XL-SIM: Extending Superresolution into Deeper Layers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
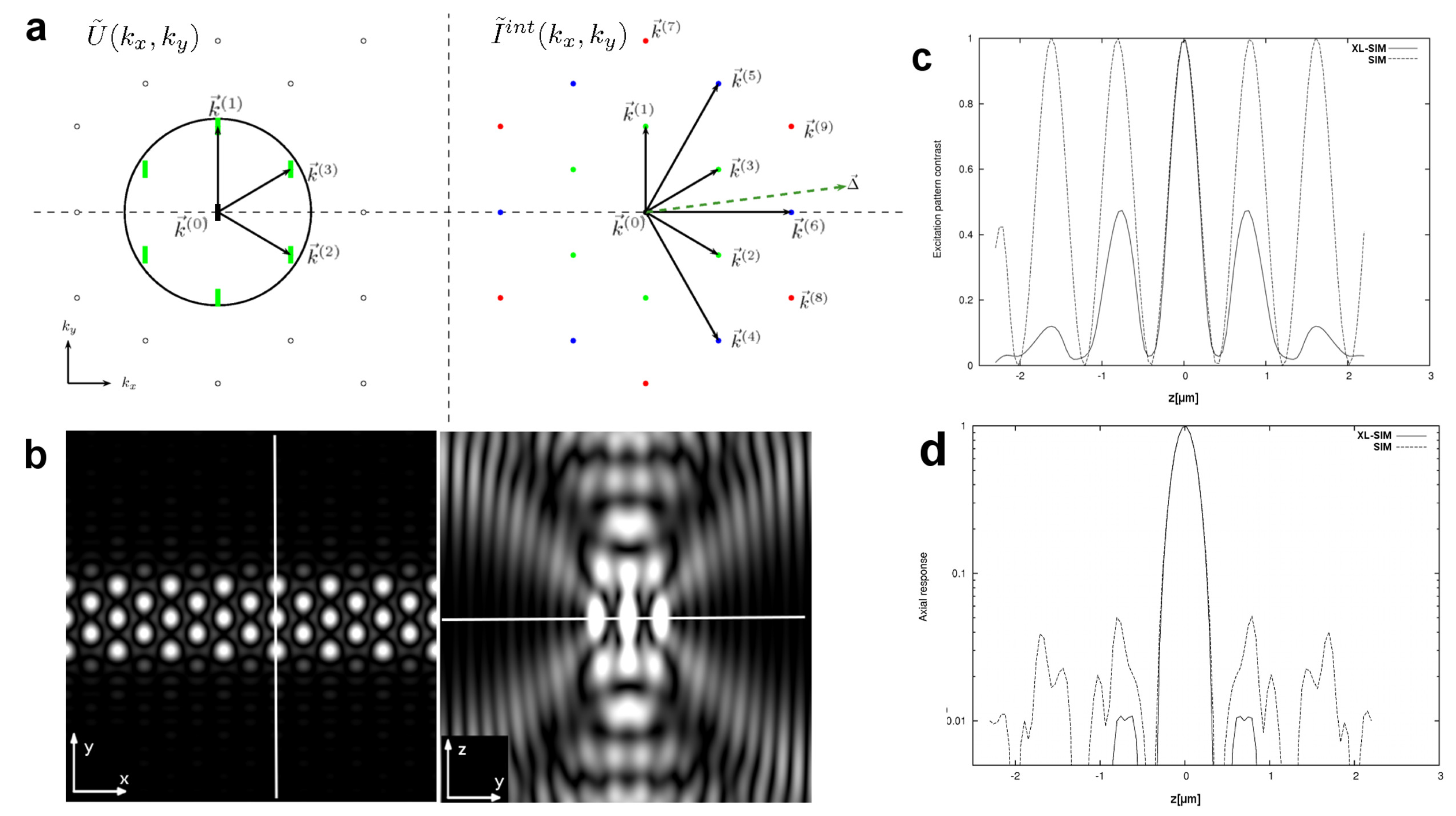
2.1. Theory
Hexagonal SIM
2.2. Resolution Doubling by XL-SIM
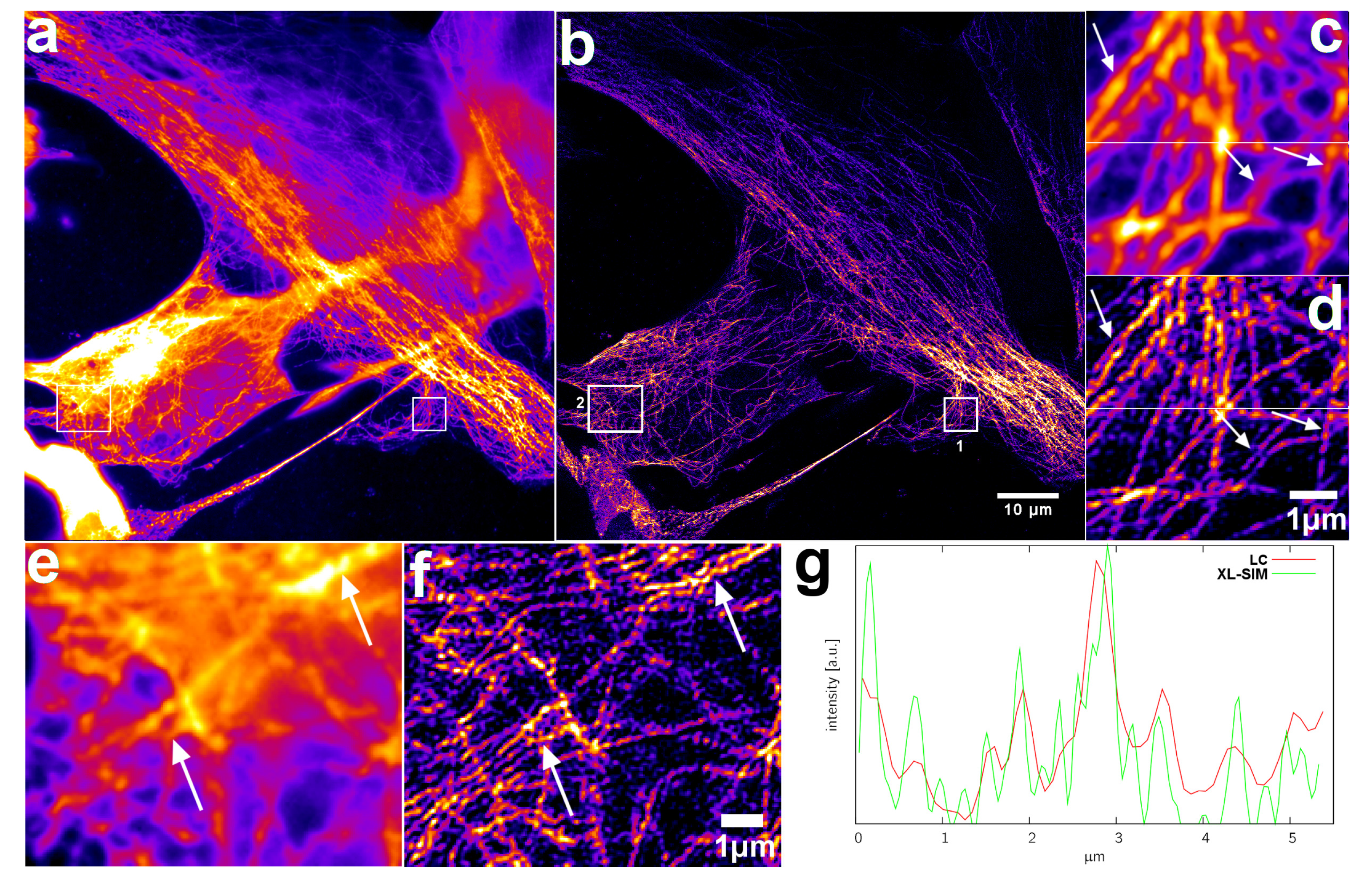
2.3. SIM Image Reconstruction
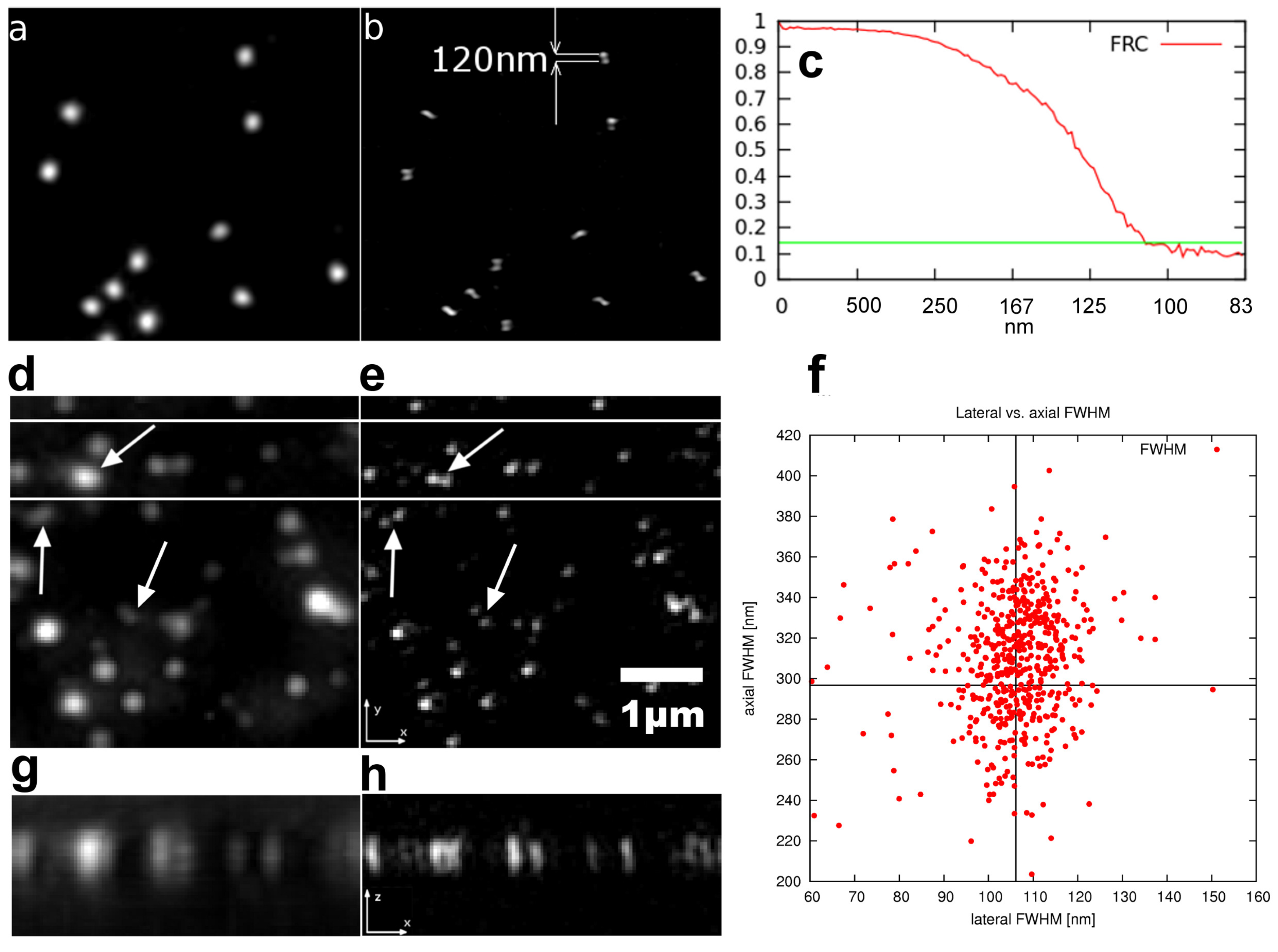
2.4. Quantitative Resolution Measurement
2.5. XL-SIM with Thick Samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
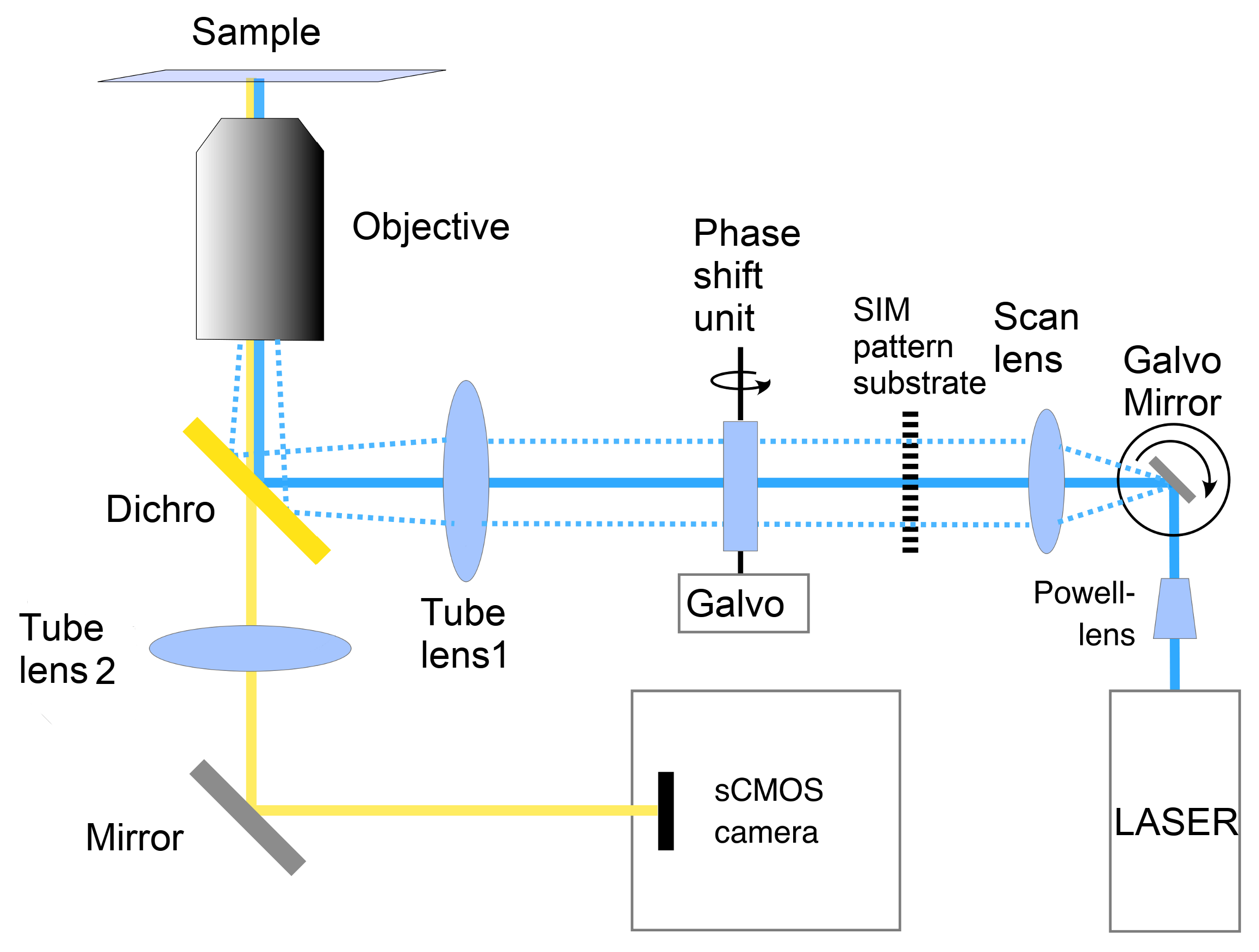
4.1. Fluorescence Excitation
4.2. Microscope Platform
4.3. Data Processing
4.4. Microscopic Samples
4.4.1. Nanorulers
4.4.2. Fluorescent Microspheres
4.4.3. Tubulin Sample
4.4.4. Mouse Kidney Sample
4.4.5. Thin Fluorescent Layers
4.5. Adjustment of Shift Angles and Calibration
4.6. Parameter Fitting in SIM Processing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| sCMOS | scientific Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor |
| OTF | optical transfer function |
| PSF | point spread function |
| WF | Wide Field (Microscopy) |
| SIM | Structured Illumination Microscopy |
| L-SIM | Lineconfocal SIM |
| X-SIM | Hexagonal SIM |
| XL-SIM | Hexagonal Lineconfocal SIM |
| S/N | Signal-to-noise Ratio |
| LC | Line-confocal |
| FRC | Fourier Ring Correlation |
| DAPI | -Diamidin-2-phenylindol |
| WGA | Wheat Germ Agglutinin |
| PALM | Photoactivated Localization Microscopy |
| STORM | Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy |
| STED | Stimulated Emission Depletion |
References
