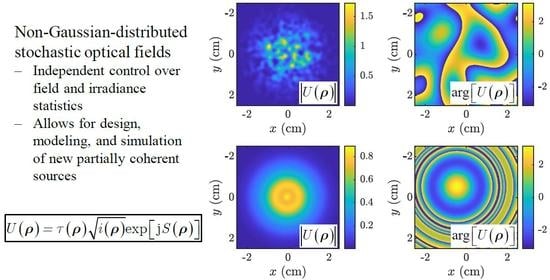
Independently Controlling Stochastic Field Realization Magnitude and Phase Statistics for the Construction of Novel Partially Coherent Sources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Stochastic Field Model
2.2. CSD Function
2.3. Covariance of Irradiance
2.4. Generating S and i
3. Results and Discussion
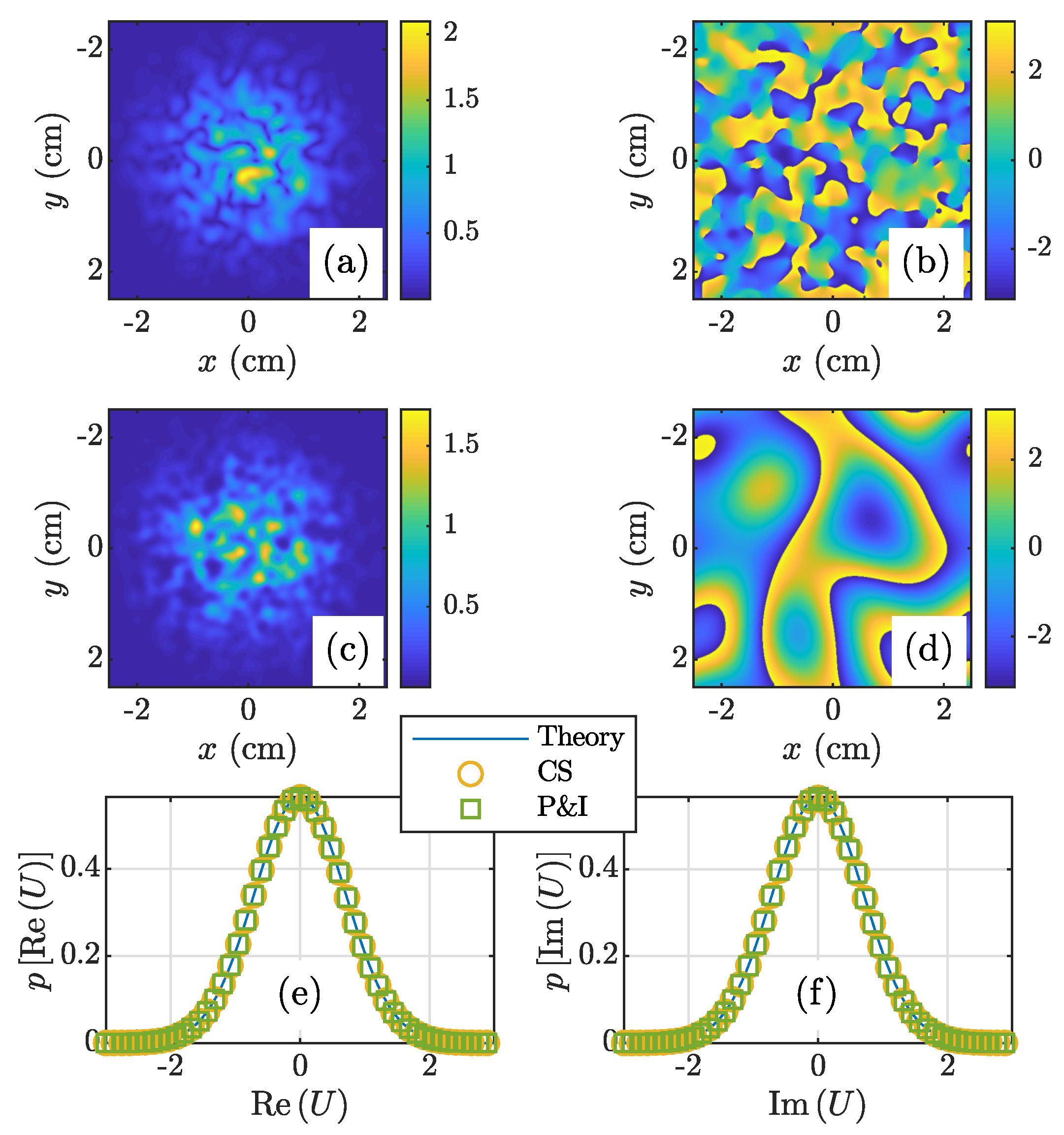
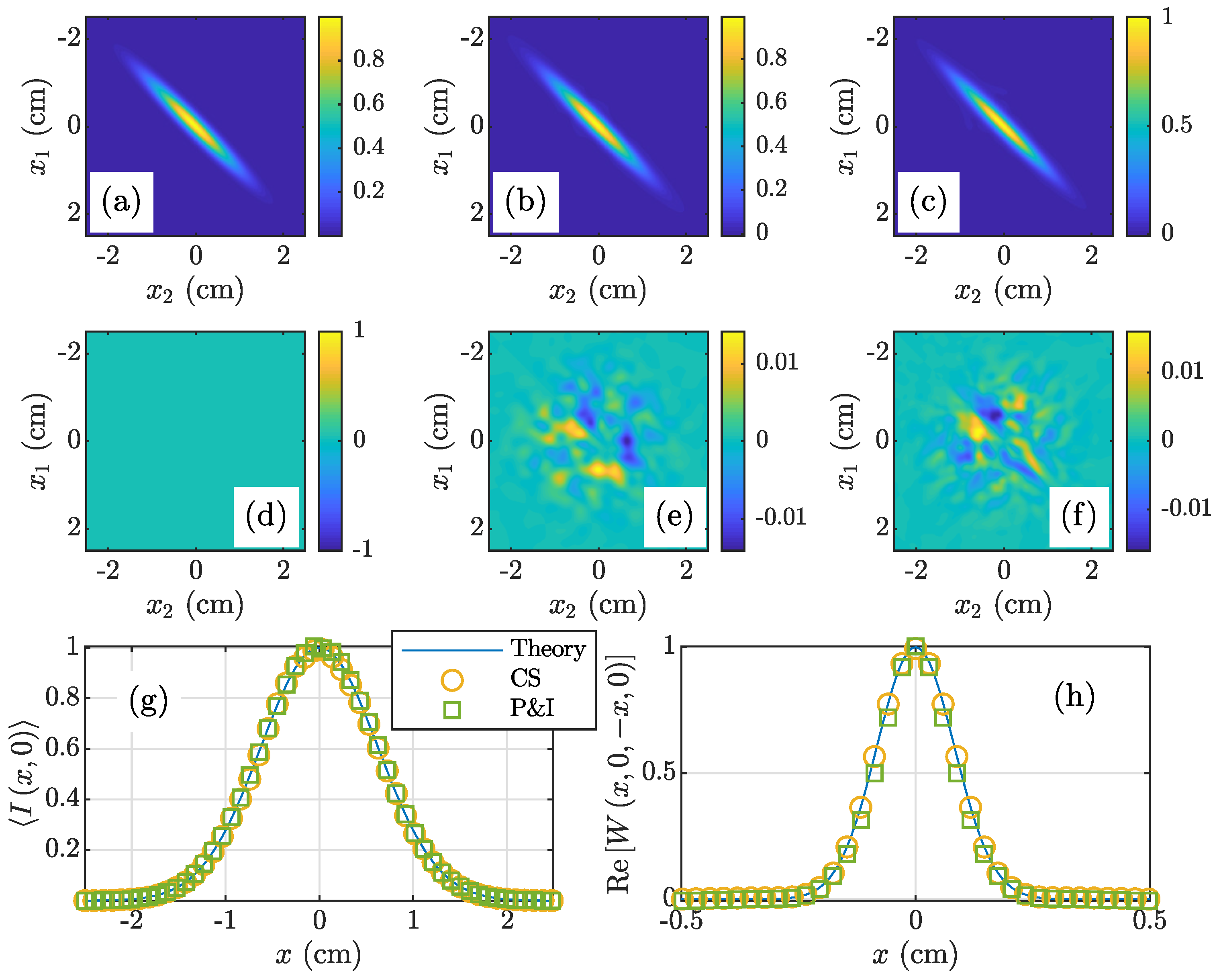
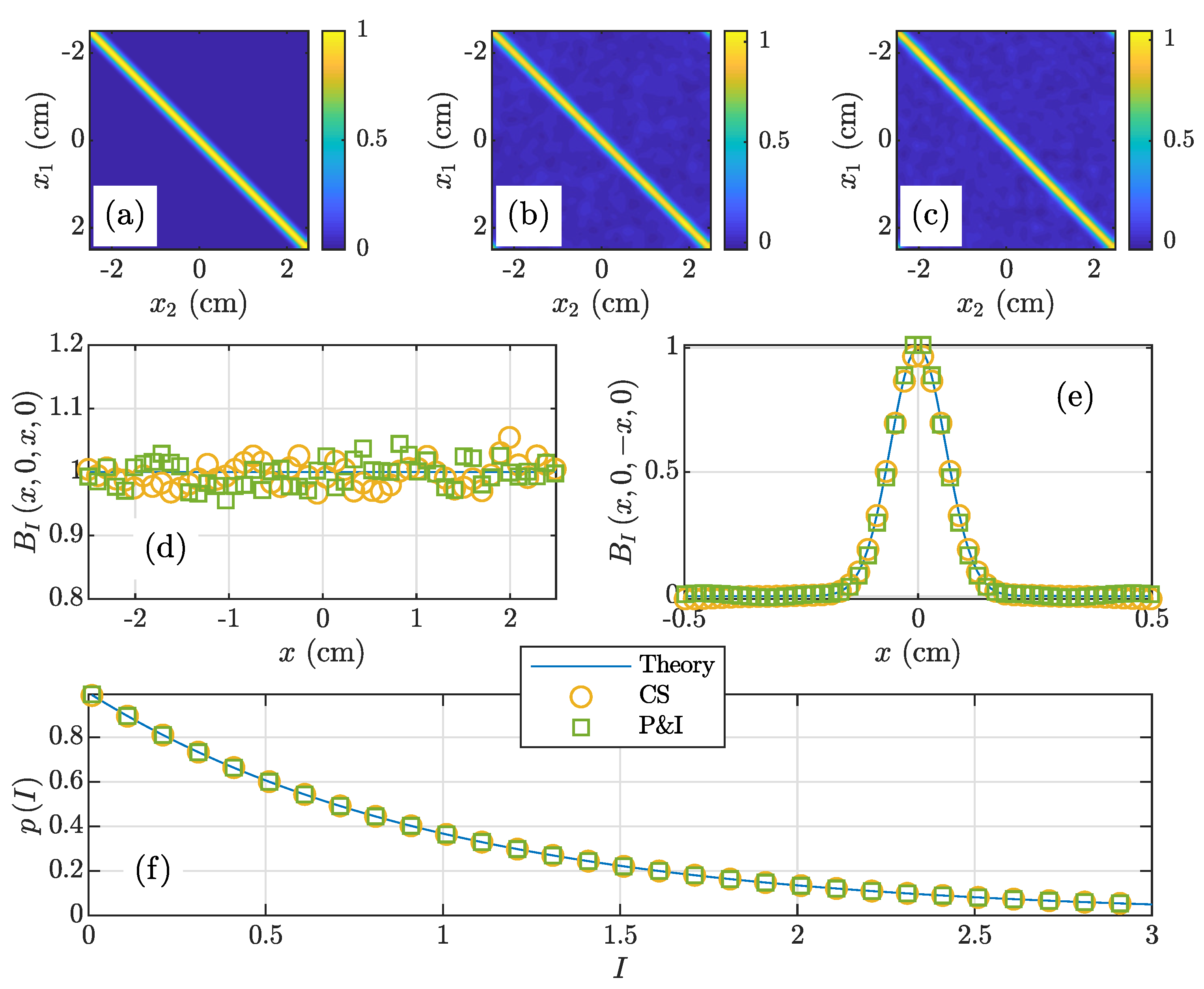
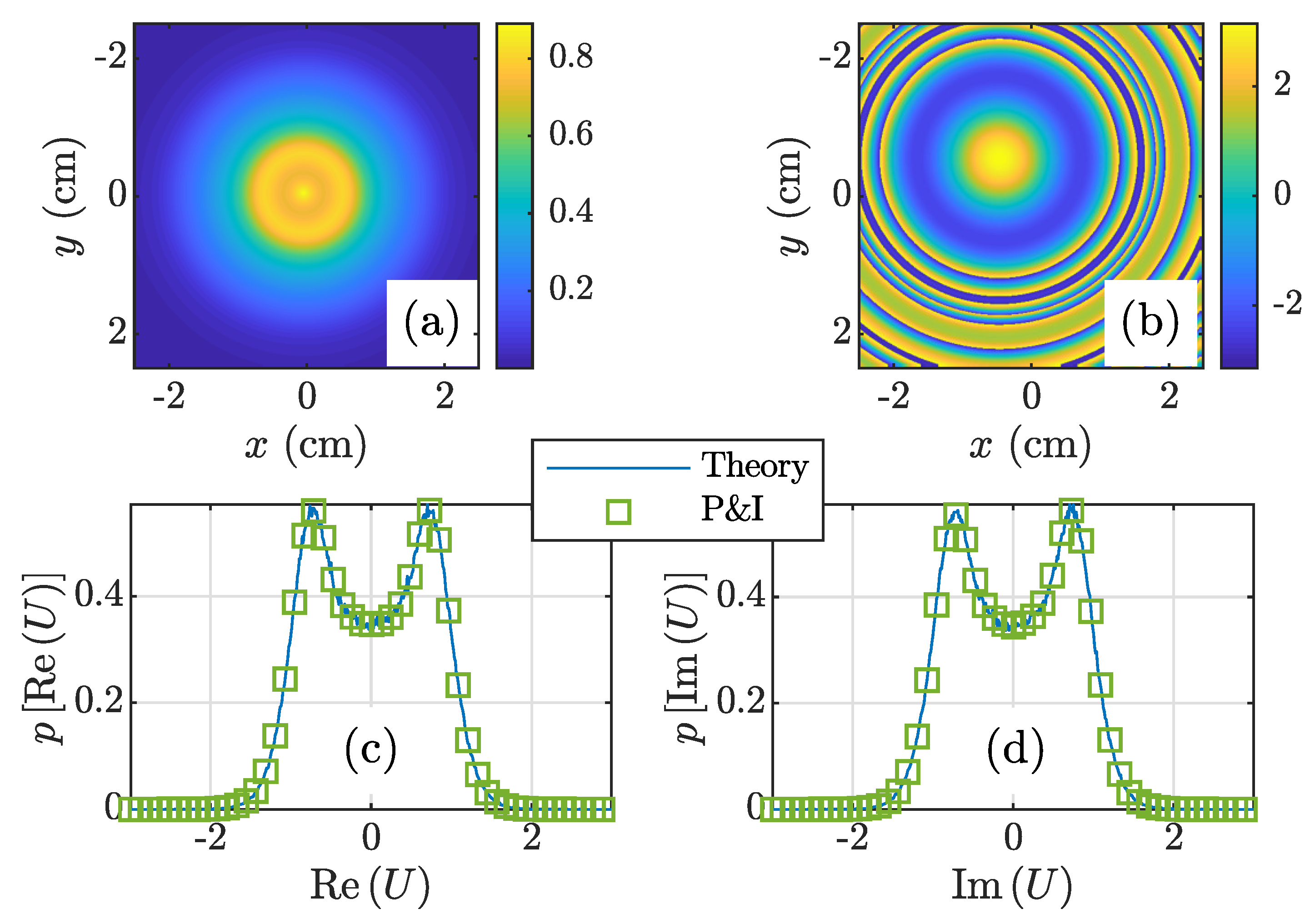
3.1. GSM Beam
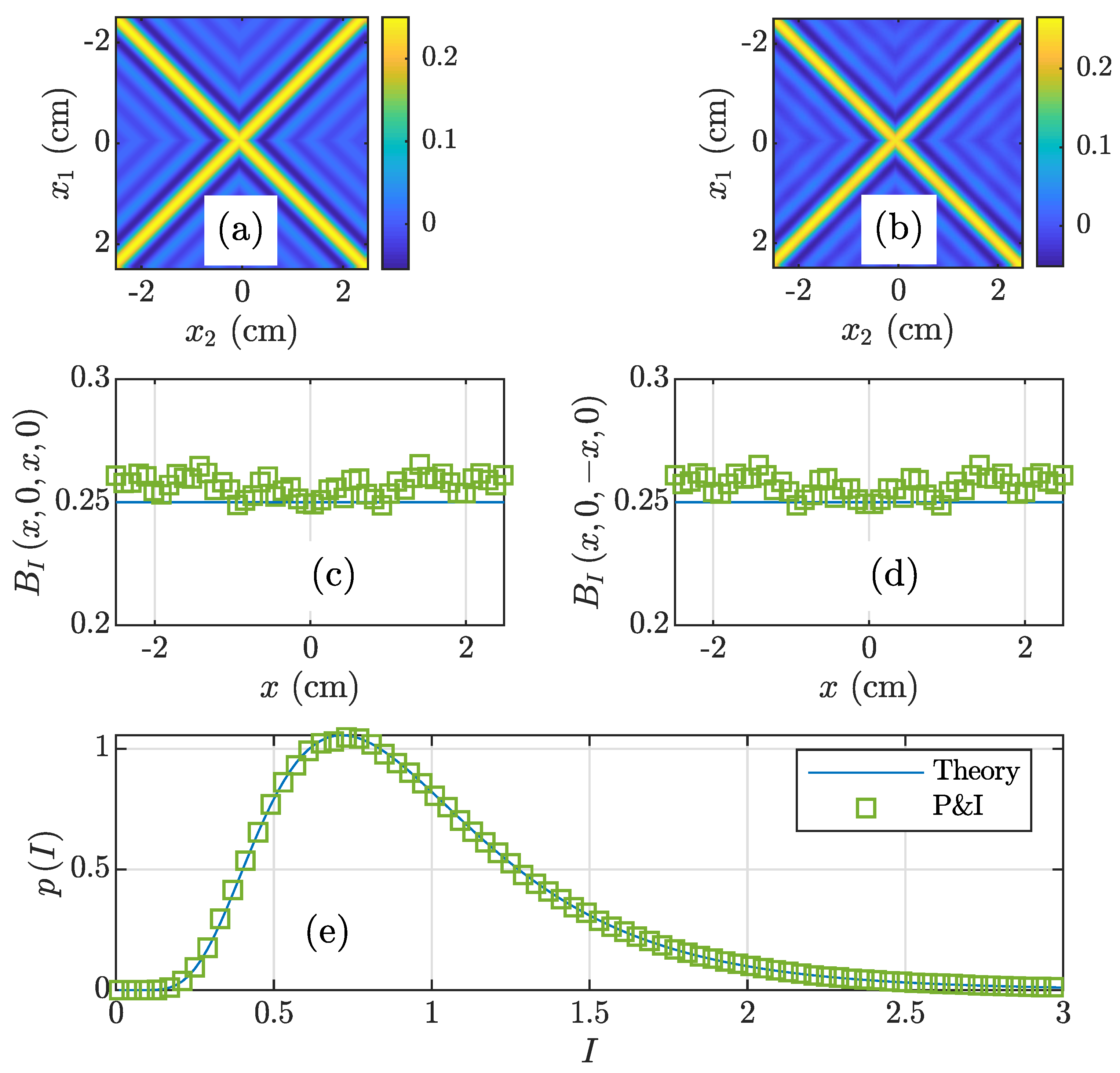
3.2. NUC Beam
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCG | circular complex Gaussian |
| CDF | cumulative distribution function |
| CS | complex screen |
| CSD | cross-spectral density |
| GSM | Gaussian Schell-model |
| JCF | joint characteristic function |
| NUC | nonuniformly correlated |
| NORTA | NORmal To Anything |
| probability density function |
Appendix A. Proof of Equation (21)
Appendix B. Generating GSM Beams Using the Complex Screen Technique
References
- Gori, F.; Santarsiero, M. Devising genuine spatial correlation functions. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 3531–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, L.; Wolf, E. Optical Coherence and Quantum Optics; Cambridge University: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, J.W. Statistical Optics, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Korotkova, O. Random Light Beams: Theory and Applications; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gbur, G.; Visser, T. The structure of partially coherent