Recent Trends in the Design of Ruthenium Homometallic Polynuclear Complexes with Bioactive Ligands for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
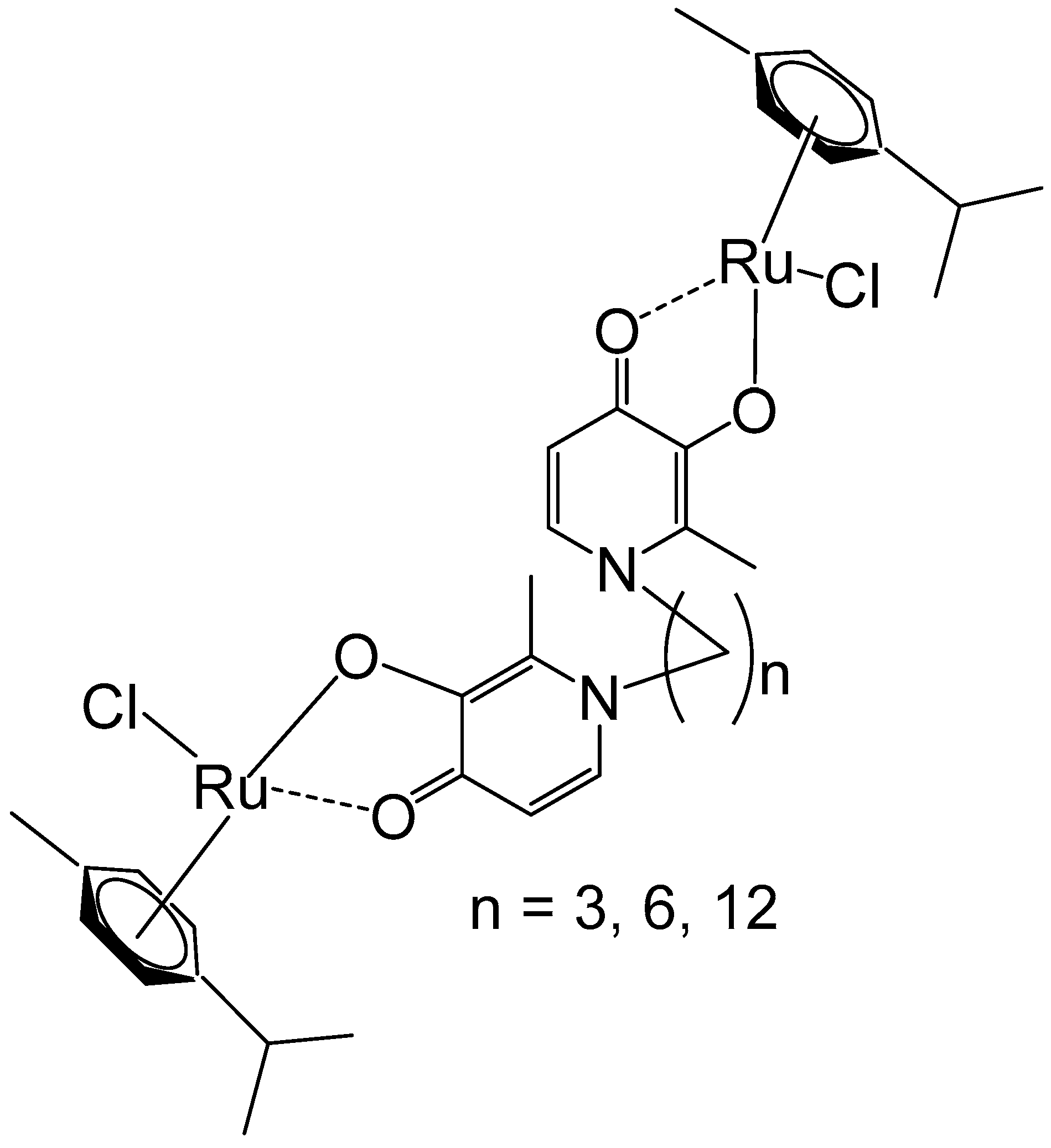
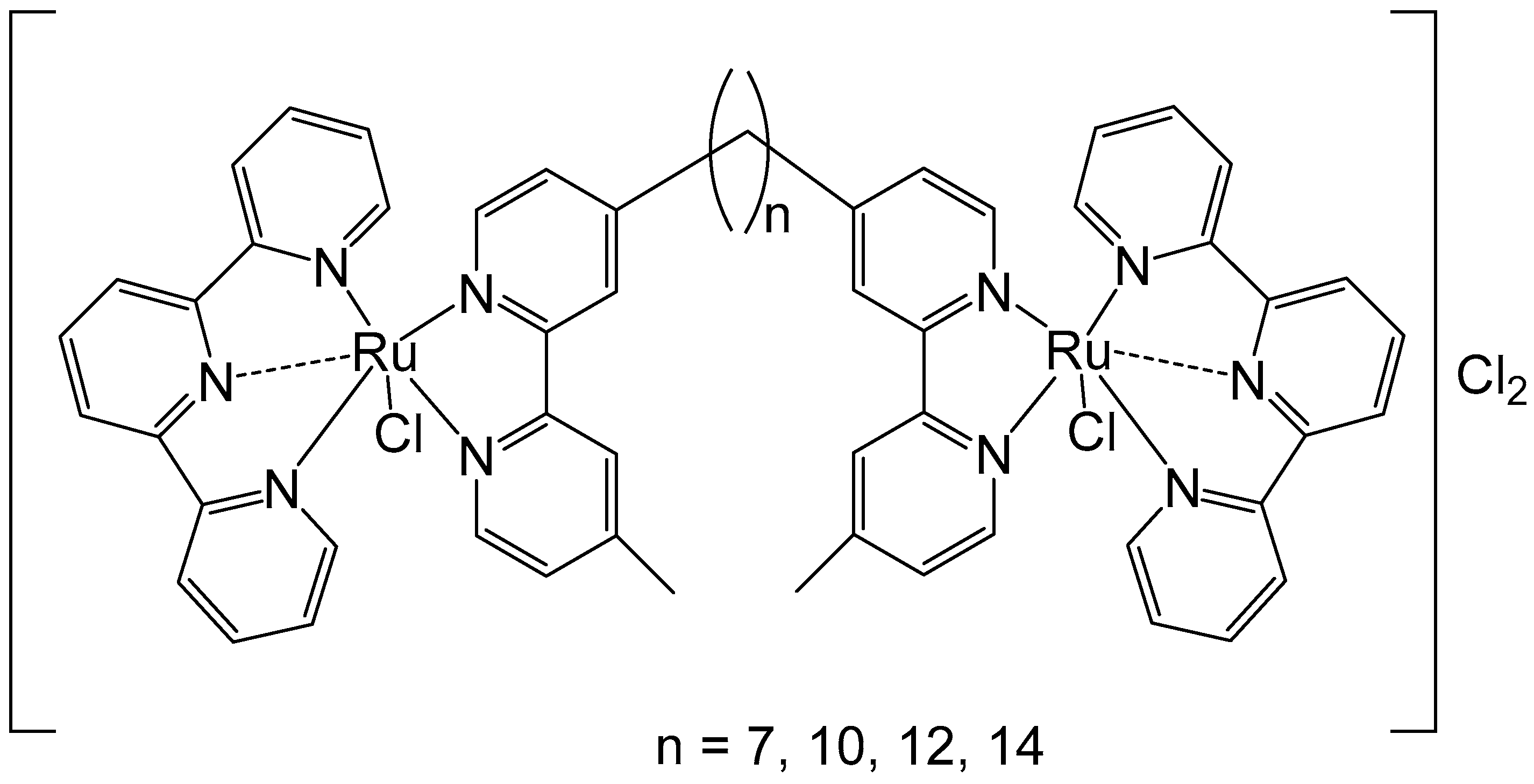
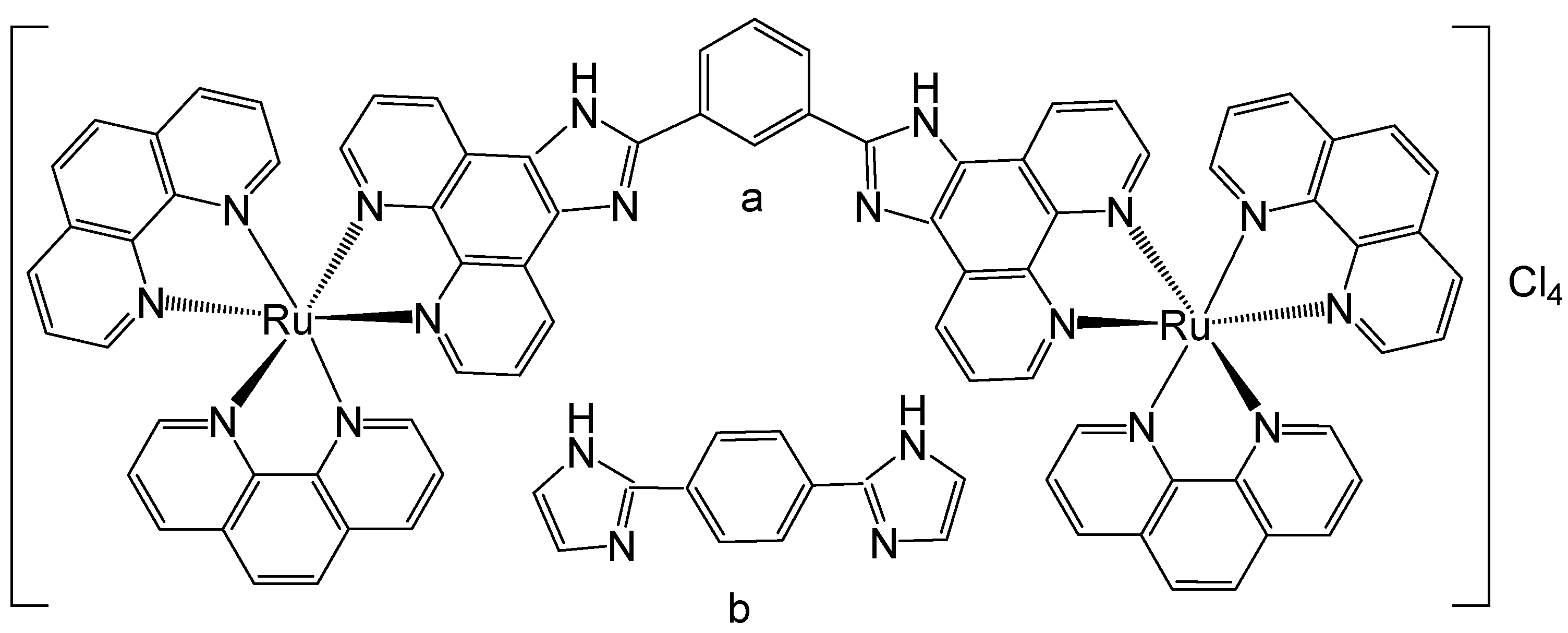
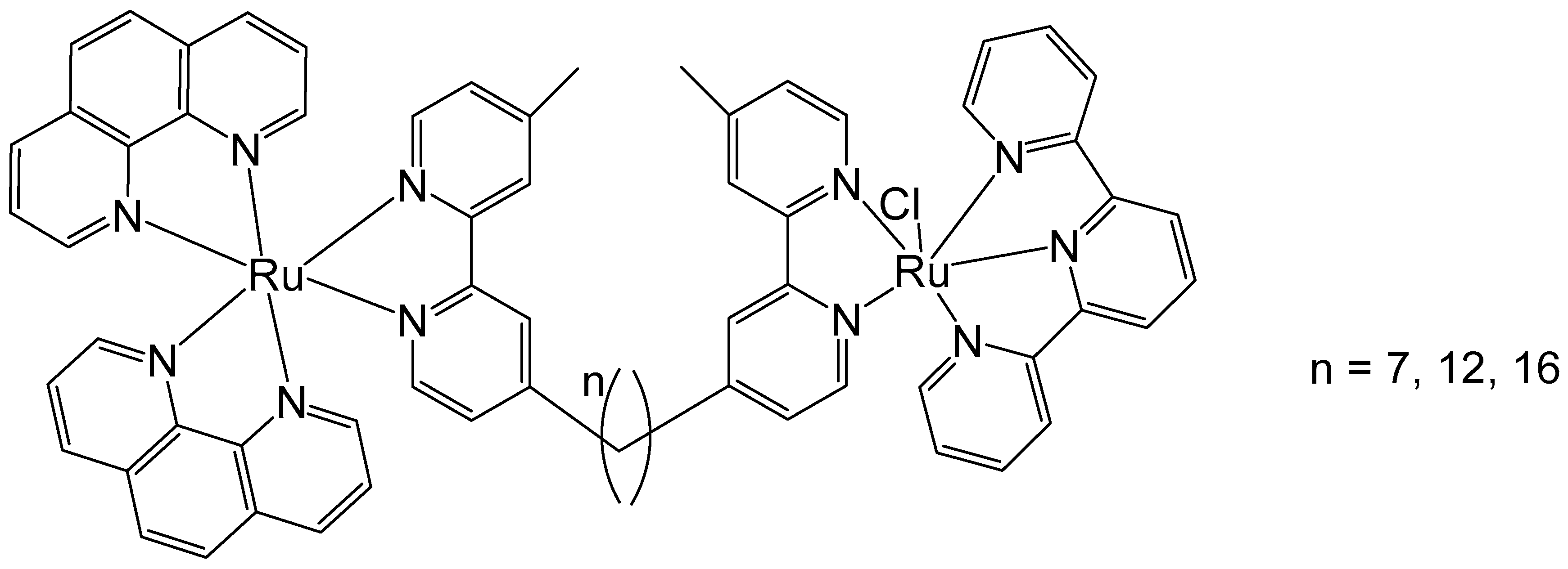
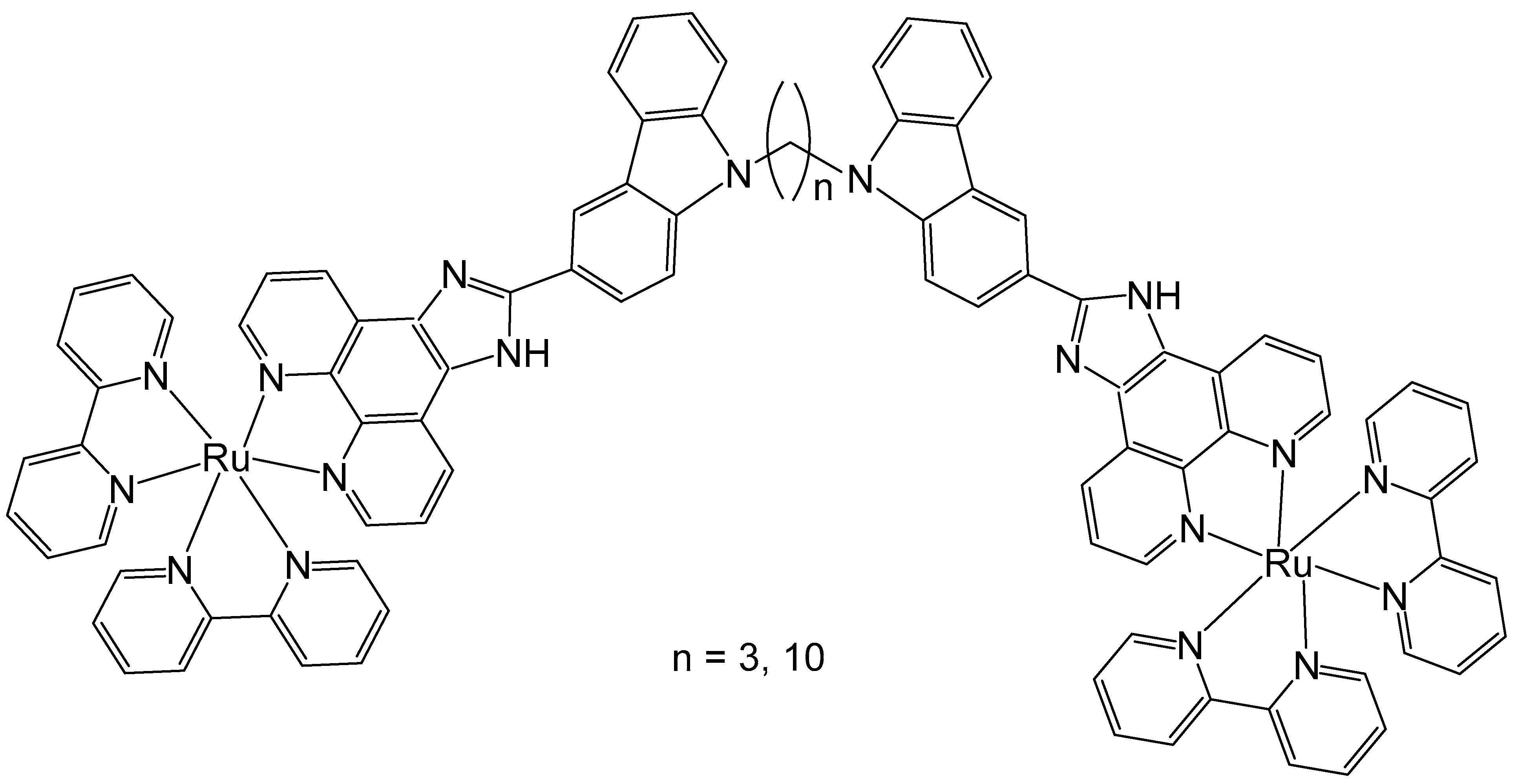
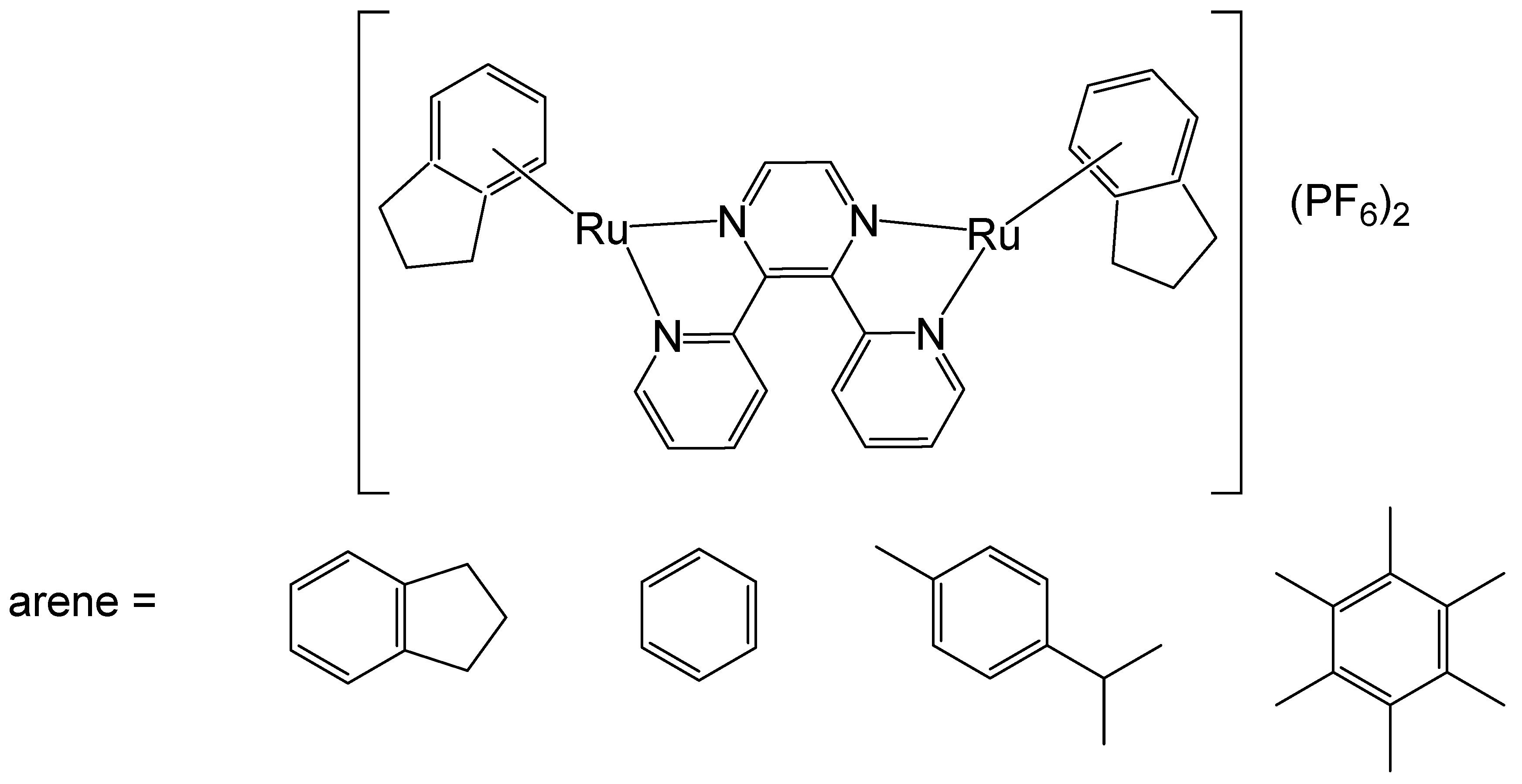
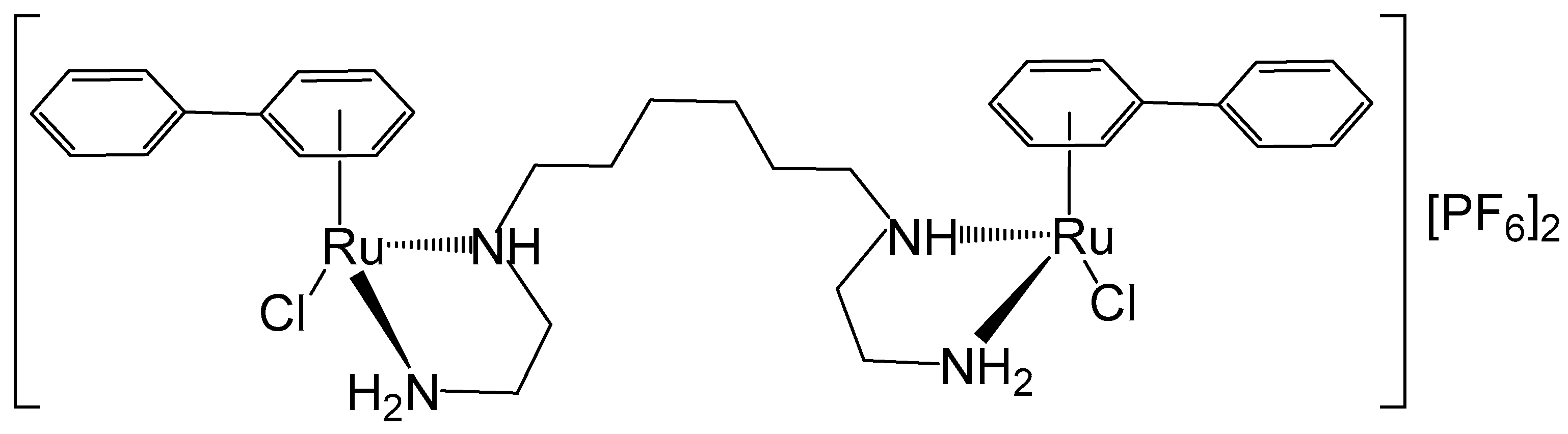
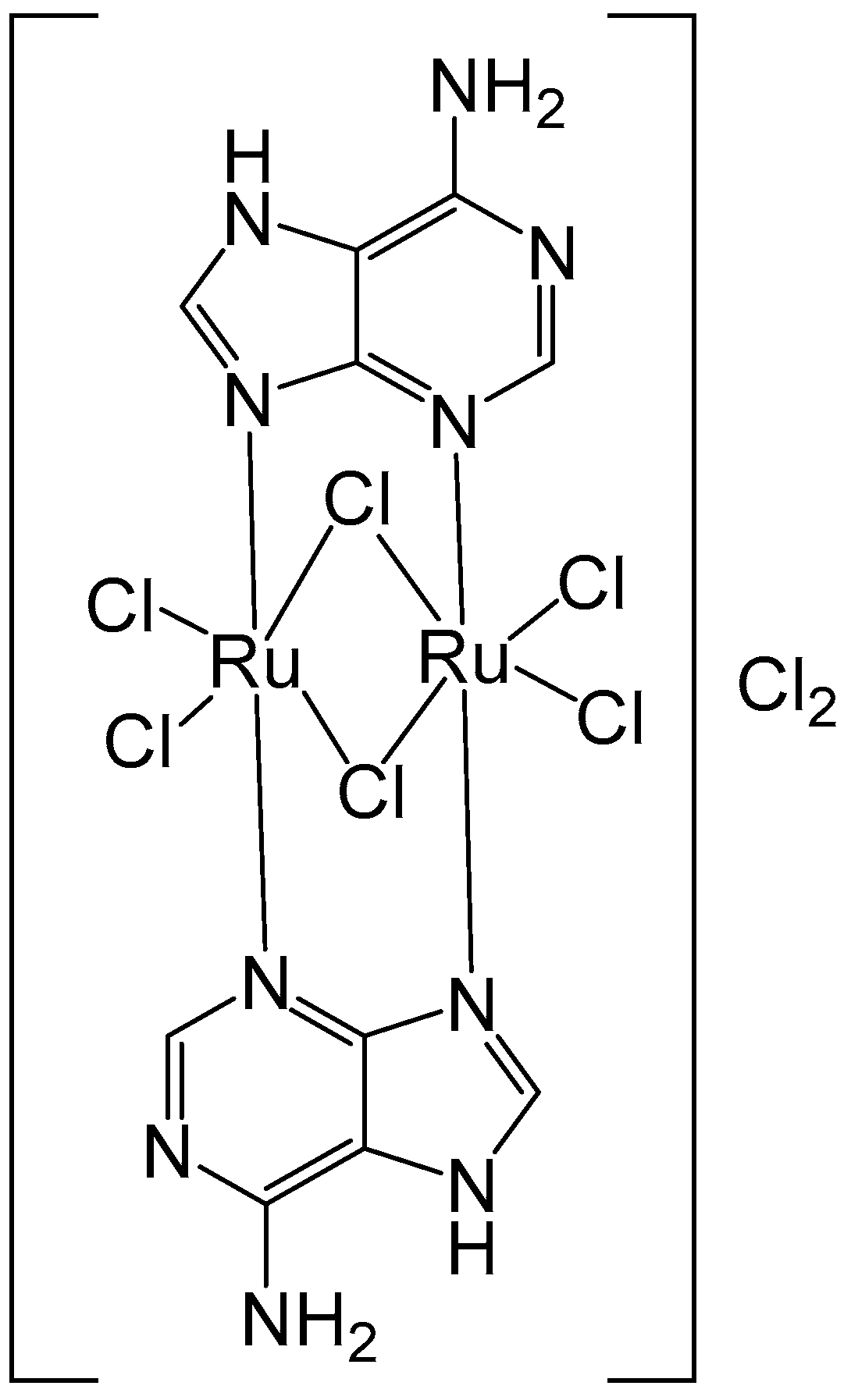
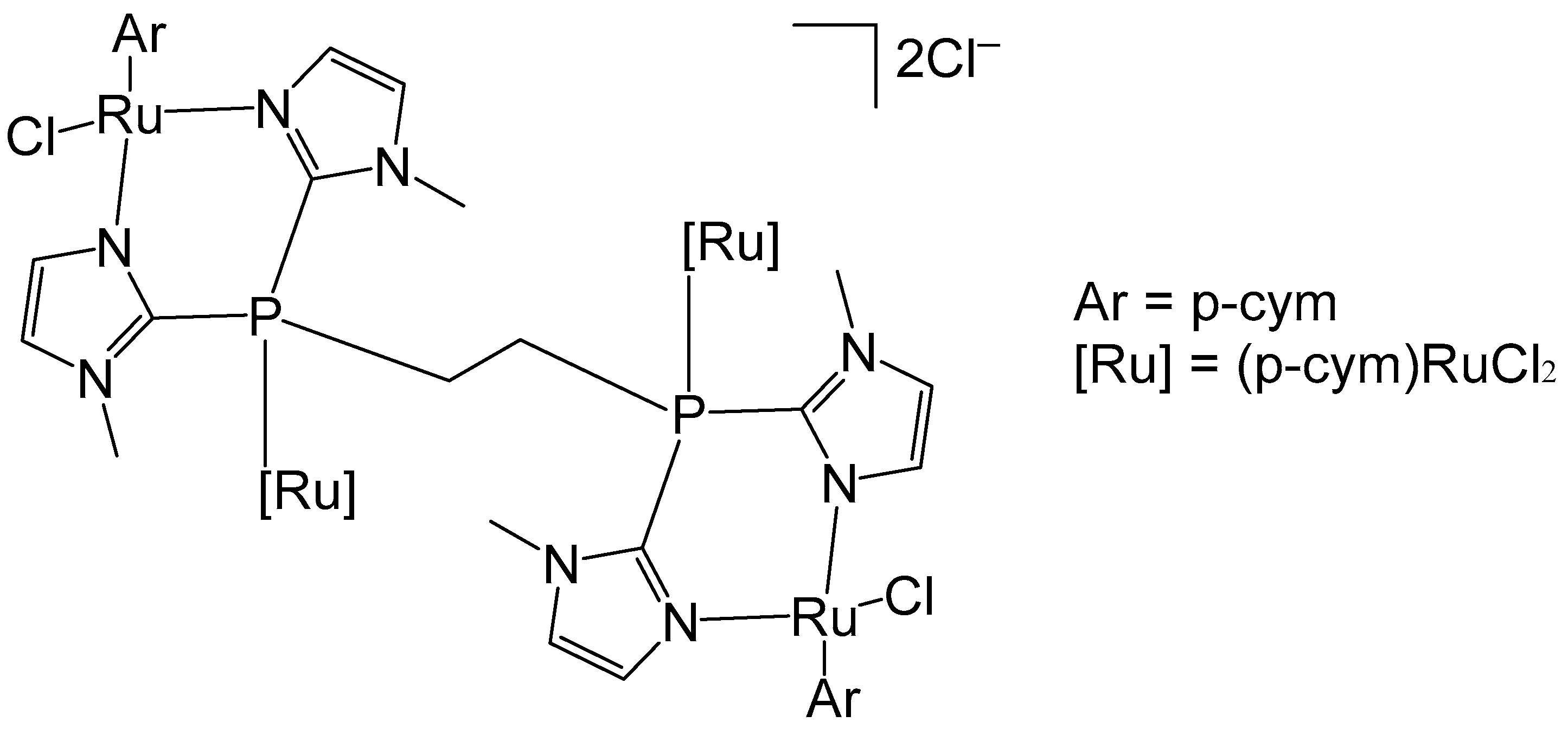
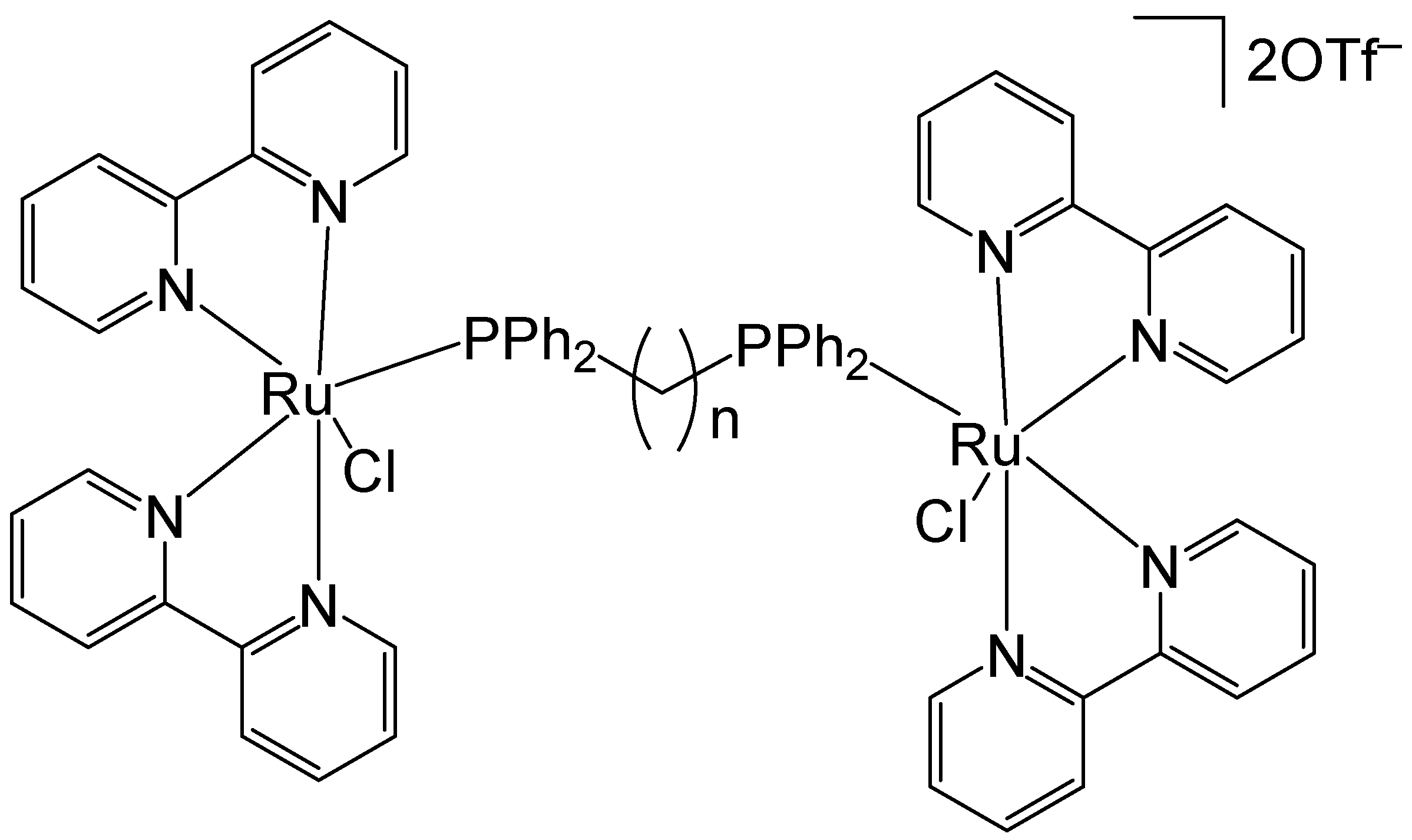
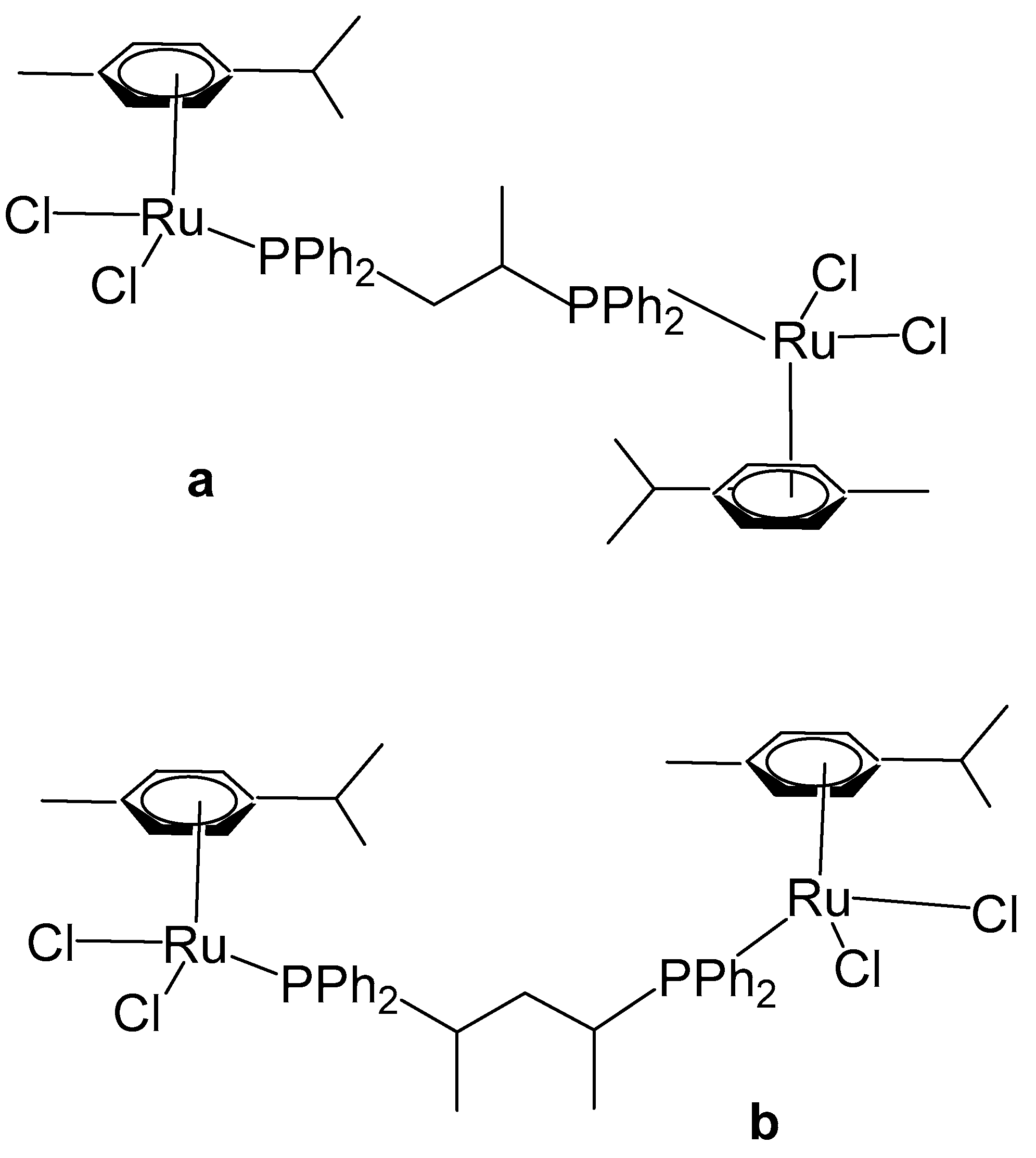
2. Homodinuclear Ru Complexes
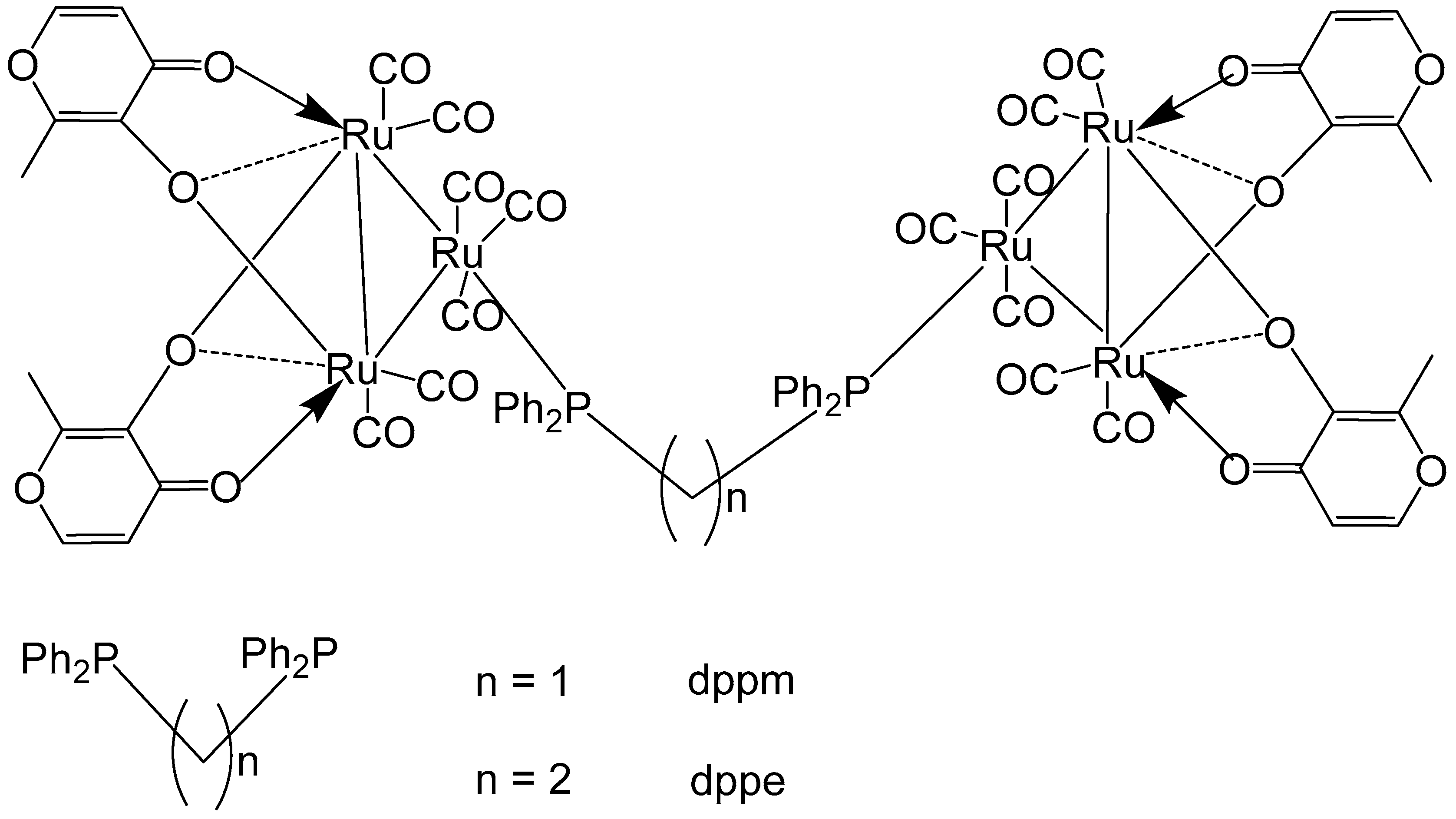
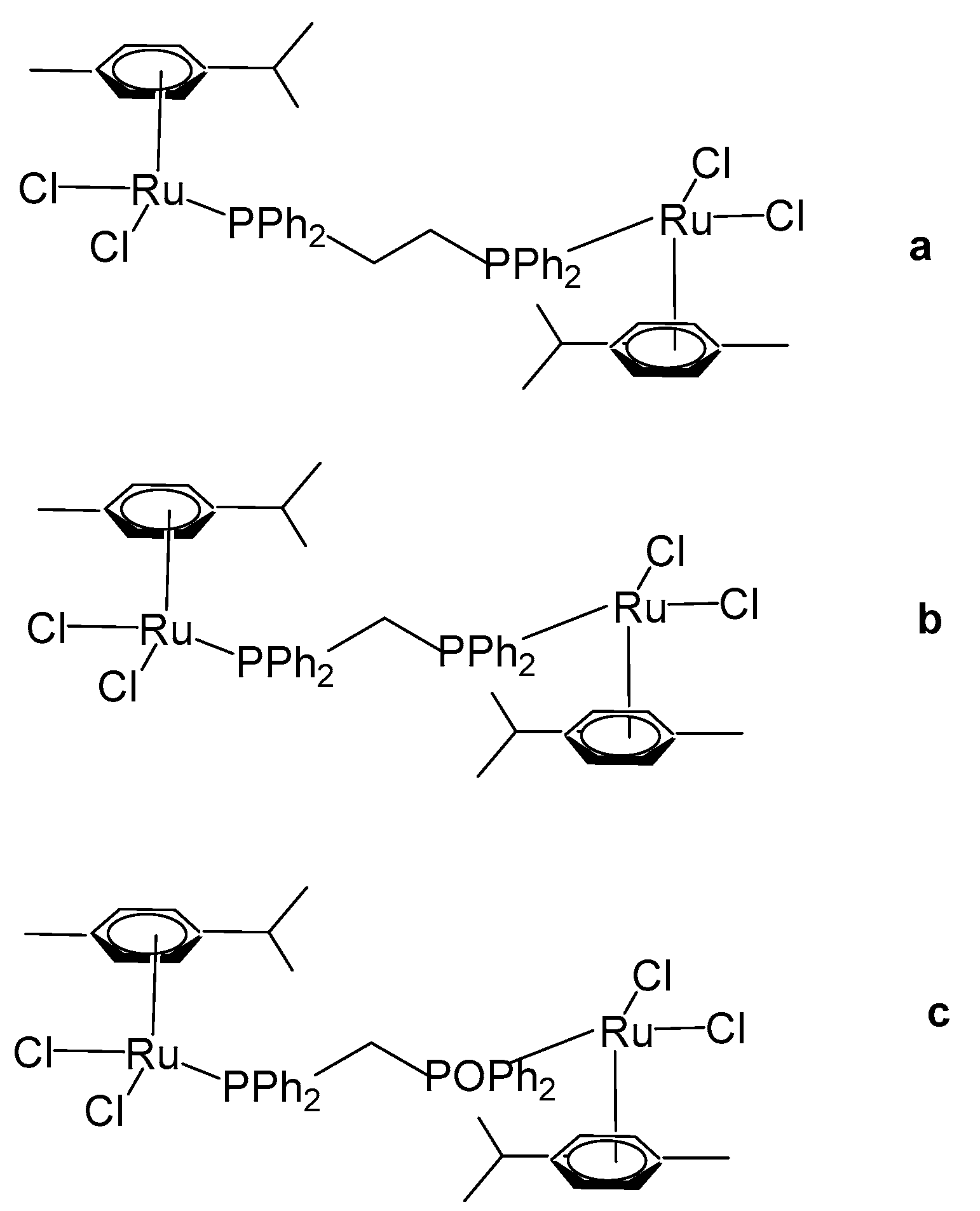
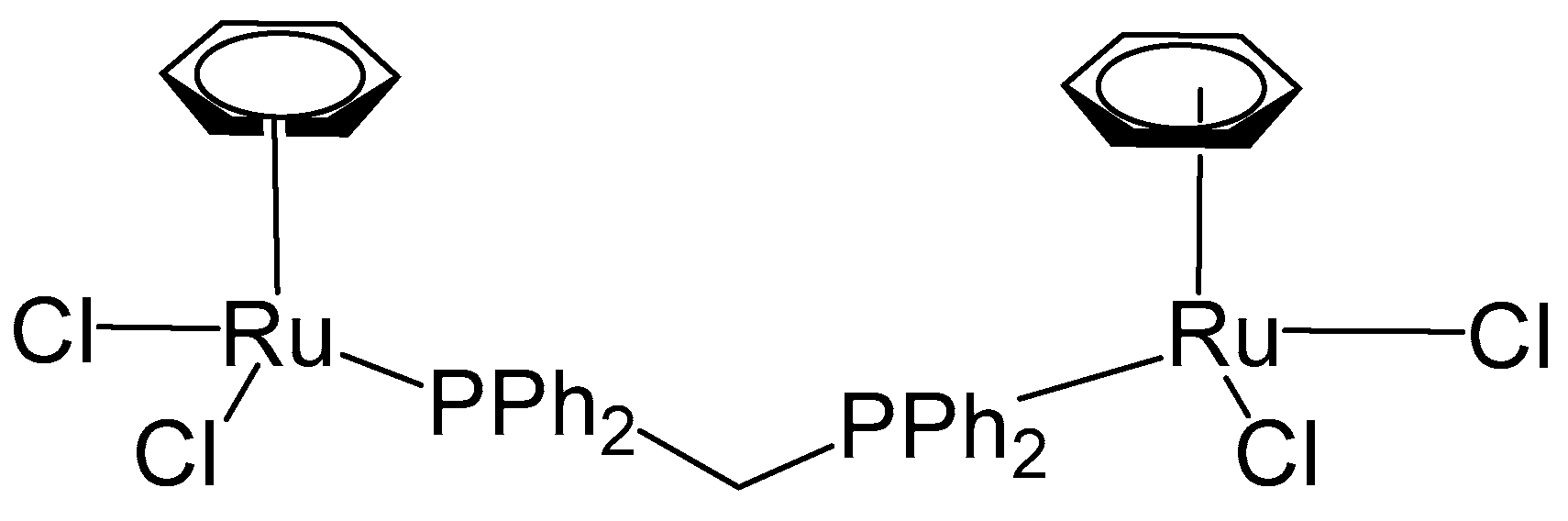
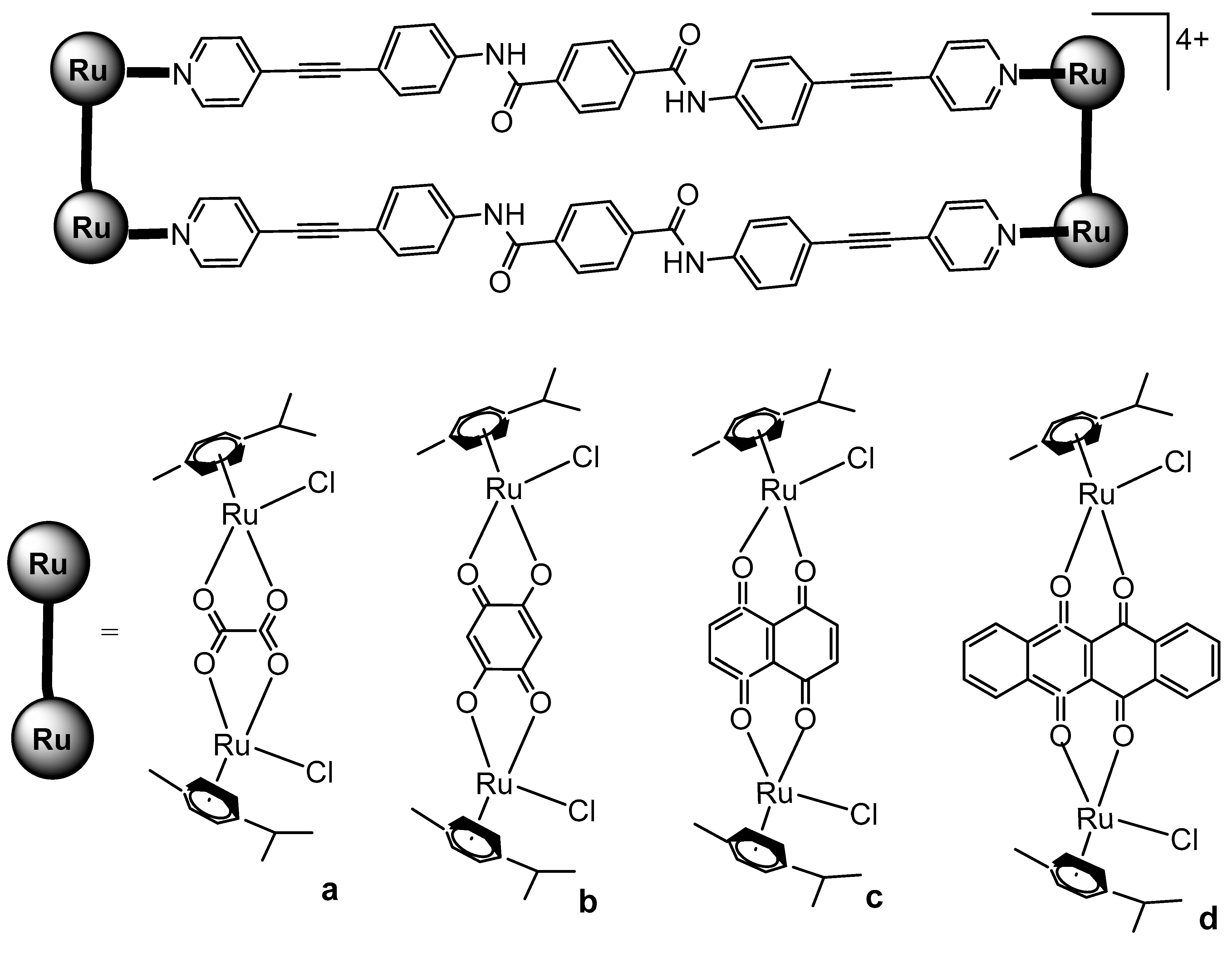
3. Complexes with Arylphosphines as Ancillary Ligands
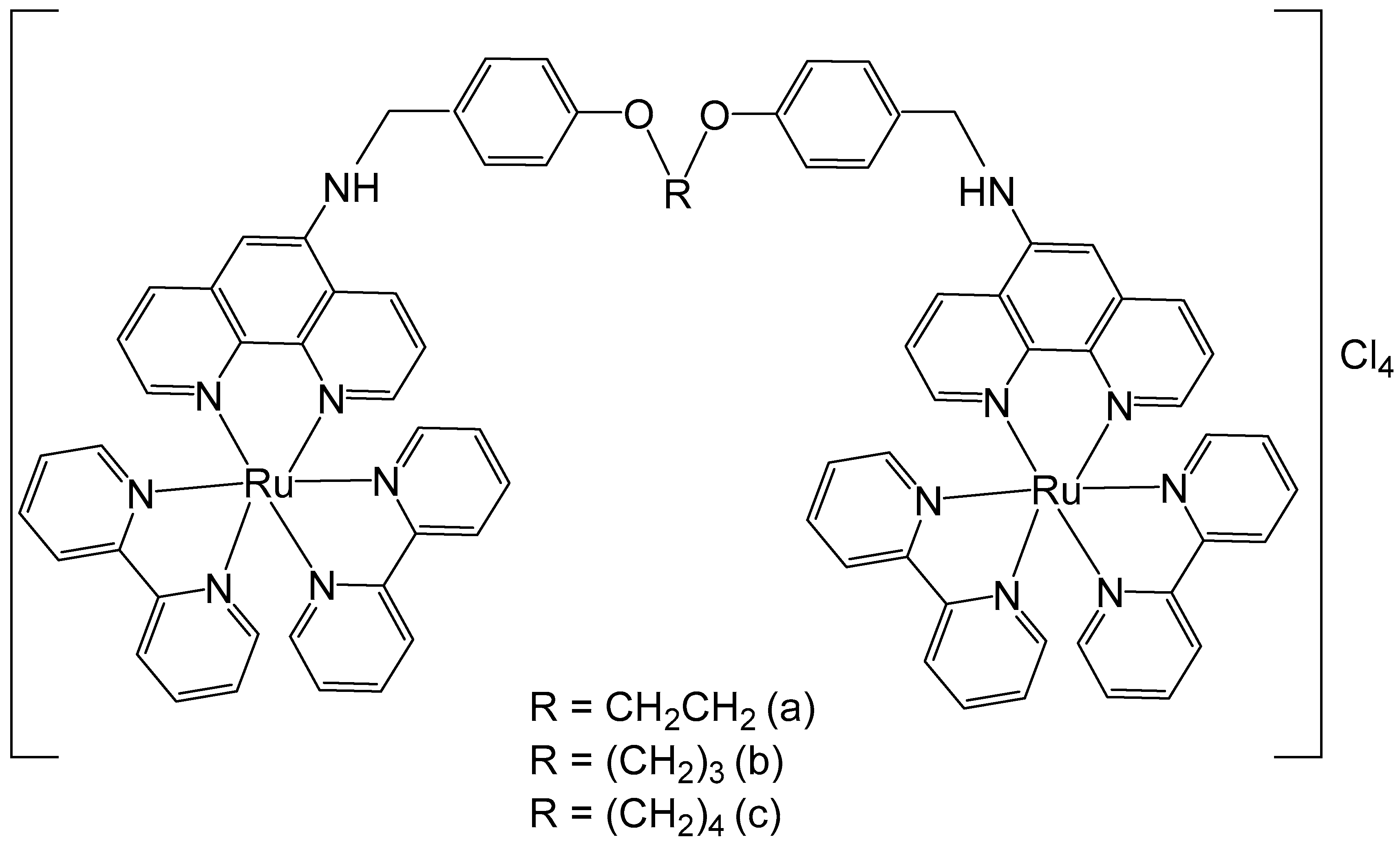
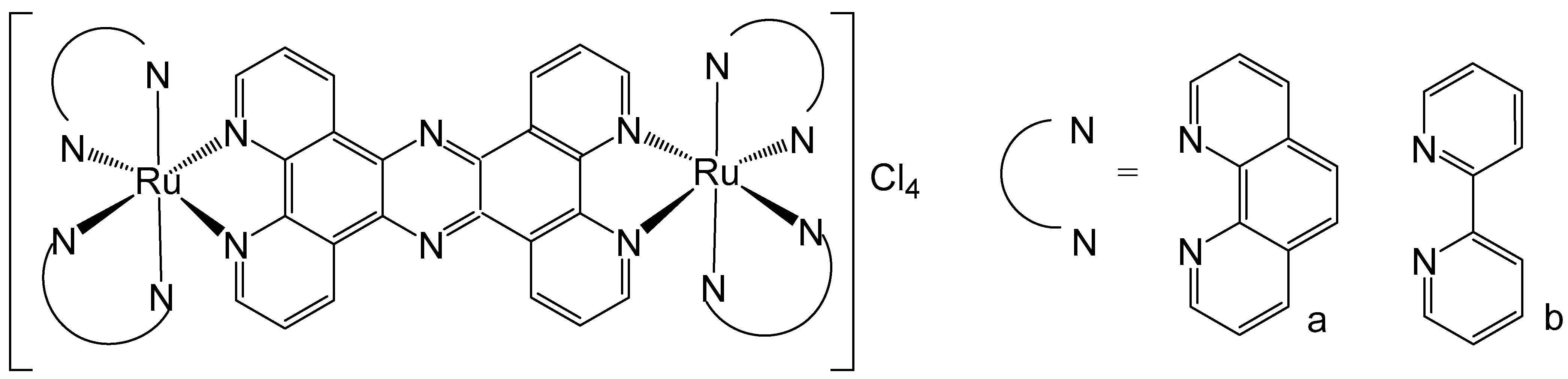
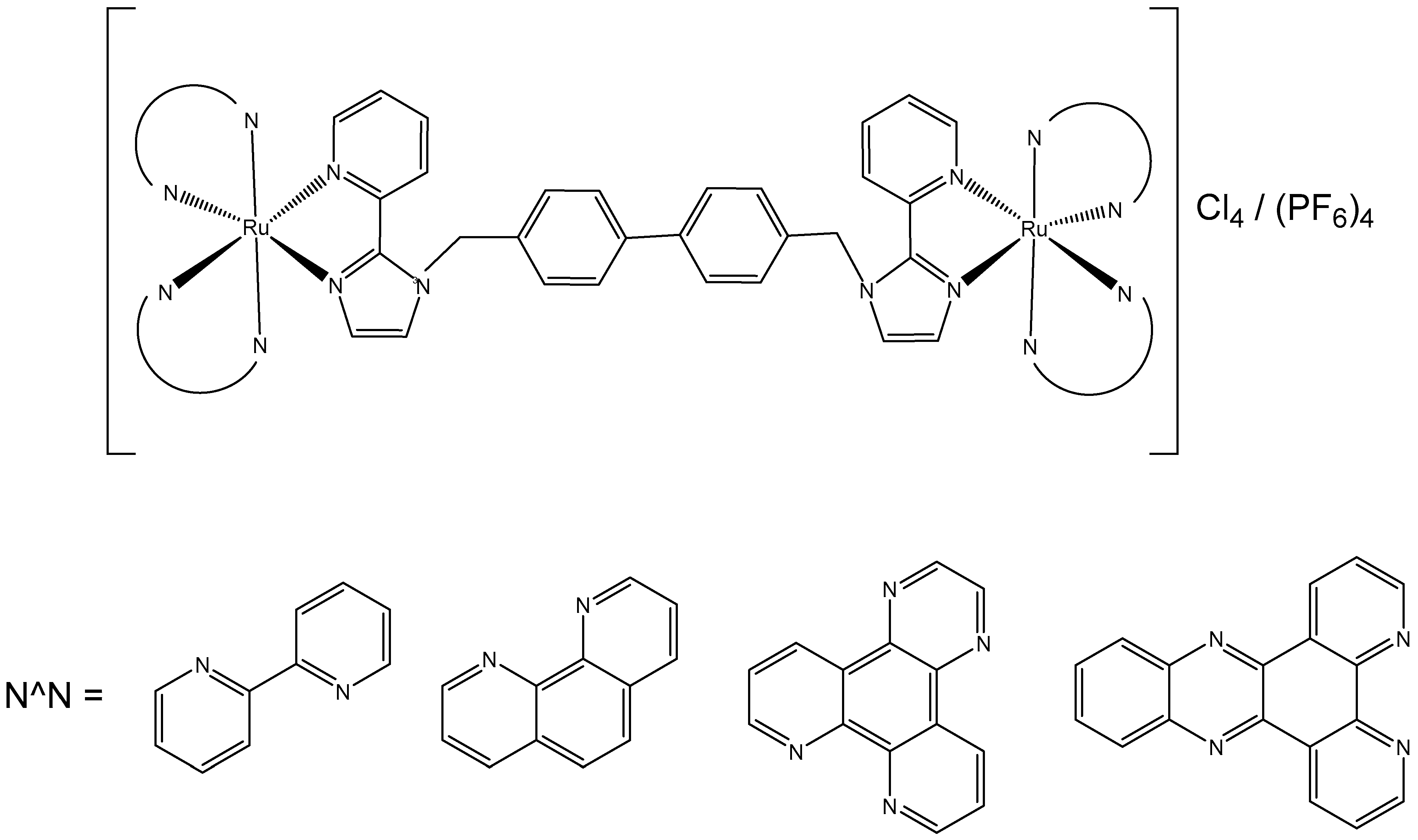
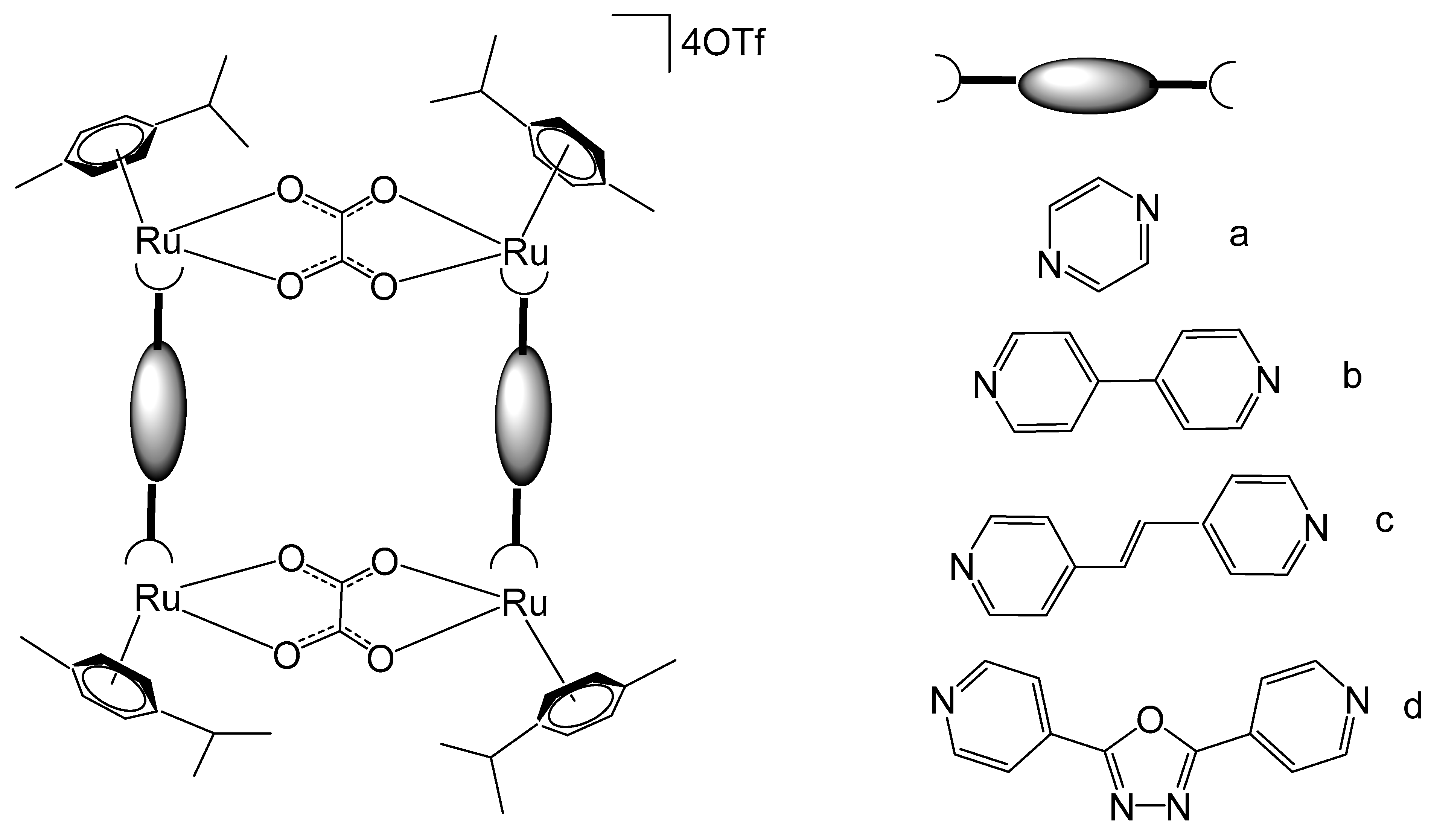
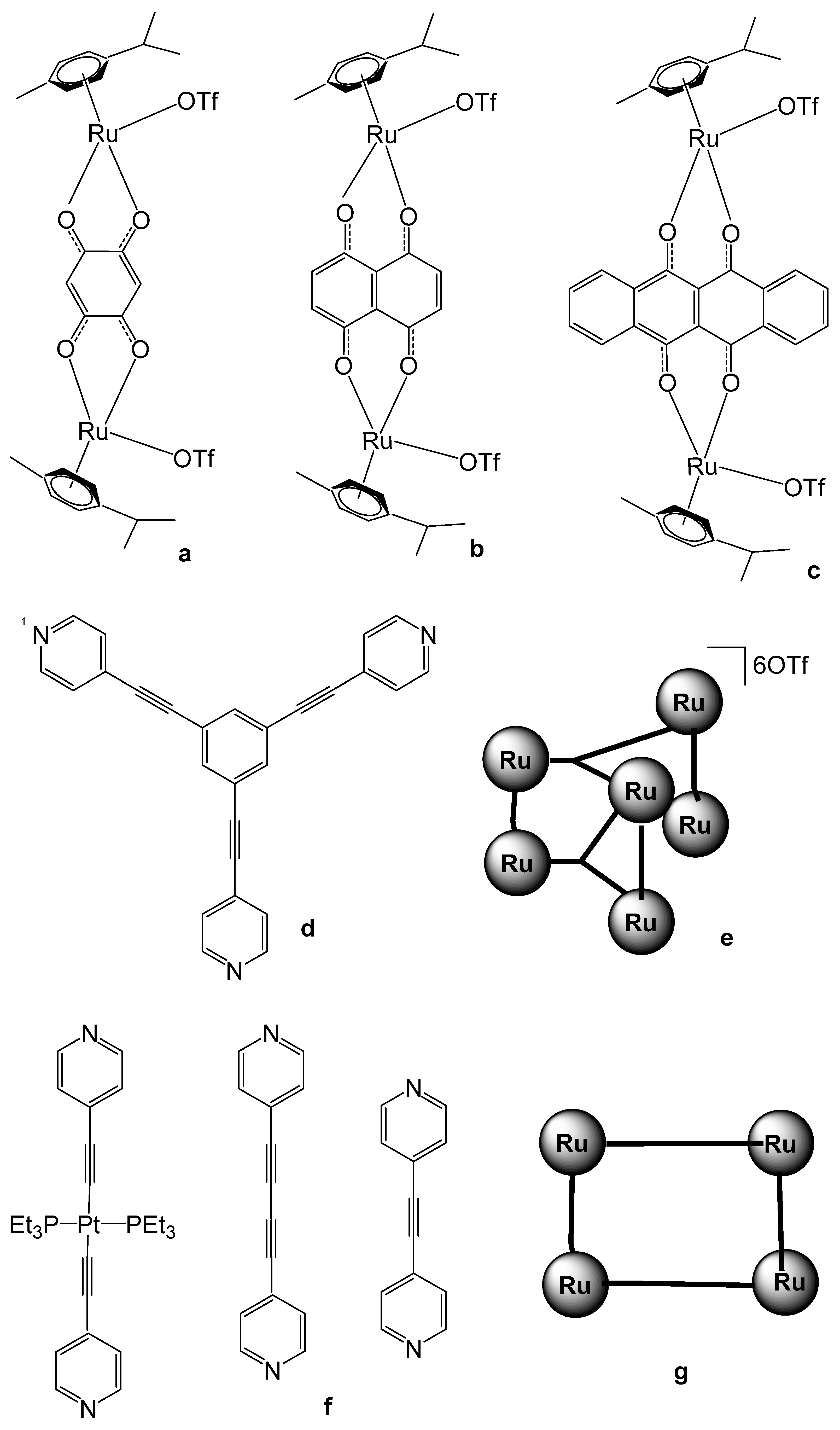
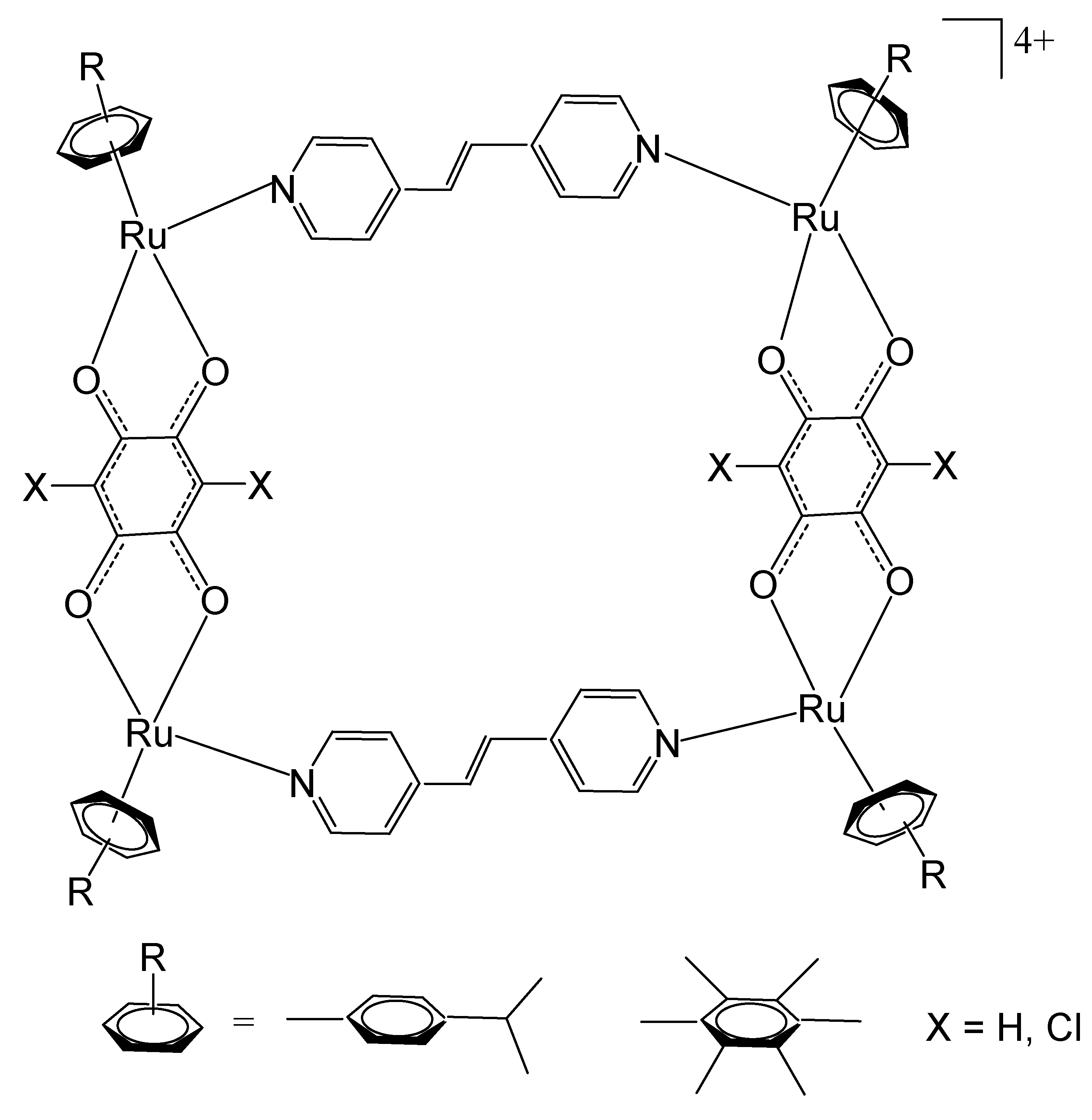
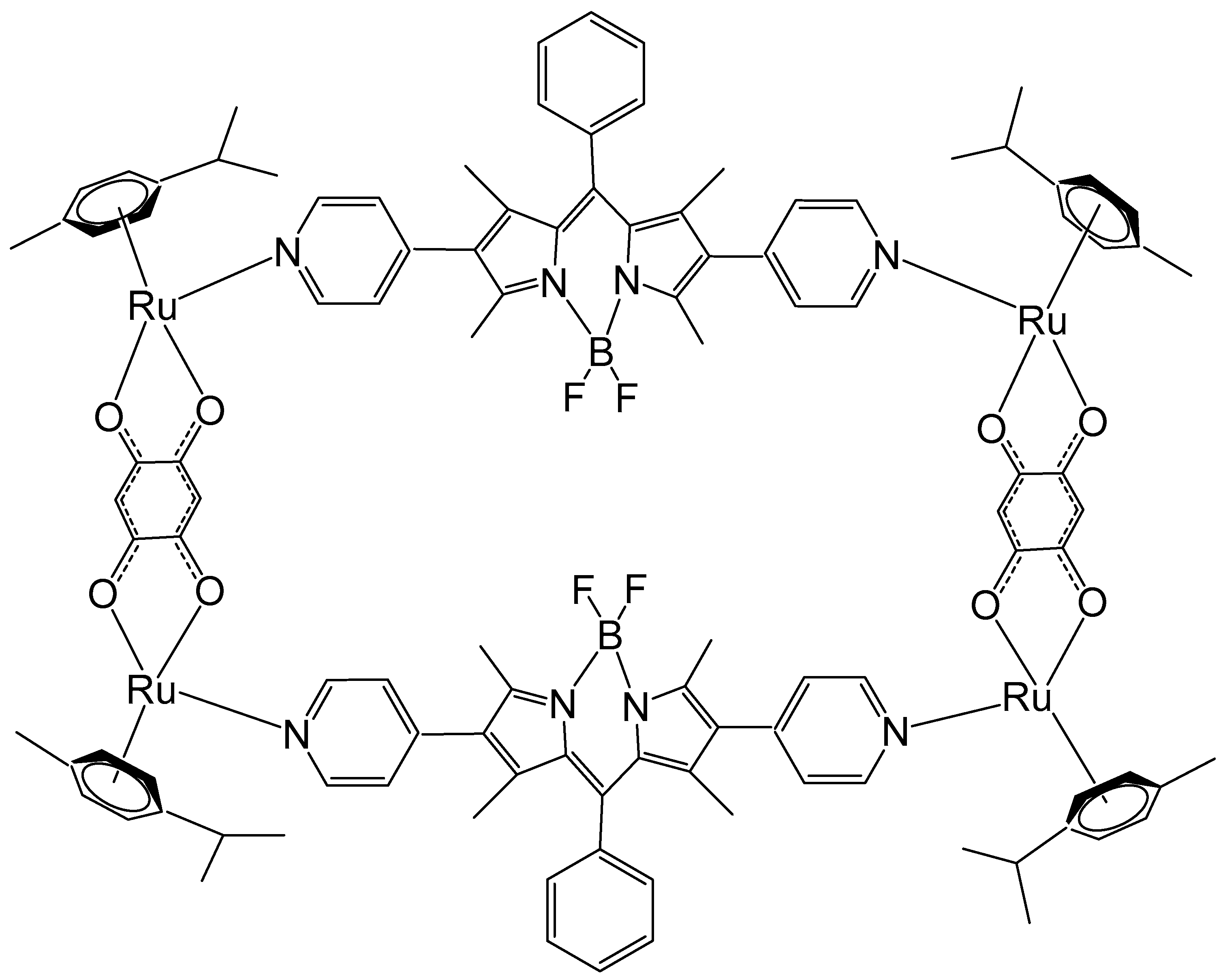
4. Ruthenium-Based Metalloassemblies
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ndagi, U.; Mhlongo, N.; Soliman, M.E. Metal complexes in cancer therapy—An update from drug design perspective. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, S. Recent advances in anticancer ruthenium Schiff base complexes. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, E. Bioinorganic Medicinal Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaoujiya, R.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, R.; Mustafa, G. Recent advances and application of ruthenium complexes in tumor malignancy. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 72, 2822–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, K.M.; Niloy, M.S.; Shakil, M.S.; Islam, M.A. Ruthenium Complexes: An Alternative to Platinum Drugs in Colorectal Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sadler, P.J. Advances in the design of organometallic anticancer complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 839, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, J.G.; Kelly, J.M. Ruthenium polypyridyl chemistry; from basic research to applications and back again. Dalton Trans. 2006, 41, 4869–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, P.J.; Sava, G. Metal-based antitumour drugs in the post genomic era. Dalton Trans. 2006, 16, 1929–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadique, S.; Baqer, A.A.; Salman, A.W.; Iqbal, M.A.; Kadim, M.M.; Jamil, F.; Altaf, A. Ruthenium complexes for breast cancer therapy. Rev. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 44, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.R.; Corrêa, R.S.; Santos, L.D.S.; Soares, M.B.P.; Batista, A.A.; Bezerra, D.P. A ruthenium-based 5-fluorouracil complex with enhanced cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction action in HCT116 cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, J.; Leung, P.K.-K.; Lo, K.K.-W. Luminescent Ruthenium(II) Polypyridine Complexes for a Wide Variety of Biomolecular and Cellular Applications. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 2231–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.-P.; Zhong, Y.-M.; Ji, L.-N.; Mao, Z.-W. Phosphorescent metal complexes as theranostic anticancer agents: Combining imaging and therapy in a single molecule. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 2357–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Wei, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Hollow mesoporous ruthenium nanoparticles conjugated bispecific antibody for targeted anti-colorectal cancer response of combination therapy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 9661–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, S.; Yuan, G.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Qin, X. RuCeO2 yolk shell nanozymes: Oxygen supply in situ enhanced dual chemotherapy combined with photothermal therapy for orthotopic/subcutaneous colorectal cancer. Biomaterials 2020, 242, 119923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska-Wawrzycka, A.; Rogala, P.; Michałkiewicz, S. Ruthenium complexes in different oxidation states: Synthesis, crystal structure, spectra and redox properties. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 6092–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Bo, H.