1. Introduction
The ocean plays a vital role in supporting life on Earth, regulating climate systems and sustaining global biodiversity and economic development. As humans explore marine environments more extensively, there is a growing demand for real-time data collection to support applications such as environmental monitoring, underwater exploration, and maritime security. To meet these demands, Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks (UWSNs) have emerged as an essential infrastructure for sensing, transmitting, and analyzing oceanic data over extended spatial and temporal scales. Due to the harsh underwater environment and limited communication range of individual nodes, data transmission in UWSNs often relies on multi-hop communication. Thus, designing efficient, reliable, and energy-aware routing protocols is highly desired, and many researchers have proposed a variety of routing strategies tailored to underwater scenarios, including depth-based routing, location-based routing, and opportunistic routing, each aiming to overcome the issues such as high latency, packet loss, and energy imbalance.
Recent advances in free-space optical (FSO) communication systems, such as adaptive relay selection and hybrid FSO architectures, have demonstrated notable improvements in link reliability under harsh conditions [
1,
2]. These approaches offered valuable theoretical insights for designing underwater optical networks operating in complex environments.
Currently, UWSNs employ three main transmission media, namely radio frequency (RF), acoustic, and optical waves. By employing RF waves, UWSNs can theoretically achieve high data rates. However, severe attenuation in seawater limits their effective range to only a few meters, making them unsuitable for most underwater applications. By employing acoustic waves, UWSNs enable long-range and omnidirectional communication, supporting large-scale deployments. Nevertheless, acoustic channels are constrained by low bandwidth, high latency, and vulnerability to environmental factors such as multipath and Doppler effects. By employing optical waves, UWSNs achieve ultra-high data rates, low latency, and energy-efficient directional transmission, making them ideal for short-range, high-throughput, and delay-sensitive underwater applications.
Given the inherent limitations of each transmission medium, efficient routing becomes essential to ensure reliable, energy-aware, and low-latency data delivery in UWSNs. Consequently, a wide range of routing protocols has been developed to address the unique challenges posed by underwater environments. By employing acoustic waves, many routing protocols have been proposed for UWSNs. In [
3], Peng Xie et al. proposed the vector-based forwarding (VBF) algorithm, which constructed a virtual pipeline from the source to the sink node and restricted forwarding to nodes within the pipeline in order to reduce redundant transmissions and alleviate congestion. However, the static nature of the pipeline made the protocol vulnerable to path disruption in sparse or dynamic network environments. To address the relay discovery failures in such environments, N. Nicolaou et al. developed the hop-by-hop vector-based forwarding (HH-VBF) algorithm [
4]. It dynamically established a local virtual pipeline at each hop, allowing candidate nodes to evaluate their forwarding eligibility based on the positions of both the sender and the sink, thereby improving adaptability and relay availability. S. M. Mazinani et al. introduced the improved vector-based forwarding (IVBF) algorithm, in which the static pipeline was replaced with a probabilistic function [
5]. This function adjusted the forwarding probability based on local node density and environmental conditions, enhancing connectivity in challenging scenarios. He Yan et al. proposed the depth-based routing (DBR) protocol, which eliminated the need for full localization by using only depth information to select relay nodes [
6]. Packets were forwarded to neighbors with shallower depths, which simplified the protocol implementation. However, DBR suffered from void regions where no eligible forwarders were present, leading to packet loss. To mitigate this limitation, Qing Guan et al. designed the distance-vector-based opportunistic routing (DVOR) protocol, which incorporated distance vector metrics with an opportunistic forwarding set [
7]. Packets were forwarded by the node that achieved the greatest progress toward the sink, thus improving robustness and delivery success rates. Finally, Dong Han et al. proposed the connectivity and energy-aware layered routing (CELR) protocol [
8]. This protocol partitioned the network into layers and selected relay nodes using multiple metrics, including distance, residual energy, and local connectivity. As a result, CELR improved relay selection, maintained end-to-end connectivity, and significantly extended the network’s operational lifetime. Cangzhu Xu et al. proposed the joint power control and multipath routing (CAMP) protocol, which jointly optimized power control and multipath transmission to enhance reliability and energy efficiency in dynamic underwater environments. By combining multipath routing at the source with single-path forwarding and power control at relays, CAMP achieved a higher packet delivery ratio, reduced latency, and increased throughput [
9].
However, acoustic communication suffers from inherent limitations such as high latency, low bandwidth, high energy consumption, and vulnerability to multipath and environmental interference. Many routing protocols employed both acoustic and optical waves in their designs to compensate for the trade-offs between long-range reliability and high-speed transmission, thereby enhancing overall network performance in diverse underwater environments. T. Hu et al. proposed the multi-level underwater routing algorithm for acoustic-optical networks (MURAO), which partitioned the network into acoustic and optical layers and applied multi-level Q-learning to train relay selection policies suitable for both long- and short-range transmissions [
10]. Similarly, P.M.C. Junior et al. introduced the CAPTAIN data collection algorithm, which constructed a routing tree based on inter-node distances to reduce latency and energy consumption in dense networks [
11]. Clustering and gateway placement methods followed. H. Yin et al. developed the surface gateway deployment (SGD) algorithm, using fuzzy clustering to determine optimal surface gateway locations, thereby shortening uplink transmission paths and reducing overall energy consumption [
12]. Adaptive medium-selection and power control techniques were also proposed [
13,
14,
15]. The CRPOA protocol dynamically chose the transmission medium based on packet size, using acoustic links for large packets and optical links for small packets, with Q-learning optimizing link selection [
13]. Z. Shen et al. proposed the power control-assisted Q-learning routing (PCAQR) algorithm, which combined game theory-based power control with Q-learning–guided routing to enhance delivery rate and prolong node life [
14]. Additionally, S. Han et al. addressed acoustic bottlenecks by introducing a carrier-switching strategy, which allowed nodes to switch automatically to optical links under congestion [
15]. Mobility-assisted and opportunistic forwarding approaches were also investigated. M. Doniec et al. presented an AUV-assisted hybrid routing architecture, where autonomous underwater vehicles provided wide-area acoustic sensing, and optical links were used for high-speed data transfer in localized areas [
16]. A. Celik et al. proposed the SectOR algorithm, which prioritized relays based on actual versus expected progress, thus improving opportunistic forwarding efficiency. Topology-aware and clustering-enabled protocols further advanced hybrid routing [
17]. Sun et al. proposed the Q-learning based multi-channel aware routing protocol (MCAPQ), which distinguished between optical and acoustic channels in the Q-learning process to reduce low-reward forwarding actions. Simulation results demonstrated that MCAPQ reduced latency, increased energy efficiency, improved throughput, and lowered packet loss compared with existing schemes [
18]. Yuan Zhou et al. proposed a Q-learning-based localization-free path routing (QLFR) protocol, which jointly considered residual energy and depth information to optimize routing decisions. By introducing depth- and energy-related reward functions and a new holding-time mechanism, QLFR effectively reduced end-to-end delay and extended network lifetime [
19]. Finally, W. Zhu et al. developed PHVP, leveraging packet hierarchy and a two-stage void-processing mechanism to ensure timely and reliable delivery of critical data [
20].
