Key Space Enhanced Correlated Random Bit Generation Based on Synchronized Electro-Optic Self-Feedback Loops with Mach–Zehnder Modulators
Abstract
1. Introduction
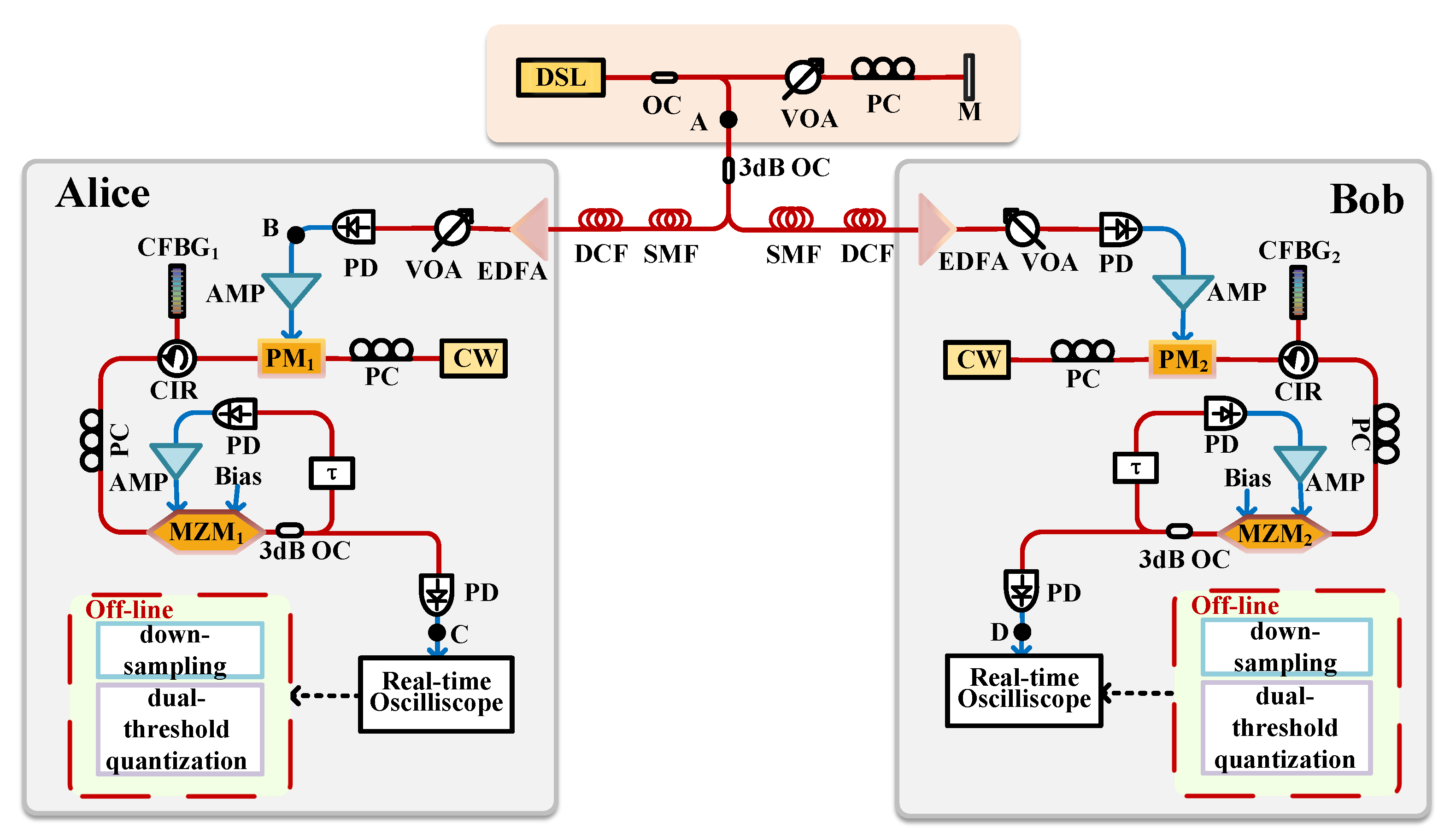
2. Principle of CRBG Setup
3. Results
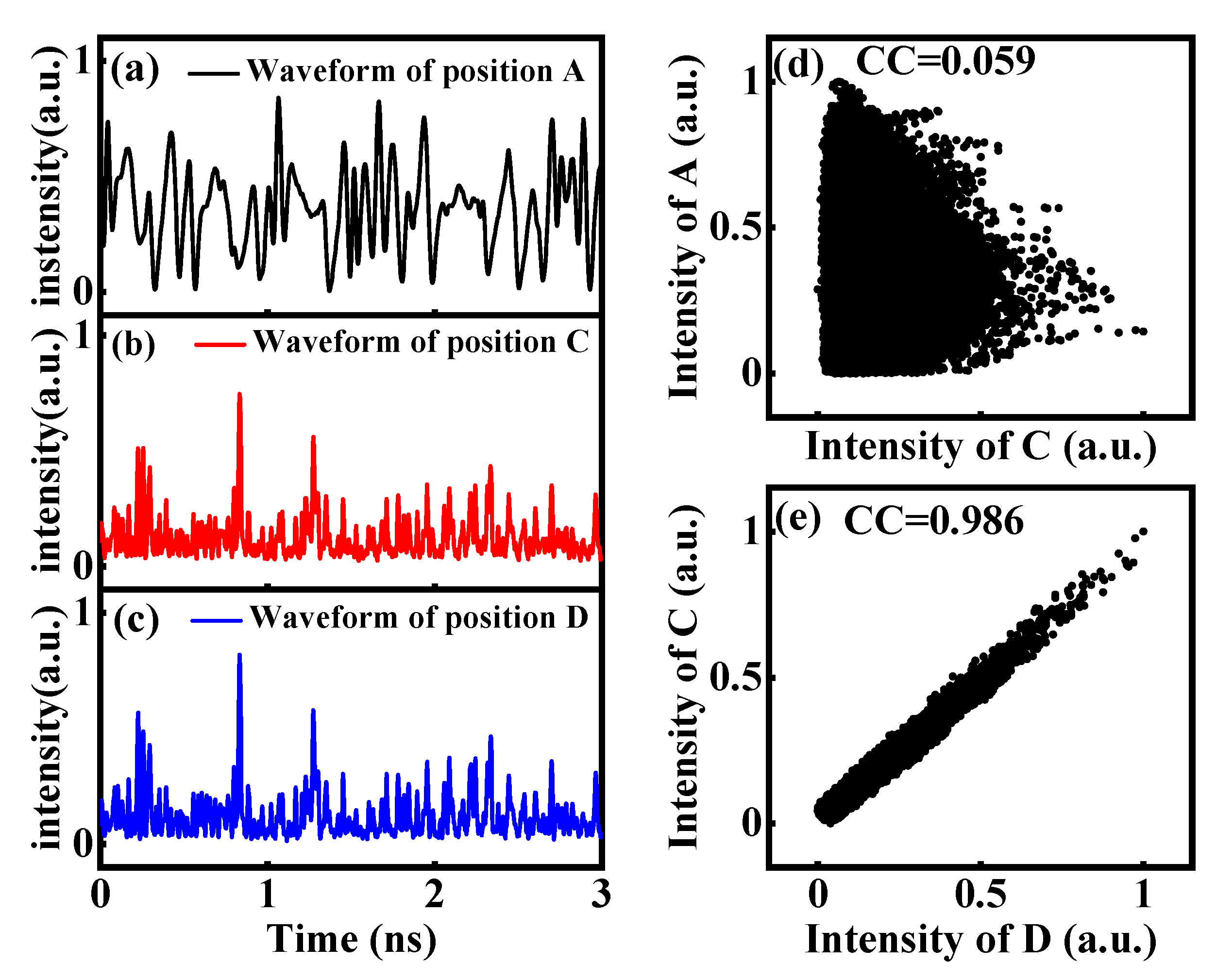
