Utilizing Biomolecule-Rich Citrus Fruit Waste as a Medium for the Eco-Friendly Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles with Antimicrobial Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Fresh Aqueous Peel Juice
2.2. Antioxidant and Total Protein Estimation of Fresh Peel Juice
2.2.1. Measurement of Total Phenols
2.2.2. Measurement of Vitamin C
2.3. 2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Radical-Scavenging Assay
2.4. Total Soluble Proteins
2.5. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
2.6. Characterization Techniques to Analyze the Synthesized Ag Particles
UV–Vis Spectra Analysis
2.7. The Average Size Analysis
2.7.1. Average Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.7.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)/Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
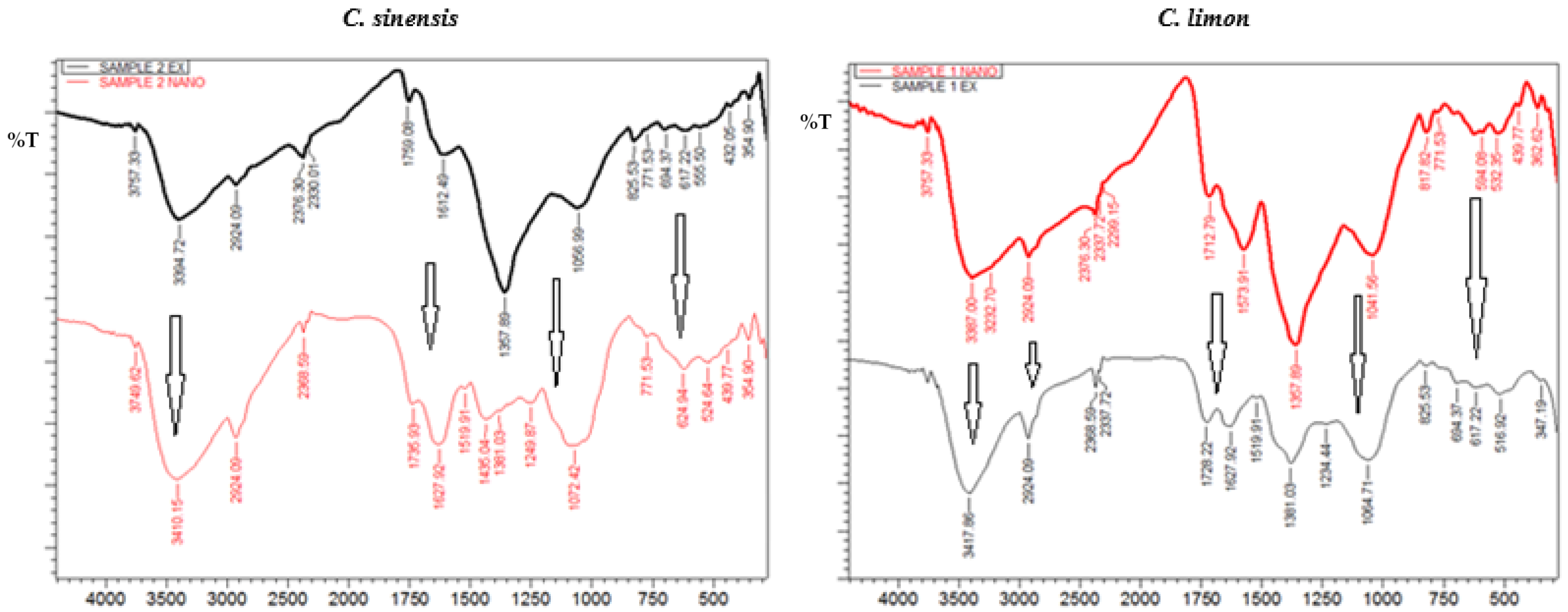
2.8. Fourier-Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.9. Antimicrobial Activity
2.9.1. Microbial Strains
2.9.2. Well Diffusion Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antioxidant and Total Protein Analysis
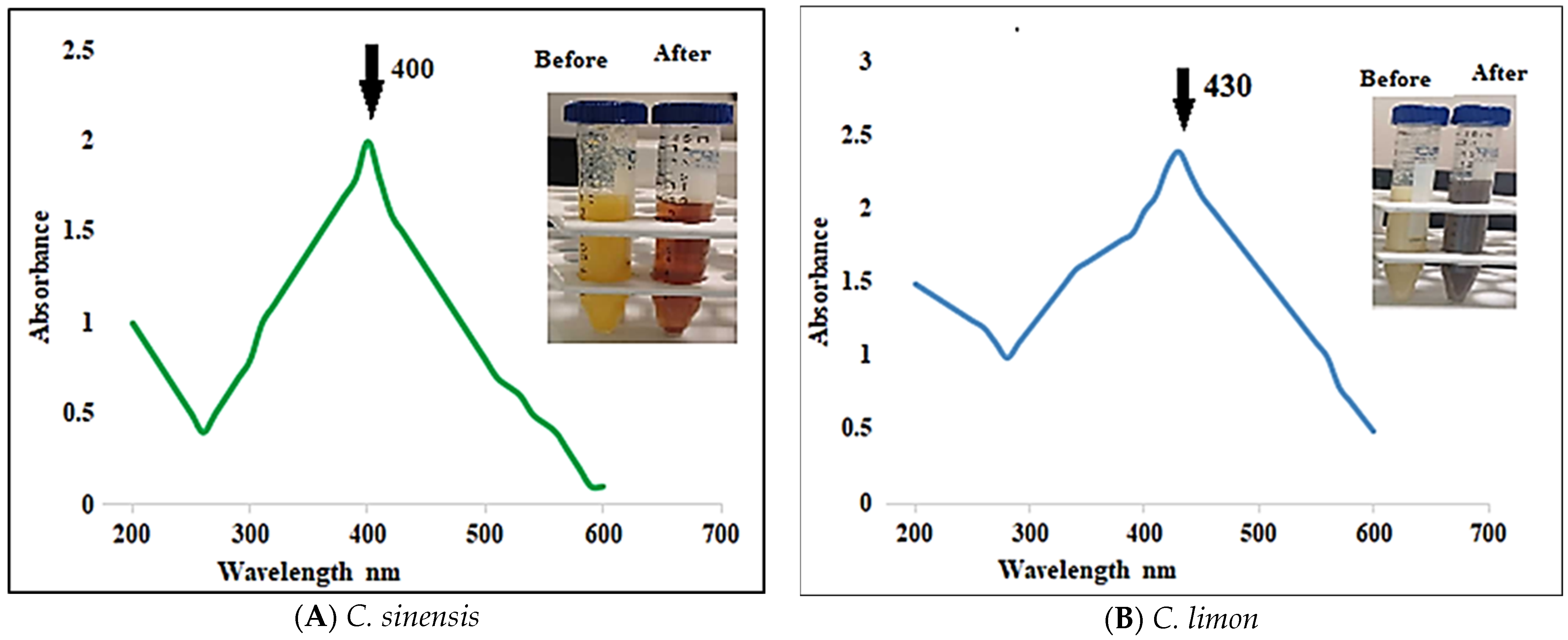
3.2. Biosynthesis of Ag Nanoparticles from Fresh Aqueous C. sinensis and C. limon Peel Juices
3.3. Characterization of Ag Nanoparticles
3.3.1. UV–Vis Spectra Analysis
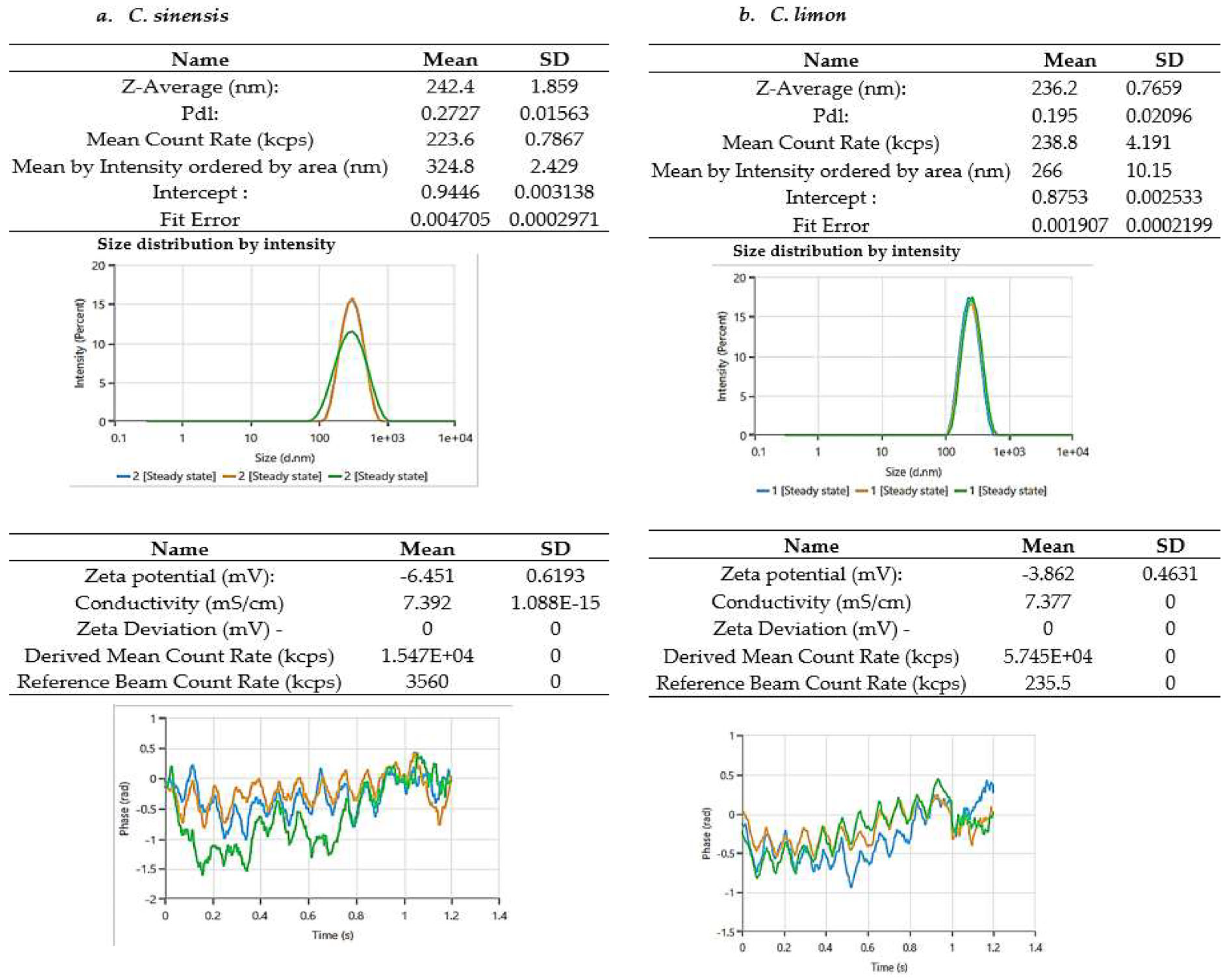
3.3.2. Zeta-Average Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analysis
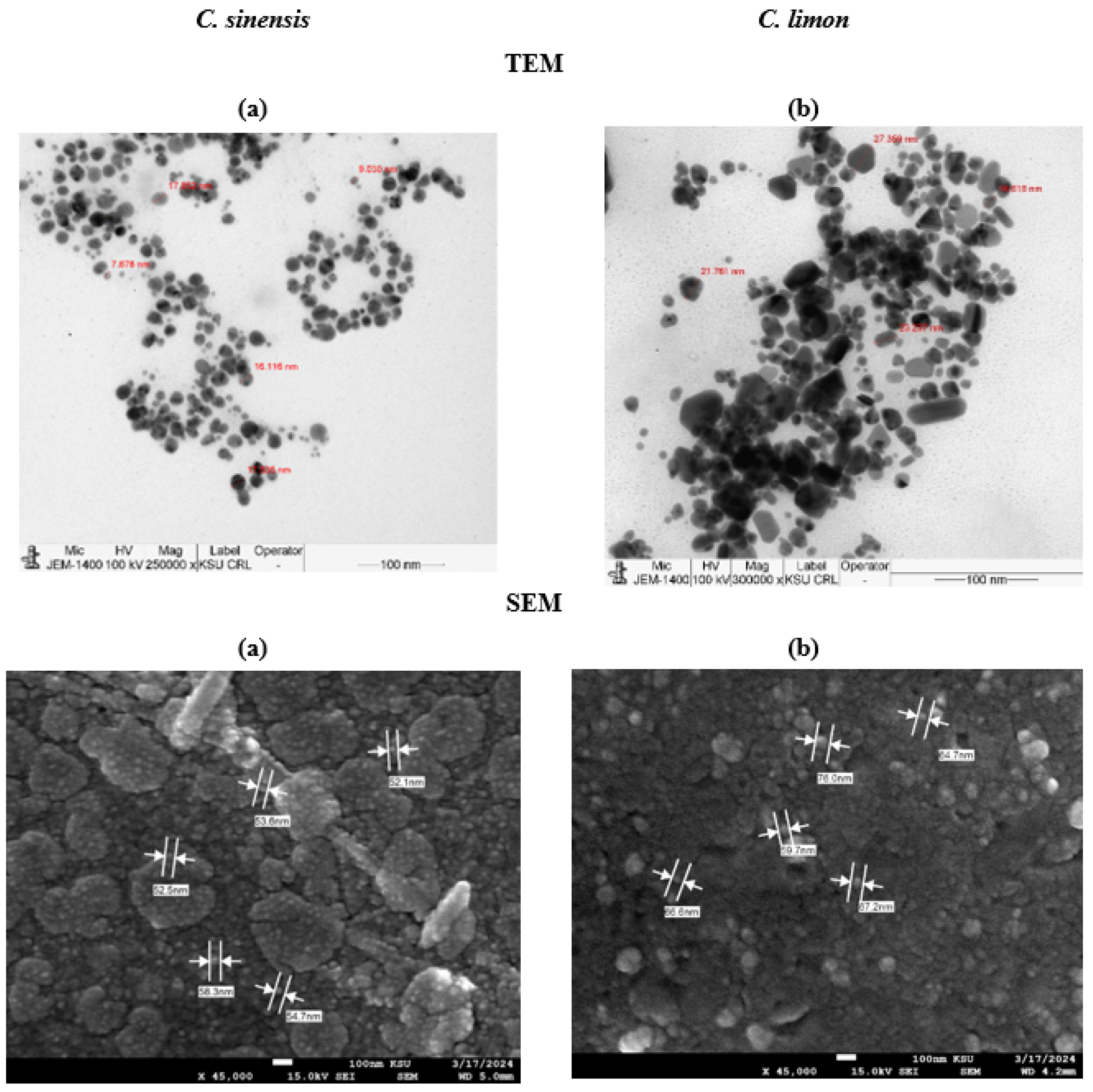
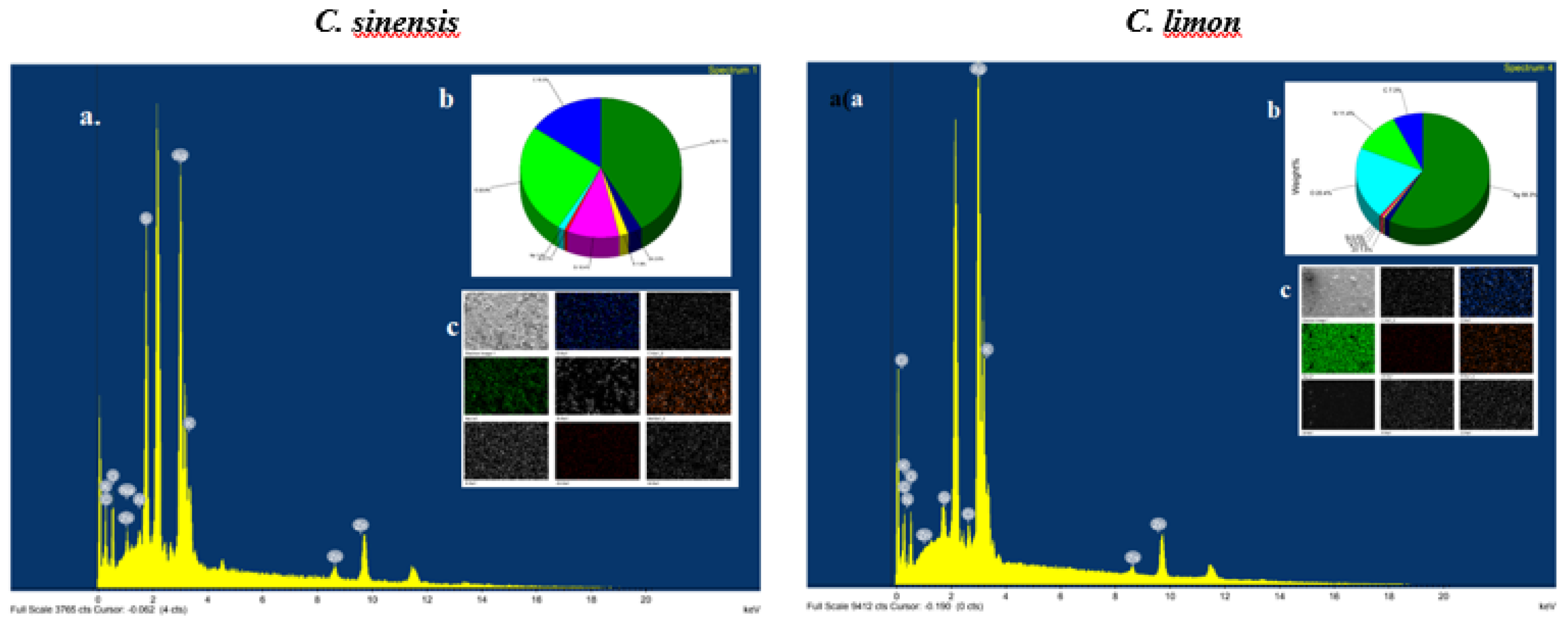
3.3.3. TEM and SEM/EDX Analysis
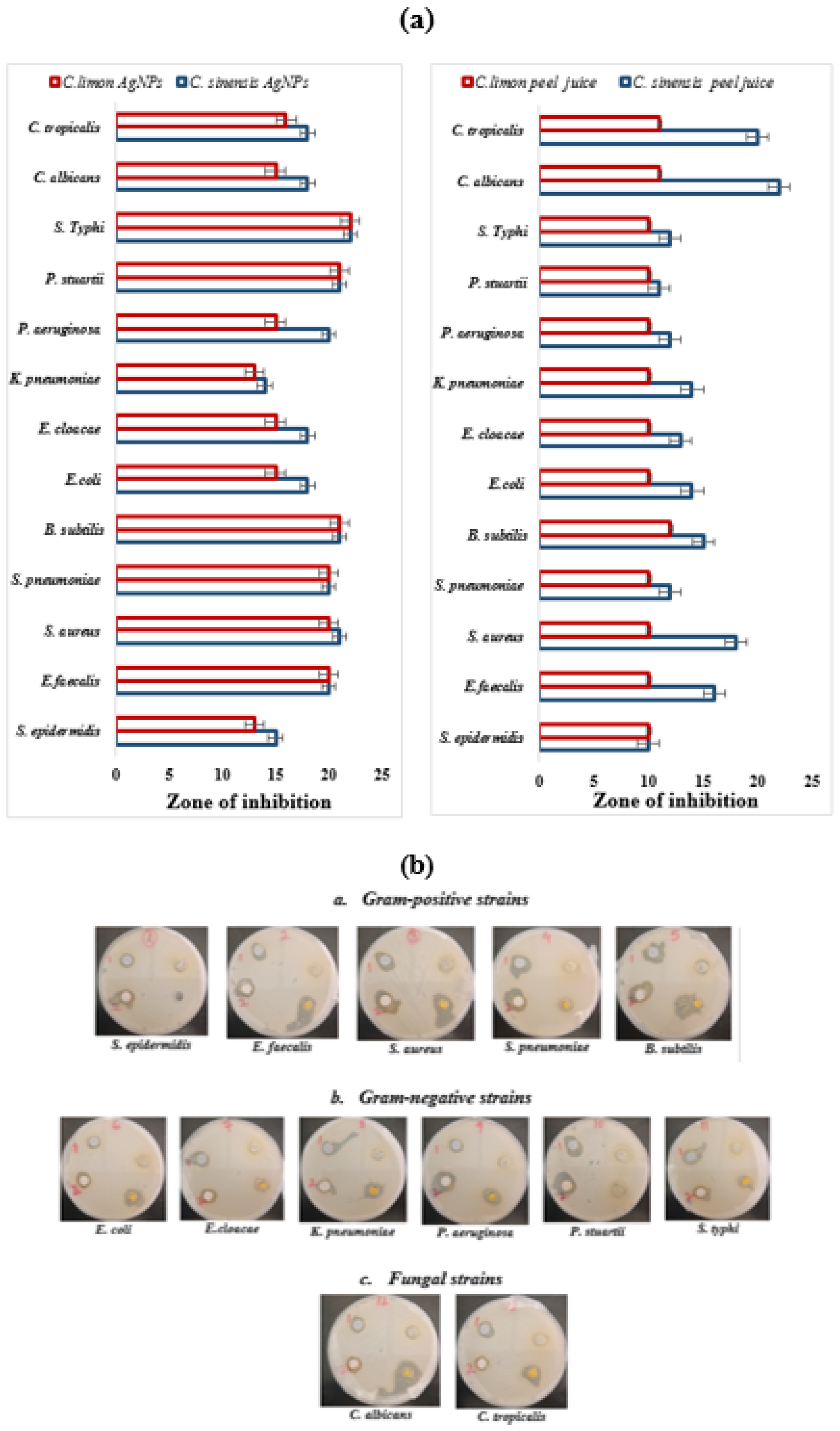
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Nanotechnology: A Revolution in Modern Industry. Molecules 2023, 28, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayilara, M.S.; Olanrewaju, O.S.; Babalola, O.O.; Odeyemi, O. Waste Management through Composting: Challenges and Potentials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, I.R.; Maniruzzaman, K.M.; Dano, U.L.; AlShihri, F.S.; AlShammari, M.S.; Ahmed, S.M.S.; Al-Gehlani, W.A.G.; Alrawaf, T.I. Environmental Sustainability Impacts of Solid Waste Management Practices in the Global South. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathi, V.P.; Meera, S.; Maria, C.G.A.; Nidhin, M. Green synthesis of nanoparticles from biodegradable waste extracts and their applications: A critical review. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Shin, H.S.; Jacob, J.M.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Bhaisare, M.; Kumar, G. New insights on the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant and waste biomaterials: Current knowledge, their agricultural and environmental applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 10164–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Zhang, Y.; Farghali MRashwan, A.K.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M. Synthesis of green nanoparticles for energy, biomedical, environmental, agricultural, and food applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 841–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, H.; Bibi, S.; Singh, I.; Hasan, M.M.; Khan, M.S.; Yousafi, Q.; Baig, A.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, F.; Emran, T.B.; et al. Green Metallic Nanoparticles: Biosynthesis to Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 874742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmal, N.P.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Mundanat, A.S.; Shah, K.; Babu, K.S.; Thorakkattu, P.; Al-Asmari, F.; Pandiselvam, R. Valorization of Fruit Waste for Bioactive Compounds and Their Applications in the Food Industry. Foods 2023, 12, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, S.P.; Modak, D.; Sarkar, S.; Roy, S.K.; Sah, S.P.; Ghatani, K.; Bhattacharjee, S. Fruit waste: A current perspective for the sustainable production of pharmacological, nutraceutical, and bioactive resources. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1260071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatyana, M.; Dube, N.P.; Kemboi, D.; Manicum, A.E.; Mokgalaka-Fleischmann, N.S.; Tembu, J.V. Advances in Phytonanotechnology: A Plant-Mediated Green Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles Using Phyllanthus Plant Extracts and Their Antimicrobial and Anticancer Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, R.; Zia, M.; Naz, S.; Ain, A.N.; Ao, Q. Role of capping agents in the application of nanoparticles in biomedicine and environmental remediation: Recent trends and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, S.; Afzal, O.; Khalid, M.; Ahmad, M.F.; Upadhyay, A.; Kumar, S.; Garg, A.; Ramzan, M.; Hussain, A.; Altamimi, M.A.; et al. Biogenic nanoparticles from waste fruit peels: Synthesis, applications, challenges and future perspectives. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 643, 123223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, J.; Herrera, W.; Hermosilla, E.; Díaz, M.; Parada, J.; Seabra, A.B.; Tortella, G.; Pesenti, H.; Ciudad, G.; Rubilar, O. Antioxidant Activity as an Indicator of the Efficiency of Plant Extract-Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzeid, H.M.; Julien, C.M.; Zhu, L.; Hashem, A.M. Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Their Energy Storage, Environmental, and Biomedical Applications. Crystals 2023, 13, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Mofijur, M.; Rafa, N.; Chowdhury, A.T.; Chowdhury, S.; Nahrin, M.; Islam, A.S.; Ong, H.C. Green approaches in synthesising nanomaterials for environmental nano bioremediation: Technological advancements, applications, benefits and challenges. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Trzcińska-Wencel, J.; Wypij, M.; Bonde, S.; Yadav, A.; Kratošová, G.; Golińska, P. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: What We Know and What Do We Need to Know? Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, C.; Maugeri, A.; Lombardo, G.E.; Musumeci, L.; Barreca, D.; Rapisarda, A.; Cirmi, S.; Navarra, M. The Second Life of Citrus Fruit Waste: A Valuable Source of Bioactive Compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyliev, G.; Vorobyova, V. Valorization of Food Waste to Produce Eco-Friendly Means of Corrosion Protection and “Green” Synthesis of Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moult, J.A.; Allan, S.R.; Hewitt, C.N.; Berners-Lee, M. Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Food Waste Disposal Options for UK Retailers. Food Policy 2018, 77, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendruscolo, F.; Albuquerque, P.M.; Streit, F.; Esposito, E.; Ninow, J.L. Apple Pomace: A Versatile Substrate for Biotechnological Applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2008, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowman, A.C.; Picard, M.C.; Lim, L.