- Conchello, J.A.; Lichtman, J.W. Optical sectioning microscopy. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neil, M.A.; Juskaitis, R.; Wilson, T. Method of obtaining optical sectioning by using structured light in a conventional microscope. Opt. Lett. 1997, 22, 1905–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neil, M.A.; Squire, A.; Juskaitis, R.; Bastiaens, P.I.; Wilson, T. Wide-field optically sectioning fluorescence microscopy with laser illumination. J. Microsc. 2000, 197, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakenhoff, G.J.; Wurpel, G.W.H.; Jalink, K.; Oomen, L.; Brocks, L.; Zwier, J.M. Characterization of sectioning fluorescence microscopy with thin uniform fluorescent layers: Sectioned Imaging Property or SIPcharts. J. Microsc. 2004, 219, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, A. Quantitation Strategies in Optically Sectioning Fluorescence Microscopy. Ph.D. Thesis, Fakultät für Biologie, Georg August Universität Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, T. Optical sectioning in fluorescence microscopy. J. Microsc. 2011, 242, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukosz, W.; Marchand, M. Optischen Abbildung unter Überschreitung der Beugungsbedingten Auflösungsgrenze. Opt. Acta Int. J. Opt. 1963, 10, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukosz, W. Optical Systems with Resolving Powers Exceeding the Classical Limit. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1966, 56, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintzmann, R.; Cremer, C. Laterally modulated excitation microscopy: Improvement of resolution by using a diffraction grating. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, M.G. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J. Microsc. 