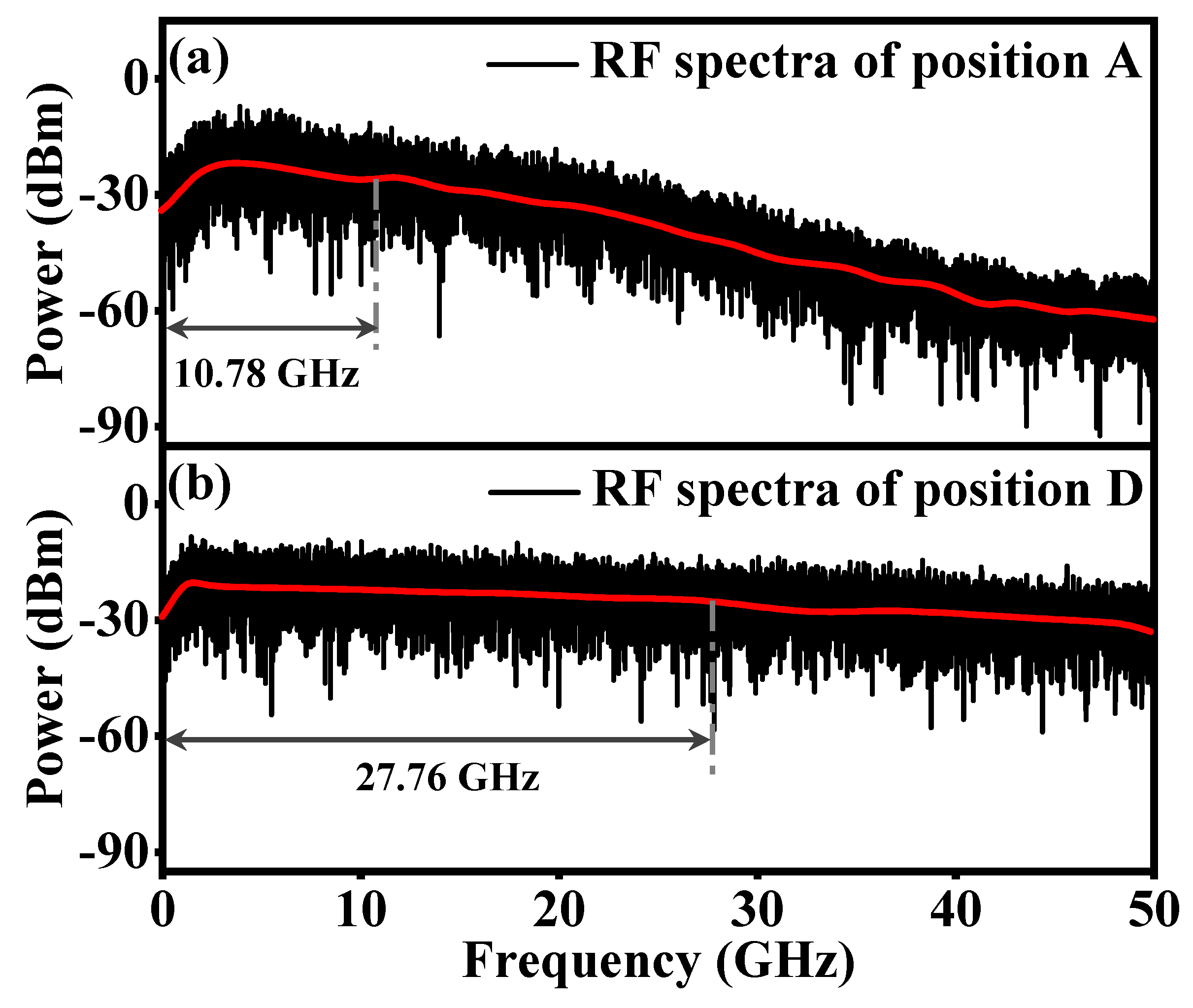
3.1. Synchronization Characteristics of Chaos
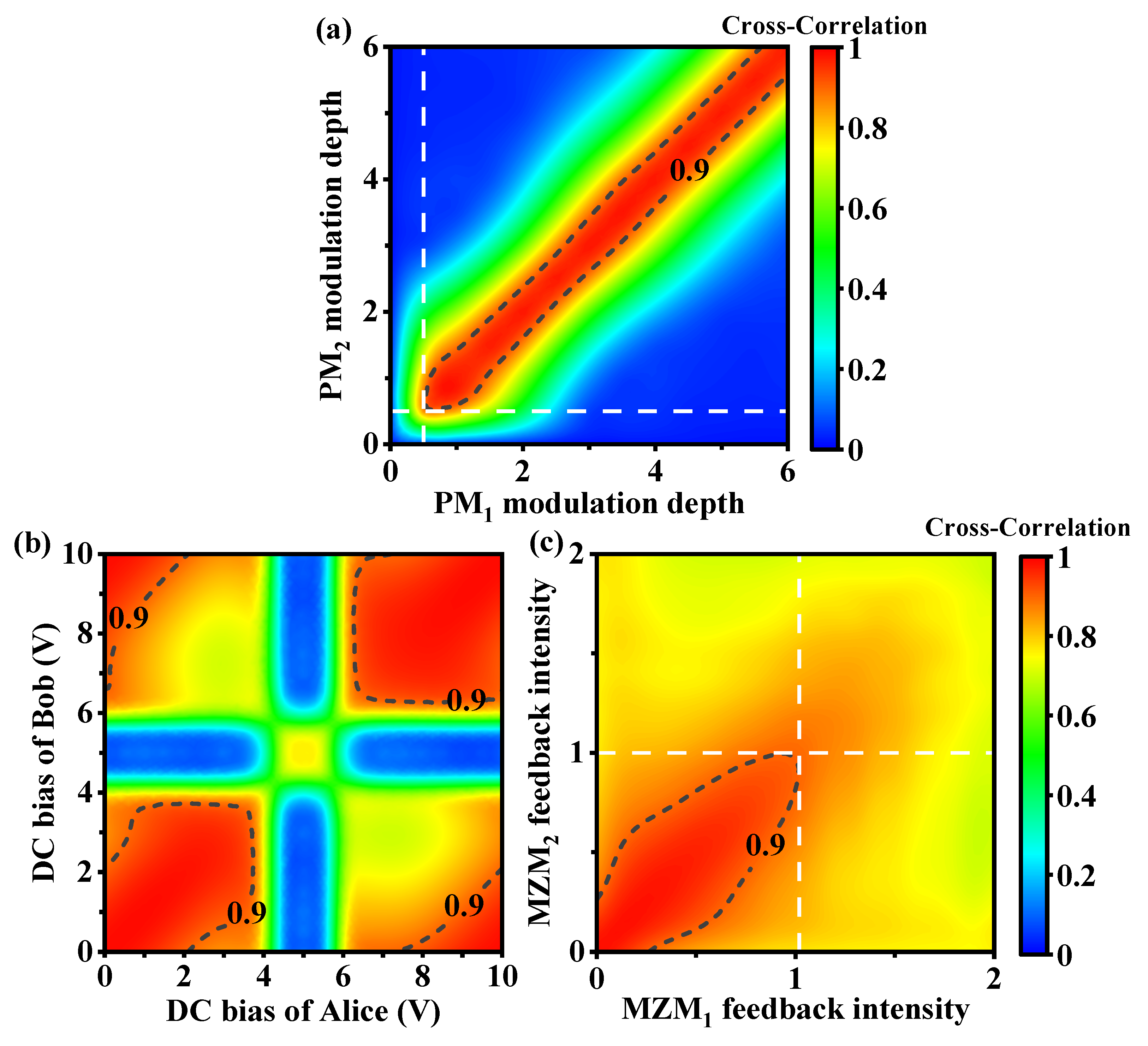
