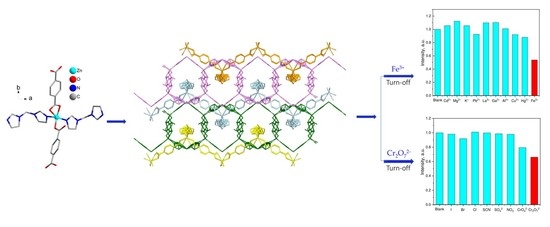
Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Luminescent Sensing Properties of a Supramolecular 3D Zinc(II) Metal–Organic Framework with Terephthalate and Bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane Linkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
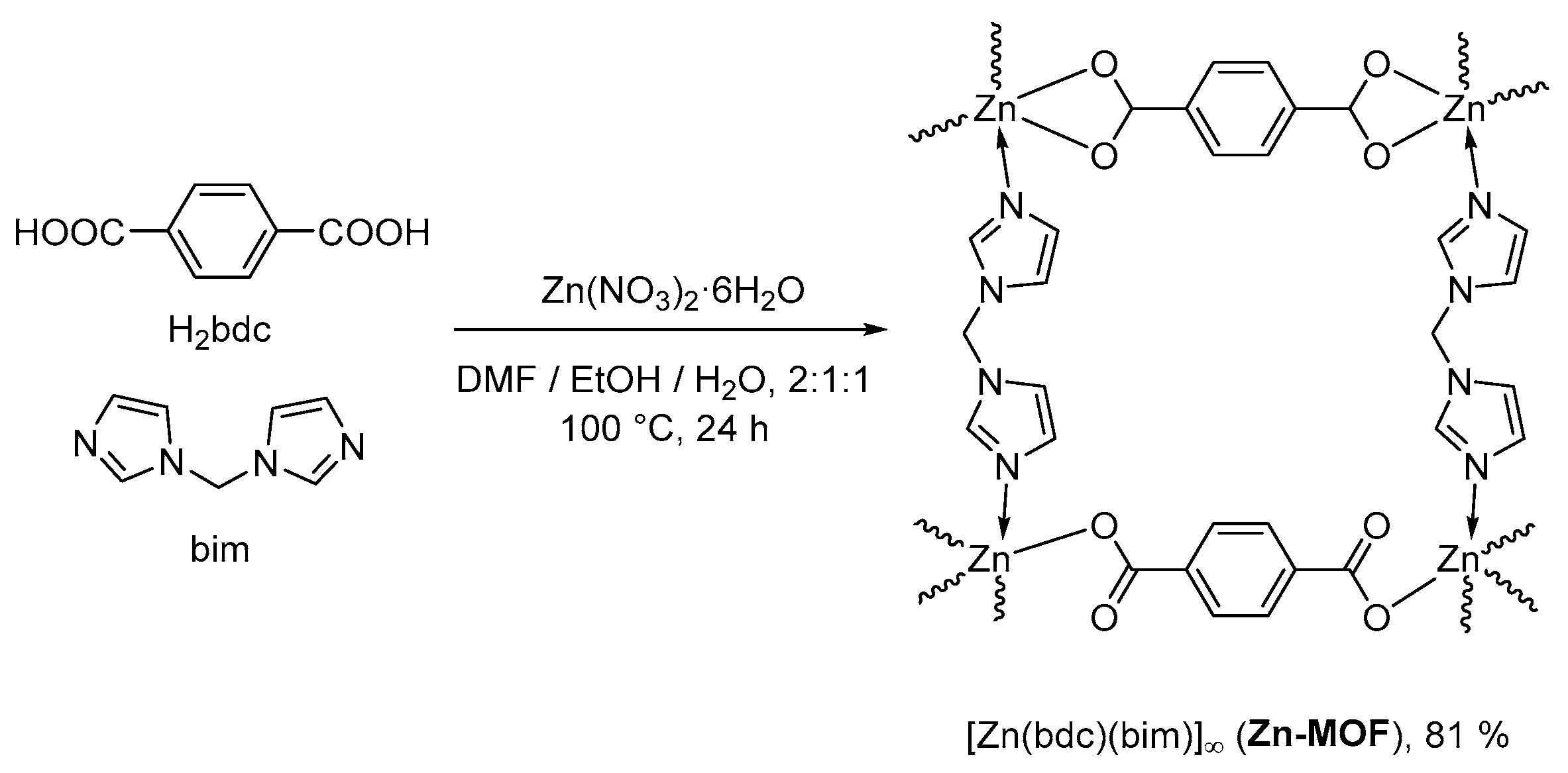
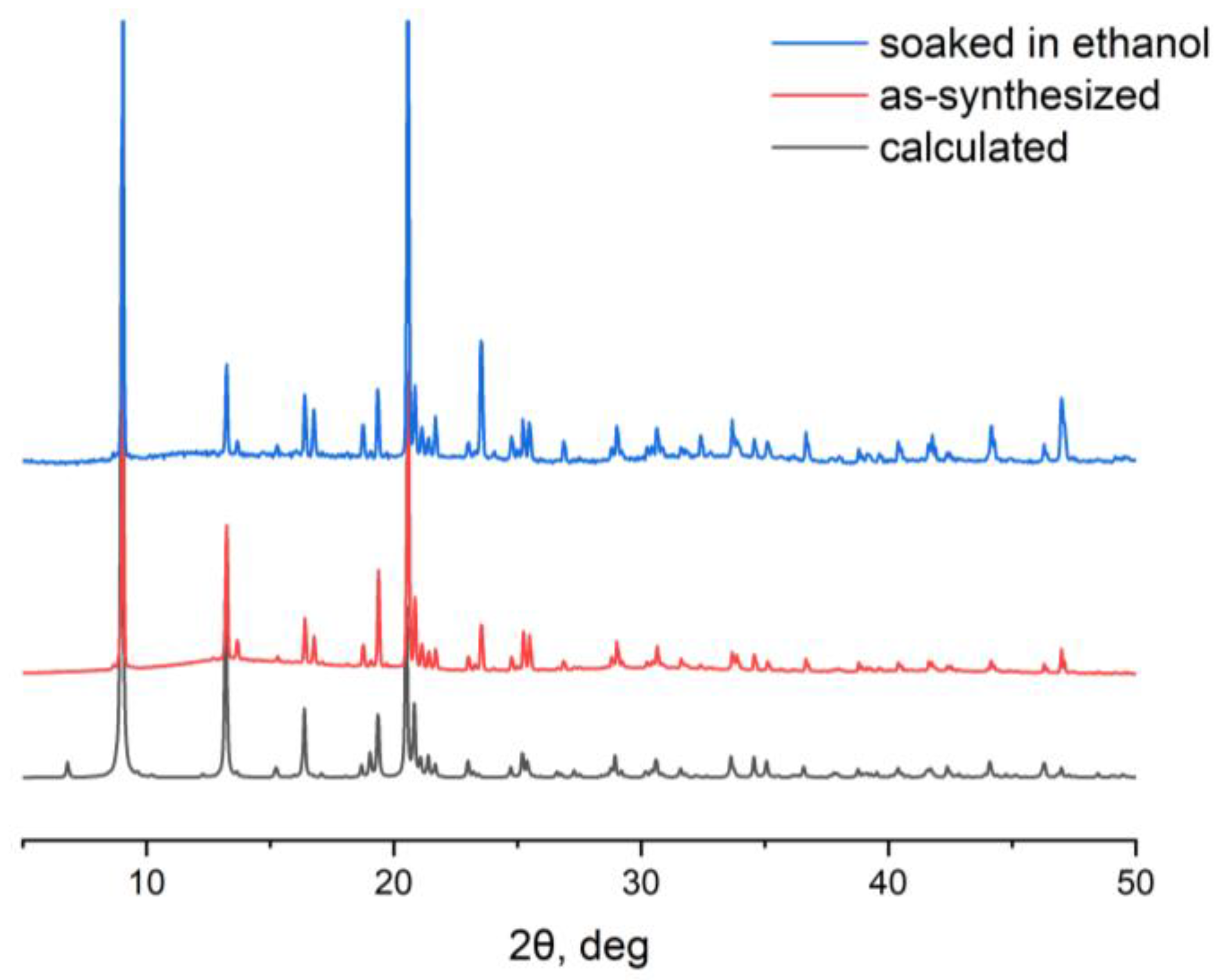
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Zn-MOF
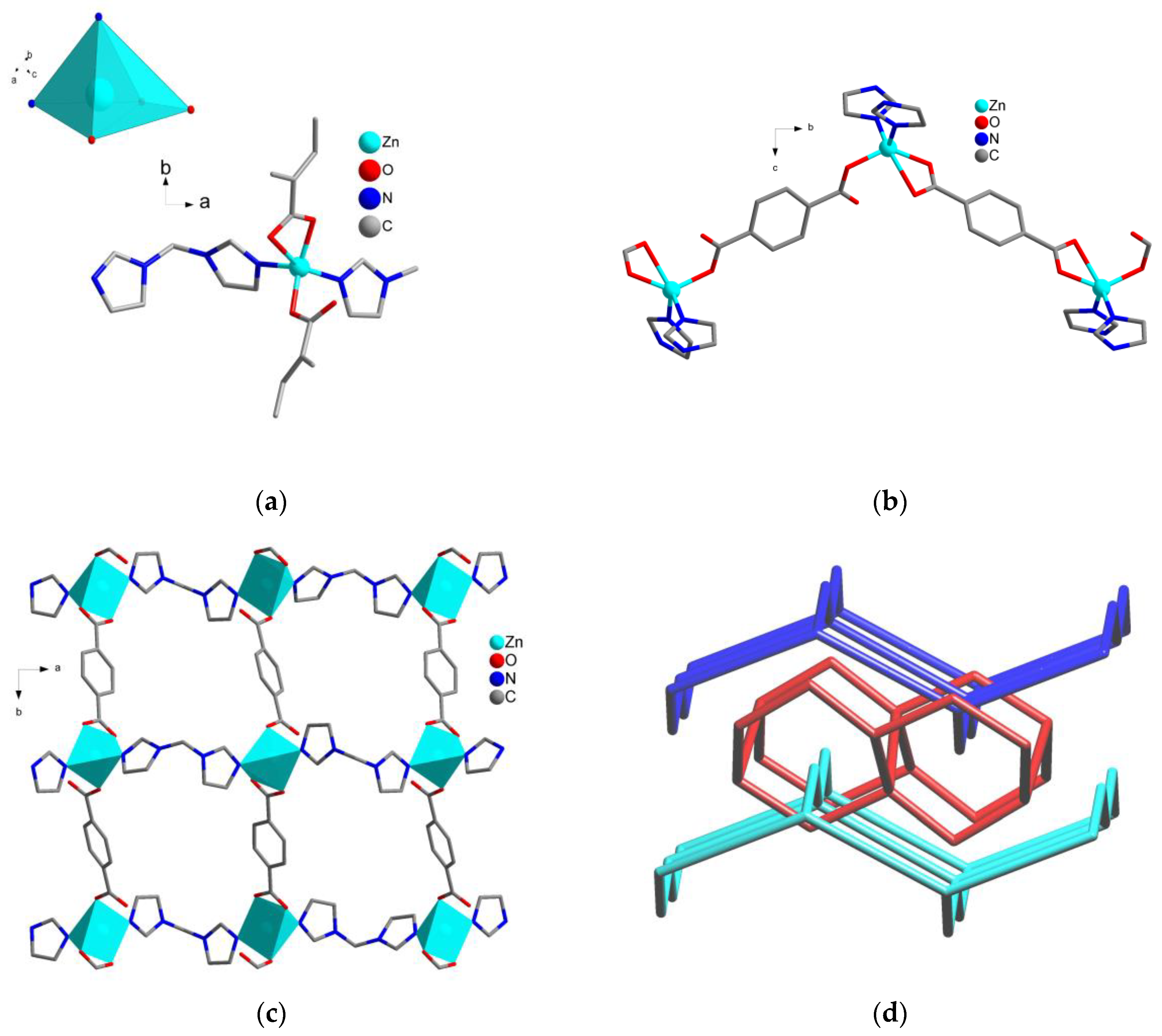
2.2. Crystal Structure of Zn-MOF
2.3. Luminescent Properties
2.4. Luminescent Sensing of Inorganic Anions and Cations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Zn-MOF
3.2. Spectral Methods and Elemental Analysis
3.3. X-ray Crystal Structure Determination
3.4. Luminescence Sensing Experiment
3.5. Computational Chemistry Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wagner, M.; Andrew Lin, K.-Y.; Oh, W.-D.; Lisak, G. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Pesticidal Persistent Organic Pollutants Detection and Adsorption—A Mini Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Filho, B.M.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Environmental Monitoring Approaches for the Detection of Organic Contaminants in Marine Environments: A Critical Review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 33, e00154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.C.G.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Barbosa, M.O.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T. A Review on Environmental Monitoring of Water Organic Pollutants Identified by EU Guidelines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.A.; Kim, J.H.; Song, H.S. Persistent Organic Pollutants, Pesticides, and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 28, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqubal, A.; Ahmed, M.; Ahmad, S.; Sahoo, C.R.; Iqubal, M.K.; Haque, S.E. Environmental Neurotoxic Pollutants: Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41175–41198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, R.; Landrigan, P.J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Bathan, G.