Study on Diamond NV Centers Excited by Green Light Emission from OLEDs
Abstract
1. Introduction
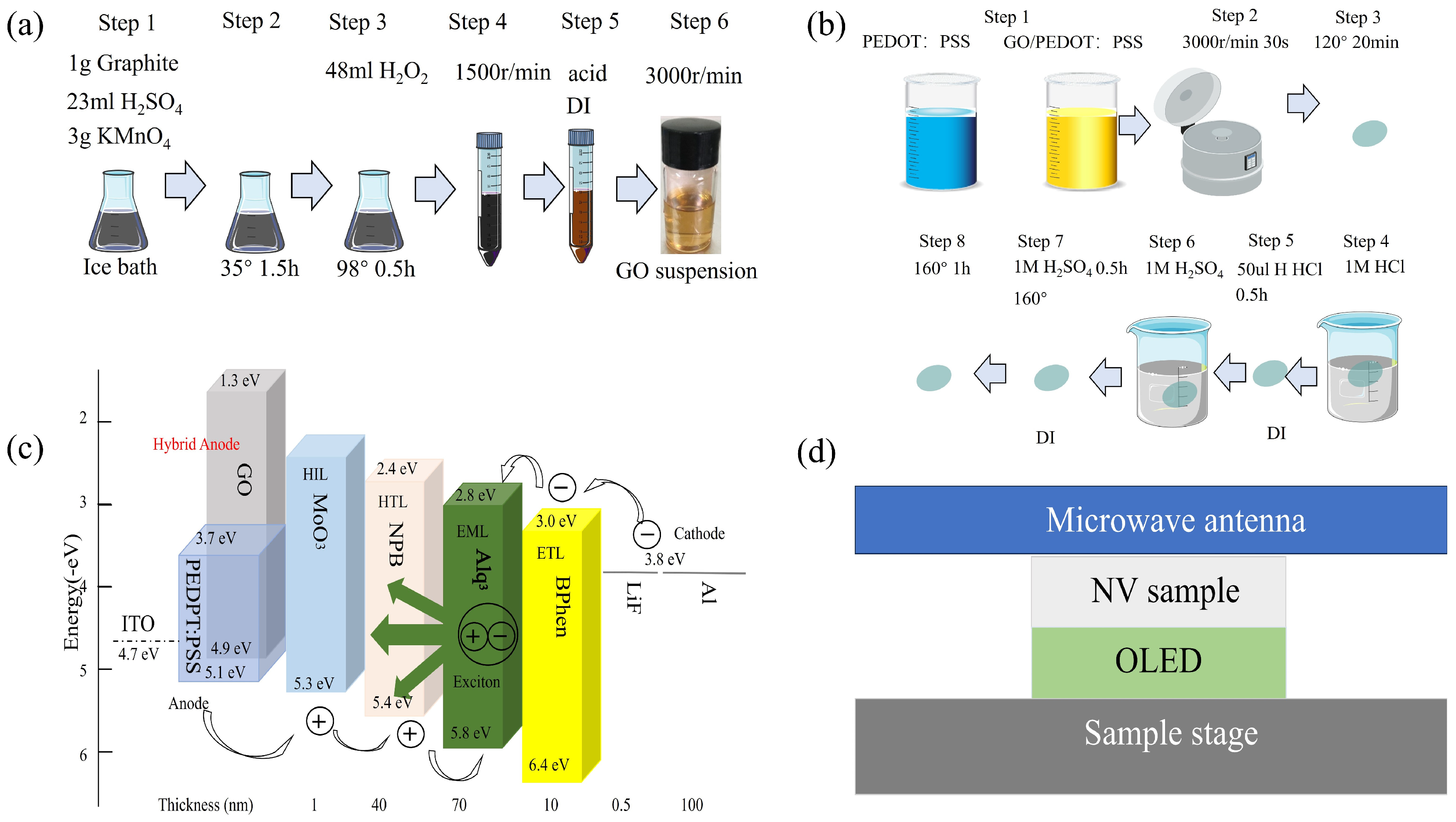
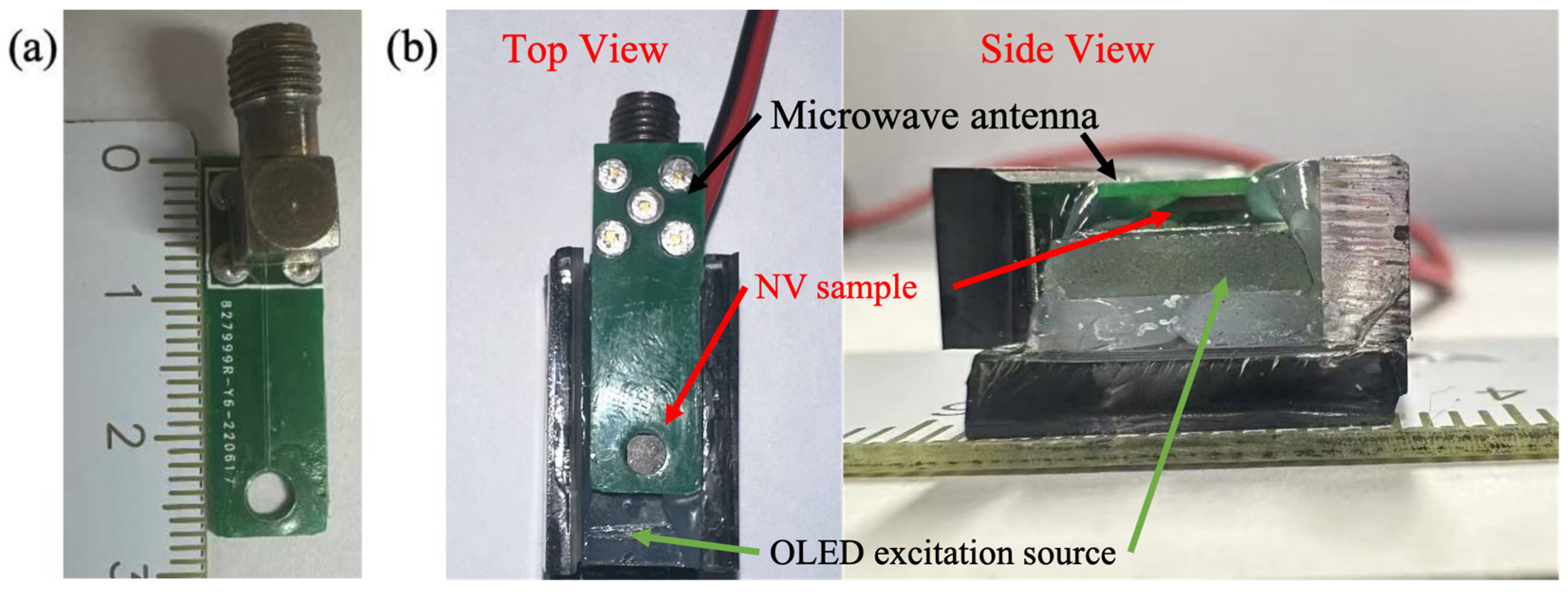
2. Materials and Methods
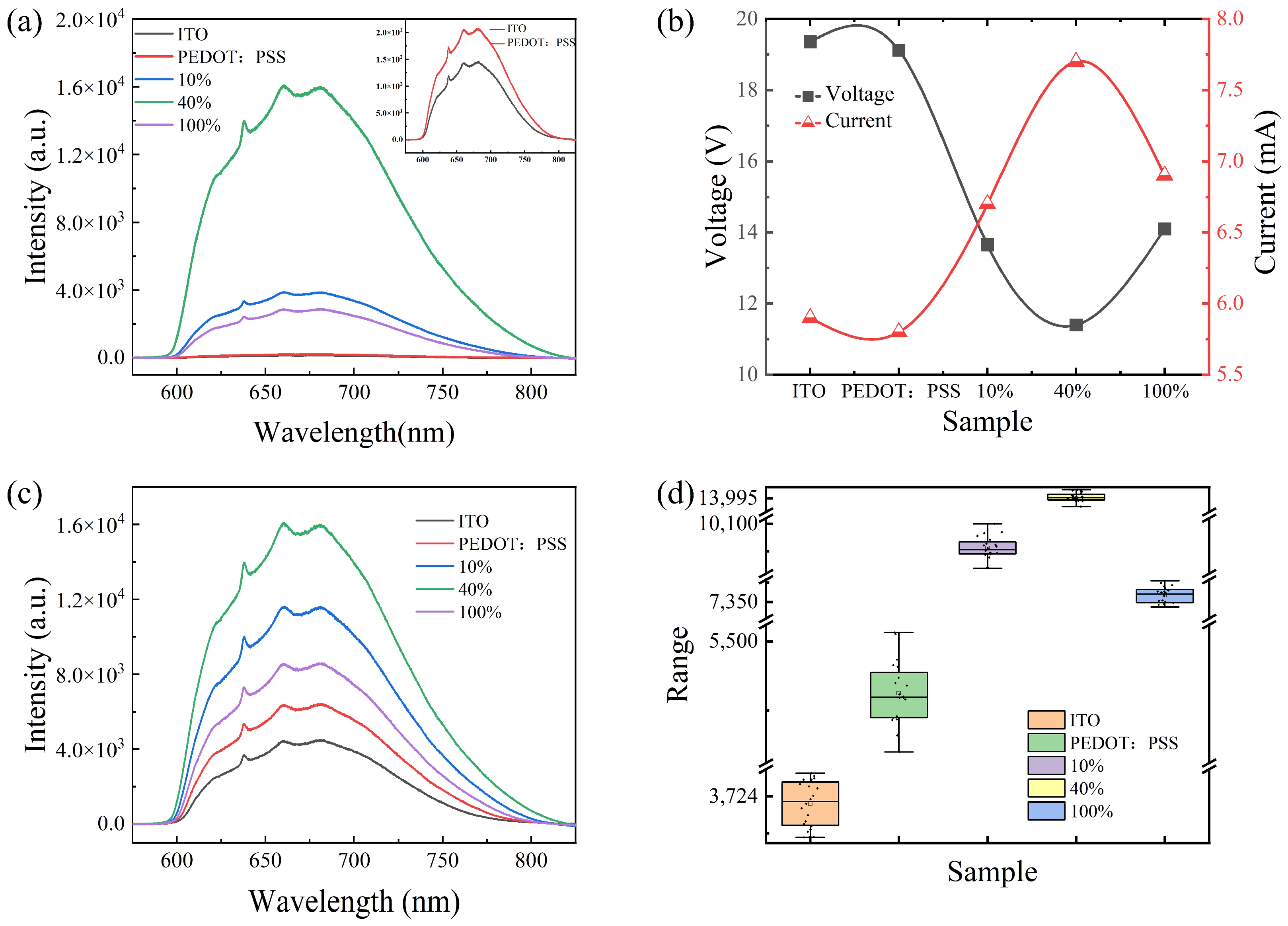
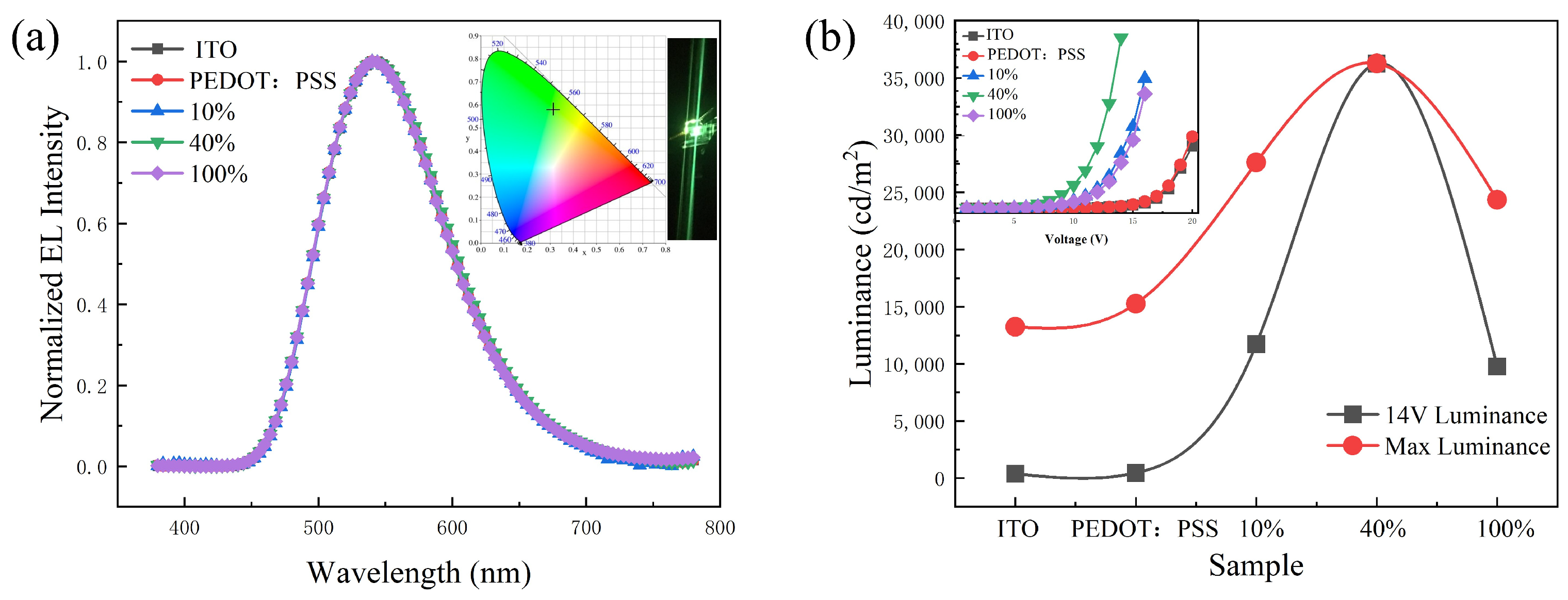
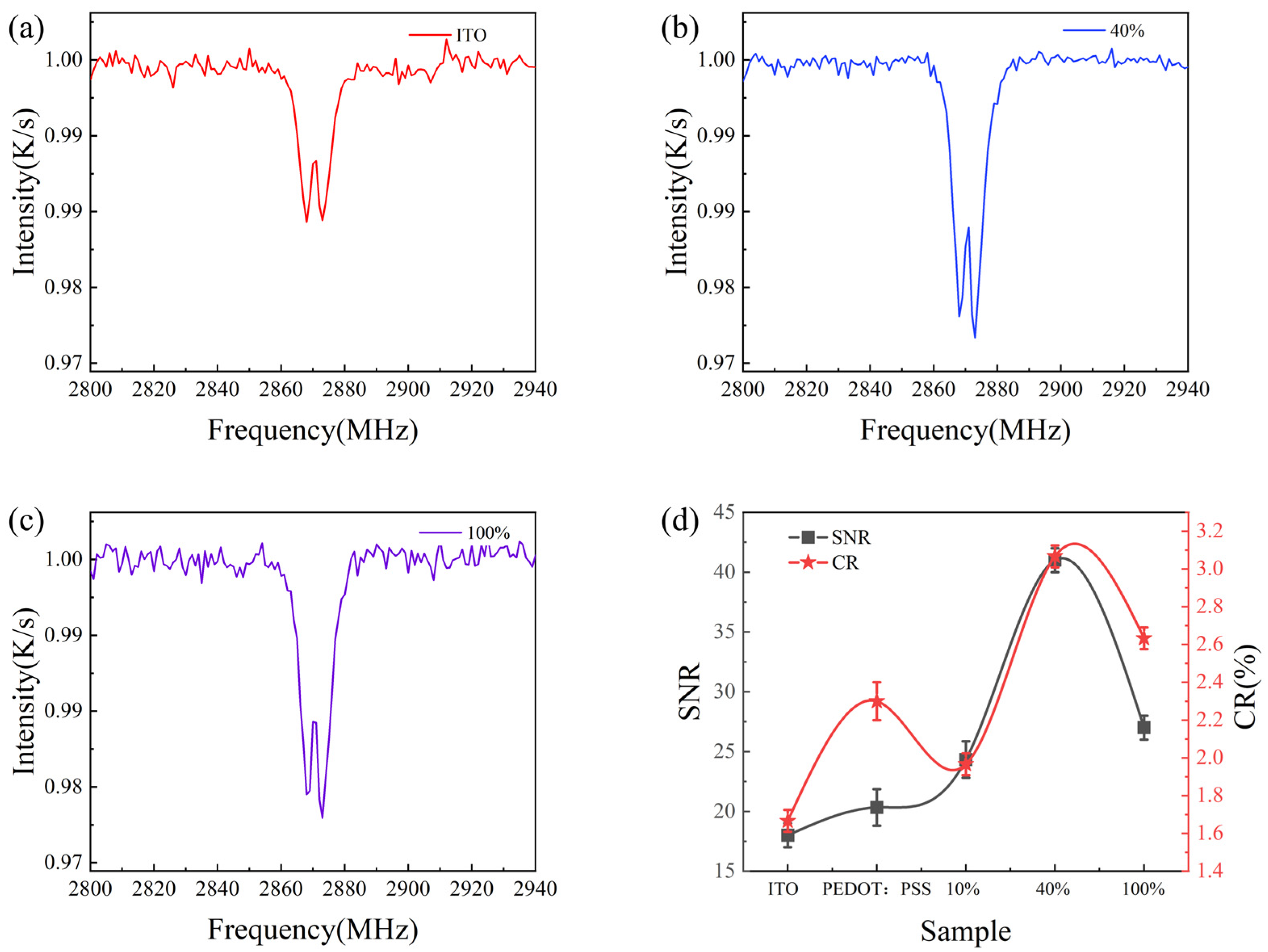
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carmiggelt, J.J.; Bertelli, I.; Mulder, R.W.; Teepe, A.; Elyasi, M.; Simon, B.G.; Bauer, G.E.W.; Blanter, Y.M.; Sar, T.V.D. Broadband microwave detection using electron spins in a hybrid diamond-magnet sensor chip. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, L.; Rohner, D.; Ganzhorn, M.; Appel, P.; Neu, E.; Müller, B.; Kleiner, R.; Koelle, D.; Maletinsky, P. Quantitative nanoscale vortex imaging using a cryogenic quantum magnetometer. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevenson, H.; Trusheim, M.E.; Teale, C.; Schröder, T.; Braje, D.; Englund, D. Broadband magnetometry and temperature sensing with a light-trapping diamond waveguide. Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W.; Song, X.; Guo, G.; Fan, L.; et al. High-sensitivity temperature sensing using an implanted single nitrogen-vacancy center array in diamond. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 155404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.; Jakobi, I.; Dolde, F.; Burk, C.; Reuter, R.; Waldher, G.; Honert, J.; Wolf, T.; Brunner, A.; Wrachtrup, J. High-precision nanoscale temperature sensing using single defects in diamond. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2738–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmola, A.; Lourette, S.; Acosta, V.M.; Birdwell, A.G.; Blümler, P.; Budker, D.; Ivanov, T.; Malinovsky, V.S. Demonstration of diamond nuclear spin gyroscope. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabl3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.A.; Lilette, E.; Fein, Y.Y.; Tomek, N.; McGuinness, L.P.; Hollenberg, L.C.; Scholten, R.E.; Marti, A.M. Quantum measurement of a rapidly rotating spin qubit in diamond. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, R.S.; Harneit, W. Real time magnetic field sensing and imaging using a single spin in diamond. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 030802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.A.; Aeppli, A.G.; Lilette, E.; Fein, Y.Y.; Stacey, A.; Hollenberg, L.C.L.; Scholten, R.E.; Martin, A.M. T2-limited sensing of static magnetic fields via fast rotation of quantum spins. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 174114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kong, F.; Zhao, P.; Huang, Z.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.; Shi, F.; Du, J. Picotesla magnetometry of microwave fields with diamond sensors. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, G.; Nomoto, S.; Kashiwaya, S.; Nomura, S. System for the remote control and imaging of MW fields for spin manipulation in NV centers in diamond. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casola, F.; Van Der Sar, T.; Yacoby, A. Probing condensed matter physics with magnetometry based on nitrogen-vacancy centres in diamond. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, N. Quantum diamond sensors. Nature 2021, 591, S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturner, F.M.; Brenneis, A.; Kassel, J.; Wostradowski, U.; Rölve, R.; Fuchs, T.; Nakamura, K.; Sumiya, H.; Onoda, S.; Isoya, J.; et al. Compact integrated magnetometer based on nitrogen-vacancy centres in diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2019, 93, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, G.J.; Ellul, E.; Robertson, I.S.; Khalid, A.; Greentree, A.D.; Gibson, B.C.; Tetienne, J.P. Handheld device for naocontact thermometry via optically detected magnetic resonance of proximate diamond sensors. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2023, 19, 054076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fo, W.Z.; Li, J.; Lei, Y.X.; Wei, B.; Zhang, Z.L. A facile and efficient preparation method for the doped light emitting layer in OLEDs: Blade-coated planar source evaporation. Org. Electron. 2024, 124, 106961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.L.; Yang, J.J.; Wu, S.X.; Ma, X.X.; Ma, Y.L.; Zhou, L.; Li, C.B.; Shen, S. Theoretical analysis and design for highly collimated planar light source based on organic light-emitting diodes using Fresnel lens. Appl. Phys. Express 2018, 11, 072101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käläntär, K. Optical performance characterization of curved OLED light sources. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2021, 29, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Kwon, J.H.; Kwon, S.; Choi, K.C. A review of flexible OLEDs toward highly durable unusual displays. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 64, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fu, W.; Chen, H. Conductive polymers for flexible and stretchable organic optoelectronic applications. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 4609–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Dang, F.; Li, Y.; Yin, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, K.; Piao, X.; Xie, W.F. An efficient flexible white organic light-emitting device with a screen-printed conducting polymer anode. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 402002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummartyotin, S.; Juntaro, J.; Wu, C.; Sain, M.; Manuspiya, H. Deposition of PEDOT:PSS nanoparticles as a conductive microlayer anode in OLEDs device by desktop inkjet printer. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 606714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Zeng, B.; Chi, F. A new structure of flexible OLED with copper nanowire anode and graphere oxide/PEDOT:PSS anode buffer layer. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2020, 27, 1950171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, S.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, T.W.; Cho, J.H. Electroplated core–shell nanowire network electrodes for highly efficient organic light-emitting diodes. Nano Converg. 2022, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; An, K.; Won, P.; Ka, Y.; Hwang, H.; Moon, H.; Kwon, Y.; Hong, S.; Kim, C.; Lee, C.; et al. A dual-scale metal nanowire network transparent conductor for highly efficient and flexible organic light emitting diodes. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.P.; Wu, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Dong, S.; Du, J.; Ma, D.; Cheng, H.M.; Ren, W. Stably doped graphene transparent electrode with improved light-extraction for efficient flexible organic light-emitting diodes. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 12788–12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Dixon, S.C.; Lee, L.Y.; Humphreys, C.J.; Guiney, I.; Fenwick, O.; Gillin, W.P. Wafer-Scale Graphene Anodes Replace Indium Tin Oxide in Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jing, L.C.; Bao, Z.; Qian, P.; Geng, W.; Ethiraj, A.S.; Geng, W.H.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Q.; Geng, H.Z. Strong adhesion and high optoelectronic performance hybrid graphene/carbon nanotubes transparent conductive films for green-light OLED devices. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 24, 101137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ethiraj, A.S.; Geng, W.M.; Geng, H.Z. High-performance transparent PEDOT:PSS/CNT films for OLEDs. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jing, L.C.; Zhu, Q.; Ethiraj, A.S.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, X.T.; Wen, J.G.; Li, L.K.; Geng, H.Z. Fabrication of architectural structured polydopamine-functionalized reduced graphene oxide/carbon nanotube/PEDOT:PSS nanocomposites as flexible transparent electrodes for OLEDs. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 500, 143997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Shao, L.; Zhang, K.; Ripe, K.P. Engineered doping of organic semiconductors for enhanced thermoelectric efficiency. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Ouyang, J. Salt-induced charge screening and significant conductivity enhancement of conducting poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(styrenesulfonate). Macromolecules 2009, 42, 4141–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Ouyang, J. Significant conductivity enhancement of conductive poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): Poly(styrenesulfonate) films through a treatment with organic carboxylic acids and inorganic acids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Cruz, I.; Reyes-Reyes, M.; López-Sandoval, R. Formation of polystyrene sulfonic acid surface structures on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): Poly(styrenesulfonate) thin films and the enhancement of its conductivity by using sulfuric acid. Thin Solid Film. 2013, 531, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S. Conductivity enhancement of PEDOT:PSS film via sulfonic acid modification: Application as transparent electrode for ITO-free polymer solar cells. Sci. China Chem. 2018, 61, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.R.; Kim, J.; Kang, D.; Lee, D.W.; Ko, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, C.L.; Kim, J.Y.; Shin, H.S.; Song, M.H. Highly efficient polymer light-emitting diodes using graphene oxide as a hole transport layer. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2984–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, B.; Bulin, C.; Li, R.H.; Xing, R.G. High-efficient synthesis of graphene oxide based on improved hummers method. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Wang, W.J. Hybrid electrode interface modification enhances OLEDs performance. Opt. Mater. Express 2024, 14, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, L.X.; Guo, Q.; Guo, H.; Wen, H.F.; Liu, W.Y.; Tang, J.; Liu, J. Optimization of optical control of nitrogen vacancy centers in solid diamond. Acta Phys. Sin. 2020, 69, 147601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, J.F.; Schloss, J.M.; Bauch, E.; Turner, M.J.; Hart, C.A.; Pham, L.M.; Walsworth, R.L. Sensitivity optimization for NV-diamond magnetometry. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Anode | Ecutoff (eV) | Φ (eV) | EHOMO edge − EF (eV) | EHOMO (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEDOT:PSS | 16.413 | 4.787 | 0.246 | 5.033 |
| 10% | 16.250 | 4.950 | 0.217 | 5.167 |
| 40% | 16.186 | 5.014 | 0.242 | 5.256 |
| 100% | 16.215 | 4.985 | 0.226 | 5.211 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, F.; Wang, W.; Li, B. Study on Diamond NV Centers Excited by Green Light Emission from OLEDs. Photonics 2025, 12, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090833
Guo Y, Li X, Shi F, Wang W, Li B. Study on Diamond NV Centers Excited by Green Light Emission from OLEDs. Photonics. 2025; 12(9):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090833
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yangyang, Xin Li, Fuwen Shi, Wenjun Wang, and Bo Li. 2025. "Study on Diamond NV Centers Excited by Green Light Emission from OLEDs" Photonics 12, no. 9: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090833
APA StyleGuo, Y., Li, X., Shi, F., Wang, W., & Li, B. (2025). Study on Diamond NV Centers Excited by Green Light Emission from OLEDs. Photonics, 12(9), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12090833





