Purification and Characterization of High Purity Nano Zirconia by Liquid-Liquid Extraction Using D2EHPA/p-Xylenes
Abstract
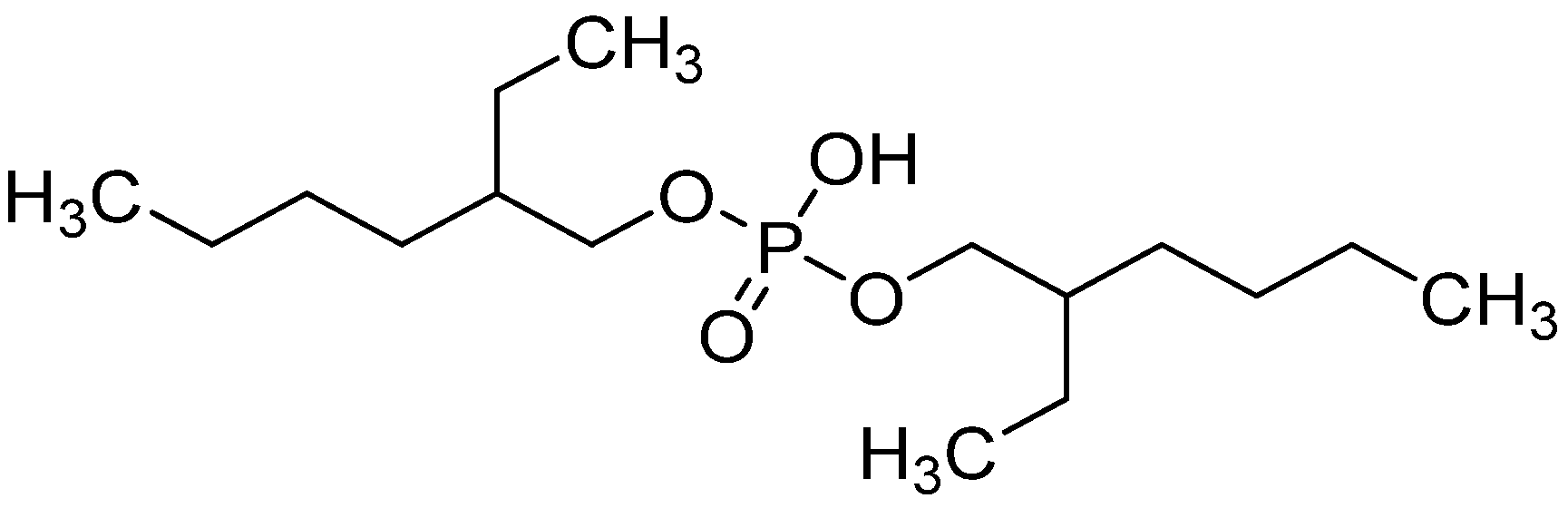
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
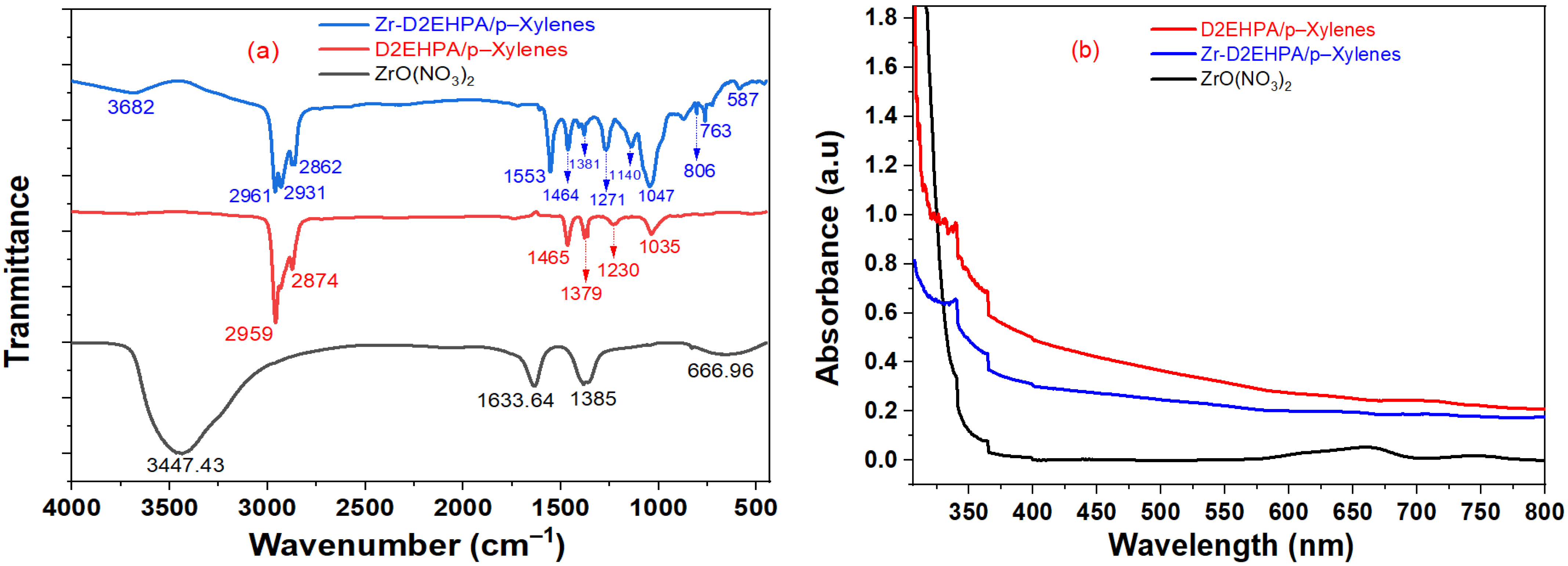
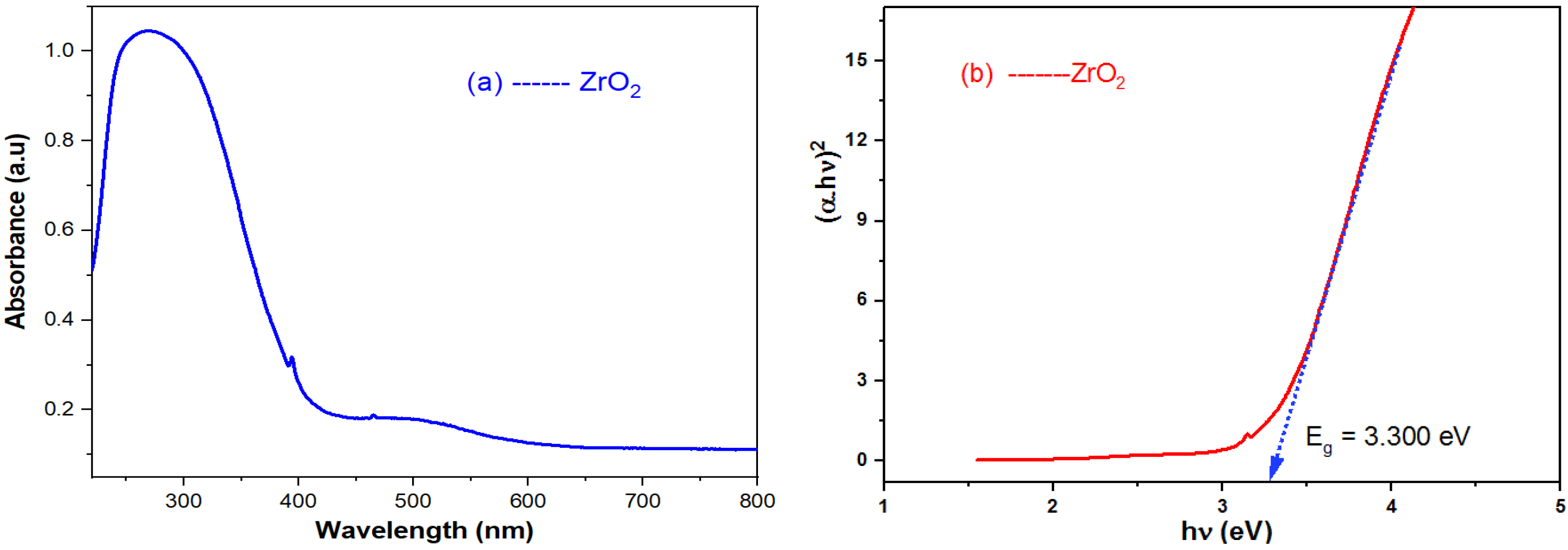
2.1. FT-IR and UV-Vis Spectra
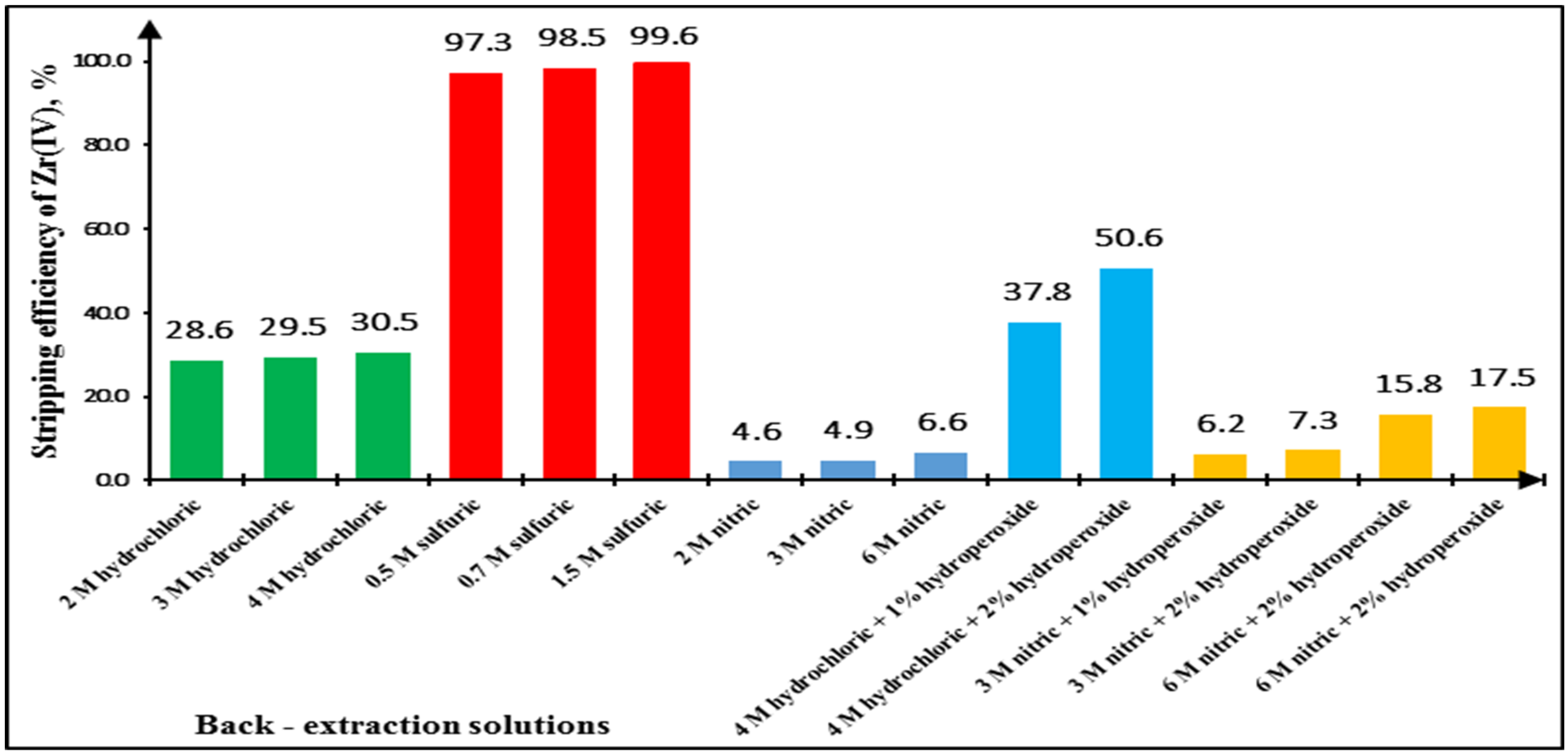
2.2. Effect of Stripping Solutions
2.3. Separation of Impurities and Purification of ZrO2
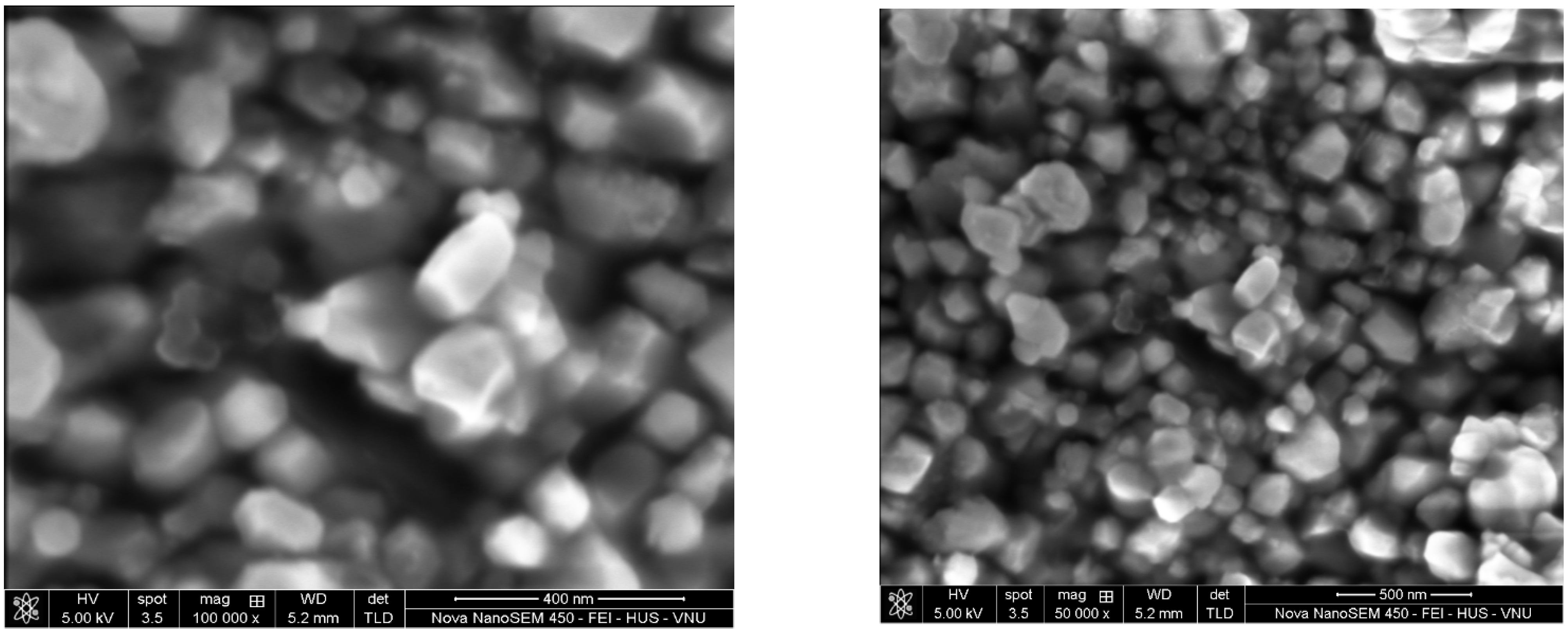
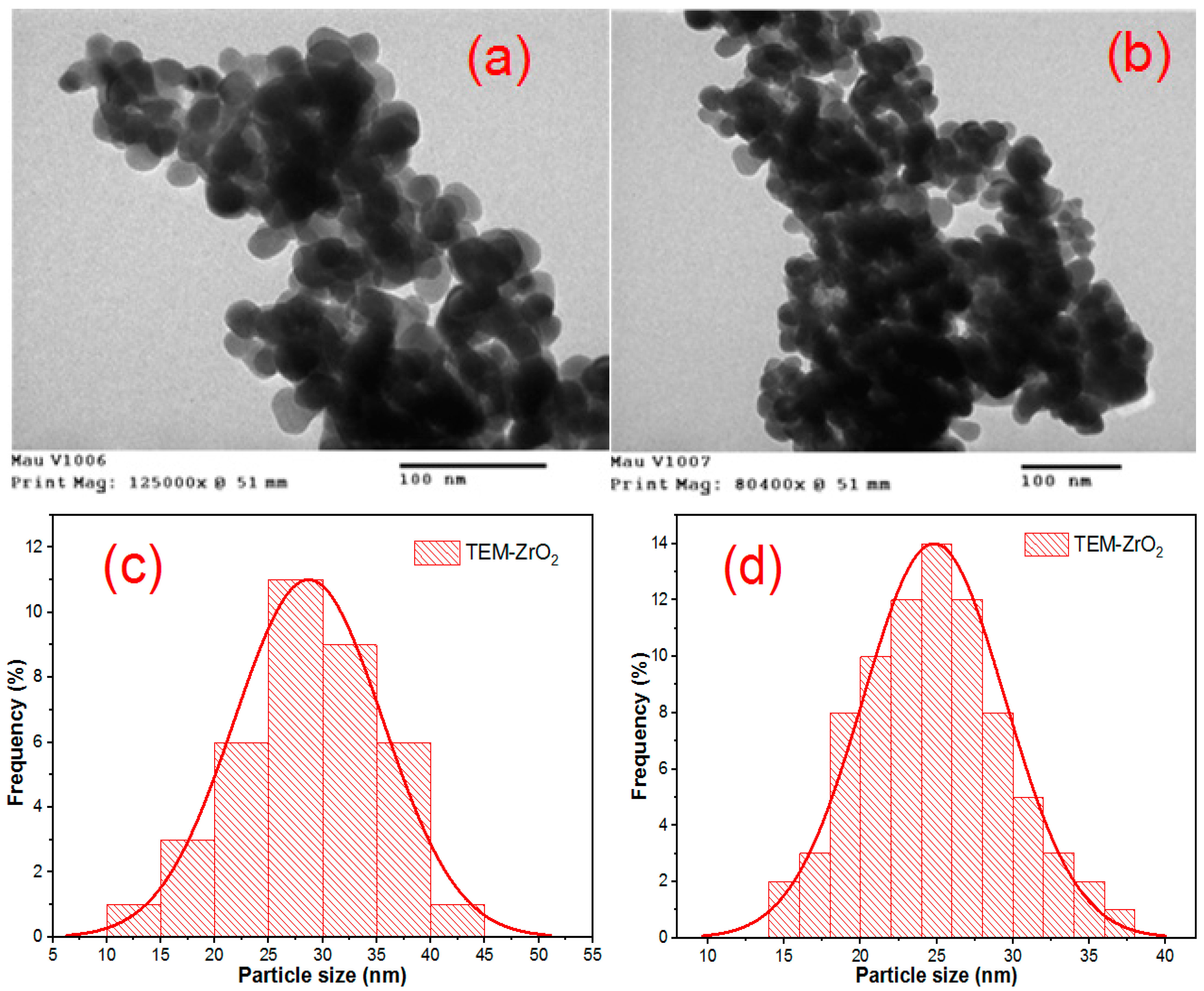
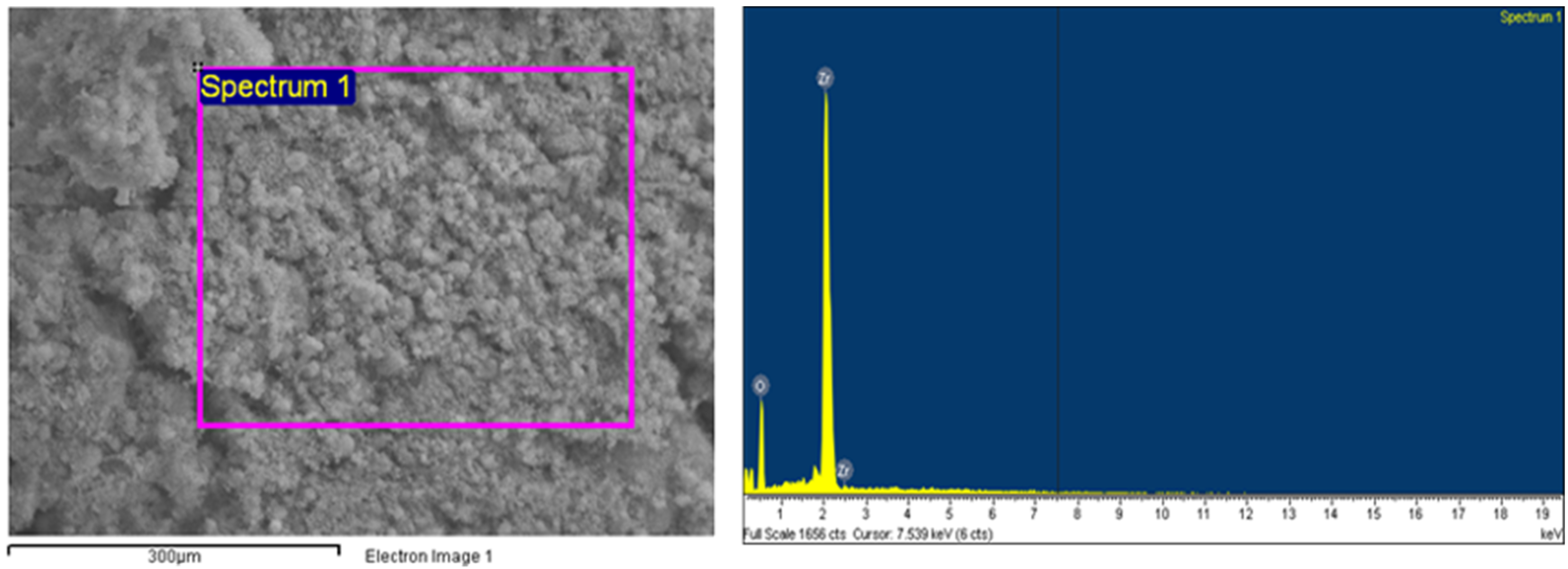
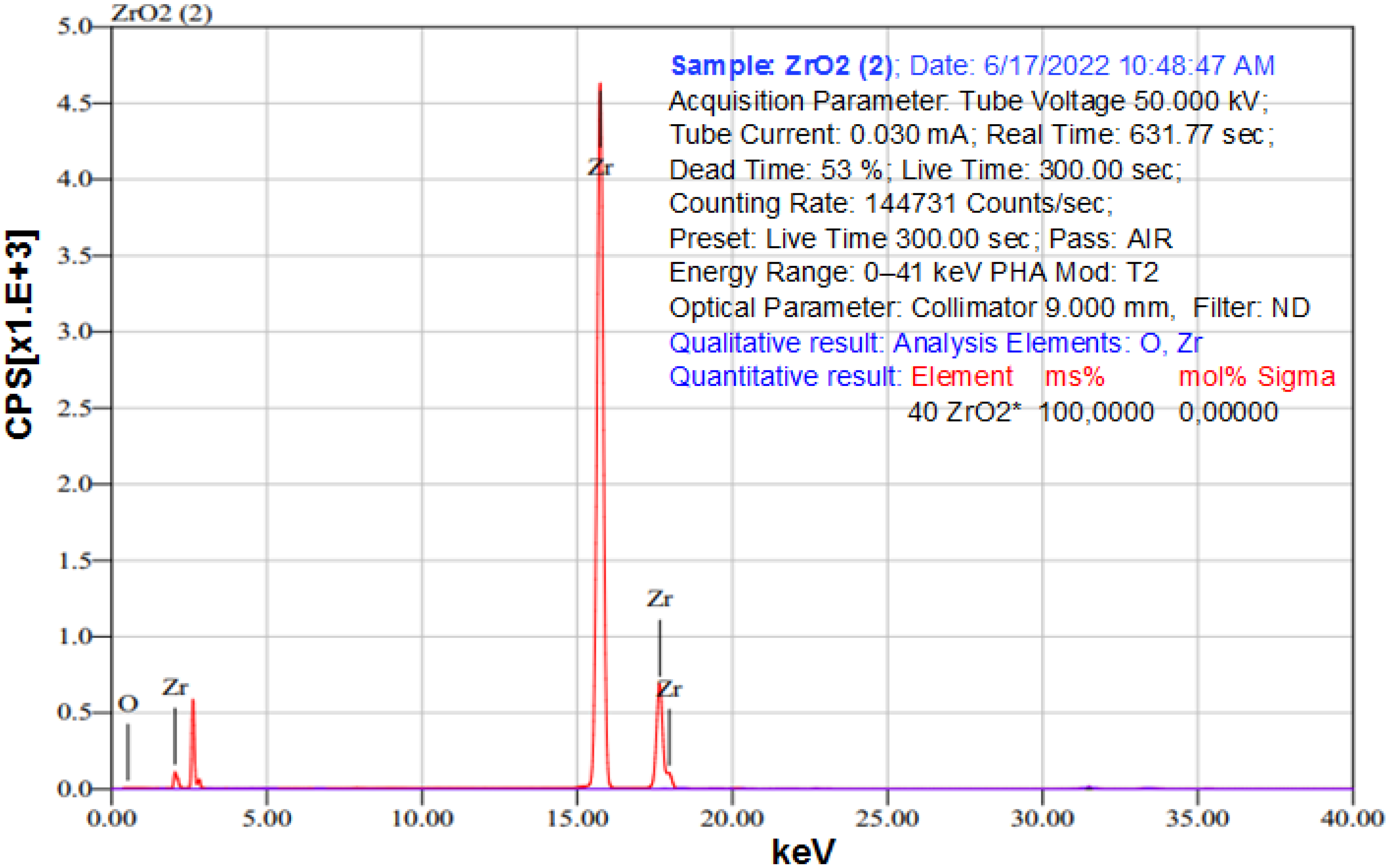
2.4. Characterization of Obtained ZrO2
3. Experimental Procedure
3.1. Preparation of the High-Purity ZrO2 Nano
3.2. Characterization of Obtained ZrO2
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biswas, R.K.; Hayat, M.A. Solvent Extraction of Zirconium(IV) from Chloride Media by D2EHPA in Kerosene. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 63, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.S. Solvent extraction of Zr(IV) and Hf(IV) with N,N,N′,N′-tetraoctyldiglycolamide. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2012, 292, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmane, M.M.; Sargar, B.M.; Mahamuni, S.V.; Anuse, M.A. Solvent Extraction Separation of Zirconium(IV) from Succinate Media with N–n–Octylaniline. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2006, 71, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.R.; Kumar, J.R.; Reddy, A.V.; Priya, D.N. Solvent Extraction of Zirconium(IV) from Acidic Chloride Solutions Using 2–EthylHexyl Phosphonic Acid Mono–2–EthylHexyl Ester (PC–88A). Hydrometallurgy 2004, 72, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.R.; Kumar, J.R.; Reddy, A.V. Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Tetravalent Zirconium from Acidic Chloride Solutions Using Cyanex 272. Anal. Sci. 2004, 20, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, B.R.; Rajesh, K.J.; Varada, R.A. Solvent Extraction of Zirconium(IV) from Acid Chloride solutions using LIX 84-IC. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 74, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazheva, I.V.; Fedorov, Y.S.; Zilberman, B.Y.; Mashirov, L.G. Extraction of Zirconium with Tributyl Phosphate from Nitric Acid Solutions. Radiochemistry 2008, 50, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Lee, M.S. A Review on the Aqueous Chemistry of Zr (IV) and Hf (IV) and Their Separation by Solvent Extraction. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, M.S. Solvent Extraction of Zirconium and Hafnium from Hydrochloric Acid Solutions Using Acidic Organophosphorus Extractants and Their Mixtures with TOPO. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, M.; Xu, Y.; Chi, R.; Li, P.; Zhao, J. Separation of Zirconium and Hafnium by Solvent Extraction Using Mixture of DIBK and P204. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Kuang, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Liao, W. Separation of Zirconium from Hafnium in Sulfate Medium Using Solvent Extraction with a New Reagent BEAP. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, J.; Antônio de Morais, C. Study of Zirconium and Hafnium Separation by Solvent Extraction Technique from Nitric and Hydrochloric Solutions with Acid, Basic and Neutral Extractants. World J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 4, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, M.R. Solvent Extraction in Hydrometallurgy: Present and Future. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2006, 11, 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- Yudaev, P.A.; Kolpinskaya, N.A.; Chistyakov, E.M. Organophosphorous Extractants for Metals. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 201, 105558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shafie, A.S.; Daher, A.M.; Ahmed, I.S.; Sheta, M.E.; Moustafa, M.M. Extraction and separation of nano-sized zirconia from nitrate medium using Cyanex 921. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2014, 2, 2956–2970. [Google Scholar]
- Shi-zhong, C. Determination of Trace Rare Earth Impurities in High Purity Zirconium Dioxide by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry after Separation by Solvent Extraction. Metall. Anal. 2006, 26, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Panday, V.K.; Becker, J.S.; Dietze, H.J. Trace Impurities in Zircaloys by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry after Removal of the Matrix by Liquid Liquid Extraction. At. Spectrosc. 1995, 16, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Shenkay, L.; Fuchung, C. Determination of Trace Elements in Zirconium Base Alloy by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 1990, 45, 527–535. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, R.; Bao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B. Synthesis of Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phosphoric Acid (D2EHPA)-Tributyl Phosphate (TBP) Impregnated Resin and Application in Adsorption of Vanadium (IV). Minerals 2018, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, H.-S.; Tsai, T.-H. Extraction Equilibrium of Indium (III) from Nitric Acid Solutions by Di (2-Ethylhexyl) Phosphoric Acid Dissolved in Kerosene. Molecules 2012, 17, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, M.N.; Nguyen, L.T.H.; Mai, X.T.; Van Thuan, D.; Bach, L.G.; Nguyen, D.C.; Nguyen, D.C. Nano