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Brauer, M.; Caravanos, J.; Chiles, T.; Cohen, A.; Corra, L.; et al. Pollution and Health: A Progress Update. Lancet Planet Health 2022, 6, e535–e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, D.; Henderson, M.A. Iron Metabolism. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 20, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Mishra, S.; Singh, A.K. Recent Progress in the Development of MOF-Based Optical Sensors for Fe3+. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 7139–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.-B.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y.-T.; Chen, L.-H.; Wu, Z.; Fan, Z.-L.; Zhu, W. Highly Selective and Sensitive Detection towards Cationic Cu2+ and Fe3+ Contaminants via an In-MOF Based Dual-Responsive Fluorescence Probe. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 122, 108273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.-J.; Kong, Y.-J.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Huang, M.-M. A Zn-Based Coordination Compound for Fluorescence Detection of Fe3+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and CrO42− Ions. Polyhedron 2021, 193, 114868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, E.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Kosinova, M.; Fedin, V.P.; Wu, S. Logic Operation for Differentiation and Speciation of Fe3+ and Fe2+ Based on Two-Dimensional Metal–Organic Frameworks with Tunable Emissions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, e6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ran, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, C.-M.; Qin, Q.-P.; Zhou, J. One Luminescent Cadmium Iodide with Free Bifunctional Azole Sites as a Triple Sensor for Cu2+, Fe3+, and Cr2O72– Ions. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 14156–14163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Pu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Multifunctional MOF-Based Probes for Efficient Detection and Discrimination of Pb2+, Fe3+ and Cr2O72−/CrO42−. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 12197–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, E.; Liu, D.; Xing, J.; Feng, Y.; Su, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, N.