3.2. Selection of System Physical Parameters
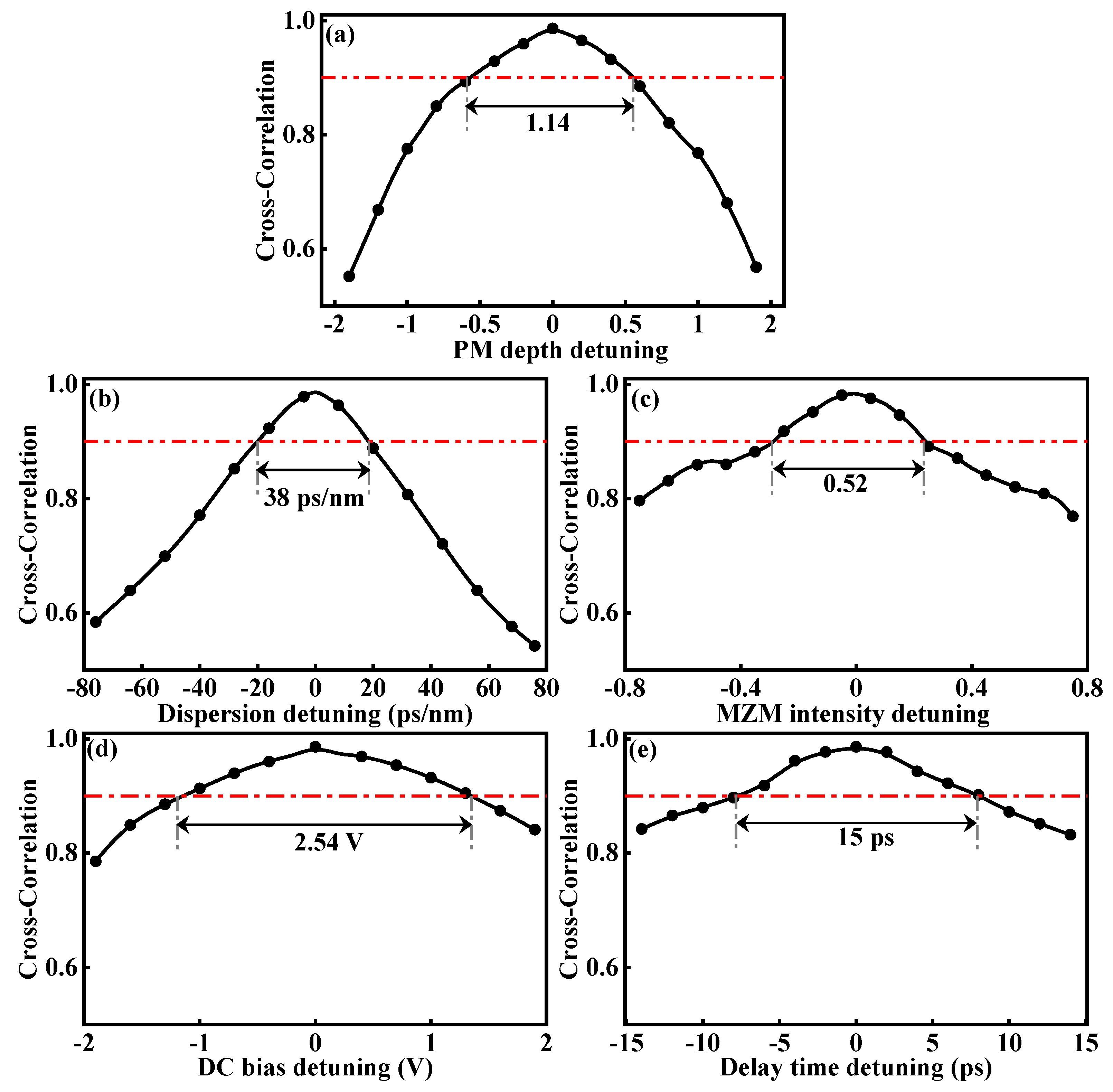
3.3. Tolerance of System Physical Parameters