ZrO2 Synthesis by Extraction of Zr (IV) from ZrO(NO3)2 by PC88A, and Determination of Extraction Impurities by ICP-MS. Metals 2018, 8, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidya, Y.S.; Gurushantha, K.; Nagabhushana, H.; Sharma, S.C.; Anantharaju, K.S.; Shivakumara, C.; Suresh, D.; Nagaswarupa, H.P.; Prashantha, S.C.; Anilkumar, M.R. Phase Transformation of ZrO2: Tb3+ Nanophosphor: Color Tunable Photoluminescence and Photocatalytic Activities. J. Alloy Compd. 2015, 622, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Abdou, A.E.H.; Sobhy, M.E. Engineered Nano-Zirconium Oxide-Crosslinked-Nanolayer of Carboxymethyl Cellulose for Speciation and Adsorptive Removal of Cr(III) and Cr(VI). Powder Technol. 2017, 321, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, M.; Meng, Q.; Gao, K.; Lü, X.; Liu, B. The Effect of ZrO2 Nanoparticles on the Microstructure and Properties of Sintered WC–Bronze-Based Diamond Composites. Materials 2016, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Wang, Z.; Han, E.-H.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q. Corrosion Performance of Nano-ZrO2 Modified Coatings in Hot Mixed Acid Solutions. Materials 2018, 11, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liang, Z.; Jin, H. Characterization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Electrochemical Deposition of Ni-Co-ZrO2. Coatings 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Qiu, X.; Luo, B.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, R.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, Q. Synthesis and room-temperature ultraviolet photoluminescence properties of Zirconia nanowires. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Tang, C.; Feng, Z.; An, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, T.; Li, C. A Highly Selective and Stable ZnO-ZrO2 Solid Solution Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.Y.; Kamata, T.; Masui, T.; Imanaka, N. Complete Toluene Oxidation on Pt/CeO2-ZrO2-ZnO Catalysts. Catalysts 2013, 3, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghabeygi, S.; Sharifi, Z.; Molahasani, N. Enhanced Photocatalytic Property of Nano-ZrO2-SnO2 NPs for Photodegradation of an Azo Dye. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2017, 12, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Fu, X. Hierarchical Macro/Mesoporous TiO2/SiO2 and TiO2/ZrO2 Nanocomposites for Environmental Photocatalysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhai, B.; Yang, M.; Han, W.; Shao, X. ZrO2/CeO2 Nanocomposite: Two Step Synthesis, Microstructure, and Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity. Mater. Lett. 2013, 112, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agorku, E.S.; Kuvarega, A.T.; Mamba, B.B.; Pandey, A.C.; Mishra, A.K. Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity of multi-elements-doped ZrO2 for degradation of indigo carmine. J. Rare Earths 2015, 33, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, P.H.; Pham, V.H.; Phuong, D.T.; Nguyen, T.H.H.; Cao, X.T. The role of Cu2+ Concentration in Luminescence Quenching of Eu3+/Cu2+ Co-doped ZrO2 Nanoparticles. VNU J. Sci. Math.-Phys. 2019, 35, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Debnath, A.; Muthe, K.; Das, N.; Parhi, P. Rapid synthesis of tetragonal zirconia nanoparticles by microwave-solvothermal route and its photocatalytic activity towards organic dyes and hexavalent chromium in single and binary component systems. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 608, 125551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, A.