F.-M.; Che, C.-M. A Dinuclear Cyclometalated Gold (III)–Phosphine Complex Targeting Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Vivo. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbiani, R.; Zehnder, T.N.; Mari, C.; Blacque, O.; Venkatesan, K.; Gasser, G. Anticancer Profile of a Series of Gold(III) (2-phenyl)Pyridine Complexes. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solvi, T.N.; Reiersølmoen, A.C.; Orthaber, A.; Fiksdahl, A. Studies towards Pyridine-Based N,N,O-Gold(III) Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization and Application. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 2020, 7062–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta Nagy, E.; Ronconi, L.; Nardon, C.; Fregona, D. Noble Metal-Dithiocarbamates Precious Allies in the Fight against Cancer. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1216–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronconi, L.; Giovagnini, L.; Marzano, C.; Bettìo, F.; Graziani, R.; Pilloni, G.; Fregona, D. Gold Dithiocarbamate Derivatives as Potential Antineoplastic Agents: Design, Spectroscopic Properties, and in Vitro Antitumor Activity. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 1867–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; Bertrand, B.; Hughes, D.L.; Waller, Z.A.; Schmidt, C.; Ott, I.; O’Connell, M.; Searcey, M.; Bochmann, M. Cyclometallated Au (III) Dithiocarbamate Complexes: Synthesis, Anticancer Evaluation and Mechanistic Studies. Metallomics 2018, 10, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaaslan, M.G.; Aktaş, A.; Gürses, C.; Gök, Y.; Ateş, B. Chemistry, Structure, and Biological Roles of Au-NHC Complexes as TrxR Inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 95, 103552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlagintweit, J.F.; Jakob, C.H.G.; Wilke, N.L.; Ahrweiler, M.; Frias, C.; Frias, J.; König, M.; Esslinger, E.-M.H.J.; Marques, F.; Machado, J.F.; et al. Gold(I) Bis(1,2,3-Triazol-5-Ylidene) Complexes as Promising Selective Anticancer Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 15747–15757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolbatov, I.; Umari, P.; Marrone, A. Mechanism of Action of Antitumor Au(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: A Computational Insight on the Targeting of TrxR Selenocysteine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Franco, M.; Saab, M.; Porchia, M.; Marzano, C.; Nolan, S.P.; Nahra, F.; Van Hecke, K.; Gandin, V. Unveiling the Potential of Innovative Gold(I) and Silver(I) Selenourea Complexes as Anticancer Agents Targeting TrxR and Cellular Redox Homeostasis. Chemistry 2022, 28, e202201898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Alkilany, A.M.; Huang, X.; Murphy, C.J.; El-Sayed, M.A. The Golden Age: Gold Nanoparticles for Biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2740–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giljohann, D.A.; Seferos, D.S.; Daniel, W.L.; Massich, M.D.; Patel, P.C.; Mirkin, C.A. Gold Nanoparticles for Biology and Medicine. In Spherical Nucleic Acids; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2020; pp. 55–90. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, T.; Strouse, G. Past, Present, and Future of Gold Nanoparticles. In Bio-Applications of Nanoparticles; Chan, W.C.W., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 620, pp. 34–47. ISBN 978-0-387-76712-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sztandera, K.; Gorzkiewicz, M.