On the Importance of Fresh Stock Solutions for Surfactant-Free Colloidal Syntheses of Gold Nanoparticles in Alkaline Alcohol and Water Mixtures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
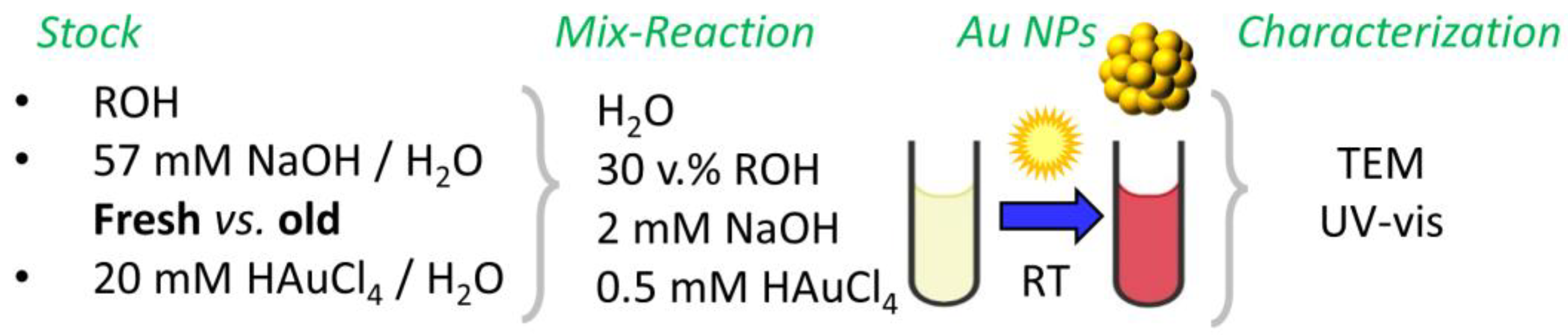
2.1. Overview
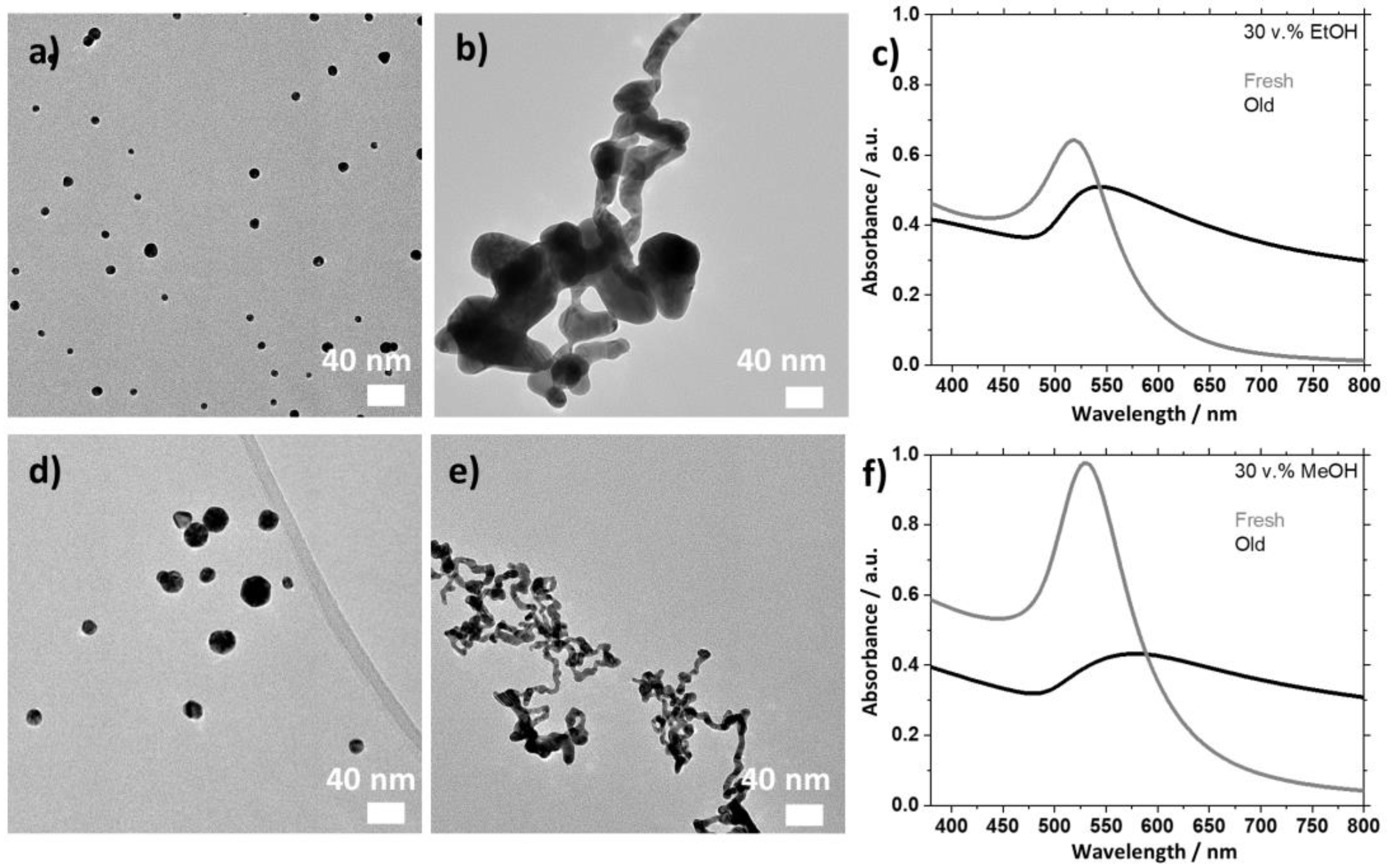
2.2. Effects of the Age of the Stock Solutions of Base
2.2.1. Using EtOH as Reducing Agent
2.2.2. Using MeOH as Reducing Agent
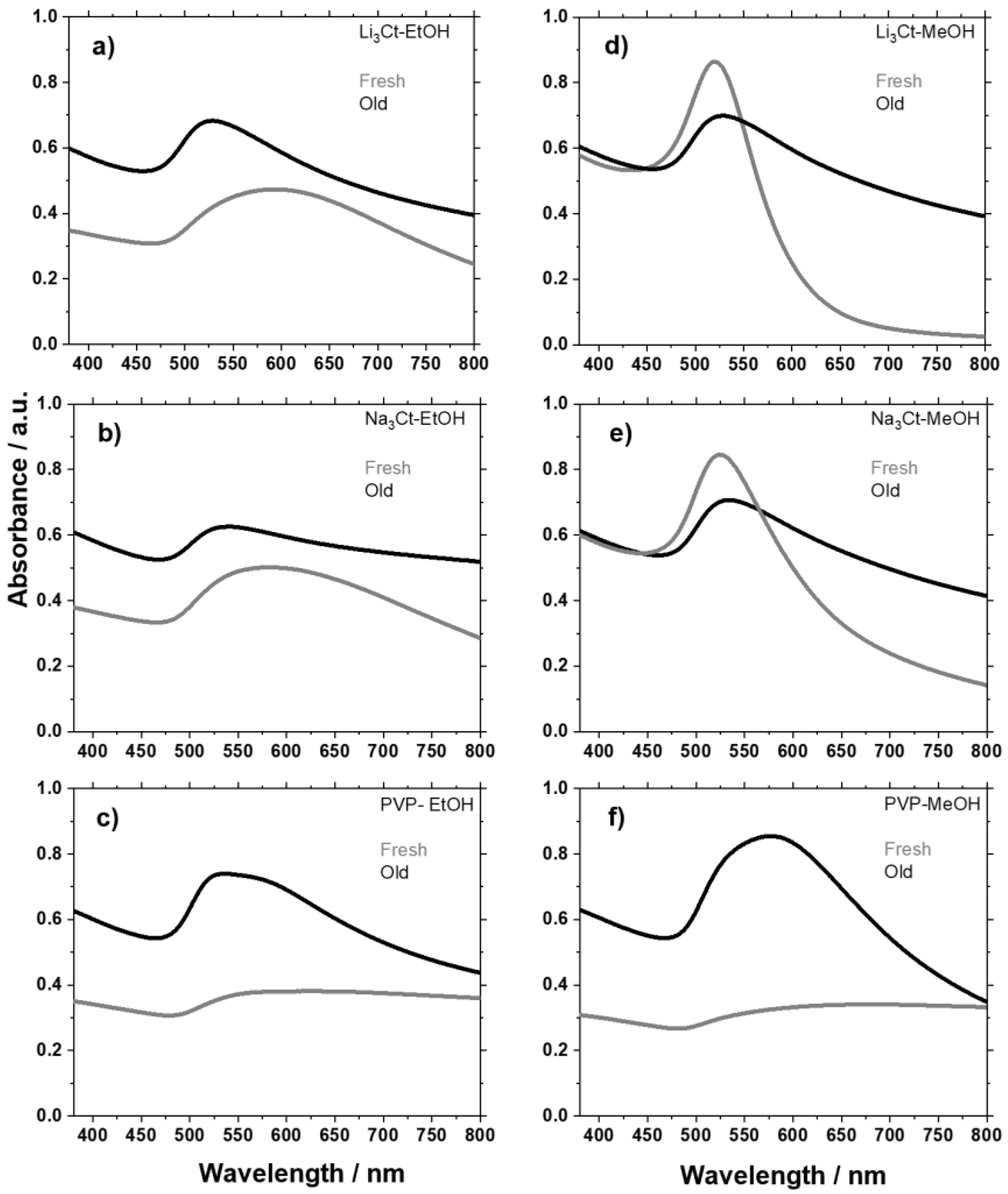
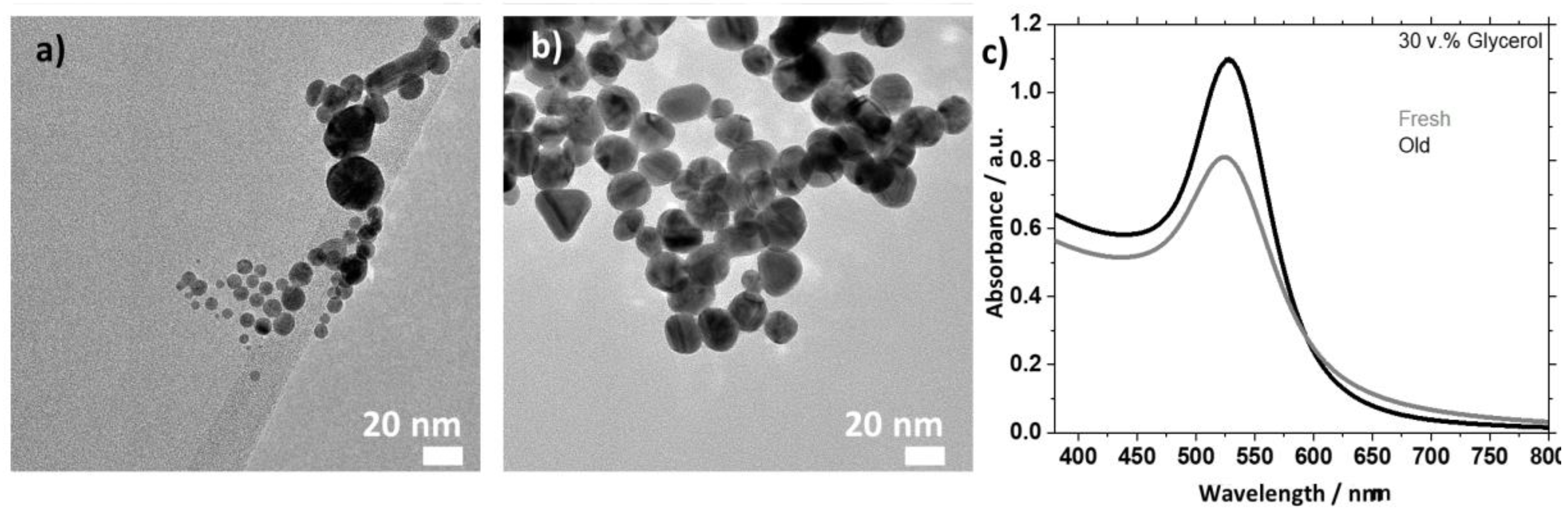
2.2.3. Synthesis in Presence of Additives
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Surfactant-Free Au NP Synthesis
4.3. Au NP Synthesis in Presence of Additives
4.4. Characterization
4.4.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.4.2. UV-Vis Spectrometry
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, L.; Zeng, G.M.; Lai, C.; Huang, D.L.; Xu, P.A.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Liu, X.G.; Liu, S.Y.; Li, B.S.; et al. “Gold rush” in modern science: Fabrication strategies and typical advanced applications of gold nanoparticles in sensing. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 359, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Chai, O.J.H.; Yao, Q.F.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.J.; Xie, J.P. Electrocatalysis of gold-based nanoparticles and nanoclusters. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 1657–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepale, N.; Fernandez-Escamilla, V.V.A.; Carreon-Alvarez, C.; Gonzalez-Coronel, V.J.; Luna-Flores, A.; Carreon-Alvarez, A.; Aguilar, J. Nanoengineering of Gold Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications. Crystals 2019, 9, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, C.D.; Nogueira, B.R.; Rostelato, M. Review of the methodologies used in the synthesis gold nanoparticles by chemical reduction. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 798, 714–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuithschick, M.; Birnbaum, A.; Witte, S.; Sztucki, M.; Vainio, U.; Pinna, N.; Rademann, K.; Emmerling, F.; Kraehnert, R.; Polte, J. Turkevich in New Robes: Key Questions Answered for the Most Common Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7052–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, M.; Walker, M.; Bethell, D.; Schiffrin, D.J.; Whyman, R. Synthesis of thiol-derivatized gold nanoparticles in a 2-phase liquid-liquid system. J. Chem. Soc.