A Straightness Error Compensation System for Topography Measurement Based on Thin Film Interferometry
Abstract
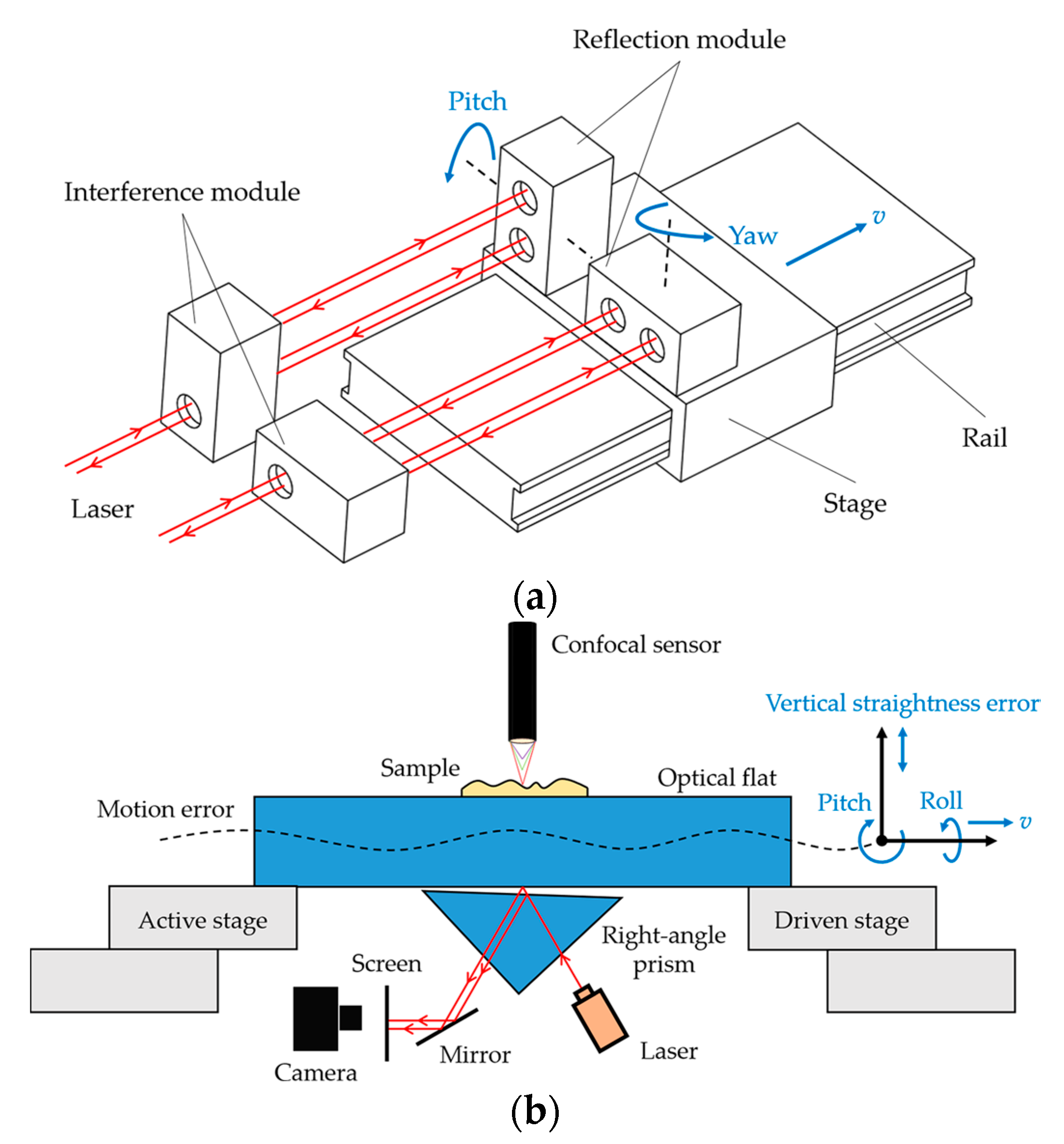
1. Introduction
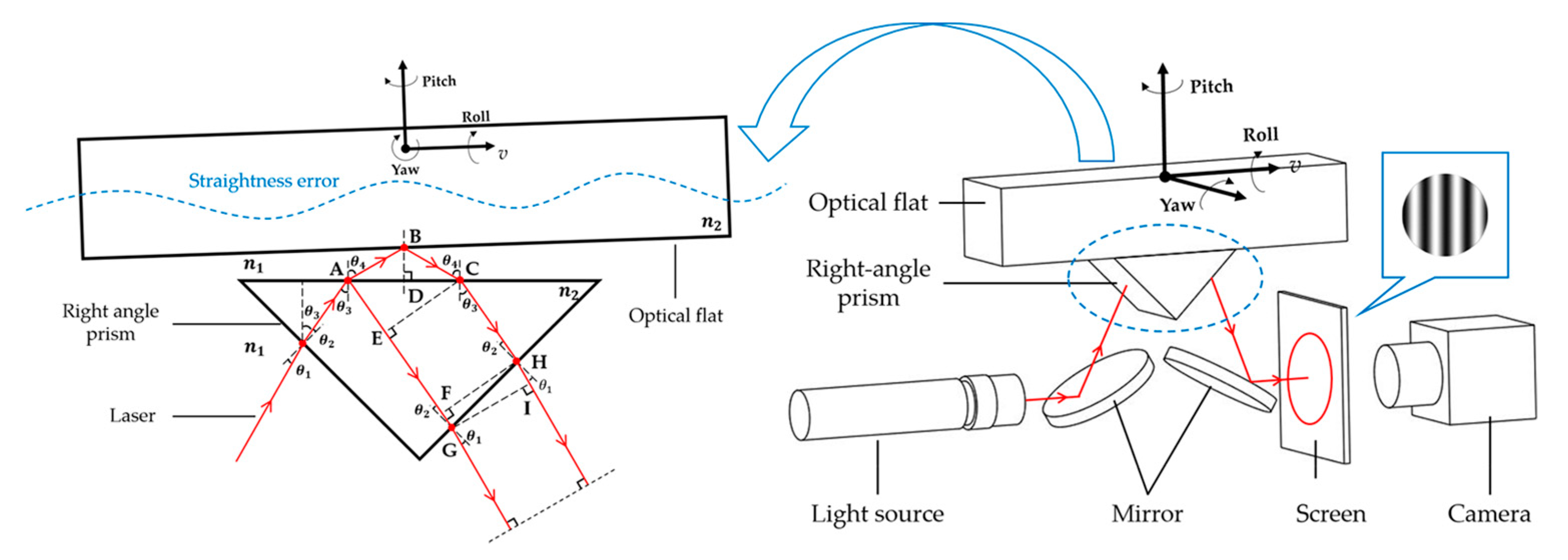
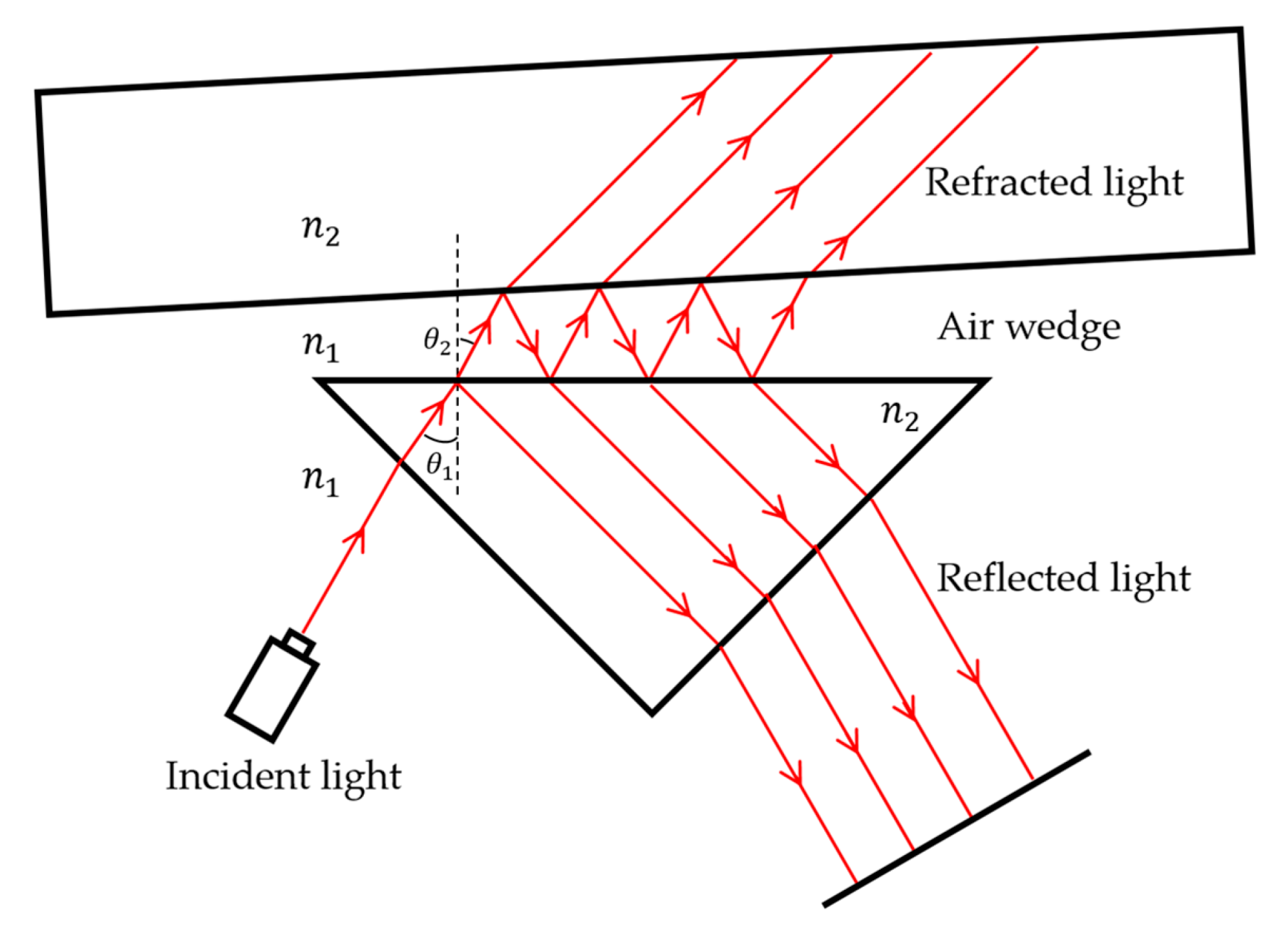
2. Principle of Film Interference Module
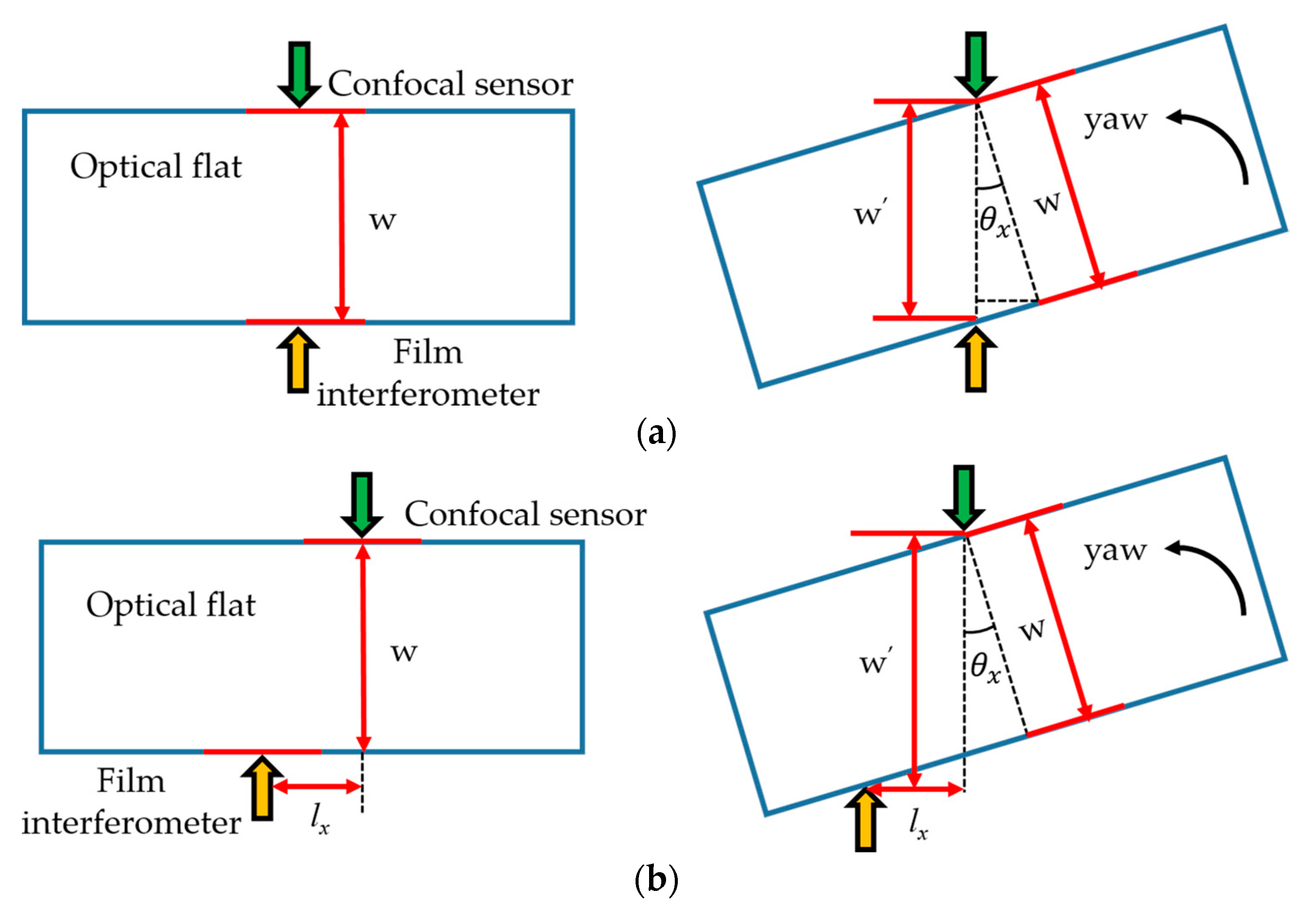
3. Analysis of Angular Motion Error
4. Phase Calculation Based on Image Processing
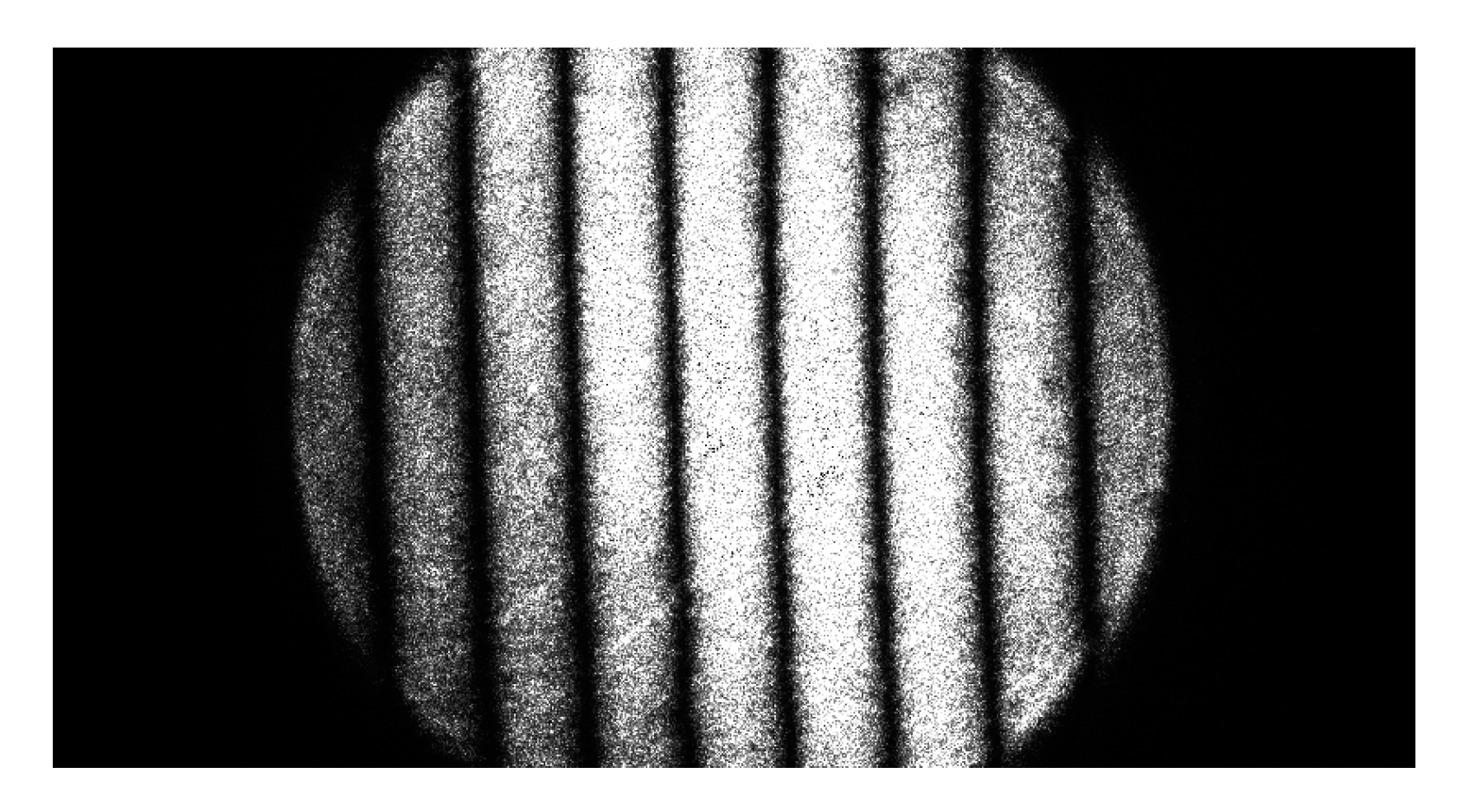
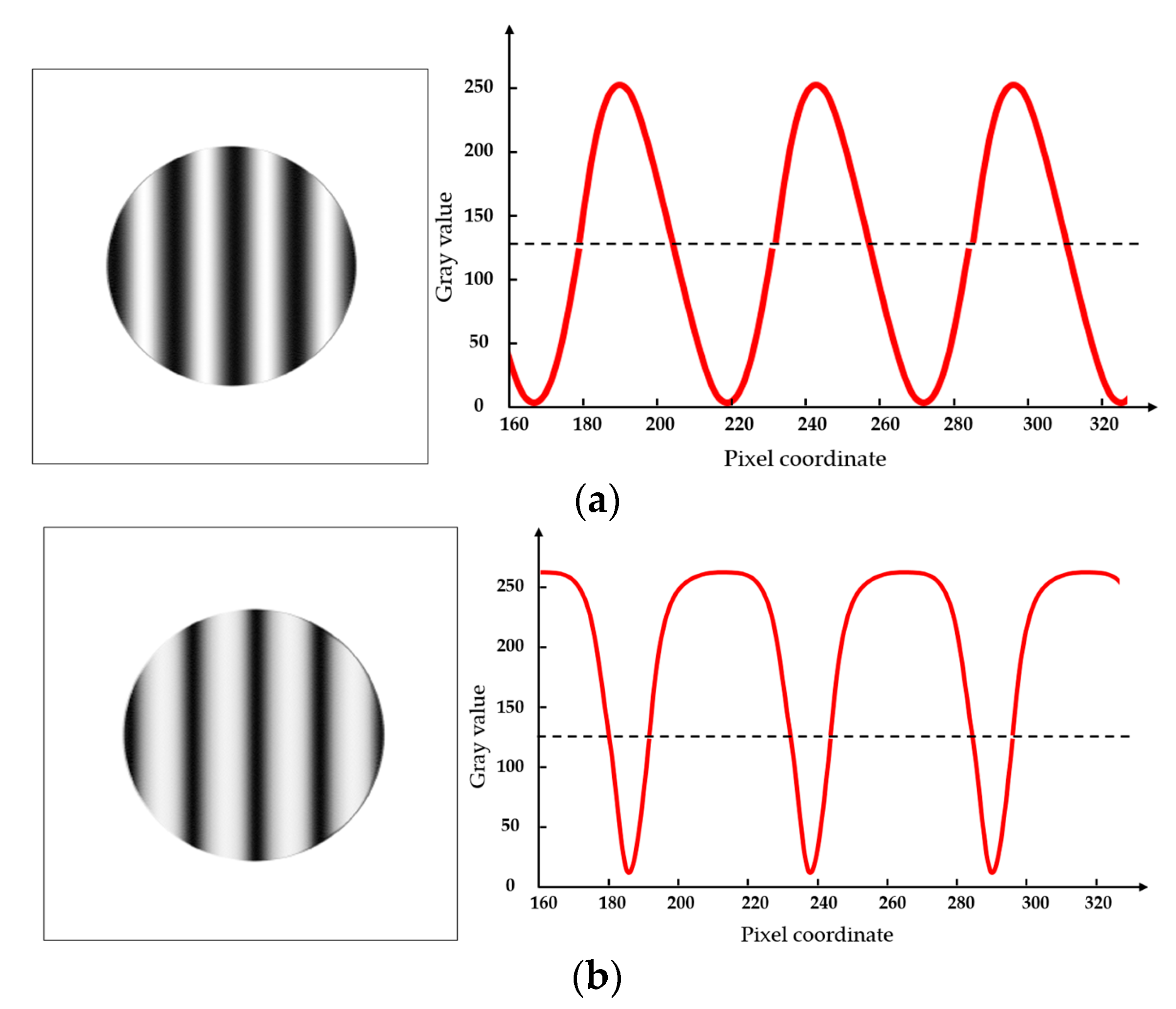
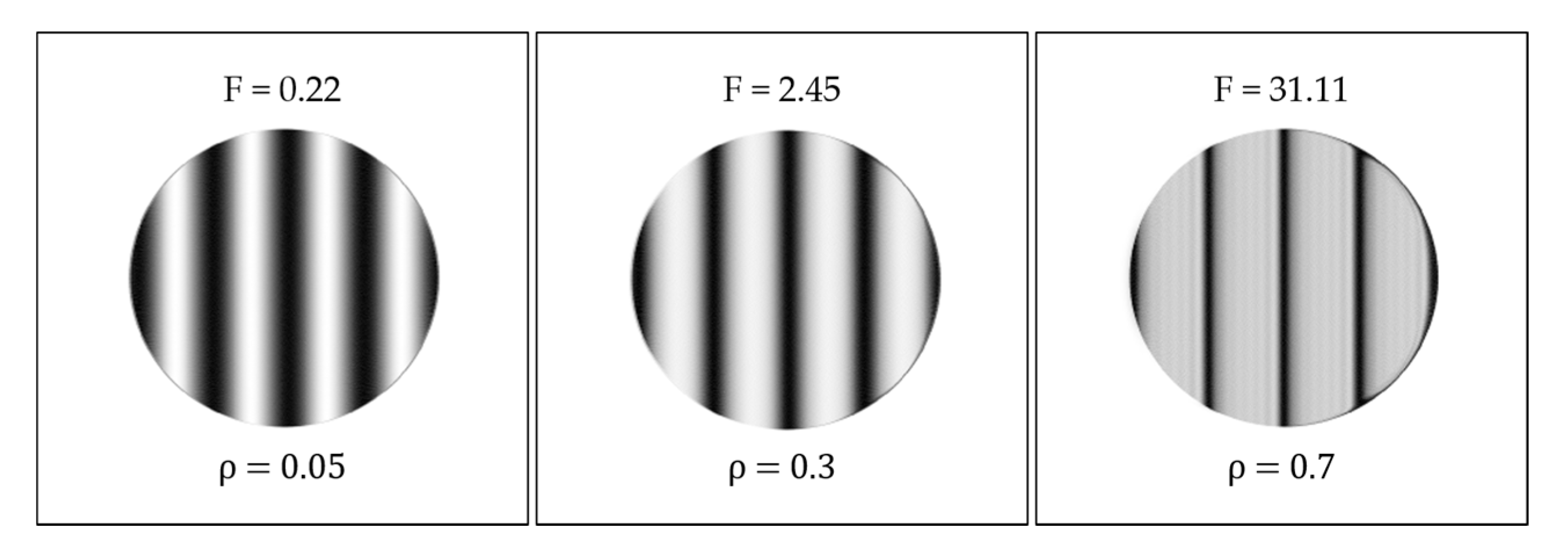
4.1. Analysis of the Cause of Fringe Distortion
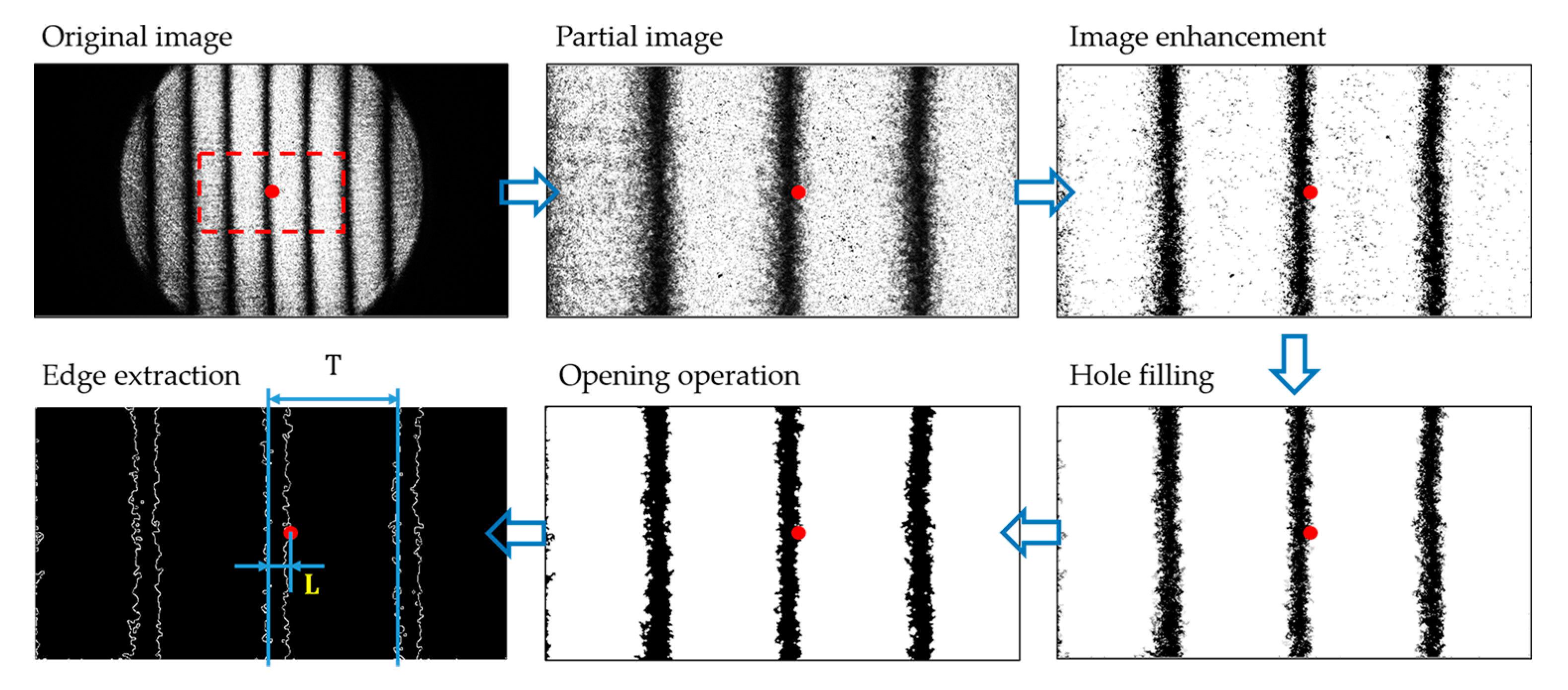
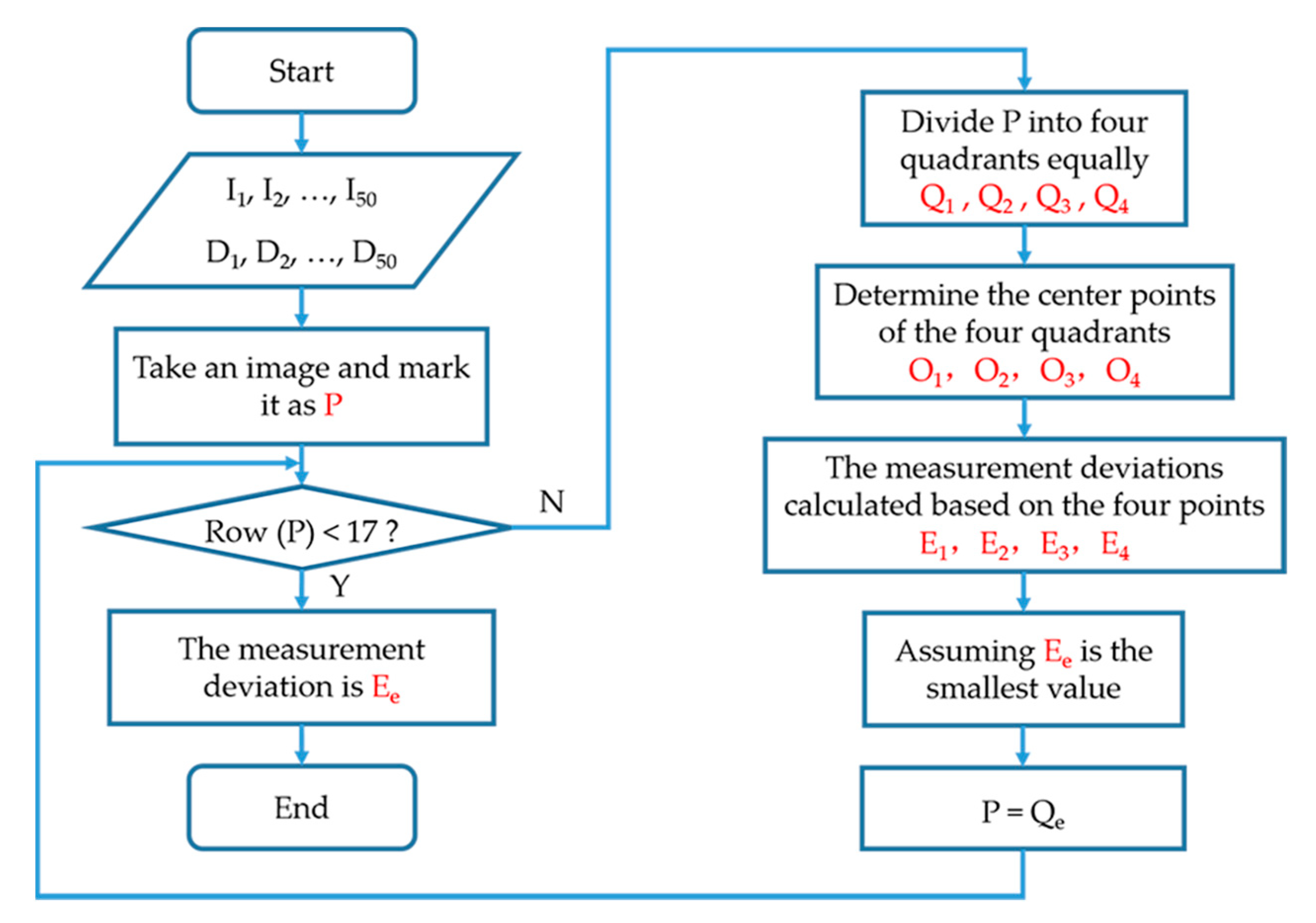
4.2. Edge Extraction and Phase Calculation
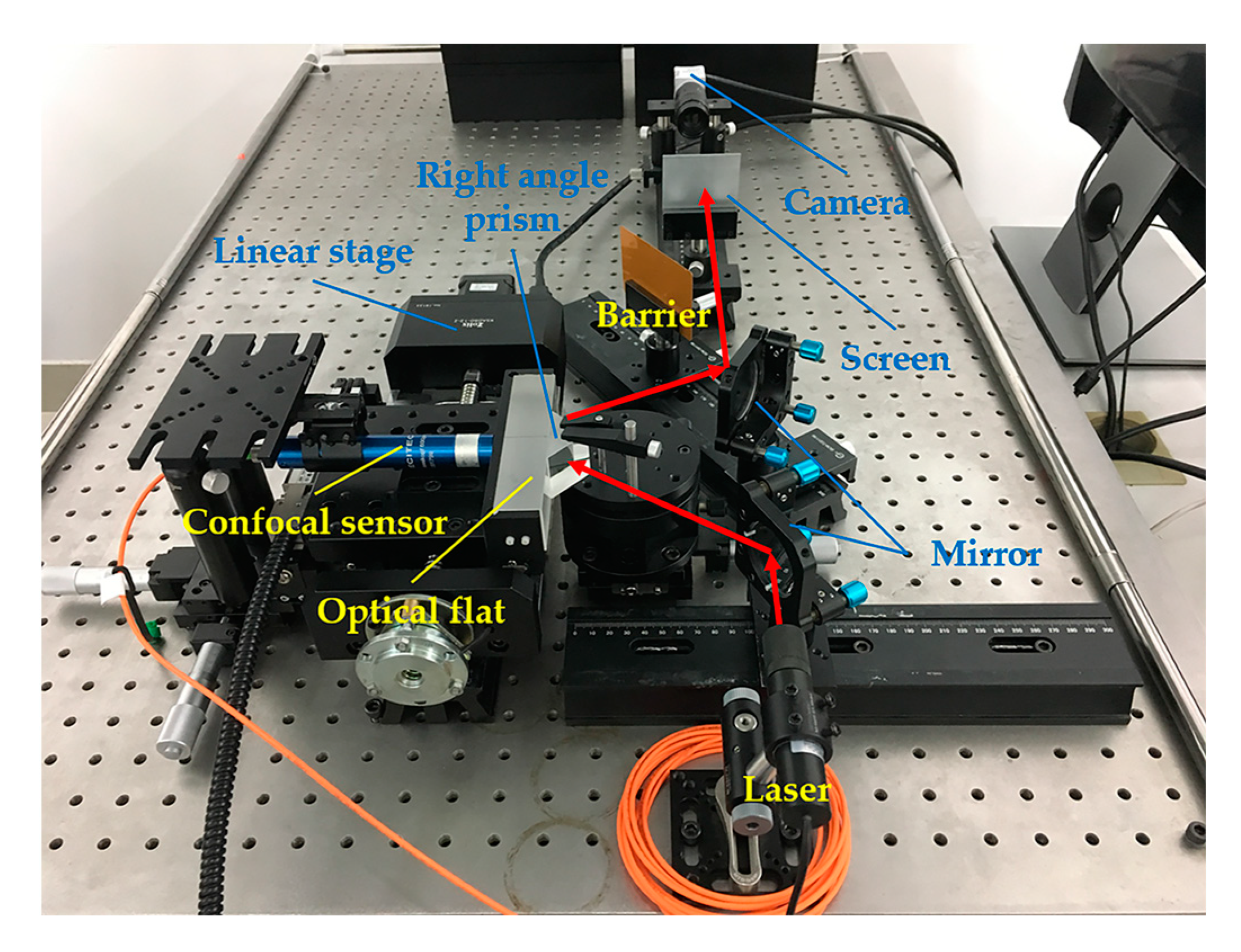
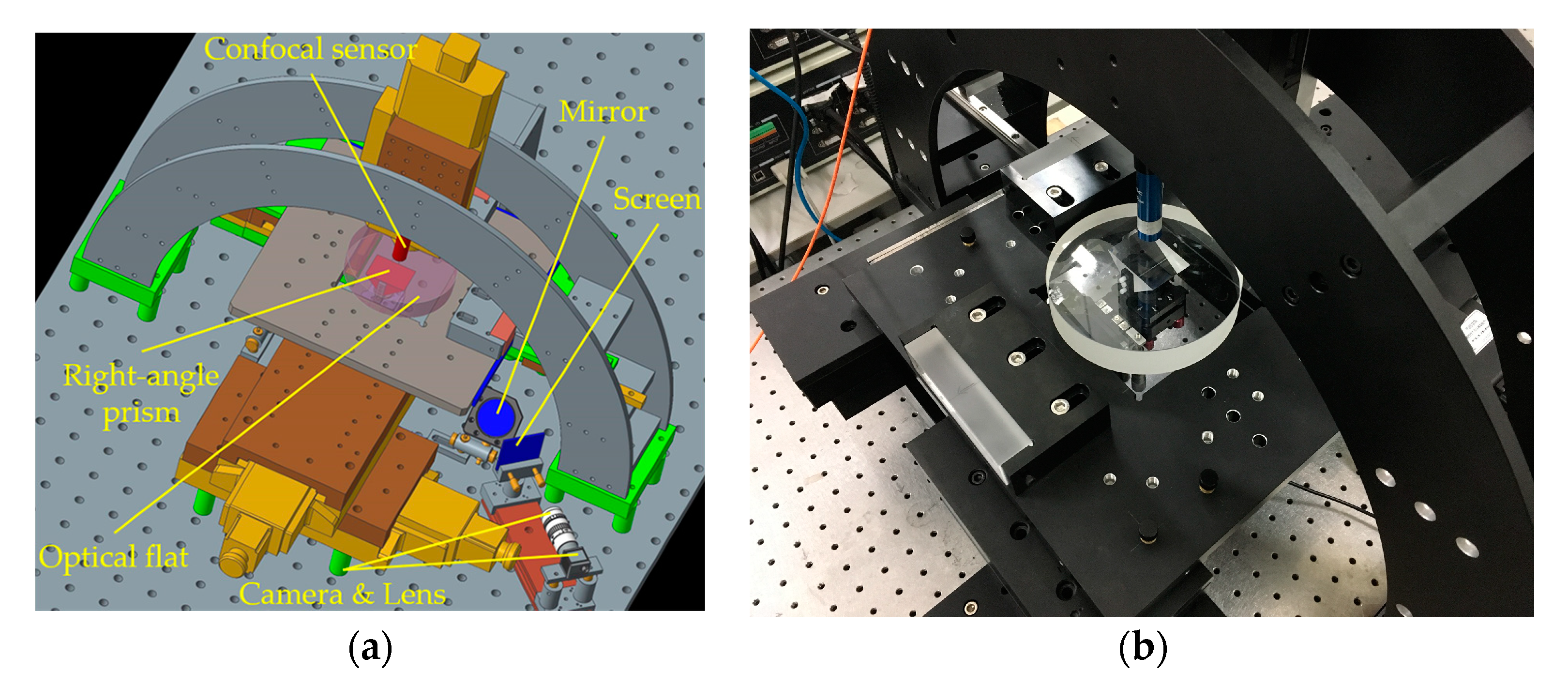
5. Experimental Analysis
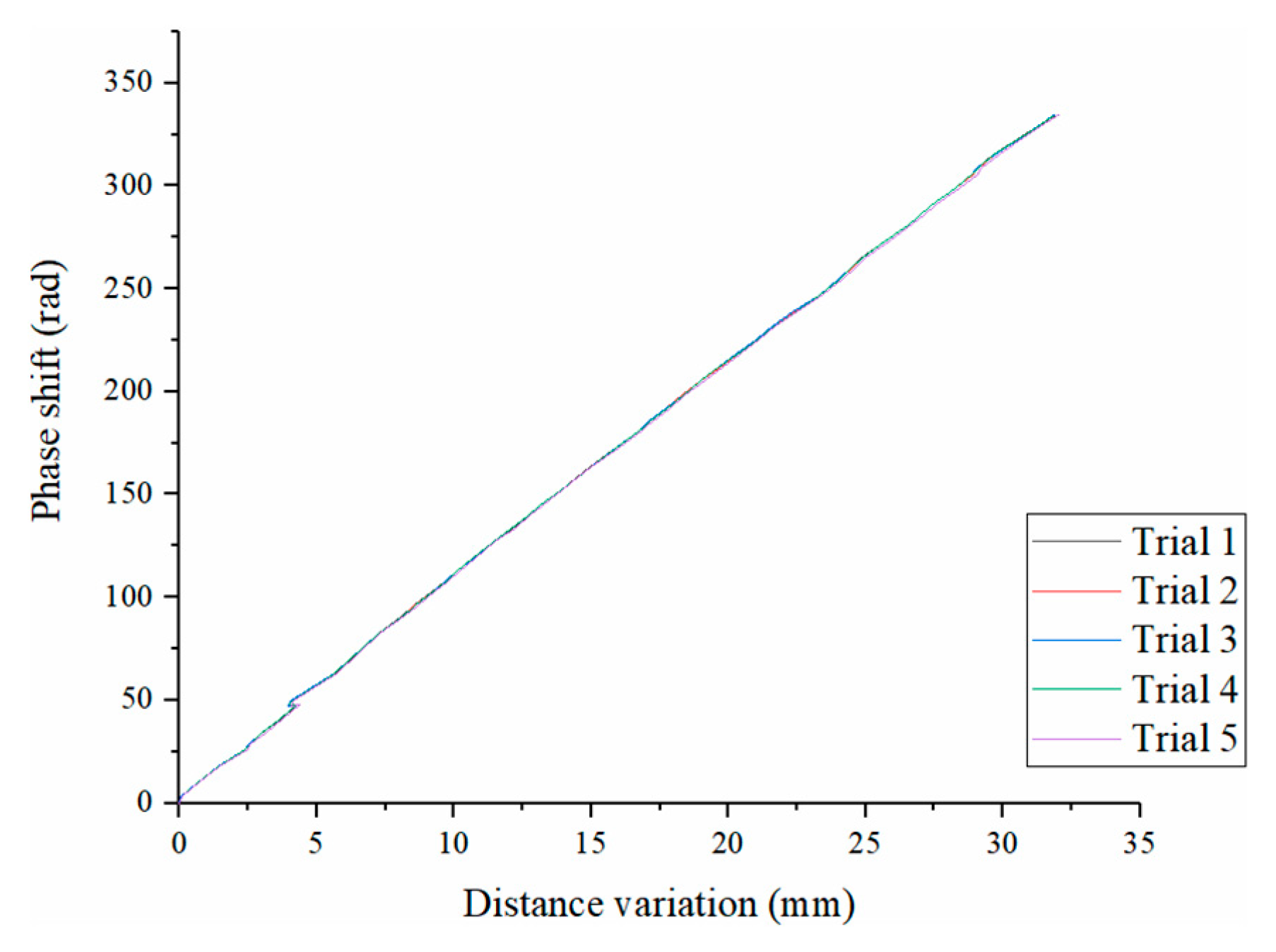
5.1. System Calibration
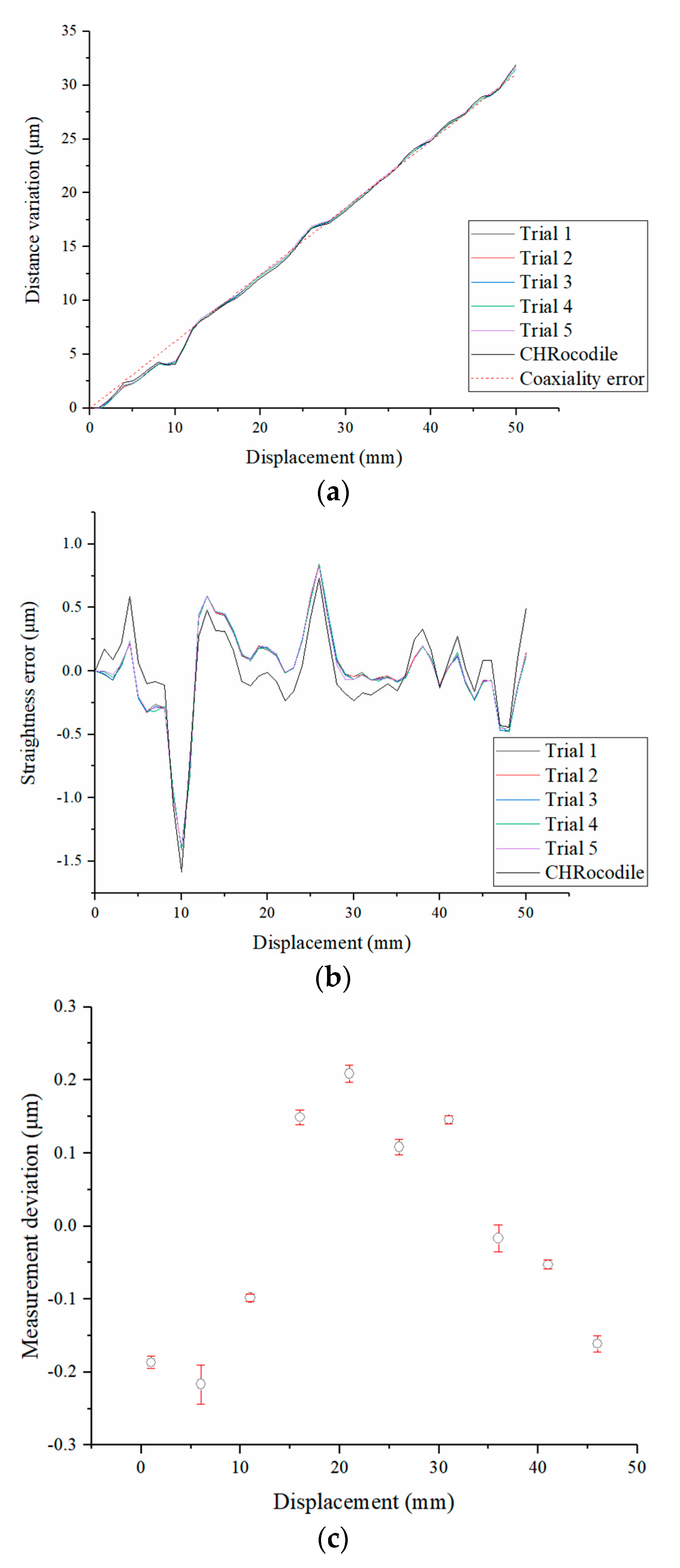
5.2. Measurement Performance
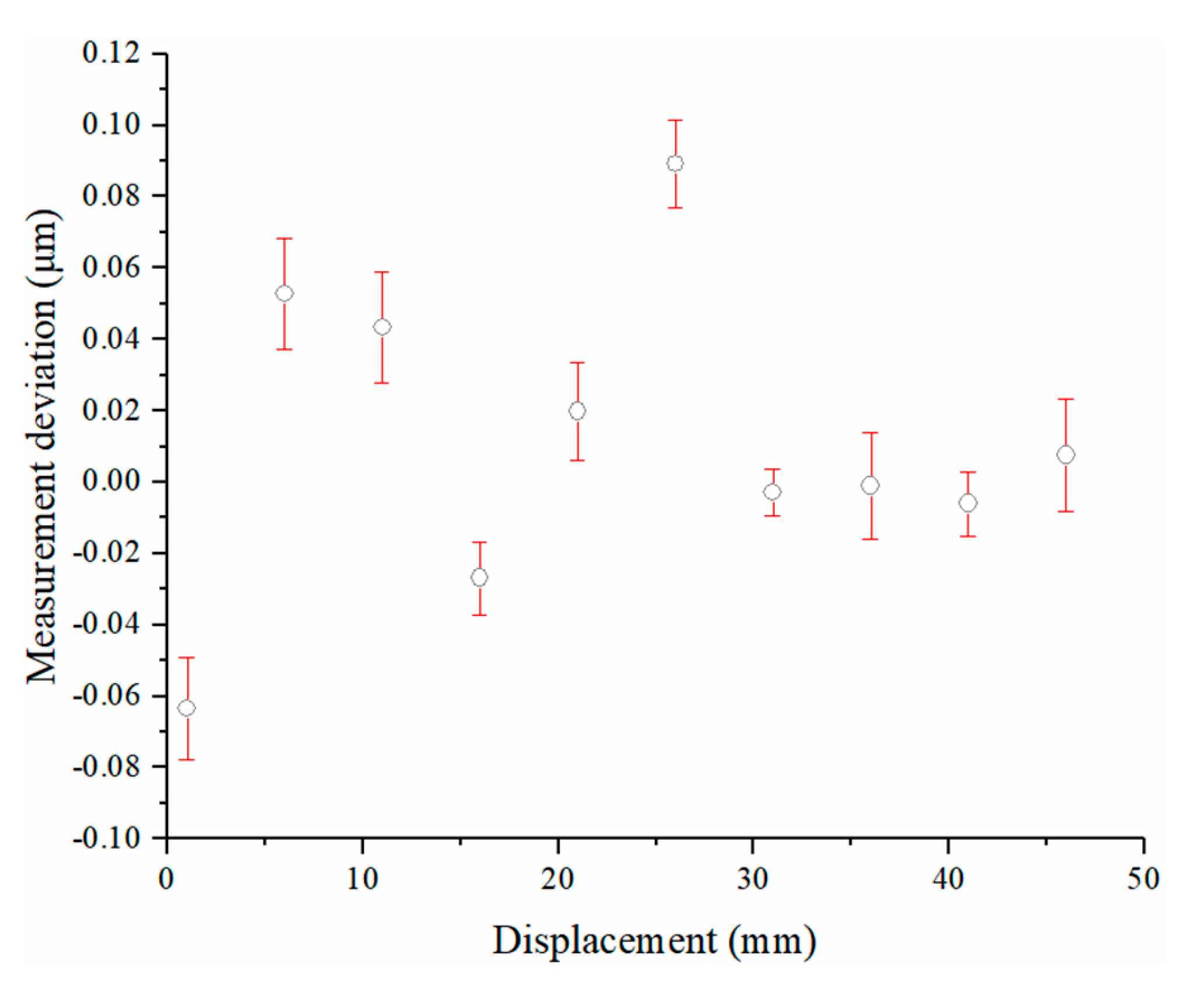
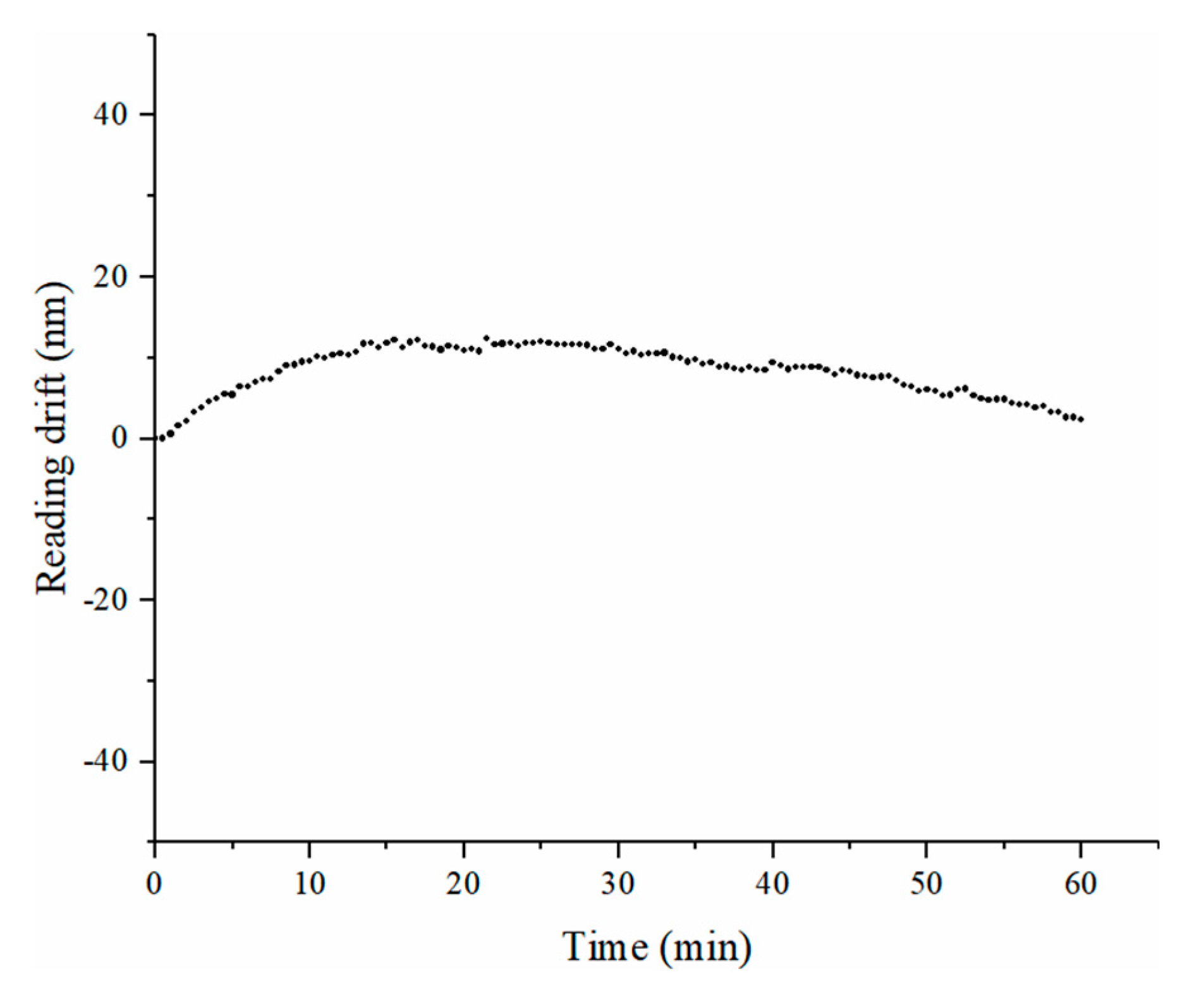
5.3. Analysis of the Source of Measurement Deviation
- (1)
- Measurement equipment
- (2)
- Measurement process
- (3)
