Abstract
Extreme ultraviolet (EUV) photomask inspection is a critical step in semiconductor manufacturing, requiring high-resolution, high-throughput solutions to detect nanometer-scale defects. Traditional actinic imaging systems relying on complex optics have a high cost of ownership and require frequent upgrades. An alternative is lensless imaging techniques based on ptychography, which offer high-fidelity reconstruction but suffer from slow throughput and high data demands. In particular, the ptychographic standard solver—the iterative Difference Map (DifMap) algorithm—requires many measurements and iterations to converge. We propose Ptycho-LDM, a hybrid framework integrating DifMap with a conditional Latent Diffusion Model for rapid and accurate phase retrieval. Ptycho-LDM alleviates high data acquisition demand by leveraging data-driven priors while offering improved computational efficiency. Our method performs coarse object retrieval using a resource-constrained reconstruction from DifMap and refines the result using a learned prior over photomask patterns. This prior enables high-fidelity reconstructions even in measurement-limited regimes where DifMap alone fails to converge. Experiments on actinic patterned mask inspection (APMI) show that Ptycho-LDM recovers fine structure and defect details with far fewer probe positions, surpassing the DifMap in accuracy and speed. Furthermore, evaluations on both noisy synthetic data and real APMI measurements confirm the robustness and effectiveness of Ptycho-LDM across practical scenarios. By combining generative modeling with physics-based constraints, Ptycho-LDM offers a promising scalable, high-throughput solution for next-generation photomask inspection.
1. Introduction
For several decades, the production of integrated circuit devices has been driven by Moore’s Law, which predicts an exponential increase in the number of transistors per unit area. The dimensional scaling required by this trend has been made possible by continuous advancements in the photolithography process, which has long been the workhorse of the semiconductor manufacturing industry.
Since 2019, extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light has been used in the lithography process for the production of modern semiconductor devices [1]. In EUV lithography, a specially designed reflective photomask is illuminated with an EUV light at a wavelength of 13.5 nm, and the pattern etched on the mask is projected onto a silicon wafer coated with a photosensitive film. Conventional EUV photomasks consist of a glass substrate coated with a multilayer mirror that reflects strongly at 13.5 nm. An absorber layer is deposited on top of the mirror and etched to create the pattern that will be printed on the wafer.
Accurate metrology is essential to ensure that the pattern on the mask is free of defects that could be replicated across thousands of wafers [2,3]. Actinic mask inspection and review are two processes used to detect, locate, and characterize EUV mask defects, and are critical for maintaining the required throughput of the EUV lithography process. An effective tool for mask defect inspection must offer high throughput, high resolution, and the ability to operate at 13.5 nm, since some defects are wavelength-specific [4]. The conventional approach to these processes involves the use of complex imaging optics, which have a high cost of ownership and must be upgraded to meet the resolution demands of current technology nodes [5,6,7,8]. For these reasons, lensless imaging for semiconductor device metrology has recently begun to attract attention. In particular, ptychography—a robust scanning phase retrieval (PR) method—removes the need for imaging optics and therefore its implementation is in principle cost-effective, simpler, and less cumbersome to scale-up than direct imaging methods [9,10,11]. Despite these advantages, other challenges arise when considering this solution for actinic mask inspection. For instance, ptychography exploits redundancy in the data to cope with the missing phase in order to reconstruct a high–fidelity image of the sample. In the ptychography framework, this translates to an overlap among successive probe positions of at least 60–70% [12]. Given that the illumination on mask at the extreme ultraviolet (EUV) wavelengths has a main lobe in the mm size range and that the mask active area is in the mm range, a straightforward implementation of ptychography leads to lengthy data acquisition times and demanding data storage requirements. Additionally, the iterative nature of phase retrieval algorithms leads to a lengthy time for target reconstruction that can be limiting for the real-world application of ptychography for EUV mask inspection.
In recent years, the research community has shown considerable interest in ptychography implementations leveraging deep neural networks (DNNs) [13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. This approach is particularly appealing due to its potential applications in EUV mask imaging and inspection. Specifically, following the training phase, DNN-based predictions are typically computationally efficient, addressing the demand for an EUV actinic mask inspection tool. Such tools can circumvent costly and complex solutions while maintaining competitiveness in imaging speed, resolution, and field-of-view.
The primary challenge in this implementation arises from the requirement for extremely accurate DNN inference: failing to detect a printable defect during the DNN prediction process could lead to catastrophic device failures in the affected regions of the mask. In this paper, we directly tackle this challenge, presenting a method that achieves the significantly faster and more accurate phase retrieval of an EUV mask layout using a DNN.
Deep learning has significantly advanced the problem of phase retrieval, with solutions broadly categorized into supervised and unsupervised methods. Deep supervised learning methods [13,14,15,16,17] leverage labeled datasets to train models that achieve high reconstruction accuracy and robustness. These approaches often integrate domain-specific priors, such as unrolling iterative algorithms into neural networks or using hybrid architectures like vision transformers to enhance interpretability and adaptability. However, their reliance on large, labeled datasets can limit generalization across diverse imaging scenarios. Deep unsupervised learning methods [18,19], circumvent the need for labeled data by embedding imaging priors and physical constraints directly into the reconstruction process. These methods, such as self-calibrating networks and physics-informed architectures, enable flexibility and independence from extensive training datasets, making them suitable for data-scarce applications. Despite their advantages, unsupervised methods may struggle to achieve the same level of precision and robustness as supervised approaches.
Recent advances in solving inverse problems have leveraged diffusion models, showcasing their efficacy in generating high-quality image reconstructions across various applications. Early works [20,21,22] employed diffusion posterior sampling (DPS) with unconditional diffusion models, iteratively sampling from a learned unconditional distribution while aligning with measurement constraints. The extensions of this paradigm [23,24] introduced optimization-based frameworks and variational perspectives to improve robustness and efficiency in noisy and nonlinear settings. To further enhance efficiency, recent methods [25,26] incorporated LDM with tailored sampling schemes, such as hard data consistency and second-order Tweedie samplers, to address the limitations of pixel-space diffusion models. Our approach leverages likelihood-based generative models, specifically introducing a novel deep learning-based phase retrieval framework grounded in LDM [27], a specialized variant of Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs) [28]. We refer to our proposed framework as Ptycho-LDM. LDM achieves faster training and inference by performing diffusion forward and backward steps in a low-dimensional latent space, which is computationally more efficient compared to the high-dimensional pixel space. Given that accelerating the reconstruction process is one of the key objectives of our work, we propose leveraging the generative capabilities of LDMs for ptychographic phase retrieval.
Another primary objective of our work is to accurately recover the phase and complex amplitude of EUV photomasks from the measured diffraction patterns. As these measurements reside in the Fourier domain, directly applying convolutional [29] or Transformer [30] layers to the diffraction patterns fails to capture meaningful representations for the phase retrieval task. This limitation arises because convolutional and Transformer layers are inherently designed to exploit local and global features in the spatial domain, whereas diffraction patterns lack a (local) spatial structure in the Fourier domain. Although prior works [17,19] apply convolutional- or Transformer-based architectures directly to diffraction patterns for phase retrieval, their effectiveness in the context of photomask inspection for semiconductor manufacturing remains unclear from their reported experimental results. Since our main envisioned application is the detection of nanoscale defects on photomasks—critical for defect-free chip fabrication—we refrain from relying solely on deep networks to recover phase information. Instead, we leverage a physics-informed initialization by incorporating the ptychographic iterative algorithm to generate an initial estimate of the photomask. This hybrid approach yields promising reconstruction quality, particularly in the defective regions, demonstrating its suitability for high-precision inspection tasks.
Standard ptychographic algorithms, such as Difference Map [10], effectively reconstructs spatial structures in the real domain from diffraction patterns in the Fourier domain. However, achieving accurate phase retrieval with these algorithms requires a large number of iterations (K) and probe positions (J), resulting in significant computational overhead (Figure 1a). This makes the reconstruction process slow and inefficient.
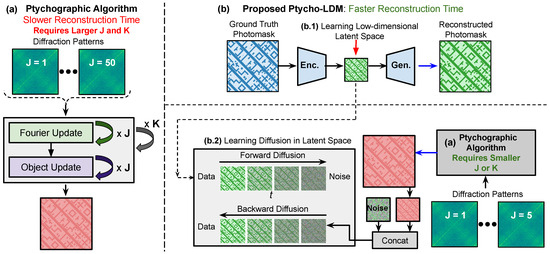
Figure 1.
