Structural and Optical Properties of InAsSbBi Grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy on Offcut GaSb Substrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
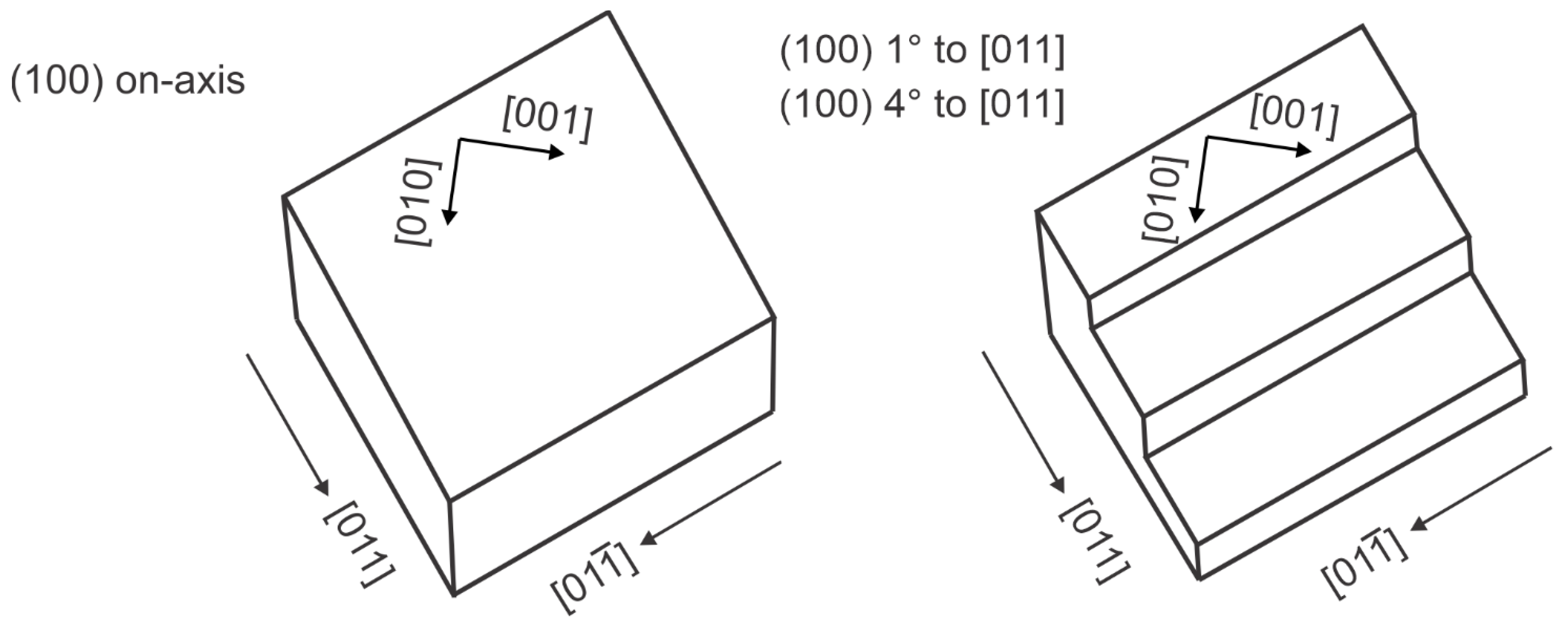
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
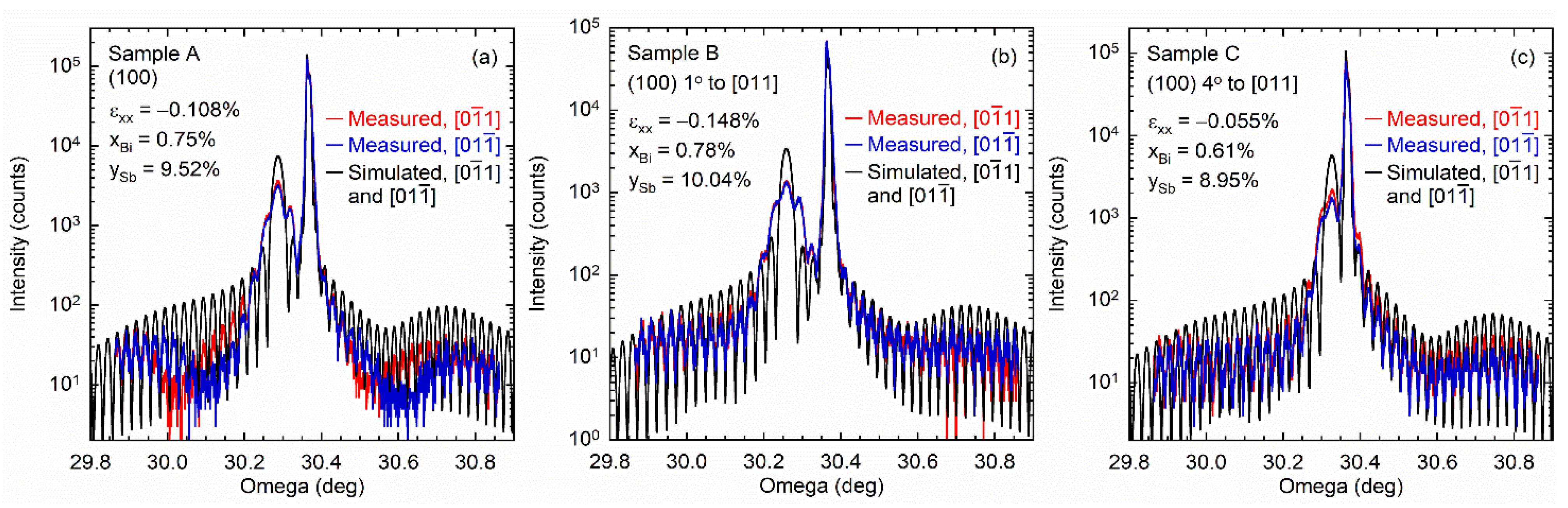
3.1. Examination of InAsSbBi Layers Using XRD
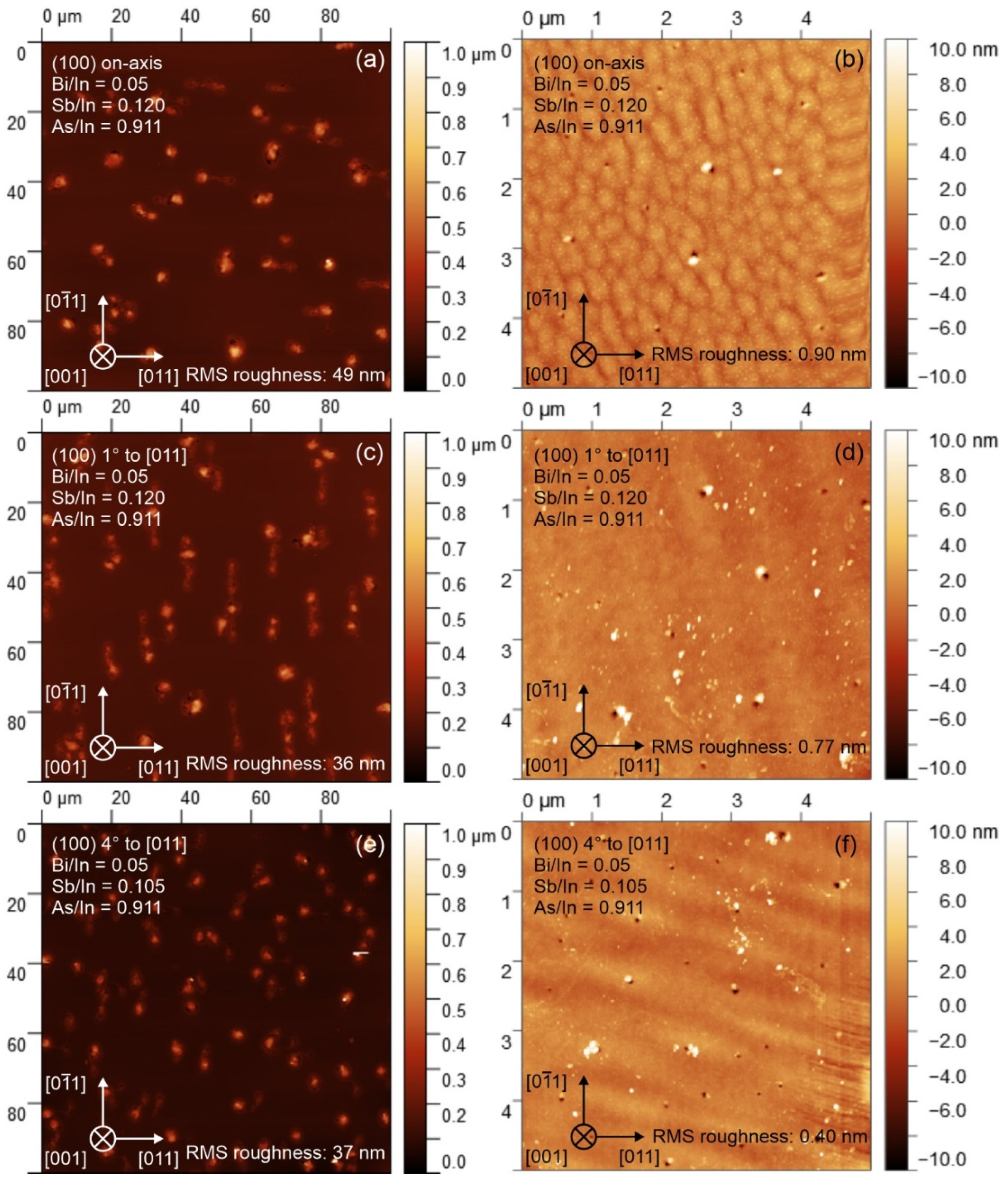
3.2. Surface Morphology of InAsSbBi Samples
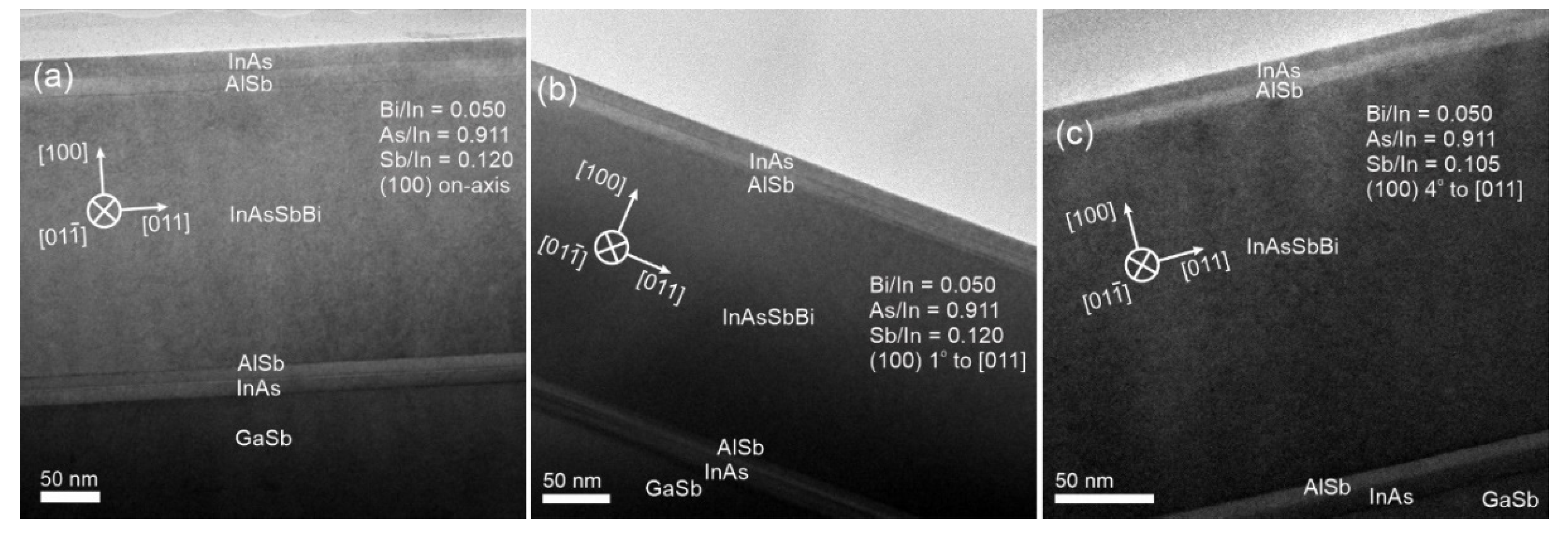
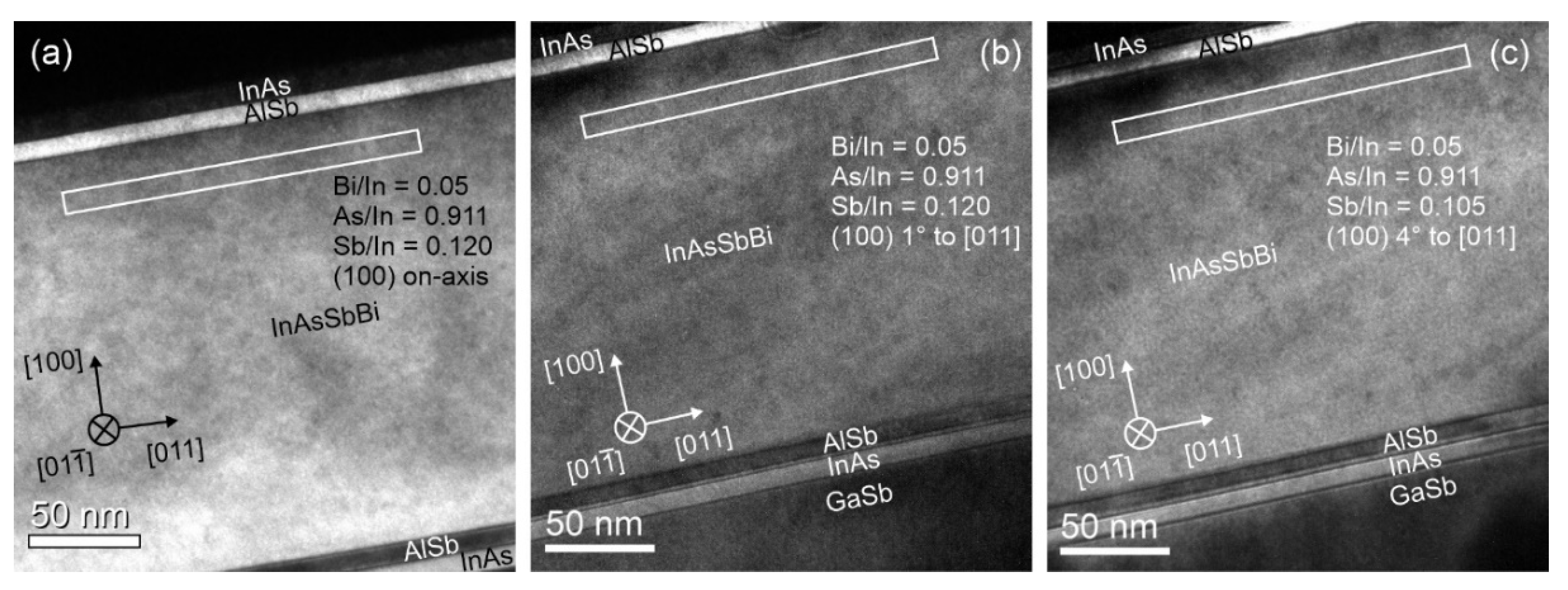
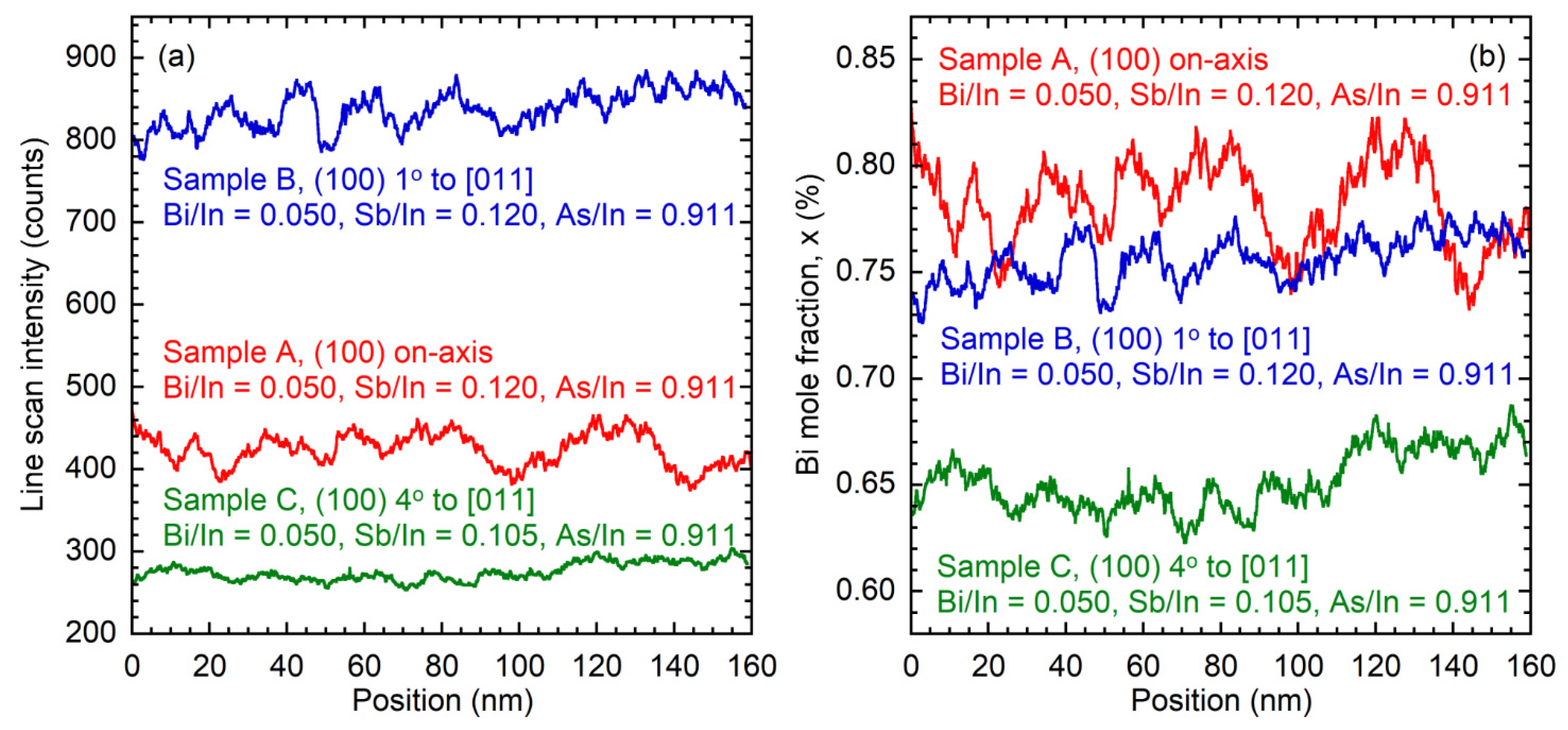
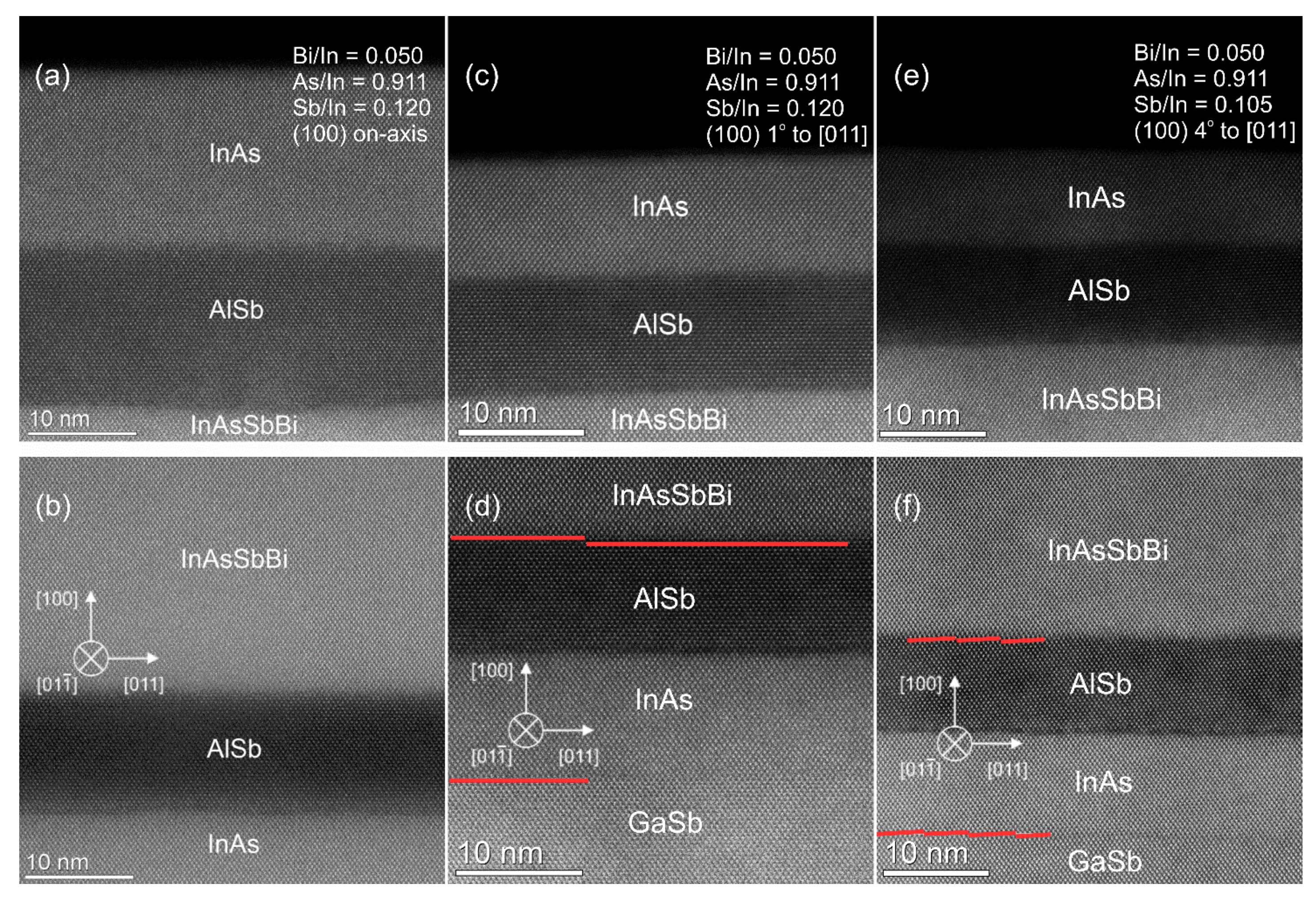
3.3. Examination of InAsSbBi Microstructure Using TEM
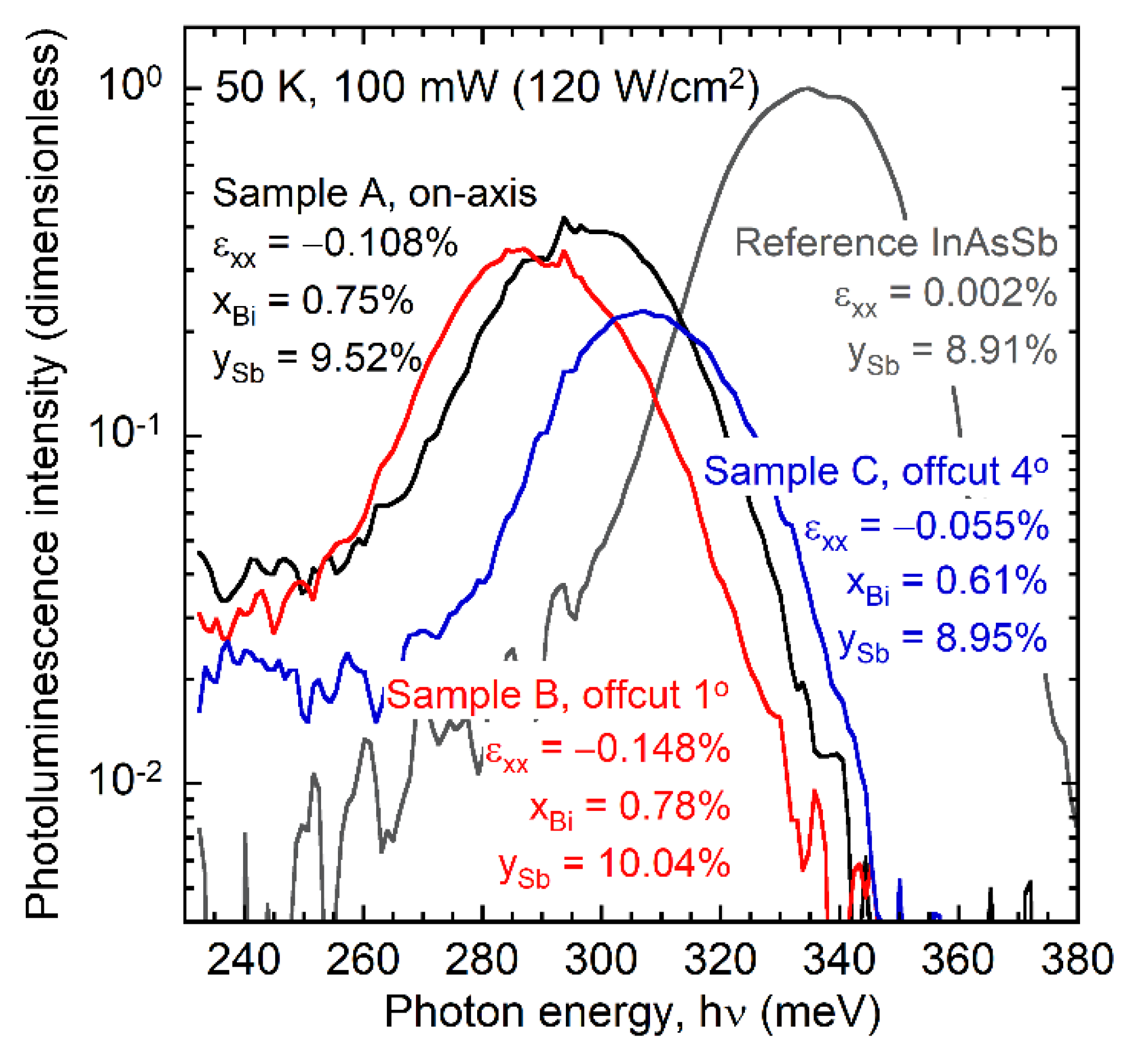
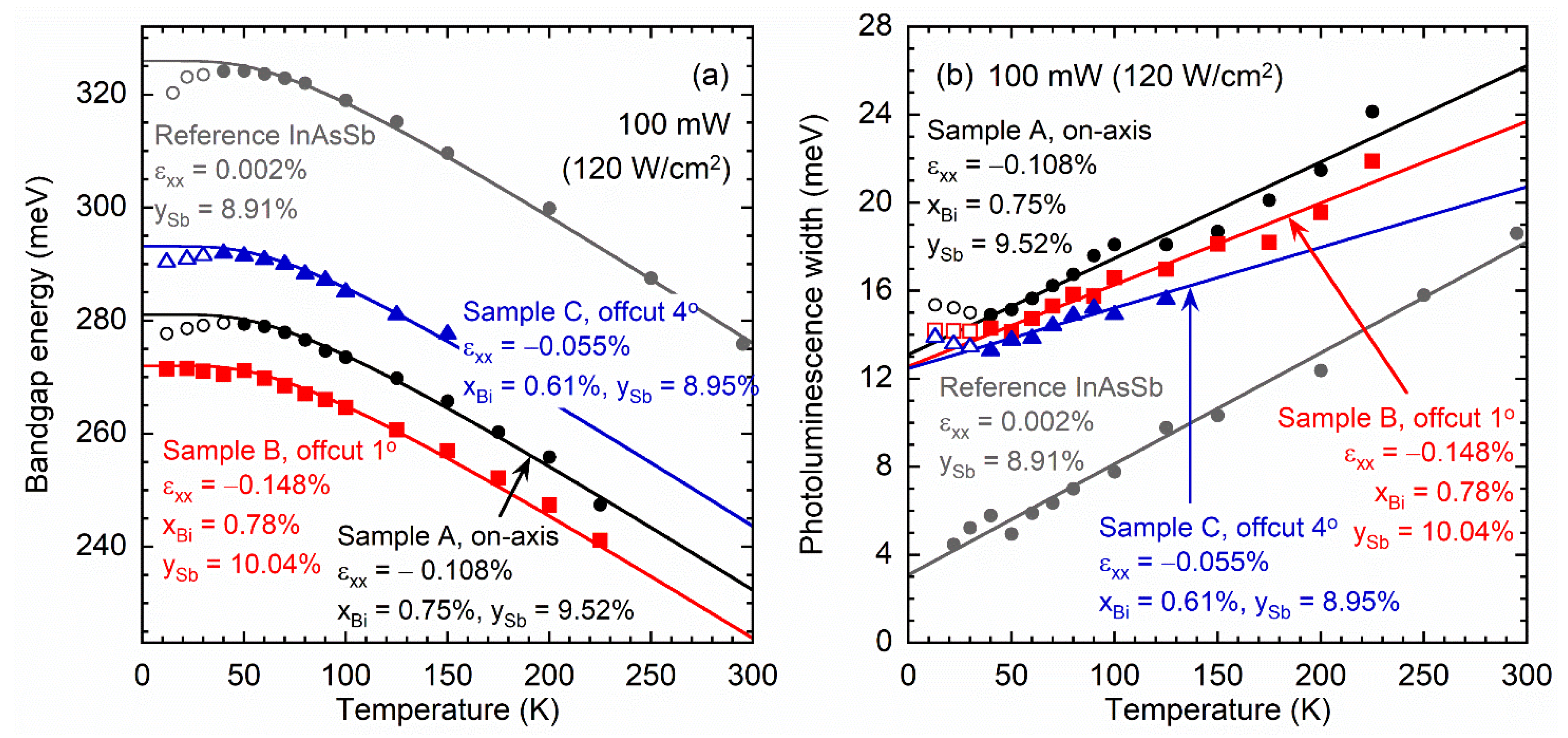
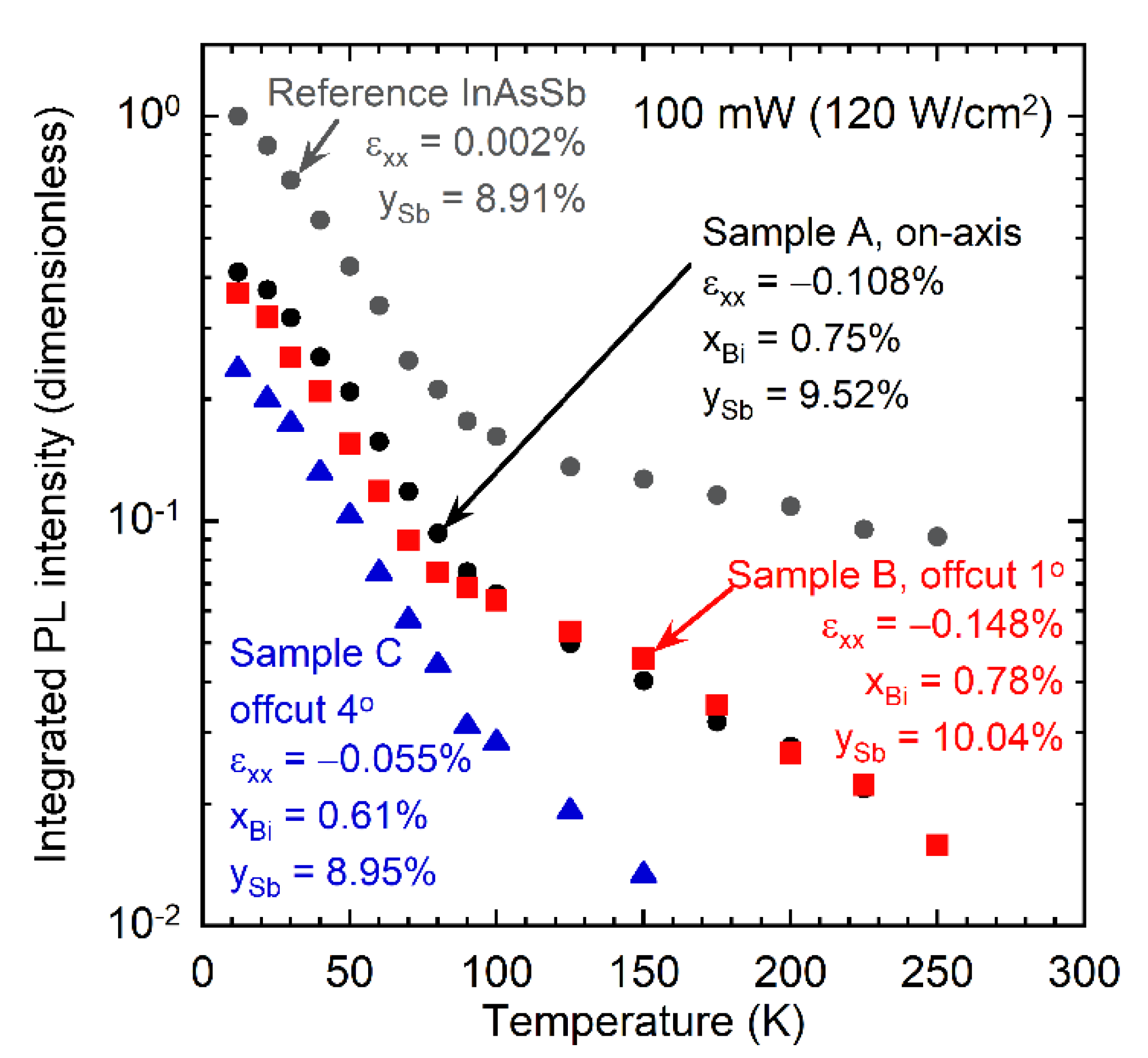
3.4. Photoluminescence Spectroscopy Measurements of InAsSbBi Layers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Downs, C.; Vandervelde, T.E. Progress in Infrared Photodetectors Since 2000. Sensors 2013, 13, 5054–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, P.T.; Shalindar, A.J.; Riordan, N.A.; Gogineni, C.; Liang, H.; Sharma, A.R.; Johnson, S.R. Optical properties of InAsBi and optimal designs of lattice-matched and strain-balanced III-V semiconductor superlattices. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 225701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.T.; Riordan, N.A.; Liu, S.; Steenbergen, E.H.; Synowicki, R.A.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Johnson, S.R. Measurement of InAsSb bandgap energy and InAs/InAsSb band edge positions using spectroscopic ellipsometry and photoluminescence spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 245706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, S.T.; Kosireddy, R.R.; Webster, P.T.; Johnson, S.R. Molecular beam epitaxy growth and optical properties of InAsSbBi. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 083101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisch, U.; Finkman, E.; Salzman, J. The anomalous bandgap bowing in GaAsN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guina, M.; Wang, S.M.; Aho, A. Molecular Beam Epitaxy of Dilute Nitride Optoelectronic Devices. In Molecular Beam Epitaxy: From Research to Mass Production, 2nd ed.; Henini, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.; Walukiewicz, W.; Ager, I.J.W.; Haller, E.E.; Geisz, J.F.; Friedman, D.J.; Olson, J.M.; Kurtz, S.R. Band Anticrossing in GaInNAs Alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Walukiewicz, W.; Wu, J.; Yu, K.M.; Ager, J.W., III; Li, S.X.; Haller, E.E.; Geisz, J.F.; Friedman, D.J.; Kurtz, S.R. Band-gap bowing effects in BxGa1−xAs alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberi, K.; Wu, J.; Walukiewicz, W.; Yu, K.M.; Dubon, O.D.; Watkins, S.P.; Wang, C.X.; Liu, X.; Cho, Y.-J.; Furdyna, J. Va-lence-band anticrossing in mismatched III–V semiconductor alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 045203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluegel, B.; Mascarenhas, A.; Ptak, A.J.; Tixier, S.; Young, E.C.; Tiedje, T. E+ transition in GaAs1−xNx and GaAs1−xBix due to isoelectronic-impurity-induced perturbation of the conduction band. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 155209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, S.; Adamcyk, M.; Tiedje, T.; Francoeur, S.; Mascarenhas, A.; Wei, P.; Schiettekatte, F. Molecular beam epitaxy growth of GaAs1-xBix. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francoeur, S.; Seong, M.