Abstract
Copper/sulfur co-doped titanium dioxide-carbon nanofibers (Cu,S-codoped TiO2 NPs, decorated-CNFs) catalysts were synthesized using the electrospinning process to produce composite nanofibers (NFs). These composite NFs were utilized for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride (SBH) to generate hydrogen gas (H2), taking advantage of their catalytic properties. The experimental results demonstrated that using 100 mg of composite NFs yielded the highest catalytic activity for H2 production, generating 79 mL of H2 gas within 6 min at 25 °C and 1000 revolutions per minute (rpm) using 1 mmol of SBH. As the catalyst dosage was reduced from 100 mg to 75, 50, and 25 mg, the reaction time increased by 9, 13, and 18 min, respectively. Kinetic studies revealed that the reaction rate followed a first-order reaction, indicating a direct proportionality between the rate of reaction and the catalyst amount. Additionally, it was observed that the concentration of SBH had no influence on the reaction rate, suggesting a zero-order reaction. Increasing the reaction temperature resulted in a reduced reaction time. The activation energy was determined to be 26.16 kJ mol−1. The composite NFs maintained their superior performance over five iterations. These findings suggest that composite nanofibers have the potential to serve as a cost-effective alternative to expensive catalysts in hydrogen production.
1. Introduction
Hydrogen (H2) as an energy carrier has gained recognition as a valuable alternative clean energy source due to its eco-friendly nature and high energy density [1,2]. It is considered a green product and a sustainable energy source. However, the H2-based economy faces a number of challenges, such as H2 release and storage control [3]. Metal hydrides play a vital role in the optimal storage of H2 [4]. Producing H2 from metal hydrides, such as sodium borohydride (SBH) and lithium borohydride (LiBH4), is considered a practical, inexpensive, and effective method. SBH stands out as a promising material for storing and producing H2 through a hydrolysis reaction due to its high H2 storage capacity (~10.8 wt.%), non-toxicity, and excellent stability in an alkaline solution without the need for a catalyst [5,6]. Proper catalysts can catalyze the dehydrogenation of SBH in an alkaline solution to produce pure H2 in a controlled manner [7]. It is important to emphasize that the dehydrogenation of SBH is extremely fast in the presence of suitable catalysts without the need for additional heat. Therefore, investigating effective catalysts for the dehydrogenation of SBH is critical for implementing the dehydrogenation process in the sustainable energy industry [7]. While it has been demonstrated that precious metals (e.g., Pd, Ru, Pt, Rh, and their alloys) supported on different matrices exhibit outstanding performance for H2 generation, their high cost and limited availability restrict their widespread usage [8,9,10,11]. To overcome this challenge, researchers are tirelessly working to develop a wide variety of catalysts based on non-precious metals, such as cobalt, nickel, and copper, and their alloys, which can catalyze the dehydrogenation of SBH and produce pure H2 [12,13,14,15,16,17]. Copper-based catalysts are widely used because they are readily available and inexpensive [1]. They have been applied as effective catalysts for the dehydrogenation of SBH to generate H2 [14]. Carbon-based materials are seen as one of the best alternatives to metal-based catalysts due to their tunable electrical characteristics, availability, and low environmental impact [1]. Doping carbon-based substances with heteroatoms (e.g., S, N, B, and P) allows for the adjustment of their electrical and surface chemistry characteristics, greatly improving the catalytic efficacy of carbon-based materials in numerous reactions. The distinct electronegativities of heteroatoms and carbon atoms contribute to an increase in the conductive properties and electron transmission rate of carbon materials. Cafer Saka [18] demonstrated the effect of S and N on the catalytic activity of carbon in the dehydrogenation of SBH. These atoms enhanced the catalytic activity of carbon, resulting in a hydrogen generation rate (HGR) of 2641 and 4923 mL·min−1·gcat−1 for pristine carbon and S-doped carbon, respectively. According to Zhang et al. [7], the addition of S in the form of sodium sulfate and sodium sulfide to a Co-based catalyst for the generation of H2 from SBH resulted in an HGR of 4425 mL·min−1·gcat−1, which is four times higher than that of cobalt oxide. Dilek Kılınc¸ [19] demonstrated that a copper (II)-Schiff Base complex-supported TiO2 matrix exhibited good catalytic activity for the dehydrogenation of SBH compared to unsupported copper (II)-Schiff Base complex, with an HGR of 215 mL·min−1·gcat−1 and 14,020 mL·min−1·gcat−1, respectively. In addition to their usage as support matrices, TiO2 possesses both redox and Lewis acidity