(a) Existing ptychographic algorithms, such as Difference Map [10], require significantly longer reconstruction times due to two primary computational bottlenecks: the number of iterations (K) needed for Fourier and complex object updates, and the number of probe positions (J) required to acquire a sufficient number of diffraction patterns for high-quality phase retrieval. (b) In contrast, our proposed Ptycho-LDM achieves significantly faster reconstruction by leveraging the state-of-the-art generative capabilities and faster sampling of conditional Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs), seamlessly integrated with a physics-based ptychographic iterative approach. Most importantly, the proposed Ptycho-LDM framework requires significantly fewer probe positions, enabling much faster and high quality image reconstruction.
Contributions. Our work makes the following key contributions:
- We propose Ptycho-LDM (Section 2.4), a novel framework for the efficient and accurate phase retrieval of EUV photomasks, which integrates a physics-informed ptychographic algorithm with a conditional LDM. Unlike existing approaches to phase retrieval using LDMs, our framework does not require designing additional diffusion posterior sampling techniques, which can introduce significant computational overhead and slow down the reconstruction process. By leveraging a conditional LDM, our method achieves high-quality phase retrieval while maintaining computational efficiency (Figure 1b).The proposed framework employs a hybrid methodology that combines the strengths of classical ptychographic algorithms and deep generative modeling. Specifically, we first perform a resource-constrained (i.e., fewer probe positions or fewer iterations) ptychographic reconstruction (Section 2.1) to recover the coarse spatial structure from diffraction patterns residing in the Fourier domain, followed by a refinement step using LDMs to enhance the fidelity of the reconstruction. This hybrid approach significantly reduces the number of required ptychographic iterations or probe positions, accelerating the overall phase retrieval process.
- We introduce a novel synthetic dataset, LAMP (Lensless Actinic Metrology for EUV Photomasks) (Section 2.2), tailored for photomask phase retrieval and defect inspection. This dataset is designed to support the training and evaluation of the proposed model.
- Our experimental results (Section 3.2) demonstrate that Ptycho-LDM achieves a superior reconstruction speed compared to traditional ptychographic method—Difference Map [10] while maintaining the quality of phase reconstruction as robust as Difference Map (with a PSNR > 40 dB). We provide a systematic study showing that a generative diffusion prior (Ptycho-LDM) improves the reconstruction quality, not only under simulated noise, but also generalizes effectively to real experimental data. Furthermore, we qualitatively validate Ptycho-LDM on nanometer-scale photomask inspection, showcasing its potential for accurate and fine-grained defect detection.Ptycho-LDM’s efficient utilization of low-dimensional latent spaces enables computationally efficient training and inference, making it particularly suitable for real-world applications in EUV mask imaging and inspection.
This work not only demonstrates the potential of integrating likelihood-based generative models with physics-informed iterative methods, but also sets a new benchmark for speed and precision in EUV mask inspection and imaging. Moreover, the proposed Ptycho-LDM framework is not restricted to EUV mask inspection and can be readily adapted to other ptychographic reconstruction tasks, such as in ptycho-tomography. The source code and dataset will be made publicly available upon acceptance of the manuscript at https://github.com/susaha/ptycho-ldm (accessed on 1 September 2025).
2. Method
In this section, we present the proposed method for ptychographic reconstruction using conditional latent diffusion models (LDMs), which offer fast and accurate phase retrieval and object (i.e., complex-valued photomask) reconstruction. We begin by introducing the problem setup for phase retrieval in ptychography, followed by a discussion of the ptychography algorithm (Section 2.1) and the proposed data generation pipeline (Section 2.2). Next, we provide a brief overview of LDM (Section 2.3), the foundation of our approach. Finally, we present the proposed approach, baselines, and implementation details (Section 2.4).
2.1. Phase Retrieval in Ptychography
Problem setup. In ptychography, we have a complex-valued object , and a complex-valued probe (see Figure 2). In this work, we assume that the object is unknown, while the probe is known. Both the object and the probe have associated phase and magnitude components. We illuminate the object by shifting the probe to each j-th location. In our case, the probe follows a Fermat spiral path across the object, generating multiple exit waves and diffraction patterns (measured Fourier amplitudes) corresponding to different probe positions, indexed by j. The variable is a two-dimensional position vector in the object domain and represents the spatial coordinates in the physical space where the object exists; is a two-dimensional position vector in the Fourier (or reciprocal) domain and represents the spatial frequency coordinates. denotes the Fourier transform of . These diffraction patterns, obtained at various probe positions, serve as our measurements. In a real setup, these patterns are captured by a detector, which records the amplitude of the impinging wave while the phase information is lost. The phase encodes crucial information about the position and alignment of structures within the object, and it is needed for a precise reconstruction of the imaged object. The goal is then to recover the missing phase from the measured diffraction patterns. With prior knowledge about the probe and the measurement locations, the object can be reconstructed. If the probe positions are chosen such that there is sufficient overlap between adjacent positions (typically 60% to 85% overlap), each update at one position contributes to the reconstruction at neighboring positions, making the recovery of the missing phase possible [12]. These interconnections make ptychographic reconstruction highly robust.
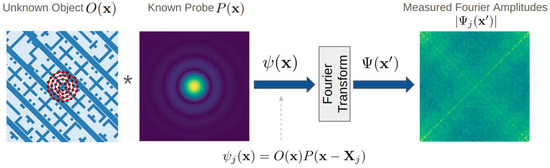
Figure 2.
Ptychography problem setup: we have multiple exit waves obtained by illuminating an unknown complex-valued object with a known complex-valued probe that shifts to different positions following a Fermat spiral path across the object. The Fermat spiral trajectory and corresponding probe positions are overlaid on the object as a red line and black dots, respectively. For each exit wave, a detector measures the Fourier amplitude .
Ptychographic Phase Retrieval Algorithm. For a comprehensive study of ptychographic algorithms, please refer to [31]. Classical ptychographic reconstruction algorithms are iterative, where the phase of the complex-valued object is initialized at random. Through multiple iterations of the Error Reduction (ER) algorithm [31], the phase is reconstructed from a set of diffraction patterns, a known probe and its corresponding positions. In this work, we use the Difference Map algorithm [10] as a baseline (Section 2.4). The algorithm is run for multiple iterations to obtain an accurate estimate of the object’s phase. We implement the Difference Map algorithm as described in Algorithms 1 and 2.
| Algorithm 1 Difference map ptychographic reconstruction. |
|
| Algorithm 2 Utility routines for Difference Map reconstruction. |
|
Algorithm 1 contains the core DifferenceMap function. At the k-th iteration, it re-computes a fresh object estimate by back-projecting the exit waves with the conjugate probe and normalizing with the scaling factor and regularization parameter inside support region . It then generates trial exit waves by multiplying the current object estimate with the probe, replaces their amplitudes in the Fourier domain with the measured data , and updates the exit-wave stack via the Difference Map update:
as shown in Algorithm 1, Line 14. After K iterations, the routine returns , the final complex-valued object. Together, the two blocks reproduce the forward model and the global object update, while isolating all bookkeeping in reusable helper functions—exactly mirroring the structure of our implementation.
Algorithm 2 groups three utility routines. BuildProbeSupport raster-scans the binary probe through every rectangular RoIj and returns the union mask . ComputeScale then accumulates the squared probe magnitudes over the same RoIs to form the pixel-wise weight map . InitPhase draws an i.i.d. uniform phase field, combines it with the measured amplitudes , and applies an inverse FFT to produce the initial exit waves .
2.2. Proposed Data Generation Pipeline for Ptychography
In this section, we describe our proposed synthetic data generation pipeline, which is used for the training and validation of the proposed approach (Section 2.4). Our synthetic data generation pipeline consists of two modules. The first module generates graphic data system (GDS) files which contain a defect-free geometry of a logic-like field on an EUV mask and a respective defective counterpart, obtained by including programmed defects (intrusions and extrusion) over the defect–free object. Each GDS is generated using the Klayout software [32] in conjunction with Python 3.10.11. The dimensions of each field are about 27 m × 27 m, and each mask contains 5 primitive shapes—Jog, Stair, Cross, Square, Gate as shown in Figure 3—arranged in random positions per field and, in some cases, powerlines. The critical dimensions of each shape are 200 nm, whereas the powerlines are 400 nm wide. As already mentioned, a defective field is associated with a defect-free one by including intrusions or extrusions/pin-dot defects in the mask field. The size and location of these defects are randomly selected, with defect sizes corresponding to values ranging between 35 nm and 200 nm for all types of defects. The simulated photomasks are complex-valued objects, with the phase varying in the range and the magnitude ranging from .