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandubert, V.J.; Lennox, R.B. Assessment of 4-(Dimethylamino)Pyridine as a Capping Agent for Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2005, 21, 6532–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegedhus, C.; Kovács, K.; Polgár, Z.; Regdon, Z.; Szabó, É.; Robaszkiewicz, A.; Forman, H.J.; Martner, A.; Virág, L. Redox Control of Cancer Cell Destruction. Redox Biol. 2018, 16, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, R.J. Silver (I) Complexes as Antimicrobial and Anticancer Drugs. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Ireland Maynooth, Maynooth, Ireland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Iacopetta, D.; Mariconda, A.; Saturnino, C.; Caruso, A.; Palma, G.; Ceramella, J.; Muià, N.; Perri, M.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Caroleo, M.C.; et al. Novel Gold and Silver Carbene Complexes Exert Antitumor Effects Triggering the Reactive Oxygen Species Dependent Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 2054–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Jin, X.; Tan, X.; Lou, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Singly Protonated Dehydronorcantharidin Silver Coordination Polymer Induces Apoptosis of Lung Cancer Cells via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 86, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batarseh, K.I.; Smith, M.A. Synergistic Activities of a Silver(I) Glutamic Acid Complex and Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): A Novel Antimicrobial and Chemotherapeutic Agent. CMC 2012, 19, 3635–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, C.; Hussain, S.M.; Schrand, A.M.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Hess, K.L.; Jones, R.L.; Schlager, J.J. Unique Cellular Interaction of Silver Nanoparticles: Size-Dependent Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 13608–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalil, M.A.; Yamada, T.; Fujinami, S.; Honjo, T.; Nishikawa, H. An Imidazole-Based P–N Bridging Ligand and Its Binuclear Copper (I), Silver (I) and Palladium (I) Complexes: Synthesis, Characterizations and X-Ray Structures. Polyhedron 2001, 20, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, J.E.; Wang, J.C. Imidazole Complexes of Nickel(II), Copper(II), Zinc(II), and Silver(I). Inorg. Chem. 1964, 3, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, L.; Jääskeläinen, S.; Oresmaa, L.; Haukka, M. Argentophilic Interactions in Multinuclear Ag Complexes of Imidazole Containing Schiff Bases. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 3509–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska-Lis, U.; Felczak, A.; Chęcińska, L.; Szabłowska-Gadomska, I.; Patyna, E.; Małecki, M.; Lisowska, K.; Ochocki, J. Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Silver (I) Complexes of Pyridine and (Benz) Imidazole Derivatives. X-Ray Crystal Structure of [Ag (2,6-Di(CH2OH)Py)2]NO3. Molecules 2016, 21, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, S.K.; Karunakaran, A.; Kumar, S.; Sekar, P.; Murugesan, M.; Karthikeyan, M. Silver Complexes as Anticancer Agents: A Perspective Review. Ger. J. Pharm. Biomater. 