-J.; Mascarenhas, A.; Tixier, S.; Adamcyk, M.; Tiedje, T. Band gap of GaAs1−xBix, 0 < x < 3.6%. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, Z.; Chatterjee, S.; Chernikov, A.; Duzik, A.; Fritz, R.; Gogineni, C.; Hild, K.; Hosea, T.J.C.; Imhof, S.; Johnson, S.R.; et al. Bismuth-containing III–V semiconductors: Epitaxial growth and physical properties. In Molecular Beam Epitaxy: From Research to Mass Production, 1st ed.; Henini, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 139–158. [Google Scholar]
- Shalindar, A.J.; Webster, P.T.; Schaefer, S.T.; Johnson, S.R. InAsBi Materials. In Molecular Beam Epitaxy: From Research to Mass Production, 2nd ed.; Henini, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; p. 181. [Google Scholar]
- Fluegel, B.; Francoeur, S.; Mascarenhas, A.; Tixier, S.; Young, E.C.; Tiedje, T. Giant Spin-Orbit Bowing in GaAs1-xBix. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 067205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosireddy, R.R.; Schaefer, S.T.; Shalindar, A.J.; Johnson, S.R. Microstructure and surface morphology of InAsSbBi grown by molecular beam epitaxy. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 095108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosireddy, R.R.; Schaefer, S.T.; Shalindar, A.J.; Webster, P.T.; Johnson, S.R. Examination of the Structural Quality of InAsSbBi Epilayers using Cross Section Transmission Electron Microscopy. Microsc. Microanal. 2018, 24, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, E.; Wu, M.; Puustinen, J.; Guina, M.; Trampert, A. Spontaneous formation of nanostructures by surface spinodal de-composition in GaAs1−x Bix epilayers. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 185302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hanke, M.; Luna, E.; Puustinen, J.; Guina, M.; Trampert, A. Detecting lateral composition modulation in dilute Ga(As,Bi) epilayers. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 425701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, E.; Puustinen, J.; Wu, M.; Hilska, J.; Guina, M.; Trampert, A. The Role of Epitaxial Strain on the Spontaneous Formation of Bi-Rich Nanostructures in Ga(As,Bi) Epilayers and Quantum Wells. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2017, 9, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, E.; Delorme, O.; Cerutti, L.; Tournié, E.; Rodriguez, J.-B.; Trampert, A. Microstructure and interface analysis of emerging Ga(Sb,Bi) epilayers and Ga(Sb,Bi)/GaSb quantum wells for optoelectronic applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 151905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzik, A.; Millunchick, J.M. Surface morphology and Bi incorporation in GaSbBi(As)/GaSb films. J. Cryst. Growth 2014, 390, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Webster, P.T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.H.; Johnson, S.R.; Smith, D.J. Investigation of MBE-grown InAs1-xBix alloys and Bi-mediated type-II superlattices by transmission electron microscopy. J. Cryst. Growth 2015, 425, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, S.T.; Milosavljevic, M.S.; Kosireddy, R.R.; Johnson, S.R. Kinetic model for molecular beam epitaxy growth of InAsSbBi alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 035303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafer Technology Ltd. 34 Maryland Road, Milton Keynes, MK15 8HJ, UK. Available online: http://wafertech.co.uk/ (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- X’pert Epitaxy Software; Panalytical B.V.: Almelo, The Netherlands, 2007.