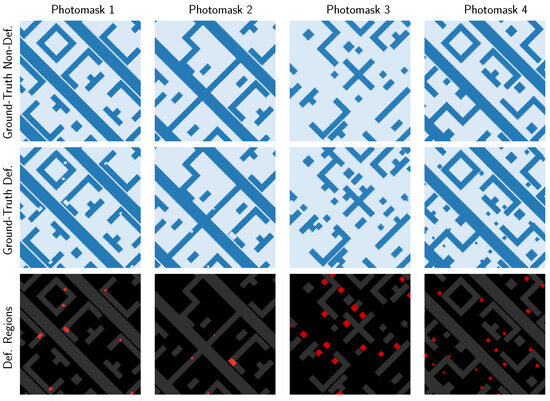
Figure 3.
Visualization of synthetic photomask samples with and without defects generated by the proposed data generation pipeline. The small primitive shapes are shared across all the photomasks, and only their locations are randomly shuffled. The defects are generated by randomly selecting the location and size of the defects. The first row shows the ground-truth non-defective photomasks, while the second row presents their corresponding defective versions. The third row highlights the defective regions using red pixel overlays. Each column corresponds to one photomask instance: the first two columns represent intrusion defects, and the last two columns represent extrusion defects. The defect size ranges between 35 nm and 200 nm both for the intrusions and the extrusions defect types.
Note that, while our proposed data generation pipeline provides paired photomask samples (defective and non-defective), the proposed Ptycho-LDM model does not rely on such paired data for training or validation. The method is fully compatible with unpaired datasets, provided that the training data includes both defective and non-defective layouts. The generation of paired samples primarily serves to support downstream tasks, such as defect inspection (see Section 3).
Once the GDS files are created, they are processed by the second data generation module. For each GDS, this module loads pairs of fields (defective and defect–free) and subsequently generates an approximation of the reflection function for the loaded objects. This approximation is obtained using the transfer matrix method (TMM) [33] and serves to give us an approximation for the ptychography object without resorting to computationally expensive methods. Therefore, overall, the data generation module creates complex photomask pairs, where each pair is comprised by a defect–free logic like the EUV mask field together with its defective counterpart.
Our proposed photomask phase retrieval and defect inspection dataset, LAMP (Lensless Actinic Metrology for EUV Photomasks), consists of 10,200 synthetically generated photomask pairs, each representing a uniquely designed photomask layout (both defect-free and defective) for chip manufacturing.
2.3. Learning Photomask Distribution Using Likelihood-Based Generative Models
In the field of deep generative modeling, Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs) [28] have demonstrated impressive results in terms of both sample quality and mode coverage [34]. In this work, we utilize a variant of DDPMs known as Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs). We begin with a brief overview of DDPMs before delving into the details of LDMs.
DDPMs are probabilistic models designed to approximate complex real-world data distributions that are unknown. The core idea behind DDPMs is to train a neural network to learn a data distribution that closely mimics the complex, unknown distribution of real-world data. DDPMs consist of two primary steps: (1) the forward diffusion process and (2) the backward diffusion process. In the forward diffusion process, random noise is gradually added to the ground truth data sample from some unknown data distribution . In T steps, the forward diffusion process converts the data sample to noise which is assumed to be from a normal distribution. The forward diffusion process is a non-homogeneous Markov chain, that implies that the corrupted data sample can be computed using the previous step’s sample , thus
The noise added to the data signal at each step t is defined by a variance schedule , with t uniformly sampled from . In the backward diffusion process, a neural network parameterized by , is trained to predict the noise from the corrupted data sample . By removing the predicted noise from , we can compute . Through this process, we can progressively eliminate the noise at every step (T to 1) from the corrupted data sample and obtain the generated samples . These generated samples follow a data distribution , which has been learned by the diffusion model and closely resembles the original data distribution . Thus, the generative model learns the backward diffusion process such that it can generate data sample from noise :
for , and , where , . A deep neural network such as U-Net could be used to implement with the following objective:
Figure 4 illustrates the forward and backward diffusion processes with a visual diagram.
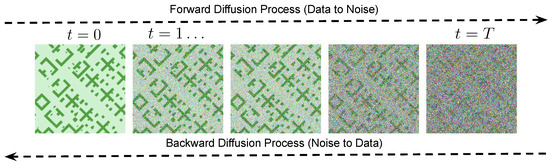
Figure 4.
Forward and backward diffusion processes. The forward diffusion process progressively adds noise to the data at each step t, reaching full noise after T steps. This process is non-trainable and fixed. The backward diffusion process, on the other hand, is trainable and implemented using a U-Net. It learns to denoise the data through multiple denoising steps, ultimately recovering the original data.
Denoising Diffusion at Latent Space. Although DDPMs have demonstrated promising generative capabilities, their training and evaluation require repeated gradient computations in the high-dimensional image space, making the process both computationally demanding and time-consuming. To address this, Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) [27] were proposed to reduce the computational demands of DDPMs while still leveraging the generative capabilities of denoising diffusion models. LDMs perform diffusion forward and backward steps in a lower-dimensional latent space learned by an autoencoder, making both training and sampling more computationally efficient and significantly faster compared to DDPMs, which operate in high-dimensional data space. We only need to train the auto-encoding stage once, after which the learned latent representation can be used to train multiple LDMs for completely different tasks. This approach enables the exploration of a wide range of LDMs for various applications. In our work, we only train the autoencoder once. LDMs are highly effective at learning conditional distributions through various token-based conditioning mechanisms. In this work, we leverage the conditional image generation capabilities of LDMs.
2.4. Proposed Approach
Since DDPMs operate in high-dimensional pixel space, they require significant computation time and energy resources. In contrast, LDMs work in a lower-dimensional latent space, making them much more efficient, as sampling is performed in the latent space. LDMs learn a latent space that is perceptually equivalent to the original image space. This latent space is learned through a GAN-based autoencoder [35]. Since the dimensionality of the learned latent space is much smaller than the original image space, it significantly reduces the computational complexity.
Due to the limited availability of real photomasks, training LDMs on actual data to approximate the true data distribution is impractical. We overcome this limitation by leveraging our generated dataset LAMP. We propose framing the ptychography reconstruction as a conditional image generation problem. In this approach, we train an LDM to generate the phase of a photomask conditioned on its noisy phase version. The noisy photomasks are produced using the Difference Map method [10] as described in Section 2.1. We use the Difference Map reconstruction as an initial guess to condition the LDM. In our experiments, we investigate how performance varies with different parameter settings, such as the number of Difference Map iterations and probe positions.
Our Ptycho-LDM framework comprises two main components: (1) a GAN-based autoencoder that learns a latent space for all photomasks in the training set, and (2) an LDM that captures the distributions of the photomasks within this latent space. Training occurs in two stages. In the first stage, the autoencoder is trained. Once the autoencoder is trained, the learned latent space is used to train the diffusion model in the second stage. Notably, the autoencoder training is a one-time process; once the latent space is established, it can be reused for training multiple diffusion models with different sets of input and conditioning images.
GAN-based autoencoder for learning photomask representation. We employ the VQGAN [35] for learning the latent representation of the photomasks. It is a GAN-based autoencoder trained for an image reconstruction task. In Figure 5a, we show an overview diagram of the VQGAN. The encoder encodes the photomask images into a latent representation , and the generator reconstructs the photomask image from the latent, i.e., . The patch-based discriminator, , is designed to distinguish between real photomask images, , and generated photomask images, , through an adversarial training process. Following [27], we apply vector quantization [36] as a regularization technique to prevent high-variance in the latent spaces. We train the VQGAN using a combination of perceptual loss and a patch-based adversarial objective to maintain good perceptual quality even at higher compression rates [35].
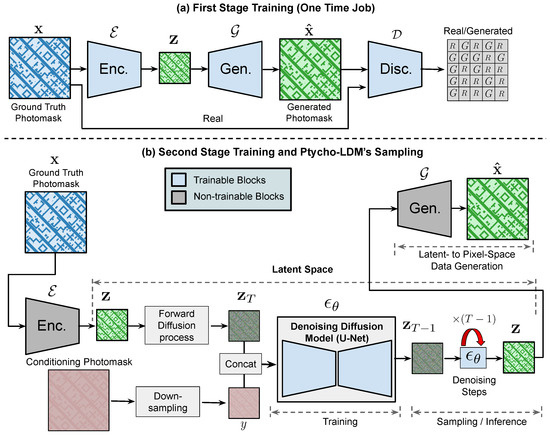
Figure 5.