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Esmaeilifar, A. Hydrothermal synthesis of zirconia nanoparticles from commercial zirconia. Procedia Eng. 2012, 42, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stojadinović, S.; Vasilić, R.; Radić, N.; Grbić, B. Zirconia films formed by plasma electrolytic oxidation: Photoluminescent and photocatalytic properties. Opt. Mater. 2015, 40, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, L.; Li, W.Z.; Xu, J.M.; Leblanc, R.M.; Wang, D.Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J. Controlled Hydrothermal Synthesis of Zirconium Oxide Nanostructures and Their Optical Properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 3874–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borilo, L.P.; Spivakova, L.N. Synthesis and Characterization of ZrO2 Thin Films. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 2, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunke, V.; Suda, U. Structural and Optical Properties of Thermally Oxidized Zirconium Dioxide Films. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2018, 77, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, C.V.; Babu, B.; Reddy, I.N.; Shim, J. Synthesis and characterization of pure tetragonal ZrO2 nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 6940–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwabi, A.T.; Acik, I.O.; Katerski, A.; Mere, A.; Krunks, M. Structural and electrical characterisation of high-k ZrO2 thin films deposited by chemical spray pyrolysis method. Thin Solid Films 2018, 662, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Impurities | Li, Mg, K, Ca, Rb, Na, Sr, Ba, Cu, Al, Ga, Tl, Sc, B, Cd, Ag, Zn, Pb, Bi, Co, Ni, Se, Mn, V, As, Ce, Nd, Pr, La, Sm, Eu, Pm, Tb, Gd, Er, Ho, and Dy | Lu, Yb, Tm | Y | Fe, Ti | Hf | Zr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aqueous phase, % | ≈100 | 95.6 | 96.5 | 69.2 | 32.7 | 23.5 |
