Resolution Enhancement in Extreme Ultraviolet Ptychography Using a Refined Illumination Probe and Small-Etendue Source
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
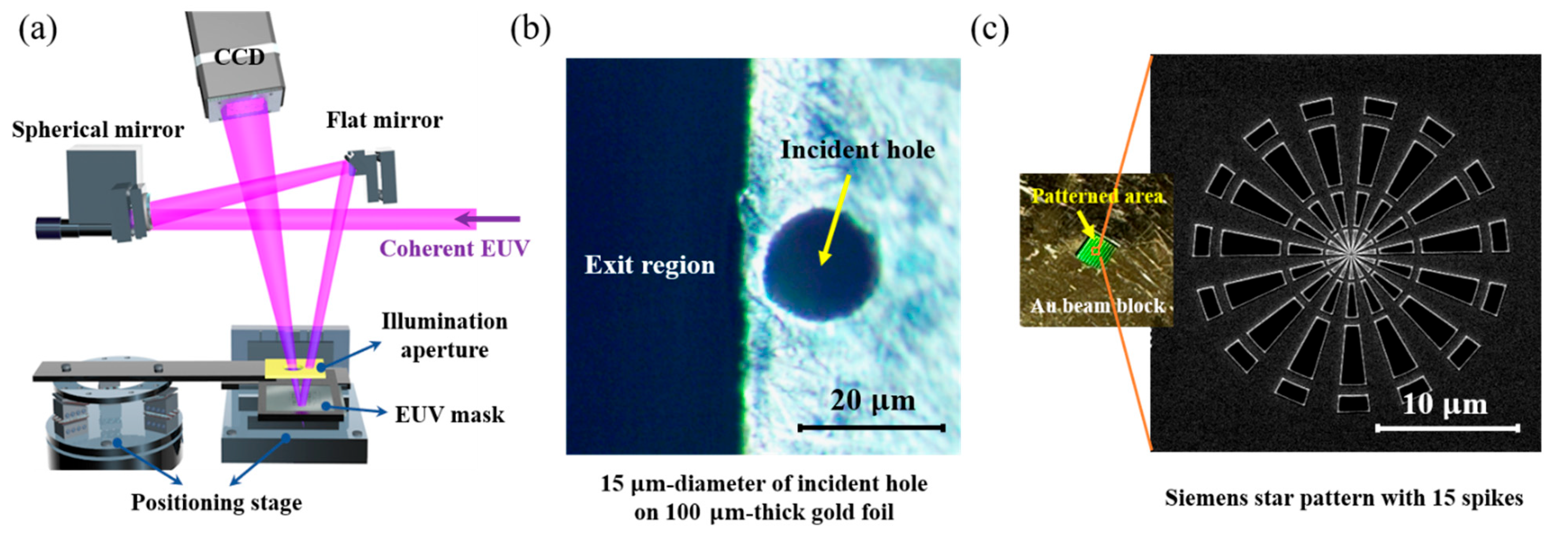
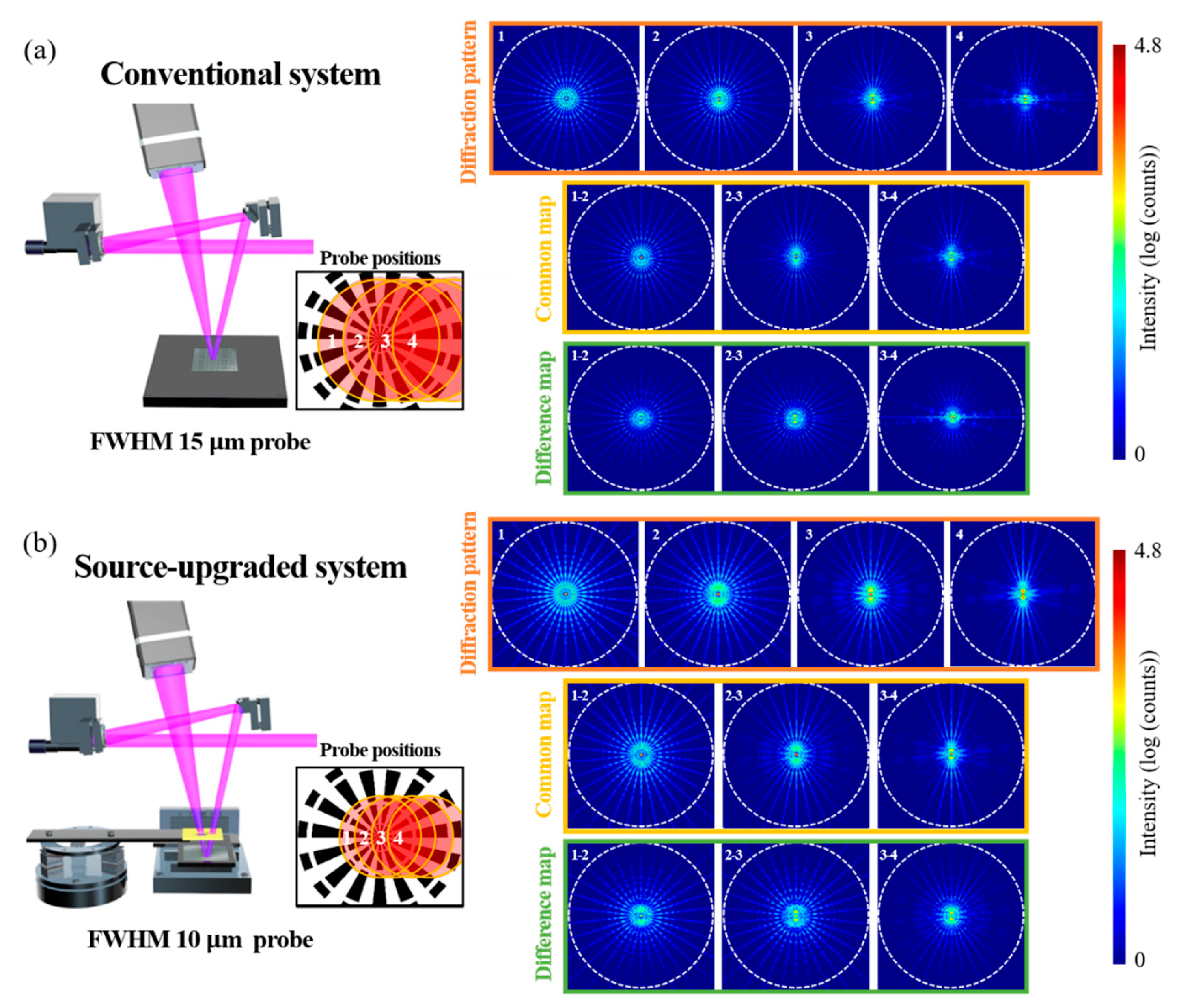
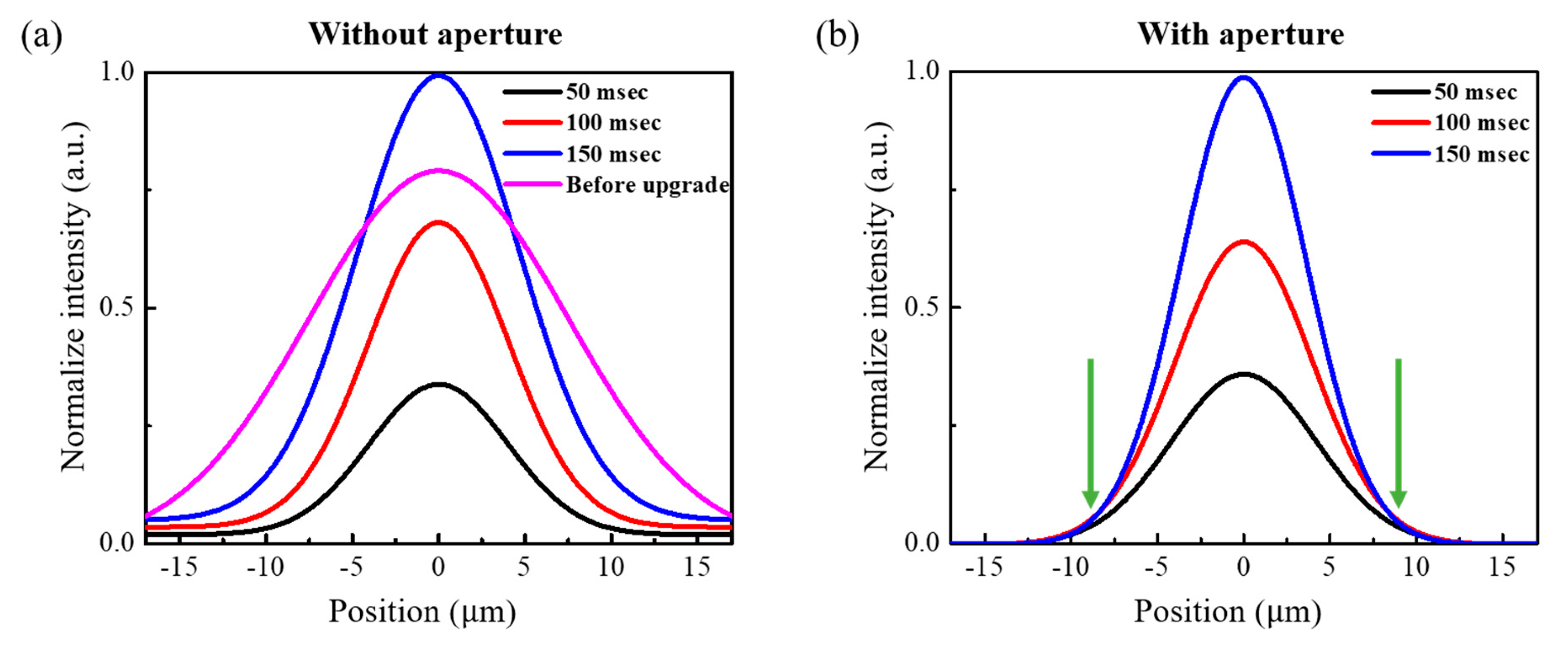
2.1. Probe Refinement Using Small-Etendue EUV Source and Illumination Aperture
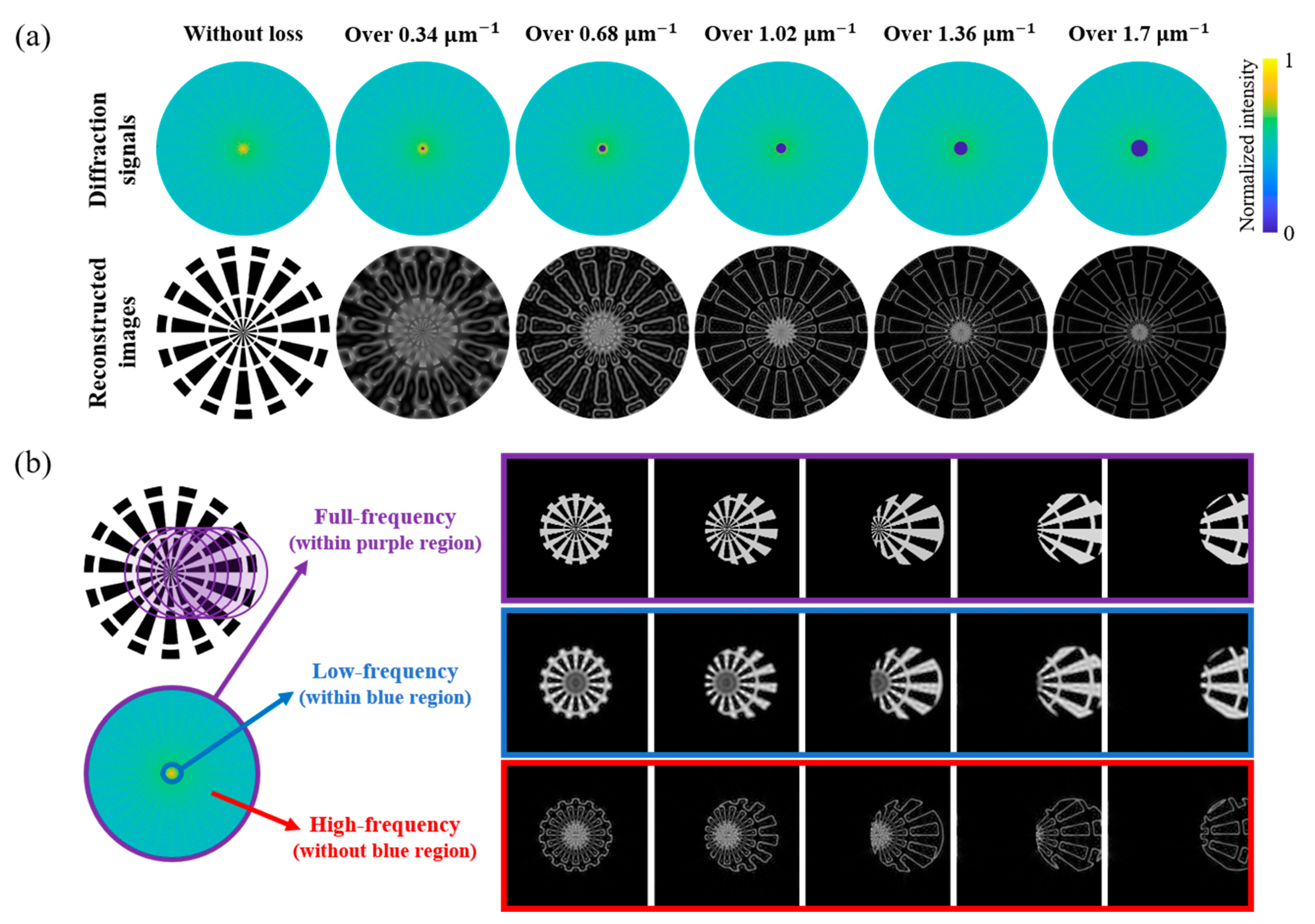
2.2. Simulation-Driven Diffraction Signal Analysis in the Fourier Domain
3. Result and Discussion
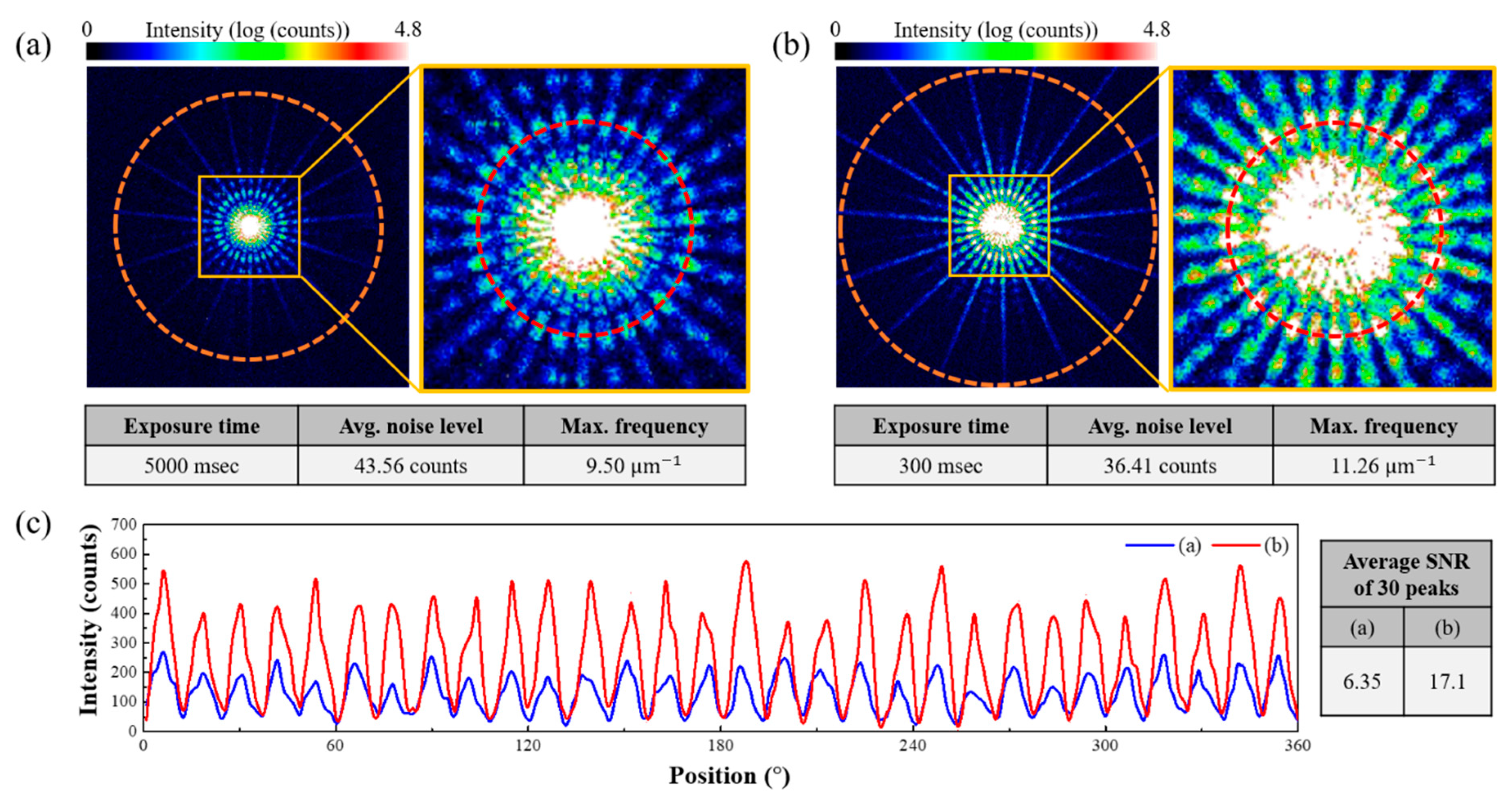
3.1. Simulation Study of HF Diffraction Signal Improvement for Ptychographic Imaging
3.2. Resolution Enhancement in Ptychographic Imaging Through High-Frequency Diffraction Signal Enhancement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.; Melvin, L.S.; Kim, S.-S. EUV mask technologies: Evolution and ecosystem for devices. In Proceedings of the Photomask Technology 2024, Monterey, CA, USA, 29 September–3 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.-H.; Wen, W.L.; Hsiang, J.Y.; Po-Sheng, W. New EUV mask blank for N3 technology node and beyond. In Proceedings of the Photomask Technology 2023, Monterey, CA, USA, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, J.; Yen, A. EUV lithography technology for high-volume production of semiconductor devices. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 2019, 32, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitrago, E.; Kulmala, T.S.; Fallica, R.; Ekinci, Y. EUV lithography process challenges. Front. Nanosci. 2016, 11, 135–176. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, T.; Miyai, H.; Sayan, S.; Mizoguchi, M.; Gondaira, K.; Nishizawa, M.; Suzuki, T.; Todoroki, T.; Li, Y.; Abboud, F. Actinic mask inspection for the era of high-numerical aperture extreme ultraviolet lithography. J. Micro/Nanopatterning Mater. Metrol. 2024, 24, 011006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondaira, K.; Todoroki, T.; Nishizawa, M.; Miyai, H. Actinic patterned mask inspection for high-NA EUV lithography. In Proceedings of the Optical and EUV Nanolithography XXXVII, San Jose, CA, USA, 25 February–1 March 2024; Volume 12953. [Google Scholar]
- Helfenstein, P.; Mohacsi, I.; Rajeev, R.; Ekinci, Y. Scanning coherent diffractive imaging methods for actinic extreme ultraviolet mask metrology. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2016, 15, 034006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Popmintchev, D.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, G.; Tang, J.; Niu, J.; et al. Highly efficient and aberration-free off-plane grating spectrometer and monochromator for EUV-soft X-ray applications. Light Sci. Appl. 2024, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Medvedev, V.; van de Kruijs, R.; Yakshin, A.; Louis, E.; Bijkerk, F. Spectral tailoring of nanoscale EUV and soft x-ray multilayer optics. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2017, 4, 011104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachulak, P.W.; Bartnik, A.; Kostecki, J.; Wegrzynski, L.; Fok, T.; Jarocki, R.; Szczurek, M.; Fiedorowicz, H. Extreme ultraviolet and soft X-ray imaging with compact, table top laser plasma EUV and SXR sources. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sec. B 2015, 364, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasako, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Takayama, Y.; Asakura, K.; Oide, M.; Okajima, K.; Oroguchi, T.; Yamamoto, M. Methods and application of coherent X-ray diffraction imaging of noncrystalline particles. Biophys. Rev. 2020, 12, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holler, M.; Guizar-Sicairos, M.; Tsai, E.H.R.; Dinapoli, R.; Müller, E.; Bunk, O.; Raabe, J.; Aeppli, G. High-resolution non-destructive three-dimensional imaging of integrated circuits. Nature 2017, 543, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakurel, K.P.; Kimura, T.; Joti, Y.; Matsuyama, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Nishino, Y. Coherent diffraction imaging of non-isolated object with apodized illumination. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 28182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, I.; Harder, R. Coherent X-ray diffraction imaging of strain at the nanoscale. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J. Computational microscopy with coherent diffractive imaging and ptychography. Nature 2025, 637, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschen, W.; Liu, C.; Steinert, M.; Penagos, M.D.S.; Siefke, T.; Zeitner, U.D.; Kasper, J.; Pertsch, T.; Limpert, J.; Rothhardt, J. Structured illumination ptychography and at-wavelength characterization with an EUV diffuser at 13.5 nm wavelength. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Brooks, N.J.; Johnsen, P.; Jenkins, N.W.; Esashi, Y.; Binnie, I.; Tanksalvala, M.; Kapteyn, H.C.; Murnane, M.M. High-fidelity ptychographic imaging of highly periodic structures enabled by vortex high harmonic beams. Optica 2023, 10, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, D.F.; Tanksalvala, M.; Shanblatt, E.R.; Zhang, X.; Galloway, B.R.; Porter, C.L.; Karl, R., Jr.; Bevis, C.; Adams, D.E.; Kapteyn, H.C.; et al. Subwavelength coherent imaging of periodic samples using a 13.5 nm tabletop high-harmonic light source. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodenburg, J.M. Ptychography and related diffractive imaging methods. Adv. Imaging Electron Phys. 2008, 150, 87–184. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Sun, W.; Xu, B.; He, Z. Resolution enhancement in coherent diffraction imaging using high dynamic range image. in Photonics. Photonics 2021, 8, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sharma, M.K.; Cossairt, O. High dynamic range coherent imaging using compressed sensing. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 30904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Lee, D.G.; Moon, S.; Ku, C.M.; Cho, J.H.; Ahn, J. Actinic patterned mask imaging using extreme ultraviolet ptychography microscope with high harmonic generation source. Appl. Phys. Express 2022, 15, 076505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Woo, D.G.; Ahn, J. Performance of extreme ultraviolet coherent scattering microscope. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Moon, S.; Choi, J.; Wi, S.J.; Ahn, J. Extreme ultraviolet pellicle wrinkles influence on mask 3D effects: Experimental demonstration. Appl. Opt. 2023, 62, 6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochi, I.; Kim, H.