Overview of the proposed ptychographic phase retrieval using conditional latent diffusion model. (a) First stage training of the VQGAN; (b) Second stage training and inference of the proposed Ptycho-LDM. During Ptycho-LDM training, the conditioning photomasks—generated using Difference Map with a reduced number of probe positions (e.g., 5)—are downsampled to match the spatial resolution of the latent feature . These downsampled masks are then concatenated with the noise vector along the channel dimension and provided as input to the diffusion model. The ground-truth photomasks are used to supervise the training process. At inference time, only the conditioning photomasks are required, which can be generated efficiently—e.g., in approximately 8 s using just 5 probe positions.
Conditional Latent Diffusion Model for Capturing Photomask Distribution. The trained VQGAN provides access to an efficient, low-dimensional latent space which is an effective photomask representation useful for LDM training. This latent space is more suitable for likelihood-based generative models compared to the high-dimensional pixel space, as it is computationally more efficient.
The LDM is trained in a second stage (Figure 5b), following the training of a VQGAN in the first stage. In the second stage, we use the pretrained encoder and generator from the VQGAN for LDM training. Notably, in the second stage, only the denoising diffusion U-Net has trainable parameters. The parameters of the VQGAN’s encoder and generator are fixed, with no backpropagation or gradient updates occurring for these parameters.
First, the photomask image is encoded into the latent space as . A forward diffusion process is applied within this latent space, resulting in the noise term . A noisy version of the complex-valued photomask, generated by a ptychographic algorithm (see Section 2.1) is downsampled to match the dimensions of the latent vector . The downsampled noisy photomask is then concatenated with , and the combined vector is passed as input to the denoising diffusion model . The model denoises the input through multiple steps (from T to 0), yielding the generated sample . Finally, the pretrained generator decodes this sampled latent vector back into pixel space, producing the generated photomask image . A deep neural network (e.g., a U-Net) is used to implement the LDM model, , with the following objective:
We use the noisy reconstructions obtained from the ptychographic phase retrieval algorithm to learn a conditional distribution of the form . This means that the LDM is trained to learn a distribution of photomasks in latent space, conditioned on the noisy photomask reconstructions. This is implemented using a conditional LDM, , paving the way for controlled photomask generation by conditioning on noisy photomasks . Figure 5b provides an overview of the conditional LDM.
Baseline method. We use Difference Map [10] (c.f. Section 2.1, Algorithms 1 and 2) as the baseline method to compare against the proposed Ptycho-LDM.
Implementation details. We adhere to the implementation details outlined in [27] for training the two stages of Ptycho-LDM, i.e., the VQGAN (first stage training) and conditional LDM (second stage training). To ensure reproducibility, we will release the code and the LAMP photomask dataset. The VQGAN and Conditional LDM were each trained for one day using 4 NVIDIA GH200 Grace Hopper Superchips on the CSCS Alps cluster [37], with a peak memory usage of 35 GB per GPU. We propose two variants of Ptycho-LDM. The first variant is trained with Difference Map conditioning inputs generated using 5 probe positions and 1000 iterations. This version is preferable for handling noisy simulated as well as real diffraction patterns, achieving an inference time of s per photomask. The second variant is trained with the Difference Map, conditioning inputs generated using 5 probe positions and 6000 iterations, and attains the best performance on simulated diffraction patterns without noise, i.e., MSE of and PSNR of dB.
For training, we employ ground truth synthetic photomask images and Difference Map generated conditioning images. The photomask images have shape , with the first and second channels corresponding to phase and magnitude values, respectively. We apply random cropping on both ground truth and conditioning photomask images with a size of during the LDM training. For VQGAN training, we apply random crop only on the ground truth training photomasks. For conditional LDM training, we use a latent feature of shape , and downsample the conditioning photomasks from to . The random crops on photomasks massively scale up the effective training dataset, enabling the models to learn more robust and diverse representations of photomask phase and complex amplitude. Moreover, the use of random cropping helps preserve high-resolution details that would otherwise be lost through resizing. At inference time, we use DDIM sampling [38] and stitch together the predictions to reconstruct the full photomask of shape , requiring only s per photomask.
The VQGAN is trained on the LAMP photomask dataset. For each combination of Difference Map iterations and probe positions, we train a separate conditional LDM model and generate a corresponding set of conditioning photomasks for all the 10,000 training examples (photomask pairs). Training multiple LDMs is essential to support the experimental analysis presented in Section 3. Since generating conditioning photomasks across multiple parameter combinations (i.e., Difference Map iterations and probe positions) for all 10 k training examples is computationally expensive, we parallelize this process across multiple compute nodes on the CSCS Alps Cluster using PyTorch 2.2.0 Distributed Data Parallel (DDP). At inference time, only the conditioning photomask needs to be computed, which takes just a few seconds. For instance, using 6000 Difference Map iterations and 5 probe positions, the generation time is approximately 8.8 s per photomask.
In our experiments, the simulated diffraction patterns are generated at a resolution of pixels. Since Ptycho-LDM is trained and evaluated on photomask image crops, the method is not limited by the overall size of the complex-valued object and can directly scale to larger fields of view (e.g., or ). The diffraction pattern resolution, however, influences the scalability of the Difference Map algorithm. To address this, we run Difference Map on GPUs, which significantly accelerates the reconstruction process and enables its use with higher-resolution diffraction data. All results reported in this paper are obtained by running the Difference Map on GPUs. To ensure a fair comparison of reconstruction time, both the Difference Map and Ptycho-LDM are evaluated under the same GPU configuration and computing setup.
3. Experiments
3.1. Experimental Setup
Dataset and evaluation metric. We train and evaluate the proposed Ptycho-LDM on our in-house LAMP dataset (see Section 2.2). Ptycho-LDM predicts both phase and magnitude, and all reported metrics are evaluated on both. For clarity and simplicity, however, we present only phase predictions in the qualitative results.
Ptychographic measurements carry a reliable signal only within the probe’s footprint, while pixels farther away are dominated by noise. To confine our quantitative metrics to this informative region, we build a data-driven support mask. We first take the probe magnitude , slide it across all J scan positions, and accumulate the result into . The term is an indicator function: it equals 1 when the pixel lies inside the j-th rectangular scan window and 0 otherwise. After normalizing by its global maximum, we apply a hard threshold and obtain the Boolean mask in Equation (5). The notation denotes the indicator function, which evaluates to 1 when the condition inside the braces is true, and 0 otherwise. This mask retains pixels where the probe magnitude is strong and suppresses areas where it fades, yielding a principled region of interest for error computation. All MSE values reported in this paper are evaluated inside . Figure 6 visualizes the mask and the corresponding evaluation region for a representative photomask.
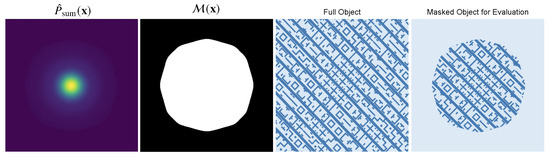
We use the mean squared error (MSE) as the evaluation metric over the support mask:
where and are the predicted and ground-truth pixel intensities at location , is the number of active mask pixels, and N is the total number of validation photomasks. The inner sum averages the squared error over the signal-bearing region selected by for each example, while the outer sum averages these errors across the entire validation set. A lower MSE therefore indicates closer agreement between the reconstruction and the ground truth within the probe-illuminated area, reflecting higher reconstruction fidelity.
To complement the masked MSE, we report the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), a widely used logarithmic metric for quantifying reconstruction fidelity. Higher PSNR values indicate better agreement between predictions and ground truth. All PSNR values are computed using , restricting the evaluation to the region defined by the support mask .
Illumination probe. In this study, we use a smooth beam for illumination (as shown in Figure 6) that closely matches the experimental setup of our RESCAN microscope at the Swiss Light Source [39]. One could argue that such a choice might be suboptimal as it has been shown in the ptychography literature that employing structured beams with broad angular spectra substantially improves the reconstruction quality [40]. However, our goal in this study is not to design an optimized experimental setup, but rather to introduce a ptychographic phase-retrieval pipeline that exploits deep generative models to learn a data-driven prior for enhanced reconstruction. As demonstrated throughout the experiments (see Section 3.2), our proposed method consistently improves the reconstruction quality regardless of the initial estimate. In our proposed pipeline, the use of a structured illumination probe would only affect the initial estimate by likely improving its quality. Arguably, one would expect this effect to propagate through our reconstruction pipeline—either by further enhancing the final reconstruction quality or by enabling additional relaxation in the data acquisition requirements to achieve a target reconstruction accuracy.
