650 W All-Fiber Single-Frequency Polarization-Maintaining Fiber Amplifier Based on Hybrid Wavelength Pumping and Tapered Yb-Doped Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
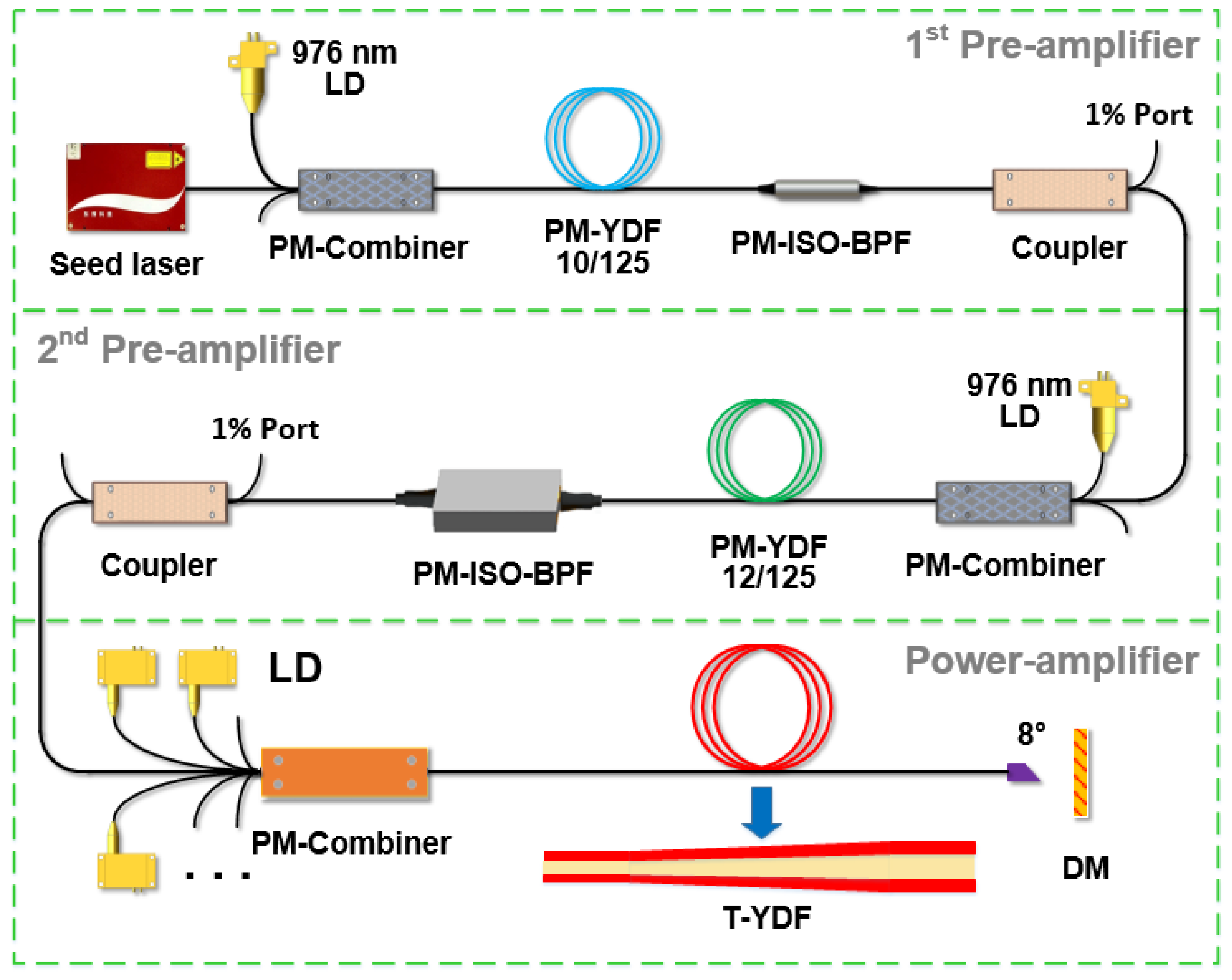
2. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Single Wavelength Pumping of 976 nm LDs
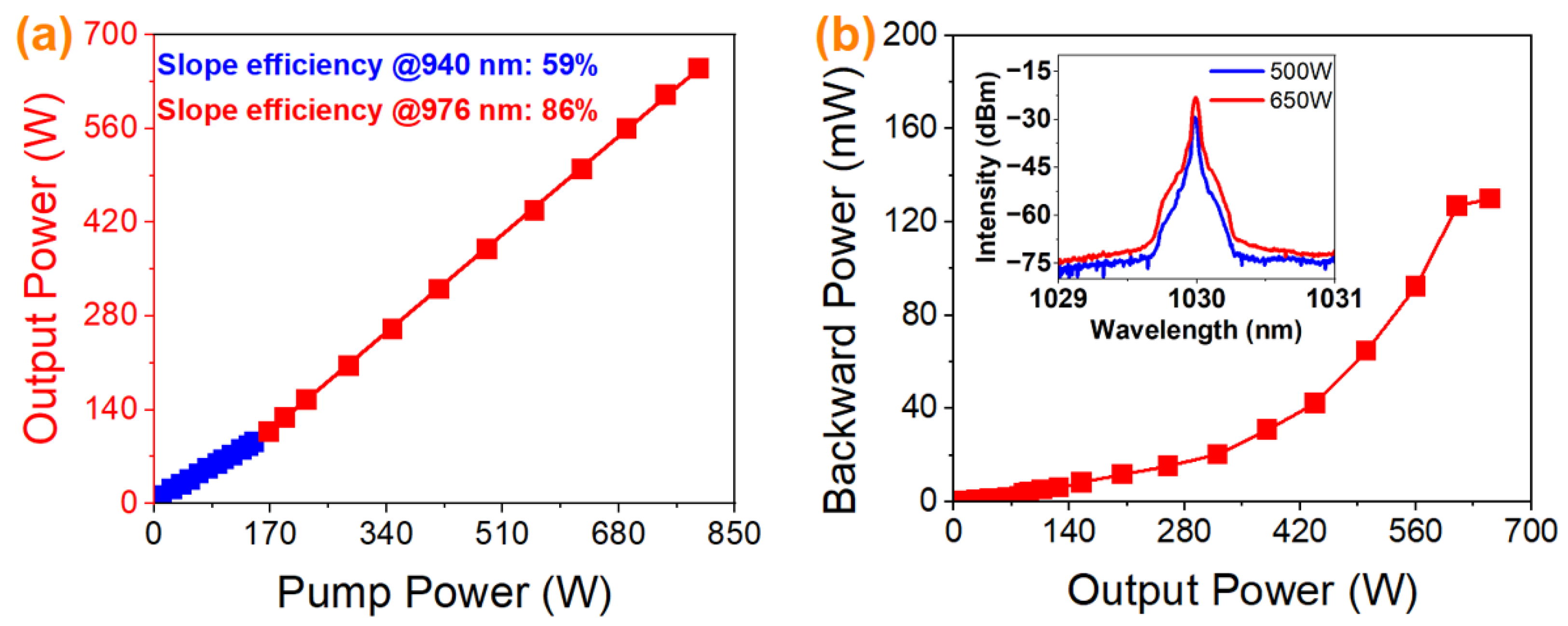
3.2. Hybrid Pumping with a Power Ratio of 1:4.4
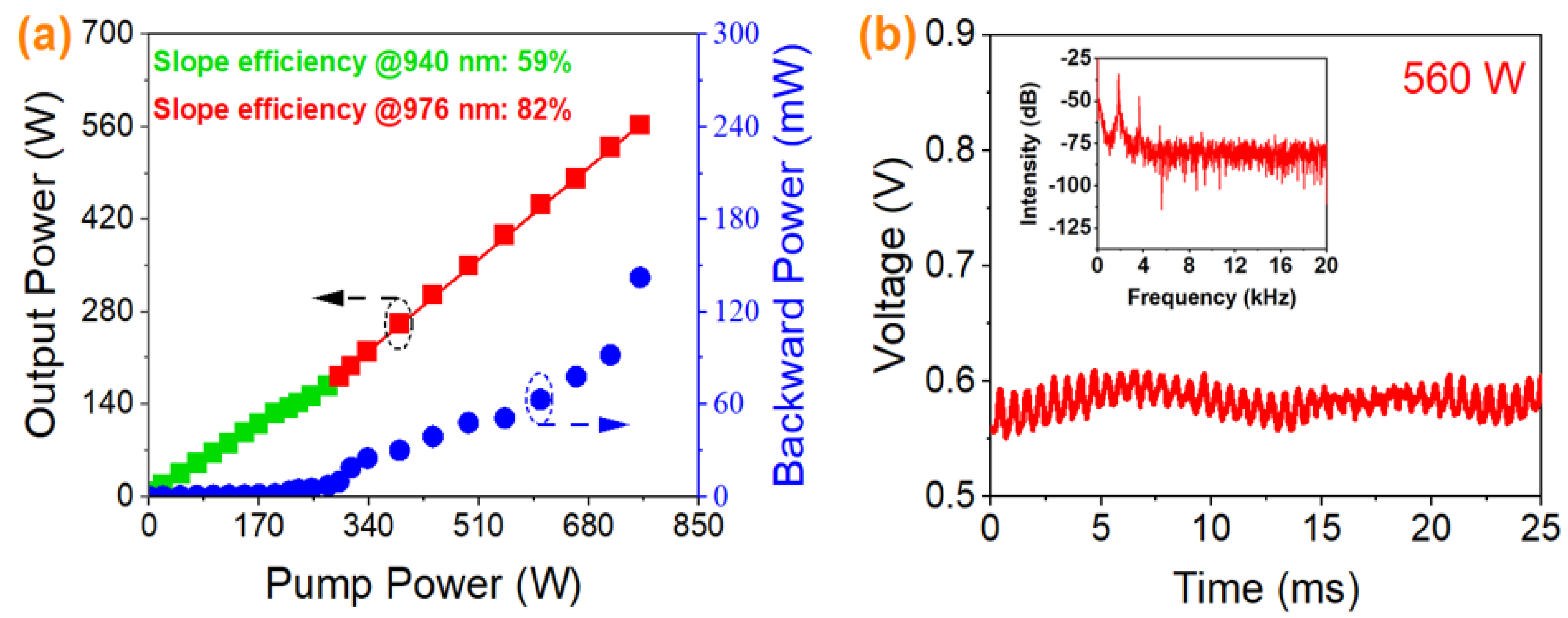
3.3. Hybrid Pumping with a Power Ratio of 1:1.7
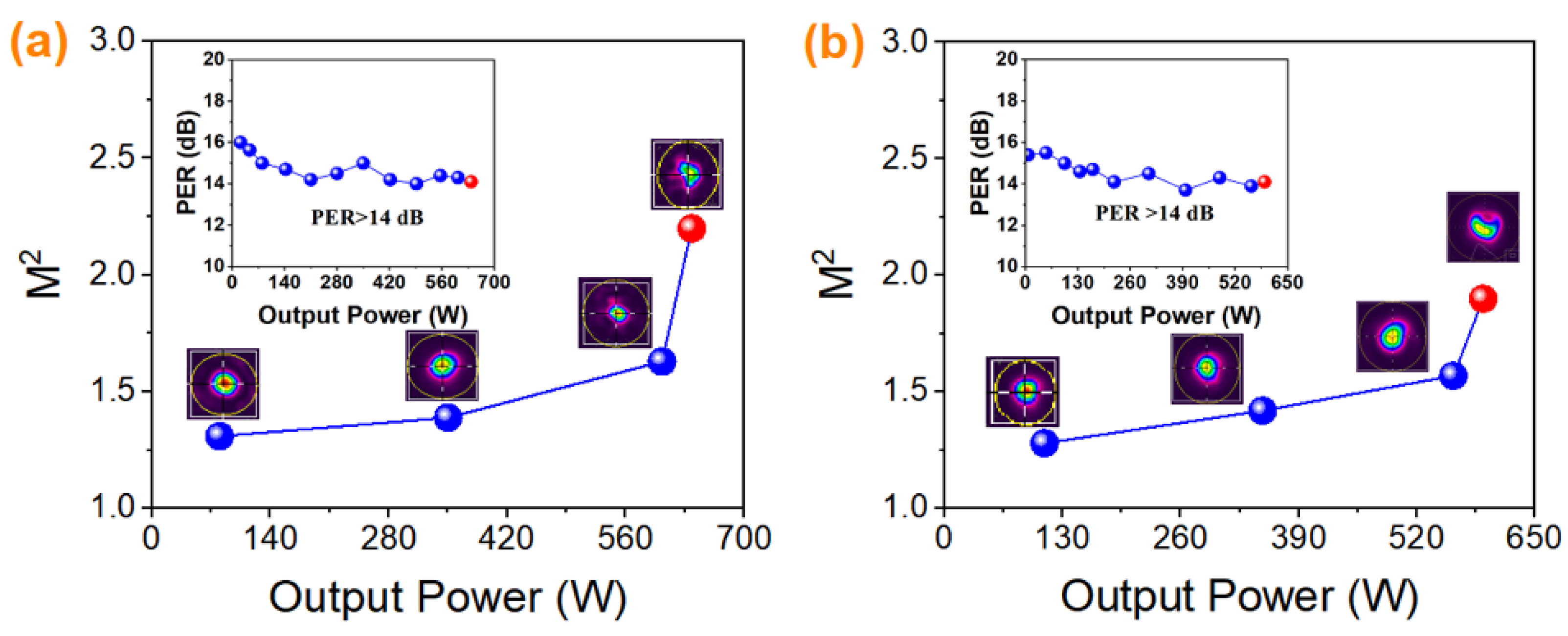
3.4. Analysis and Comparison
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Z.; Peng, M.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S. 1120 nm kHz-linewidth single-polarization single-frequency Yb-doped phosphate fiber laser. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 29794–29799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wei, X.; Qian, Q.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, S.; Peng, M.; Qiu, J. 400 mW ultrashort cavity low-noise single-frequency Yb3+-doped phosphate fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 3708–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Xu, S.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhou, K.; Lin, W.; Gan, J.; Yang, Z. All-optical frequency and intensity noise suppression of single-frequency fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1964–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Yang, C.; Gu, Q.; Wang, W.; Tan, T.; Zhao, Q.; Lin, W.; Wei, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S. 55 W kilohertz-linewidth core- and in-band-pumped linearly polarized single-frequency fiber laser at 1950 nm. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2343–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Huang, Z.; Deng, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gan, J.; Cheng, H.; Feng, Z.; Peng, M.; Yang, Z. Ultra-compact all-fiber narrow-linewidth single-frequency blue laser at 489 nm. J. Opt. 2018, 20, 025803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, P.; Su, R.; Tao, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, P. High-power coherent beam polarization combination of fiber lasers: Progress and prospect. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2017, 34, A7–A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellmann, F.; Steinke, M.; Meylahn, F.; Bode, N.; Willke, B.; Overmeyer, L.; Neumann, J.; Kracht, D. High power, single-frequency, monolithic fiber amplifier for the next generation of gravitational wave detectors. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 28523–28533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmat, M.J.; Dashtabi, M.M.; Manavi, S.R.; Hassanpour, E.; Massudi, R. Study of the stimulated Brillouin scattering power threshold in high power double-clad fiber lasers. Laser Phys. 2012, 23, 025104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregui, C.; Otto, H.J.; Stutzki, F.; Jansen, F.; Limpert, J.; Tünnermann, A. Passive mitigation strategies for mode instabilities in high-power fiber laser systems. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 19375–19386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Tao, R.; Li, C.; Wang, B.; Guo, C.; Shu, Q.; Zhao, P.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Jing, F.; et al. 3.7 kW monolithic narrow linewidth single mode fiber laser through simultaneously suppressing nonlinear effects and mode instability. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 9716–9724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y. Stimulated-Brillouin-scattering-suppressed high-power single-frequency polarization-maintaining Raman fiber amplifier with longitudinally varied strain for laser guide star. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 4796–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theeg, T.; Sayinc, H.; Neumann, J.; Kracht, D. All-fiber counter-propagation pumped single frequency amplifier stage with 300-W output power. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2012, 24, 1864–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, S.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Feng, Y. 170 W, single-frequency, single-mode, linearly-polarized, Yb-doped all-fiber amplifier. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 5456–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Wu, H.; Li, R.; Li, L.; Ma, P.; Wang, X.; Leng, J.; Zhou, P. 414 W near-diffraction-limited all-fiberized single-frequency polarization-maintained fiber amplifier. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, C.; Dajani, I.; Pulford, B. Modal instability-suppressing, single-frequency photonic crystal fiber amplifier with 811 W output power. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Ma, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z. 1.3 kW monolithic linearly polarized single-mode master oscillator power amplifier and strategies for mitigating mode instabilities. Photonics Res. 2015, 3, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, C.; Tao, R.; Ma, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, P. Towards tapered-fiber-based all-fiberized high power narrow linewidth fiber laser. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Lin, X.; Yang, B.; Xi, X.; Shi, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, X. Tapered Yb-doped fiber enabled a 4 kW near-single-mode monolithic fiber amplifier. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 2162–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Ma, P.; Liu, W.; Huang, L.; Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, P. 550 W single frequency fiber amplifiers emitting at 1030 nm based on a tapered Yb-doped fiber. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 20908–20919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, B.; Robin, C.; Dajani, I. Origin of thermal modal instabilities in large mode area fiber amplifiers. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 11407–11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregui, C.; Stihler, C.; Limpert, J. Transverse mode instability. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2020, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Xiao, H.; Meng, D.; Liu, W.; Tao, R.; Leng, J.; Ma, Y.; Su, R.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z. High power all-fiberized and narrow-bandwidth MOPA system by tandem pumping strategy for thermally induced mode instability suppression. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, K.; Dutta, N.K. Spectroscopic properties of Yb-doped silica glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, S.; Deng, H.; Feng, Z.; Yang, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gan, J.; Yang, Z. A broad continuous temperature tunable DBR single-frequency fiber laser at 1064 nm. IEEE Photonics J. 2016, 8, 1501107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Chen, D.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S. An efficient low-noise single-frequency 1033 nm Yb3+-doped MOPA phosphate fiber laser system. J. Opt. 2017, 19, 065502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Fu, S.; Deng, X.; Sheng, Q.; Xu, Y.; Fang, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Yao, J. 435 W single-frequency all-fiber amplifier at 1064 nm based on cascaded hybrid active fibers. Opt. Commun. 