characteristics. Various types of nanostructures have been utilized as effective catalysts for the generation of H2 from SBH. Among them, nanofibers (NFs) have a notable advantage in H2 production from SBH due to their higher surface-to-volume ratio and highly porous structure [3,20,21,22,23]. Electrospinning is widely regarded as a highly convenient and versatile methodology for fabricating NFs. During the electrospinning process, a high electrical potential is applied to overcome the surface tension in the solution, leading to the expulsion of the charged precursor solution from the needle and its subsequent gathering on the collecting mandrel [20]. The electrospinning technique is capable of generating NFs ranging in size from 50 to 900 nm. In this study, Cu,S-codoped TiO2 NPs decorated on CNFs were synthesized using the electrospinning technique. The utilization of this composite made of Cu,S-codoped TiO2 NPs-decorated CNFs for the production of H2 from SBH has not previously been described, to the best of the author’s knowledge. The structure and catalytic performance of the new composite are exploited for H2 production. The prepared composite NFs have shown superior catalytic activity for the dehydrogenation of SBH and subsequent H2 generation.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization Results
Copper sulfide demonstrates low solubility in commonly used solvents. Consequently, the addition of sulfide ions (S2−) to a solution containing copper ions (Cu2+) leads to the formation of a finely dispersed precipitate known as CuS. Therefore, a green colloidal solution was generated by adding a few drops of ammonium sulfide to the copper ion sol-gel [6]. Electrospinning is a widely used method for producing polymer NFs [24]. Recently, our research group utilized electrospinning to synthesize NFs from a colloidal solution with an optimal nanofibrous shape [25,26,27]. Figure 1a depicts the SEM image of TIIP-PVP electrospun NF mats after calcination at 800 °C in an Ar atmosphere. As shown in the figure, the generated NFs are smooth, continuous, and free of beads.
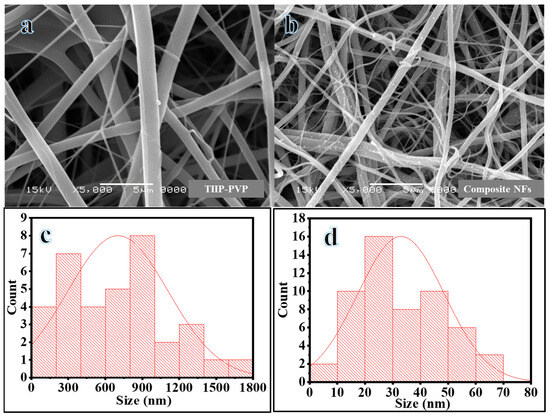
Figure 1.
SEM images of obtained powder after calcination of TIIP-PVP (a) and composite NFs (b) at 800 °C in Ar and their respective average size (c,d).
Due to the susceptibility of TIIP to rapid hydrolysis upon exposure to atmospheric moisture, the NFs, upon ejection from the electrospinning needle, were able to form continuous networks (gels) of TiO2 sols [28]. SEM images of the electrospun green colloidal solution following calcination at 800 °C in an Ar environment are presented in Figure 1b. It can be observed that the NFs retained their nanofibrous structure, and continuous NFs were formed despite the unusual sintering conditions. Additionally, densely dispersed white nanoparticles (NPs) were generated on the surface of the NFs. It is well-known that increasing the calcination temperature of electrospun NFs mat while processing it in a vacuum and in the presence of argon gas slows down the rate of polymer decomposition, leading to the production of carbon as a byproduct of the calcination process [29,30]. The TiO2-CNFs exhibited an average diameter of up to 702 nm (Figure 1c), whereas the composite NFs had an average diameter of 33 nm (Figure 1d). This could be attributed to the increased electrical conductivity of the solution due to the addition of Cu precursor and ammonium sulfide, resulting in the stretching of the produced NFs in the electrospinning process.
Figure 2a illustrates the typical XRD analysis of the composite NFs. Five distinct peaks are clearly visible at 2θ values of 26.98°, 35.72°, 40.88°, 54.08°, and 68.62°, corresponding to the (110), (101), (211), (211), and (002) crystal planes of the rutile phase of TiO2 (JCPDS#21-1276), respectively. Additionally, there is a prominent diffraction peak at a 2θ value of approximately 42.95°, which corresponds to the (111) crystal planes of metallic copper (JCPDS#04-0836). Furthermore, the presence of a sharp peak at a 2θ value of around 24.89° may indicate the presence of graphite-like carbon resulting from the graphitization of polymer NFs [31]. The absence of a peak in the detection of CuS could be attributed to the thermal degradation of CuS into metallic copper and sulfur at elevated temperatures in a vacuum system containing an argon atmosphere. Moreover, the lack of sulfur peaks may be due to the incorporation of sulfate ions into the TiO2 and/or carbon structure [32], which could also explain the negative deviation in the peaks of TiO2, copper, and carbon. Raman spectroscopy was also employed to investigate the chemical structure of the graphite-like carbon obtained. Figure 2b reveals two peaks centered at approximately 1346.78 and 1593.93 cm−1, corresponding to the D and G bands of graphite, respectively. This indicates that the polymer has undergone a transformation into graphite with a certain amount of disordered sp2 C–C bonding [28].