Although hybrid acoustic–optical routing algorithms leverage both acoustic and optical waves, they are still constrained by the inherent limitations of each medium: acoustic communication suffers from high latency and low bandwidth, while optical links are susceptible to misalignment and scattering in turbid water. To overcome these drawbacks and simplify system design, many researchers have shifted toward optical-only routing schemes in UOWSNs.
In [
21], T. Hu and Y. Fei proposed QELAR—a Q-learning-based adaptive routing protocol for UWSNs—which layered nodes by depth and selected next-hop candidates by optimizing a reward integrating residual energy and link delivery metrics (PDR/BER). Simulations on Aqua-Sim demonstrated that QELAR significantly balanced energy load, enhanced PDR and BER performance, and extended network lifetime by approximately 20% compared to VBF. In [
22], the distributed sector-based (DS) algorithm was introduced by R. Alghamdi et al., in which candidate nodes within a sender-defined divergence angle were scanned, and the one with the smallest deviation angle was selected as the next hop to shorten the transmission path and reduce energy consumption. To overcome DS’s limited candidate region, they further proposed the distributed scanning and sector-based (DSS) algorithm, which expanded the scanning sector dynamically and applied a probabilistic forwarding strategy, significantly improving the packet delivery ratio (PDR) and mitigating void region effects. To enhance link reliability, R. Alghamdi et al. also developed the distributed routing protocol (DRP), which selected relays based on real-time estimation of bit error rate (BER), choosing the most reliable paths accordingly [
23]. J. Liu et al. proposed the distributed energy-efficient and balanced (DEEB) routing algorithm, which utilized a virtual energy consumption model and node-level energy thresholds to guide forwarding decisions, thereby prolonging the network lifetime [
24]. A. Celik et al. presented the light path routing (LiPaR) protocol, which eliminated the need for traditional pointing–acquisition–tracking (PAT) mechanisms [
25]. By jointly considering beam divergence and communication distance, LiPaR enabled flexible light link establishment even in scenarios without accurate localization. Z. Shen et al. proposed the routing-benefited deployment approach (RBDA) [
26], which integrated static node monitoring and dynamic repositioning using a virtual force model to improve coverage, reduce energy usage, and enhance overall system performance. Energy-aware opportunistic hybrid mechanisms were advanced. B. Yan et al. proposed an MEOR algorithm, which partitioned nodes by energy level and employed opportunistic forwarding to enhance reliability and balance energy consumption [
27].
Although the above-mentioned protocols have significantly improved various aspects of optical routing, most of them do not explicitly address energy imbalance among forwarding nodes, nor do they incorporate advancement strategies that jointly consider both directionality and energy awareness. In addition, their neighbor discovery processes are often limited to single-hop information, which may lead to suboptimal relay selection and reduced robustness in sparse networks. To address these limitations, this paper proposes an optical-based routing protocol named EPAR, which integrates an energy partitioning mechanism, a tunable advancement function, and a hop-by-hop neighbor query strategy. Simulation results indicate that the proposed method achieves moderate improvements in packet delivery ratio, energy efficiency, and network lifetime compared to existing schemes. The main contributions in this paper are summarized as follows:
- (1)
An energy-partitioned relay selection mechanism is proposed for 3D UOWSNs, in which nodes are dynamically classified into high-energy and low-energy categories based on their residual energy. An adaptive weighting strategy is applied to prioritize high-energy nodes during the forwarding process, enabling balanced energy consumption and prolonging the network lifetime.
- (2)
A tunable advancement function is designed to jointly evaluate the Euclidean distance and steering angle toward the sink node. By adjusting a parameter α, this function supports directionally optimal and energy-efficient single-hop routing, effectively guiding data transmission in 3D underwater optical networks.
- (3)
A hop-by-hop neighbor discovery mechanism is incorporated, allowing each node to periodically update its local neighbor set through hello-based exchanges. This mechanism enhances relay selection accuracy and mitigates the impact of void regions, thereby improving packet delivery performance in sparse or dynamic topologies.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 introduces the employed system model.
Section 3 presents the details of the proposed EPAR algorithm.
Section 4 investigates the performance of EPAR algorithm.
Section 5 concludes the paper.
3. Details of the Proposed EPAR Algorithm
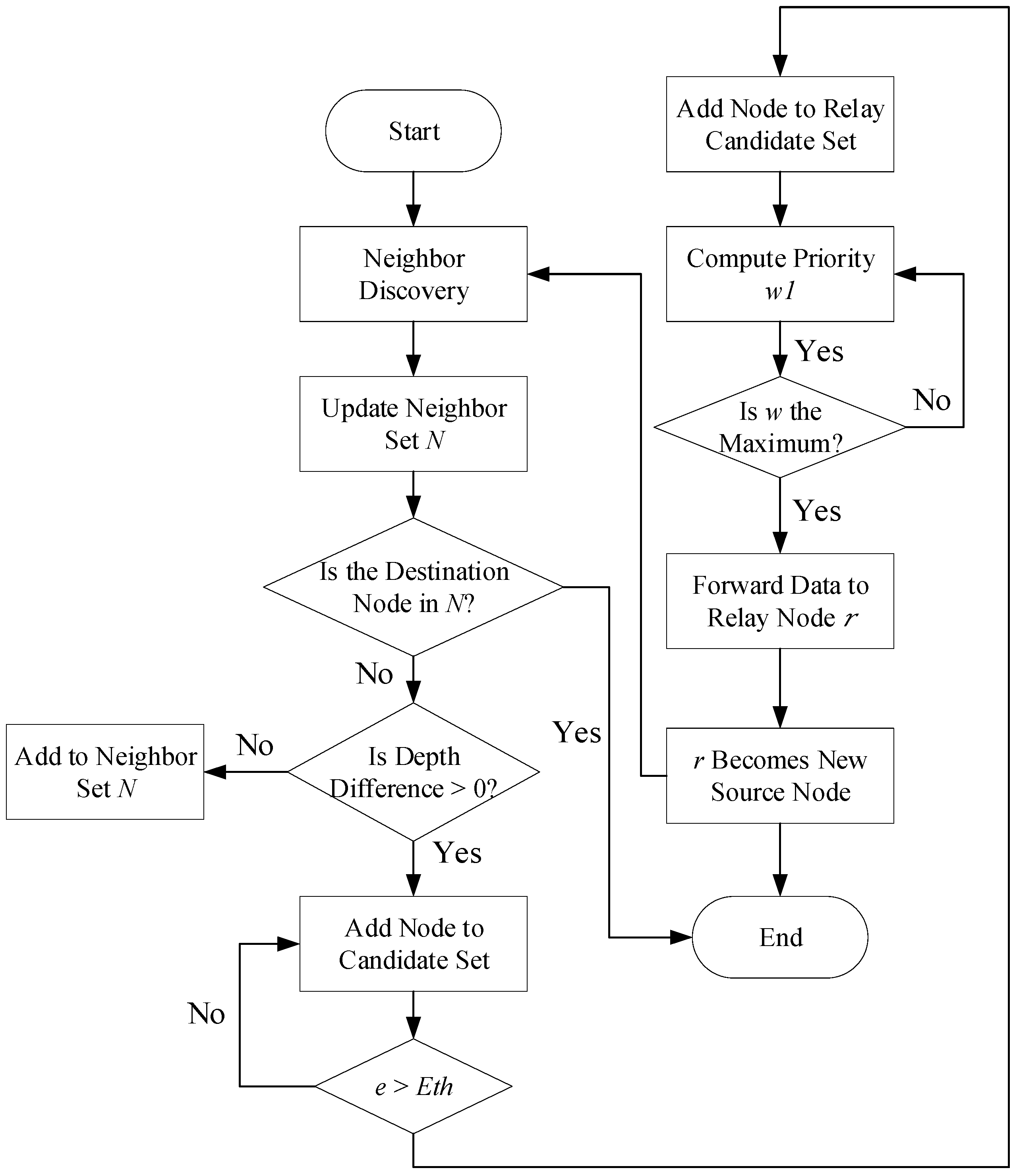