-T.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Fruit Waste Valorization for Biodegradable Biocomposite Applications: A Review. Bioresources 2019, 14, 10047–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, F.; Da Silva, S.; Massironi, A.; Mirpoor, S.F.; Lignou, S.; Ghawi, S.K.; Charalampopoulos, D. Silver Bionanocomposites as Active Food Packaging: Recent Advances & Future Trends Tackling the Food Waste Crisis. Polymers 2023, 15, 4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Kaur, G.; Sharma, P.; Singh, S.; Ikram, S. Fruit waste (peel) as bio-reductant to synthesize silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities. J. Appl. Biomed. 2018, 16, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Guo, X.; Bi, X.; Liu, X.; Shui, Y.; Lin, H.; et al. Antimicrobial Nanoparticles Incorporated in Edible Coatings and Films for the Preservation of Fruits and Vegetables. Molecules 2019, 24, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, Z.; Khalid, W.; Atiq, H.T.; Koraqi, H.; Javaid, Z.; Alhag, S.K.; Al-Shuraym, L.A.; Bader, D.M.D.; Almarzuq, M.; Afifi, M.; et al. Citrus Waste as Source of Bioactive Compounds: Extraction and Utilization in Health and Food Industry. Molecules 2023, 28, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Huayou, C. Promising future of citrus waste into fermented high-quality bio-feed in the poultry nutrition and safe environment. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhao, S.; Ning, Z.; Zeng, H.; Shu, Y.; Tao, O.; Xiao, C.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Citrus fruits as a treasure trove of active natural metabolites that potentially provide benefits for human health. Chem. Cent. J. 2015, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.; Durani, A.I.; Asari, A.; Ahmed, M.; Ahmad, M.; Yousaf, N.; Muddassar, M. Investigation of antioxidant and antibacterial effects of citrus fruits peels extracts using different extracting agents: Phytochemical analysis with in silico studies. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; Dominguez-López, I.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. The Chemistry Behind the Folin-Ciocalteu Method for the Estimation of (Poly)phenol Content in Food: Total Phenolic Intake in a Mediterranean Dietary Pattern. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17543–17553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagota, S.; Dani, H. A new colorimetric technique for the estimation of vitamin C using Folin phenol reagent. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 127, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliyan, S.; Mukherjee, R.; Priyadarshini, A.; Vibhuti, A.; Gupta, A.; Pandey, R.P.; Chang, C.M. Determination of Antioxidants by DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity and Quantitative Phytochemical Analysis of Ficus religiosa. Molecules 2022, 27, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, S.M.; Akbari, A. Metal nanoparticles synthesis through natural phenolic acids. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Mosleh, I.; Abbaspourrad, A. Impact of protein/peptide templates on metallic nanoparticle synthesis and applications. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2022, 30, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, A.; Anjum, L.; Faisal, Z.; Akram, N.; Shah, Y.A.; Irfan, R.; Saeed, F.; Afzaal, M.; Asif Shah, M. Recent advances in protein-based nanoparticles and their applications in the delivery of bioactive compounds. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 2866–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhag, R.; Kumar, R.; Dhiman, A.; Sharma, A.; Prabhakar, P.K.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Kumar, R.; Singh, A. Fruit peel bioactives, valorisation into nanoparticles and potential applications: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 6757–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugh, G.; Singh, B.R.; Adholeya, A.; Barrow, C.J. Role of proteins in the biosynthesis and functioning of metallic nanoparticles. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.T.; Lee, Y.J.; Krauland, E.M.; Kottmann, S.T.; Belcher, A.M. Peptide-mediated reduction of silver ions on engineered biological scaffolds. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakannan, P.R.; Swami, A.; Srisathiyanarayanan, D.; Shirude, P.S.; Pasricha, R.; Mandale, A.B.; Sastry, M. Synthesis of aqueous Au core-Ag shell nanoparticles using tyrosine as a pH-dependent reducing agent and assembling phase-transferred silver nanoparticles at the air-water interface. Langmuir 2004, 20, 7825–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Yang, B.; Gu, Q. Review of phytochemical and nutritional characteristics and food applications of Citrus L. fruits. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 968604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; He, C.; Liu, H.; Shen, G.; Feng, J. Compositional Analysis of Four Kinds of Citrus Fruits with an NMR-Based Method for Understanding Nutritional Value and Rational Utilization: From Pericarp to Juice. Molecules 2022, 27, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dbass, A.M.; Daihan, S.A.; Al-Nasser, A.A.; Al-Suhaibani, L.S.; Almusallam, J.; Alnwisser, B.I.; Saloum, S.; Alotaibi, R.S.; Alessa, L.A.; Bhat, R.S. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles from Two Varieties of Agaricus bisporus and Their Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sennett, P.; Olivier, J.P. Colloidal Dispersions, Electrokinetic Effects, and the Concept of Zeta Potential. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1965, 57, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, C. Precise Analysis of Nanoparticle Size Distribution in TEM Image. Methods Protoc. 2023, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Pallares, R.M.; Thanh, N.T. Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: Comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12871–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganaie, T.A.; Masoodi, F.A.; Rather, S.A.; Wani, S.M. Physicochemical, antioxidant and FTIR-ATR spectroscopy evaluation of Kashmiri honeys as food quality traceability and Himalayan brand. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 4139–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, R.S.; Alghamdi, J.M.; Aldbass, A.M.; Aljebrin, N.A.; Alangery, A.B.; Soliman, D.A.; Al-Daihan, S. Biochemical and FT-IR pro-filing of Tritium aestivum L. seedling in response to sodium fluoride treatment. Fluoride 2022, 55, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, R.S.; Al-Dbass, A.M.; Alghamdia, J.M.; Alonazia, M.A.; Al-Daihan, S. Trigonella foenum-graecum L. Seed germination under sodium halide salts