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. A Recyclable Bi-Functional Luminescent Zinc (II) Metal–Organic Framework as Highly Selective and Sensitive Sensing Probe for Nitroaromatic Explosives and Fe3+ Ions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ryadun, A.A.; Kovalenko, K.A.; Guselnikova, T.; Ponomareva, V.G.; Potapov, A.; Fedin, V.P. 4 in 1: Multifunctional Europium-Organic Framework with Luminescent Sensing Properties, White Light Emission, Proton Conductivity and Reverse Acetylene-Carbon Dioxide Adsorption Selectivity. Dalton Trans. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Q.; Luo, Z.-D.; Pan, Y.; Kumar Singh, A.; Trivedi, M.; Kumar, A. Recent Developments in Luminescent Coordination Polymers: Designing Strategies, Sensing Application and Theoretical Evidences. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 406, 213145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorai, T.; Schmitt, W.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Highlights of the Development and Application of Luminescent Lanthanide Based Coordination Polymers, MOFs and Functional Nanomaterials. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, S. A Water-Stable Eu-MOF as Multi-Responsive Luminescent Sensor for High-Efficiency Detection of Fe3+, MnO4− Ions and Nicosulfuron in Aqueous Solution. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 316, 123598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, B.; Bisht, K.K.; Rachuri, Y.; Suresh, E. Zn(Ii)/Cd(Ii) Based Mixed Ligand Coordination Polymers as Fluorosensors for Aqueous Phase Detection of Hazardous Pollutants. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 1082–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Matveevskaya, V.; Pavlov, D.; Yakunenkov, A.; Potapov, A. Coordination Polymers Based on Highly Emissive Ligands: Synthesis and Functional Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffeneder, T.; Bauer, W.; Weber, B. X-ray Structure and Magnetic Properties of Two New Iron(II) 1D Coordination Polymers with Bis(Imidazolyle)Methane as Bridging Ligand. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2010, 636, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsukova, M.; Goncharova, T.; Samsonenko, D.; Dybtsev, D.; Potapov, A. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Luminescent Properties of New Zinc(II) and Cadmium(II) Metal-Organic Frameworks Based on Flexible Bis(Imidazol-1-yl)Alkane Ligands. Crystals 2016, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsukova, M.O.; Sapchenko, S.A.; Kovalenko, K.A.; Samsonenko, D.G.; Potapov, A.S.; Dybtsev, D.N.; Fedin, V.P. Exploring the Multifunctionality in Metal-Organic Framework Materials: How Do the Stilbenedicarboxylate and Imidazolyl Ligands Tune the Characteristics of Coordination Polymers? New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 6408–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.-Y.; Xue, Y.-N.; Liu, X.-M.; Li, N.-F.; Wang, J.-L.; Mei, H.; Xu, Y. An unprecedented polyoxometalate-encapsulated organo–metallophosphate framework as a highly efficient cocatalyst for CO2 photoreduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 3469–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Song, W.-C.; Yang, Q.; Bu, X.-H. Zn(II) and Cd(II) Coordination Polymers Assembled by Di(1H-Imidazol-1-Yl)Methane and Carboxylic Acid Ligands. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 4217–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, W. Synthesis, Luminescence, and Structural Characterization of Zn and Cd Coordination Polymers of Flexible Bis(Imidazolyl) Derivatives. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2007, 10, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.J.; Qin, Q.P. Two N-Donor Auxiliary Ligands Mediated Zn(II) Coordination Polymers Incorporating 5-Nitro-1,2,3-Benzenetricarboxylate Ligand: Syntheses, Crystal Structures, and Luminescent Properties. Jiegou Huaxue 2020, 39, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, W.W.; Li, C.; Mou, Y.Q.; Mu, Z.H.; Li, D.S. Encapsulation of Discrete (H2O)4 Clusters in a 1D Tube-Like Metal-Organic Coordination Polymer. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 2012, 42, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y. Five New Metal(II) Complexes with 3-D Network Structures Based on Carboxylate and Bis(Imidazole) Ligands: Syntheses and Structures. J. Coord. Chem. 2012, 65, 1953–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, S.; Pahari, G.; Maiti, A.; Ghoshal, D. Solvent Induced Reversible Single-Crystal-to-Single-Crystal Structural Transformation in Dynamic Metal Organic Frameworks: A Case of Enhanced Hydrogen Sorption in Polycatenated Framework. CrystEngComm 2023, 25, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuitema, A.M.; Engelen, M.; Koval, I.A.; Gorter, S.; Driessen, W.L.; Reedijk, J. New Didentate Bispyrazole Ligands Forming Uncommon Eight-Ring Chelates with Divalent Copper, Zinc and Cobalt. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2001, 324, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, G.B.; Phillips, R.J. Relationships between the Carbon-Oxygen Stretching Frequencies of Carboxylato Complexes and the Type of Carboxylate Coordination. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1980, 33, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, A.W.; Rao, T.N.; Reedijk, J.; van Rijn, J.; Verschoor, G.C. Synthesis, Structure, and Spectroscopic Properties of Copper(II) Compounds Containing Nitrogen-Sulphur Donor Ligands; the Crystal and Molecular Structure of Aqua[1,7-Bis(N-Methylbenzimidazol-2’-yl)-2,6-Dithiaheptane]Copper(II) Perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1984, 7, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-L.; Cui, G.-H.; Batten, S.R.; Li, J.-R.; Bu, X.-H. Multidimensional Metal−Organic Frameworks Constructed from Flexible Bis(Imidazole) Ligands. Cryst. Growth. Des. 2005, 5, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciocchi, N.; Pettinari, C.; Alberti, E.; Pettinari, R.; Di Nicola, C.; Figini Albisetti, A.; Sironi, A. Structural and Thermodiffractometric Analysis of Coordination Polymers. Part II:1 Zinc and Cadmium Derivatives of the Bim Ligand [Bim = Bis(1-Imidazolyl)Methane]. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 10501–10509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatov, V.A.; Shevchenko, A.P.; Proserpio, D.M. Applied Topological Analysis of Crystal Structures with the Program Package ToposPro. Cryst. Growth. Des. 2014, 14, 3576–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, P.R.; Turner, M.J.; McKinnon, J.J.; Wolff, S.K.; Grimwood, D.J.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M.A. CrystalExplorer: A Program for Hirshfeld Surface Analysis, Visualization and Quantitative Analysis of Molecular Crystals. J. Appl. Cryst. 2021, 54, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlak, P.V.; Kovalenko, K.A.; Samsonenko, D.G.; Fedin, V.P. Cadmium(II)-Organic Frameworks Containing the 1,3-Bis(2-Methylimidazolyl)Propane Ligand. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2022, 48, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlak, P.V.; Samsonenko, D.G.; Kovalenko, K.A.; Fedin, V.P. Synthesis, Structure and Luminescent Properties of Zn(II) Metal–Organic Frameworks Constructed by Flexible and Rigid Ligands. Polyhedron 2022, 222, 115880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ryadun, A.A.; Potapov, A.S.; Fedin, V.P. Ultra-Low Limit of Luminescent Detection of Gossypol by Terbium(III)-Based Metal-Organic Framework. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, D.I.; Sukhikh, T.S.; Ryadun, A.A.; Matveevskaya, V.V.; Kovalenko, K.A.; Benassi, E.; Fedin, V.P.; Potapov, A.S. A Luminescent 2,1,3-Benzoxadiazole-Decorated Zirconium-Organic Framework as an Exceptionally Sensitive Turn-On Sensor for Ammonia and Aliphatic Amines in Water. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2022, 10, 5567–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, R.; Ghosh, A.; Maji, T.K. Charge Transfer in Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 1569–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsukova, M.O.; Samsonenko, D.G.; Goncharova, T.V.; Potapov, A.S.; Sapchenko, S.A.; Dybtsev, D.N.; Fedin, V.P. Coordination Polymers with Adjustable Dimensionality Based on CuII and Bis-Imidazolyl Bridging Ligand. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2016, 65, 2914–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS, Program for Empirical X-ray Absorption Correction; ScienceOpen, Inc.: Burlington, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Rev. D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-Functional Exchange-Energy Approximation with Correct Asymptotic Behavior. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti Correlation-Energy Formula into a Functional of the Electron Density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vosko, S.H.; Wilk, L.; Nusair, M. Accurate Spin-Dependent Electron Liquid Correlation Energies for Local Spin Density Calculations: A Critical Analysis. Can. J. Phys. 1980, 58, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J.; Devlin, F.J.; Chabalowski, C.F.; Frisch, M.J. Ab Initio Calculation of Vibrational Absorption and Circular Dichroism Spectra Using Density Functional Force Fields. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 11623–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, A.D.; Chandler, G.S. Contracted Gaussian Basis Sets for Molecular Calculations. I. Second Row Atoms, Z = 11 – 18. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 5639–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Binkley, J.S.; Seeger, R.; Pople, J.A. Self-consistent Molecular Orbital Methods. XX. A Basis Set for Correlated Wave Functions. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Spitznagel, G.W.; Schleyer, P.V.R. Efficient Diffuse Function-augmented Basis Sets for Anion Calculations. III. The 3-21+G Basis Set for First-row Elements, Li–F. J. Comput. Chem. 1983, 4, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Pople, J.A.; Binkley, J.S. Self-consistent Molecular Orbital Methods 25. Supplementary Functions for Gaussian Basis Sets. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 3265–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the Damping Function in Dispersion Corrected Density Functional Theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.; Loew, G.H.; Komornicki, A. Structure and Relative Spin-State Energetics of [Fe(H2O)6]3+: A Comparison of UHF, Møller–Plesset, Nonlocal DFT, and Semiempircal INDO/S Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. A 1997, 101, 3959–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
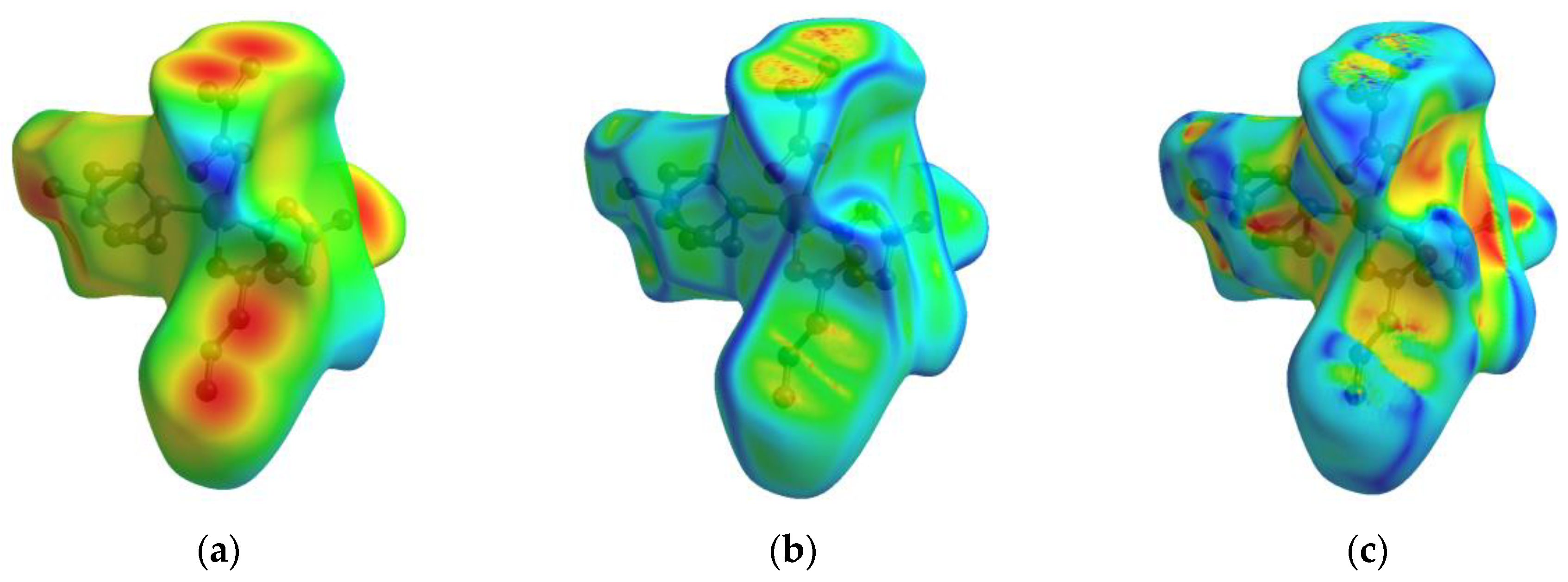

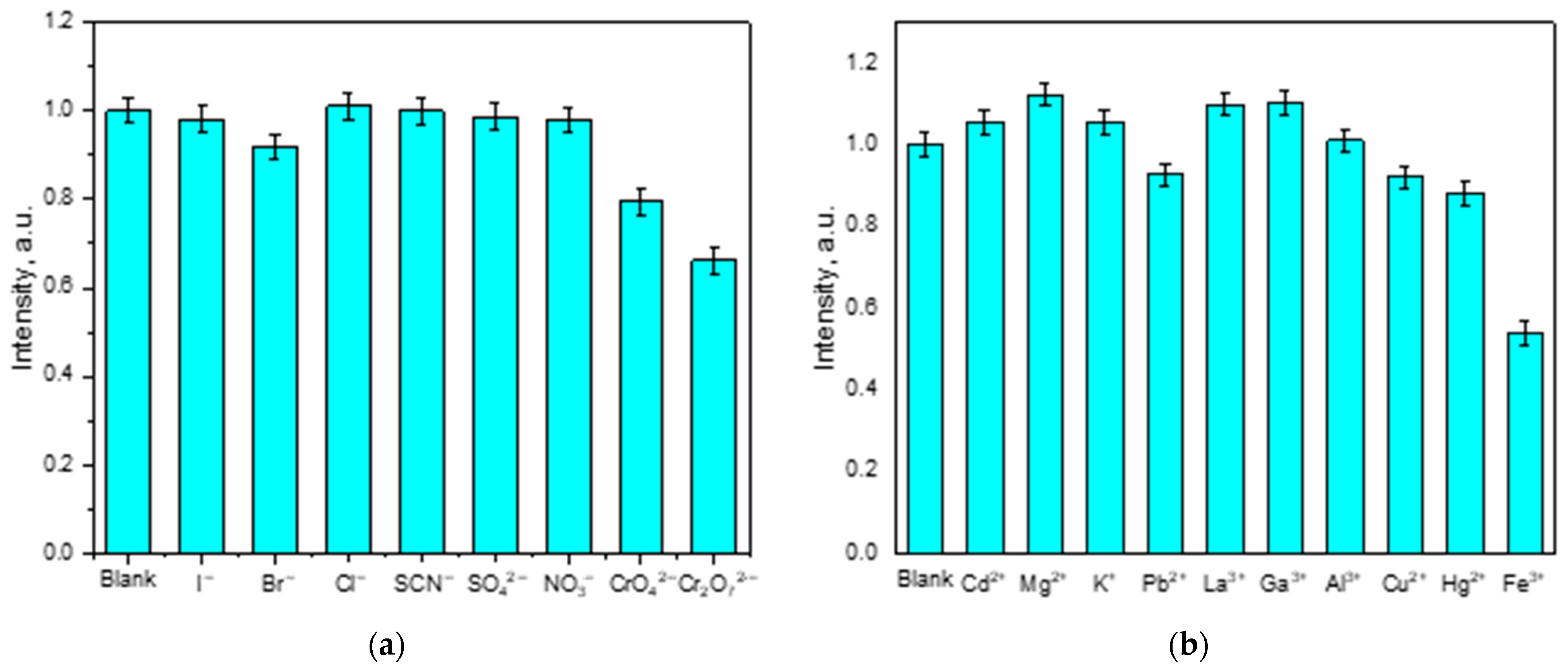
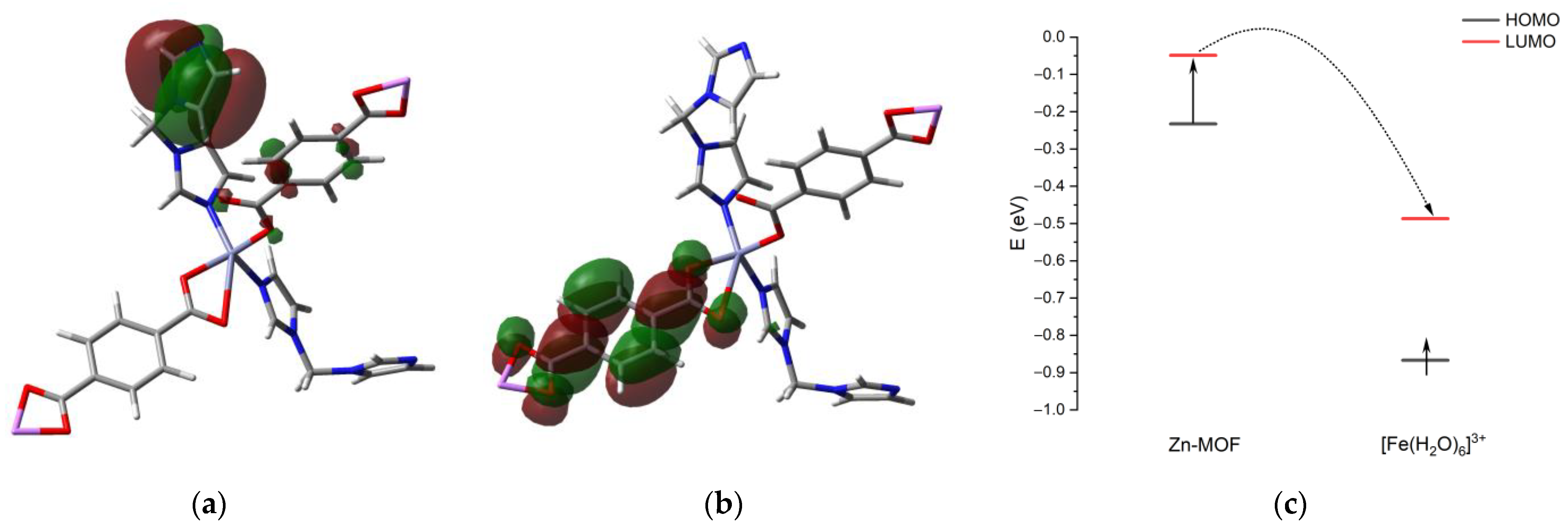
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C15H12N4O4Zn |
| Formula weight | 377.68 |
| Temperature, K | 290 (2) |
| Crystal system | tetragonal |
| Space group | P42/n |
| a, Å | 18.3186 (3) |
| b, Å | 18.3186 (3) |
| c, Å | 11.6298 (4) |
| Volume, Å3 | 3902.62 (19) |
| Z | 8 |
| ρcalc, g/cm3 | 1.283 |
| μ, mm−1 | 1.281 |
| F(000) | 1530 |
| Crystal size, mm3 | 0.10 × 0.05 × 0.05 |
| 2Θ range for data collection, ° | 4.724 to 57.388 |
| Index ranges | −18 ≤ h ≤ 22 −18 ≤ k ≤ 21 −15 ≤ l ≤ 13 |
| Reflections collected | 13026 |
| Independent reflections | 4505 (Rint = 0.021, Rsigma = 0.0239) |
| Restraints/Parameters | 0/267 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.047 |
| Final R indexes (I ≥ 2σ (I)) | R1 = 0.0487, wR2 = 0.0965 |
| Final R indexes (all data) | R1 = 0.0358, wR2 = 0.0898 |
