Complete Suppression of Color Dispersion in Quantum-Dot Backlights by Optimizing Optical Configuration of Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kybayashi, S.; Mikoshiba, S.; Lim, S. (Eds.) LCD Backlights; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, E.F.; Kim, J.K.; Luo, H.; Xi, J.-Q. Solid-state lighting—A benevolent technology. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2006, 69, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pust, P.; Schmidt, P.J.; Schnick, W. A revolution in lighting. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Liu, R.-S. Advances in phosphors for light-emitting diodes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKittrick, J.; Shea-Rohwer, L.E. Down conversion materials for solid-state lighting. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-W.; Choi, M.H.; Ko, J.-H. Effect of Temperature on the Luminous Properties of White-light-emitting Diodes with Red and Green Phosphors. New Phys. Sae Mulli 2013, 63, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, T.; Demir, H.V. Color science of nanocrystal quantum dots for lighting and displays. Nanophotonics 2013, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.K.; Lim, J.; Lee, D.; Park, M.; Lee, H.; Kwak, J.; Char, K.; Lee, C.; Lee, S. R/G/B/natural white light thin colloidal quantum dot-based light-emitting devices. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.J.; Zahid, M.U.; Le, P.; Ma, L.; Entenberg, D.; Harney, A.S.; Condeelis, J.; Smith, A.M. Brightness-equalized quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Park, Y.S.; Wu, K.; Yun, H.J.; Klimov, V.I. Droop-free colloidal quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denault, K.A.; Mikhailovsky, A.A.; Brinkley, S.; DenBaars, S.P.; Seshadri, R. Improving color rendition in solid state white lighting through the use of quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-R.; Chen, S.