This section depicts the details of the proposed EPAR algorithm, which consists of four main stages, namely network initialization, candidate region selection, relay node selection and weight updating. In the first stage, each node periodically broadcasts hello messages to discover and update its local neighbor set, establishing the basis for subsequent routing decisions. In the second stage, the source node identifies the candidate region by comparing the depth of each neighbor and selecting those with shallower depth, as they are considered to be closer to the surface and thus more suitable as forwarders. In the third stage, the relay selection strategy evaluates the residual energy of the candidate nodes, retaining those above a predefined energy threshold to form the relay candidate set. In the final stage, the source node computes the forwarding priority of each relay candidate using a tunable advancement function that jointly considers Euclidean distance and steering angle. The node with the highest weight is selected as the next-hop relay. After data forwarding, the selected relay becomes the new source node, and the process is repeated until the destination is reached. The flowchart of the proposed EPAR algorithm is illustrated as shown in
Figure 2. Note that in the flowchart
N denotes the neighbor set of a node, while
r denotes the candidate relay node. The weight
W (or
w1) represents the weight value for relay priority calculation with
e and
Eth representing the residual energy of a node and the predefined energy threshold, respectively.
3.1. Network Initialization
The proposed EPAR algorithm configures underwater nodes and gathers neighbor information during initialization, including positional data, energy setup, and clearing the neighbor table and candidate set to facilitate efficient neighbor and candidate screening. Each node is assigned a unique ID. Post-configuration, nodes periodically broadcast hello packets to detect surroundings, whose structure is shown in
Figure 3. The hello packet includes a PID field for packet type identification (hello, ACK, or data), an SID field for the sender’s ID, and an SL field for positional data, enabling ACK replies from receiving nodes.
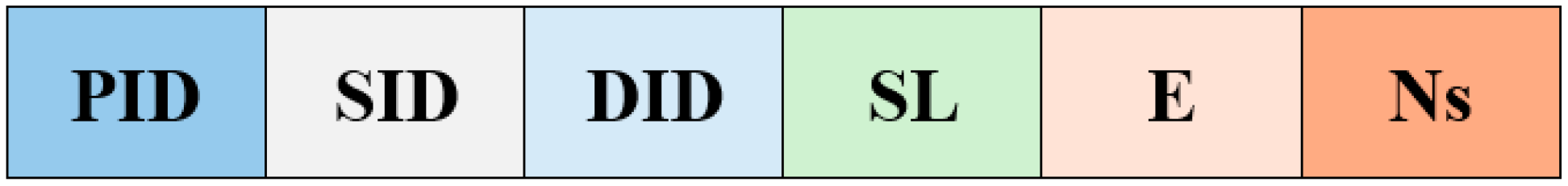
As illustrated in
Figure 4, the ACK packet contains the PID (packet ID), SID (sender ID), DID (recipient ID corresponding to the hello sender), SL (sender location), E (residual energy), and Ns (neighbor count). Nodes within the optical transmission range reply to a hello packet with an ACK, enabling the sender to update its neighbor table dynamically.
Node
i broadcasts a hello packet. Neighbor node
j checks the PID to confirm that it is a hello packet, extracts the SL field for the sender’s position, and calculates the distance. If within optical range,
j sends an ACK packet with its ID, position, energy, and neighbor count to
i. If out of range,
j ignores it. The network initialization can be described in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: Algorithm for network initialization |
Data: The hello packet with PID, SID, SL in its header; node i
send, node j receive; d is distance i between and j, D is
communication distance. |
| 1 | begin |
| 2 | | node j check PID; |
| 3 | | if it is hello packet then |
| 4 | | | node j calculate d; |
| 5 | | | if d <= D then |
| 6 | | | | SID ← IDj; |
| 7 | | | | SL ← SLj; |
| 8 | | | | E ← ej; |
| 9 | | | | Ns ← nsj; |
| 10 | | | | node j send ACK packet; |
| 11 | | | else |
| 12 | | | | node j discard this packet; |
| 13 | | | end if |
| 14 | | else |
| 15 | | end if |
| 16 | end |
3.2. Candidate Region Selection
After gathering neighbor node data, the proposed EPAR algorithm screens them to form a candidate set, reducing priority calculation complexity and boosting speed, while ensuring selected nodes can forward packets. Screening uses geographic data, with the forwarding node (e.g., node
i in
Figure 5) choosing only nodes above it—those with lower depth—toward the water surface. In
Figure 5, node
i’s communication sphere includes neighbors
f and
k, but only
f, above
i, is selected as a candidate, while
k, below, is excluded.
After initial screening, the candidate set is filtered by energy to form a relay set. The proposed EPAR algorithm uses a threshold: high-energy nodes above it join the relay set with priority, and low-energy nodes stay in the candidate set. The forwarding node picks from the relay set, switching to the candidate set if empty. As the energy of a relay node drops below the threshold, it is moved to the candidate set. This ensures that selected relays remain high in energy and close to the surface, thereby balancing energy consumption and preventing void regions.
3.3. Relay Node Selection
Relay node selection is critical for routing and requires an optimal choice at each hop. The proposed EPAR algorithm uses an advancement function and neighbor query to pick relays, ensuring data move toward the destination while balancing delivery and energy. Unlike distance-only protocols limited in 3D underwater spaces, EPAR considers distance and direction. With energy-saving unicast and retransmission, it avoids multicast’s redundant forwarding and collisions, optimizing relays by proximity. The advancement function is given as follows:
where
represents the Euclidean distance between the forwarding node
i and the candidate node
f,
θ denotes the angle between the line connecting the candidate node
f and the destination node
s and the line connecting the sending node
i and the destination node
s, as illustrated in
Figure 6.
D is the maximum communication range for underwater wireless optical communication. The parameter
α is an influence factor used to balance the relationship between
and
θ, with its value ranging between 0 and 1. When
α = 0, the optimal candidate node is the node itself. When
α = 1, the advancement function becomes a function solely of the distance, and the forwarding node considers only the distance between itself and the candidate node
f.