exposure. Res. Rep. Fluoride 2023, 56, 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Campanale, C.; Savino, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy to Assess the Degree of Alteration of Artificially Aged and Environmentally Weathered Microplastics. Polymers 2023, 15, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to current antibacterial agents and approaches to resolve it. Molecules 2020, 25, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.I.; Salama, N.R. The gram-negative bacterial periplasm: Size matters. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2004935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Virulence Mech. Bact. Pathog. 2016, 22, 481–511. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, R.; Shineh, G.; Mobaraki, M.; Doughty, S.; Tayebi, L. Structural parameters of nanoparticles affecting their toxicity for biomedical applications: A review. J. Nanopart. Res. 2023, 25, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P. Reactive Oxygen Species-Related Nanoparticle Toxicity in the Biomedical Field. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.S.; Almusallam, J.; Al Daihan, S.; Al-Dbass, A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaves: Characterisation and impact on Staphylococcus aureus growth and glutathione-S-transferase activity. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zahrani, S.A.; Bhat, R.S.; Al Rashed, S.A.; Mahmood, A.; Al Fahad, A.; Alamro, G.; Almusallam, J.; Al Subki, R.; Orfali, R.; Al Daihan, S. Green-synthesized silver nanoparticles with aqueous extract of green algae Chaetomorpha ligustica and its anticancer potential. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduraihem, N.S.; Bhat, R.S.; Al-Zahrani, S.A.; Elnagar, D.M.; Alobaid, H.M.; Daghestani, M.H. Anticancer and Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Pods of Acacia nilotica. Processes 2023, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter (ug/mL) | C. sinensis | C. limon |
|---|---|---|
| Total phenol (standard—GA) | 178 ± 1.1 | 130 ± 1.5 |
| Ascorbic acid (standard—AA) | 33 ± 1.0 | 22 ± 1.6 |
| DPPH IC50 (standard AA-IC50-26) | 30 ± 0.7 | 31.5 ± 0.5 |
| Total protein (standard—BSA) | 93 ± 2.0 | 75 ± 0.7 |