-S.; Wang, K.-W.; Siao, C.-B. Promotion of solid-state lighting for ZnCdSe quantum dot modified-YAG-based white light-emitting diodes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 51989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Murase, N. Synthesis of Highly Luminescent Glasses Incorporating CdTe Nanocrystals through Sol-Gel Processing. Langmuir 2004, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, C.; Mulvaney, P.; Sada, C.; Ferrari, M.; Chiasera, A.; Martucci, A. Incorporation of a highly luminescent semiconductor quantum dot in ZrO2–SiO2 hybrid sol–gel glass film. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsuya, H.; Ebina, T.; Mizukami, F. Highly luminescent flexible quantum dot-clay films. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlugun, E.; Hernandez-Martinez, P.L.; Eroglu, C.; Coskun, Y.; Erdem, T.; Sharma, V.K.; Unal, E.; Panda, S.K.; Hicky, S.G.; Gaponik, N.; et al. Large-Area (over 50 cm × 50 cm) Freestanding Films of Colloidal InP/ZnS Quantum Dots. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Yang, H. White lighting device from composite films embedded with hydrophilic Cu(In, Ga)S2/ZnS and hydrophobic InP/ZnS quantum dots. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 225601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-J.; Chiang, R.-K.; Wang, S.-L. High color-rendering warm-white lamps using quantum-dot color conversion films. Opt. Express 2016, 24, A1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, E.; Jun, S.; Jang, H.; Lim, J.; Kim, B.; Kim, Y. White-light-emitting diodes with quantum dot color converters for display backlights. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, S.; Lee, J.; Jang, E. Highly luminescent and photostable quantum dot–silica monolith and its application to light-emitting diodes. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y.; Genc, S.; Talpur, M.Y.; Mutlugun, E. CdSe/ZnS quantum dot films for high performance flexible lighting and display applications. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 295604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-W.; Zhu, R.-D.; He, J.; Duan, W.; Hu, W.; Lu, Y.-Q.; Li, M.-C.; Lee, S.-L.; Dong, Y.-J.; Wu, S.-T. Going beyond the limit of an LCD’s color gamut. Light Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e17043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S.; Joos, J.J.; Martin, L.I.D.; Hens, Z.; Smet, P.F. Hybrid remote quantum dot/powder phosphor designs for display backlights. Light Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e16271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Xie, H.; Huang, J.; Miu, H.; Shao, G.; Li, Y.; Guo, T.; Xu, S.; Ye, Y. Flexible/curved backlight module with quantum-dots microstructure array for liquid crystal displays. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lan, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.-S.; Yang, H.-Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.-W. Highly Stable White Light-Emitting Diodes Based on Quantum-Dots Dispersed Into the Backlight Lens for Display Backlight. IEEE Photonics J. 2019, 11, 8200707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Jang, H.W.; Lee, J.-G.; Ko, J.-H.; Ko, Y.W.; Kim, Y. Substantial Improvement of Color-Rendering Properties of Conventional White LEDs Using Remote-Type Red Quantum-Dot Caps. New Phys. Sae Mulli 2019, 69, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-G.; Ko, J.