Low-Complexity Chromatic Dispersion Equalization FIR Digital Filter for Coherent Receiver
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Operation Principles
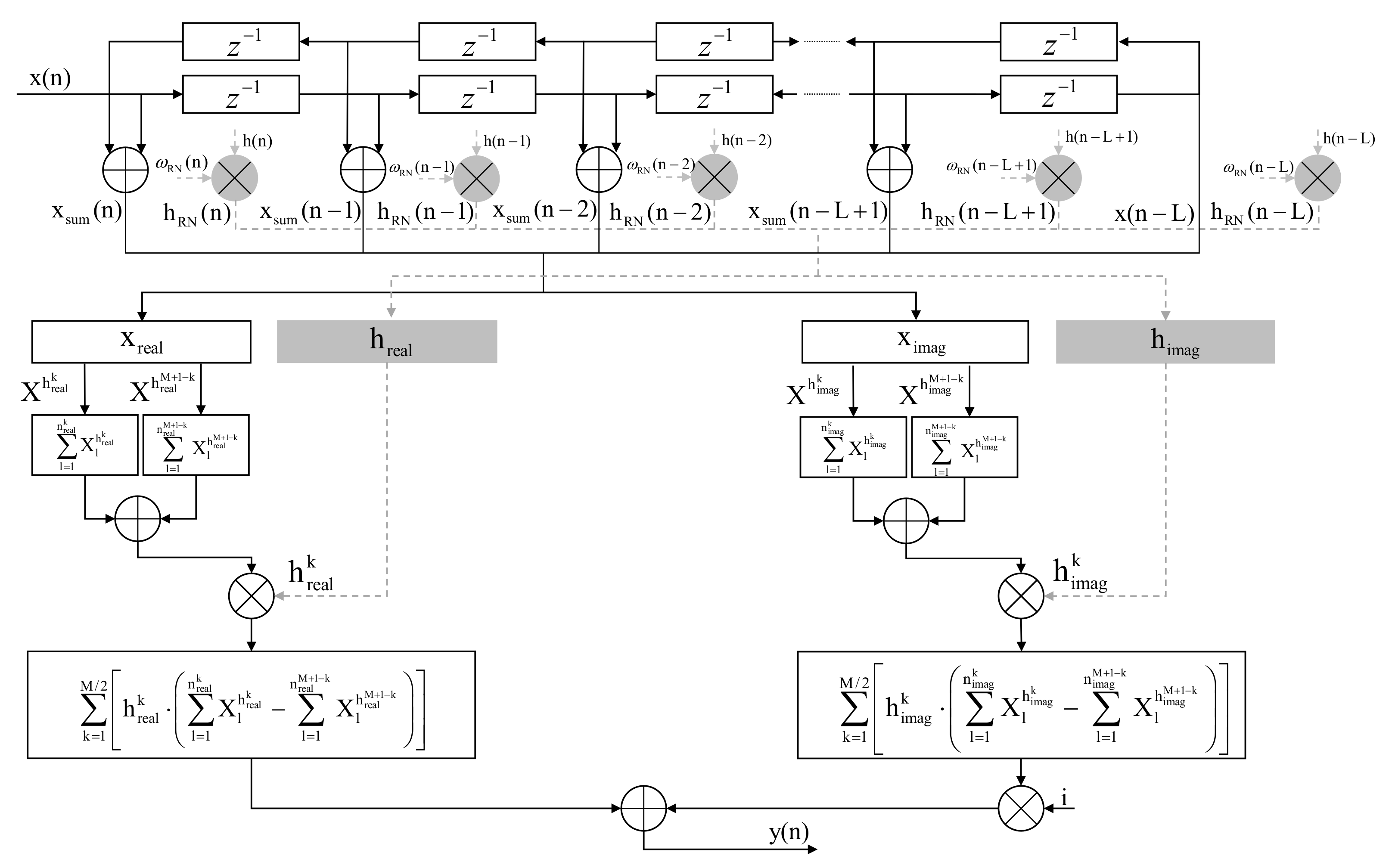
2.1. Time-Domain Equalization Implementation
2.2. Optimize Time-Domain Equalization Implementation
2.2.1. Window Function Weight Optimization
2.2.2. Window Function Weight Optimization
- In this paper, the filter complex tap coefficients are independently written as their real and imaginary parts for operation. This operation can increase the diversity of filter tap coefficients, which is inversely proportional to the computational complexity of TD-CDE.