| Organic phase, % | Not detected | 4.40 | 3.50 | 31.8 | 68.3 | 76.5 |
| Ref. [27] | Ref. [35] | Ref. [36] | Ref. [37] | Ref. [38] | Ref. [39] | Ref. [40] | This | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research | ||||||||
| Method | Templates | Microwave mediated solvothermal process | Hydrother-mal process | Plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) | Hydrother-mal route | Sol-gel | Thermal oxidation | Liquid-liquid |
| method | Technology | extraction | ||||||
| Resources | ZrOCl2·8H2O | Commercial ZrO2 (yellow powder) | Zirconium | ZrOCl2·8H2O | Metallic Zr films | ZrSiO4 (Thua Thien Hue, Viet Nam) | ||
| foils | ||||||||
| Conditions | 0.7 g ZrOCl2·8H2O+ 20 mL 1,4-butanediol; stirred 15 min; heated in microwave at 180 °C; 800 W power; 10 min; dried at 100 °C; 24 h | 10 M NaOH; | Constant current density of | 96% ethanol; 0.4 M Zr(IV); 60 °C; 30 min | 300–500 °C | 50% D2EHPA | ||
| 150 °C; 85 h | 100 mA/cm2, | /p-xylenes; | ||||||
| at 20 °C; 0.1 M citric acid; 600 s | extraction 3.0 HNO3; scrubbing 6.0 M nitric; | |||||||
| stripping 1.5 M sulfuric | ||||||||
| Optimum heating | Heated under refluxing and stirring at 180 °C; 4 h | 110 °C | 600–1000 °C for 1 h | 550 °C | ||||
| temperature | for 6 h | for 3 h | ||||||
| Phase formed | t–ZrO2 | Single phase | 72% (cubic and tetragonal); 28% monoclinic | ZrO2 films; | pure m–ZrO2 | ZrO2 | m–ZrO2 and polycrystalline, | t–ZrO2 and |
| zirconia nanowires | t–ZrO2 | mainly composed monoclinic | thin films on glass or quartz substrates | thin films | m–ZrO2 | |||
| Particle | 10.69 nm | 23.55 nm | 19–27 nm | 24.25 nm | ||||
| crystallite size | ||||||||
| The | Average 80 nm, length of over 10 μm | 30 nm | 32.5 nm | Thicknesses of 40–120 nm; refractive index 1.86–2.08 | Refractive index 2.05–2.02 | 25–30 nm | ||