- Matthews, J.; Blakeslee, A. Defects in epitaxial multilayers. J. Cryst. Growth 1974, 27, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečas, D.; Klapetek, P. Gwyddion: An open-source software for SPM data analysis. Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 2012, 10, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bithell, E.G.; Stobbs, W.M. Composition determination in the GaAs/(Al, Ga)As system using contrast in dark-field transmission electron microscope images. Philos. Mag. A 1989, 60, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, P.A.; Turner, P.S. Relativistic Hartree–Fock X-ray and electron scattering factors. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1968, 24, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegard, L. Die Konstitution der Mischkristalle und die Raumfüllung der Atome. Z. Phys. 1921, 5, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vurgaftman, I.; Meyer, J.R.; Ram-Mohan, L.R. Band parameters for III–V compound semiconductors and their alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 5815–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalindar, A.J.; Webster, P.T.; Wilkens, B.J.; Alford, T.L.; Johnson, S.R. Measurement of InAsBi mole fraction and InBi lattice constant using Rutherford backscattering spectrometry and X-ray diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 145704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennycook, S.J.; Chisholm, M.F.; Lupini, A.R.; Varela, M.; Borisevich, A.; Oxley, M.; Luo, W.D.; Van Benthem, K.; Oh, S.-H.; Sales, D.L.; et al. Aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy: From atomic imaging and analysis to solving energy problems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 3709–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.J.; Lu, J.; Aoki, T.; McCartney, M.R.; Zhang, Y.-H. Observation of compound semiconductors and heterovalent interfaces using aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.R.; Tiedje, T. Temperature dependence of the Urbach edge in GaAs. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 78, 5609–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viña, L.; Logothetidis, S.; Cardona, M. Temperature dependence of the dielectric function of germanium. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 30, 1979–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannow, L.C.; Rubel, O.; Badescu, S.C.; Rosenow, P.; Hader, J.; Moloney, J.V.; Tonner, R.; Koch, S.W. Configuration de-pendence of band gap narrowing and localization in dilute GaAs1-xBix alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 205202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.T.; Riordan, N.A.; Liu, S.; Steenbergen, E.H.; Synowicki, R.A.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Johnson, S.R. Absorption properties of type-II InAs/InAsSb superlattices measured by spectroscopic ellipsometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 061907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, D.; Tahan, Z.E. A new method for the determination of optical band gap and the nature of optical transitions in semiconductors. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 119, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, T.M.; Alberi, K.; Beaton, D.A.; Fluegel, B.; Mascarenhas, A. Spectrally resolved localized states in GaAs1−xBix. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 56, 35801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, W.; Liang, D.; Quhe, R.; Wang, S.; Guan, P.; Lu, P. Effects of Bi on band gap bowing in InP1-xBix alloys. Opt. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohmad, A.R.; Bastiman, F.; Hunter, C.J.; Richards, R.; Sweeney, S.; Ng, J.S.; David, J.P.R.; Majlis, B.Y. Localization effects and band gap of GaAsBi alloys. Phys. Status Solidi B 2014, 251, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohmad, A.R.; Bastiman, F.; Hunter, C.J.; Ng, J.S.; Sweeney, S.J.; David, J.P.R. The effect of Bi composition to the optical quality of GaAs1−xBix. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 42107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, R.K.; Curless, J.A.; Kramer, G.D.; Peffley, M.S.; Rode, D.L. Effects of substrate misorientation on the properties of (Al, Ga)As grown by molecular beam epitaxy. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 58, 2570–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, D.L.; Wagner, W.R.; Schumaker, N.E. Singular instabilities on LPE GaAs, CVD Si, and MBE InP growth surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1977, 30, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, B.G.; Johnson, M.D.; Orme, C.; Sudijono, J.; Hunt, A.W. The surface evolution and kinetic roughening during ho-moepitaxy of GaAs (001). Solid-State Electron. 1994, 37, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tersoff, J. Step Energies and Roughening of Strained Layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwoebel, R.L.; Shipsey, E.J. Step Motion on Crystal Surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1966, 37, 3682–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Fang, Z.; Cohen, R.; Stringfellow, G. OMVPE growth and characterization of Bi-containing III–V alloys. J. Cryst. Growth 1991, 107, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.R.; Ding, D.; Wang, J.-B.; Yu, S.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-H. Excitation dependent photoluminescence measurements of the nonradiative lifetime and quantum efficiency in GaAs. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. 2007, 25, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, S.; Thränhardt, A.; Chernikov, A.; Koch, M.; Köster, N.S.; Kolata, K.; Chatterjee, S.; Koch, S.W.; Lu, X.; Johnson, S.R.; et al. Clustering effects in Ga(AsBi). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 131115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogineni, C.; Riordan, N.A.; Johnson, S.R.; Lu, X.; Tiedje, T. Disorder and the Urbach edge in dilute bismide GaAsBi. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 041110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciatto, G.; Young, E.C.; Glas, F.; Chen, J.; Mori, R.A.; Tiedje, T. Spatial correlation between Bi atoms in dilute GaAs1-xBix: From random distribution to Bi pairing and clustering. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 035325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, H.F.; Zhang, L.Y.; Kang, C.Z.; Wu, M.J.; Pan, W.W.; Lu, P.F.; Gong, Q.; Wang, S.M. InPBi Single Crystals Grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hader, J.; Badescu, S.C.; Bannow, L.C.; Moloney, J.V.; Johnson, S.R.; Koch, S.W. Extended band anti-crossing model for dilute bismides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 062103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Substrate Orientation | Growth Temperature | V/In Flux Ratios | Excess V/In Flux Ratios | Surface Droplets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi/In | Sb/In | As/In | Bi/In | Sb/In | As/In | ||||
| A | (100) | 400 °C | 0.050 | 0.120 | 0.911 | 0.043 | 0.025 | 0.014 | Yes |
| B | (100) 1° to [011] | 400 °C | 0.050 | 0.120 | 0.911 | 0.042 | 0.020 | 0.019 | Yes |
| C | (100) 4° to [011] | 400 °C | 0.050 | 0.105 | 0.911 | 0.044 | 0.015 | 0.007 | Yes |
| Sample | A, (100) on-axis | B, (100) 1° to [011] | C, (100) 4° to [011] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simulated thickness (nm) | 194 ± 1 | 189 ± 1 | 190 ± 1 |
| Out-of-plane distortion (%) | 0.2264 ± 0.0019 | 0.3092 ± 0.0019 | 0.1148 ± 0.0019 |
| In-plane biaxial strain (%) | −0.1083 ± 0.0009 | −0.1479 ± 0.0009 | −0.0550 ± 0.0009 |
| Lattice constant (Å) | 6.1025 ± 0.0001 | 6.1049 ± 0.0001 | 6.0993 ± 0.0001 |
| (arcsec) | 273.6 ± 2.3 | 373.6 ± 2.3 | 138.7 ± 2.3 |
| (arcsec) | 270.9 | 375.0 | 129.8 |
| (arcsec) | 272.5, 273.2 | 373.9, 375.3 | 129.3, 129.0 |
| Sample | Substrate Orientation | Flux Ratios | RMS Roughness (nm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi/In | Sb/In | As/In | 100 µm by 100 µm | 5 µm by 5 µm | 1 µm by 1 µm | ||
| A | (100) on-axis | 0.050 | 0.120 | 0.911 | 49 | 0.90 | 0.46 |
| B | (100) 1° to [011] | 0.050 | 0.120 | 0.911 | 36 | 0.77 | 0.52 |
| C | (100) 4° to [011] | 0.050 | 0.105 | 0.911 | 37 | 0.44 | 0.41 |
| Sample | A, (100) on-axis | B, (100) 1° to [011] | C, (100) 4° to [011] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Nomarski | AFM | Nomarski | AFM | Nomarski | AFM |
| Density (cm−2) | 1.8 × 106 | 1.04 × 106 | 2.4 × 106 | 1.19 × 106 | 3.2 × 106 | 1.88 × 106 |
| Diameter (µm) | 2.6 | 2.02 | 2.1 | 2.17 | 1.9 | 1.90 |
| Average height (nm) | - | 79.5 | - | 68.7 | - | 69.6 |
| Surface coverage (%) | 9.6 | 8.1 | 8.3 | 12.6 | 9.1 | 12.6 |
| Volume/unit area (nm) | - | 8.6 | - | 10.2 | - | 10.0 |
| Bi droplet accumulation (%) | - | 18.9 | - | 9.2 | - | 12.4 |
| In droplet accumulation (%) | - | 3.5 | - | 4.6 | - | 4.4 |
| Sample | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 6.1025 | 6.1097 | 0.16367 | 2.9013 | 6.4757 | 4.7338 | 7.0097 | 8.7681 |
| B | 6.1049 | 6.1147 | 0.16354 | 2.9035 | 6.4790 | 4.7364 | 7.0134 | 8.7722 |
| C | 6.0993 | 6.1029 | 0.16386 | 2.8983 | 6.4714 | 4.7304 | 7.0047 | 8.7626 |
| Sample | TEM + XRD Mole Fractions (%) | PL + XRD Mole Fractions (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi | Sb | As | Bi | Sb | As | |
| A, on-axis | 0.78 ± 0.020 | 9.47 ± 0.16 | 89.74 ± 0.18 | 0.71 ± 0.22 | 9.57 ± 0.28 | 89.72 ± 0.50 |
| B, offcut 1° | 0.73 ± 0.011 | 10.08 ± 0.14 | 89.16 ± 0.15 | 0.82 ± 0.22 | 10.00 ± 0.28 | 89.18 ± 0.51 |
| C, offcut 4° | 0.65 ± 0.014 | 8.91 ± 0.15 | 90.44 ± 0.16 | 0.57 ± 0.21 | 8.98 ± 0.28 | 90.45 ± 0.49 |
| Sample | A, on-axis | B, Offcut 1° | C, Offcut 4° |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-temperature bandgap, (meV) | 281.1 | 272.0 | 293.1 |
| Coupling parameter, (dimensionless) | 2.678 | 2.650 | 2.721 |
| Photoluminescence width slope, (dimensionless) | 0.507 | 0.431 | 0.319 |
| Photoluminescence width intercept, (meV) | 13.10 | 12.56 | 12.47 |
| Sample | Mole Fractions (%) | Incorporation Coefficients (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi | Sb | As | Bi | Sb | As | |
| A, on-axis | 0.75 ± 0.12 | 9.52 ± 0.22 | 89.73 ± 0.34 | 14.9 ± 2.4 | 79.3 ± 1.8 | 98.5 ± 0.4 |
| B, offcut 1° | 0.78 ± 0.12 | 10.04 ± 0.21 | 89.17 ± 0.33 | 15.5 ± 2.3 | 83.7 ± 1.8 | 97.9 ± 0.4 |
| C, offcut 4° | 0.61 ± 0.11 | 8.95 ± 0.22 | 90.44 ± 0.33 | 12.1 ± 2.2 | 85.2 ± 1.8 | 99.3 ± 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosireddy, R.R.; Schaefer, S.T.; Milosavljevic, M.S.; Johnson, S.R. Structural and Optical Properties of InAsSbBi Grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy on Offcut GaSb Substrates. Photonics 2021, 8, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060215
Kosireddy RR, Schaefer ST, Milosavljevic MS, Johnson SR. Structural and Optical Properties of InAsSbBi Grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy on Offcut GaSb Substrates. Photonics. 2021; 8(6):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060215
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosireddy, Rajeev R., Stephen T. Schaefer, Marko S. Milosavljevic, and Shane R. Johnson. 2021. "Structural and Optical Properties of InAsSbBi Grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy on Offcut GaSb Substrates" Photonics 8, no. 6: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060215
APA StyleKosireddy, R. R., Schaefer, S. T., Milosavljevic, M. S., & Johnson, S. R. (2021). Structural and Optical Properties of InAsSbBi Grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy on Offcut GaSb Substrates. Photonics, 8(6), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060215