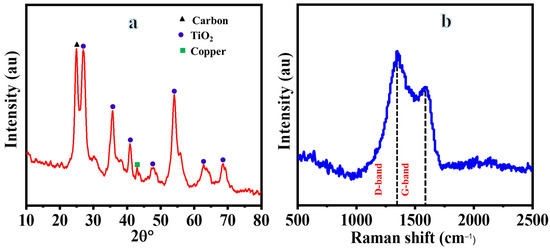
Figure 2.
XRD (a) and Raman (b) analyses of composite NFs after sintering at 800 °C in Ar.
Figure 3a shows a typical TEM image of the composite NFs, revealing the nanoparticles (NPs) adhered to the surface of the NFs. Figure 3b displays the EDX spectra of the composite NFs, indicating the presence of titanium, oxygen, copper, and carbon as the only elements in the spectra.
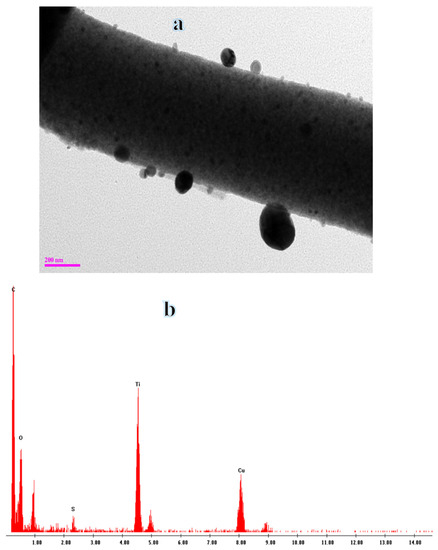
Figure 3.
Normal TEM (a) and EDX (b) of composite NFs after sintering at 800 °C in Ar.
Figure 4a displays the STEM image of the composite NFs, showing the even dispersion of nanoparticles (NPs) inserted within the surface of the selected NF. TEM-EDX analysis was performed along the line indicated in Figure 4a, revealing that the distributions of Ti (Figure 4b), O (Figure 4c), S (Figure 4d), and Cu (Figure 4e) are consistent. Additionally, it has been observed that carbon is the furthest element. The protective carbon coating on the active NPs allows for their long-term preservation during catalytic processes.
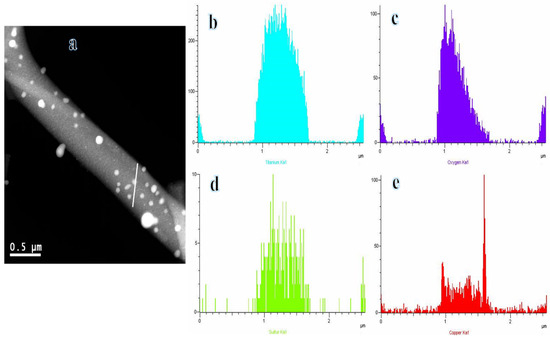
Figure 4.
One STEM image (a), and TEM-EDX of Ti (b), O (c), S (d), and Cu (e) of composite NFs after sintering at 800 °C in Ar.
2.2. Hydrolysis of SBH
2.2.1. Effect of NaOH Percentages
The hydrolysis reaction of SBH is highly sensitive to the alkalinity of the solution. The rate of hydrolysis in an alkaline solution is slower compared to that in pure water due to the hydrolysis of NaBO2, which produces NaOH [14,19]. Figure 5 illustrates the volume of H2 generated by varying concentrations of [NaOH] (0%, 5%, 7%, and 10%) when mixed with 50 mg of catalytic composite NFs and 1 mM of SBH at 25 °C and 1000 rpm. It can be observed that as the [NaOH] increased from 0% to 7%, the completion time of the SBH hydrolysis reaction decreased (17 min, 13 min, and 10 min, respectively). However, when the [NaOH] was further increased to 10%, an increase in the hydrolysis reaction completion time (15 min) was observed. This is likely due to the presence of OH in the hydrolysis of NaBH4. The HGR (hydrogen generation rate) can be enhanced by increasing the concentration of NaOH, which accelerates the catalyzed hydrolysis of SBH. However, if the NaOH concentration is too high, NaBO2 may become less soluble, precipitate out of the solution, and attach to the catalyst’s surface, obstructing its active sites [14]. This can hamper the contact between BH4+ ions and the catalyst’s surface, resulting in a slower rate of hydrolysis. Based on these findings, the addition of 7% NaOH to the composite NFs significantly enhanced H2 production, reduced reaction durations, and increased the volume of generated H2. Therefore, the optimal [NaOH] concentration for SBH hydrolysis catalysis was determined to be 7% for further kinetic investigations.