-S.; Locans, U.; Dejkameh, A.; Nebling, R.; Kazazis, D.; Ekinici, Y. Illumination control in lensless imaging for EUV mask inspection and review. In Proceedings of the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography XI, San Jose, CA, USA, 23–27 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tuitje, F.; Eschen, W.; Tadesse, G.K.; Limpert, J.; Rothhardt, J.; Spielmann, C. Reliability of ptychography on periodic structures. OSA Contin. 2020, 3, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunk, O.; Dierolf, M.; Kynde, S.; Johnson, I.; Marti, O.; Pfeiffer, F. Influence of the overlap parameter on the convergence of the ptychographical iterative engine. Ultramicroscopy 2008, 108, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loetgering, L.; Du, M.; Flaes, D.B.; Aidukas, T.; Wechsler, F.; Molina, D.S.P.; Rose, M.; Pelekanidis, A.; Eschen, W.; Hess, J.; et al. PtyLab.m/py/jl: A cross-platform, open-source inverse modeling toolbox for conventional and Fourier ptychography. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 13763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiden, A.; Johnson, D.; Li, P. Further improvements to the ptychographical iterative engine. Optica 2017, 4, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heel, M.; Schatz, M. Fourier shell correlation threshold criteria. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 151, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiden, A.M.; Rodenburg, J.M. An improved ptychographical phase retrieval algorithm for diffractive imaging. Ultramicroscopy 2009, 109, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veen, F.v.d.; Pfeiffer, F. Coherent x-ray scattering. Matter 2004, 16, 5003. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-S.; Nebling, R.; Dejkameh, A.; Shen, T.; Mochi, I.; Ekinci, Y.; Renwick, S.P. Resolution limit and photon flux dependency in EUV ptychography. In Proceedings of the Photomask Technology 2021, Online, 27 September–8 October 2021. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, S.; Hong, J.; Lee, T.; Ahn, J. Resolution Enhancement in Extreme Ultraviolet Ptychography Using a Refined Illumination Probe and Small-Etendue Source. Photonics 2025, 12, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12080831
Moon S, Hong J, Lee T, Ahn J. Resolution Enhancement in Extreme Ultraviolet Ptychography Using a Refined Illumination Probe and Small-Etendue Source. Photonics. 2025; 12(8):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12080831
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Seungchan, Junho Hong, Taeho Lee, and Jinho Ahn. 2025. "Resolution Enhancement in Extreme Ultraviolet Ptychography Using a Refined Illumination Probe and Small-Etendue Source" Photonics 12, no. 8: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12080831
APA StyleMoon, S., Hong, J., Lee, T., & Ahn, J. (2025). Resolution Enhancement in Extreme Ultraviolet Ptychography Using a Refined Illumination Probe and Small-Etendue Source. Photonics, 12(8), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12080831