2022, 1, 6–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, M.G.; Cirri, D.; Pratesi, A.; Ciofi, L.; Marzo, T.; Guerri, A.; Nistri, S.; Dell’Accio, A.; Gamberi, T.; Severi, M.; et al. A Fluorescent Silver(I) Carbene Complex with Anticancer Properties: Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Studies. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.J.; Sadiq, M.; Baronou, E.; Cooper, P.A.; Dunnill, C.; Georgopoulos, N.T.; Latif, A.; Shepherd, S.; Shnyder, S.D.; Stratford, I.J. Preclinical Anti-Cancer Activity and Multiple Mechanisms of Action of a Cationic Silver Complex Bearing N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands. Cancer Lett. 2017, 403, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, L.; Dixit, V.; Assad, L.O.N.; Ribeiro, T.P.; Queiroz, D.D.; Kellett, A.; Casey, A.; Colleran, J.; Pereira, M.D.; Rochford, G.; et al. Water-Soluble and Photo-Stable Silver(I) Dicarboxylate Complexes Containing 1,10-Phenanthroline Ligands: Antimicrobial and Anticancer Chemotherapeutic Potential, DNA Interactions and Antioxidant Activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 159, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtekocak, F.; Demirbolat, G.M.; Cevik, O. TRAIL Conjugated Silver Nanoparticle Synthesis, Characterization and Therapeutic Effects on HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2021, 20, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Youssef, M.A.M.; Soliman, S.M.; Langer, V.; Gohar, Y.M.; Hasanen, A.A.; Makhyoun, M.A.; Zaky, A.H.; Öhrström, L.R. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Quantum Chemical Calculations, DNA Interactions, and Antimicrobial Activity of [Ag(2-Amino-3-Methylpyridine)2]NO3 and [Ag(Pyridine-2-Carboxaldoxime)NO3]. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 9788–9797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktepe, N.; Kocyigit, A.; Yukselten, Y.; Taskin, A.; Keskin, C.; Celik, H. Increased DNA Damage and Oxidative Stress Among Silver Jewelry Workers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 164, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszewski, M.; Grądzka, I.; Bartłomiejczyk, T.; Chwastowska, J.; Sommer, S.; Grzelak, A.; Zuberek, M.; Lankoff, A.; Dusinska, M.; Wojewódzka, M. Oxidative DNA Damage Corresponds to the Long Term Survival of Human Cells Treated with Silver Nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 219, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, D.F.; Netto, A.V.; Frem, R.C.; Mauro, A.E.; da Silva, P.B.; Fernandes, J.A.; Paz, F.A.; Dias, A.L.; Silva, N.C.; de Almeida, E.T. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Ternary Silver Compounds Bearing N, N-Chelating Ligands and Thiourea: X-Ray Structure of [{Ag(Bpy)(μ-Tu)}2](NO3)2 (Bpy = 2, 2′-Bipyridine; Tu = Thiourea). Polyhedron 2014, 79, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.P.; Obata, M.M.; Libardi, S.H.; Trevisan, R.O.; Deflon, V.M.; Abram, U.; Ferreira, F.B.; Costa, L.A.S.; Patrocínio, A.O.; da Silva, M.V. Gold (I) and Silver (I) Complexes Containing Hybrid Sulfonamide/Thiourea Ligands as Potential Leishmanicidal Agents. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.A.; Badshah, A.; Tahir, M.N.; Khan, E. Gold (I), Silver (I) and Copper (I) Complexes of 2, 4, 6-Trimethylphenyl-3-Benzoylthiourea; Synthesis and Biological Applications. Polyhedron 2020, 181, 114485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D. In-Situ Preparation of Epoxy/Silver Nanocomposites by Thermal Decomposition of Silver–Imidazole Complex. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3529–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, M.; Pellei, M.; Cimarelli, C.; Dias, H.R.; Marzano, C.; Tisato, F.; Porchia, M.; Gandin, V.; Santini, C. Novel Multicharged Silver (I)–NHC Complexes Derived from Zwitterionic 1, 3-Symmetrically and 1, 3-Unsymmetrically Substituted Imidazoles and Benzimidazoles: Synthesis and Cytotoxic Properties. J. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 806, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávalos, A.; Haza, A.I.; Morales, P. Manufactured Silver Nanoparticles of Different Sizes Induced DNA Strand Breaks and Oxidative DNA Damage in Hepatoma and Leukaemia Cells and in Dermal and Pulmonary Fibroblasts. Folia Biol. 2015, 61, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darviot, C.; Gosselin, B.; Martin, F.; Patskovsky, S.; Jabin, I.; Bruylants, G.; Trudel, D.; Meunier, M. Multiplexed Immunolabelling of Cancer Using Bioconjugated Plasmonic Gold–Silver Alloy Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 4385–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakiya-Teruya, M.; Palomino-Marcelo, L.; Pierce, S.; Angeles-Boza, A.M.; Krishna, V.; Rodriguez-Reyes, J.C.F. Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Conjugated with Synthetic Peptide by Click Chemistry. J. Nanopart Res. 2020, 22, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobi, A.; Willmore, A.A.; Kilk, K.; Sidorenko, V.; Braun, G.B.; Soomets, U.; Sugahara, K.N.; Ruoslahti, E.; Teesalu, T. Silver Nanocarriers Targeted with a CendR Peptide Potentiate the Cytotoxic Activity of an Anticancer Drug. Adv. Ther. 2021, 4, 2000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollok, N.E.; Rabin, C.; Smith, L.; Crooks, R.M. Orientation-Controlled Bioconjugation of Antibodies to Silver Nanoparticles. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 3078–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, M.A.; Abu-Youssef, M.A.; Soliman, S.M.; Haukka, M.; Al-Majid, A.M.; Barakat, A.; Badr, A.M. Synthesis, X-Ray Structure, Hirshfeld, and Antimicrobial Studies of New Ag (I) Complexes Based on Pyridine-Type Ligands. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1264, 133210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Dai, X.; Fang, G.; Wu, R.; Zhao, L.; Ma, X.; Tian, X.; Lee, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C. Palladium Concave Nanocrystals with High-Index Facets Accelerate Ascorbate Oxidation in Cancer Treatment. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolengovski, E.L.; Fayzullin, R.R.; Kholin, K.V.; Voloshina, A.D.; Lyubina, A.P.; Sapunova, A.S.; Shamsutdinova, L.R.; Rizvanov, I.K.; Sinyashin, O.G.; Budnikova, Y.H. Stable Cyclometallated Palladium Complexes of Arylamides: Synthesis, Redox and Anticancer Activities. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 27, e202400426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, A.; Marzo, T.; Scaletti, F.; Massai, L.; Bartoli, G.; Hoogenboom, R.; Messori, L.; Van Deun, R.; Van Hecke, K. New Platinum(II) and Palladium(II) Complexes with Substituted Terpyridine Ligands: Synthesis and Characterization, Cytotoxicity and Reactivity towards Biomolecules. Biometals 2019, 32, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eryazici, I.; Moorefield, C.N.; Newkome, G.R. Square-Planar Pd(II), Pt(II), and Au(III) Terpyridine Complexes: Their Syntheses, Physical Properties, Supramolecular Constructs, and Biomedical Activities. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 1834–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.; Schubert, U.S. Metal-Terpyridine Complexes in Catalytic Application—A Spotlight on the Last Decade. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 2890–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenko, E.A.; Baykov, S.V.; Novikov, A.S.; Boyarskiy, V.P. Nucleophilic Properties of the Positively Charged Metal Center in the Solid State Structure of Palladium (II)-Terpyridine Complex. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1199, 126957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Bi, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, W.; Wei, D.; Li, T.; Xu, W.; Liu, M.; Wu, Y. Terpyridine-Based Pd (II)/Ni (II) Organometallic Framework Nano-Sheets Supported on Graphene Oxide—Investigating the Fabrication, Tuning of Catalytic Properties and Synergetic Effects. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23080–23090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezza, M.; Dou, Q.P.; Xiao, Y.; Samouei, H.; Rashidi, M.; Samari, F.; Hemmateenejad, B. In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Activities and DNA Binding Mode of Five Coordinated Cyclometalated Organoplatinum(II) Complexes Containing Biphosphine Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6166–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, I.; Sirajuddin, M.; Nadeem, S.; Tirmizi, S.A.; Imad, R.; Sajjad, W. Synthesis, Spectral Characterization and Evaluation of Biological Properties of Pd (II) Tris-4-Cholorophenyl Phosphine Complexes of Thioureas and Heterocyclic Thiones. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2018, 40, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-H.; Shih, W.-C.; Chang, H.C.; Kuo, Y.-Y.; Hung, W.-C.; Ong, T.-G.; Li, W.-S. Preparation and Characterization of Amino-Linked Heterocyclic Carbene Palladium, Gold, and Silver Complexes and Their Use as Anticancer Agents That Act by Triggering Apoptotic Cell Death. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 5245–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romashev, N.F.; Abramov, P.A.; Bakaev, I.V.; Fomenko, I.S.; Samsonenko, D.G.; Novikov, A.S.; Tong, K.K.H.; Ahn, D.; Dorovatovskii, P.V.; Zubavichus, Y.V.; et al. Heteroleptic Pd(II) and Pt(II) Complexes with Redox-Active Ligands: Synthesis, Structure, and Multimodal Anticancer Mechanism. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 2105–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, E.Z.; Divsalar, A.; Saboury, A.A.; Khaleghizadeh, S.; Mansouri-Torshizi, H.; Kostova, I. Palladium Complexes: New Candidates for Anti-Cancer Drugs. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2016, 13, 967–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtek, M.; Marques, M.P.M.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Mota-Filipe, H.; Diniz, C. Anticancer Activity of Palladium-Based Complexes against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

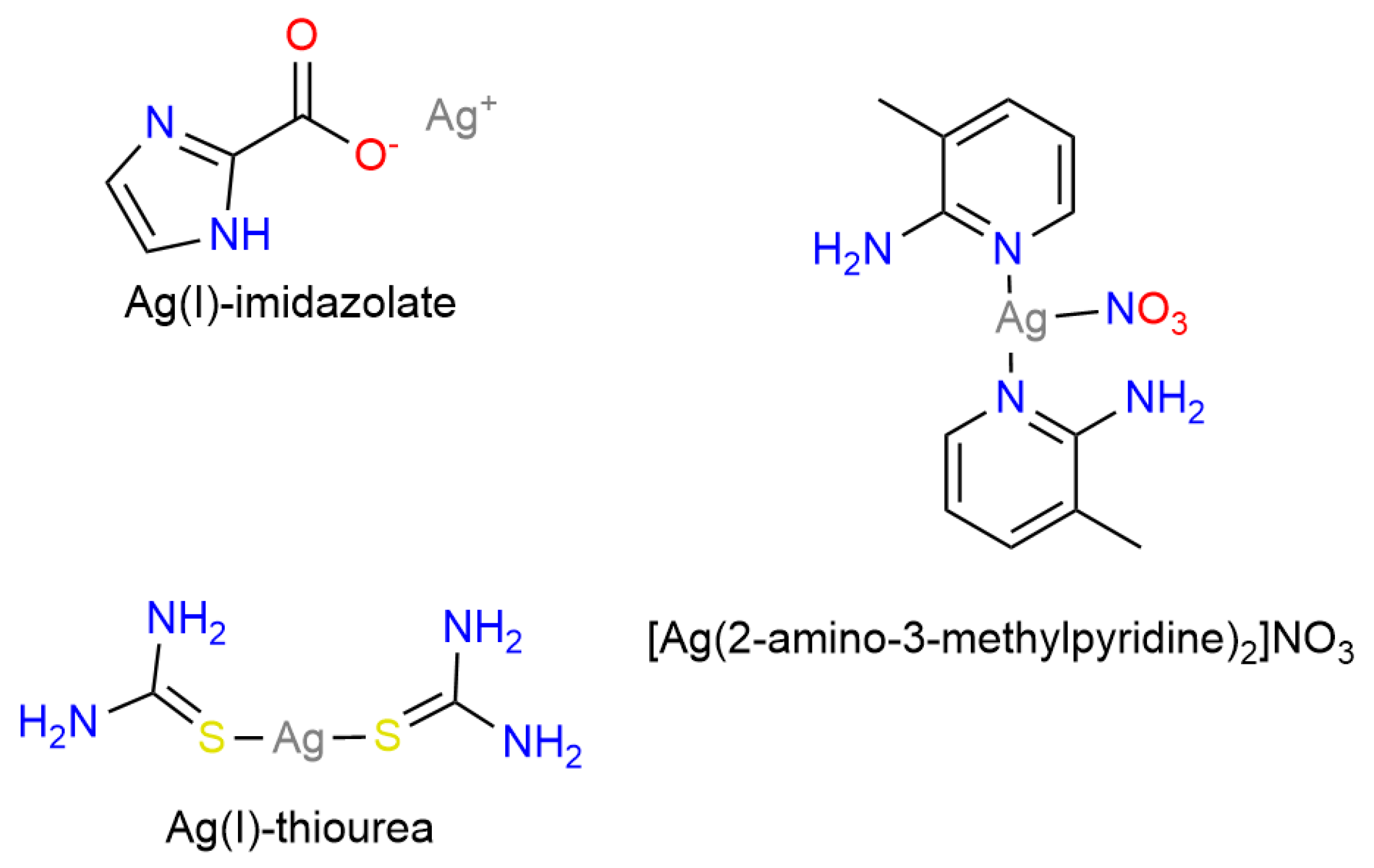

| Platinum Complex | Primary Target | Redox Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin | DNA (guanine residues) | ROS generation, DNA damage | [12,20,21,22] |