3.2. Experimental Results
In this section, we present the quantitative and qualitative evaluation results of the proposed Ptycho-LDM on the LAMP dataset. We compare its performance with Difference Map (DifMap), demonstrating that Ptycho-LDM achieves a remarkably high quality reconstruction (an MSE of ) for both the phase and complex amplitude even in highly constrained configurations, including as few as 5 probe positions or a reduced number of iterations during the initial image generation phase. Moreover, Ptycho-LDM achieves faster reconstruction times compared to the traditional Difference Map algorithm. As previously discussed, two key parameters primarily impact reconstruction quality and processing time. These two parameters are the numbers of Difference Map (a) probe positions, and (b) iterations. To achieve accurate and faster reconstructions, we first analyze the effect of these parameters on reconstruction quality.
3.2.1. Effect of Difference Map Iterations and Probe Positions on Reconstruction Quality
In this setup, we generate noisy conditioning photomask images using Difference Map, initializing the complex object with a random phase. We conduct two sets of experiments to analyze the impact of probe positions and iterations on reconstruction quality. In the first set, we vary Difference Map iterations across the range , while keeping probe positions fixed at 50. In the second set, we vary probe positions across the range , while keeping iterations fixed at 1000. From these various combinations of iterations and probe positions, we generate a total of 17 sets of Difference Map reconstructions for all 10k training photomasks, resulting in 170k reconstructions. Using these 17 sets of reconstructions as conditioning images, we train 17 distinct Ptycho-LDM models, and present the evaluation results in Figure 7. For both setups, we compare the MSE and PSNR of Ptycho-LDM against the Difference Map baseline.
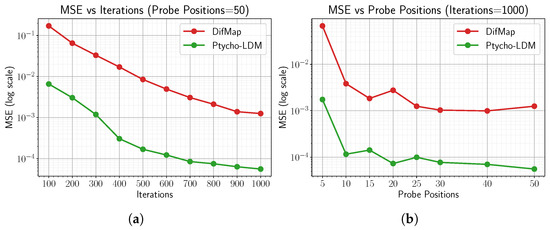
Figure 7.
We report the ptychographic reconstruction accuracy for varying numbers of Difference Map iterations and probe positions. We generate conditioning photomasks using Difference Map by initializing the complex object with a random phase. (a) We study the MSE by varying the number of iterations and set the probe positions to 50. (b) We study the MSE by varying the number of probe positions and set the iterations to 1000. We observe that, across all combinations of iterations and probe positions, the proposed Ptycho-LDM significantly improves the reconstruction quality, yielding substantially lower MSEs.
The plots in Figure 7 clearly illustrate that the proposed Ptycho-LDM consistently outperforms the Difference Map baseline in reconstruction quality across two experimental settings, characterized by varying iterations and probe positions values. Notably, under constrained conditions with fewer number of Difference Map iterations, e.g., iterations , or a reduced number of probe positions, e.g., probe positions , Ptycho-LDM demonstrates substantial gains in PSNR values. Specifically, Ptycho-LDM achieves PSNR values of 37.72 dB and 41.34 dB against Difference Map’s 20.71 dB and 25.58 dB in both these settings. These results underscore the efficacy of Ptycho-LDM for ptychographic reconstruction in resource-constrained scenarios where lower computational overhead and faster processing are critical. It is important to note that both Difference Map iterations and probe positions are directly proportional to computational demands and processing time, further emphasizing the suitability of Ptycho-LDM in such settings.
3.2.2. Ptycho-LDM’s Robust Reconstruction Under Severely Constrained Conditions
As shown in Section 3.2.1, varying the number of Difference Map iterations or probe positions reveals that Ptycho-LDM consistently enhances the photomask reconstruction quality. Based on the findings from Section 3.2.1, we further explore the potential of Ptycho-LDM by training and evaluating its reconstruction quality under severely constrained scenarios—specifically, with a significantly reduced number of probe positions. More specifically, we generate the conditioning photomask inputs for LDM by fixing the number of probe positions to 5 and varying the number of Difference Map iterations from 1000 to 6000. Consistent with the setting in Section 3.2.1, we generate conditioning photomasks using the Difference Map, initializing the complex object with a random phase. Subsequently, we train six distinct LDM models using the six corresponding conditioning training sets and present the evaluation results in Figure 8a. These results clearly indicate that Ptycho-LDM consistently improves the reconstruction quality, even when limited to just 5 probe positions. This offers two major advantages: (1) a substantial reduction in required measurements (i.e., 5 instead of 50 diffraction patterns) for ptychographic phase retrieval; and (2) faster and high-quality reconstructions—e.g., achieving a high-quality reconstruction of dB PSNR in s. Notably, when the Difference Map begins to plateau at around 5000–6000 iterations, Ptycho-LDM continues to provide significant gains in reconstruction fidelity. For instance, the Difference Map achieves an MSE of at 6000 iterations, whereas Ptycho-LDM attains a substantially lower MSE of . Figure 8a illustrates that the Difference Map algorithm plateaus and appears to become trapped in a local minimum or saddle point. Due to the non-convex nature of the optimization landscape, the Difference Map is highly sensitive to initialization. In contrast, Ptycho-LDM demonstrates a more robust convergence behavior and appears to mitigate these issues.
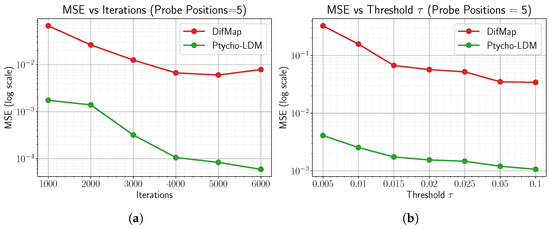
Figure 8.
(a) MSE vs. iterations for Ptycho-LDM and Difference Map using only 5 probe positions. Ptycho-LDM achieves a consistently lower reconstruction error, demonstrating its effectiveness under severely constrained measurements. While the Difference Map performance plateaus beyond 5000 iterations, Ptycho-LDM achieves a significantly lower MSE () with faster and higher-quality reconstructions. (b) Reconstruction accuracy (MSE, log scale) of Difference Map and Ptycho-LDM with 5 probe positions and 1000 iterations across different thresholds . Smaller includes more noisy pixels, while a larger is restricted to high-confidence regions. Ptycho-LDM consistently outperforms Difference Map, showing robustness to the choice of .
Effect of support threshold on reconstruction performance. We analyze the effect of varying the threshold (see Section 3.1) on the reconstruction performance. We evaluate both Difference Map and Ptycho-LDM under a resource-constrained setting with 5 probe positions and 1000 iterations. Figure 8b reports the reconstruction accuracy in terms of MSE across different thresholds . We select as a balanced choice, since it covers a sufficiently informative region of the photomask while excluding most noise-dominated pixels (see Figure 6). Importantly, as shown in Figure 8b, the improvements achieved by Ptycho-LDM over DifMap remain consistent across all threshold values. This demonstrates that our method is robust and not sensitive to the particular choice of .
3.2.3. Reconstruction Quality vs. Computation Time Trade-Off
There is an inherent trade-off between reconstruction quality and reconstruction time. As discussed in Section 1, the Difference Map algorithm can yield high-quality reconstructions given sufficient measurements, albeit at the cost of significantly longer reconstruction times. However, under limited measurement conditions, it often fails to converge to high-quality solutions and becomes prone to stagnation. By carefully selecting the values for Difference Map iterations and probe positions, we can have a high quality reconstruction in relatively faster reconstruction time.
Figure 9 and Table 1 present a comparative analysis of MSE versus iteration count for Difference Map and our proposed method, Ptycho-LDM, with the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) encoded as a bubble size and annotated computation time. The plots consider two sampling densities, 5 probe positions versus 20. In both regimes, Ptycho-LDM achieves a significantly lower MSE with fewer iterations and markedly reduced computation time.
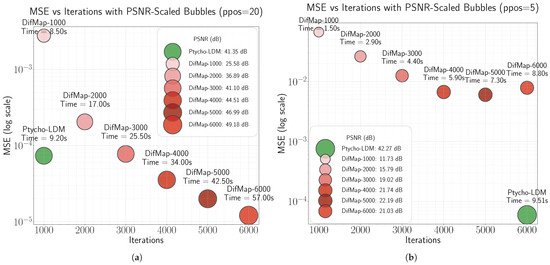
Figure 9.