-H. Simulation Study on the Improvement of the Luminance and the Color Uniformities of Integrated Quantum-Dot Backlights for LCD Applications. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2020, 77, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Shin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; Yang, D.-K. Aligned polymer dispersed liquid crystal film for light enhancement of quantum dot backlight. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 43241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.J.; Lee, J.-G.; Kim, Y.; Park, T.; Ko, Y.W.; Ko, J.-H. The effect of the reflective property of a reflection film on the performance of backlight units with quantum-dot films for LCD applications. J. Inf. Disp. 2021, 22, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Ye, Z.T.; Lai, W.; Chiu, C.C.; Lin, K.W.; Han, P. Application of mini-LEDs with microlens arrays and quantum dot film as extra-thin, large-area, and high-luminance backlight. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Chen, E.; Sun, L.; Guo, T. Quantum-dot color conversion film patterned by screen printing and overprinting process for display backlights. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 145, 107486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-Y.; Huang, W.-T.; Chen, J.-H.; Liu, W.-B.; Chang, S.-W.; Chen, F.-C.; Kuo, H.-C. Optimized design with artificial intelligence quantum dot white mini LED backlight module development. Crystals 2023, 13, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.-T. Wide color gamut LCD with a quantum dot backlight. Opt. Express 2023, 21, 26269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Cai, J.; Deng, L.; Xu, S.; Ye, Y.; Yan, Q.; Guo, T.; Chen, E. Uniformity improvement of a mini-LED backlight by a quantum-dot color conversion film with nonuniform thickness. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Choo, H.-H.; Jang, J.-H.; Kwak, M.-J.; Baek, E.; Kim, S.; Ko, J.-H. Correlation between the gain factor of a reflective polarizer and the optical structure of quantum dot-based backlights for LCD applications. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2024, 85, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, B.; Lemmer, U. A Review on Quantum Dot-Based Color Conversion Layers for Mini/Micro-LED Displays: Packaging, Light Management, and Pixelation. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2024, 12, 2300873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Chang, Y.; Deng, Z. Research Progress on Quantum Dot-Embedded Polymer Films and Plates for LCD Backlight Display. Polymers 2025, 17, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, E.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.; Song, J.; Yoo, J.; Park, S.M.; Lee, J.-M.; Ko, J.-H. Color Rendering Index over 95 Achieved by Using Light Recycling Process Based on Hybrid Remote-Type Red Quantum-Dot Components Applied to Conventional LED Lighting Devices. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Lee, H.; Cho, J.; Choi, I.; Park, S.M.; Ko, J.-H. Study on High-Efficiency White Light-Emitting Diodes Using a Remote Phosphor with Cadmium-Free Quantum Dots. New Phys. Sae Mulli 2023, 73, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Baek, E.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Park, S.M.; Ko, J.-H. Tunable viewing angle characteristics of QD-enhanced LED lighting through combinations of holographic diffuser and prism film. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2025, 86, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, S. Over 32.5% Efficient Top-Emitting Quantum-Dot LEDs with Angular-Independent Emission. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 30039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, B.-L.; Ji, J.-W.; Wu, B.-H.; Chen, K.-A.; Kuroda, H.; Kou, H.-C.; Akada, T.; Li, C.-Y. Investigation and comparison of the influence of modified DBR and yellow color filters for quantum dot color conversion-based micro LED applications. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, R.; Wu, L.; Lin, X.; Xia, X.; Ao, Z.; Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, S. Ultrabright and stable top-emitting quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with negligible angular color shift. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.G.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Nahm, K.-B.; Ko, J.-H.; Kim, J.H. Light output characteristics of rounded prism films in the backlight unit for liquid crystal display. J. Inf. Disp. 2006, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.; Boyd, G.T. Mobile Displays; Bhowmik, A.K., Li, Z., Bos, P.J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Won, Y.-H.; Cho, O.; Kim, T.; Chung, D.-Y.; Kim, T.; Chung, H.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Jang, E. Highly efficient and stable InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nature 2019, 575, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

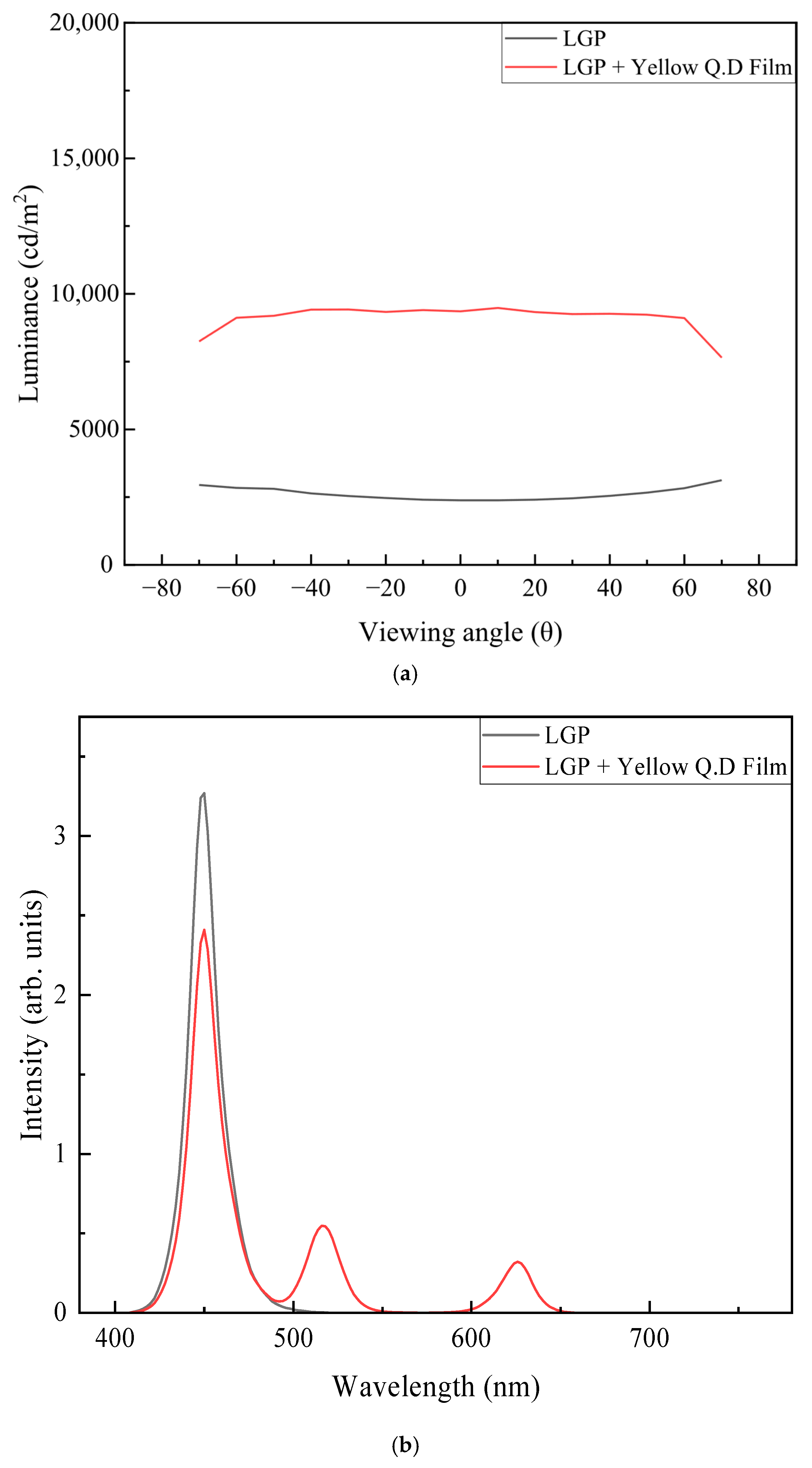
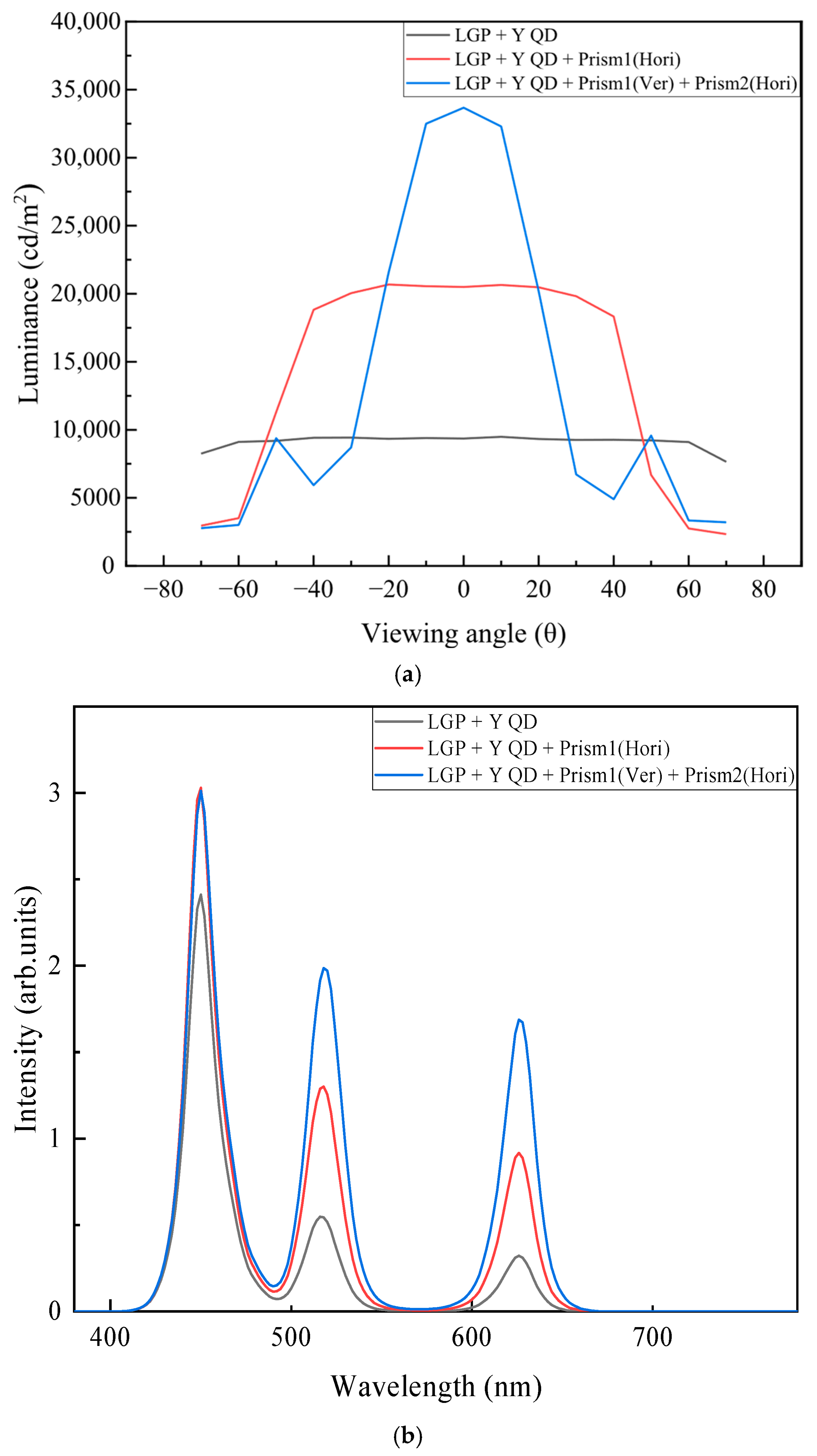
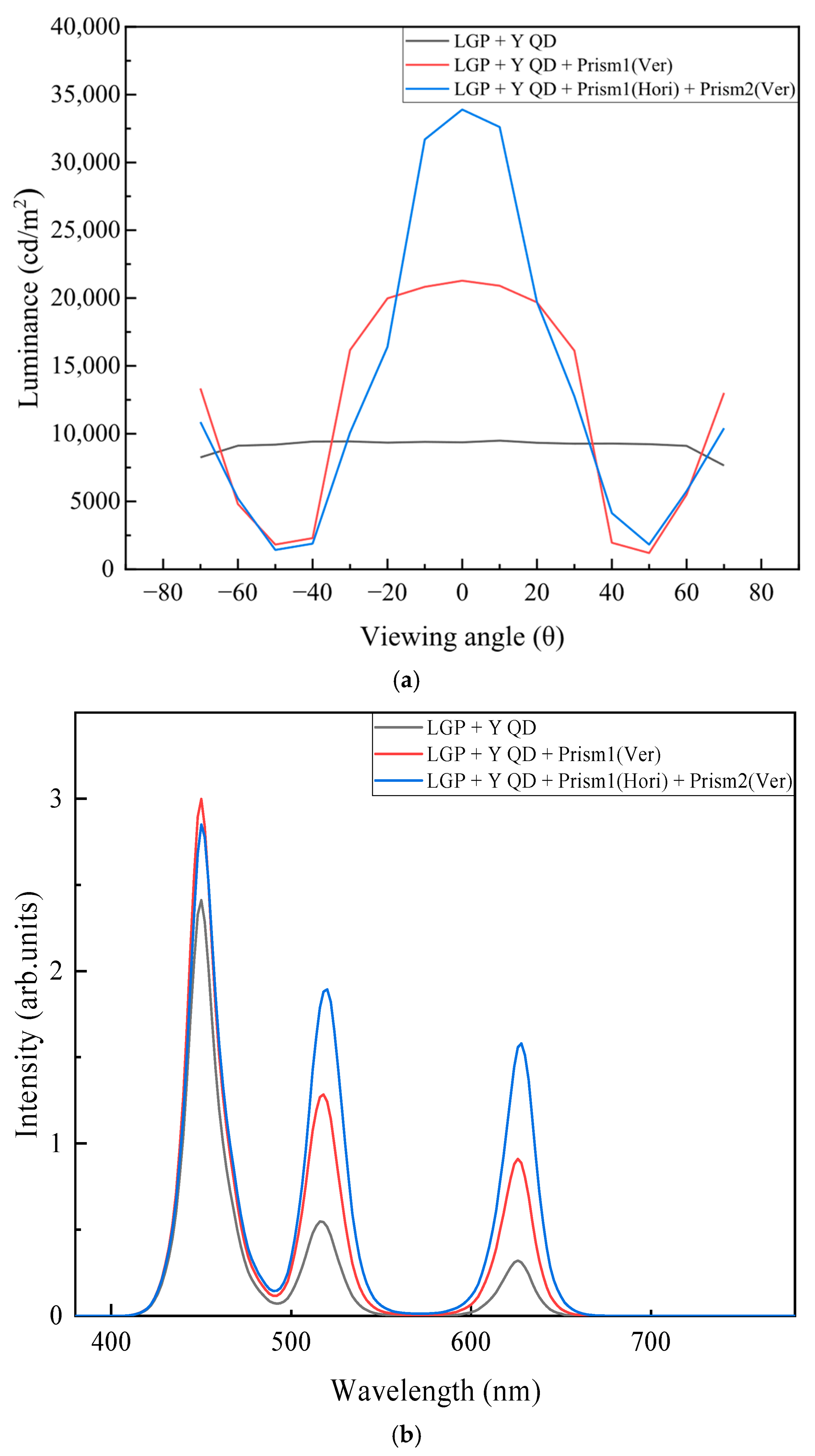
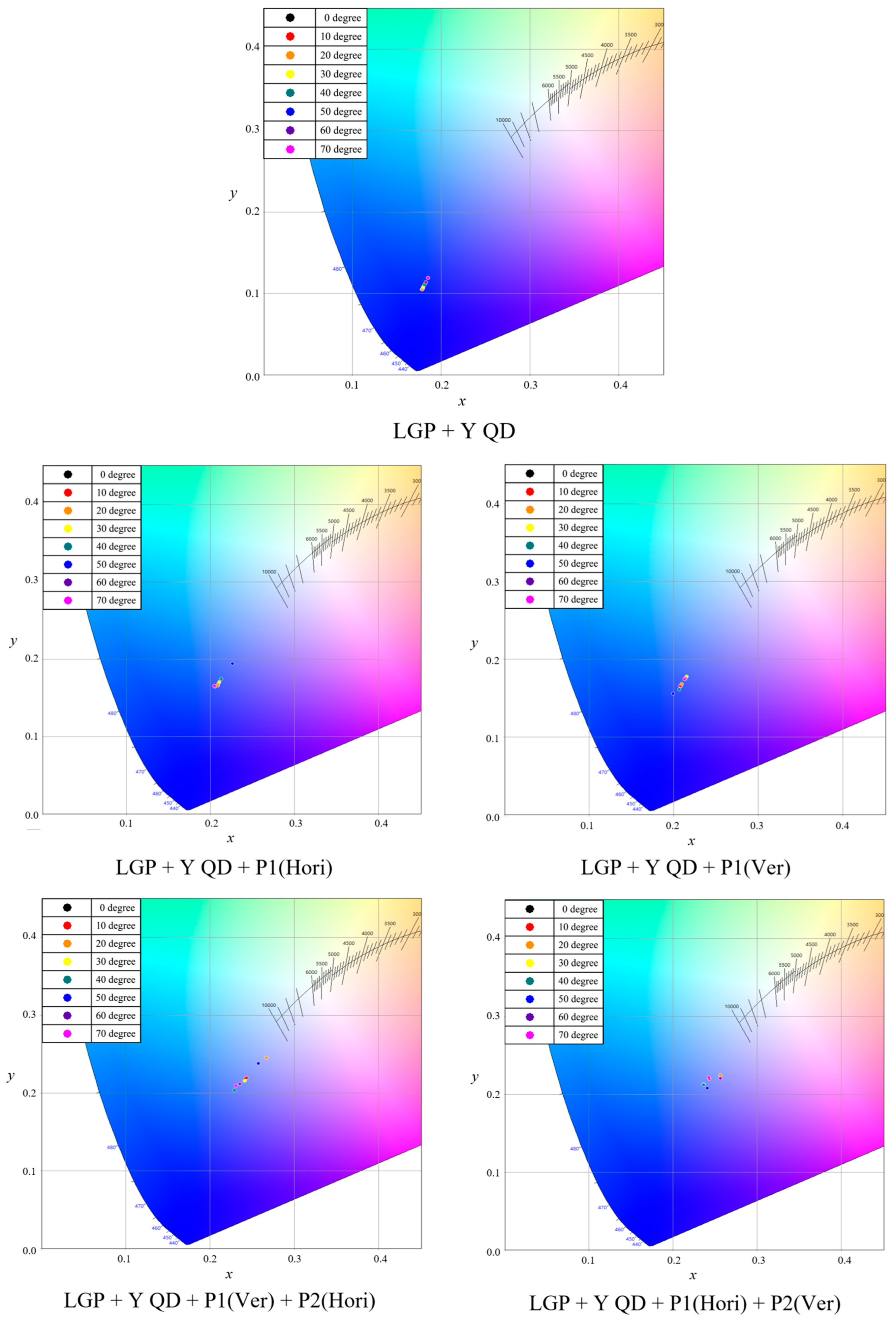

| Haze | Total Transmittance | Parallel Transmittance | Diffuse Transmittance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF(HighH) | 97.07 | 95.55 | 2.8 | 92.75 |
| DF(LowH) | 67.96 | 91.38 | 29.28 | 62.10 |
