Quantitative Phase Imaging to Study the Effect of Sodium Dodecyl Surfactant on Adherent L929 Fibroblasts on Tissue Culture Plates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fibroblast Cell Preparation
2.2. SDS Solution Preparation
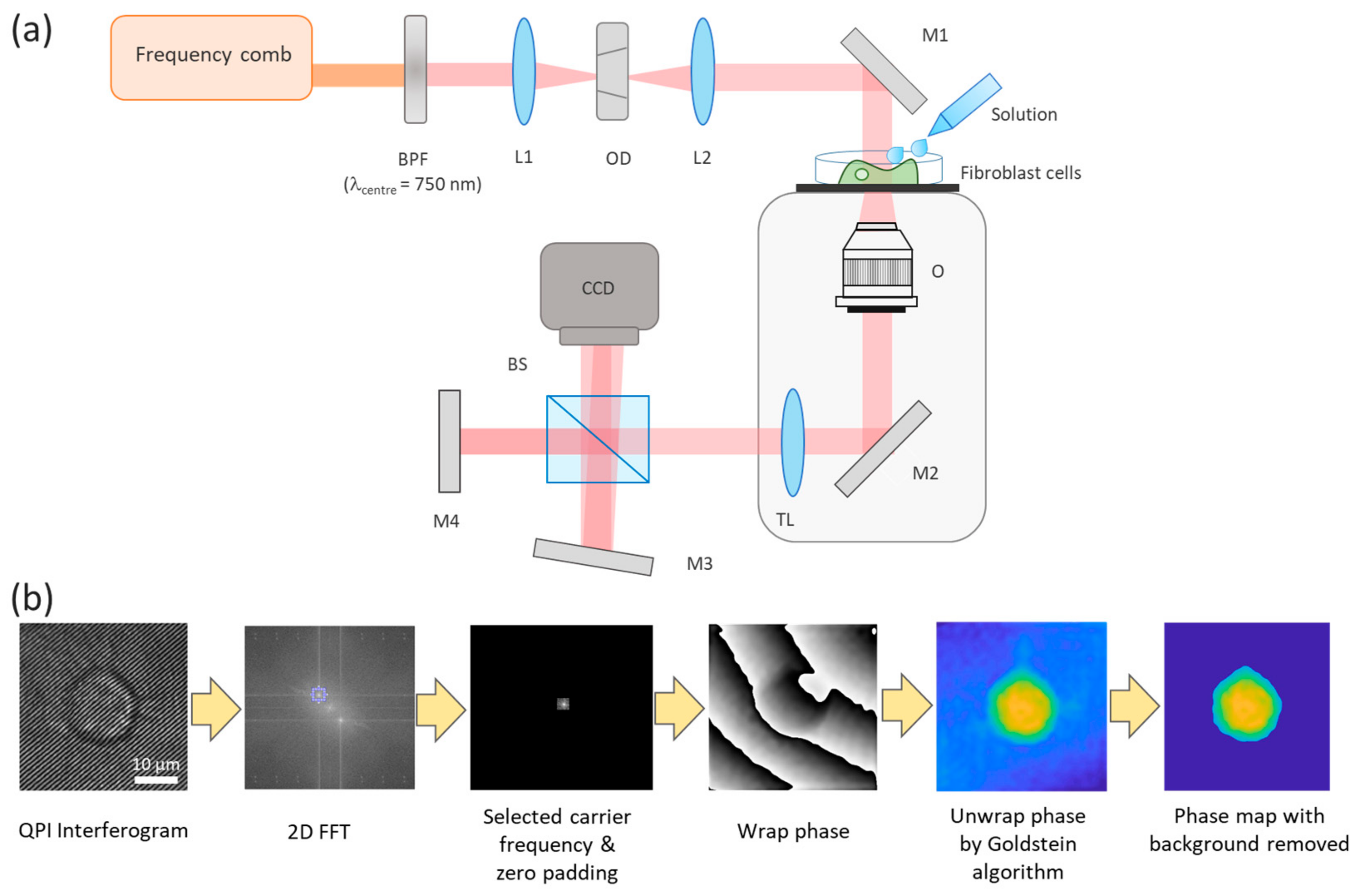
2.3. QPI Setup
2.4. Observation of Solution–Cell Interactions
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilbert, T.W.; Sellaro, T.L.; Badylak, S.F. Decellularization of tissues and organs. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3675–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badylak, S.F.; Freytes, D.O.; Gilbert, T.W. Extracellular matrix as a biological scaffold material: Structure and function. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, G.S.; Keane, T.J.; Badylak, S.F. The extracellular matrix of the gastrointestinal tract: A regenerative medicine platform. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crapo, P.M.; Gilbert, T.W.; Badylak, S.F. An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Callanan, A. Comparison of methods for whole-organ decellularization in tissue engineering of bioartificial organs. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sitthisang, S.; Leong, M.F.; Chian, K.S. Perfusion decellularization of porcine esophagus: Study of two processing factors affecting the folded mucosal structure of the esophageal scaffold. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021, 109, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Depeursinge, C.; Popescu, G. Quantitative phase imaging in biomedicine. Nat. Photonics 2018, 12, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Fang-Yen, C.; Badizadegan, K.; Oh, S.; Lue, N.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Tomographic phase microscopy. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastl, L.; Isbach, M.; Dirksen, D.; Schnekenburger, J.; Kemper, B. Quantitative phase imaging for cell culture quality control. Cytom. Part A 2017, 91, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eldridge, W.J.; Sheinfeld, A.; Rinehart, M.T.; Wax, A. Imaging deformation of adherent cells due to shear stress using quantitative phase imaging. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.; Jang, J.; Park, Y. Dynamic spectroscopic phase microscopy for quantifying hemoglobin concentration and dynamic membrane fluctuation in red blood cells. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 9673–9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.C.; Pagani, R.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Peña, J.; Rámila, A.; Izquierdo, I.; Portolés, M.T. In vitro biocompatibility assessment of poly(ε-caprolactone) films using L929 mouse fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5603–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, Y.; Gong, D.; Xia, C.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z. Efficient decellularization for bovine pericardium with extracellular matrix preservation and good biocompatibility. Interact. Cardiovascular Thorac. Surg. 2018, 26, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, G.; Hou, J.; Liu, R.; Lu, Y.; Liu, C. Spontaneous generation of germline characteristics in mouse fibrosarcoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetkish, S.; Kajbafzadeh, A.M.; Sabetkish, N.; Khorramirouz, R.