2022, 502, 127428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Ma, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z. Mitigating of modal instabilities in linearly-polarized fiber amplifiers by shifting pump wavelength. J. Opt. 2015, 17, 045504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, W.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Gu, Q.; Huang, J.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, K.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S. 650 W All-Fiber Single-Frequency Polarization-Maintaining Fiber Amplifier Based on Hybrid Wavelength Pumping and Tapered Yb-Doped Fibers. Photonics 2022, 9, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080518
Jiang W, Yang C, Zhao Q, Gu Q, Huang J, Jiang K, Zhou K, Feng Z, Yang Z, Xu S. 650 W All-Fiber Single-Frequency Polarization-Maintaining Fiber Amplifier Based on Hybrid Wavelength Pumping and Tapered Yb-Doped Fibers. Photonics. 2022; 9(8):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080518
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Wanpeng, Changsheng Yang, Qilai Zhao, Quan Gu, Jiamin Huang, Kui Jiang, Kaijun Zhou, Zhouming Feng, Zhongmin Yang, and Shanhui Xu. 2022. "650 W All-Fiber Single-Frequency Polarization-Maintaining Fiber Amplifier Based on Hybrid Wavelength Pumping and Tapered Yb-Doped Fibers" Photonics 9, no. 8: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080518
APA StyleJiang, W., Yang, C., Zhao, Q., Gu, Q., Huang, J., Jiang, K., Zhou, K., Feng, Z., Yang, Z., & Xu, S. (2022). 650 W All-Fiber Single-Frequency Polarization-Maintaining Fiber Amplifier Based on Hybrid Wavelength Pumping and Tapered Yb-Doped Fibers. Photonics, 9(8), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080518