| Largest diff. peak/hole, e·Å−3 | 0.375/−0.320 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1—N202 | 1.941 (15) | Zn1—N2 | 2.0414 (18) |
| Zn1—O3 | 1.9435 (15) | Zn1—C5 | 2.581 (2) |
| Zn1—O1 | 1.9870 (16) | ||
| N202—Zn1—O3 | 103.9 (4) | N2—Zn1—C5 | 130.57 (8) |
| N202—Zn1—O1 | 110.2 (4) | C5—O1—Zn1 | 103.41 (16) |
| O3—Zn1—O1 | 133.47 (7) | C1—O3—Zn1 | 118.69 (14) |
| N202—Zn1—N2 | 103.0 (3) | C10—N2—Zn1 | 132.10 (15) |
| O3—Zn1—N2 | 98.70 (7) | C12—N2—Zn1 | 122.28 (16) |
| O1—Zn1—N2 | 103.20 (7) | O2—C5—Zn1 | 74.56 (15) |
| N202—Zn1—C5 | 104.3 (3) | O1—C5—Zn1 | 48.48 (12) |
| O3—Zn1—C5 | 113.43 (8) | C2—C5—Zn1 | 165.7 (2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matveevskaya, V.V.; Pavlov, D.I.; Ryadun, A.A.; Fedin, V.P.; Potapov, A.S. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Luminescent Sensing Properties of a Supramolecular 3D Zinc(II) Metal–Organic Framework with Terephthalate and Bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane Linkers. Inorganics 2023, 11, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11070264
Matveevskaya VV, Pavlov DI, Ryadun AA, Fedin VP, Potapov AS. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Luminescent Sensing Properties of a Supramolecular 3D Zinc(II) Metal–Organic Framework with Terephthalate and Bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane Linkers. Inorganics. 2023; 11(7):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11070264
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatveevskaya, Vladislava V., Dmitry I. Pavlov, Alexey A. Ryadun, Vladimir P. Fedin, and Andrei S. Potapov. 2023. "Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Luminescent Sensing Properties of a Supramolecular 3D Zinc(II) Metal–Organic Framework with Terephthalate and Bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane Linkers" Inorganics 11, no. 7: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11070264
APA StyleMatveevskaya, V. V., Pavlov, D. I., Ryadun, A. A., Fedin, V. P., & Potapov, A. S. (2023). Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Luminescent Sensing Properties of a Supramolecular 3D Zinc(II) Metal–Organic Framework with Terephthalate and Bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane Linkers. Inorganics, 11(7), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11070264