-B.; Hao, X.-J.; Wang, J.-Q. Applications of Ruthenium Complex in Tumor Diagnosis and Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, C.; Musumeci, D.; Trifuoggi, M.; Irace, C.; Paduano, L.; Montesarchio, D. Anticancer Ruthenium(III) Complexes and Ru(III)-Containing Nanoformulations: An Update on the Mechanism of Action and Biological Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluga, P.; Hartinger, C.G.; Egger, A.; Reisner, E.; Galanski, M.; Jakupec, M.A.; Keppler, B.K. Redox behavior of tumor-inhibiting ruthenium(III) complexes and effects of physiological reductants on their binding to GMP. Dalton Trans. 2006, 14, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, J.; Fandzloch, M.; Łakomska, I. The reduction of ruthenium(III) complexes with triazolopyrimidine ligands by ascorbic acid and mechanistic insight into their action in anticancer therapy. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 484, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazevic, A.; Hummer, A.A.; Heffeter, P.; Berger, W.; Filipits, M.; Cibin, G.; Keppler, B.K.; Rompel, A. Electronic State of Sodium trans-[Tetrachloridobis (1 H-indazole) ruthenate (III)](NKP-1339) in Tumor, Liver and Kidney Tissue of a SW480-bearing Mouse. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, S.; Pump, E.; Fischer, R. On the chloride lability in electron-rich second-generation ruthenium benzylidene complexes. Monatsh Chem. 2015, 146, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. The next generation of platinum drugs: Targeted Pt (II) agents, nanoparticle delivery, and Pt (IV) prodrugs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3436–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostova, I. Ruthenium complexes as anticancer agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1085–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motswainyana, W.M.; Ajibade, P.A. Anticancer Activities of Mononuclear Ruthenium(II) Coordination Complexes. Adv. Chem. 2015, 2015, 859730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, M.; Arsenijevic, A.; Milovanovic, J.; Stojanovic, B.; Stankovic, V.; Rilak Simovic, A.; Lazic, D.; Arsenijevic, N.; Milovanovic, M. Antitumor Activity of Ruthenium(II) Terpyridine Complexes towards Colon Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Molecules 2020, 25, 4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushi, S.; Yoshino, H.; Yoshizawa, A.; Kashiwakura, I. p53-independent structure-activity relationships of 3-ring mesogenic compounds’ activity as cytotoxic effects against human non-small cell lung cancer lines. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groessl, M.; Tsybin, Y.; Hartinger, C. Ruthenium versus platinum: Interactions of anticancer metallodrugs with duplex oligonucleotides characterised by electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 15, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groessl, M.; Zava, O.; Dyson, P. Cellular uptake and subcellular distribution of ruthenium-based metallodrugs under clinical investigation versus cisplatin. Metallomics 2011, 3, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herić, A.; Dibranin, N.; Martić, L.; Hodžić, E.; Zahirović, A.; Kozarić, A.K. Ruthenium-based complexes as anti-tumor agents. J. Health Sci. 2024, 14, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrović, E.; Zahirović, A.; Pavelić, S.K.; Turkušić, E.; Harej, A. In vitro anticancer activity of binuclear Ru(II) complexes with Schiff bases derived from 5-substituted salicylaldehyde and 2-aminopyridine with notably low IC50 values. J. Coord. Chem. 2017, 70, 1683–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.J. Ruthenium metallopharmaceuticals. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 232, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davia, K.; King, D.; Hong, Y.; Swavey, S. A porphyrin–ruthenium photosensitizer as a potential photodynamic therapy agent. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2008, 11, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaplana, R.A.; Delmani, F.; Manteca, C.; Torreblanca, J.; Moreno, J.; García-Herdugo, G.; González-Vílchez, F. Synthesis, interaction with double-helical DNA and biological activity of the water soluble complex cis-dichloro-1, 2-propylenediamine-N, N, N′, N′-tetraacetato ruthenium (III)(RAP). J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han Ang, W.; Dyson, P.J. Classical and non-classical ruthenium-based anticancer drugs: Towards targeted chemotherapy. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 2006, 4003–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, V.; Nováková, O. DNA binding mode of ruthenium complexes and relationship to tumor cell toxicity. Drug Resist. Upd. 2006, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Ferri, M.G.; Hartinger, C.G.; Mendoza, M.A.; Groessl, M.; Egger, A.E.; Eichinger, R.E.; Mangrum, J.B.; Farrell, N.P.; Maruszak, M.; Bednarski, P.J.; et al. Transferring the concept of multinuclearity to ruthenium complexes for improvement of anticancer activity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Noguchi, Y.; Nakai, M.; Yamauchi, O.; Nakabayashi, Y.; Sato, T.; Mino, Y. Solvolysis and cytotoxicity of dinuclear ruthenium (II)-2, 2′-bipyridine complexes with various bridged-ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2013, 394, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyana, Y.; Collins, J.G.; Keene, F.R. Synthesis, nucleic acid binding and cytotoxicity of oligonuclear ruthenium complexes containing labile ligands. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2011, 71, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorle, A.K.; Ammit, A.J.; Wallace, L.; Keene, F.R.; Collins, J.G. Multinuclear ruthenium(II) complexes as anticancer agents. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4049–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, E.; Hotze, A.C.; Den Dulk, H.; Leczkowska, A.; Rodger, A.; Hannon, M.J.; Reedijk, J. Ruthenium polypyridyl complexes and their modes of interaction with DNA: Is there a correlation between these interactions and the antitumor activity of the compounds? J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 14, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lai, L.; Cai, P.; Cheng, G.Z.; Xu, X.M.; Liu, Y. Synthesis, characterization and anticancer activity of dinuclear ruthenium(II) complexes linked by an alkyl chain. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 5805–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, B.Y.; Wang, K.Z. Synthesis, DNA binding and photocleavage, and cellular uptake of an alkyl chain-linked dinuclear ruthenium(II) complex. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2015, 143, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckford, F.A.; Niece, M.B.; Lassiter, B.P.; Beebe, S.J.; Holder, A.A. Polynuclear ruthenium organometallic complexes containing a 1, 3, 5-triazine ligand: Synthesis, DNA interaction, and biological activity. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 23, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarević, T.; Rilak, A.; Bugarčić, Ž.D. Platinum, palladium, gold and ruthenium complexes as anticancer agents: Current clinical uses, cytotoxicity studies and future perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 142, 8–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, M.R.; Garcia-Lara, J.; Foster, S.J.; Smythe, C.; Battaglia, G.; Thomas, J.A. A ruthenium (II) polypyridyl complex for direct imaging of DNA structure in living cells. Nature Chem. 2009, 1, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggaley, E.; Gill, M.R.; Green, N.H.; Turton, D.; Sazanovich, I.V.; Botchway, S.W.; Thomas, J.A. Dinuclear Ruthenium (II) Complexes as Two-Photon, Time-Resolved Emission Microscopy Probes for Cellular DNA. Angew. Chem. Intern. Ed. 2014, 53, 3367–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, F.R.; Andersson, J.; Åmand, H.L.; Lincoln, P. Effects of chirality on the intracellular localization of binuclear ruthenium (II) polypyridyl complexes. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 17, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, M.; Vinck, R.; Gibert, B.; Gasser, G. Strategies for the nuclear delivery of metal complexes to cancer cells. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2311437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Heimann, K.; Li, F.; Warner, J.M.; Keene, F.R.; Collins, J.G. Dinuclear ruthenium (II) complexes containing one inert metal centre and one coordinatively-labile metal centre: Syntheses and biological activities. Dalt. Trans. 2016, 45, 4017–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Wu, B.Y.; Liu, J.; Dai, Y.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, K.Z. DNA binding and photocleavage properties, cellular uptake and localization, and in-vitro cytotoxicity of dinuclear ruthenium (II) complexes with varying lengths in bridging alkyl linkers. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Kumbhar, A.S.; Khan, A. Honeycomb-like Ordered Assembly of DNA Induced by Flexible Binuclear Ruthenium (II)–Polypyridyl Complexes. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 15760–15771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Qian, Y.; Wang, F.X.; Habtemariam, A.; Mao, Z.W.; Sadler, P.J.; Liu, H.K. Ruthenium (II)–arene metallacycles: Crystal structures, interaction with DNA, and cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2017, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magennis, S.W.; Habtemariam, A.; Novakova, O.; Henry, J.B.; Meier, S.; Parsons, S.; Sadler, P.J. Dual triggering of DNA binding and fluorescence via photoactivation of a dinuclear ruthenium (II) arene complex. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 5059–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, A.F.; Sadler, P.J. Medicinal organometallic chemistry: Designing metal arene complexes as anticancer agents. Chem. Asian J. 2008, 3, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Parkinson, J.A.; Nováková, O.; Bella, J.; Wang, F.; Dawson, A.; Sadler, P.J. Induced-fit recognition of DNA by organometallic complexes with dynamic stereogenic centers. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14623–14628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruijnincx, P.C.; Sadler, P.J. Controlling platinum, ruthenium, and osmium reactivity for anticancer drug design. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 61, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orts-Arroyo, M.; Gutiérrez, F.; Gil-Tebar, A.; Ibarrola-Villava, M.; Jiménez-Martí, E.; Silvestre-Llora, A.; Castro, I.; Ribas, G.; Martínez-Lillo, J. A Novel Adenine-Based Diruthenium(III) Complex: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Electrochemical Properties and Evaluation of the Anticancer Activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2022, 232, 111812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, L.K.; Flamme, M.; Felder, P.S.; Karges, J.; Bonhomme, F.; Gandioso, A.; Malosse, C.; Gasser, G.; Hollenstein, M. A ruthenium–oligonucleotide bioconjugated photosensitizing aptamer for cancer cell specific photodynamic therapy. RSC Chem. Biol. 2022, 3, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolamiol, E.; Visentin, F.; Scattolin, T. Recent advances in bioconjugated transition metal complexes for cancer therapy. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.D.; Dayal, D.; Szalda, D.J.; Cosenza, S.C.; Reddy, M.R. Syntheses, structures, and anticancer activity of novel organometallic ruthenium–maltol complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2012, 700, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noffke, A.L.; Bongartz, M.; Wätjen, W.; Böhler, P.; Spingler, B.; Kunz, P.C. Synthesis, X-ray crystal structure and cytotoxicity of a new tetranuclear ruthenium arene complex. J. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 696, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, P.C.; Wetzel, C.; Bongartz, M.; Noffke, A.L.; Spingler, B. Novel multitopic diphos-type ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 2010, 695, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenis-Rojas, O.A.; Roma-Rodrigues, C.; Fernandes, A.R.; Marques, F.; Perez-Fernandez, D.; Guerra-Varela, J.; Fernandez, J.J. Dinuclear RuII (bipy) 2 derivatives: Structural, biological, and in vivo zebrafish toxicity evaluation. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 7127–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Sinha, S.; Britto, R.; Somasundaram, K.; Samuelson, A.G. Cytotoxicity of half sandwich ruthenium (II) complexes with strong hydrogen bond acceptor ligands and their mechanism of action. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herry, B.; Batchelor, L.K.; Roufosse, B.; Romano, D.; Baumgartner, J.; Borzova, M.; Reifenstahl, T.; Collins, T.; Benamrane, A.; Weggelaar, J.; et al. Heterobimetallic Ru (μ-dppm) Fe and homobimetallic Ru (μ-dppm) Ru complexes as potential anti-cancer agents. J. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 901, 120934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaimanee, E.; Nhukeaw, T.; Saithong, S.; Ratanaphan, A.; Phongpaichit, S.; Tantirungrotechai, Y.; Leesakul, N. Half-sandwich ruthenium (II) p-cymene complexes based on organophosphorus ligands: Structure determination, computational investigation, in vitro antiproliferative effect in breast cancer cells and antimicrobial activity. Polyhedron 2021, 204, 115244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntharalingam, K.; Łęczkowska, A.; Furrer, M.A.; Wu, Y.; Kuimova, M.K.; Therrien, B.; Vilar, R. A cyclometallated platinum complex as a selective optical switch for quadruplex DNA. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.; Freudenreich, J.; Barry, N.P.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Süss-Fink, G.; Therrien, B. Organometallic cages as vehicles for intracellular release of photosensitizers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaroo, D.; Perez, E.; Aggarwal, A.; Wills, A.; O’Connor, N. Strategies for delivering porphyrinoid-based photosensitizers in therapeutic applications. Therap. Deliv. 2014, 5, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.W.; Barry, N.P.; Furrer, M.A.; Zava, O.; Dyson, P.J.; Therrien, B.; Kim, B.H. Delivery of floxuridine derivatives to cancer cells by water-soluble organometallic cages. Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, 23, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furrer, M.A.; Schmitt, F.; Wiederkehr, M.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Therrien, B. Cellular delivery of pyrenyl-arene ruthenium complexes by a water-soluble arene ruthenium metalla-cage. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 7201–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitto-Barry, A.; Barry, N.P.; Zava, O.; Deschenaux, R.; Dyson, P.J.; Therrien, B. Double Targeting of Tumours with Pyrenyl-Modified Dendrimers Encapsulated in an Arene–Ruthenium Metallaprism. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 1966–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascu, G.I.; Hotze, A.C.; Sanchez-Cano, C.; Kariuki, B.M.; Hannon, M.J. Dinuclear ruthenium (II) triple-stranded helicates: Luminescent supramolecular cylinders that bind and coil DNA and exhibit activity against cancer cell lines. Ang. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4374–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Kimura, H.; Okuhara, T.; Yamamura, M.; Nabeshima, T. A hierarchical self-assembly system built up from preorganized tripodal helical metal complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Duan, C. Biomedical applications of multinuclear Pt (II)/Ru (II)/Ir (III) metallo-supramolecular assemblies for intensive cancer therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 495, 215366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, B. Biologically relevant arene ruthenium metalla-assemblies. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2015, 17, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostova, I. Recent Advances in Anticancer Research of Osmium and Rhodium Complexes. Med. Chem. 2024, 21, 619–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostova, I. Recent Developments in Antitumor Activity of Organometallic Rhodium Complex Compounds with Macrocyclic Ligands. In Anticancer Potential of Macrocyclic Metal Complexes; ACS Symposium Series; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2025; Chapter 9; Volume 1492, pp. 197–233. [Google Scholar]
- Kostova, I. Homo-and Hetero-Multinuclear Iridium (III) Complexes with Cytotoxic Activity. Inorganics 2025, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostova, I. Cytotoxic Organometallic Iridium(III) Complexes. Molecules 2025, 30, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozumi, T.; Matsuoka, R.; Nakamura, T.; Nabeshima, T. Solvent-dependent fac/mer-isomerization and self-assembly of triply helical complexes bearing a pivot part. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 7720–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, B. Unmasking arene ruthenium building blocks. Chem. Record 2021, 21, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.J.; Narayana, Y.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Huang, W.H.; Su, W.N.; Li, Y.P.; Yu, W.Y. Rational synthesis of ruthenium-based metallo-supramolecular polymers as heterogeneous catalysts for catalytic transfer hydrogenation of carbonyl compounds. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 312, 121383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, X.; Li, J.; Xie, M.; Wang, X.; Sun, M.; Wu, Y.; Yu, L. Self-assembled supramolecular materials based on ruthenium (ii) complexes with exceptional optical and photothermal properties. Mater. Chem. Front. 