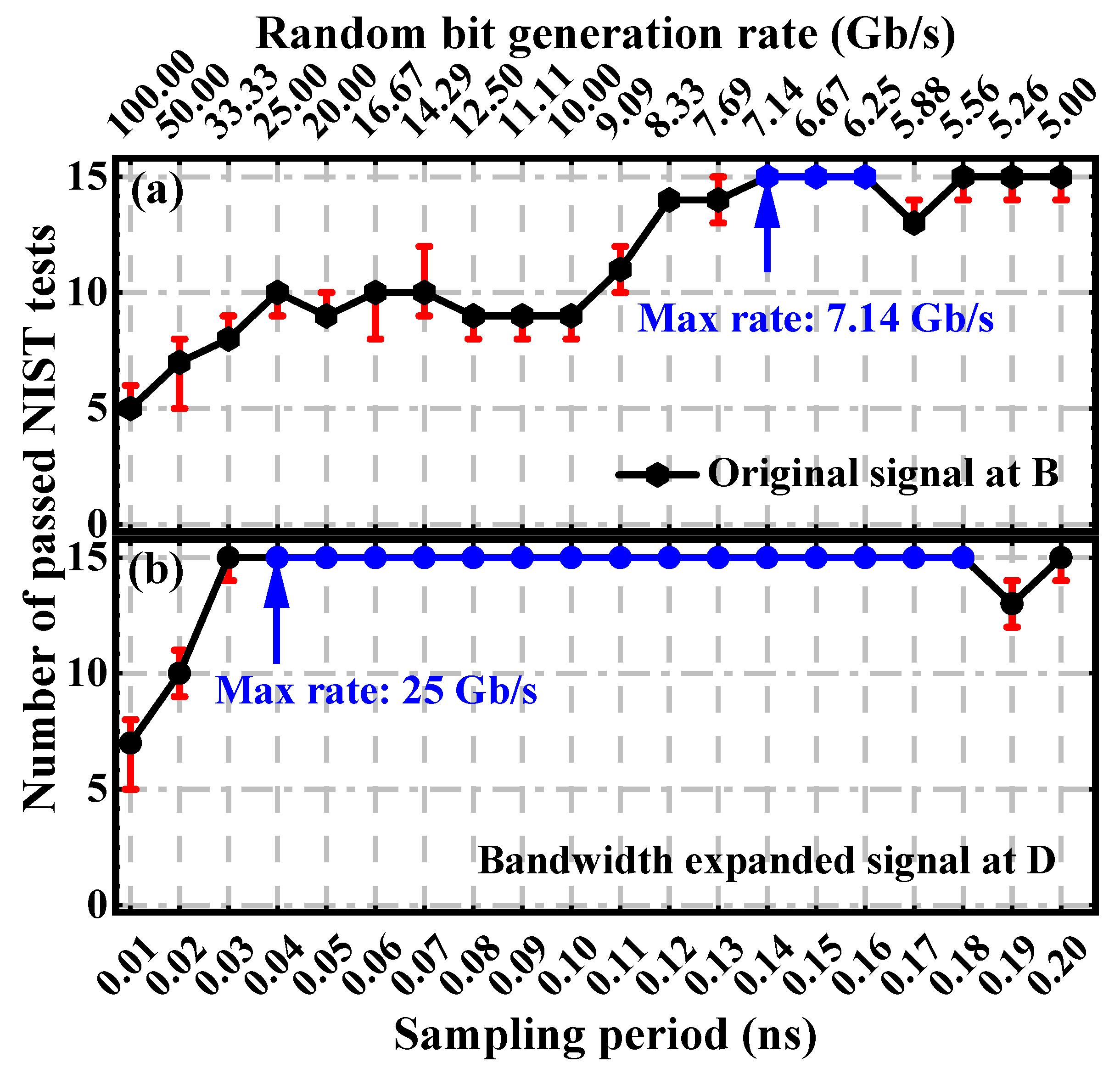
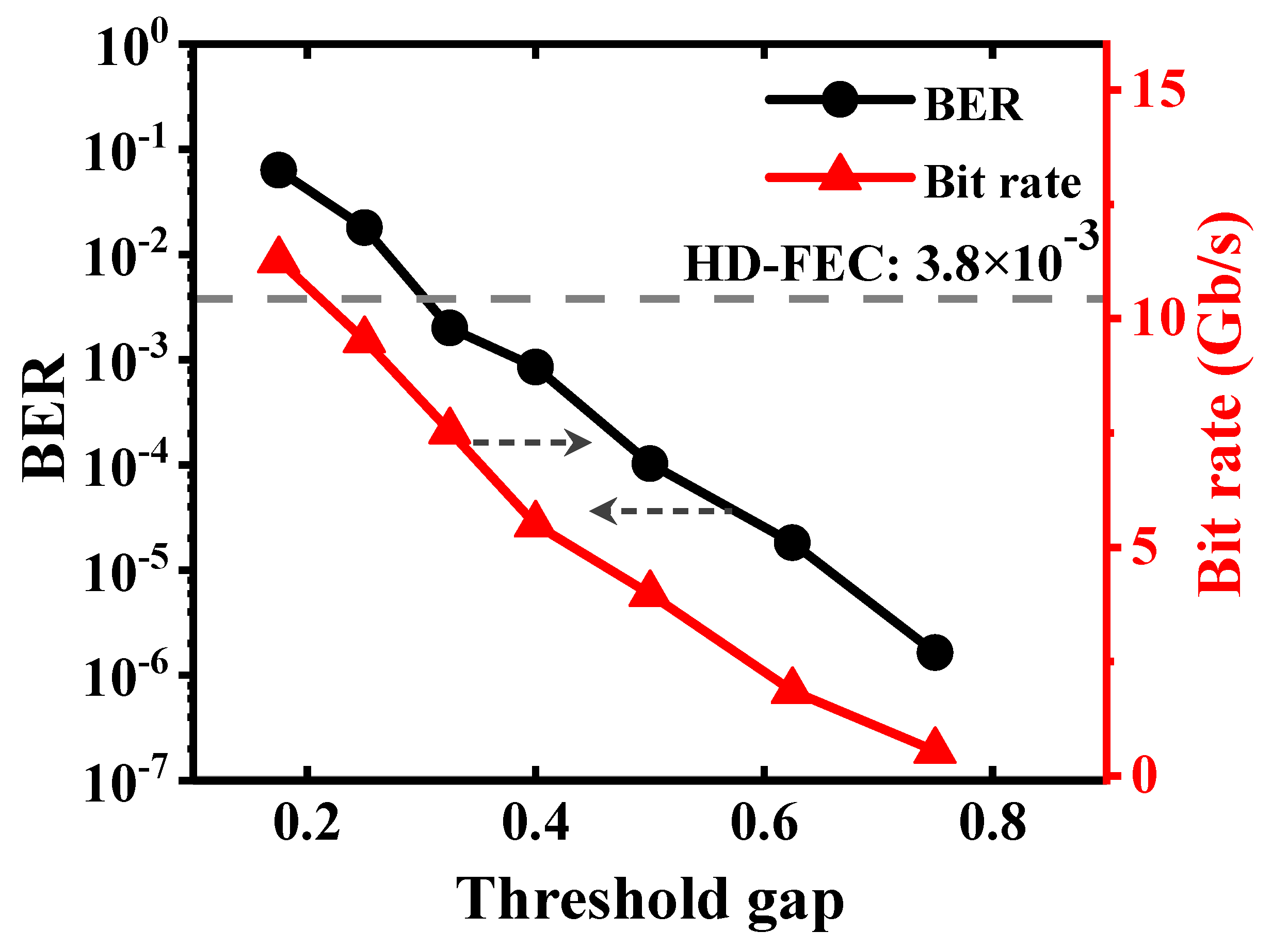
3.4. Estimation of Entropy Source Rate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eastlake, D., 3rd; Schiller, J.; Crocker, S. Randomness Requirements for Security. Technical Report, No. rfc4086. 2005.