| Combination of Optical Films | Luminance (cd/m2) | x | y |
|---|---|---|---|
| LGP | 2380 | 0.1532 | 0.0232 |
| LGP + YQD | 9357 | 0.1787 | 0.1045 |
| LGP + YQD + P1(Hori) | 20,500 | 0.2076 | 0.1674 |
| LGP + YQD + P1(Ver) | 21,280 | 0.2081 | 0.1647 |
| LGP + YQD + P1(Ver) + P2(Hori) | 33,310 | 0.2422 | 0.2176 |
| LGP + YQD + P1(Hori) + P2(Ver) | 33,900 | 0.2433 | 0.2199 |
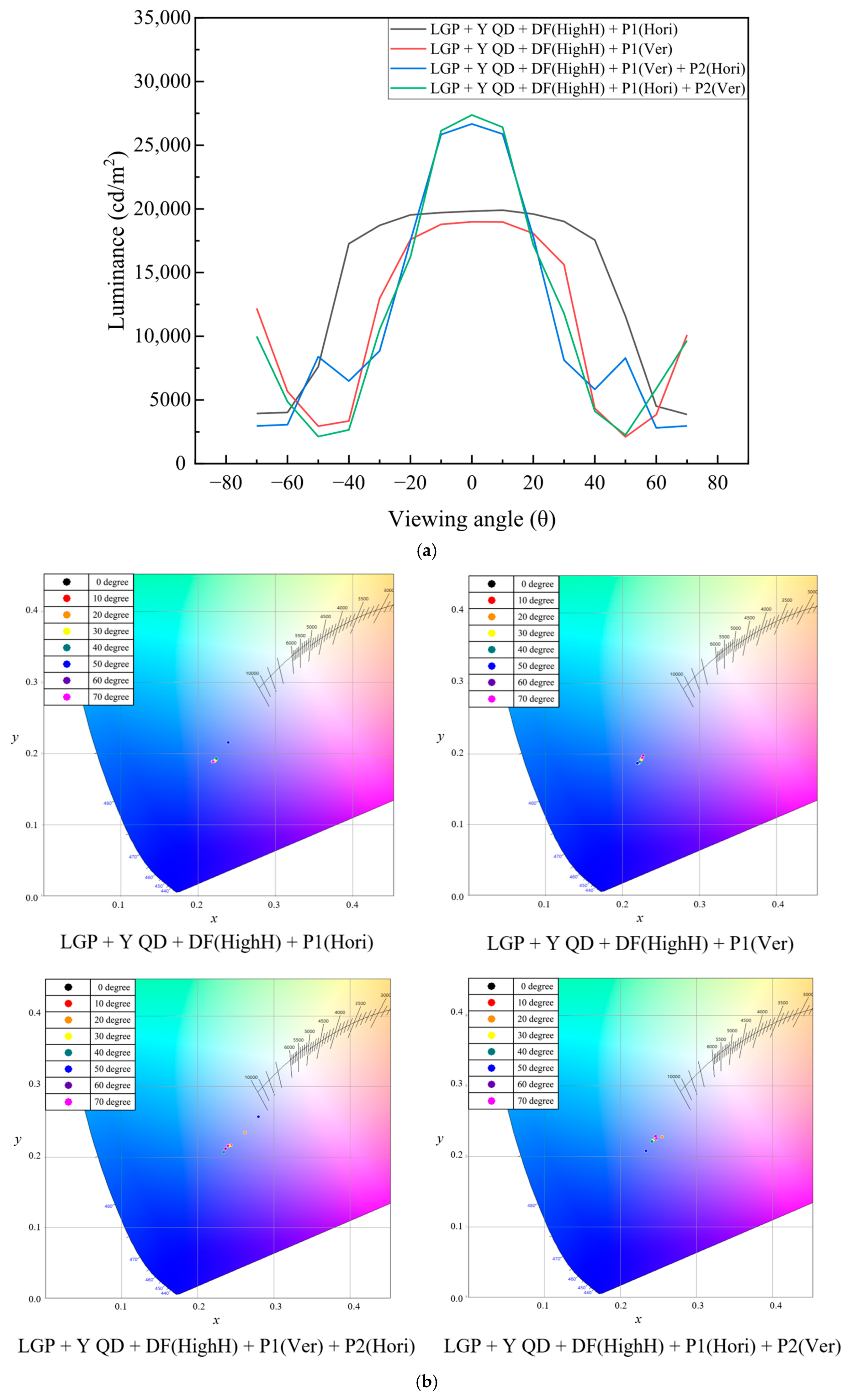
| LGP + YQD + DF(HighH) + P1(Hori) | 19,820 | 0.2216 | 0.189 |
| LGP + YQD + DF(HighH) + P1(Ver) | 18,990 | 0.2212 | 0.1867 |
| LGP + YQD + DF(HighH) + P1(Ver) + P2(Hori) | 27,240 | 0.2426 | 0.2151 |
| LGP + YQD + DF(HighH) + P1(Hori) + P2(Ver) | 27,370 | 0.2465 | 0.2243 |
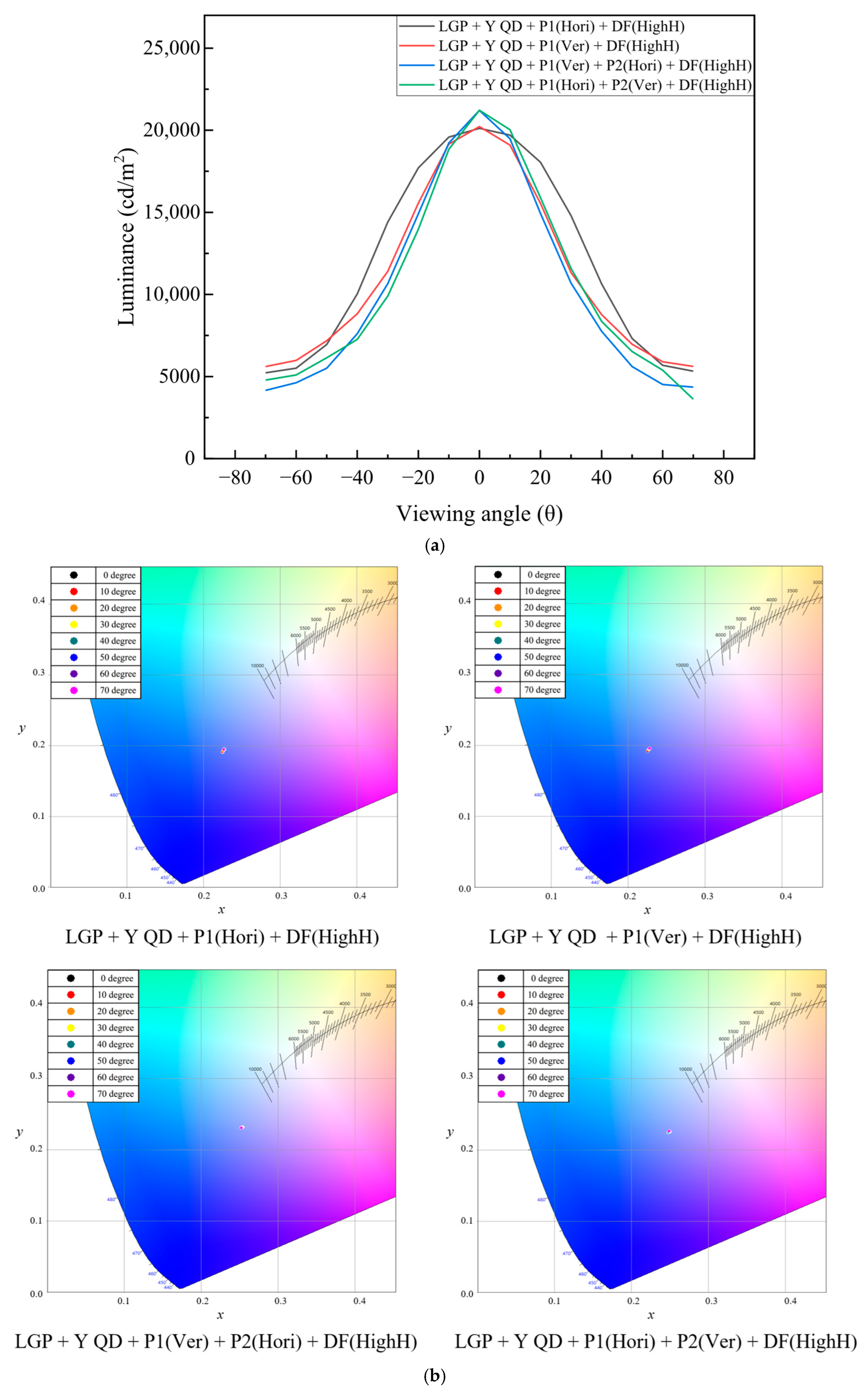
| LGP + YQD + P1(Hori) + DF(HighH) | 20,120 | 0.2247 | 0.1907 |
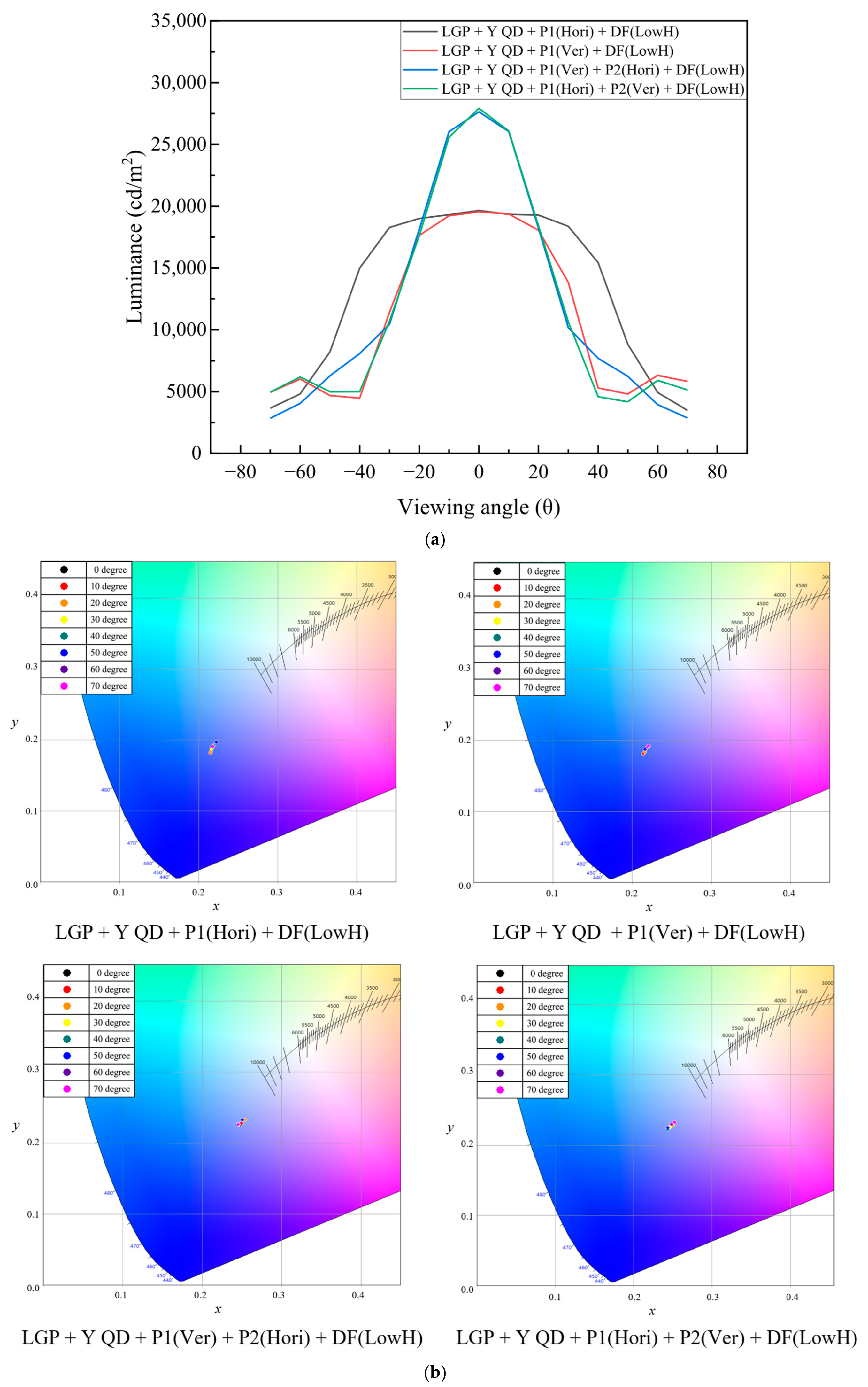
| LGP + YQD + P1(Hori) + DF(LowH) | 19,660 | 0.2149 | 0.181 |
| LGP + YQD + P1(Ver) + DF(HighH) | 20,220 | 0.2255 | 0.1915 |
| LGP + YQD + P1(Ver) + DF(LowH) | 19,560 | 0.2145 | 0.1808 |
| LGP + YQD + P1(Ver) + P2(Hori) + DF(HighH) | 21,210 | 0.2544 | 0.2319 |
| LGP + YQD + P1(Ver) + P2(Hori) + DF(LowH) | 27,640 | 0.2482 | 0.2257 |
| LGP + YQD + P1(Hori) + P2(Ver) + DF(HighH) | 16,080 | 0.2498 | 0.2256 |
| LGP + YQD + P1(Hori) + P2(Ver) + DF(LowH) | 27,930 | 0.2477 | 0.2262 |
| Combination of Optical Films | Reference (0°) | Angle | Δx | Δy | Δxy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGP + Y QD + P1(Hori) + P2(Ver) | (0.2433, 0.2199) | 10° | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| 30° | −0.0066 | −0.0074 | 0.0099 | ||
| 50° | −0.0023 | −0.0123 | 0.0125 | ||
| 70° | −0.0005 | 0.0012 | 0.0013 | ||
| LGP + Y QD + DF(HighH) + P1(Ver) + P2(Hori) | (0.2426, 0.2151) | 10° | 0.0009 | 0.0015 | 0.0017 |
| 30° | −0.0003 | 0.0007 | 0.0008 | ||