(a) MSE versus the iteration count for Difference Map and Ptycho-LDM at probe positions , with PSNR encoded as a bubble size and the computation time annotated. Ptycho-LDM achieves high-fidelity reconstruction (PSNR = 41.35 dB) in just 9.2 s, significantly outperforming the Difference Map in accuracy at lower iteration budgets. (b) MSE versus iteration count for Difference Map and Ptycho-LDM at probe positions , illustrating performance under a low-sampling regime. Despite the challenging setting, Ptycho-LDM attains a superior reconstruction quality (PSNR = 42.27 dB) with a lower MSE compared to Difference Map, which saturates at 21.03 dB PSNR even after 6000 iterations.

Table 1.
Reconstruction accuracy and efficiency comparison of Ptycho-LDM and Difference Map at different probe position counts (probe positions and 5). Ptycho-LDM uses Difference Map iterations 1 K and 6 K for probe positions 20 and 5, respectively.
For probe position (Figure 9a), Ptycho-LDM consistently outperforms the Difference Map across early iteration budgets (1000, 2000, and 3000), attaining a PSNR of 41.35 dB in just 9.2 s. In contrast, Difference Map requires 3000 iterations and 25.5 s to reach a comparable PSNR of 41.10 dB. Given that a PSNR above 40 dB is generally indicative of high-quality reconstruction, further extending Difference Map to 6000 iterations to obtain a further improvement (PSNR = 49.18 dB) incurs a substantial computational cost (57 s per photomask), which may not be justifiable for practical deployments.
Under the more challenging low-sampling scenario, i.e., probe positions (Figure 9b), Ptycho-LDM still yields superior reconstruction quality with a PSNR of 42.27 dB and lowest MSE, outperforming the Difference Map even at its maximum iteration count (6000), where the PSNR plateaus around 21.03 dB. These results underscore the central contribution of our work: by leveraging a data-driven prior, Ptycho-LDM drastically reduces the number of measurements required to achieve a reconstruction quality that is otherwise unattainable with conventional iterative methods. It is important to emphasize that, regardless of the number of iterations, traditional iterative methods like Difference Map are fundamentally limited by the number of measurements available. As evident from Figure 9b, even after 5000 iterations, the reconstruction quality of Difference Map plateaus, failing to reach the fidelity achieved by Ptycho-LDM. In contrast, Ptycho-LDM delivers significantly superior reconstructions under minimal measurement conditions, demonstrating the critical advantage of incorporating a learned prior to compensate for highly underdetermined acquisition setups. This highlights both the efficiency and robustness of our approach in enabling high-fidelity reconstructions at a substantially lower computational and measurement cost.
3.2.4. Qualitative Results
To visually assess the reconstruction quality, Figure 10 presents qualitative comparisons across two representative photomask examples. The first and third rows show the ground-truth mask (left, blue colormap), Difference Map reconstruction (center, green colormap), and our proposed Ptycho-LDM reconstruction (right, green colormap). The second and fourth rows show magnified views of the rectangular regions highlighted in the first and third rows, respectively. Compared to the Difference Map, Ptycho-LDM consistently yields sharper and more accurate reconstructions, particularly in regions with dense feature patterns and at the corners where probe intensity typically diminishes. Difference Map reconstructions often exhibit residual noise and blurred structures due to limited probe coverage and iterative convergence issues. In contrast, Ptycho-LDM effectively suppresses noise and preserves fine-grained geometric patterns, thanks to its learned generative priors and conditioning mechanisms. The improved fidelity is especially pronounced under zoom-in inspection, where subtle differences in line widths and feature boundaries become apparent. These results highlight the robustness of Ptycho-LDM in recovering high-frequency details even under constrained acquisition settings.
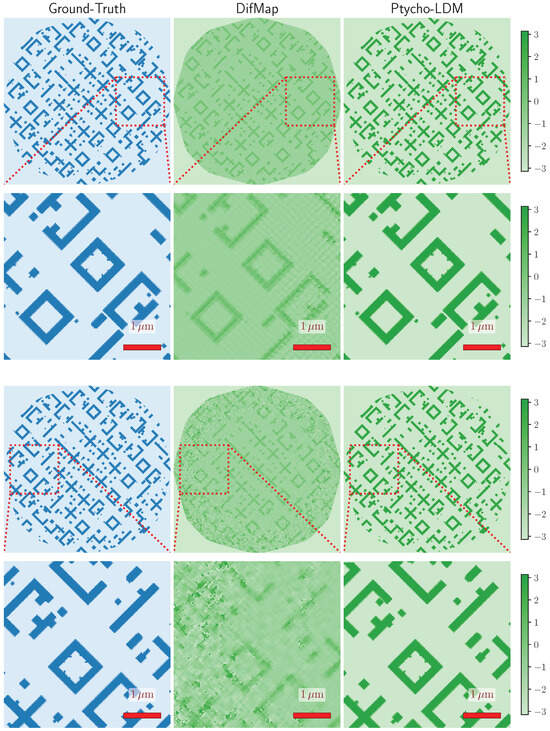
Figure 10.
Qualitative comparison of the reconstructed photomask (masked region for evaluation). The first and third rows show the ground-truth (left, blue colormap), Difference Map (center, green colormap), and our proposed Ptycho-LDM reconstructions (right, green colormap). The second and fourth rows show the magnified views of the rectangular regions highlighted in the first and third rows, respectively. The first and second rows show reconstructions from noise-free measurements (diffraction patterns), while the third and fourth rows present reconstructions from noisy measurements both for DifMap and Ptycho-LDM (w/ Noise, w/ Training). Despite conditioning on noisy measurements, Ptycho-LDM achieves higher-quality reconstructions compared to the DifMap baseline. Both the Difference Map and Ptycho-LDM use probe positions and iterations.
EUV photomask inspection. Finally, we visually demonstrate the potential of the proposed Ptycho-LDM in addressing real-world challenges, such as extreme ultraviolet (EUV) photomask inspection. Figure 11 presents the phase reconstructions of two EUV photomask samples. For each sample, we compare the reconstructions generated by Ptycho-LDM against the ground truth EUV photomask phase. The results highlight that the "intrusion" and "extrusion" defects are accurately reconstructed by Ptycho-LDM. While the Difference Map reconstructions may appear visually limited in resolving certain fine-scale defects, it is important to note that, in most cases, Ptycho-LDM does not hallucinate or invent the information absent from the conditioning input. Instead, it leverages the powerful denoising and restoration capabilities of diffusion models to enhance the noisy Difference Map reconstructions. The model learns to recognize subtle patterns—potentially imperceptible to the human eye—that correlate with defects in the noisy input and maps them back to noise-free structures. This highlights a key contribution of our approach: the ability of generative models to amplify and reconstruct meaningful signals from faint cues present in the conditioning image, rather than recovering information that is entirely missing. We also acknowledge a limitation of Ptycho-LDM: the model occasionally exhibits misdetections and false positives in certain photomask regions outside of the probe support mask (Section 3.1).
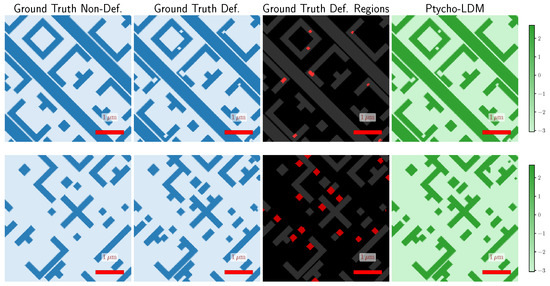
Figure 11.
Qualitative visualization of photomask samples with and without defects. The first column shows the ground-truth non-defective photomasks, while the second column presents their corresponding defective versions. The third column highlights the defective regions using red pixel overlays. The fourth column shows the reconstructions produced by Ptycho-LDM. Each row corresponds to one photomask instance: the top row represents intrusion defects, and the bottom row represents extrusion defects. The results highlight that Ptycho-LDM achieves high-fidelity reconstructions, preserving subtle structural variations and defect regions critical for downstream analysis. Ptycho-LDM uses probe positions and iterations.
Scope and limitations on defect analysis. Ptycho-LDM reconstructs the full complex amplitude of the object, which inherently includes both amplitude and phase information. This makes the framework, in principle, applicable to phase-only defects as well. A systematic investigation of phase-only defects and their minimum resolvable phase shift is an important future direction, but it lies beyond the scope of the present work. Note that our study does not aim to solve the defect detection problem. The defect-related example is included only to illustrate that the latent representations learned by Ptycho-LDM carry structural cues that could be leveraged for downstream defect inspection. In this work, we study the reconstruction of complex-valued samples from their diffraction data, including programmed defects; however, we do not study the reconstruction of different defects types. We emphasize that the ptychographic reconstruction of phase defects—i.e., pits and bumps in the multilayer—has been demonstrated, e.g., in [41].