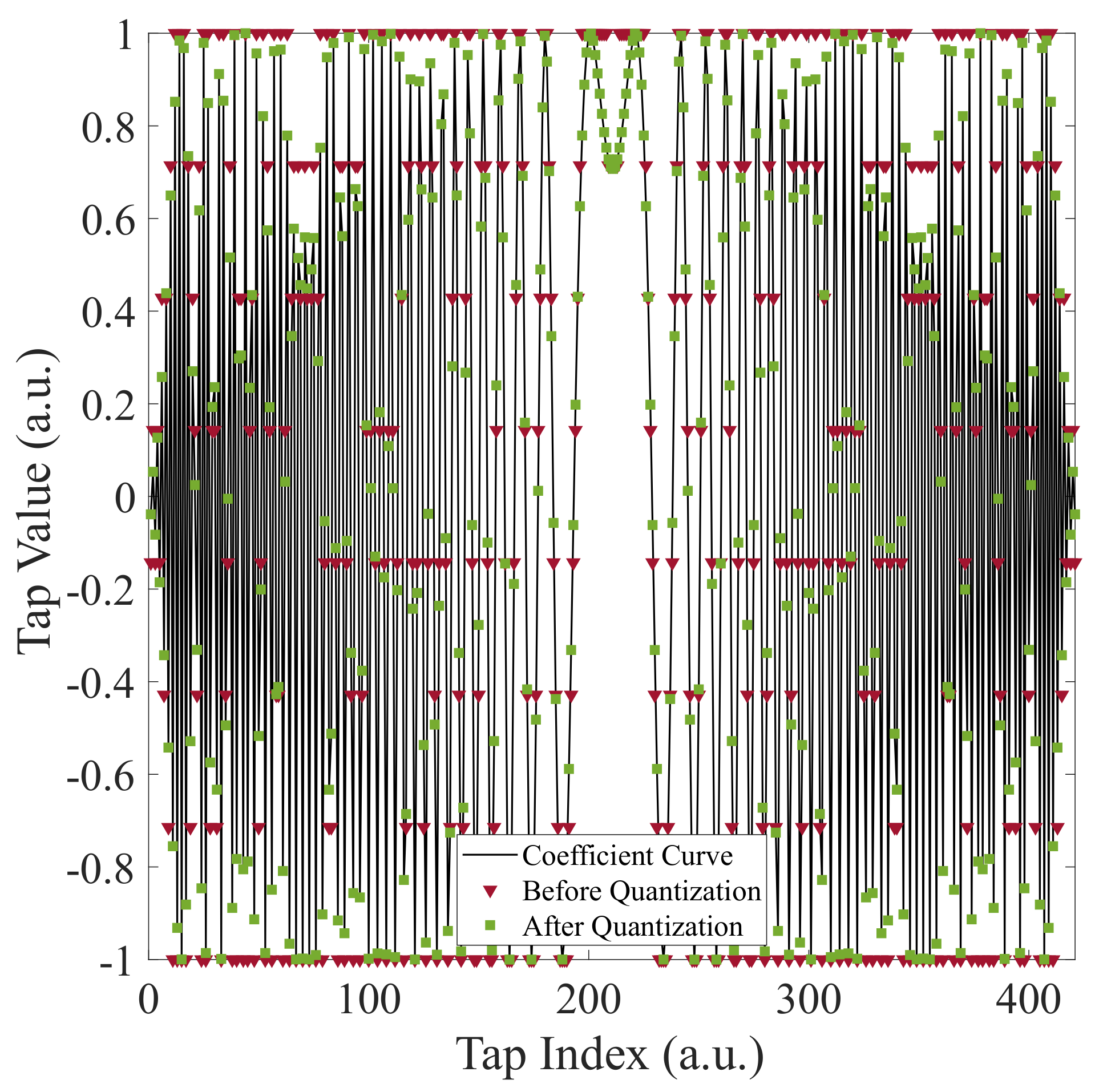
- It can be seen from Equation (5) that the tap coefficient of the filter is symmetrical about the central coefficient [21]. Assuming the symmetric length is L, then . If the tap coefficients are uniformly quantized, the quantized value is also approximately symmetric about the central coefficient.