- Measurement environment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, T.; Ji, H.; Hou, W.; Le, Y.; Shen, L. Measurement of straightness without Abbe error using an enhanced differential plane mirror interferometer. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.; Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Tie, G.; Meng, G. High accurate measurement and calibration of the squareness on ultra-precision machine based on error separation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B 2019, 233, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Pan, Y.C. Automated visual inspection in the semiconductor industry: A survey. Comput. Ind. 2015, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Yoo, J.M.; Yang, S.H.; Choi, Y.M.; Dagalakis, N.G.; Gupta, S.K. Design, fabrication and testing of a serial kinematic MEMS XY stage for multifinger manipulation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 85029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouira, H.; El-Hayek, N.; Yuan, X.; Anwer, N. Characterization of the main error sources of chromatic confocal probes for dimensional measurement. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 044011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Jywe, W.Y.; Chen, G.W.; Wang, M.S. A geometric error measurement system for linear guideway assembly and calibration. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, N.; Yin, Z.; Yao, J. High Accuracy Profile Measurement with a New Virtual Multi-Probe Scanning System. IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 158727–158734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichert, C.; Bosse, H.; Flügge, J.; Köning, R.; Köchert, P.; Wiegmann, A.; Kunzmann, H. Implementation of straightness measurements at the Nanometer Comparator. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 65, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küng, A.; Bircher, B.A.; Meli, F. Low-Cost 2D Index and Straightness Measurement System Based on a CMOS Image Sensor. Sensors 2019, 19, 5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, E.H.K.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.Z.; Wong, W.O. A novel Fourier-Eight-Sensor (F8S) method for separating straightness, yawing and rolling motion errors of a linear slide. Measurement 2014, 47, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.C.; Chen, M.J. A 6-Degree-of-freedom measurement system for the accuracy of X-Y stages. Precis. Eng. 2000, 24, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Gillmer, S.R.; Woody, S.C.; Ellis, J.D. Development of a compact, fiber-coupled, six degree-of-freedom measurement system for precision linear stage metrology. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 065109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Arai, Y.; Shibuya, A.; Kiyono, S.; Parke, C.H. Measurement of multi-degree-of-freedom error motions of a precision linear air-bearing stage. Precis. Eng. 2006, 30, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.L.; Pan, S.W. Development of a grating-based interferometer for six-degree-of-freedom displacement and angle measurements. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 2451–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisov, O.; Fletcher, S.; Longstaff, A.; Myers, A. New low cost sensing head and taut wire method for automated straightness measurement of machine tool axes. Opt. Laser Eng. 2013, 51, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Liu, C.H. High precision optical sensors for real-time on-line measurement of straightness and angular errors for smart manufacturing. Smart Sci. 2016, 4, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lou, Z.; Ling, S.; Liao, B.; Fan, K. Development of a compact three-degree-of-freedom laser measurement system with self-wavelength correction for displacement feedback of a nanopositioning stage. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Saito, Y.; Muto, H.; Arai, Y.; Shimizu, Y. A three-axis autocollimator for detection of angular error motions of a precision stage. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 60, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Gao, W.; Zeng, L.J. Position and out-of-straightness measurement of a precision linear air-bearing stage by using a two-degree-of-freedom linear encoder. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 054005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Takamura, T.; Takahashi, S.; Takamasu, K.; Sato, O.; Osawa, S.; Takatsuji, T. Development of high-precision micro-coordinate measuring machine: Multi-probe measurement system for measuring yaw and straightness motion error of XY linear stage. Precis. Eng. 2011, 35, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, B.; Yan, L.; Zhang, E.; Liu, Y. Laser straightness interferometer system with rotational error compensation and simultaneous measurement of six degrees of freedom error parameters. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 9052–9073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wei, C.; Jia, W.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Li, M.; Xiang, C.; Xiang, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; et al. Two-degree-freedom displacement measurement based on a short period grating in symmetric Littrow configuration. Opt. Commun. 2016, 380, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Cheng, L.; Yan, L.; Zhang, E.; Lou, Y. A heterodyne straightness and displacement measuring interferometer with laser beam drift compensation for long-travel linear stage metrology. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 035114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J.H.; Zhang, Z.H. A method for measuring the guideway straightness error based on polarized interference principle. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manu. 2009, 49, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Hu, C. Real-time displacement calculation and offline geometric calibration of the grating interferometer system for ultra-precision wafer stage measurement. Precis. Eng. 2019, 60, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Zou, J.; Su, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Q. A differential measurement system for surface topography based on a modular design. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Chen, B.; Zheng, H.; Teng, X.; Yan, L. Note: Comparison experimental results of the laser heterodyne interferometer for angle measurement based on the Faraday effect. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 046104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, G.; Furutani, R. Interferometer for pitch and yaw measurement using LC-screen and four ball lenses. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 094016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosdoff, D.; Widom, A. Snell’s law from an elementary particle viewpoint. Am. J. Phys. 2005, 73, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Tan, H. Engineering Optics, 3rd ed.; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 358–359. [Google Scholar]

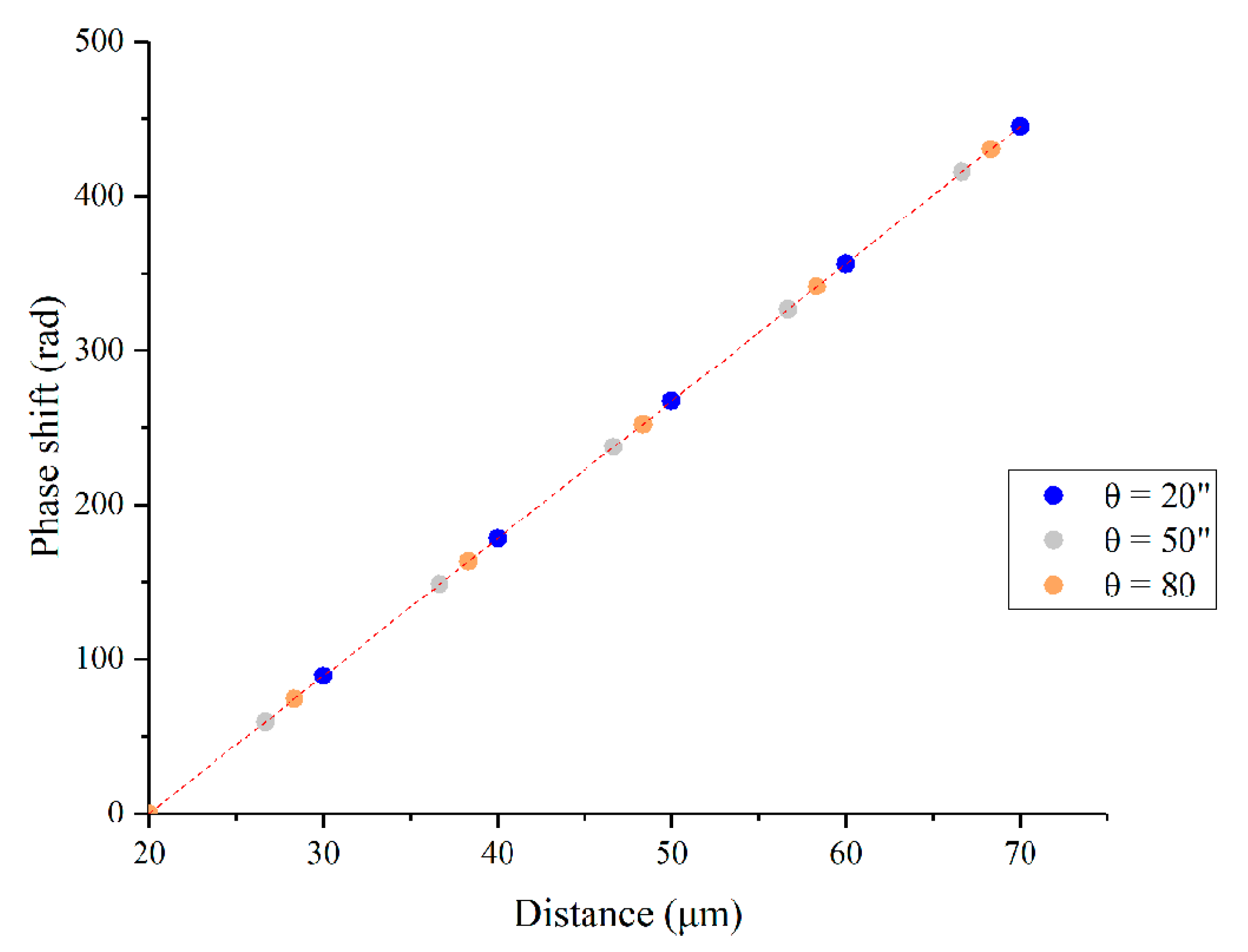



| Order | Δh (μm) | Δφ (rad) | c (rad/μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| θ = 20″ | 10.00 30.00 50.00 | 89.01 267.04 445.07 | 8.901 8.901 8.901 |
| θ = 50″ | 6.67 26.67 46.67 | 59.37 237.40 415.42 | 8.901 8.901 8.901 |
| θ = 80″ | 8.33 28.33 48.33 | 74.15 252.16 430.17 | 8.902 8.901 8.901 |
| Component | Supplier | Type | Specifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light source | Minghui Optics | M650D50-20100 | Power: 50 mW, Wavelength: 650 nm, Spot diameter: 15 mm. |
| Right-angle prism | Daheng Optics | GCL-030107A | Material: K9 glass, Flatness: ≤0.06 μm, Dimension (mm): 30 × 30 × 30. |
| Optical flat | Sanfeng Standard Measuring Implements | 120 × 30 × 25 | Material: K9 glass, Flatness: ≤0.05 μm, Dimension (mm): 120 × 30 × 25. |
| Linear stage | Zolix | KSA050-12-Z | Travel range: 50 mm, Positioning accuracy: ≤±3 μm, Straightness: ≤10 μm. |
| Confocal sensor | Precitec | CHRocodile SE | Measuring range: 600 μm, Linearity error: <0.2 μm, Resolution: 3 nm. |
| Lens | Moritex | ML-MC50HR | Magnification: 0.5~0.8, Focal length: 50 mm, Maximum compatible target: 2/3″. |
| Camera | Basler | acA2000-165um | Target size: 2/3″, Frame rate: 165 fps, Resolution: 2048 × 1088. (2 MP) |
| Trial | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Average | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope (rad/μm) | 10.461 | 10.456 | 10.464 | 10.459 | 10.426 | 10.453 | 0.013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, H.; Ye, R.; Cheng, F.; Cui, C.; Yu, Q. A Straightness Error Compensation System for Topography Measurement Based on Thin Film Interferometry. Photonics 2021, 8, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8050149
Su H, Ye R, Cheng F, Cui C, Yu Q. A Straightness Error Compensation System for Topography Measurement Based on Thin Film Interferometry. Photonics. 2021; 8(5):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8050149
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Hang, Ruifang Ye, Fang Cheng, Changcai Cui, and Qing Yu. 2021. "A Straightness Error Compensation System for Topography Measurement Based on Thin Film Interferometry" Photonics 8, no. 5: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8050149
APA StyleSu, H., Ye, R., Cheng, F., Cui, C., & Yu, Q. (2021). A Straightness Error Compensation System for Topography Measurement Based on Thin Film Interferometry. Photonics, 8(5), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8050149