-Chem. Commun. 1994, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz-Marzan, L.M. Gold nanoparticle research before and after the Brust-Schiffrin method. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, B.; Zaker, Y.; Bigioni, T.P. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles: Challenges and opportunities. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 12, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, J.E. The Road to Sustainable Nanotechnology: Challenges, Progress and Opportunities. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5907–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, L.M.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Plata, D.L.; Hutchison, J.E.; Anastas, P.T. Designing nanomaterials to maximize performance and minimize undesirable implications guided by the Principles of Green Chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5758–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.H.; Wang, D.S.; Li, Y.D. Green chemistry for nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5778–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinson, J. Surfactant-free precious metal colloidal nanoparticles for catalysis. Front. Nanotechnol. 2021, 3, 770281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinson, J.; Aalling-Frederiksen, O.; Dacayan, W.L.; Bjerregaard, J.D.; Jensen, K.D.; Jørgensen, M.R.V.; Kantor, I.; Sørensen, D.R.; Theil Kuhn, L.; Johnson, M.S.; et al. Surfactant-free colloidal syntheses of gold-based nanomaterials in alkaline water and mono-alcohol mixtures. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 2173–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Q.; Man, S.Q. Green Synthesis of Colloidal Gold by Ethyl Alcohol and NaOH at Normal Temperature. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2013, 42, 2232–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Ullah, S.; Sgarbi, R.; Tremiliosi, G. One-pot ligand-free synthesis of gold nanoparticles: The role of glycerol as reducing-cum-stabilizing agent. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 565, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalawade, P.; Mukherjee, T.; Kapoor, S. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Glycerol as a Reducing Agent. Adv. Nanopart. 2013, 2, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz-Marzan, L.M.; Kagan, C.R.; Millstone, J.E. Reproducibility in Nanocrystal Synthesis? Watch Out for Impurities! ACS Nano 2020, 14, 6359–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarabelli, L.; Sanchez-Iglesias, A.; Perez-Juste, J.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. A “Tips and Tricks” Practical Guide to the Synthesis of Gold Nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 4270–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amri, N.; Roger, K. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) impurities drastically impact the outcome of nanoparticle syntheses. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 576, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettenmeier, P.; Majchel, J.; Wang, L.; Saveleva, V.A.; Zafeiratos, S.; Savinova, E.R.; Gallet, J.J.; Bournel, F.; Gago, A.S.; Friedrich, K.A. Highly active nano-sized iridium catalysts: Synthesis and operando spectroscopy in a proton exchange membrane electrolyzer. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 3570–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Editorial, N. Rewarding negative results keeps science on track. Nature 2017, 551, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.W.; Santos, L.B.D.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci. Data 2019, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabor, D.P.; Roch, L.M.; Saikin, S.K.; Kreisbeck, C.; Sheberla, D.; Montoya, J.H.; Dwaraknath, S.; Aykol, M.; Ortiz, C.; Tribukait, H.; et al. Accelerating the discovery of materials for clean energy in the era of smart automation. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendel, T.; Wuithschick, M.; Kettemann, F.; Birnbaum, A.; Rademann, K.; Polte, J. In Situ Determination of Colloidal Gold Concentrations with UV-Vis Spectroscopy: Limitations and Perspectives. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11115–11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparotto, L.H.S.; Garcia, A.C.; Gomes, J.F.; Tremiliosi-Filho, G. Electrocatalytic performance of environmentally friendly synthesized gold nanoparticles towards the borohydride electro-oxidation reaction. J. Power Sources 2012, 218, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.B.; Gomes, J.F.; Tremiliosi-Filho, G.; Gasparotto, L.H.S. One-pot eco-friendly synthesis of gold nanoparticles by glycerol in alkaline medium: Role of synthesis parameters on the nanoparticles characteristics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 55, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crundwell, F.K. On the Mechanism of the Dissolution of Quartz and Silica in Aqueous Solutions. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gin, S.; Jollivet, P.; Fournier, M.; Berthon, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Mitroshkov, A.; Zhu, Z.H.; Ryan, J.V. The fate of silicon during glass corrosion under alkaline conditions: A mechanistic and kinetic study with the International Simple Glass. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 151, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiss, W.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Aveyard, J.; Fernig, D.G. Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-Vis spectra. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larm, N.E.; Essner, J.B.; Thon, J.A.; Bhawawet, N.; Adhikari, L.; St Angelo, S.K.; Baker, G.A. Single Laboratory Experiment Integrating the Synthesis, Optical Characterization, and Nanocatalytic Assessment of Gold Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Educ. 2020, 97, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.J.; Lv, M.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.X. Colorimetric determination of copper(II) ions using gold nanoparticles as a probe. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 102311–102317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Mishra, P.; Shivange, G.; Kodipelli, N.; Moros, M.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Anindya, R. Citrate-capped gold nanoparticles for the label-free detection of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-1. Analyst 2015, 140, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merk, V.; Rehbock, C.; Becker, F.; Hagemann, U.; Nienhaus, H.; Barcikowski, S. In Situ Non-DLVO Stabilization of Surfactant-Free, Plasmonic