3. Simulation and Analysis
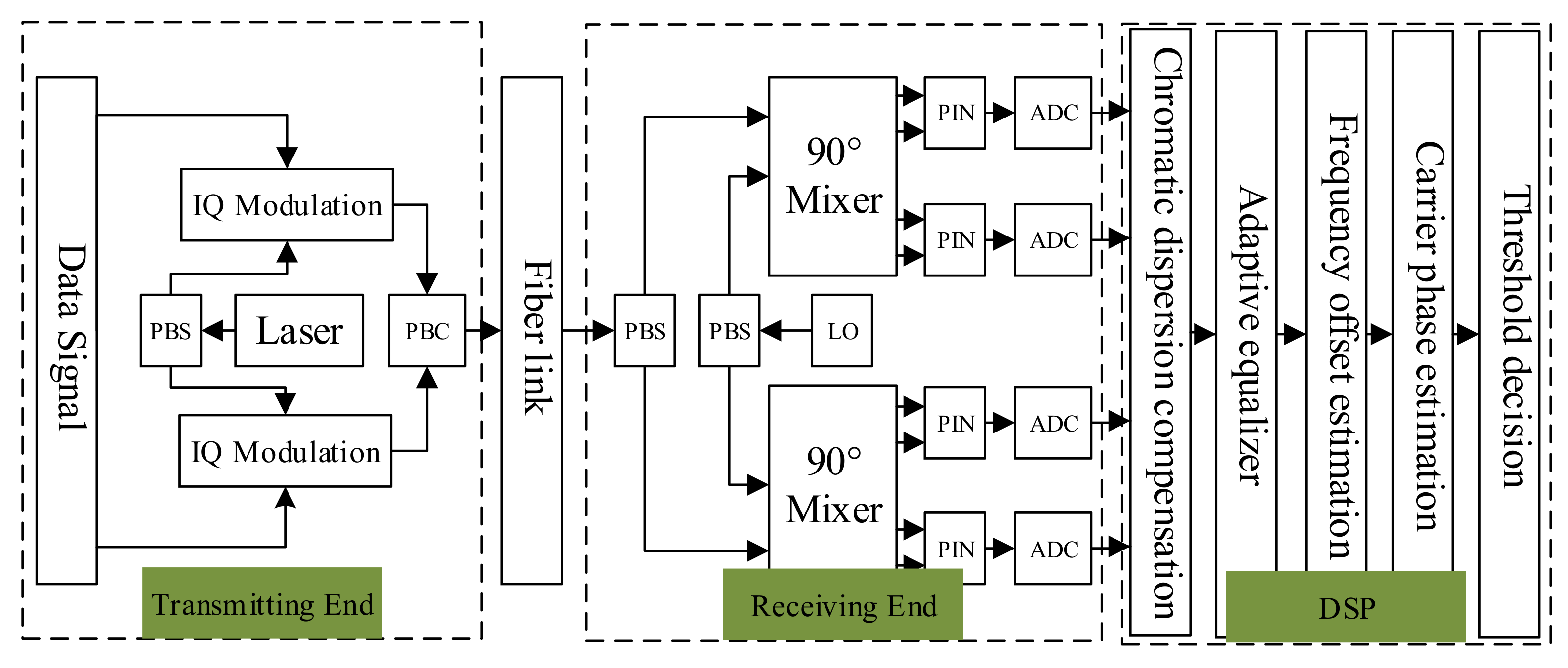
3.1. Environment
3.2. Result Simulation
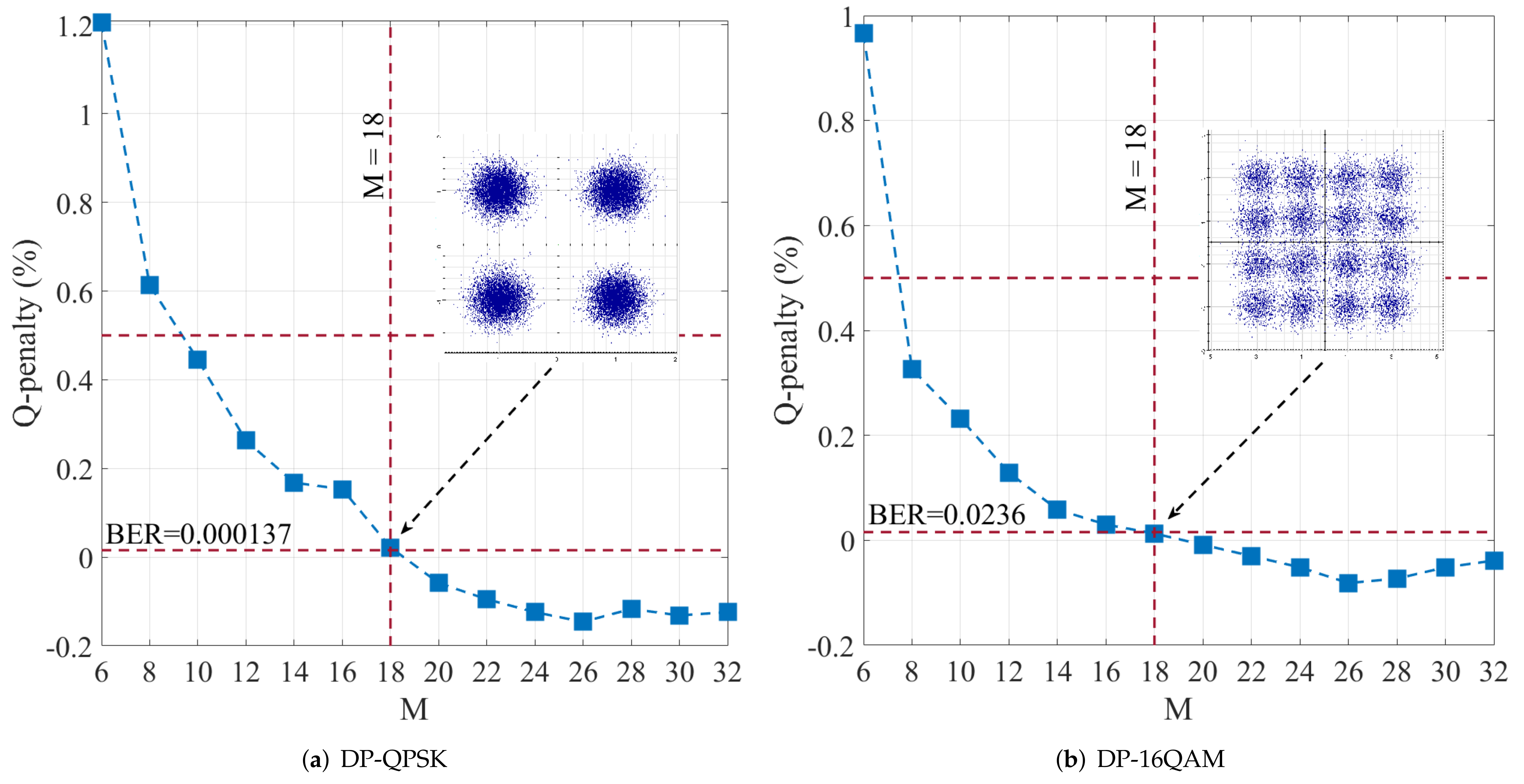
3.2.1. Weight Optimization Performance Analysis
3.2.2. Coefficient Quantification Performance Analysis
3.2.3. Coefficient Quantification and Q-Penalty
4. Discussion
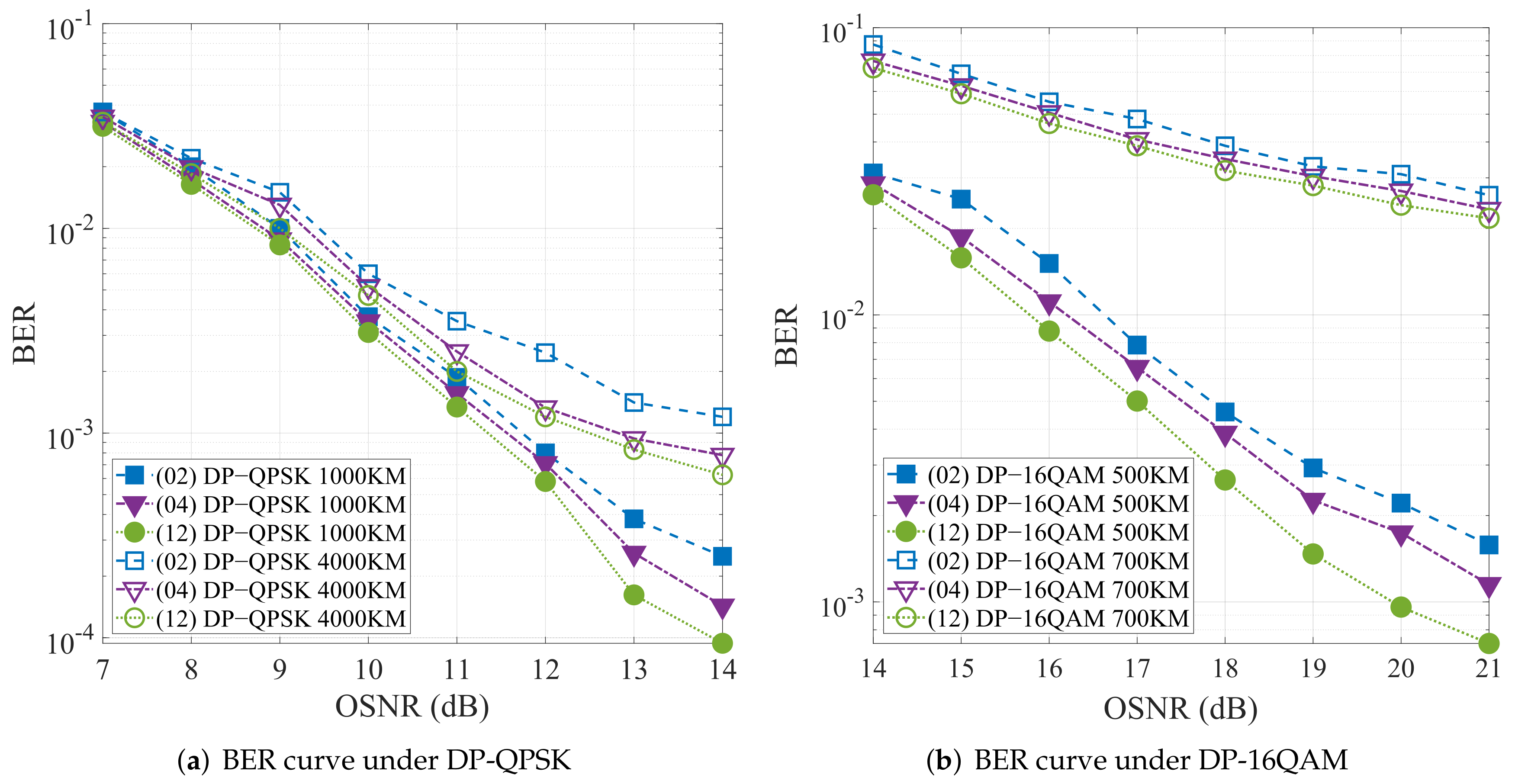
4.1. Comparision of TD-CDE and CQWO-TD-CDE
4.2. Comparision of FD-CDE and CQWO-TD-CDE
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charlet, G.; Pecci, P. 5—Ultra-long haul submarine transmission. In Undersea Fiber Communication Systems, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 10, pp. 165–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Jiang, H.; Liang, G.; Zhan, Q.; Su, Z.; Li, Z. Chromatic dispersion equalization FIR filter design based on discrete least-squares approximation. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 20387–20394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Nelson, L.E. 400G WDM Transmission on the 50 GHz Grid for Future Optical Networks. J. Light. Technol. 2012, 30, 3779–3792. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Jin, C.; Zhang, S.; Jacobsen, G.; Liu, T. Phase Noise Cancellation in Coherent Communication Systems Using a Radio Frequency Pilot Tone. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, T. Advanced DSP for Coherent Optical Fiber Communication. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuschnerov, M.; Hauske, F.N.; Piyawanno, K.; Spinnler, B.; Alfiad, M.S.; Napoli, A.; Lankl, B. DSP for Coherent Single-Carrier Receivers. J. Light. Technol. 