3.2.5. Impact of Photon and Detector Read-Out Noise on Reconstruction Quality
We conduct an experimental analysis to investigate the impact of photon and detector read-out noise on Ptycho-LDM’s reconstruction performance. To this end, we introduce noise into the simulated diffraction patterns and use them to generate conditioning inputs for Ptycho-LDM. Table 2 reports a comparison of the reconstruction quality between Difference Map and Ptycho-LDM under both noisy and noise-free measurement settings. Even when conditioned on noisy measurements, Ptycho-LDM consistently achieves higher-quality reconstructions compared to the Difference Map baseline. More specifically, Ptycho-LDM reduces the MSE from to , achieving an order-of-magnitude improvement. Figure 10 (third and fourth rows) presents qualitative results demonstrating the advantage of Ptycho-LDM: while noise in the diffraction patterns severely degrades the reconstruction quality of the Difference Map, Ptycho-LDM continues to produce sharper and less noisy reconstructions.

Table 2.
Impact of the photon and read-out noise on reconstruction quality. We compare the Difference Map and two variants of Ptycho-LDM—w/o Training (no fine-tuning on noisy inputs) and w/ Training (fine-tuned on noisy inputs)—under both noise-free and noisy measurement settings. Difference Map-based conditioning inputs are generated using our resource-constrained setup with 5 probe positions and 1000 iterations. Even when conditioned on noisy measurements, Ptycho-LDM achieves an order-of-magnitude MSE improvement, reducing it from to .
We evaluate two variants of Ptycho-LDM: one applied without fine-tuning on noisy conditioning inputs, denoted as Ptycho-LDM w/o Training, and another fine-tuned on noisy conditioning inputs, denoted as Ptycho-LDM w/ Training in Table 2. We observe that training Ptycho-LDM with noisy conditioning inputs improves the reconstruction quality, increasing the PSNR from 13.23 dB to 18.86 dB. We generate Difference Map-based conditioning inputs using our proposed resource-constrained setup with 5 probe positions and 1000 iterations.
Modeling photon and read-out noise in the simulated diffraction dataset. We considered as a reference the noise distribution in a typical ptychography dataset collected with the RESCAN microscope at the Swiss Light Source [39]. In a typical experiment with RESCAN, each diffraction pattern is collected at multiple exposure times from 50 ms to 40 s to synthesize a high-dynamic-range (HDR) image and remove unwanted saturation effects. To simulate the noise distribution in the measured HDR diffraction patterns, we added a photon shot noise term matching the number of photons in each pixel of the image (which ranges from 0, for dark pixels to about 131,000 for pixels in the central speckle) and a Gaussian noise term with a standard deviation of 200 counts, corresponding to the uncertainty introduced by the read-out of the detector (Princeton Instruments MTE2-EUV CCD) for an exposure time of 40 s.
3.2.6. Ptycho-LDM’s Generalizability on Real Data
In this section, we evaluate the generalizability of Ptycho-LDM on real measurements. Specifically, we apply a pretrained Ptycho-LDM to conditioning inputs generated by Difference Map from real diffraction patterns. It is important to mention that the conditioning input images we used were obtained with a multi-mode probe approach [42] to account for the partial coherence of the illumination in the experimental setup. Figure 12 presents a visual comparison between reconstructions obtained by Difference Map and those predicted by Ptycho-LDM. We provide intermediate Difference Map reconstructions as conditioning inputs and compare the resulting Ptycho-LDM predictions against the final Difference Map outputs. Despite being trained solely on synthetic data, Ptycho-LDM produces meaningful and informative reconstructions on real measurements, demonstrating strong transferability beyond simulated settings. This suggests that further training or fine-tuning on real data could substantially enhance its effectiveness for fast and accurate ptychographic reconstruction.
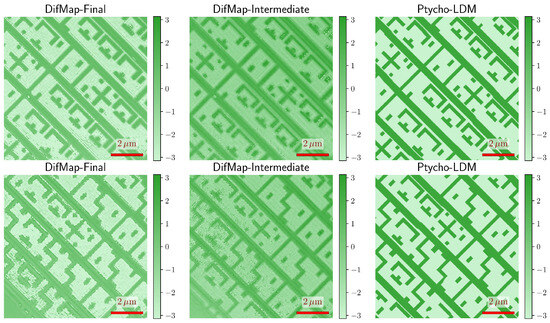
Figure 12.
The qualitative comparison of reconstructions on real diffraction measurements. Columns show final Difference Map reconstructions, intermediate Difference Map reconstructions (used as conditioning inputs), and Ptycho-LDM predictions. Although trained exclusively on synthetic data, Ptycho-LDM produces sharper and more structured reconstructions than Difference Map, highlighting its potential for generalization to real measurements.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we present Ptycho-LDM, a novel framework for fast and accurate EUV photomask ptychographic phase retrieval. By combining a resource-constrained ptychographic solver with a conditional Latent Diffusion Model (LDM), Ptycho-LDM addresses the critical limitations of traditional reconstruction methods—namely slow inference and dense data requirements. Our approach capitalizes on the strengths of both physics-based algorithms and generative models. It performs an initial coarse recovery using a lightweight ptychographic setup, followed by a diffusion-based refinement in latent space. This significantly reduces the computation time while maintaining high reconstruction fidelity.
To support this study, we introduced the LAMP dataset, a large-scale synthetic benchmark tailored for EUV photomask inspection. Using LAMP, we conducted extensive evaluations comparing Ptycho-LDM with the state-of-the-art Difference Map method. Our findings underscore a key limitation of conventional iterative solvers: their reconstruction quality is inherently constrained by the number of available measurements. Even with extensive iterations, methods like Difference Map are unable to recover high-fidelity images in severely undersampled regimes. In contrast, Ptycho-LDM consistently produces accurate reconstructions under minimal measurement conditions, highlighting the transformative impact of integrating data-driven priors. This capability not only reduces acquisition demands but also enables practical deployment in settings where traditional approaches fail to converge to meaningful solutions.
We have proposed our own implementation of the Difference Map (see Algorithms 1 and 2) as the initial estimate. However, this specific choice is not intended to claim superiority as the best implementation or iterative algorithm for conditioning the latent diffusion model. Alternative implementations of the Difference Map (e.g., PtyPy [43]) or other iterative ptychographic algorithms could equally be integrated into our pipeline for LDM conditioning that could potentially yield improved performance.
Our experimental evaluation confirms the practical relevance of Ptycho-LDM. By explicitly modeling photon shot noise and detector readout noise, we show that Ptycho-LDM retains strong reconstruction quality even under realistic noisy conditions, reducing the MSE by up to an order of magnitude compared to Difference Map. Moreover, despite being trained solely on synthetic data, Ptycho-LDM demonstrates a meaningful transfer to real diffraction measurements, producing informative reconstructions that suggest strong generalization capability. These results highlight the robustness of our method and its potential for deployment in real-world EUV mask inspection workflows.
Visual inspections further confirm the superiority of Ptycho-LDM, particularly in reconstructing intricate mask structures and defect regions. Unlike Difference Map, which suffers from noise and artifact accumulation at reduced sampling, Ptycho-LDM robustly preserves detail even under highly constrained acquisition settings. By integrating deep generative priors with physical measurement constraints, Ptycho-LDM demonstrates that high-quality and efficient reconstructions are achievable even in highly constrained, minimal-measurement regimes. This hybrid methodology holds promise not only for semiconductor metrology but also for broader applications in inverse imaging and microscopy.