| Strains | Zone of Inhibition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. sinensis | C. limon | |||
| Peel Juices | AgNPs | Peel Juices | AgNP | |
| S. epidermidis | 10 ± 1.0 | 15 ± 1.5 | 10 ± 0.0 | 13 ± 2.0 |
| E. faecalis | 16 ± 1.5 | 20 ± 1.5 | 10 ± 1.0 | 20 ± 1.0 |
| S. aureus | 18 ± 1.0 | 21 ± 2.0 | 11 ± 1.0 | 20 ± 1.5 |
| S. pneumoniae | 12 ± 1.0 | 20 ± 1.0 | 10 ± 1.5 | 20 ± 2.0 |
| B. subtilis | 15 ± 2.0 | 21 ± 1.5 | 11 ± 1.0 | 20 ± 1.0 |
| E. coli | 14 ± 1.0 | 18 ± 1.0 | 10 ± 1.5 | 15 ± 1.0 |
| E. cloacae | 13 ± 1.0 | 18 ± 2.0 | 10 ± 2.0 | 15 ± 2.0 |
| K. pneumoniae | 14 ± 1.5 | 14 ± 1.0 | 10 ± 1.5 | 13 ± 1.0 |
| P. aeruginosa | 12 ± 1.5 | 20 ± 1.0 | 10 ± 1.0 | 15 ± 2.0 |
| P. stuartii | 11 ± 1.0 | 21 ± 2.0 | 10 ± 1.5 | 21 ± 1.0 |
| S. Typhi | 12 ± 1.5 | 22 ± 1.0 | 10 ± 2.0 | 22 ± 1.5 |
| C. albicans | 22 ± 2.0 | 18 ± 1.5 | 11 ± 1.0 | 15 ± 1.0 |
| C. tropicalis | 20 ± 2.0 | 18 ± 00 | 11 ± 1.0 | 16 ± 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhat, R.S.; Al-Dbass, A.M.; Khayyat, A.I.A.; Al-Daihan, S. Utilizing Biomolecule-Rich Citrus Fruit Waste as a Medium for the Eco-Friendly Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles with Antimicrobial Properties. Inorganics 2024, 12, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12070180
Bhat RS, Al-Dbass AM, Khayyat AIA, Al-Daihan S. Utilizing Biomolecule-Rich Citrus Fruit Waste as a Medium for the Eco-Friendly Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles with Antimicrobial Properties. Inorganics. 2024; 12(7):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12070180
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhat, Ramesa Shafi, Abeer M. Al-Dbass, Arwa Ishaq A. Khayyat, and Sooad Al-Daihan. 2024. "Utilizing Biomolecule-Rich Citrus Fruit Waste as a Medium for the Eco-Friendly Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles with Antimicrobial Properties" Inorganics 12, no. 7: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12070180
APA StyleBhat, R. S., Al-Dbass, A. M., Khayyat, A. I. A., & Al-Daihan, S. (2024). Utilizing Biomolecule-Rich Citrus Fruit Waste as a Medium for the Eco-Friendly Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles with Antimicrobial Properties. Inorganics, 12(7), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12070180







