Physiology-Enhanced Data Analytics to Evaluate the Effect of Altitude on Intraocular Pressure and Ocular Hemodynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Mont Blanc Study
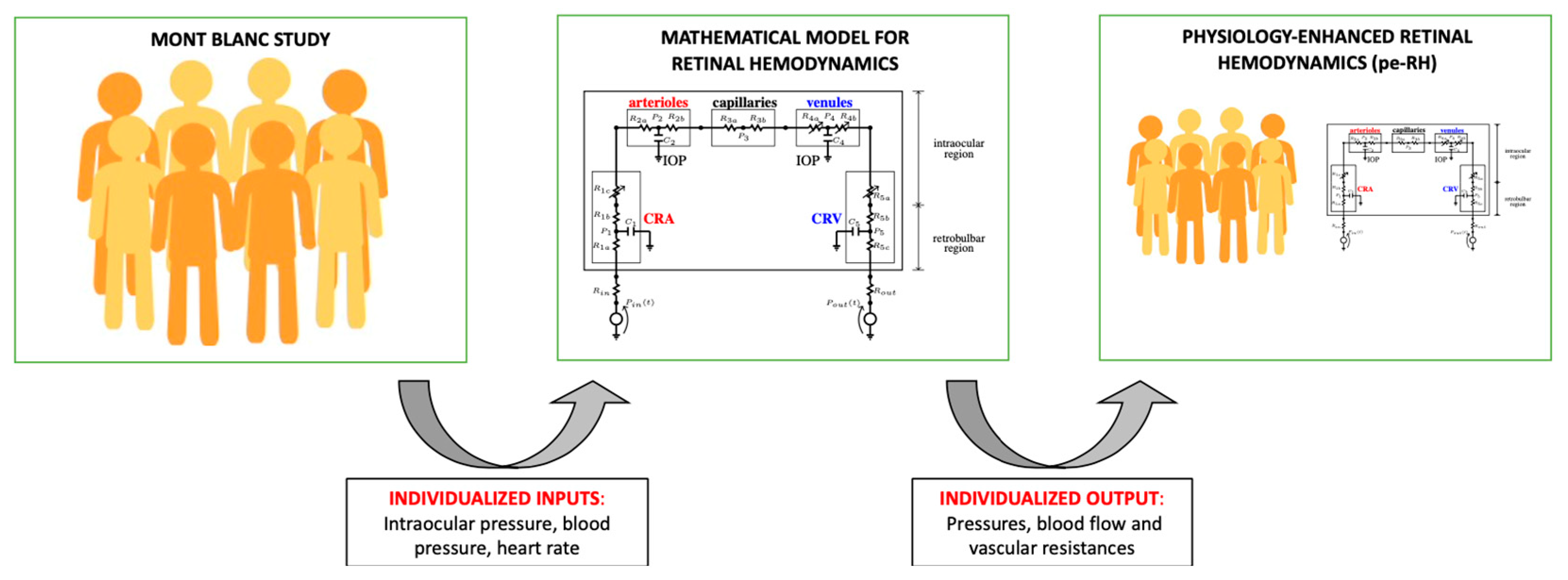
2.2. Mathematical Model of Retinal Hemodynamics
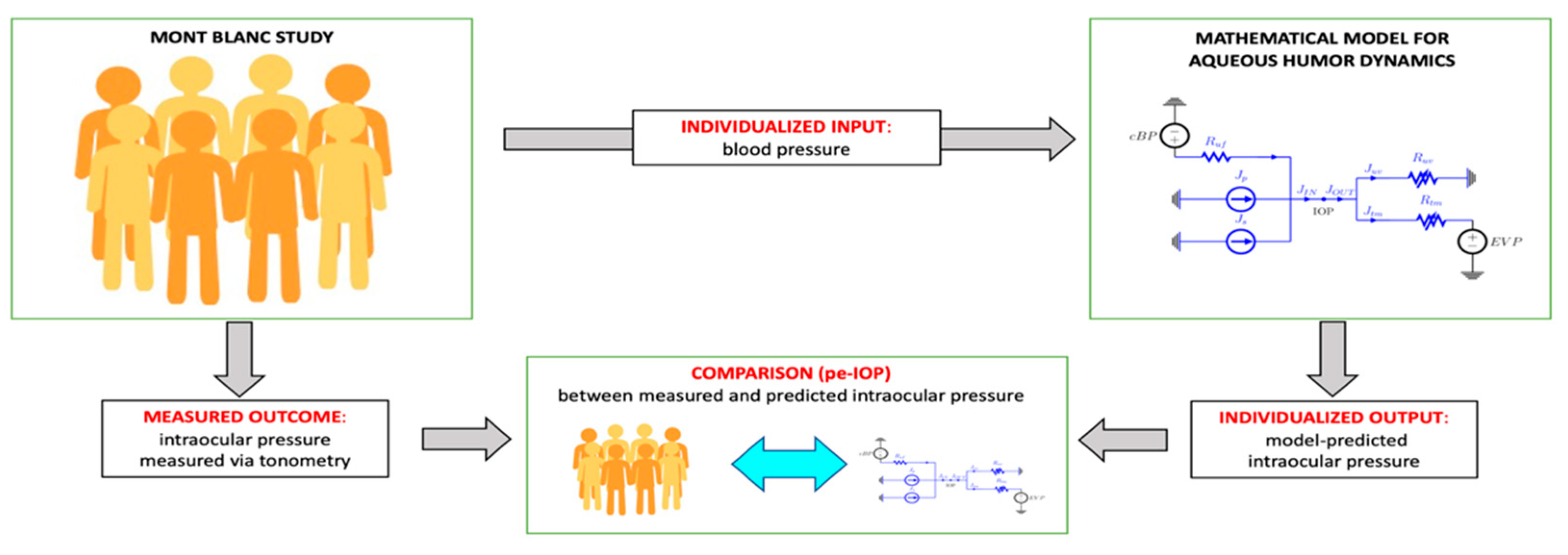
2.3. Mathematical Model of Aqueous Humor Dynamics
3. Results
3.1. Physiology-Enhanced Data Analytics: Retinal Hemodynamics
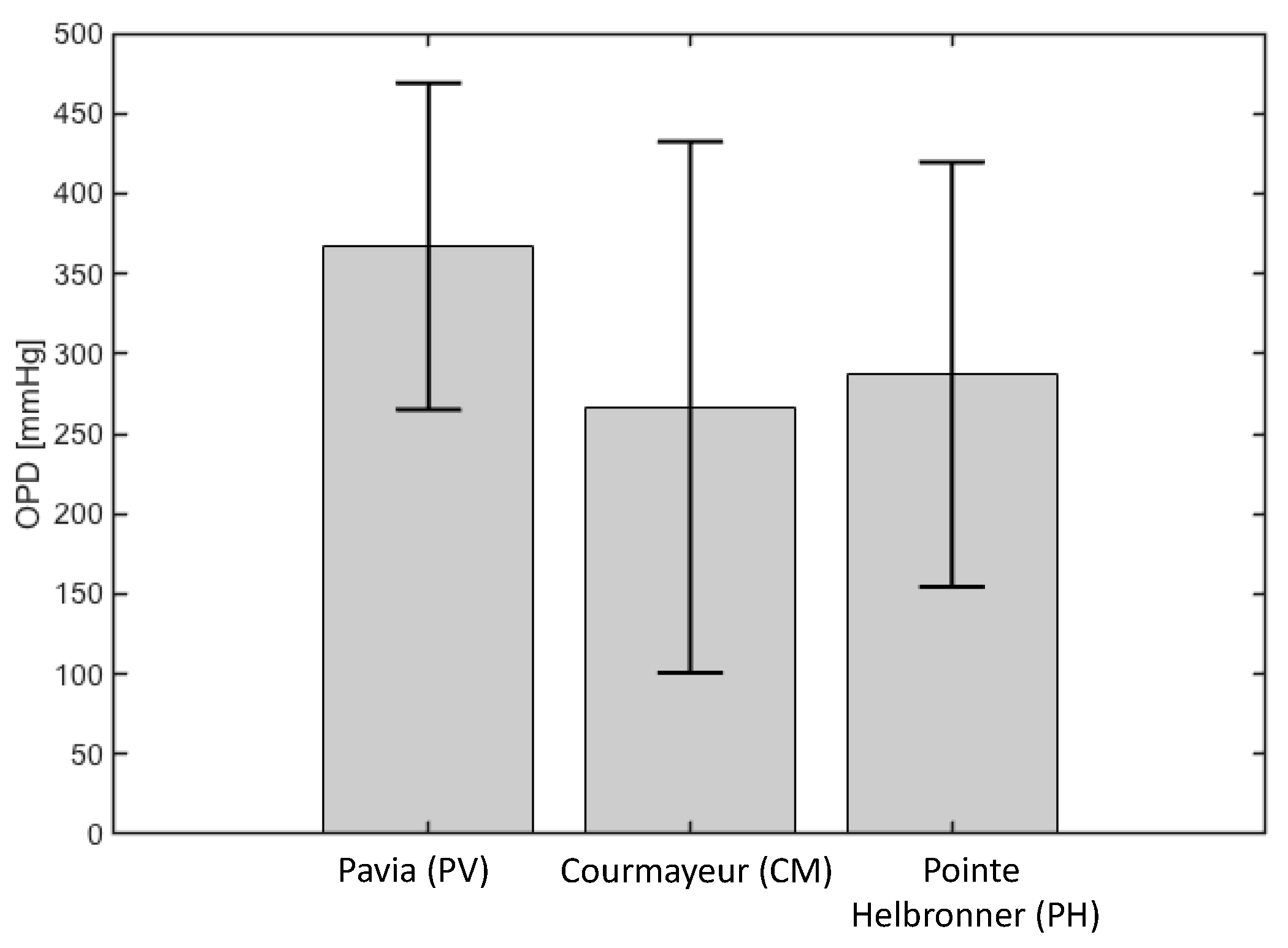
3.2. Physiology-Enhanced Data Analytics: Aqueous Humor Dynamics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tham, Y.C.; Li, X.; Wong, T.Y.; Quigley, H.A.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.Y. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, M.A.; Heuer, D.K.; Higginbotham, E.J.; Johnson, C.A.; Keltner, J.L.; Miller, J.P.; Parrish, R.K., 2nd; Wilson, M.R.; Gordon, M.O. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: A randomized trial determines that topical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, V.P.; Arcieri, E.S.; Harris, A. Blood pressure and glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kook, M.S. Systemic and Ocular Hemodynamic Risk Factors in Glaucoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 141905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, L.; Katsanos, A.; Russo, A.; Riva, I. 24-hour intraocular pressure and ocular perfusion pressure in glaucoma. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2013, 58, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmanova, E.; Pluhacek, F.; Botek, M.; Krejci, J.; Jarosova, J. Intraocular Pressure Response to Short-Term Extreme Normobaric Hypoxia Exposure. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y.; Yang, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Nguyen, A.H.; Chen, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Association Between Arterial Blood Gas Variation and Intraocular Pressure in Healthy Subjects Exposed to Acute Short-Term Hypobaric Hypoxia. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinchmann-Hansen, O.; Myhre, K. Blood pressure, intraocular pressure, and retinal vessels after high altitude mountain exposure. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1989, 60, 970–976. [Google Scholar]