The advancement function prioritizes candidate nodes based on both distance and alignment with the path to the destination. By introducing the parameter α, it guides data packets to move closer to the destination in the x- and y-directions, reducing unnecessary hops. Nodes that are closer and better aligned are more likely to be selected, while those farther away or deviating from the path contribute less to forward progress and are less efficient in energy use.
The influence factor α determines the relative weight of distance d and angle θ in the advancement function. When α > 0.5, the function prioritizes the angle, making it the key factor in relay priority; when α < 0.5, it prioritizes distance, making it dominant; at α = 0.5, both factors have equal influence. Thus, selecting an appropriate α is vital for effective relay selection.
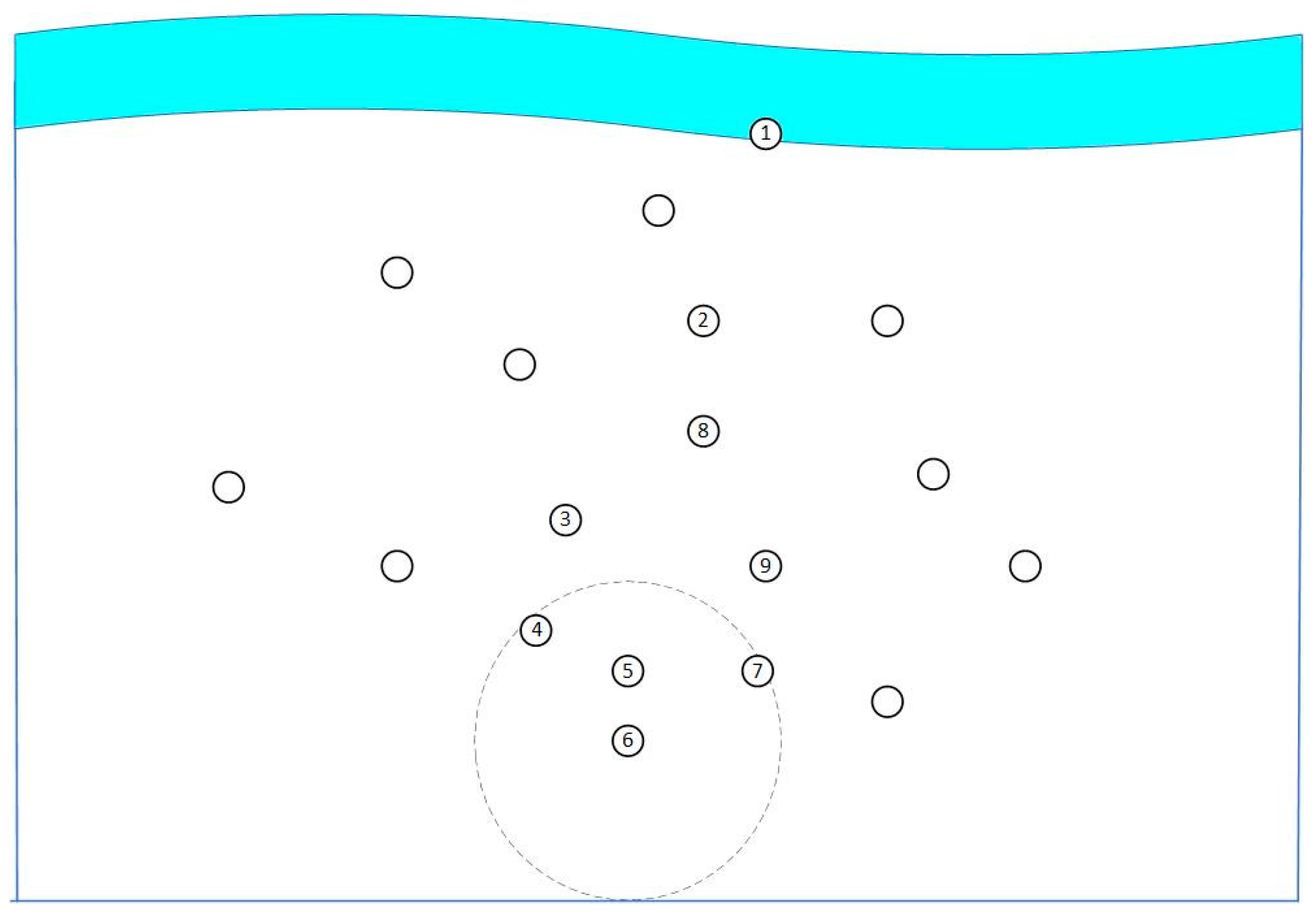
Figure 6 shows the next-hop selection. When α is small, node 6 prioritizes candidates aligned with the source-destination line, minimizing distance impact, and selects node 5 as the relay over distant nodes 4 or 7. Though node 5 moves the packet toward node 1 in
x-,
y-, and
z-directions, its short hop distance requires more hops, an effect intensifying with higher node density. When α is large, node 6 prioritizes distance from the source, minimizing the angle’s effect, and selects distant node 7 as relay over optimal nodes 4 or 5. With the angle’s minor role, the relay may deviate from the destination, causing horizontal-only transmission, more hops, and potential failure in sparse networks.
The proposed EPAR algorithm is a unicast routing protocol. Although it is more energy-efficient than multicast routing by reducing redundant data packet forwarding, it relies on a single link for data transmission. Consequently, if any hop in the transmission fails, the data packet cannot be correctly delivered to the surface sink node, leading to a decline in packet delivery rate. To address this issue, the proposed EPAR algorithm incorporates a neighbor query mechanism, which integrates neighbor information about candidate nodes into the priority calculation process.
Figure 7 shows the neighbor query mechanism’s role in EPAR. Compared with
Figure 6, which shows the effect of the advancement factor α,
Figure 7 emphasizes the role of neighbor awareness in avoiding void regions. Node 6’s neighbors are nodes 5 and 7. Without this mechanism, node 6 would pick node 5 with higher weight, but node 5’s next hop, node 4, has no neighbors, risking packet loss to a void region. With the mechanism, node 7, having neighbors 8 and 9, gains higher priority, leading node 6 to choose node 7. More neighbors expand candidate options, reducing void region transmission and boosting the delivery rate.
The weight formula for calculating the priority of relay nodes is as follows:
In this formulation, ADV denotes the advancement function of the candidate node, while NEI denotes the normalized neighbor index. The advancement function ensures directional progress toward the destination, whereas the neighbor index reflects the connectivity of the candidate. The normalized neighbor index is defined as
In Equation (15), denotes the actual number of neighbors of a candidate node, and represents the average neighbor count per node across the entire network, derived under the assumption of uniform random deployment. Therefore, provides a statistical measure of the expected number of neighbors surrounding a typical node. A candidate node with > statistically provides more reliable relay opportunities and is thus assigned a higher relay priority.
Consider a uniform random deployment of
N nodes in a 3D underwater environment of dimensions
X × Y × Z, where
X,
Y, and
Z correspond to the length, width, and height, respectively. The node density is then given by
. For a spherical communication range with radius
D, the expected neighbor count is derived as the product of the node density and the spherical volume, as expressed in Equation (16).