2009, 27, 3614–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geyer, J.C.; Fludger, C.R.S.; Duthel, T.; Schulien, C.; Schmauss, B.J.I. Efficient Frequency Domain Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in a Coherent Polmux QPSK-Receiver. In Proceedings of the 2010 Conference on Optical Fiber Communication (OFC/NFOEC), Collocated National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2010; Wiley Telecom: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Felipe, A.; de Souza, A.L. Chirp-Filtering for Low-Complexity Chromatic Dispersion Compensation. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 2954–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, B.S.G.; Sedighi, B.; Guan, K.; Anthapadmanabhan, N.P.; Shieh, W.; Hinton, K.J.; Tucker, R.S. End-to-End Energy Modeling and Analysis of Long-Haul Coherent Transmission Systems. IEEE/OSA J. Light. Technol. 2014, 32, 3093–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachris, C.; Tomkos, I. A Survey on Optical Interconnects for Data Centers. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2012, 14, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlen, P.; Skubic, B.; Rostami, A.; Fiorani, M.; Monti, P.; Ghebretensae, Z.; Martensson, J.; Kun, W.; Wosinska, L. Data Plane and Control Architectures for 5G Transport Networks. J. Light. Technol. 2015, 34, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Plant, D.V. Optimal Design of Dispersion Filter for Time-Domain Split-Step Simulation of Pulse Propagation in Optical Fiber. J. Light. Technol. 2012, 30, 1405–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorapoj, P. Performance Analysis of Digital FIR LP Filter Implementation based on 5 Window Techniques: Rectangular, Barlett, Hann, Hamming and Blackman. Int. J. Simul. Syst. 2019, 20, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Lei, L.; Dong, J.; Zhang, X. Triangular-shaped pulse generation based on self-convolution of a rectangular-shaped pulse. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 2258–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Teng, Z.; Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T. Hanning self-convolution window and its application to harmonic analysis. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2009, 52, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, F.; Yang, Y. Harmonic Estimation Using Symmetrical Interpolation FFT Based on Triangular Self-Convolution Window. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2015, 11, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, A.; Johansson, H.; Gustafsson, O.; Savory, S.J. Optimal Least-Squares FIR Digital Filters for Compensation of Chromatic Dispersion in Digital Coherent Optical Receivers. J. Light. Technol. 2014, 32, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xie, C. Enabling Technologies for High Spectral-Efficiency Coherent Optical Communication Networks; Wiley Telecom: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 13–64. [Google Scholar]
- Spinnler, B. Equalizer Design and Complexity for Digital Coherent Receivers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2010, 16, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Sun, S.; Zhao, H.; Yang, J. Laser Doppler signal processing based on trispectral interpolation of Nuttall window. Optik 2020, 205, 163364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Jacobsen, G.; Popov, S.; Li, J.; Vanin, E.; Wang, K.; Friberg, A.T.; Zhang, Y. Chromatic dispersion compensation in coherent transmission system using digital filters. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 16243–16257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Jacobsen, G.; Popov, S.; Forzati, M.; Mårtensson, J.; Mussolin, M.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Friberg, A.T. Frequency Domain Chromatic Dispersion Equalization Using Overlap-Add Methods in Coherent Optical System. J. Opt. Commun. 2011, 32, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 1550 nm | Chromatic dispersion coefficient | 16.5 ps/nm/km |