2025, 9, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Bai, Y.; Pang, J.; Fan, L.; Tian, W. Ruthenium (II)-coordinated supramolecular metallodrug complex realizing oxygen self-supply in situ for overcoming hypoxic tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Liu, C.; Tian, W. Ruthenium (II)-Coordinated Supramolecular Drug Self-assembly for Efficient Combination Chemotherapy. Supramol. Mater. 2025, 4, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, S.; Ma, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gou, S. Boosting phototherapy efficacy of NIR-absorbing ruthenium (II) complex via supramolecular engineering. Mater. Today Nano 2022, 18, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Adon, T.; Dsouza, K.; Kumar, H.Y. Exploring the Future of Metal-Based Anticancer Agents: A Comprehensive Review of Ruthenium-Based Complexes. ChemistrySelect 2025, 10, e202404147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.; Li, C.; Ding, Q.; Sharma, A.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Sun, Y. Augmenting cancer therapy with a supramolecular immunogenic cell death inducer: A lysosome-targeted NIR-light-activated ruthenium (II) metallacycle. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 8991–9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Le, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Ruthenium-based antitumor drugs and delivery systems from monotherapy to combination therapy. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 16339–16375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaoujiya, R.; Singh, D.; Minocha, T.; Yadav, S.K.; Srivastava, S. Synthesis, characterization of ruthenium (III) macrocyclic complexes of 1, 4, 8, 11-tetraazacyclotetradecane (cyclam) and in vitro assessment of anti-cancer activity. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 3143–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, C.; Chi, C.; Wu, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gou, S. A supramolecular photosensitizer derived from an Arene-Ru (II) complex self-assembly for NIR activated photodynamic and photothermal therapy. Nature Commun. 2022, 13, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, B. Transporting and shielding photosensitisers by using water-soluble organometallic cages: A new strategy in drug delivery and photodynamic therapy. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 8378–8386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehn, J.M. Toward complex matter: Supramolecular chemistry and self-organization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4763–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, D.; Lin, Z.; Duan, C. Chirality transfer through helical motifs in coordination compounds. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 2007, 3451–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howson, S.E.; Scott, P. Approaches to the synthesis of optically pure helicates. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 10268–10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaner, R.A.; Scott, P. Metallohelices: Potential mimetics of α-helical peptides in cancer treatment? Fut. Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champness, N.R. The future of metal–organic frameworks. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 10311–10315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howson, S.E.; Bolhuis, A.; Brabec, V.; Clarkson, G.J.; Malina, J.; Rodger, A.; Scott, P. Optically pure, water-stable metallo-helical ‘flexicate’assemblies with antibiotic activity. Nature Chem. 2012, 4, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich-Wright, J.R. Resolutely pure helices. Nature Chem. 2012, 4, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Postings, M.; Scott, P.; Rogers, N.J. Metallohelices emulate the properties of short cationic α-helical peptides. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 1620–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehn, J.M.; Rigault, A.; Siegel, J.; Harrowfield, J.; Chevrier, B.; Moras, D. Spontaneous assembly of double-stranded helicates from oligobipyridine ligands and copper (I) cations: Structure of an inorganic double helix. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 2565–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoentjes, B.; Lehn, J.M. Interaction of Double-Helical Polynuclear Copper (I) complexes with double-stranded DNA. Helv. Chim. Acta 1995, 78, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.J.; Cooke, D.; Davidson, F.S.; Elliott, P.I.; Faulkner, R.A.; Griffiths, H.B.; Harper, O.J.; Hussain, O.; Owen-Lynch, P.J.; Phillips, R.M.; et al. Ruthenium-containing linear helicates and mesocates with tuneable p53-selective cytotoxicity in colorectal cancer cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9799–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, B.; Ang, W.H.; Chérioux, F.; Vieille-Petit, L.; JuilleratJeanneret, L.; Süss-Fink, G.; Dyson, P.J. Remarkable anticancer activity of triruthenium-arene clusters compared to tetrarutheniumarene clusters. J. Clust. Sci. 2007, 18, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Süss-Fink, G.; Neels, A.; Stoeckli-Evans, H. Mono-, di-and tetra-nuclear p-cymeneruthenium complexes containing oxalato ligands. Dalton Trans. 1997, 22, 4345–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.F.; Jia, W.G.; Lin, Y.J.; Jin, G.X. Stepwise formation of molecular rectangles of half-sandwich rhodium and ruthenium complexes containing bridging chloranilate ligands. Organometallics 2008, 27, 5002–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.F.; Jia, W.G.; Lin, Y.J.; Jin, G.X. Extending Rectangular Metal–Organic Frameworks to the Third Dimension: Discrete Organometallic Boxes for Reversible Trapping of Halocarbons Occurring with Conservation of the Lattice. Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 6352–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, F.; Galindo, M.A.; Galli, S.; Romero, M.A.; Navarro, J.A.; Barea, E. Tetranuclear coordination assemblies based on half-sandwich ruthenium (II) complexes: Noncovalent binding to DNA and cytotoxicity. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 7413–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, B. The role of the second coordination sphere in the biological activity of arene ruthenium metalla-assemblies. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.R.; Vajpayee, V.; Lee, M.H.; Stang, P.J.; Chi, K.W. Biomedical and biochemical applications of self-assembled metallacycles and metallacages. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2464–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Jeong, Y.J.; Jo, J.H.; Kang, S.C.; Kim, H.; Chi, K.W. Coordination-Driven Self-Assembly and Anticancer Potency Studies of Arene-Ruthenium-Based Molecular Metalla-Rectangles. Organometallics 2014, 33, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Jung, H.; Park, J.W.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, H.; Stang, P.J.; Chi, K.W. Anticancer Activity of Self-Assembled Molecular Rectangles via Arene-Ruthenium Acceptors and a New Unsymmetrical Amide Ligand. Organometallics 2012, 31, 3519–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, A.; Jeong, Y.J.; Jo, J.H.; Woo, S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.; Chi, K.W. Anticancer activity and autophagy involvement of self-assembled arene–ruthenium metallacycles. Organometallics 2015, 34, 4507–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Jeong, Y.J.; Jo, J.H.; Kang, S.C.; Lah, M.S.; Chi, K.W. Anticancer Potency Studies of Coordination Driven Self-Assembled Arene–Ru-Based Metalla-Bowls. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Jang, S.; Jo, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, D.W.; Kim, I.; Chi, K.W. Coordination-driven self-assembly and anticancer potency studies of Ruthenium–Cobalt-Based heterometallic rectangles. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 16157–16164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.; Govindaswamy, P.; Süss-Fink, G.; Ang, W.H.; Dyson, P.J.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Therrien, B. Ruthenium porphyrin compounds for photodynamic therapy of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.; Govindaswamy, P.; Zava, O.; Süss-Fink, G.; Juillerat, J.L.; Therrien, B. Combined arene ruthenium porphyrins as chemotherapeutics and photosensitizers for cancer therapy. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 14, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, J.; Govindaswamy, P.; Renfrew, A.K.; Dyson, P.J.; Štěpnička, P.; Süss-Fink, G.; Therrien, B. Synthesis, molecular structure, and anticancer activity of cationic arene ruthenium metallarectangles. Organometallics 2009, 28, 4350–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Das, A.; Ghate, N.B.; Kim, T.; Ryu, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.Y. Novel BODIPY-based Ru (II) and Ir (III) metalla-rectangles: Cellular localization of compounds and their antiproliferative activities. Chem. Comm. 2016, 52, 4274–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Das, A.; Panja, S.; Ryu, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Mandal, N.; Lee, C.Y. Self-assembly of novel thiophene-based BODIPY RuII rectangles: Potential antiproliferative agents selective against cancer cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 17199–17203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Yu, X.; Sun, Y. Construction of emissive ruthenium (II) metallacycle over 1000 nm wavelength for in vivo biomedical applications. Nature Commun. 2022, 13, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, B.; Süss-Fink, G.; Govindaswamy, P.; Renfrew, A.K.; Dyson, P.J. The “Complex-in-a-Complex” Cations [(acac)2M⊂Ru6 (p!iPrC6H4Me)6(tpt)2(dhbq)3]6+: A Trojan Horse for Cancer Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 3773–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freudenreich, J.; Barry, N.P.; Süss-Fink, G.; Therrien, B. Permanent encapsulation or host–guest behavior of aromatic molecules in hexanuclear arene ruthenium prisms. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 2400–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenreich, J.; Dalvit, C.; Süss-Fink, G.; Therrien, B. Encapsulation of photosensitizers in hexa-and octanuclear organometallic cages: Synthesis and characterization of carceplex and host–guest systems in solution. Organometallics 2013, 32, 3018–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, J.; Govindaswamy, P.; Furrer, J.; Sei, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Süss-Fink, G.; Therrien, B. Encapsulation of aromatic molecules in hexanuclear arene ruthenium cages: A strategy to build up organometallic carceplex prisms with a dangling arm standing out. Organometallics 2008, 27, 4346–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, N.P.E.; Therrien, B. Host–Guest Chemistry in the Hexanuclear (Arene) ruthenium Metalla-Prismatic cage [Ru6(p-cymene)6(tpt)2(dhnq)3]6+. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 4695–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garci, A.; Dobrov, A.A.; Riedel, T.; Orhan, E.; Dyson, P.J.; Arion, V.B.; Therrien, B. Strategy to Optimize the Biological Activity of Arene Ruthenium Metalla-Assemblies. Organometallics 2014, 33, 3813–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Oggu, G.S.; Nagesh, N.; Bokara, K.K.; Therrien, B. Anticancer activity of large metalla-assemblies built from half-sandwich complexes. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2016, 18, 4952–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Villagrán, M.; Paulus, L.; Charissoux, J.L.; Leger, D.Y.; Vergne-Salle, P.; Therrien, B.; Liagre, B. Ruthenium-based assemblies incorporating tetrapyridylporphyrin panels: A photosensitizer delivery strategy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by photodynamic therapy. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 9673–9680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, A.A.; Shettar, A.; Bhat, I.A.; Kondaiah, P.; Mukherjee, P.S. Self-assembly of discrete RuII8 molecular cages and their in vitro anticancer activity. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, A.A.; Shettar, A.; Bhat, I.A.; Kondaiah, P.; Mukherjee, P.S. Coordination-driven self-assembly of ruthenium (II) architectures: Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity studies. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 8466–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kostova, I. Recent Trends in the Design of Ruthenium Homometallic Polynuclear Complexes with Bioactive Ligands for Cancer Treatment. Inorganics 2025, 13, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13120380
Kostova I. Recent Trends in the Design of Ruthenium Homometallic Polynuclear Complexes with Bioactive Ligands for Cancer Treatment. Inorganics. 2025; 13(12):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13120380
Chicago/Turabian StyleKostova, Irena. 2025. "Recent Trends in the Design of Ruthenium Homometallic Polynuclear Complexes with Bioactive Ligands for Cancer Treatment" Inorganics 13, no. 12: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13120380
APA StyleKostova, I. (2025). Recent Trends in the Design of Ruthenium Homometallic Polynuclear Complexes with Bioactive Ligands for Cancer Treatment. Inorganics, 13(12), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13120380