| average | ||||||||
| particle size | ||||||||
| Bandgap value and purity of nano ZrO2 | Eg = 5.33 eV | Eg = 3.67–5.0 eV | XRD (99.45% ZrO2; 0.11% SiO2 and another) | Eg = 3.76–6.2 eV | Eg = 4.28 eV | Eg = 5.0–5.2 eV | Eg = 5.42–5.46 eV | Eg = 3.300 eV; |
| EDS (69.29% Zr; 30.71% O); | ||||||||
| XRF (100% ZrO2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, M.N.; Truong, M.X.; Nguyen, T.H.L.; Do, T.H.; Duong, T.T.A.; Tran, T.K.N.; Ngo, T.C.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.L.; Vu, T.H.; Pham, M.A. Purification and Characterization of High Purity Nano Zirconia by Liquid-Liquid Extraction Using D2EHPA/p-Xylenes. Inorganics 2022, 10, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10070093
Chu MN, Truong MX, Nguyen THL, Do TH, Duong TTA, Tran TKN, Ngo TCQ, Nguyen TTL, Vu TH, Pham MA. Purification and Characterization of High Purity Nano Zirconia by Liquid-Liquid Extraction Using D2EHPA/p-Xylenes. Inorganics. 2022; 10(7):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10070093
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Manh Nhuong, Mai Xuan Truong, Thi Hien Lan Nguyen, Tra Huong Do, Thi Tu Anh Duong, Thi Kim Ngan Tran, Thi Cam Quyen Ngo, Thi To Loan Nguyen, Thi Hau Vu, and Mai An Pham. 2022. "Purification and Characterization of High Purity Nano Zirconia by Liquid-Liquid Extraction Using D2EHPA/p-Xylenes" Inorganics 10, no. 7: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10070093
APA StyleChu, M. N., Truong, M. X., Nguyen, T. H. L., Do, T. H., Duong, T. T. A., Tran, T. K. N., Ngo, T. C. Q., Nguyen, T. T. L., Vu, T. H., & Pham, M. A. (2022). Purification and Characterization of High Purity Nano Zirconia by Liquid-Liquid Extraction Using D2EHPA/p-Xylenes. Inorganics, 10(7), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10070093