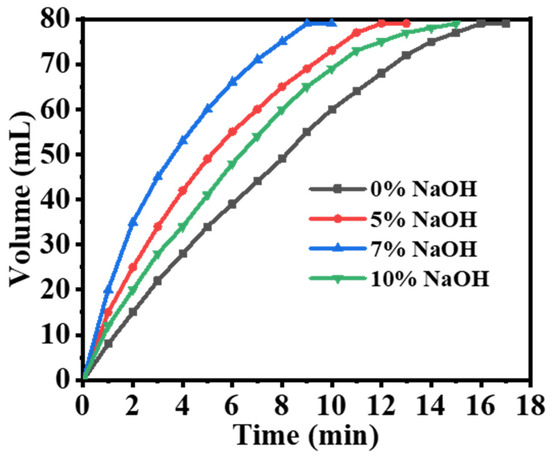
Figure 5.
Effect of NaOH % on the hydrolysis of SBH used ([SBH] = 1 mmol, composite NFs = 25 mg, 25 °C, and 1000 rpm).
2.2.2. Effect of Catalyst Amount
Figure 6a demonstrates a positive correlation between the amount of catalyst (ranging from 25 to 100 mg) and the volume of H2 generation in the presence of 1 mM SBH, 25 °C, 7% NaOH, and 1000 rpm. In the absence of a catalyst, only 13 mL of hydrogen gas was generated over a duration of 56 min. Although SBH is inherently unstable in atmospheric conditions, it exhibits a slow reaction rate with water in the absence of a catalyst, resulting in limited H2 production [33]. However, the introduction of a small amount of catalyst (25 mg) significantly increased the volume of H2 production within 18 min. Hydrolysis reactions were conducted with 50 mg, 75 mg, and 100 mg of catalyst, resulting in the production of 79 mL of H2 in 13, 9, and 6 min, respectively. The enhanced catalytic activity can be attributed to the increased specific surface area and exposure of active sites facilitated by the incorporation of composite NFs [34]. As the SBH hydrolysis process progressed, a decrease in the rate of H2 production was observed. This may be due to the formation of H2 aggregates and the blocking of active sites, hindering the generation of new active sites for subsequent catalytic cycles [34]. The H2 generation rate (HGR) was determined by analyzing the linear segment of each plot shown in Figure 6a. The logarithmic scale values of the HGR relative to the initial amount of composite NFs are depicted in Figure 6b. The slope of the straight line is close to first order (slope = 0.89), indicating that the catalytic hydrolysis of SBH follows a nearly first-order dependence on the catalyst amount.
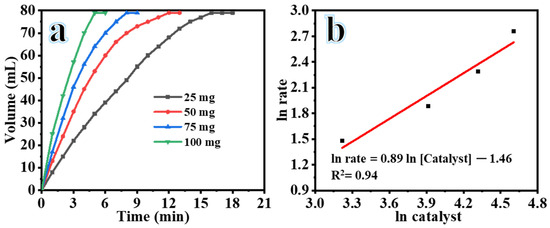
Figure 6.
H2 production volume versus time from hydrolysis of SBH using different composite NF doses at 25 °C, [SBH] = 1 mmol, and 1000 rpm (a), and logarithmic plot of H2 production rate versus catalyst loading amount (b).
2.2.3. Effect of SBH Concentration
To investigate the influence of the starting concentration of SBH ([SBH]) on the hydrolysis process, experiments were conducted using 25 mg of composite NFs, 25 °C, 7% NaOH, and 1000 rpm. As shown in Figure 7a, the maximum volumes of H2 produced were 79 mL in 18 min, 144 mL in 32 min, 223 mL in 42 min, and 303 mL in 60 min when utilizing 1, 2, 3, and 4 mM SBH, respectively. This trend indicates that increasing [SBH] from 1 to 4 mM led to a corresponding increase in H2 production. The correlation between [SBH] and the volume of produced H2 is evident from the data. Based on these findings, an [SBH] of 1 mM was selected for the remaining experiments due to economic considerations. While higher SBH concentrations could potentially lead to greater H2 production, it is important to consider the practical aspects. Using a lower SBH concentration allows for greater contact between H2O and BH4− with the active sites on the catalyst’s surface, resulting in H2 production at higher SBH concentrations. However, it is worth noting that the production of NaBO2 occurs simultaneously with H2 production. If the starting [SBH] is increased, NaBO2 may accumulate on the catalyst and in the solution due to its limited solubility in alkaline solutions. This can increase the viscosity of the solution, reduce mass transfer, and subsequently decrease H2 production [35,36]. Previous studies have also shown that higher concentrations of SBH can lead to a decrease in catalytic activity due to a limited number of available active sites for the desired reaction [35,37]. Figure 7b depicts the values of the HGR plotted against the starting concentration of SBH on a logarithmic scale. The slope of the linear regression analysis suggests that the catalytic hydrolysis of SBH exhibits a 0.065 order dependence on [SBH], indicating that the reaction follows zero-order kinetics with respect to [SBH].