| 50° | 0.0372 | 0.0422 | 0.0563 | ||
| 70° | −0.0028 | 0.0007 | 0.0029 | ||
| LGP + Y QD + P1(Hori) + P2(Ver) + DF(HighH) | (0.2498, 0.2256) | 10° | −0.0002 | −0.0001 | 0.0002 |
| 30° | −0.0016 | −0.0012 | 0.002 | ||
| 50° | −0.0004 | 0.0004 | 0.0006 | ||
| 70° | −0.0006 | 0.0007 | 0.0009 | ||
| LGP + Y QD + P1(Ver) + P2(Hori) + DF(LowH) | (0.2482, 0.2257) | 10° | 0.0015 | 0.0019 | 0.0024 |
| 30° | −0.002 | 0 | 0.002 | ||
| 50° | 0.0027 | 0.0065 | 0.007 | ||
| 70° | −0.0026 | 0.0001 | 0.0026 | ||
| 65-Inch QD-Mini LED TV | (0.2989, 0.2619) | 10° | −0.0002 | −0.0001 | 0.0002 |
| 30° | 0.0033 | 0.0037 | 0.005 | ||
| 50° | 0.0026 | 0.0028 | 0.0038 | ||
| 70° | 0.0044 | 0.0055 | 0.007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Seo, M.-H.; Yang, J.-S.; Ko, J.-H. Complete Suppression of Color Dispersion in Quantum-Dot Backlights by Optimizing Optical Configuration of Films. Photonics 2025, 12, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090864
Kim D-H, Kim J-Y, Seo M-H, Yang J-S, Ko J-H. Complete Suppression of Color Dispersion in Quantum-Dot Backlights by Optimizing Optical Configuration of Films. Photonics. 2025; 12(9):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090864
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Do-Hyeon, Jin-Young Kim, Mu-Hyeok Seo, Ju-Seok Yang, and Jae-Hyeon Ko. 2025. "Complete Suppression of Color Dispersion in Quantum-Dot Backlights by Optimizing Optical Configuration of Films" Photonics 12, no. 9: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090864
APA StyleKim, D.-H., Kim, J.-Y., Seo, M.-H., Yang, J.-S., & Ko, J.-H. (2025). Complete Suppression of Color Dispersion in Quantum-Dot Backlights by Optimizing Optical Configuration of Films. Photonics, 12(9), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090864