Gold Nanoparticles: Effect of Hofmeister’s Anions. Langmuir 2014, 30, 4213–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinson, J.; Bucher, J.; Simonsen, S.B.; Kuhn, L.T.; Kunz, S.; Arenz, M. Monovalent Alkali Cations: Simple and Eco-Friendly Stabilizers for Surfactant-Free Precious Metal Nanoparticle Colloids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13680–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ROH | ROH v.% | NaOH | λspr/nm (Δλ/λspr) | Relative Yield * | A650/Aspr | dN/nm | Data from |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EtOH | 10 | Old | 612 (x.x%) | 0.26 | 0.97 | X | This work |
| Fresh | 530 (7.0%) | 1.00 | 0.20 | 9.1 ± 6.4 | [14] | ||
| 30 | Old | 544 (15.6%) | 0.75 | 0.78 | Network (>20) | This work | |
| Fresh | 517 (6.4%) | 0.64 | 0.12 | 9.9 ± 2.3 | [14] | ||
| MeOH | 10 | Old | 584 (x.x%) | 0.15 | X | X | This work |
| Fresh | 570 (x.x%) | 0.65 | 0.96 | Network (15) | [14] | ||
| 30 | Old | 557 (15.3%) | 0.81 | 0.77 | Network (10) | This work | |
| Fresh | 531 (6.3%) | 1.00 | 0.17 | 21.2 ± 7.1 | [14] | ||
| 50 | Old | X | X | X | Network (15) | This work | |
| Fresh | 542 (8.4%) | 0.74 | 0.47 | 28.3 ± 11.1 | [14] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quinson, J. On the Importance of Fresh Stock Solutions for Surfactant-Free Colloidal Syntheses of Gold Nanoparticles in Alkaline Alcohol and Water Mixtures. Inorganics 2023, 11, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040140
Quinson J. On the Importance of Fresh Stock Solutions for Surfactant-Free Colloidal Syntheses of Gold Nanoparticles in Alkaline Alcohol and Water Mixtures. Inorganics. 2023; 11(4):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040140
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuinson, Jonathan. 2023. "On the Importance of Fresh Stock Solutions for Surfactant-Free Colloidal Syntheses of Gold Nanoparticles in Alkaline Alcohol and Water Mixtures" Inorganics 11, no. 4: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040140
APA StyleQuinson, J. (2023). On the Importance of Fresh Stock Solutions for Surfactant-Free Colloidal Syntheses of Gold Nanoparticles in Alkaline Alcohol and Water Mixtures. Inorganics, 11(4), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040140