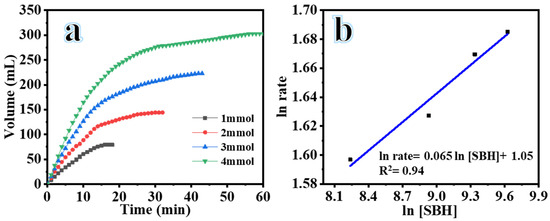
Figure 7.
H2 production volume versus time from hydrolysis of SBH using different [SBH] at 25 °C, composite NFs amount = 25 mg, and 1000 rpm (a), and logarithmic plot of H2 production rate versus [SBH] (b).
2.2.4. Effect of Temperature
Figure 8a demonstrates the variation in the volume of H2 generated during the SBH hydrolysis process at different temperatures: 20, 30, 40, and 50 °C. The experiments were conducted using solutions containing 50 mg of composite NFs, 1 mM SBH, 7% NaOH, and 1000 rpm. As expected, an increase in temperature led to a decrease in the completion time of the SBH hydrolysis process and an increase in the rate of H2 generation. For example, the time required to reach a cumulative volume of 79 mL of H2 was 18, 14, 11, and 7 min at temperatures of 298, 303, 318, and 328 K, respectively. Previous studies [38] have shown that increasing the temperature results in a higher availability of highly active reacting molecules leads to an accelerated rate of H2 generation. This can be attributed to the increased kinetic energy and activity within the reaction system as the temperature is raised. Furthermore, the kinetic behavior of the SBH hydrolysis process catalyzed by composite NFs was studied at different temperatures (Figure 8b). The linear portions of the H2 production graphs at different temperatures were used to determine the rate constant (k) for the H2 production from the hydrolysis process. The relationship between k and 1/T is shown in Figure 8b. The apparent activation energy (Ea) was determined using the Arrhenius plot and equation. The slope of the straight line yielded an Ea value of 26.16 kJ mol–1 for the SBH hydrolysis catalyzed by composite NFs. Comparing the obtained Ea value with those of different catalysts for H2 production from SBH (Table 1), the prepared NFs exhibited a relatively low activation energy. This suggests that the composite NFs are efficient catalysts for the hydrolysis of SBH, resulting in a rapid reaction rate. The entropy (ΔS) and enthalpy (ΔH) of the hydrolysis reaction process were calculated using the Eyring equation and were found to be 0.044 kJ mol−1 K−1 and 23.56 kJ mol−1, respectively. These ΔH and ΔS values can be used to calculate ΔG using Equation (1) and rewritten in Equation (2) as follows:
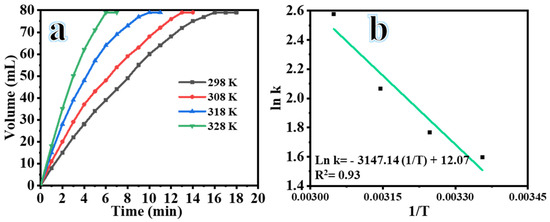
Figure 8.
Influence of reaction temperature on the hydrolysis of SBH catalyzed by composite NFs (a) and the Arrhenius plot of ln rate versus 1/T (b) used ([SBH] = 1 mmol, composite NFs = 25 mg and 1000 rpm).

Table 1.
Activation energies of different catalysts for H2 generation from SBH.
2.2.5. Reusability Test
To assess the reusability of composite NFs as catalysts for the hydrolysis of SBH, identical experimental conditions were maintained (25 mg of composite NFs, 1 mM SBH, 7% NaOH, 25 °C, and 1000 rpm) in a recycling study (Figure 9). It was observed that the catalytic activity of the composite NFs declined after the third cycle. In the first cycle, the composite NFs were able to produce the full stoichiometric amount of H2. However, in the third cycle, only 87% of the total yield of produced H2 was collected. This decline in catalytic activity can be attributed to the accumulation of boron compounds such as NaBO2. These compounds can hinder the active sites of the catalyst and reduce its catalytic activity [45].