2000, 198, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betzig, E.; Patterson, G.H.; Sougrat, R.; Lindwasser, O.W.; Olenych, S.; Bonifacino, J.S.; Davidson, M.W.; Lippincott-schwartz, J.; Hess, H.F. Imaging Intracellular Fluorescent Proteins at Nanometer Resolution. Science 2006, 313, 1642–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rust, M.J.; Bates, M.; Zhuang, X. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hell, S.W. Toward fluorescence nanoscopy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Shao, L.; Chen, B.C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Moses, B.; Milkie, D.E.; Beach, J.R.; Hammer, J.A.I.; Pasham, M.; et al. Extended-resolution structured illumination imaging of endocytic and cytoskeletal dynamics. Science 2015, 349, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Kner, P.; Rego, E.H.; Gustafsson, M.G.L. Super-resolution 3D microscopy of live whole cells using structured illumination. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 1044–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Betzig, E. Response to Comment on “Extended-resolution structured illumination imaging of endocytic and cytoskeletal dynamics”. Science 2016, 352, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kner, P.; Chhun, B.B.; Griffis, E.R.; Winoto, L.; Gustafsson, M.G.L. Super-resolution video microscopy of live cells by structured illumination. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, N.; Gao, L.; Tkaczyk, T.S. Quantitative sectioning and noise analysis for structured illumination microscopy. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, S. OMX-A Novel High Speed and High Resolution Microscope and its Application to Nuclear and Chromosomal Structure Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Humboldt-Universitat zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, M.G.L.; Agard, D.A.; Sedat, J.W. Doubling the lateral resolution of wide-field fluorescence microscopy using structured illumination. Proc. SPIE 2000, 3919, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, M.G.L.; Shao, L.; Carlton, P.M.; Wang, C.J.R.; Golubovskaya, I.N.; Cande, W.Z.; Agard, D.A.; Sedat, J.W. Three-Dimensional Resolution Doubling in Wide-Field Fluorescence Microscopy by Structured Illumination. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 4957–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandula, O.; Kielhorn, M.; Wicker, K.; Krampert, G.; Kleppe, I.; Heintzmann, R. Line scan–structured illumination microscopy super-resolution imaging in thick fluorescent samples. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 24167–24174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schropp, M.; Uhl, R. Two-dimensional structured illumination microscopy. J. Microsc. 2014, 256, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohn, J.T. Super-Resolution Fluorescence Microscopy by Structured Light Illumination. Ph.D. Thesis, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Heintzmann, R. Saturated patterned excitation microscopy with two-dimensional excitation patterns. Micron 2003, 34, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Holleran, K.; Shaw, M. Polarization effects on contrast in structured illumination microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 4603–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shroff, S.A.; Fienup, J.R.; Williams, D.R. OTF compensation in structured illumination