- Palatini, P.; Guzzardi, G.; Penzo, M.; Dorigatti, F.; Anaclerio, M.; Pessina, A.C. Effect of high and low altitude exposure on the blood pressure response to physical exercise. Cardiologia 1991, 36, 853–859. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, M.M.; Merz, T.M.; Barthelmes, D.; Petrig, B.L.; Truffer, F.; Bloch, K.E.; Turk, A.; Maggiorini, M.; Hess, T.; Schoch, O.D.; et al. New insights into ocular blood flow at very high altitudes. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, E.A.; Hopkins, S.R.; Perthen, J.E.; Buxton, R.B.; Dubowitz, D.J. Regional cerebral blood flow during acute hypoxia in individuals susceptible to acute mountain sickness. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2008, 160, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karakucuk, S.; Mujdeci, M.; Baskol, G.; Arda, H.; Gumus, K.; Oner, A. Changes in central corneal thickness, intraocular pressure, and oxidation/antioxidation parameters at high altitude. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2012, 83, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somner, J.E.; Morris, D.S.; Scott, K.M.; MacCormick, I.J.; Aspinall, P.; Dhillon, B. What happens to intraocular pressure at high altitude? Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 1622–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, M.M.; Barthelmes, D.; Merz, T.M.; Truffer, F.; Knecht, P.B.; Petrig, B.; Bloch, K.E.; Hefti, U.; Schubiger, G.; Landau, K. Intraocular pressure during a very high altitude climb. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 1609–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Qiong Da, C.R.; Liu, J.; Yan, X. Intraocular pressure and axial length changes during altitude acclimatization from Beijing to Lhasa. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersanli, D.; Yildiz, S.; Sonmez, M.; Akin, A.; Sen, A.; Uzun, G. Intraocular pressure at a simulated altitude of 9000 m with and without 100% oxygen. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2006, 77, 704–706. [Google Scholar]
- Foulsham, W.; Tatham, A.J. High Altitude-associated Changes in Intraocular Pressure Abrogated by Trabeculectomy. J. Glaucoma 2017, 26, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, J.; Kanchanaranya, N.; Devenyi, R.G.; Lam, W.C. Evaluating the safety of air travel for patients with scleral buckles and small volumes of intraocular gas. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 1226–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, R.; Sen, A.; Golemez, H.; Basmak, H.; Yildirim, N.; Karadurmus, N.; Koseoglu, E.; Akin, A. The effect of short-term hypobaric hypoxic exposure on intraocular pressure. Curr. Eye Res. 2008, 33, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, R.; Sen, A.; Yildirim, N.; Basmak, H.; Golemez, H.; Cakir, E.; Akin, A. The relation between intraocular pressure change and plasma natriuretic peptide under simulated hypobaric conditions. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 58, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baertschi, M.; Dayhaw-Barker, P.; Flammer, J. The effect of hypoxia on intra-ocular, mean arterial, retinal venous and ocular perfusion pressures. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2016, 63, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amit, A.; Gaurav, K.; Vikas, A.; Ashok, K.; Harpreet, A.S.; Shivani, A. Evaluation of intraocular pressure and corneal thickness in individuals at high altitude area (10,000 ft above sea level). Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 63, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, H.; Nilforushan, N.; Sedaghat, A.; Soudi, R.; Irani, A.; Gordiz, A.; Hatamkhani, S. Intraocular pressure after exposure to moderate altitude. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2013, 251, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, M.; Stupp, T.; Georgalas, I.; Georgiadou, E.; Moschos, M.; Thanos, S. Intraocular pressure changes during high-altitude acclimatization. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2006, 244, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmann, G.; Schommer, K.; Schultheiss, M.; Fischer, M.D.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.U.; Gekeler, F.; Schatz, A. Effect of High Altitude Exposure on Intraocular Pressure Using Goldmann Applanation Tonometry. High. Alt. Med. Biol. 2017, 18, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cao, K.; Li, S.; Fan, S.; Huang, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, N. Intraocular Pressure Changes of Healthy Lowlanders at Different Altitude Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sun, Y.X.; Han, Y.; Yang, D.Y.; Yang, Y.Q.; Cao, K.; Li, S.N.; Li, X.; Lu, X.X.; Wu, S.Z.; et al. Longitudinal observation of intraocular pressure variations with acute altitude changes. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 3226–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albis-Donado, O.; Rodriguez-Camacho, B.; Bhartiya, S.; Ramirez-Neria, P.; Lopez-Star, E.; Gonzalez-Daher, P.; Badillo-Fernandez, M.; Stalmans, I. Effects of Acute Atmospheric Pressure Changes on Dynamic Contour Tonometry and Goldmann Applanation Tonometry in Normal Individuals: A Pilot Study. J. Glaucoma 2020, 29, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cymerman, A.; Rock, P.B.; Muza, S.R.; Lyons, T.P.; Fulco, C.S.; Mazzeo, R.S.; Butterfield, G.; Moore, L.G. Intraocular pressure and acclimatization to 4300 M altitude. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2000, 71, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Bayer, A.; Mutlu, F.M.; Akay, F.; Bayraktar, M.Z. An assessment of intraocular pressure change in healthy subjects during air flight. Curr. Eye Res. 2008, 33, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, A.; Yumusak, E.; Sahin, O.F.; Uysal, Y. Intraocular pressure measured at ground level and 10,000 feet. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2004, 75, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruttini, C.; Verticchio Vercellin, A.; Klersy, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Tinelli, C.; Riva, I.; Oddone, F.; Katsanos, A.; Quaranta, L. The Mont Blanc Study: The effect of altitude on intra ocular pressure and central corneal thickness. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, D.; Sun, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, N. Retinal vessel oxygen saturation and vessel diameter in healthy individuals during high-altitude exposure. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, R.T.; Taylor, G.R.; Rock, P.; Mader, T.H.; Hunter, N.; Cymerman, A. An automated method of quantifying retinal vascular responses during exposure to novel environmental conditions. Ophthalmology 1990, 97, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelmes, D.; Bosch, M.M.; Merz, T.M.; Petrig, B.L.; Truffer, F.; Bloch, K.E.; Holmes, T.A.; Cattin, P.; Hefti, U.; Sellner, M.; et al. Delayed appearance of high altitude retinal hemorrhages. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhende, M.P.; Karpe, A.P.; Pal, B.P. High altitude retinopathy. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 61, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushing, T.; Paterson, R.; Haukoos, J.; Harris, N.S. Intraocular pressure is not associated with acute mountain sickness. High. Alt. Med. Biol. 2013, 14, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Guidoboni, G.; Siesky, B.; Mathew, S.; Verticchio Vercellin, A.C.; Rowe, L.; Arciero, J. Ocular blood flow as a clinical observation: Value, limitations and data analysis. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 100841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidoboni, G.; Harris, A.; Cassani, S.; Arciero, J.; Siesky, B.; Amireskandari, A.; Tobe, L.; Egan, P.; Januleviciene, I.; Park, J. Intraocular pressure, blood pressure, and retinal blood flow autoregulation: A mathematical model to clarify their relationship and clinical relevance. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 4105–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szopos, M.; Cassani, S.; Guidoboni, G.; Prud’homme, C.S.; Ricardo; Siesky, B.; Harris, A. Mathematical modeling of aqueous humor flow and intraocular pressure under uncertainty: Towards individualized glaucoma management. J. Modeling Ophthalmol. 2016, 1, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, L. Mathematical Modelling and Simulation of Ocular Blood Flows and Their Interactions. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Strasbourg, Strasbourg, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verticchio Vercellin, A.; Harris, A.; Belamkar, A.; Zukerman, R.; Carichino, L.; Szopos, M.; Siesky, B.; Quaranta, L.; Bruttini, C.; Oddone, F.; et al. Physiology-Enhanced Data Analytics to Evaluate the Effect of Altitude on Intraocular Pressure and Ocular Hemodynamics. Photonics 2022, 9, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9030158
Verticchio Vercellin A, Harris A, Belamkar A, Zukerman R, Carichino L, Szopos M, Siesky B, Quaranta L, Bruttini C, Oddone F, et al. Physiology-Enhanced Data Analytics to Evaluate the Effect of Altitude on Intraocular Pressure and Ocular Hemodynamics. Photonics. 2022; 9(3):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9030158
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerticchio Vercellin, Alice, Alon Harris, Aditya Belamkar, Ryan Zukerman, Lucia Carichino, Marcela Szopos, Brent Siesky, Luciano Quaranta, Carlo Bruttini, Francesco Oddone, and et al. 2022. "Physiology-Enhanced Data Analytics to Evaluate the Effect of Altitude on Intraocular Pressure and Ocular Hemodynamics" Photonics 9, no. 3: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9030158
APA StyleVerticchio Vercellin, A., Harris, A., Belamkar, A., Zukerman, R., Carichino, L., Szopos, M., Siesky, B., Quaranta, L., Bruttini, C., Oddone, F., Riva, I., & Guidoboni, G. (2022). Physiology-Enhanced Data Analytics to Evaluate the Effect of Altitude on Intraocular Pressure and Ocular Hemodynamics. Photonics, 9(3), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9030158