- Bucci, M.; Germani, L.; Luzzi, R.; Trifiletti, A.; Varanonuovo, M. A high-speed oscillator-based truly random number source for cryptographic applications on a smart card IC. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2003, 52, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, C.S.; Connelly, J.A. A Noise-Based IC Random Number Generator for Applications in Cryptography. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Part I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2000, 47, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovski, T.; Pihl, J.; Kocarev, L. Chaos-based random number generators. Part II: Practicalrealization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2001, 48, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, M.A.; Kwiat, P.G. Low-bias high-speed quantum random number generator via shaped optical pulses. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 9351–9357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Chan, S.C. Random bit generation using an optically injected semiconductor laser in chaos with oversampling. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y. 2.87-Gb/s random bit generation based on bandwidth-enhanced chaotic laser. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2011, 9, 031404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguimdo, R.M.; Verschaffelt, G.; Danckaert, J.; Leijtens, X.; Bolk, J.; Guy, V. Fast random bits generation based on a single chaotic semiconductor ring laser. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 28603–28613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, H.; Morikatsu, S.; Aida, H.; Nozawa, T.; Kakesu, I.; Uchida, A.; Yoshimura, K.; Muramatsu, J.; Davis, P. Information-theoretic secure key distribution based on common random-signal induced synchronization in unidirectionally-coupled cascades of semiconductor lasers. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 17869–17893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanter, I.; Butkovski, M.; Peleg, Y.; Zigzag, M.; Kinzel, W. Synchronization of random bit generators based on coupled chaotic lasers and application to cryptography. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 18292–18302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Deng, L.; Liu, D. Chaos Synchronization Based on Hybrid Entropy Sources and Applications to Secure Communication. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2021, 33, 1038–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Muramatsu, J.; Davis, P.; Harayama, T.; Okumura, H.; Morikatsu, S.; Aida, H.; Uchida, A. Secure Key Distribution Using Correlated Randomness in Lasers Driven by Common Random Light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 070602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Li, S.S.; Chan, S.C. Correlated Random Bit Generation Using Chaotic Semiconductor Lasers under Unidirectional Optical Injection. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Jiang, X.; Deng, L.; Ke, C.; Fu, S.; Tang, M.; Zhang, M.; Shum, P.; Liu, D. Wavelength division multiplexing secure communication scheme based on an optically coupled phase chaos system and PM-to-IM conversion mechanism. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 94, 1949–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyris, A. Sub-Tb/s Physical Random Bit Generators Based on Direct Detection of Amplified Spontaneous Emission Signals. J. Light. Technol. 2012, 30, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tian, L.; Zou, H. Practical quantum random number generator based on measuring the shot noise of vacuum states. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symul, T.; Assad, S.M.; Lam, P.K. Real time demonstration of high bitrate quantum random number generation with coherent laser light. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Tang, W.; Yu, L.; Wei, W. Truly Random Number Generation Based on Measurement of Phase Noise of Laser. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2010, 81, 051137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanter, I.; Aviad, Y.; Reidler, I.; Cohen, E.; Rosenbluh, M. An optical ultrafast random bit generator. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbe, J.; Atchoffo, W.N.; Tchitnga, R.; Woafo, P. Dynamics of Time-delayed Optoelectronic Oscillators with Nonlinear Amplifiers And Its Potential Application to Random numbers Generation. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2021, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, A.; Jiang, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Qiu, K. Correlated random bit generation based on common-signal-induced synchronization of wideband complex physical entropy sources. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wu, S.; Deng, Z.; Huang, C.; Gao, X.; Fu, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y. Private correlated random bit generation based on synchronized wideband physical entropy sources with hybrid electro-optic nonlinear transformation. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 3788–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciamanna, M.; Shore, K.A. Physics and Applications of Laser Diode Chaos. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Gao, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Shore, K.A.; Wang, A. Real-Time 2.5-Gb/s Correlated Random Bit Generation Using Synchronized Chaos Induced by a Common Laser with Dispersive Feedback. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2020, 56, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhm, F.; Sahakian, S.; Dooms, A.; Verschaffelt, G.; Sande, G. Stable High-Speed Encryption Key Distribution via Synchronization of Chaotic Optoelectronic Oscillators. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2020, 13, 064014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Morikatsu, S.; Okumura, H.; Davis, P. Fast random bit generation with bandwidth-enhanced chaos in semiconductor lasers. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 5512–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; NIST Special Publication: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.; Oowada, I.; Yip, H.; Uchida, A.; Yoshimori, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Muramatsu, J.; Goto, S.I.; Davis, P. Common-chaotic-signal induced synchronization in semiconductor lasers. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 3974–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y. Generation of wideband chaos with suppressed time-delay signature by delayed self-interference. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 8701–8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Spencer, P.S.; Shore, K.A. Wideband Chaos with Time-Delay Concealment in Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers with Optical Feedback and Injection. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2014, 50, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.M.; Wang, L.S.; Guo, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, A.B. Key space enhancement of optical chaos secure communication: Chirped FBG feedback semiconductor laser. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuraba, R.; Iwakawa, K.; Kanno, K.; Uchida, A. Tb/s physical random bit generation with bandwidth-enhanced chaos in three-cascaded semiconductor lasers. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, L.; Pu, L.; Wang, Y. Minimal-post-processing 320-Gbps true random bit generation using physical white chaos. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 3153–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Kakesu, I.; Mitsui, Y.; Rontani, D.; Inubushi, M. Common-signal-induced synchronization in photonic integrated circuits and its application to secure key distribution. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 26029–26044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, L.; Zhang, J.; Sang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Real-time online photonic random number generation. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 2699–2702. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| f | Center frequency of DSL | 193.1 THz |
| L | Length of SMF | 25 km |
| Modulation depth of | 2.8 | |
| Modulation depth of | 2.7 | |
| Feedback intensity of | 1.2 | |
| Feedback intensity of | 1.2 | |
| Feedback time delay of Alice | 3.03 ns | |
| Feedback time delay of Bob | 3.03 ns | |
| Dispersion of | 400 ps/nm | |
| Dispersion of | 400 ps/nm | |
| Bandwidth of PD | 40 GHz | |
| Bandwidth of MZM | 40 GHz | |
| I | Insertion loss of MZM | 6 dB |
| R | Extinction ratio of MZM | 35 dB |
| 15 NIST Tests | P-Value | Proportion | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 0.20953 | 98.3 | Success |
| Block Frequency | 0.87433 | 99.7 | Success |
| Cumulative Sums | 0.33427 | 98.6 | Success |
| Runs | 0.21352 | 99.0 | Success |
| Longest Run | 0.69613 | 98.5 | Success |
| Rank | 0.81684 | 99.8 | Success |
| FFT | 0.34325 | 98.1 | Success |
| Non-Overlapping Template | 0.67723 | 99.4 | Success |
| Overlapping Template | 0.95799 | 99.1 | Success |
| Universal | 0.50993 | 99.7 | Success |
| Approximate Entropy | 0.43752 | 98.2 | Success |
| Random Excursions | 0.93138 | 98.4 | Success |
| Random Excursions Variant | 0.71700 | 99.7 | Success |
| Serial | 0.62051 | 99.8 | Success |
| Linear Complexity | 0.74785 | 98.3 | Success |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.; Gao, X.; Wu, S.; Gu, W.; Su, B.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Gao, Z. Key Space Enhanced Correlated Random Bit Generation Based on Synchronized Electro-Optic Self-Feedback Loops with Mach–Zehnder Modulators. Photonics 2022, 9, 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9120952
Huang C, Gao X, Wu S, Gu W, Su B, Wang Y, Qin Y, Gao Z. Key Space Enhanced Correlated Random Bit Generation Based on Synchronized Electro-Optic Self-Feedback Loops with Mach–Zehnder Modulators. Photonics. 2022; 9(12):952. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9120952
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chuyun, Xulin Gao, Sile Wu, Wenfu Gu, Biao Su, Yuncai Wang, Yuwen Qin, and Zhensen Gao. 2022. "Key Space Enhanced Correlated Random Bit Generation Based on Synchronized Electro-Optic Self-Feedback Loops with Mach–Zehnder Modulators" Photonics 9, no. 12: 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9120952
APA StyleHuang, C., Gao, X., Wu, S., Gu, W., Su, B., Wang, Y., Qin, Y., & Gao, Z. (2022). Key Space Enhanced Correlated Random Bit Generation Based on Synchronized Electro-Optic Self-Feedback Loops with Mach–Zehnder Modulators. Photonics, 9(12), 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9120952