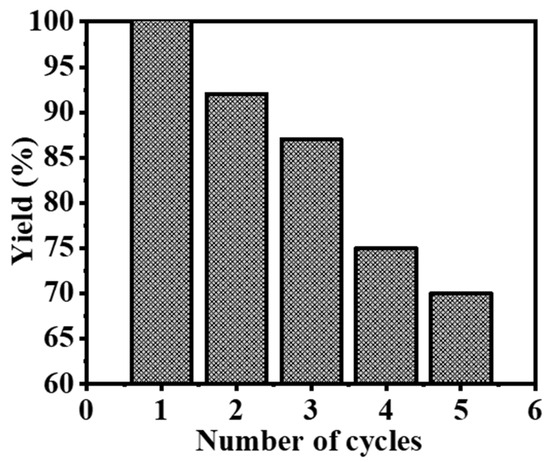
Figure 9.
The reusability of the composite NFs catalyst.
3. Experimental
3.1. Preparation of Cu,S-Co-Doped TiO2 NPs, Decorated-CNFs
Stock solution of 15% polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP, average Mw ~1,300,000, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) solution was prepared using a mixture of PVP powder, acetic acid (100%, Showa Chemicals Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), and ethanol (99%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The preceding mixture was kept in stirrer overnight at room temperature. A total of 2 g of titanium tetraisopropoxide (TIIP; 97%, Sigma-Aldrich) solution is added dropwise to the previous solution. The two solutions were kept magnetically agitated at room temperature until they produced a translucent yellow sol-gel. After the sol-gel had been prepared, 1 g of copper (II) acetate monohydrate (CuAc, 98%, Sigma-Aldrich) was introduced and vigorously stirred for 3 h at 60 °C to ensure a uniform mixture. After that, ammonium sulfide ((NH4)2S, 40–48 wt.%, Sigma-Aldrich) was added dropwise to the aforementioned CuAc- contained Sol-gel. The formed colloidal green sol-gel that resulted was kept in the magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 5 h. For the purpose of fabricating NFs, the formed colloidal solution was put through an electrospinning apparatus, much as was carried out in our earlier research [18]. A micro-tip plastic syringe of 5 cm was filled with the colloidal solution. The plastic end was positively charged by a metallic wire that was immersed in the tip. The wire was connected to a high-voltage power supply. There was a gap of 18 cm that separated the cylindrical steel rotating drum covered with wax foil negative side from the tip of the plastic needle. Then, 20 kV was applied between the two electrodes. After the consumption the colloidal solution, the system was turned off and the formed mats were detached from the foil. The NF mats were vacuum dried at 50 °C overnight. After drying, they were calcined under vacuum in an Ar environment at 800 °C for 5 h. Pristine TiO2-CNFs were also prepared using the same procedure excluding the CuAc and ammonium sulfide addition procedures.
3.2. Characterization
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Hitachi S-7400, Tokyo, Japan) was used to examine the surface morphology of the composite NFs. X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Rigaku Co., Tokyo, Japan) using Cu K radiation (λ = 1.54056 Å) was employed to study the crystalline structure of the composite NFs. The high-resolution pictures were captured using a 200-kilovolt JEOL JEM-2200FS transmission electron microscope (TEM) from JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, equipped with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). The identification of the structure of CNFs was achieved through the utilization of Raman spectroscopy, with a laser excitation wavelength of 532 nm.
3.3. Hydrolysis Reaction
The hydrolysis process for H2 generation was carried out in a 150 mL two-neck round-bottom flask used as a reaction vessel, and the volume of H2 was estimated using the traditional water-displacement method. Typically, 25 mg of composite NFs catalyst, 1 mM alkaline SBH, 7% NaOH, 1000 rpm, and 25 °C were mixed in the flask. The yield of H2 was calculated based on the volume of H2 obtained from the SBH hydrolysis reaction vessel. Several independent experiments were conducted to determine the optimal values for the parameters involved in the reaction, such as NaOH concentration, catalyst amount, SBH concentration, and temperature. The yield of produced H2 was determined using Equation (3).
H2 yield (%) = (Produced H2/theoretical H2) × 100
4. Conclusions
In this study, a composite NFs catalyst was synthesized using electrospinning techniques and employed as a catalyst for the hydrolysis of SBH, resulting in the production of H2. The catalyst demonstrated significant catalytic efficiency, with a notable production of H2 achieved using 100 mg of the catalyst. The presence of NaOH in the reaction mixture played a crucial role in the hydrolysis process. Increasing the NaOH concentration from 0% to 7% led to a reduction in the reaction time for SBH hydrolysis. However, further increasing the NaOH concentration to 10% resulted in an increased reaction time. This suggests that the optimal NaOH concentration for efficient SBH hydrolysis lies within the range of 7%. Moreover, increasing the amount of catalyst led to an improvement in the rate of H2 production, indicating a near first-order dependence of the hydrolysis reaction on the catalyst dosage. On the other hand, the hydrolysis reaction exhibited a zero-order dependence on the SBH concentration, indicating that changes in SBH concentration did not significantly affect the reaction rate. The composite NFs demonstrated exceptional catalytic activity, as evidenced by the low activation energy (Ea) value of 26.16 kJ mol−1. This low Ea suggests that the composite NFs exhibit efficient catalytic performance for the hydrolysis of SBH. Additionally, the composite NFs exhibited stable and consistent H2 generation during the reusability and stability tests for up to five cycles. This indicates their potential as a feasible catalyst for practical applications, as they maintained their catalytic activity over multiple cycles without significant degradation. Overall, the study establishes the effectiveness of the composite NFs catalyst for SBH hydrolysis, highlighting its potential as a promising catalyst for hydrogen production.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia grant number [ISP22-31].