The first term is the volume of the node’s underwater transmission range, with R as the communication range. The second term is the average nodes per unit volume, where L, W, and H are the length, width, and height of the underwater environment, and N is the total number of deployed nodes.
3.4. Weight Updating
The proposed EPAR algorithm adjusts its weight formula through an energy partitioning mechanism based on the residual energy of nodes, thereby optimizing next-hop selection and data transmission. Energy is divided into high-energy and low-energy categories based on a predefined threshold. Nodes in the high-energy category engage in efficient single-hop transmission with minimal overhead. In contrast, nodes in the low-energy category prioritize residual energy to balance the load, which reduces local energy depletion but may increase hop count and energy consumption due to suboptimal forwarding paths. This extends the network lifetime, with energy above the threshold focused on transmission and below it balancing the load for prolonged survival.
As a relay node transmits data, its energy depletes. To avoid early exhaustion, when energy falls to the threshold, the sending node updates the weight formula, adding an energy factor to prioritize relay selection. The updated weight formula is as follows:
In EPAR, (remaining energy) and (initial energy) with influence factors a and b balance advancement, normalized energy, and neighbor count in priority. High-energy nodes enter the relay set, and low-energy nodes join the candidate set. Relay priority uses Equation (14) without energy; below threshold, nodes shift to the candidate set, using Equation (17) with energy factors when the relay set is empty, enhancing efficiency and reducing consumption.
It is important to note that Equation (17) is not universally applicable in the relay selection process. If the residual energy of all nodes exceeds the predefined threshold, the energy constraint is considered inactive. In this case, relay selection is determined solely by Equations (14)–(16). In the high-energy regime, prioritizing advancement and neighbor connectivity mitigates route fluctuations arising from minor energy variations. Conversely, if the residual energy of candidate nodes drops below the threshold, the energy constraint becomes active and is incorporated into the relay selection process. In the low-energy regime, Equation (17) is applied to simultaneously account for advancement, connectivity, and residual energy, thereby prolonging the network lifetime by mitigating the premature depletion of critical nodes.
Figure 8 shows the structure of data packets. PID identifies packet type and number. SID is the sending node ID, DID is the destination node ID, RID is the next-hop forwarding node ID, and data holds the payload.
After selecting a relay node, the source embeds the relay ID into the packet header and transmits the packet. Upon reception, neighboring nodes first examine the PID field to confirm that the packet is a data packet. They then compare the RID, SID, and DID fields with their own IDs. If the RID matches, the node acts as the relay. It then forwards the packet to the next hop. If the RID does not match, the node discards the packet. To ensure reliable delivery, EPAR employs an acknowledgment-based retransmission mechanism. Once the relay successfully receives a packet, it immediately sends an acknowledgment to the source. Upon receiving this acknowledgment, the source regards the transmission as successful. It then proceeds with subsequent packets. If the relay fails to receive the packet, the transmission is considered unsuccessful. Similarly, if the source does not receive the acknowledgment, the packet is regarded as lost. In either case, the source retransmits the packet. This mechanism effectively mitigates packet loss caused by link instability. It maintains routing performance in dynamic underwater environments. It also compensates for the degradation in packet delivery that is commonly observed in unicast transmissions. The relay selection process of the proposed EPAR algorithm is described in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2: Algorithm for relay node selection |
s is source node; Set is neighbor set of s; d is node depth;
Eth is energy threshold; RCS is relay candidate set; CS is candidate set. |
| 1 | begin |
| 2 | | if Set = Ø then |
| 3 | | | transmission packet failed; |
| 4 | | else |
| 5 | | | for i ∊ Set do |
| 6 | | | | if di > = ds then |
| 7 | | | | | if ei >= Eth then |
| 8 | | | | | | add node i into RCS; |
| 9 | | | | |
else |
| 10 | | | | | | add node i into CS; |
| 11 | | | | | end if |
| 12 | | | | end if |
| 13 | | | end for |
| 14 | | | if RCS = Ø then |
| 15 | | | | for j ∊ RCS do |
| 16 | | | | | calculate w; |
| 17 | | | | end for |
| 18 | | | | select a node with the largest w forward; |
| 19 | | | else |
| 20 | | | | if CS = Ø then |
| 21 | | | | | for k ∊ CS do |
| 22 | | | | | | calculate w; |
| 23 | | | | | end for |
| 24 | | | | | select a node with the largest w forward; |
| 25 | | | | else |
| 26 | | | | | transmission packet failed; |
| 27 | | | | end if |
| 28 | | | end if |
| 29 | | end if |
| 30 | end |
4. Performance Evaluation
This section presents the simulation setup and investigates the performance of the proposed EPAR algorithm. All simulations are implemented in C++ using Visual Studio 2019. In the simulations, sensor nodes are randomly deployed in a 3D underwater region of 100 m × 100 m × 100 m. The sink node is fixed at the center of the water surface, while the source node is selected from the maximum depth layer to simulate worst-case routing scenarios. After each transmission, another node at maximum depth is randomly selected as the new source. The communication radius is set to 60 m, and the number of nodes varies from 100 to 300. The detailed simulation parameters are summarized in
Table 1.
The initial energy of each node is set to 200 J, and the energy threshold is fixed at 100 J, i.e., 50% of the initial energy. The advancement factor α was evaluated in preliminary simulations. A small α favors directionality. This increases hop count and energy consumption. In contrast, a large α overemphasizes distance and degrades link reliability. A value of α = 0.4 provides a balanced trade-off and is therefore adopted in the subsequent simulations. In addition, both parameter a and parameter b are set to 0.5, which implies that advancement, normalized energy, and neighbor count are considered equally important in the priority calculation. In our simulations, packet delivery rate is defined as the ratio of successfully received packets to generated packets. Residual energy refers to the average remaining energy of all nodes at the end of simulation, and network lifetime is measured as the time until the first node depletes its energy.
In the implementation, the relay priority is computed as the sum of the advancement factor and the normalized residual energy. The advancement factor is represented by PDR. Moreover, the normalized residual energy is defined as the remaining energy divided by the initial energy. The assignment of a = b = 0.5 reflects that these two metrics are considered equally important in the design. However, this does not imply that they always contribute in the same proportion under all conditions. In contrast, the NEI, although introduced for completeness, is not directly included in this summation. Instead, NEI is applied during the candidate filtering stage. This ensures stable network connectivity and avoids routing through sparsely connected nodes.
In order to investigate the performance of the proposed EPAR algorithm in PDR, energy efficiency and network lifetime, three typical algorithms, known as QELAR [
21], DSS [
22], and MEOR [
27], are adopted as the compared algorithms in the simulations. All results are averaged over multiple independent runs with different random seeds to mitigate randomness. The observed trends remain consistent and stable across runs.