Finally, we acknowledge several current limitations of the proposed Ptycho-LDM framework. First, due to the limited availability of real photomask data, we were unable to train or validate the model on real-world samples. Second, computational constraints restricted our experiments to localized chip regions rather than full-chip inspection; however, the method is scalable and could support full-chip analysis given sufficient resources. Third, while our approach demonstrates high-fidelity object reconstruction, it does not explicitly address defect detection. In some peripheral regions, particularly those beyond the probe’s high-signal support, Ptycho-LDM exhibits occasional misdetections and false positives. We view these challenges as promising directions for future work, including adapting the framework specifically for defect detection tasks. Overall, Ptycho-LDM lays the groundwork for next-generation computational imaging systems by leveraging the synergy between physical priors and deep generative modeling.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.M. and B.B.H.; methodology, S.S., L.B. and B.B.H.; software, S.S., P.A., I.M. and B.B.H.; validation, S.S., P.A., L.B., I.M. and B.B.H.; formal analysis, S.S. and B.B.H.; investigation, S.S.; resources, B.B.H.; data curation, S.S. and P.A.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S.; writing—review and editing, S.S., P.A., L.B., I.M. and B.B.H.; visualization, S.S.; supervision, I.M. and B.B.H.; project administration, S.S.; funding acquisition, I.M. and B.B.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been funded in part by the Swiss Data Science Center under grant no. C21-17L and from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska–Curie grant agreement No. 884104 (PSI–FELLOW–III–3i).
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study will be openly available in https://github.com/susaha/ptycho-ldm, accessed on 28 August 2025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bakshi, V. EUV Lithography; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bonam, R.; Tien, H.Y.; Chou, A.; Meli, L.; Halle, S.; Wu, I.; Huang, X.; Lei, C.; Kuan, C.; Wang, F.; et al. EUV mask and wafer defectivity: Strategy and evaluation for full die defect inspection. In Proceedings of the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography VII; Panning, E.M., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9776, p. 97761C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Tezuka, Y.; Jager, M.; Chakravorty, K.; Sayan, S.; Frendberg, E.; Satyanarayana, S.; Ghadiali, F.; Zhang, G.; Abboud, F. EUV mask infrastructure and actinic pattern mask inspection. In Proceedings of the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography XI; Felix, N.M., Lio, A., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11323, p. 1132310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, K.A.; Mochi, I. Wavelength-specific reflections: A decade of extreme ultraviolet actinic mask inspection research. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2010, 28, C6E1–C6E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchikoulaeva, A.; Miyai, H.; Kohyama, T.; Takehisa, K.; Kusunose, H. Enabling EUVL high-volume manufacturing with actinic patterned mask inspection. In Proceedings of the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography XI; Felix, N.M., Lio, A., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11323, p. 113231K. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, K.; Benk, M.P.; Wojdyla, A.; Verduijn, E.; Wood II, O.R.; Mangat, P. EUV actinic brightfield mask microscopy for predicting printed defect images. In Proceedings of the Photomask Technology 2015; Hayashi, N., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9635, p. 963514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoroki, T.; Miyai, H. Actinic patterned mask inspection for EUV lithography. In Proceedings of the Photomask Japan 2023: XXIX Symposium on Photomask and Next-Generation Lithography Mask Technology; Kojima, Y., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2023; Volume 12915, p. 1291502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesch, M.; Kersteen, G.; Verch, A.; Albert, M.; Heringlake, P.; Gwosch, K.; Capelli, R. Quantitative access to phase effects in High-NA photomasks using AIMS EUV. In Proceedings of the 39th European Mask and Lithography Conference (EMLC 2024); Behringer, U.F., Finders, J., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; Volume 13273, p. 132731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodenburg, J. Ptychography and Related Diffractive Imaging Methods. Adv. Imaging Electron Phys. 2008, 150, 87–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, P.; Dierolf, M.; Bunk, O.; Menzel, A.; Pfeiffer, F. Probe retrieval in ptychographic coherent diffractive imaging. Ultramicroscopy 2009, 109, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiden, A.M.; Rodenburg, J.M. An improved ptychographical phase retrieval algorithm for diffractive imaging. Ultramicroscopy 2009, 109, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunk, O.; Dierolf, M.; Kynde, S.; Johnson, I.; Marti, O.; Pfeiffer, F. Influence of the overlap parameter on the convergence of the ptychographical iterative engine. Ultramicroscopy 2008, 108, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyder, R.; Cai, Z.; Asif, M.S. Solving phase retrieval with a learned reference. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 425–441. [Google Scholar]
- Metzler, C.; Schniter, P.; Veeraraghavan, A.; Baraniuk, R. prDeep: Robust phase retrieval with a flexible deep network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 3501–3510. [Google Scholar]
- Rivenson, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Günaydın, H.; Teng, D.; Ozcan, A. Non-iterative holographic image reconstruction and phase retrieval using a deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the CLEO: Science and Innovations, San Jose, CA, USA, 13–18 May 2018; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Guo, C.; Lin, S.; Jiang, J.; Ji, X. Physics-based iterative projection complex neural network for phase retrieval in lensless microscopy imaging. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 10523–10531. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, W.; Zhai, Q.; McCann, M.T.; Cardona, C.G.; Kamilov, U.S.; Wohlberg, B. PtychoDV: Vision Transformer-Based Deep Unrolling Network for Ptychographic Image Reconstruction. IEEE Open J. Signal Process. 2024, 5, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan, E.; Heckel, R.; Chen, M.; Kellman, M.; Waller, L. Deep phase decoder: Self-calibrating phase microscopy with an untrained deep neural network. Optica 2020, 7, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoidn, O.; Mishra, A.A.; Mehta, A. Physics constrained unsupervised deep learning for rapid, high resolution scanning coherent diffraction reconstruction. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Shen, L.; Xing, L.; Ermon, S. Solving Inverse Problems in Medical Imaging with Score-Based Generative Models. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS 2021 Workshop on Deep Learning and Inverse Problems, Virtual Conference, 6–14 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.; Sim, B.; Ryu, D.; Ye, J.C. Improving diffusion models for inverse problems using manifold constraints. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 25683–25696. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.; Kim, J.; Mccann, M.T.; Klasky, M.L.; Ye, J.C. Diffusion Posterior Sampling for General Noisy Inverse Problems. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Vahdat, A.; Mardani, M.; Kautz, J. Pseudoinverse-guided diffusion models for inverse problems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mardani, M.; Song, J.; Kautz, J.; Vahdat, A. A Variational Perspective on Solving Inverse Problems with Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 7–11 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.; Kwon, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Qu, Q.; Shen, L. Solving Inverse Problems with Latent Diffusion Models via Hard Data Consistency. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 7–11 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, L.; Chen, Y.; Kumar, A.; Caramanis, C.; Shakkottai, S.; Chu, W.S. Beyond first-order tweedie: Solving inverse problems using latent diffusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 9472–9481. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A. Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 8780–8794. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Konijnenberg, S. An introduction to the theory of ptychographic phase retrieval methods. Adv. Opt. Technol. 2017, 6, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köfferlein, M. Available online: https://www.klayout.de (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light, 7th (expanded) ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Kreis, K.; Vahdat, A. Tackling the generative learning trilemma with denoising diffusion gans. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.07804. [Google Scholar]
- Esser, P.; Rombach, R.; Ommer, B. Taming transformers for high-resolution image synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 12873–12883. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Oord, A.; Vinyals, O. Neural discrete representation learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6309–6318. [Google Scholar]
- Swiss National Supercomputing Centre (CSCS). Alps Supercomputer at the Swiss National Supercomputing Centre (CSCS). Available online: https://www.cscs.ch/computers/alps (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Song, J.; Meng, C.; Ermon, S. Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models. arXiv 2010, arXiv:2010.02502. [Google Scholar]
- Mochi, I.; Helfenstein, P.; Rajeev, R.; Fernandez, S.; Kazazis, D.; Yoshitake, S.; Ekinci, Y. Actinic inspection of EUV reticles with arbitrary pattern design. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography 2017, Monterey, CA, USA, 1–5 October 2017; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10450, pp. 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Guizar-Sicairos, M.; Holler, M.; Diaz, A.; Vila-Comamala, J.; Bunk, O.; Menzel, A. Role of the illumination spatial-frequency spectrum for ptychography. Phys. Rev. B—Condensed Matter Mater. Phys. 2012, 86, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochi, I.; Fernandez, S.; Nebling, R.; Locans, U.; Helfenstein, P.; Rajeev, R.; Dejkameh, A.; Kazazis, D.; Tseng, L.T.; Ekinci, Y. Absorber and phase defect inspection on EUV reticles using RESCAN. In Proceedings of the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography X, San Jose, CA, USA, 24–28 February 2019; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 10957, pp. 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Helfenstein, P.; Rajeev, R.; Mochi, I.; Kleibert, A.; Vaz, C.A.F.; Ekinci, Y. Beam drift and partial probe coherence effects in EUV reflective-mode coherent diffractive imaging. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 12242–12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enders, B.; Thibault, P. A computational framework for ptychographic reconstructions. Proc. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 472, 20160640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).