super resolution images. Proc. SPIE 2008, 7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintzmann, R. Structured Illumination Methods. In Handbook of Confocal Microscopy; Springer Science + Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Chapter 13; pp. 265–279. [Google Scholar]
- Righolt, C.H.; Slotman, J.A.; Young, I.T.; Vliet, L.J.V.; Stallinga, S. Image filtering in structured illumination microscopy using the Lukosz bound. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, W.; Baumeister, W. The correlation averaging of a regularly arranged bacterial cell envelope protein. J. Microsc. 1982, 127, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, K.H.; Lemke, E.A.; Beck, M. Fourier ring correlation as a resolution criterion for super-resolution microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 2013, 183, 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuizen, R.P.J.; Lidke, K.A.; Bates, M.; Puig, D.L.; Stallinga, S.; Rieger, B. Measuring image resolution in optical nanoscopy. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agard, D.A.; Hiraoka, Y.; Shaw, P.; Sedat, J.W. Fluorescence microscopy in three dimensions. Methods Cell Biol. 1989, 30, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schermelleh, L.; Carlton, P.M.; Haase, S.; Shao, L.; Winoto, L.; Kner, P.; Burke, B.; Cardoso, M.C.; Agard, D.A.; Gustafsson, M.G.L.; et al. Subdiffraction Multicolor Imaging of the Nuclear Periphery with 3D Structured Illumination Microscopy. Science 2008, 320, 1332–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrington, W.; Lynch, R.; Moore, E.; Isenberg, G.; Fogarty, K.E.; Fay, F. Super-resolution three-dimensional images of fluorescence in cells with minimal light exposure. Science 1995, 268, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrova, N.; Rieger, B.; Stallinga, S. Deconvolution methods for structured illumination microscopy. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 2016, 33, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmied, J. Testing and Pushing the Limits of Super-Resolution Microscopy. Opt. & Photonik 2016, 11, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Smeets, D.; Markaki, Y.; Schmid, V.J.; Kraus, F.; Tattermusch, A.; Cerase, A.; Sterr, M.; Fiedler, S.; Demmerle, J.; Popken, J.; et al. Three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy of the inactive X chromosome territory reveals a collapse of its active nuclear compartment harboring distinct Xist RNA foci. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2014, 7, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schropp, M.; Seebacher, C.; Uhl, R. XL-SIM: Extending Superresolution into Deeper Layers. Photonics 2017, 4, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics4020033
Schropp M, Seebacher C, Uhl R. XL-SIM: Extending Superresolution into Deeper Layers. Photonics. 2017; 4(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics4020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchropp, Martin, Christian Seebacher, and Rainer Uhl. 2017. "XL-SIM: Extending Superresolution into Deeper Layers" Photonics 4, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics4020033
APA StyleSchropp, M., Seebacher, C., & Uhl, R. (2017). XL-SIM: Extending Superresolution into Deeper Layers. Photonics, 4(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics4020033