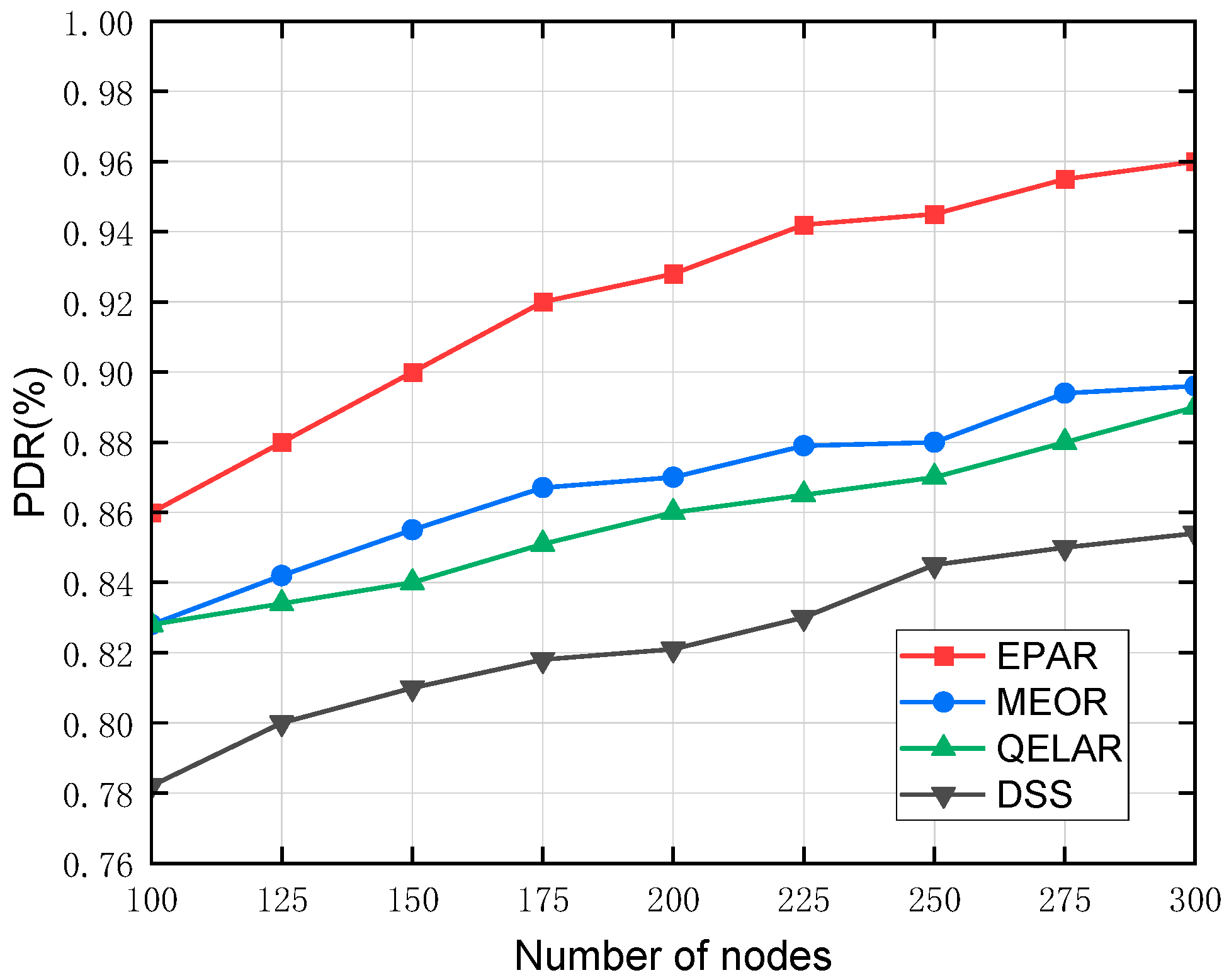
Figure 9 illustrates the PDR performance of the proposed EPAR protocol under varying node densities in comparison with the MEOR, QELAR, and DSS algorithms. As shown in
Figure 9, the PDR of EPAR consistently outperforms those of the other three algorithms across all densities. In particular, when the number of nodes is 100, the PDR of EPAR is approximately 5.0%, 7.0%, and 10.0% higher than those of MEOR, QELAR, and DSS, respectively. As the number of nodes increases, the PDR of all four protocols rises due to improved network connectivity. However, EPAR maintains a clear advantage in sparse deployments. This superiority is attributed to EPAR’s hop-by-hop neighbor query mechanism and adaptive relay selection strategy, which enable robust path identification and effectively avoid void regions. In contrast, the MEOR algorithm adopts an opportunistic forwarding strategy but lacks fine-grained relay screening in sparse scenarios, resulting in suboptimal next-hop choices. QELAR, while employing reinforcement learning, requires extensive environmental interaction to converge, thus limiting its effectiveness under low-density conditions. DSS exhibits the lowest PDR due to its static sector-based selection, which fails to respond to dynamic topology changes. At 300 nodes, EPAR still retains approximately 2.3%, 4.6%, and 7.8% higher PDR than MEOR, QELAR, and DSS, respectively, indicating sustained superiority in both sparse and dense network conditions. Overall, the proposed EPAR protocol enhances delivery reliability through its energy-aware unicast strategy and multi-hop neighbor screening, which jointly contribute to improved robustness and PDR, especially in challenging underwater environments.