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The author extends his appreciation to the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project number ISP22-31.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Balbay, A.; Saka, C. Effect of phosphoric acid addition on the hydrogen production from hydrolysis of NaBH4 with Cu based catalyst. Energy Sources A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2018, 40, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, C.W.; Baker, R.T.; Staubitz, A.; Manners, I. B–N compounds for chemical hydrogen storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Dong, Y.; Xie, P.; Li, Q. Hydrogen production through hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: Highly dispersed CoB particles immobilized in carbon nanofibers as a novel catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 32145–32156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakintuna, B.; Lamari-Darkrim, F.; Hirscher, M. Metal hydride materials for solid hydrogen storage: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouli, N.; Maafa, I.M.; Abutaleb, A.; Yousef, A.; El-Halwany, M.M. Electrospun NiPd Nanoparticles Supported on Polymer Membrane Nanofibers as an Efficient Catalyst for NaBH4 Dehydrogenation. Polymers 2023, 15, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enizi, A.M.; Nafady, A.; El-Halwany, M.; Brooks, R.M.; Abutaleb, A.; Yousef, A. Electrospun carbon nanofiber-encapsulated NiS nanoparticles as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen production from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 21716–21725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, K.; Fan, G.; Jiang, W. Efficient hydrogen generation from the NaBH4 hydrolysis by cobalt-based catalysts: Positive roles of sulfur-containing salts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 9376–9386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Patton, B.; Zanchetta, C.; Fernandes, R.; Guella, G.; Kale, A.; Miotello, A. Pd-C powder and thin film catalysts for hydrogen production by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.C.; Nie, M.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Liu, H.L. Kinetics of NaBH4 hydrolysis on carbon-supported ruthenium catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 12343–12351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, C.; Wu, F.; Yi, B. Carbon-supported platinum catalysts for on-site hydrogen generation from NaBH4 solution. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 2236–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Ceccato, R.; Raj, R. Superefficient thin film multilayer catalyst for generating hydrogen from sodium borohydride. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhang, H.; Xu, D.; Ma, L.; Yi, B. Hydrogen generation utilizing alkaline sodium borohydride solution and supported cobalt catalyst. J. Power Sources 2007, 164, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, G.; Özer, A.; Yurtcan, A.B. Hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride with Ni and Co based catalysts supported on Co3O4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 22205–22214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimi, A.S.; Nohan, M.A.N.M.; Chin, S.X.; Khiew, P.S.; Zakaria, S.; Chia, C.H. Copper nanowires as highly efficient and recyclable catalyst for rapid hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saka, C.; Şahin, Ö.; Demir, H.; Karabulut, A.; Sarikaya, A. Hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis with a Cu–Co-based catalyst: A kinetic study. Energy Sources A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2015, 37, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Gao, X.; Ning, X.; Qiu, Z.; Xing, L.; Yang, H.; Li, D.; Dou, J.; Meng, Y. Cobalt-nickel bimetal carbon sphere catalysts for efficient hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: The role of synergy and confine effect. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 3413–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouli, N.; Maafa, I.M.; Abutaleb, A.; Yousef, A.; El-Halwany, M.M. Membrane Nanofiber-Supported Cobalt–Nickel Nanoparticles as an Effective and Durable Catalyst for H2 Evolution via Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis. Polymers 2023, 15, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saka, C. Phosphorus and sulphur-doped microalgae carbon as a highly active metal-free catalyst for efficient hydrogen release in NaBH4 methanolysis. Fuel 2022, 309, 122183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılınç, D.; Şahin, Ö. Effective TiO2 supported Cu-Complex catalyst in NaBH4 hydrolysis reaction to hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 18858–18865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaugule, A.A.; Tamboli, A.H.; Sheikh, F.A.; Kim, H. Preparation and application of Sm–Ni oxide doped TiO2 nanofiber as catalyst in hydrogen production from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 484, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboli, A.H.; Chaugule, A.A.; Sheikh, F.A.; Chung, W.-J.; Kim, H. Synthesis and application of CeO2–NiO loaded TiO2 nanofiber as novel catalyst for hydrogen production from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Energy 2015, 89, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboli, A.H.; Gosavi, S.W.; Terashima, C.; Fujishima, A.; Pawar, A.A.; Kim, H. Synthesis of cerium and nickel doped titanium nanofibers for hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filiz, B.C.; Figen, A.K. Hydrogen production from sodium borohydride originated compounds: Fabrication of electrospun nano-crystalline Co3O4 catalyst and its activity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 9883–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enizi, A.M.; Yousef, A.; Shaikh, S.F.; Pandit, B.; El-Halwany, M.M. Electrospun Nickel Nanoparticles@ Poly (vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) Nanofibers as Effective and Reusable Catalyst for H2 Generation from Sodium Borohydride. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.; Barakat, N.A.; Kim, H.Y. Electrospun Cu-doped titania nanofibers for photocatalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 467, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.; Brooks, R.M.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Khamaj, J.A.; El-Halwany, M.; Barakat, N.A.; EL-Newehy, M.H.; Kim, H.Y. Electrospun NiCu nanoalloy decorated on carbon nanofibers as chemical stable electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 2015, 4, F51–F55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.; Brooks, R.M.; El-Halwany, M.; EL-Newehy, M.H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Barakat, N.A. Cu0/S-doped TiO2 nanoparticles-decorated carbon nanofibers as novel and efficient photocatalyst for hydrogen generation from ammonia borane. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, B.; Barakat, N.A.M.; Pant, H.R.; Park, M.; Saud, P.S.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, H.-Y. Synthesis and photocatalytic activities of CdS/TiO2 nanoparticles supported on carbon nanofibers for high efficient adsorption and simultaneous decomposition of organic dyes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 434, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afeesh, R.; Barakat, N.A.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Yousef, A.; Kim, H.Y. Nematic shaped cadmium sulfide doped electrospun nanofiber mat: Highly efficient, reusable, solar light photocatalyst. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 409, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.; Barakat, N.A.; Khalil, K.A.; Unnithan, A.R.; Panthi, G.; Pant, B.; Kim, H.Y. Photocatalytic release of hydrogen from ammonia borane-complex using Ni (0)-doped TiO2/C electrospun nanofibers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 410, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Yang, X. Photocatalytic hydrogen production from methanol aqueous solution under visible-light using Cu/S–TiO2 prepared by electroless plating method. Catal. Commun. 2015, 59, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, G.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Song, K.H. Behavior of hydrogen evolution of aqueous sodium borohydride solutions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, Z.; Jian, Z.; Guo, F.; Gao, C. Carbon nanotubes-promoted Co–B catalysts for rapid hydrogen generation via NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 19868–19877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, S.; Bandal, H.A.; Appiah-Ntiamoah, R.; Jadhav, A.R.; Kim, H. Cobalt nanoparticles supported on magnetic core-shell structured carbon as a highly efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 9296–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Zhang, T.; Wang, G.; Xie, G. Hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride solution using supported amorphous alloy catalysts (Ni–Co–P/γ-Al2O3). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 14935–14941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Zou, Y.C.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, J.Q. Ni–Fe–B catalysts for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hou, X.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Han, S. Co-Mo nanoparticles loaded on three–dimensional graphene oxide as efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29075–29082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, X.; Jing, C.; Hu, W.; Tian, S.; Tian, J. In situ synthesis of cobalt-based tri-metallic nanosheets as highly efficient catalysts for sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, K.; Zhang, D.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Xie, Y.; Li, G.; Bai, S. Cobalt–copper–boron nanoparticles as catalysts for the efficient hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 9845–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, Q.; Su, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Zhou, W. Preparation and catalytic activity of wheat straw cellulose based hydrogel-nanometal composites for hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 9978–9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Su, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B. A novel Enteromorpha based hydrogel for copper and nickel nanoparticle preparation and their use in hydrogen production as catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 6746–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didehban, A.; Zabihi, M.; Shahrouzi, J.R. Experimental studies on the catalytic behavior of alloy and core-shell supported Co-Ni bimetallic nano-catalysts for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20645–20660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Zabihi, M.J.I. Hydrogen generation by catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride using the nano-bimetallic catalysts supported on the core-shell magnetic nanocomposite of activated carbon. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 12331–12346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingersoll, J.; Mani, N.; Thenmozhiyal, J.; Muthaiah, A. Catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride by a novel nickel–cobalt–boride catalyst. J. Power Sources 2007, 173, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loghmani, M.H.; Shojaei, A.F.; Khakzad, M. Hydrogen generation as a clean energy through hydrolysis of sodium borohydride over Cu-Fe-B nano powders: Effect of polymers and surfactants. Energy 2017, 126, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Wang, K.; Du, G.; Asiri, A.M.; Sun, X. 3D hierarchical CuO/Co3O4 core–shell nanowire array on copper foam for on-demand hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 88846–88850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).