fields. Prog. Opt. 2010, 55, 285–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, L. Generation of partially coherent beams. Prog. Opt. 2017, 62, 157–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F. Generation and propagation of partially coherent beams with nonconventional correlation functions: A review. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2014, 31, 2083–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, G.S.; Classen, A. Partial coherence in modern optics: Emil Wolf’s legacy in the 21st century. Prog. Opt. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotkova, O.; Gbur, G. Applications of optical coherence theory. Prog. Opt. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbur, G. Partially coherent beam propagation in atmospheric turbulence. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2014, 31, 2038–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Cai, Y. Propagation of partially coherent beam in turbulent atmosphere: A review. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2015, 150, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, L.C.; Phillips, R.L. Laser Beam Propagation through Random Media, 2nd ed.; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, T.; Wolf, E. Coherence and polarization of electromagnetic beams modulated by random phase screens and their changes on propagation in free space. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2004, 21, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirai, T.; Korotkova, O.; Wolf, E. A method of generating electromagnetic Gaussian Schell-model beams. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2005, 7, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbur, G.J. Simulating fields of arbitrary spatial and temporal coherence. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 7567–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Voelz, D. Wave optics simulation approach for partial spatially coherent beams. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 6986–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.J. Simulation of vector fields with arbitrary second-order correlations. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 2837–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydberg, C.; Bengtsson, J. Efficient numerical representation of the optical field for the propagation of partially coherent radiation with a specified spatial and temporal coherence function. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2006, 23, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Herrero, R.; Mejías, P.M.; Gori, F. Genuine cross-spectral densities and pseudo-modal expansions. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 1399–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelz, D.; Xiao, X.; Korotkova, O. Numerical modeling of Schell-model beams with arbitrary far-field patterns. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Cai, Y. Experimental synthesis of partially coherent sources. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 1874–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarsiero, M.; Martínez-Herrero, R.; Maluenda, D.; de Sande, J.C.G.; Piquero, G.; Gori, F. Synthesis of circularly coherent sources. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 4115–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piquero, G.; Santarsiero, M.; Martínez-Herrero, R.; de Sande, J.C.G.; Alonzo, M.; Gori, F. Partially coherent sources with radial coherence. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 2376–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Speckle Phenomena in Optics: Theory and Applications, 2nd ed.; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lajunen, H.; Saastamoinen, T. Propagation characteristics of partially coherent beams with spatially varying correlations. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 4104–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sande, J.C.G.; Martínez-Herrero, R.; Piquero, G.; Santarsiero, M.; Gori, F. Pseudo-Schell model sources. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 3963–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, P.; Spizzichino, A. The Scattering of Electromagnetic Waves from Rough Surfaces; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1986; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ishimaru, A. Wave Propagation and Scattering in Random Media; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Voelz, D.G. Computational Fourier Optics: A MATLAB Tutorial; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Hyde, M.W.; Xiao, X.; Voelz, D.G.; Korotkova, O. Computational approaches for generating electromagnetic Gaussian Schell-model sources. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 31691–31707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, J.E. Understanding Surface Scatter Phenomena: A Linear Systems Formulation; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yura, H.T.; Hanson, S.G. Digital simulation of an arbitrary stationary stochastic process by spectral representation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2011, 28, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yura, H.T.; Hanson, S.G. Digital simulation of two-dimensional random fields with arbitrary power spectra and non-Gaussian probability distribution functions. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, C77–C83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriu, M. Crossing of non-Gaussian translation processes. J. Eng. Mech. 1984, 110, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, F.; Shinozuka, M. Digital generation of non-Gaussian stochastic fields. J. Eng. Mech. 1988, 114, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, F.; Arwade, S.; Graham-Brady, L. A translation model for non-stationary, non-Gaussian random processes. Probab. Eng. Mech. 2005, 20, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, F. Simulation of spatially varying non-Gaussian and nonstationary seismic ground motions by the spectral representation method. J. Eng. Mech. 2018, 144, 04017143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cario, M.C.; Nelson, B.L. Modeling and Generating Random Vectors with Arbitrary Marginal Distributions and Correlation Matrix; Tech. Rep.; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Henderson, S.G. Behavior of the NORTA method for correlated random vector generation as the dimension increases. ACM Trans. Model. Comput. Simul. 2003, 13, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, M.W. Stochastic complex transmittance screens for synthesizing general partially coherent sources. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2020, 37, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, D.L.; Vaughn, J.L. Branch cuts in the phase function. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 2865–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, J.W. Introduction to Fourier Optics, 3rd ed.; Roberts & Company: Englewood, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hyde, M.W., IV. Independently Controlling Stochastic Field Realization Magnitude and Phase Statistics for the Construction of Novel Partially Coherent Sources. Photonics 2021, 8, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8020060
Hyde MW IV. Independently Controlling Stochastic Field Realization Magnitude and Phase Statistics for the Construction of Novel Partially Coherent Sources. Photonics. 2021; 8(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8020060
Chicago/Turabian StyleHyde, Milo W., IV. 2021. "Independently Controlling Stochastic Field Realization Magnitude and Phase Statistics for the Construction of Novel Partially Coherent Sources" Photonics 8, no. 2: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8020060
APA StyleHyde, M. W., IV. (2021). Independently Controlling Stochastic Field Realization Magnitude and Phase Statistics for the Construction of Novel Partially Coherent Sources. Photonics, 8(2), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8020060