| Sequence length | 131,072 | Group velocity dispersion coefficient | 0.2 ps/km |
| Symbol rate | 28 GBaud | Laser line width | 0.1 MHz |
| Modulation format | QPSK/16QAM | Attenuation coefficient | 0.2 db/km |
| Roll-off factor | 0.25/1 | Signal power | 10 dbm |
| L/km | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 207 | 415 | 623 | ||||||
| M | 8 | 12 | 16 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 8 | 12 | 16 |
| 97.4 | 96.1 | 94.8 | 98.7 | 98.1 | 97.4 | 99.1 | 98.7 | 98.3 | |
| 41.9 | 41.4 | 40.8 | 42.4 | 42.1 | 41.9 | 42.6 | 42.2 | 42.2 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Huang, Z.; Shen, F.; Zhao, Y. Low-Complexity Chromatic Dispersion Equalization FIR Digital Filter for Coherent Receiver. Photonics 2022, 9, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9040263
Wu Z, Li S, Huang Z, Shen F, Zhao Y. Low-Complexity Chromatic Dispersion Equalization FIR Digital Filter for Coherent Receiver. Photonics. 2022; 9(4):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9040263
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zicheng, Sida Li, Zhiping Huang, Fangqi Shen, and Yongjie Zhao. 2022. "Low-Complexity Chromatic Dispersion Equalization FIR Digital Filter for Coherent Receiver" Photonics 9, no. 4: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9040263
APA StyleWu, Z., Li, S., Huang, Z., Shen, F., & Zhao, Y. (2022). Low-Complexity Chromatic Dispersion Equalization FIR Digital Filter for Coherent Receiver. Photonics, 9(4), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9040263