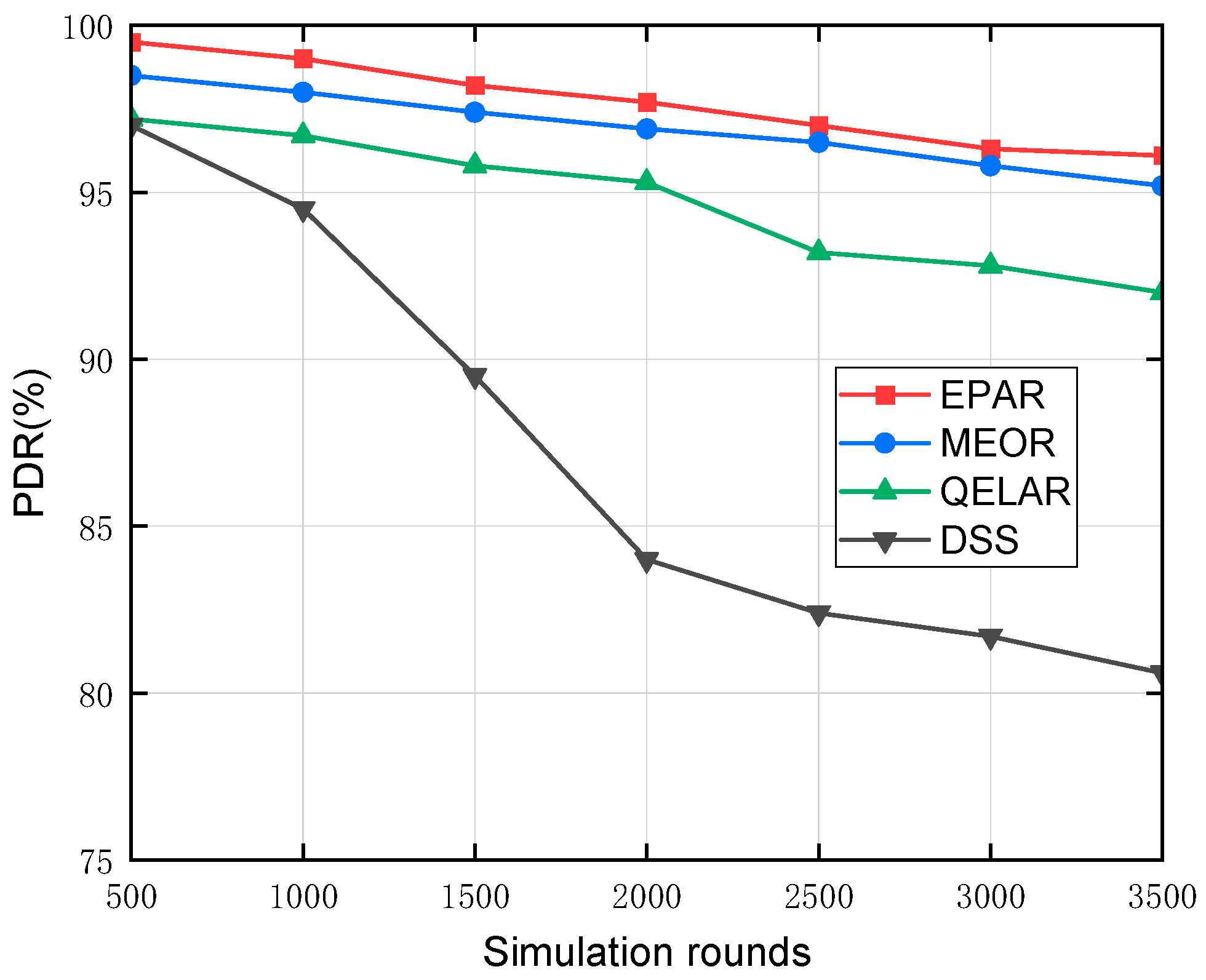
Figure 10 presents the PDR performance of the proposed EPAR protocol compared with the MEOR, QELAR, and DSS algorithms over an increasing number of simulation rounds, where each round represents a network transmission instance initiated by a randomly selected source node. As illustrated, all four protocols initially maintain comparable PDR values, with EPAR exhibiting a slight advantage of less than 2% within the first 500 rounds. However, as simulation progresses, notable disparities emerge due to cumulative energy depletion. At 2000 rounds, the PDR of DSS drops sharply to below 83%, while MEOR and QELAR decline gradually, maintaining around 91.5% and 90.2%, respectively. In contrast, EPAR maintains a PDR of approximately 94.8%, surpassing MEOR by 3.3%, QELAR by 4.6%, and DSS by 11.8%. As the simulation continues to 3500 rounds, the performance gap widens further. EPAR retains a PDR of about 95.5%, whereas MEOR, QELAR, and DSS drop to around 93.0%, 90.1%, and 78.6%, respectively. This performance degradation is primarily due to energy exhaustion among relay nodes, resulting in void region formation and disrupted routing paths. EPAR outperforms other protocols by leveraging its hop-by-hop neighbor query and energy-partitioned relay selection mechanisms, which dynamically identify reliable relays and prevent routing through depleted areas. In contrast, DSS relies on static depth-based relay selection, making it prone to path failures in evolving topologies. QELAR’s reinforcement learning-based strategy suffers from limited convergence under long-term dynamic conditions. MEOR, while incorporating energy awareness, lacks EPAR’s adaptive neighbor filtering, leading to moderate degradation. As analyzed above, the proposed EPAR protocol demonstrates superior long-term routing robustness and delivery stability in dynamic underwater environments.
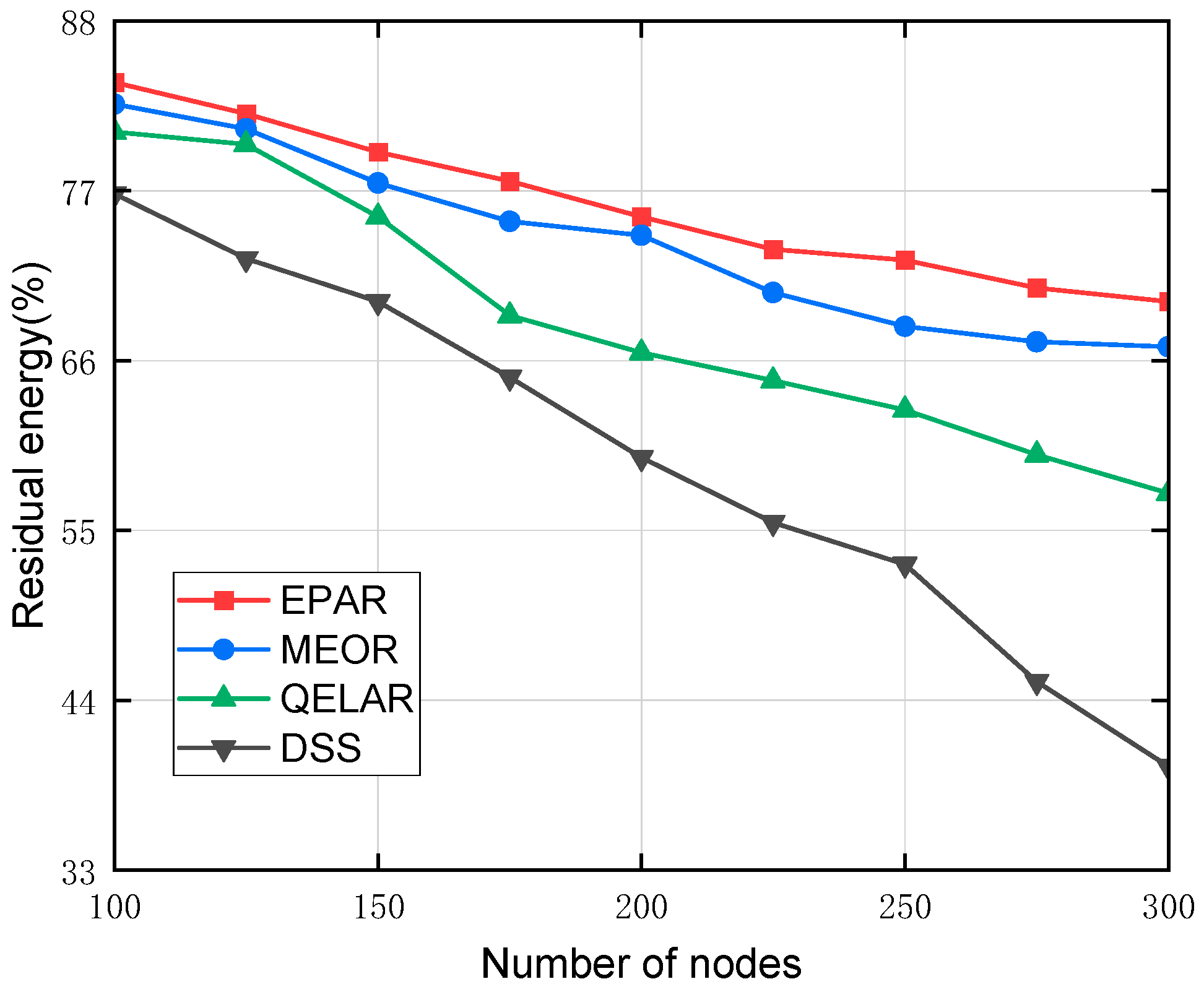
Figure 11 presents the residual energy performance of the proposed EPAR protocol compared with MEOR, QELAR, and DSS protocols under increasing node densities, with identical initial energy and communication parameters across all scenarios. As the number of nodes increases from 100 to 300, all protocols exhibit a steady decline in average residual energy due to heightened transmission frequency and routing overhead in denser environments. At 100 nodes, EPAR, MEOR, and QELAR maintain comparable energy levels above 80%, while DSS trails slightly below. However, as node count reaches 300, EPAR retains approximately 70% of residual energy, which is 8% higher than MEOR, 15% higher than QELAR, and nearly 30% higher than DSS. This superior performance is attributed to EPAR’s energy-partitioned relay selection mechanism, which classifies nodes into high- and low-energy groups to distribute energy consumption more evenly, as well as its advancement function, which minimizes unnecessary detours in transmission paths. In comparison, MEOR, although incorporating residual energy into its relay metric, lacks explicit partitioning or energy-based restrictions, resulting in concentrated energy depletion in frequently used nodes. QELAR employs a Q-learning-based adaptive strategy, but its trial-and-error exploration in uncertain underwater environments leads to redundant path testing and faster energy drainage. DSS, which neither considers energy levels nor implements an effective neighbor screening mechanism, suffers the most from excessive retransmissions and inefficient path selection. Overall, the proposed EPAR protocol demonstrates clear advantages in energy conservation under varying network densities, thereby enhancing long-term network sustainability.