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Seyedian, S.L.; Pasalar, P.; Orangian, S.; Beigi, R.S.; Aryan, Z.; et al. Whole-organ tissue engineering: Decellularization and recellularization of three-dimensional matrix liver scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 1498–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackbar, R.; Ainoedhofer, H.; Gugatschka, M.; Saxena, A.K. Decellularized ovine esophageal mucosa for esophageal tissue engineering. Technol. Health Care 2012, 20, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonruangkan, J.; Farrokhi, H.; Rohith, T.M.; Toh, H.T.; Mishra, A.; Sup Yoon, H.; Kwok, S.; Carney, T.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, Y.-J. Coherence-Tailored Multiwavelength High-Speed Quantitative Phase Imaging with a High Phase Stability via a Frequency Comb. Adv. Photonics Res. 2021, 2, 2000088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonruangkan, J.; Farrokhi, H.; Kwok, S.; Carney, T.; Kim, Y.-J. Fast and Sensitive Quantitative Phase Imaging Using a Frequency Comb. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, San Jose, CA, USA, 5–10 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Park, Y. Quantitative phase imaging unit. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 3630–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.; Bhaduri, B.; Wang, R.; Zhu, R.; Popescu, G. Chapter 3—Quantitative Phase Imaging. In Progress in Optics; Wolf, E., Ed.; Elsevier: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 57, pp. 133–217. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A.; Werner, C.L. Satellite radar interferometry: Two-dimensional phase unwrapping. Radio Sci. 1988, 23, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haines, T.H. Water transport across biological membranes. FEBS Lett. 1994, 346, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groulx, N.; Boudreault, F.; Orlov, S.N.; Grygorczyk, R. Membrane Reserves and Hypotonic Cell Swelling. J. Membr. Biol. 2006, 214, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sitthisang, S.; Boonruangkan, J.; Leong, M.F.; Chian, K.S.; Kim, Y.-J. Quantitative Phase Imaging to Study the Effect of Sodium Dodecyl Surfactant on Adherent L929 Fibroblasts on Tissue Culture Plates. Photonics 2021, 8, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8110508
Sitthisang S, Boonruangkan J, Leong MF, Chian KS, Kim Y-J. Quantitative Phase Imaging to Study the Effect of Sodium Dodecyl Surfactant on Adherent L929 Fibroblasts on Tissue Culture Plates. Photonics. 2021; 8(11):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8110508
Chicago/Turabian StyleSitthisang, Sonthikan, Jeeranan Boonruangkan, Meng Fatt Leong, Kerm Sin Chian, and Young-Jin Kim. 2021. "Quantitative Phase Imaging to Study the Effect of Sodium Dodecyl Surfactant on Adherent L929 Fibroblasts on Tissue Culture Plates" Photonics 8, no. 11: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8110508
APA StyleSitthisang, S., Boonruangkan, J., Leong, M. F., Chian, K. S., & Kim, Y.-J. (2021). Quantitative Phase Imaging to Study the Effect of Sodium Dodecyl Surfactant on Adherent L929 Fibroblasts on Tissue Culture Plates. Photonics, 8(11), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8110508