| Oxaliplatin | DNA, ROS pathways | Oxidative stress, apoptosis | [23,24,25,26,27] |
| Pt(IV) prodrugs | Tumor-specific reduction | Redox-sensitive reduction, ROS activation | [28,29] |
| Gold Complex | Mechanism | Key Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auranofin | TrxR inhibition | ROS generation, selective redox disruption, apoptosis | [41,42] |
| Au (III)-phosphine | ROS generation, DNA binding | Mitochondrial dysfunction, DNA binding, apoptosis | [43] |
| Au(I)-thiolates | ROS generation, mitochondrial damage | ROS-induced mitochondrial damage, apoptosis | [44,45] |
| Au(I)-NHC complexes | Redox cycling, DNA intercalation | ROS generation, selective cytotoxicity, apoptosis | [46] |
| Au(III)-pyridine | DNA interaction, oxidative stress | DNA intercalation, ROS-induced apoptosis | [47,48] |
| Au(III)-dithiocarbamates | Metal ion exchange, ROS generation | ROS-induced DNA damage, apoptosis | [49,50,51] |
| Silver Complex | Primary Mechanism | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag(I)-thiourea | ROS-mediated DNA damage | Lung, breast | [79,80,81] |
| Ag(I)-imidazolate | Oxidative stress, apoptosis | Prostate, colon | [82,83] |
| AgNPs | Amplified ROS, mitochondrial dysfunction | Colon, cervical, breast | [84,85] |
| Ag(I)-peptide/antibody conjugates | ROS generation, selective targeting | Various cancers (lung, breast) | [86,87,88] |
| Palladium Complex | Mechanism of Action | Target Cells/Cancer Types | Key References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pd(II)-terpyridine complexes | ROS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis | Breast cancer, colorectal cancer | [92] |
| Pd(II)-terpyridine complexes | DNA binding, oxidative stress-induced apoptosis | Ovarian cancer, lung cancer | [96] |
| Pd(II) complexes with phosphine ligands | DNA intercalation, ROS generation | Melanoma, liver cancer | [97] |
| Pd(II) complexes with heterocyclic ligands | Redox cycling, ROS production | Pancreatic cancer, breast cancer | [98,99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefanache, A.; Miftode, A.M.; Constantin, M.; Bogdan Goroftei, R.E.; Olaru, I.; Gutu, C.; Vornicu, A.; Lungu, I.I. Noble Metal Complexes in Cancer Therapy: Unlocking Redox Potential for Next-Gen Treatments. Inorganics 2025, 13, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13020064
Stefanache A, Miftode AM, Constantin M, Bogdan Goroftei RE, Olaru I, Gutu C, Vornicu A, Lungu II. Noble Metal Complexes in Cancer Therapy: Unlocking Redox Potential for Next-Gen Treatments. Inorganics. 2025; 13(2):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13020064
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefanache, Alina, Alina Monica Miftode, Marcu Constantin, Roxana Elena Bogdan Goroftei, Iulia Olaru, Cristian Gutu, Alexandra Vornicu, and Ionut Iulian Lungu. 2025. "Noble Metal Complexes in Cancer Therapy: Unlocking Redox Potential for Next-Gen Treatments" Inorganics 13, no. 2: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13020064
APA StyleStefanache, A., Miftode, A. M., Constantin, M., Bogdan Goroftei, R. E., Olaru, I., Gutu, C., Vornicu, A., & Lungu, I. I. (2025). Noble Metal Complexes in Cancer Therapy: Unlocking Redox Potential for Next-Gen Treatments. Inorganics, 13(2), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13020064