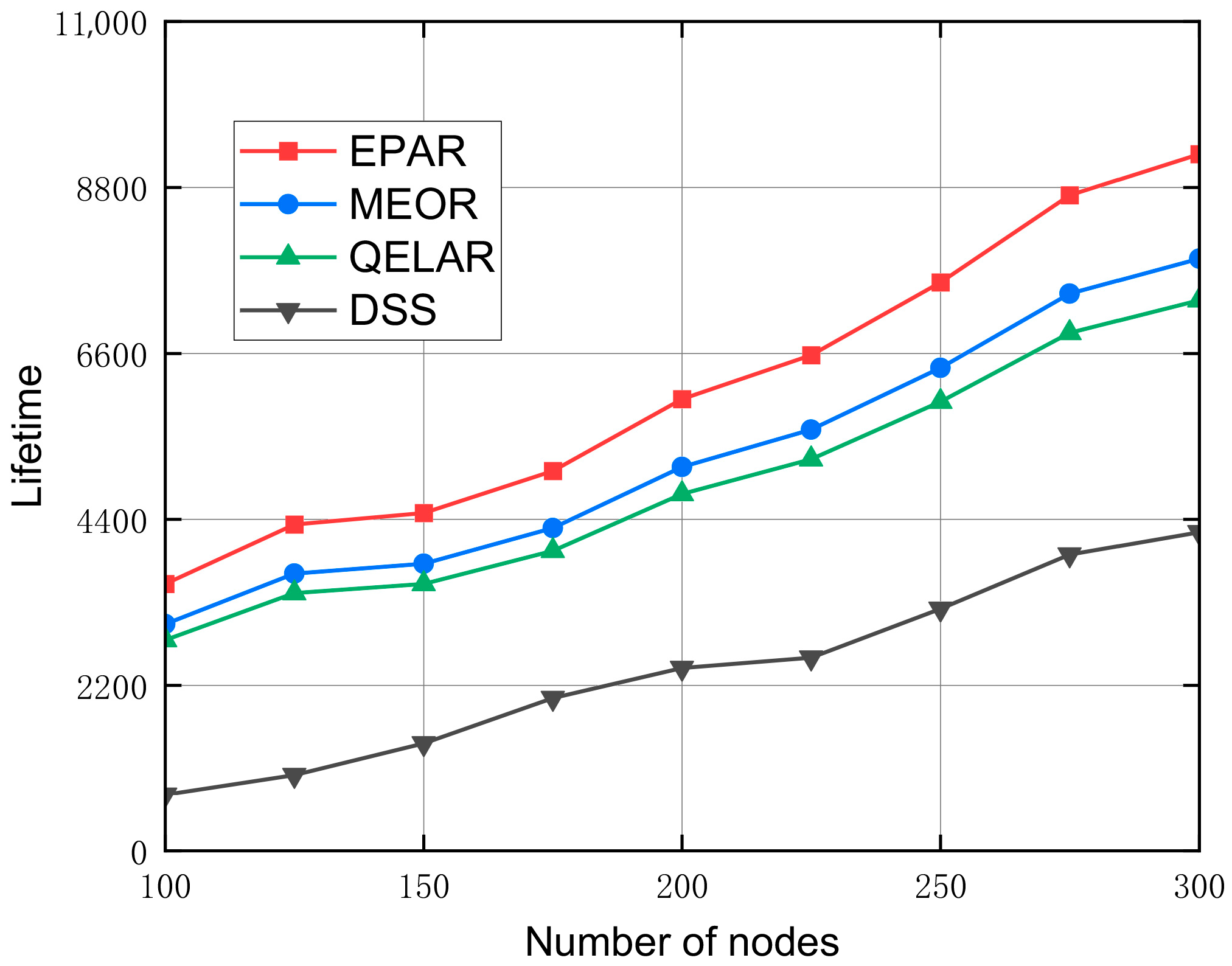
Figure 12 compares the network lifetime performance of the proposed EPAR protocol with MEOR, QELAR, and DSS under varying node densities ranging from 100 to 300 nodes, assuming uniform initial energy and packet generation settings. As the number of nodes increases, all protocols show a gradual improvement in network lifetime due to enhanced connectivity and greater relay diversity. At 100 nodes, the network lifetime achieved by EPAR exceeds that of DSS by approximately 3700 rounds and outperforms MEOR and QELAR by around 2600 and 2700 rounds, respectively. As node count increases to 300, EPAR extends network operation to nearly 9000 rounds, while MEOR and QELAR reach approximately 7200 and 6900 rounds, and DSS terminates at only 4200 rounds. These results clearly demonstrate the superiority of EPAR in prolonging network longevity. This is primarily attributed to EPAR’s energy-partitioned relay selection, which prevents the overuse of critical high-energy nodes; its neighbor-aware advancement function, which optimizes directionality and reduces hop count; and its unicast routing strategy, which eliminates unnecessary broadcast overhead. In contrast, MEOR, although incorporating opportunistic forwarding and residual energy awareness, does not implement explicit energy segmentation, which leads to uneven relay load distribution. QELAR, driven by reinforcement learning, requires extensive environmental feedback to stabilize, making it less robust in long-term dynamic conditions. DSS, devoid of any energy-aware mechanism, suffers from early exhaustion of central relay nodes, resulting in rapid network partitioning and significantly reduced operational lifespan. In summary, the proposed EPAR protocol demonstrates outstanding performance in maintaining prolonged and stable network functionality, especially under increasing network scale.